How Connected Is China’s Systemic Financial Risk Contagion Network?—A Dynamic Network Perspective Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Literature
3. Methodology
3.1. High-Dimensional Dynamic Network Model of Systemic Risk Contagion
3.2. Ripple-Spreading Network Model of Systemic Risk Contagion
4. Empirical Results and Analysis
4.1. Sample Selection and Data Description
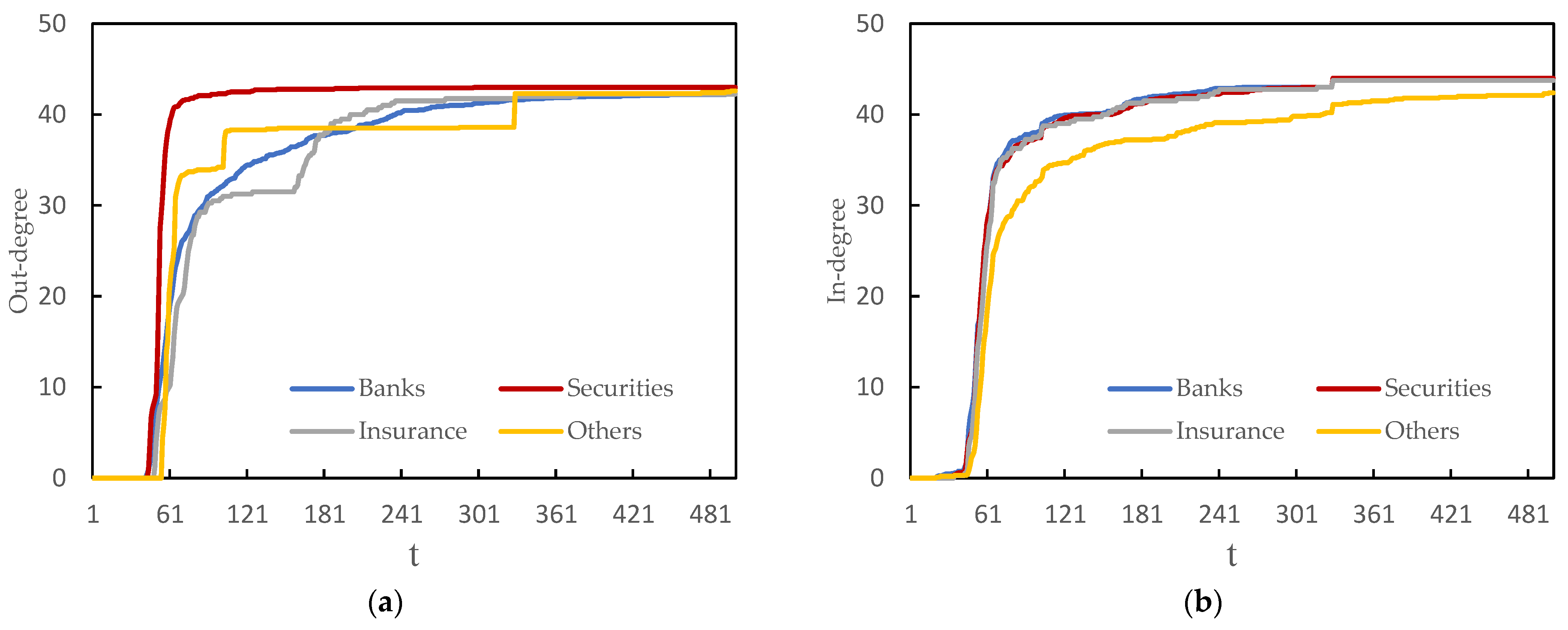
4.2. High-Dimensional Financial Network Connectedness Analysis
4.3. Ripple-Spreading Network Analysis of Systemic Risk Contagion
4.3.1. Parameter Specification for Risk Ripple-Spreading Network
4.3.2. Dynamic Ripple-Spreading Process of Systemic Risk under Internal Shocks
4.3.3. Dynamic Ripple-Spreading Process of Systemic Risk under External Shocks
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yadav, M.P.; Rao, A.; Abedin, M.Z.; Tabassum, S.; Lucey, B. The domino effect: Analyzing the impact of Silicon Valley Bank’s fall on top equity indices around the world. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.W.J. Can We Improve the Perceived Quality of Economic Forecasts? J. Appl. Econom. 1996, 11, 455–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostanci, G.; Yilmaz, K. How connected is the global sovereign credit risk network? J. Bank. Financ. 2020, 113, 105761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, F.; Hautsch, N.; Peltonen, T.A.; Schienle, M. Systemic risk spillovers in the European banking and sovereign network. J. Financ. Stab. 2016, 25, 206–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, C.; Siklos, P.L. Analyzing credit risk transmission to the nonfinancial sector in Europe: A network approach. J. Appl. Econ. 2020, 35, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, J.C. Risk Management and Financial Institutions; Wiley Finance Series: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F. Modeling the Paths of China’s Systemic Financial Risk Contagion: A Ripple Network Perspective Analysis. Comput. Econ. 2022, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Xu, F. Dynamic identification of systemically important financial markets in the spread of contagion: A ripple network based collective spillover effect approach. J. Multinatl. Financ. Manag. 2021, 60, 100681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-B.; Wang, M.; Leeson, M.; Hines, E.L.; Di Paolo, E. Deterministic ripple-spreading model for complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 83, 046123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-B.; Wang, M.; Leeson, M.S. Ripple-Spreading Network Model Optimization by Genetic Algorithm. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 176206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, K.-W.; Liu, S.-Y.; Sun, X.-J.; Xu, Y.-C. A dynamic ripple-spreading algorithm for solving mean–variance of shortest path model in uncertain random networks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 167, 113081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soramäki, K.; Bech, M.L.; Arnold, J.; Glass, R.J.; Beyeler, W.E. The topology of interbank payment flows. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2007, 379, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, M.R.; Ulica, L.; Gubareva, M. Systemic risk in the Angolan interbank payment system–A network approach. Appl. Econ. 2020, 52, 4900–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistrulli, P.E. Assessing financial contagion in the interbank market: Maximum entropy versus observed interbank lending patterns. J. Bank. Financ. 2011, 35, 1114–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudici, P.; Sarlin, P.; Spelta, A. The interconnected nature of financial systems: Direct and common exposures. J. Bank. Financ. 2020, 112, 105149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, P.; Tanna, S.; Zhou, D. Financial contagion in a core-periphery interbank network. Eur. J. Financ. 2019, 26, 691–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, A. Financial Contagion in Core–Periphery Networks and Real Economy. Comput. Econ. 2020, 55, 779–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, S.; Colliard, J.-E.; Hurlin, C.; Pérignon, C. Where the Risks Lie: A Survey on Systemic Risk. Rev. Financ. 2017, 21, 109–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Wei, P.; Ren, X. Climate risk and financial systems: A nonlinear network connectedness analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 340, 117878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, E.J.D.A.L.; Ferreira, P.J.S.; da Silva, M.F.; Miranda, J.G.V.; Pereira, H.B. Multiscale network for 20 stock markets using DCCA. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 529, 121542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, F.; Mohmand, Y.T.; Ferreira, P.; Memon, B.A.; Khan, M.; Khan, M. Network analysis of global stock markets at the beginning of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak. Borsa Istanb. Rev. 2020, 20, S49–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billio, M.; Getmansky, M.; Lo, A.W.; Pelizzon, L. Econometric measures of connectedness and systemic risk in the finance and insurance sectors. J. Financ. Econ. 2012, 104, 535–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, C.; Harris, J.H.; Mankad, S.; Michailidis, G. Interconnectedness in the interbank market. J. Financ. Econ. 2019, 133, 520–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, H.; Tang, W.; Wu, J. Time-varying comovement and changes of comovement structure in the Chinese stock market: A causal network method. Econ. Model. 2019, 81, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diebold, F.X.; Yılmaz, K. On the network topology of variance decompositions: Measuring the connectedness of financial firms. J. Econ. 2014, 182, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.X.D.; Mateut, S.; Chevapatrakul, T. Business-linkage volatility spillovers between US industries. J. Bank. Financ. 2020, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härdle, W.K.; Wang, W.; Yu, L. TENET: Tail-Event driven NETwork risk. J. Econ. 2016, 192, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sun, T. Tail Risk Networks of Insurers around the Globe: An Empirical Examination of Systemic Risk for G-SIIs vs Non-G-SIIs. J. Risk Insur. 2020, 87, 285–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduraimova, K. Contagion and tail risk in complex financial networks. J. Bank. Financ. 2022, 143, 106560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-J.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Si, H.-B.; Xie, C.; Chevallier, J. Multilayer information spillover networks analysis of China’s financial institutions based on variance decompositions. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2021, 73, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zhou, X. Multilayer networks in the frequency domain: Measuring extreme risk connectedness of Chinese financial institutions. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2023, 65, 101944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.S.H.; Chu, A.M.Y.; So, M.K.P. A moving-window bayesian network model for assessing systemic risk in financial markets. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0279888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Sun, Q.; Ye, T.; Wang, Q. Identification of systemically important financial institutions in a multiplex financial network: A multi-attribute decision-based approach. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2023, 611, 128446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirer, M.; Diebold, F.X.; Liu, L.; Yilmaz, K. Estimating global bank network connectedness. J. Appl. Econ. 2018, 33, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlees, C.; Hans, C.; Nualart, E. Bank credit risk networks: Evidence from the Eurozone. J. Monet. Econ. 2021, 117, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, D.L.; Fulghieri, P. Uncertainty Aversion and Systemic Risk. J. Political Econ. 2019, 127, 1118–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yao, Y.; Chen, M.; Jeon, B.N. Economic uncertainty and bank risk: Evidence from emerging economies. J. Int. Financ. Mark. Inst. Money 2020, 68, 101242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.R.; Bloom, N.; Davis, S.J. Measuring Economic Policy Uncertainty. Q. J. Econ. 2016, 131, 1593–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varotto, S.; Zhao, L. Systemic risk and bank size. J. Int. Money Financ. 2018, 82, 45–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




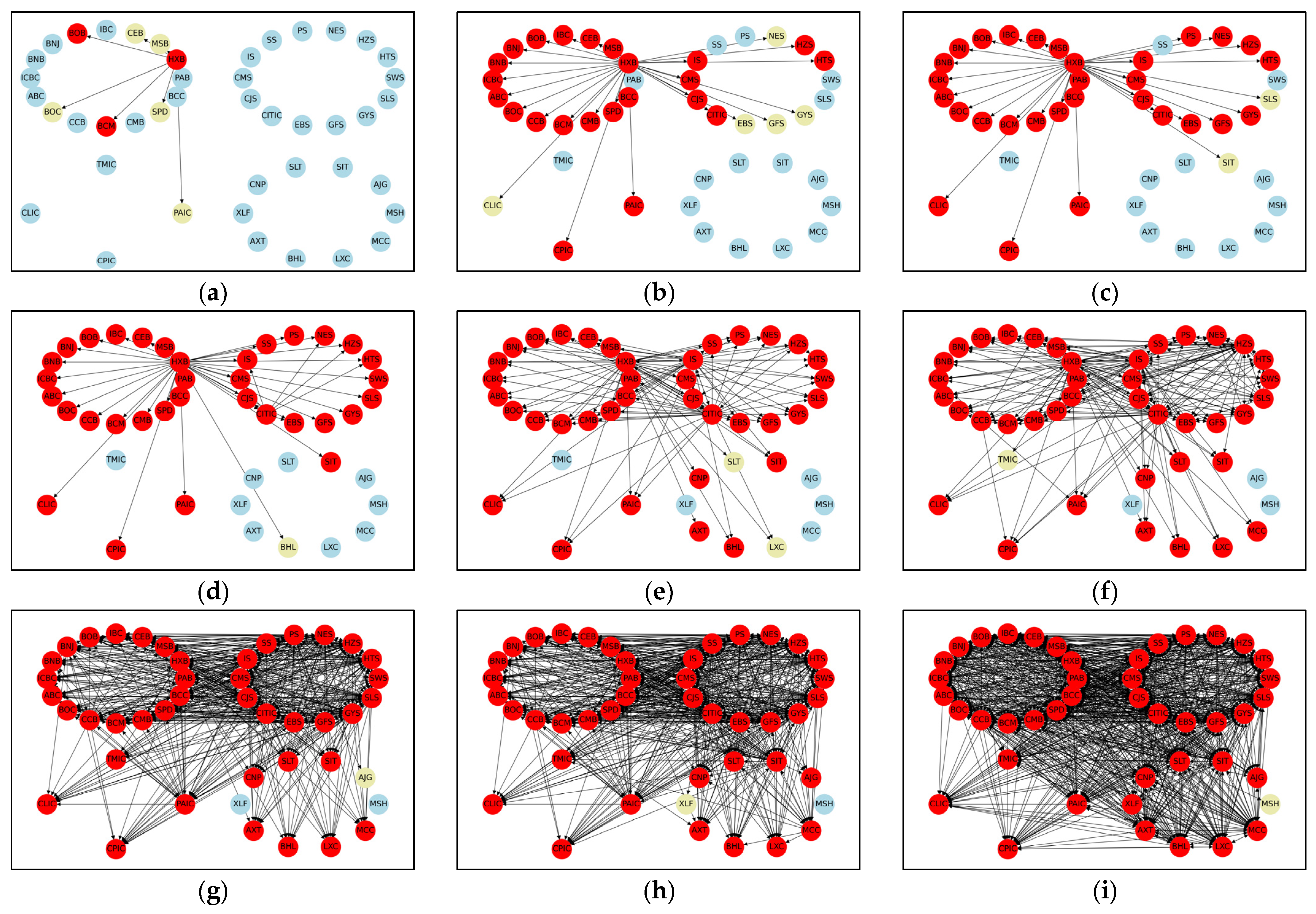

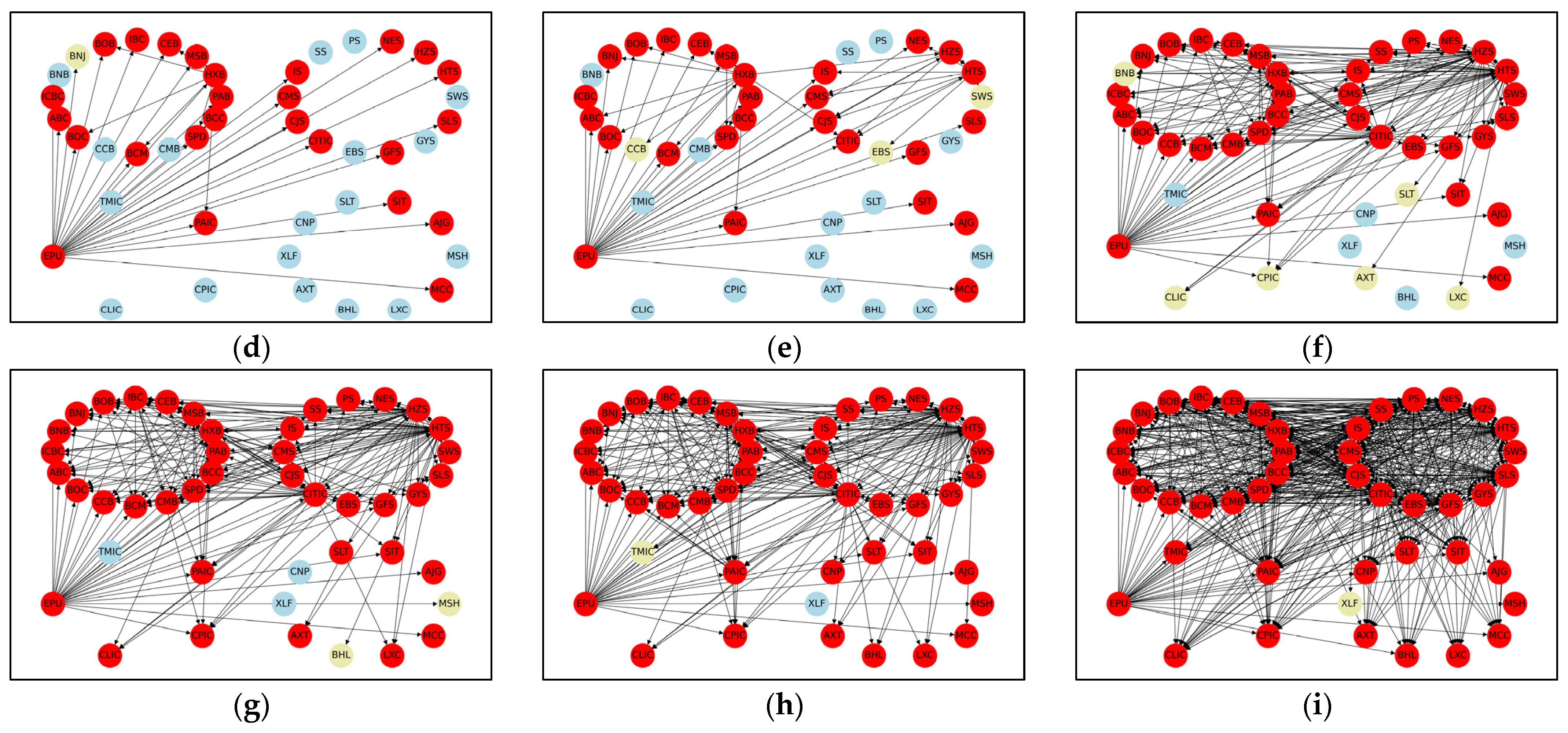
| Institution Name | Abbr. | Institution Name | Abbr. | Institution Name | Abbr. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial and Commercial Bank of China | ICBC | Bank of Ningbo | BNB | China Life Insurance | CLIC |
| Agricultural Bank of China | ABC | China Merchants Securities | CMS | China Pacific Insurance | CPIC |
| Bank of China | BOC | Changjiang Securities | CJS | China Ping An Insurance | PAIC |
| China Construction Bank | CCB | CITIC securities | CITIC | Tianmao Insurance Company | TMIC |
| Bank of Communications | BCM | Everbright Securities | EBS | Xinli Finance | XLF |
| China Merchants Bank | CMB | GF securities | GFS | Anxin Trust and Investment | AXT |
| Shanghai Pudong Development Bank | SPD | Guoyuan Securities | GYS | Bohai Leasing | BHL |
| China CITIC Bank | BCC | Sinolink securities | SLS | Luxin Venture Capital | LXC |
| Ping An Bank | PAB | Southwest Securities | SWS | Minmetals Capital Company | MCC |
| Huaxia Bank | HXB | Haitong Securities | HTS | Minsheng Holdings | MSH |
| China Minsheng Bank | MSB | Huatai Securities | HZS | Aijian Group | AJG |
| China Everbright Bank | CEB | Northeast Securities | NES | Shaanxi International Turst | SIT |
| China’s Industrial Bank | IBC | Pacific Securities | PS | Sunny Loan Top | SLT |
| Bank of Beijing | BOB | Sealand Securities | SS | Cnpc Capital Company Limited | CNP |
| Bank of Nanjing | BNJ | Industrial Securities | IS |
| Panel A: Cross-sectoral network connectedness (2011–2023) | |||||||||
| (Group Influence) | IN-Mean | OUT-Mean | IFO-Mean | OTO-Mean | |||||
| Banks | Securities | Insurance | Others | ||||||
| Banks | 4.021 | 1.293 | 2.287 | 0.415 | 2.133 | 2.585 | 1.332 | 1.998 | |
| Securities | 1.966 | 3.449 | 1.645 | 0.902 | 2.137 | 2.223 | 1.504 | 1.795 | |
| Insurance | 2.831 | 1.812 | 2.625 | 0.900 | 2.036 | 1.885 | 1.848 | 1.763 | |
| Others * | 1.198 | 2.280 | 1.358 | 1.917 | 1.715 | 0.933 | 1.612 | 0.739 | |
| Panel B: Cross-sectoral network connectedness (2015) | |||||||||
| (Group Influence) | IN-Mean | OUT-Mean | IFO-Mean | OTO-Mean | |||||
| Banks | Securities | Insurance | Others | ||||||
| Banks | 3.106 | 2.286 | 2.289 | 0.594 | 2.179 | 2.412 | 1.723 | 2.097 | |
| Securities | 2.228 | 3.227 | 2.108 | 0.828 | 2.193 | 2.525 | 1.721 | 2.268 | |
| Insurance | 2.445 | 2.524 | 2.625 | 0.846 | 2.112 | 2.131 | 1.938 | 2.053 | |
| Others * | 1.617 | 1.994 | 1.761 | 2.065 | 1.847 | 1.001 | 1.791 | 0.756 | |
| Panel C: Cross-sectoral network connectedness (2020) | |||||||||
| (Group Influence) | IN-Mean | OUT-Mean | IFO-Mean | OTO-Mean | |||||
| Banks | Securities | Insurance | Others | ||||||
| Banks | 2.860 | 2.148 | 1.650 | 1.504 | 2.200 | 2.092 | 1.767 | 1.834 | |
| Securities | 1.697 | 3.047 | 1.555 | 1.997 | 2.162 | 2.567 | 1.750 | 2.332 | |
| Insurance | 2.453 | 2.007 | 3.522 | 1.334 | 2.122 | 1.772 | 1.932 | 1.650 | |
| Others * | 1.350 | 2.840 | 1.746 | 2.447 | 2.102 | 1.846 | 1.979 | 1.612 | |
| ICBC | ABC | BOC | CCB | BCM | CMB | SPD | BCC | PAB | HXB | MSB | |
| 16.358 | 10.333 | 9.306 | 12.730 | 3.604 | 6.132 | 2.663 | 2.338 | 1.907 | 0.944 | 2.351 | |
| 1.101 | 1.098 | 1.089 | 1.087 | 1.083 | 1.083 | 1.082 | 1.091 | 1.094 | 1.082 | 1.092 | |
| 0.065 | 0.190 | 0.093 | 0.961 | 0.326 | 0.364 | 0.466 | 0.147 | 0.784 | 0.510 | 0.478 | |
| CEB | IBC | BOB | BNJ | BNB | CMS | CJS | CITIC | EBS | GFS | GYS | |
| 1.662 | 2.972 | 1.026 | 0.587 | 0.970 | 1.007 | 0.379 | 2.159 | 0.570 | 1.059 | 0.311 | |
| 1.085 | 1.088 | 1.091 | 1.092 | 1.107 | 1.072 | 1.077 | 1.068 | 1.092 | 1.082 | 1.089 | |
| 0.497 | 0.636 | 0.463 | 0.812 | 0.716 | 0.601 | 1.109 | 1.385 | 1.127 | 1.051 | 1.300 | |
| SLS | SWS | HTS | HZS | NES | PS | SS | IS | CLIC | CPIC | PAIC | |
| 0.308 | 0.310 | 1.261 | 1.094 | 0.204 | 0.220 | 0.225 | 0.442 | 6.528 | 2.381 | 8.046 | |
| 1.124 | 1.115 | 1.076 | 1.071 | 1.085 | 1.099 | 1.106 | 1.084 | 1.107 | 1.098 | 1.096 | |
| 1.824 | 0.868 | 1.044 | 1.097 | 1.579 | 2.291 | 3.368 | 1.795 | 0.104 | 0.454 | 0.790 | |
| TMIC | XLF | AXT | BHL | LXC | MCC | MSH | AJG | SIT | SLT | CNP | |
| 0.192 | 0.044 | 0.223 | 0.216 | 0.134 | 0.187 | 0.036 | 0.135 | 0.127 | 0.037 | 0.516 | |
| 1.291 | 2.031 | 1.198 | 1.206 | 1.241 | 1.259 | 2.124 | 1.402 | 1.133 | 1.261 | 1.314 | |
| 1.226 | 2.760 | 1.433 | 1.116 | 1.454 | 2.298 | 2.060 | 1.603 | 1.854 | 2.812 | 0.977 |
| ICBC | ABC | BOC | CCB | BCM | CMB | SPD | BCC | PAB | HXB | MSB | |
| Out-degree | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 31 | 41 | 20 |
| In-degree | 30 | 30 | 31 | 30 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 32 | 29 | 31 | 30 |
| CEB | IBC | BOB | BNJ | BNB | CMS | CJS | CITIC | EBS | GFS | GYS | |
| Out-degree | 30 | 28 | 21 | 40 | 39 | 35 | 41 | 41 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| In-degree | 30 | 30 | 31 | 31 | 30 | 30 | 31 | 31 | 27 | 27 | 27 |
| SLS | SWS | HTS | HZS | NES | PS | SS | IS | CLIC | CPIC | PAIC | |
| Out-degree | 41 | 40 | 41 | 41 | 41 | 42 | 42 | 42 | 0 | 0 | 40 |
| In-degree | 27 | 27 | 32 | 32 | 28 | 26 | 24 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| TMIC | XLF | AXT | BHL | LXC | MCC | MSH | AJG | SIT | SLT | CNP | |
| Out-degree | 13 | 0 | 40 | 39 | 40 | 41 | 0 | 0 | 42 | 43 | 18 |
| In-degree | 25 | 5 | 27 | 24 | 26 | 24 | 1 | 13 | 26 | 25 | 25 |
| ICBC | ABC | BOC | CCB | BCM | CMB | SPD | BCC | PAB | HXB | MSB | |
| Out-degree | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 0 | 15 | 36 | 33 |
| In-degree | 16 | 18 | 17 | 18 | 18 | 16 | 17 | 17 | 15 | 17 | 17 |
| CEB | IBC | BOB | BNJ | BNB | CMS | CJS | CITIC | EBS | GFS | GYS | |
| Out-degree | 0 | 29 | 28 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28 | 40 | 0 | 34 | 0 |
| In-degree | 18 | 16 | 16 | 17 | 17 | 18 | 16 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| SLS | SWS | HTS | HZS | NES | PS | SS | IS | CLIC | CPIC | PAIC | |
| Out-degree | 41 | 0 | 40 | 40 | 41 | 39 | 40 | 42 | 0 | 0 | 31 |
| In-degree | 15 | 13 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 12 | 16 | 16 | 17 | 17 |
| TMIC | XLF | AXT | BHL | LXC | MCC | MSH | AJG | SIT | SLT | CNP | |
| Out-degree | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| In-degree | 8 | 1 | 9 | 11 | 8 | 9 | 1 | 4 | 14 | 9 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Xie, X.; Li, C. How Connected Is China’s Systemic Financial Risk Contagion Network?—A Dynamic Network Perspective Analysis. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11102267
Zhang B, Xie X, Li C. How Connected Is China’s Systemic Financial Risk Contagion Network?—A Dynamic Network Perspective Analysis. Mathematics. 2023; 11(10):2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11102267
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Beibei, Xuemei Xie, and Chunmei Li. 2023. "How Connected Is China’s Systemic Financial Risk Contagion Network?—A Dynamic Network Perspective Analysis" Mathematics 11, no. 10: 2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11102267
APA StyleZhang, B., Xie, X., & Li, C. (2023). How Connected Is China’s Systemic Financial Risk Contagion Network?—A Dynamic Network Perspective Analysis. Mathematics, 11(10), 2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11102267








