LQR Chaos Synchronization for a Novel Memristor-Based Hyperchaotic Oscillator
Abstract
:1. Introduction
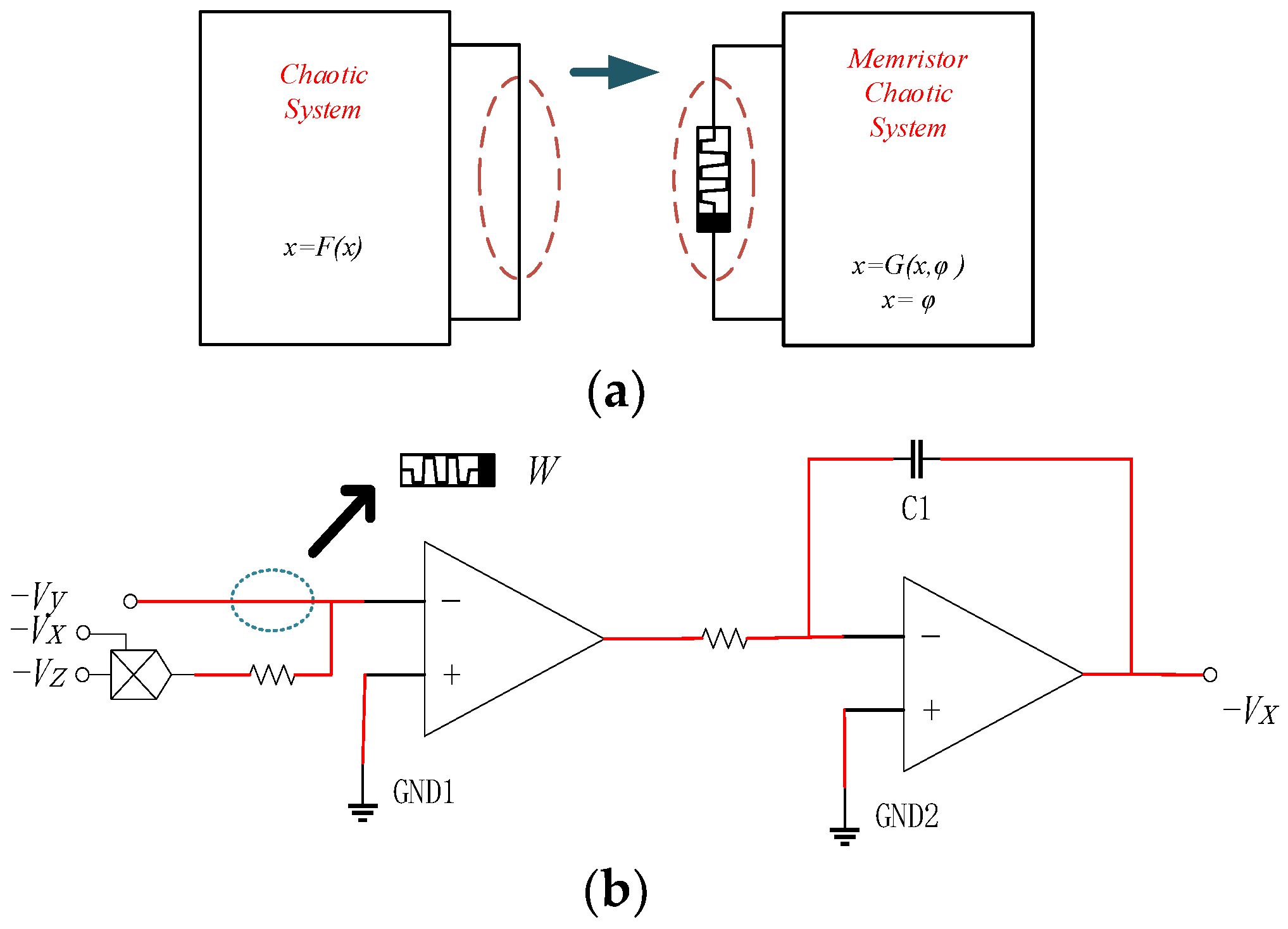
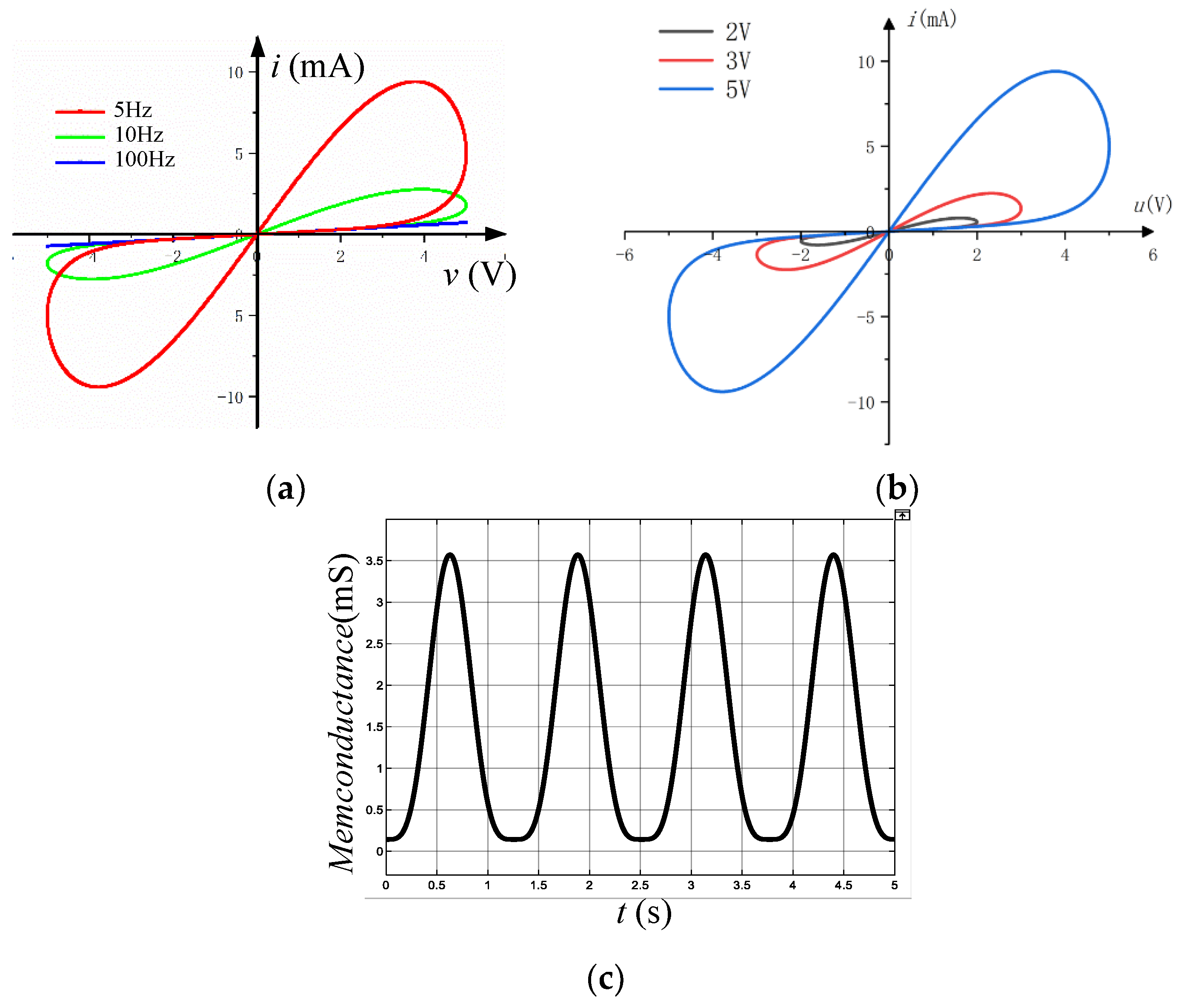
2. Hyperchaotic Systems Based on Memristor Circuit
2.1. Construction of the System
2.2. Equilibrium Point and Stability Analysis
3. Properties of the MHS
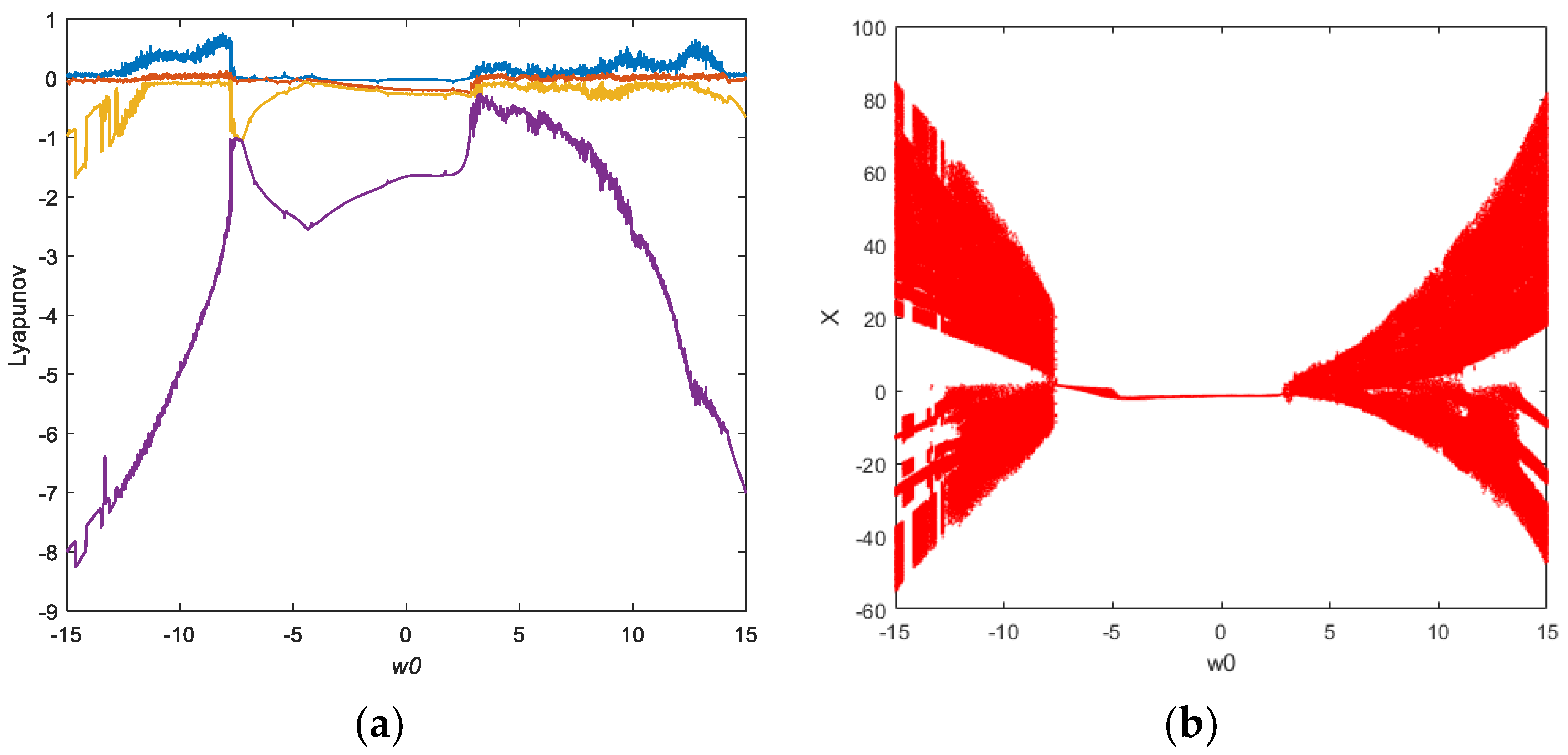
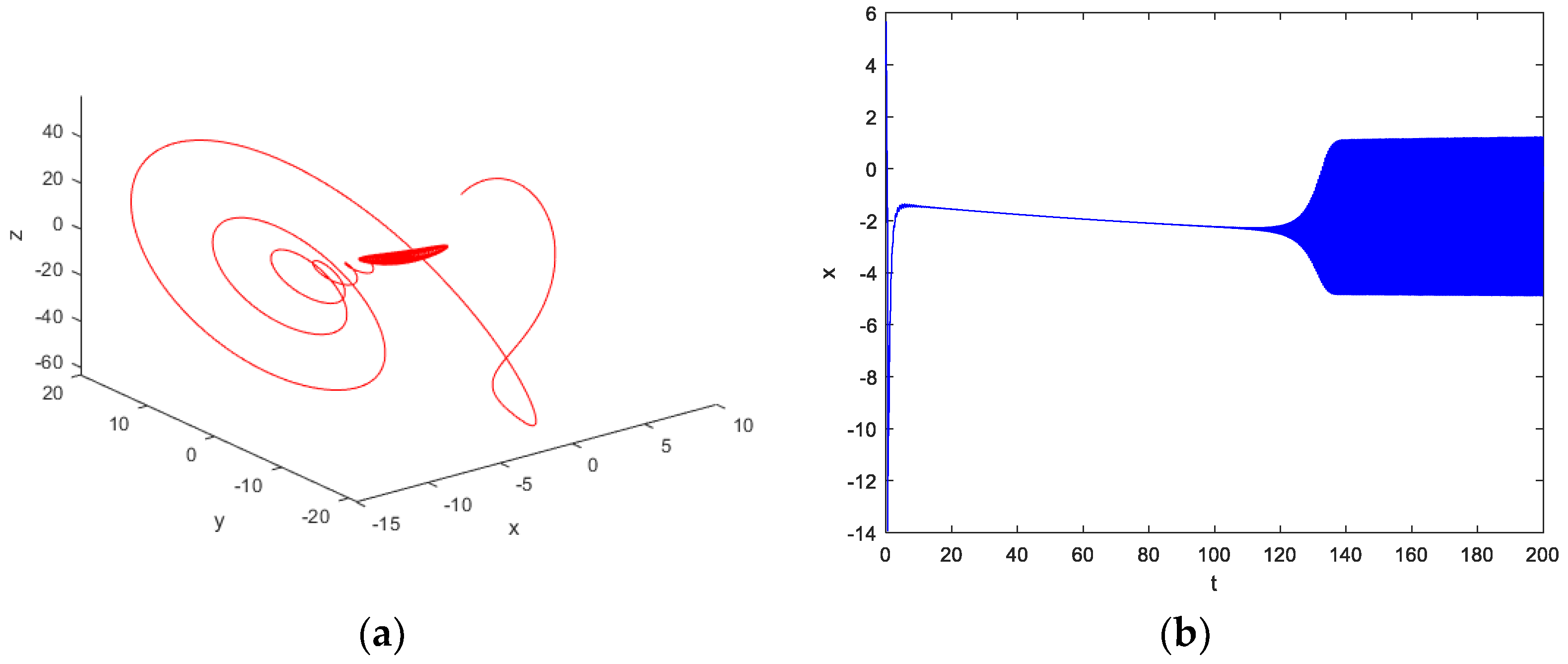
3.1. Hyperchaotic Behavior Depending on Parameters
3.2. Hyperchaotic Behavior Relying on Memristor Initial Condition
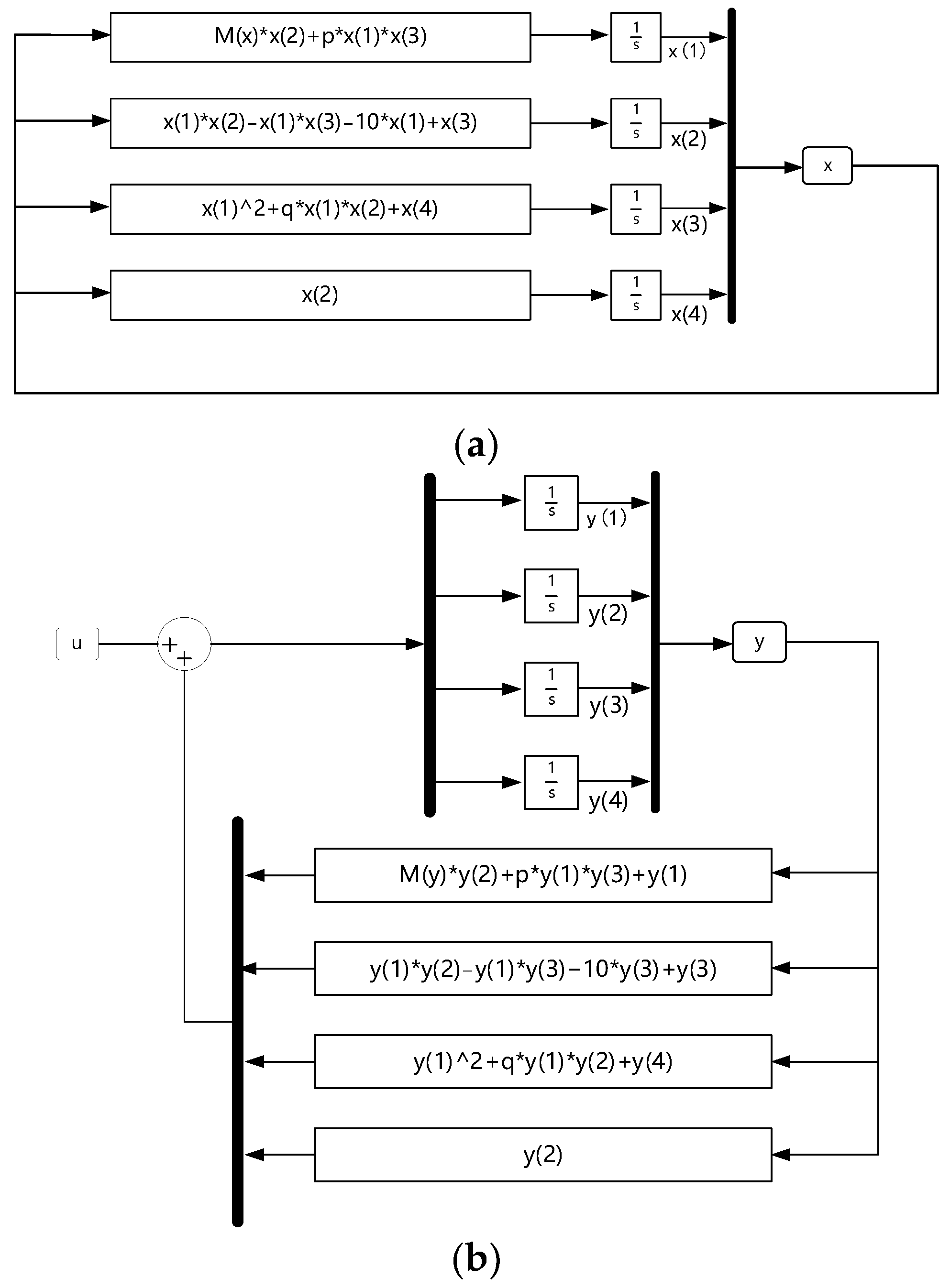
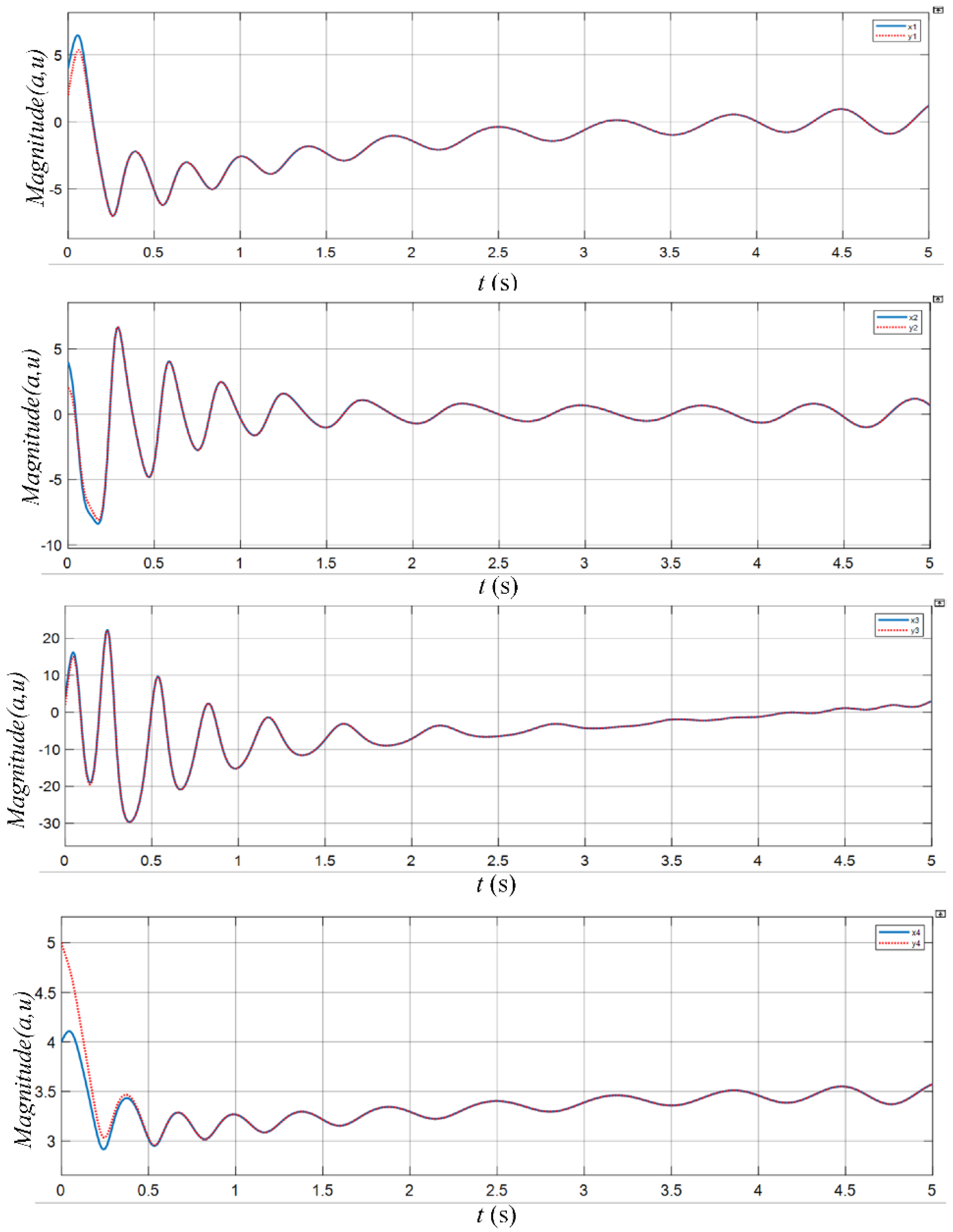
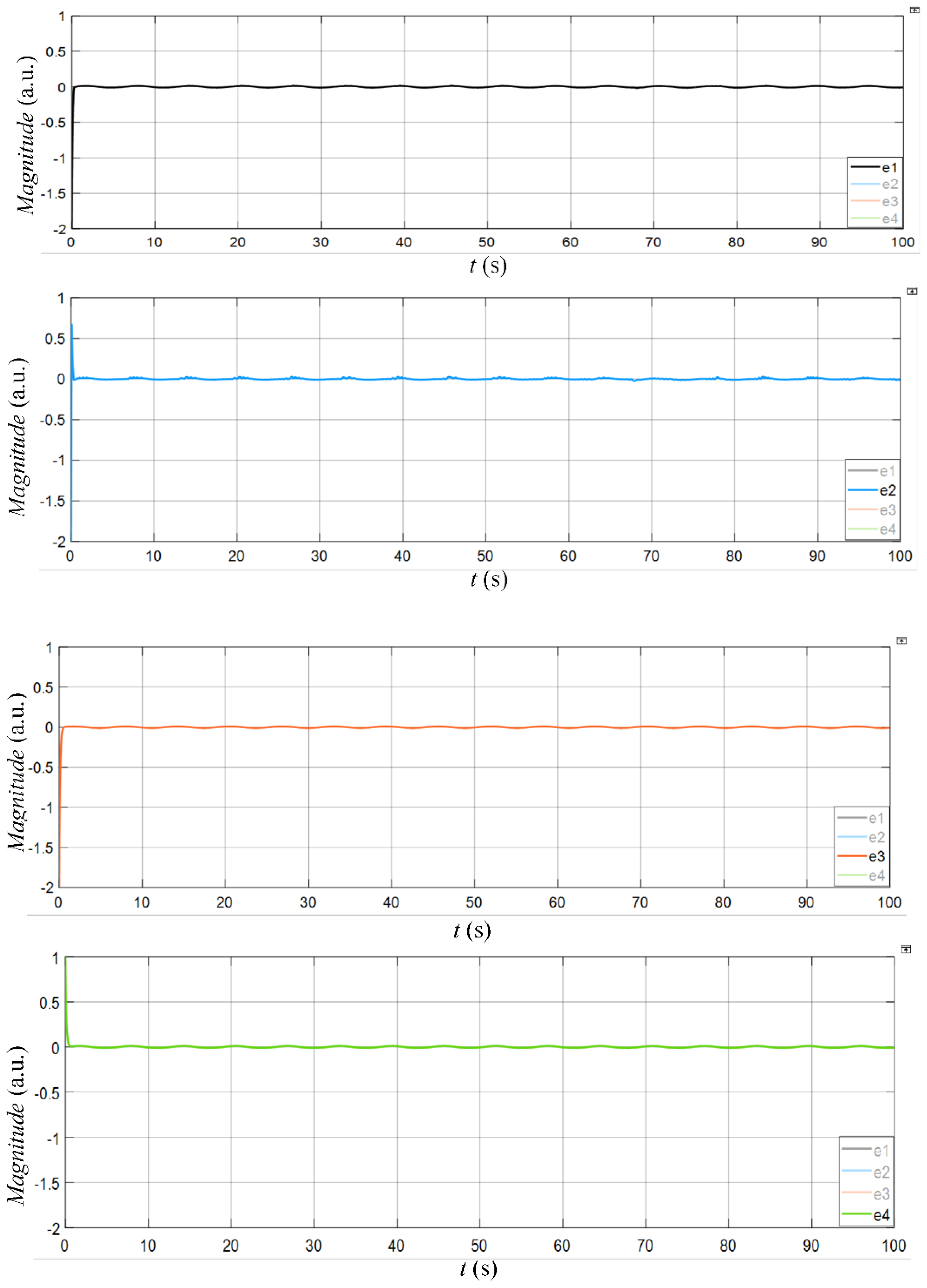
4. Synchronization by Using the LQR Method
5. Circuit Simulation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.; Zeng, H.; Li, J. Hyperchaos in a 4D memristive circuit with infinitely many stable equilibria. Nonlinear Dyn. 2015, 79, 2295–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Zou, X.; Liu, Z.; Hu, F. Generalized Memory Element And Chaotic Memory System. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2013, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L.O. The fourth element. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 1920–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L. Resistance switching memories are memristors. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2011, 102, 765–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buscarino, A.; Fortuna, L.; Frasca, M.; Gambuzza, L.V. A gallery of chaotic oscillators based on hp memristor. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2013, 23, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.C.; Liu, Z.; Xu, B.P. Dynamical analysis of memristor chaotic oscillator. Acta Phys. Sin. 2010, 59, 3785–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L.O.; Kang, S.M. Memristive devices and systems. Proc. IEEE 1976, 64, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuswamy, B.; Kokate, P. Memristor-Based Chaotic Circuits. IETE Tech. Rev. 2009, 26, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, R.; Wang, C. A New Simple Chaotic Circuit Based on Memristor. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2016, 26, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscarino, A.; Fortuna, L.; Frasca, M.; Gambuzza, L.V. A chaotic circuit based on hewlett-packard memristor. Chaos 2012, 22, 023136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Jiang, P.; Wu, H.; Hu, F. Complex transient dynamics in periodically forced memristive Chua’s circuit. Nonlinear Dyn. 2015, 79, 2333–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.; Ranjan, A. An Autonomous Simple Chaotic Jerk System with Stable and Unstable Equilibria Using Reverse Sine Hyperbolic Functions. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2020, 30, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.; Ranjan, A. Investigation of dynamical properties in hysteresis-based a simple chaotic waveform generator with two stable equilibrium. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 134, 109693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneev, I.A.; Vadivasova, T.E.; Semenov, V.V. Hard and soft excitation of oscillations in memristor-based oscillators with a line of equilibria. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 89, 2829–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Xu, X.; Ding, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, B.; Sun, K.; Yin, L. Application of a memristor-based oscillator to weak signal detection. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Yao, W.; Tan, Y. Chaotic dynamics in a neural network with different types of external stimuli. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2020, 90, 105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.-H.; Xu, X.-M.; Yang, B.-C.; Yin, L.-Z. Implication of Two-Coupled Differential Van der Pol Duffing Oscillator in Weak Signal Detection. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 85, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T. Generating N-Scroll Chaotic Attractors from a Memristor-Based Magnetized Hopfield Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Cui, L.; Sun, Y.; Xu, C.; Yu, F. Brain-Like Initial-Boosted Hyperchaos and Application in Biomedical Image Encryption. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 8839–8850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Xu, C.; Zhang, X.; Iu, H.H.C. A Memristive Synapse Control Method to Generate Diversified Multi-Structure Chaotic Attractors. IEEE Trans. Comput. Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2022, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volos, C.K.; Akgul, A.; Pham, V.-T.; Baptista, M.S. Antimonotonicity, Crisis and Multiple Attractors in a Simple Memristive Circuit. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2018, 27, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Xia, H. Multi-piecewise quadratic nonlinearity memristor and its 2N-scroll and 2N + 1-scroll chaotic attractors system. Chaos 2017, 27, 033114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xia, H.; Zhou, L. A Memristive Hyperchaotic Multiscroll Jerk System with Controllable Scroll Numbers. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2017, 27, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X. A universal emulator for memristor, memcapacitor, and meminductor and its chaotic circuit. Chaos 2019, 29, 013141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Xu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, K.; Xiao, C. A color image encryption algorithm based on hyperchaotic map and Rubik’s Cube scrambling. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 110, 2869–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheukem, A.; Tsafack, A.S.K.; Kingni, S.T.; André, C.C.; Pone, J.R.M. Permanent magnet synchronous motor: Chaos control using single controller, synchronization and circuit implementation. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiu, C.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, S.; Xu, G. Memristive hyperchaos secure communication based on sliding mode control. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 104, 789–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plata, C.; Prieto, P.J.; Ramirez-Villalobos, R.; Coria, L.N. Chaos Synchronization for Hyperchaotic Lorenz-Type System via Fuzzy-Based Sliding-Mode Observer. Math. Comput. Appl. 2020, 25, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noussaiba, G.; Hamidi, F.; Boussaid, B.; Abdelkrim, M.N. Sliding mode controller for global chaos synchronization of two chaotic systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 17th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices (SSD), Monastir, Tunisia, 20–23 July 2020; pp. 1133–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopal, K.; Karthikeyan, A.; Srinivasan, A.K. FPGA implementation of novel fractional-order chaotic systems with two equilibriums and no equilibrium and its adaptive sliding mode synchronization. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 87, 2281–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, K.; Guessas, L.; Karthikeyan, A.; Srinivasan, A.; Adam, G. Fractional Order Memristor No Equilibrium Chaotic System with Its Adaptive Sliding Mode Synchronization and Genetically Optimized Fractional Order PID Synchronization. Complexity 2017, 2017, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Z.; Wang, C.; Yao, W.; Lin, H. Observer-based synchronization of memristive neural networks under DoS attacks and actuator saturation and its application to image encryption. Appl. Math. Comput. 2022, 425, 127080. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, Z.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Yao, W.; Lin, H. Cluster output synchronization for memristive neural networks. Inf. Sci. 2022, 589, 459–477. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Xi, L. Fuzzy neural network-based chaos synchronization for a class of fractional-order chaotic systems: An adaptive sliding mode control approach. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 100, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sprott, J. Chaotic flows with a single nonquadratic term. Phys. Lett. A 2014, 378, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1963, 20, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Ueta, T. Yet another chaotic attractor. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 1999, 9, 1465–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Chen, G. A new chaotic attractor coined. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2002, 12, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitch, A.L.; Yu, D.; Iu, H.H.C.; Sreeram, V. Hyperchaos in a memristor-based modified canonical Chua’s circuit. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2012, 22, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.; Wu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, C. Chaos Control and Synchronization of a Complex Rikitake Dynamo Model. Entropy 2020, 22, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Svinin, M. Function Approximation Technique Based Adaptive Control for Chaos Synchronization between Different Systems with Unknown Dynamics. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2021, 19, 2611–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azil, S.; Odibat, Z.; Shawagfeh, N. On the dynamics of a Caputo-like discrete fractional rössler system: Chaos, stabilization and synchronization. Phys. Scr. 2022, 97, 035203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Azzawi, S.F.; Al-Talib, Z.S. Generalized function projective synchronization via nonlinear controller strategy. J. Interdiscip. Math. 2022, 25, 1753–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Jiang, P.; Xu, Q.; Chen, M. Hidden attractors in a practical Chua’s circuit based on a modified Chua’s diode. Electron. Lett. 2016, 52, 23–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Lin, Y.; Bao, B.; Chen, M. Multiple attractors in a non-ideal active voltage-controlled memristor based Chua’s circuit. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2016, 83, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Hu, F.; Chen, M.; Xu, Q.; Yu, Y. Self-Excited and Hidden Attractors Found Simultaneously in a Modified Chua’s Circuit. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2015, 25, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, M.; Yu, Q.; Bao, B.; Xu, Q.; Wang, J. Dynamics of self-excited attractors and hidden attractors in generalized memristor-based Chua’s circuit. Nonlinear Dyn. 2015, 81, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| References | Types of System | Order | Methods | Time Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [27] | Autonomous | 5 | Sliding mode control | t = 6.3 s |
| [26] | Non-autonomous | 3 | Linear feedback control | t = 8 s |
| [28] | Autonomous | 4 | Sliding mode control | t = 4.8 s |
| [29] | Autonomous | 3 | Sliding mode control | t = 4.1 s |
| [40] | Non-autonomous | 5 | Feedback control method | t = 13 s |
| [34] | Autonomous | 2 | Fuzzy neural network Function approximation | t = 1 s |
| [41] | Autonomous | 3 | Function approximation technique | t = 1 s |
| [42] | Non-autonomous | 3 | Feedback controller | t = 40 s |
| [43] | Non-autonomous | 4 | Generalized function projective | t = 6 s |
| this paper | Autonomous | 4 | Linear quadratic regulator | t = 0.7 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Q.; Xu, X.; Xiao, C. LQR Chaos Synchronization for a Novel Memristor-Based Hyperchaotic Oscillator. Mathematics 2023, 11, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11010011
Fu Q, Xu X, Xiao C. LQR Chaos Synchronization for a Novel Memristor-Based Hyperchaotic Oscillator. Mathematics. 2023; 11(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Qifeng, Xuemei Xu, and Chuwen Xiao. 2023. "LQR Chaos Synchronization for a Novel Memristor-Based Hyperchaotic Oscillator" Mathematics 11, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11010011
APA StyleFu, Q., Xu, X., & Xiao, C. (2023). LQR Chaos Synchronization for a Novel Memristor-Based Hyperchaotic Oscillator. Mathematics, 11(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11010011





