A Modified Black-Scholes-Merton Model for Option Pricing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Previous Models and Methods
2.1. Black–Scholes–Merton with Time-Varying Parameters
2.2. Standard Fractional Brownian Model
2.3. Conformable Derivatives
3. Solving the BSM with Time-Varying Parameters via Conformable Calculus
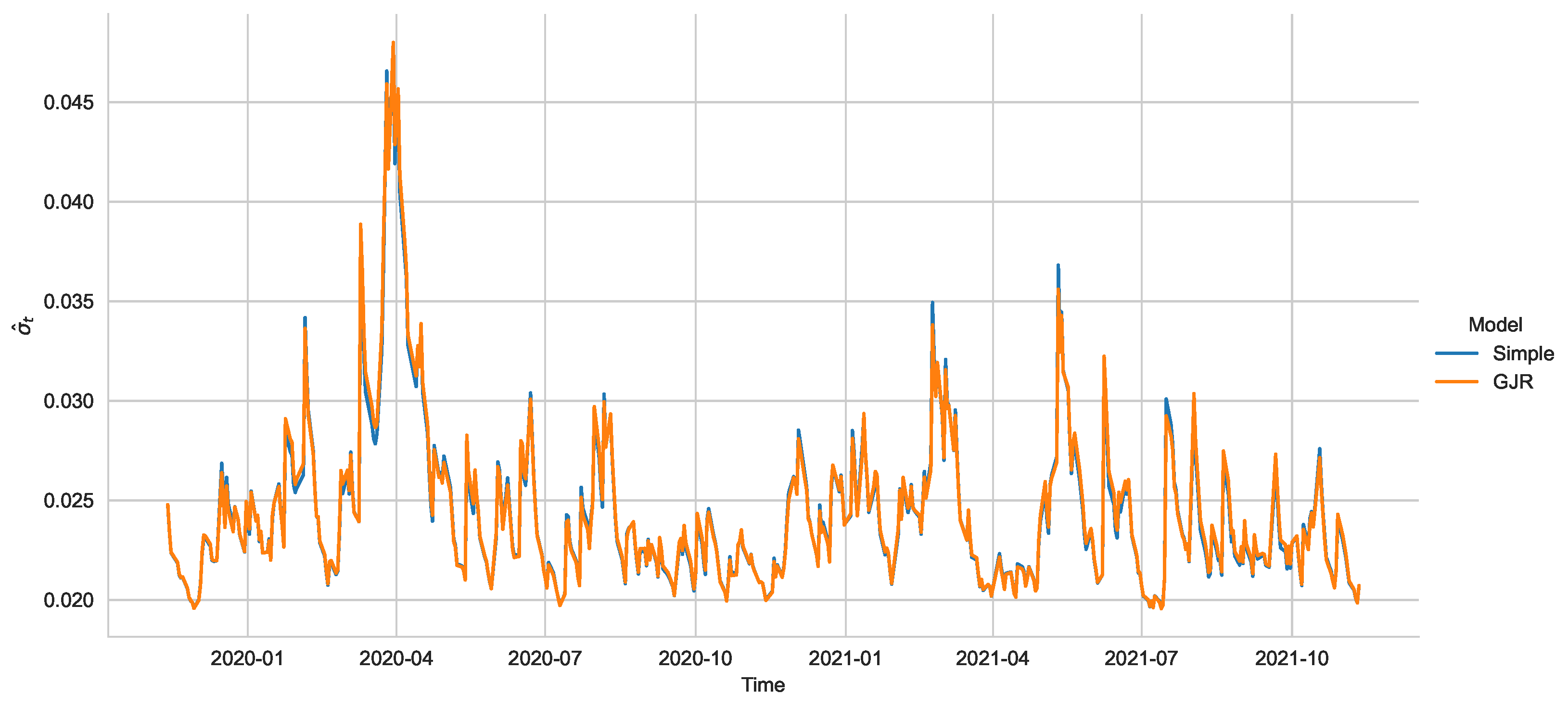
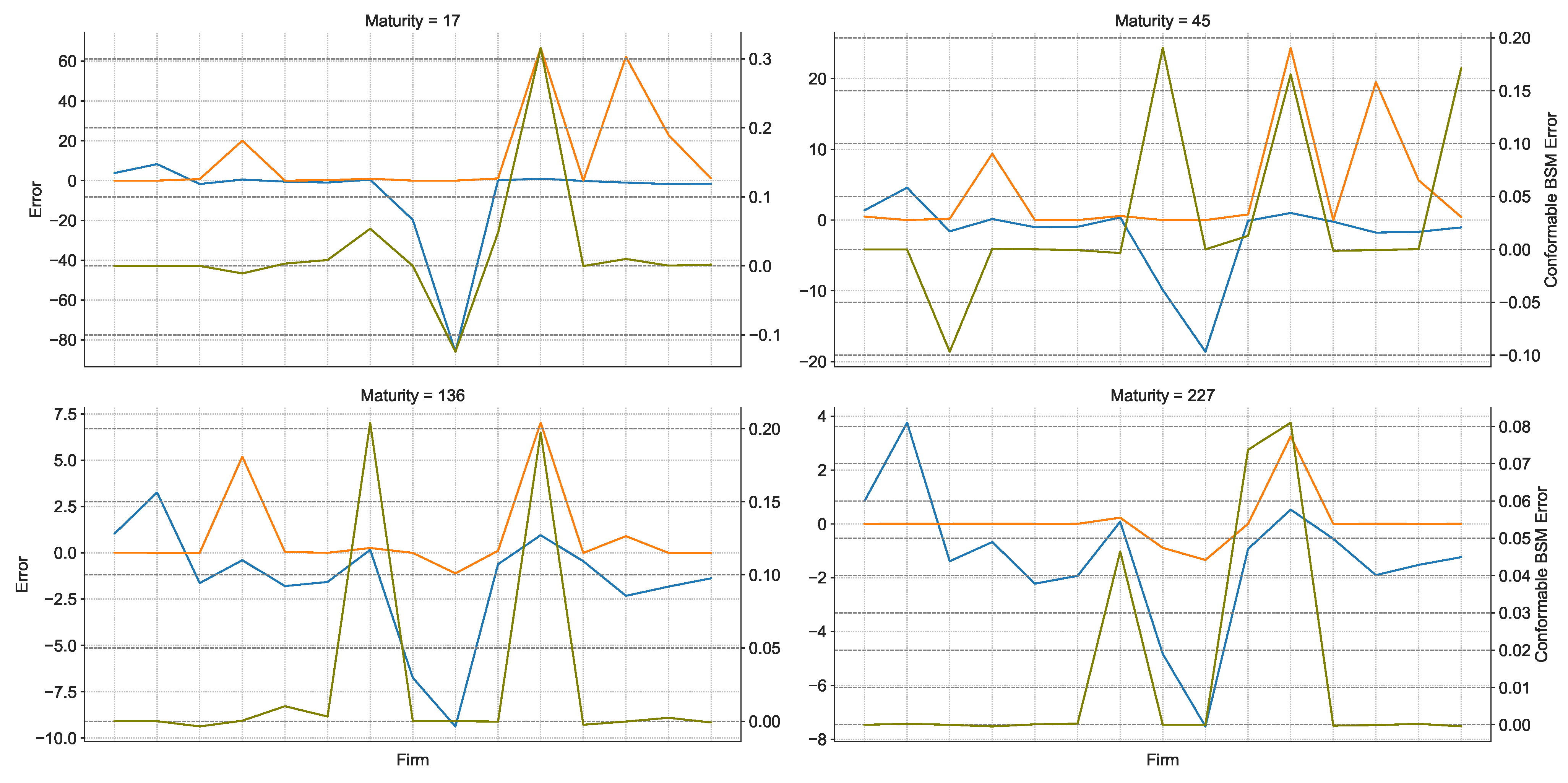
4. Empirical Analysis
- First, we estimate the GJR-GARCH (1, 1) process of [25] with skewed t innovations to each of the underlying assets;
- We then fit a quadratic regression to the estimated volatility process and use these coefficients to solve the conformable Black–Scholes equation with time-varying parameters.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMS | Black–Scholes–Merton |
| fBMS | Fractional Black–Scholes–Merton |
| CBMS | Conformable Black–Scholes–Merton |
References
- Exchange-Traded Derivatives Statistics. Available online: https://www.bis.org/statistics/extderiv.htm (accessed on 18 April 2022).
- World GDP. Bloomberg Terminal. Available online: https://bba.bloomberg.net/?utm_source=bloomberg-menu&utm_medium=company (accessed on 18 April 2022).
- Mikosch, T. Elementary Stochastic Calculus with Finance in View; Advanced Series in Statistical Science & Applied Probability; World Scientific: Singapore, 1998; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Karatzas, I.; Shreve, S.E. Brownian Motion and Stochastic Calculus; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Black, F.; Scholes, M. The Pricing of Options and Corporate Liabilities. J. Political Econ. 1973, 81, 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merton, R.C. Theory of Rational Option Pricing. Bell J. Econ. 1973, 4, 141–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, M.R.; Mamon, R.S. An alternative approach to solving the Black–Scholes equation with time-varying parameters. Appl. Math. Lett. 2006, 19, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Njomen, D.A.N.; Djeutcha, E. Solving Black-Schole Equation Using Standard Fractional Brownian Motion. J. Math. Res. 2019, 11, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyss, W. The fractional Black–Scholes equation. Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal. Int. J. Theory Appl. 2000, 1, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, F.; Turner, I.; Yang, Q. Numerical solution of the time fractional Black–Scholes model governing European options. Comput. Math. Appl. 2016, 71, 1772–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, M. Novel solution methods for initial boundary value problems of fractional order with conformable differentiation. Int. J. Optim. Control. Theor. Appl. 2018, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, M.; Özdemir, N. A different approach to the European option pricing model with new fractional operator. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 2018, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samorodnitsky, G. Long Range Dependence. Found. Trends® Stoch. Syst. 2007, 1, 163–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagini, F.; Hu, Y.; Øksendal, B.; Zhang, T. Stochastic Calculus for Fractional Brownian Motion and Applications; Springer: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cont, R. Long range dependence in financial markets. In Fractals in Engineering; Springer: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Necula, C. Option Pricing in a Fractional Brownian Motion Environment; Advances in Economic and Financial Research—DOFIN Working Paper Series 2; Bucharest University of Economics, Center for Advanced Research in Finance and Banking—CARFIB: Bucharest, Romania, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, R.; Al Horani, M.; Yousef, A.; Sababheh, M. A new definition of fractional derivative. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2014, 264, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilbas, A.A.; Srivastava, H.M.; Trujillo, J.J. Theory and Applications of Fractional Differential Equations; Volume 204 (North-Holland Mathematics Studies); Elsevier Science Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Abdeljawad, T. On conformable fractional calculus. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2015, 279, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Parvaneh, F.; Alamri, S.; Rajhi, A.A.; Anqi, A.E. Some exact wave solutions to a variety of the Schrödinger equation with two nonlinearity laws and conformable derivative. Results Phys. 2021, 31, 104929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo-Maldonado, J.C.; Fernandez-Anaya, G.; Ruiz-Martinez, O. Stability of conformable linear differential systems: A behavioural framework with applications in fractional-order control. IET Control. Theory Appl. 2020, 14, 2900–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Crescenzo, A.; Kaabar, M.K.A.; Martínez, F.; Martínez, I.; Siri, Z.; Paredes, S. Novel Investigation of Multivariable Conformable Calculus for Modeling Scientific Phenomena. J. Math. 2021, 2021, 3670176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.; Camrud, E.; Ulness, D. On the nature of the Conformable derivative and its applications to Physics. J. Fract. Calc. Appl. 2019, 10, 92–135. [Google Scholar]
- Hull, J. Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives, 6th ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Glosten, L.R.; Jagannathan, R.; Runkle, D.E. On the relation between the expected value and the volatility of the nominal excess return on stocks. J. Financ. 1993, 48, 1179–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cont, R. Empirical properties of asset returns: Stylized facts and statistical issues. Quant. Financ. 2001, 1, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, R. Analysis of Financial Time Series; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.Y.; Lo, A.W.; MacKinlay, A.C. The Econometrics of Financial Markets; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ghalanos, A. Rugarch: Univariate GARCH Models, R Package Version 1.4-7. 2022.
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Engle, R.F. Autoregressive Conditional Heteroscedasticity with Estimates of the Variance of United Kingdom Inflation. Econometrica 1982, 50, 987–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franq, C.; Zakoïan, J.M. GARCH Models: Structure, Statistical Inference and Financial Applications, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]

| Alfa, S.A.B. de C. V. | Grupo Aeroportuario del Centro Norte S.A.B. de C.V. |
| América Móvil, S.A.B. de C. V. | Grupo México S.A.B. de C.V. |
| Grupo Bimpo S.A.B. de C.V. | Orbia Advance Coorporation S.A.B. de C.V. |
| Cemex S.A.B. de C.V. | Grupo Aeroportuario del Sureste S.A.B. de C.V. |
| Grupo Aeroportuario del Pacífico S.A.B. de C.V. | Industrias Peñoles S.A.B. de C.V. |
| Coca-Cola FEMSA S.A.B. de C.V. | GMexico Transportes S.A.B. de C.V. |
| Fomento Económico Mexicano S.A.B. de C.V. | Grupo Televisa S.A.B. |
| Gruma, S.A.B. de C.V. | Walmart Inc. |
| Firm | Industry | Sector (GICS) | Stock Price on Expiration Date (USD) | Price Range for the Option (USD) | Implicit Market Volatility | GJR-GARCH Volatility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alsea, S.A.B. de. C. V. | Consumer Discretionary | Restaurants | 19.08 | 17–21 | 1.51% | 3.56% |
| América Móvil S.A.B. de C.V. | Communication Services | Wireless Telecommunication Services | 15.17 | 12–14 | 0.89% | 4.10% |
| Grupo Bimbo S.A.B. de C.V. | Consumer Staples | Packaged Foods and Meats | 42.45 | 38–46 | 2.12% | 2.79% |
| Cemex S.A.B. de C.V. | Materials | Construction Materials | 8.77 | 8–10 | 1.69% | 1.05% |
| Grupo Aeroportuario del Pacífico S.A.B. de C.V. | Industrial | Airport Services | 218.75 | 170–190 | 2.49% | 1.22% |
| Coca-Cola Femsa S.A.B. de C.V. | Consumer Staples | Soft Drinks | 82.10 | 70–90 | 1.04% | 1.11% |
| Fomento Económico Mexicano S.A.B. de C.V. | Consumer Staples | Alcoholic Beverages | 115.34 | 110–125 | 1.08 % | 1.14% |
| Gmexico Transportes S.A.B. de C.V. | Transportation | Railroads | 21.25 | 22–30 | 1.67 % | 0.43 % |
| Grupo Lala S.A.B. de C.V. | Consumer Staples and Packaged Foods | Meats | 12.66 | 8–16 | 1.0% | 1.39 % |
| Grupo Aeroportuario del Centro Norte S.A.B. de C. V. | Industrials | Airport Services | 100.79 | 90–110 | 3.84% | 1.29% |
| Grupo México S.A.B. de C. V. | Materials | Diversified Materials and Mining | 61.68 | 42–50 | 1.79% | 1.22% |
| Orbia Advance Corporation S.A.B. de C.V. | Materials | Commodity Chemicals | 37.26 | 32–38 | 1.18% | 1.26% |
| Grupo Aeroportuario del Sureste S.A.B. de C. V. | Industrials | Airport Services | 327.37 | 210–230 | 1.34% | 2.37%% |
| Industrias Peñoles S.A.B. de C.V. | Materials | Precious Metals and Minerals | 333.98 | 320–380 | 1.90% | 2.81% |
| Grupo Televisa S.A.B. | Communication Services | Cable and Satelite | 28.25 | 24–32 | 2.17% | 1.63% |
| Walmart de México S.A.B. de C.V. | Consumer Staples | Hypermarkets and Super Centers | 3054.45 | 50–58 | 1.42% | 3.56% |
| Mean | Median | Max | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | BSM | CBSM | fBSM | BSM | CBSM | fBSM | BSM | CBSM | fBSM |
| Firm | |||||||||
| Alsea | 2.2011% | 0.0000% | 0.4439% | 1.2171% | 0.0000% | 0.0000% | 12.1989% | 0.0000% | 3.9220% |
| América Móvil | 6.0480% | 0.0001% | 0.5273% | 4.0211% | 0.0000% | 0.0007% | 29.8127% | 0.0008% | 5.5578% |
| Bimbo | −1.9798% | −0.0251% | 11.9321% | −1.6125% | −0.0000% | 0.0000% | −0.5929% | 0.0000% | 159.5435% |
| Cemex | −0.0819% | −0.0026% | 46.6565% | −0.1854% | −0.0000% | 4.2657% | 0.9442% | 0.0034% | 703.9487% |
| Coca Cola Femsa | −2.4881% | 0.0035% | 90.2049% | −1.2365% | 0.0001% | 0.0021% | −0.0243% | 0.0519% | 906.5598% |
| Femsa | −4.5734% | 0.0028% | 379.2278% | −1.3620% | 0.0001% | 0.0029% | 0.0971% | 0.0390% | 7229.0118% |
| Grupo Aeroportuario Centro Del Norte | 0.3063% | 0.0752% | 3.2827% | 0.2084% | 0.0088% | 0.3010% | 0.9111% | 0.5211% | 22.9041% |
| Grupo Aeroportuario Del Pacífico | −39.3931% | 0.0476% | −0.4437% | −7.0531% | 0.0000% | −0.0000% | −3.8737% | 0.9519% | 0.1505% |
| Grupo Aeroportuario Del Sureste | −493.4705% | −0.0311% | −2.7148% | −11.3131% | 0.0000% | −0.7136% | −2.2531% | 0.0002% | 0.0004% |
| Grupo Lala | −0.6511% | 0.0336% | 122.5084% | −0.1883% | −0.0000% | 0.3233% | 0.9983% | 0.3705% | 1213.2169% |
| Grupo Mexicano De Transportes | 0.8386% | 0.1899% | 229.5076% | 0.9933% | 0.0001% | 9.3984% | 1.0000% | 0.9871% | 2944.7110% |
| Grupo México | −0.3340% | −0.0010% | 0.0069% | −0.3033% | −0.0004% | −0.0001% | 0.0121% | 0.0007% | 0.1442% |
| Orbia | −2.3285% | 0.0023% | 214.7498% | −1.6844% | −0.0000% | 1.2961% | −0.1739% | 0.0867% | 2642.7659% |
| Peñoles | −3.9684% | 0.0008% | 106.3420% | −1.6802% | 0.0001% | 0.0009% | −0.2050% | 0.0140% | 1866.8535% |
| Televisa | −1.2619% | 0.0429% | 56.3791% | −1.3056% | −0.0001% | 0.1331% | 0.0876% | 0.8513% | 929.9902% |
| Walmart | −1855.4816% | −0.1556% | −1770.1676% | −1170.4865% | 0.0000% | −1017.0738% | −582.6037% | 0.3518% | 0.0000% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morales-Bañuelos, P.; Muriel, N.; Fernández-Anaya, G. A Modified Black-Scholes-Merton Model for Option Pricing. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10091492
Morales-Bañuelos P, Muriel N, Fernández-Anaya G. A Modified Black-Scholes-Merton Model for Option Pricing. Mathematics. 2022; 10(9):1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10091492
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorales-Bañuelos, Paula, Nelson Muriel, and Guillermo Fernández-Anaya. 2022. "A Modified Black-Scholes-Merton Model for Option Pricing" Mathematics 10, no. 9: 1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10091492
APA StyleMorales-Bañuelos, P., Muriel, N., & Fernández-Anaya, G. (2022). A Modified Black-Scholes-Merton Model for Option Pricing. Mathematics, 10(9), 1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10091492







