Iron Transport across Brain Barriers: Model and Numerical Parameter Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Biological Background
1.2. Previous Mathematical Models
1.3. Aim of the Work
2. Methods
2.1. Mathematical Model
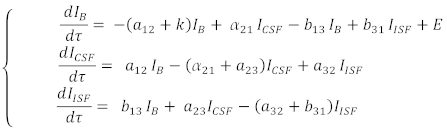 | (1) |
| (2) | |
| (3) |
2.2. Parameters Estimation
3. Results
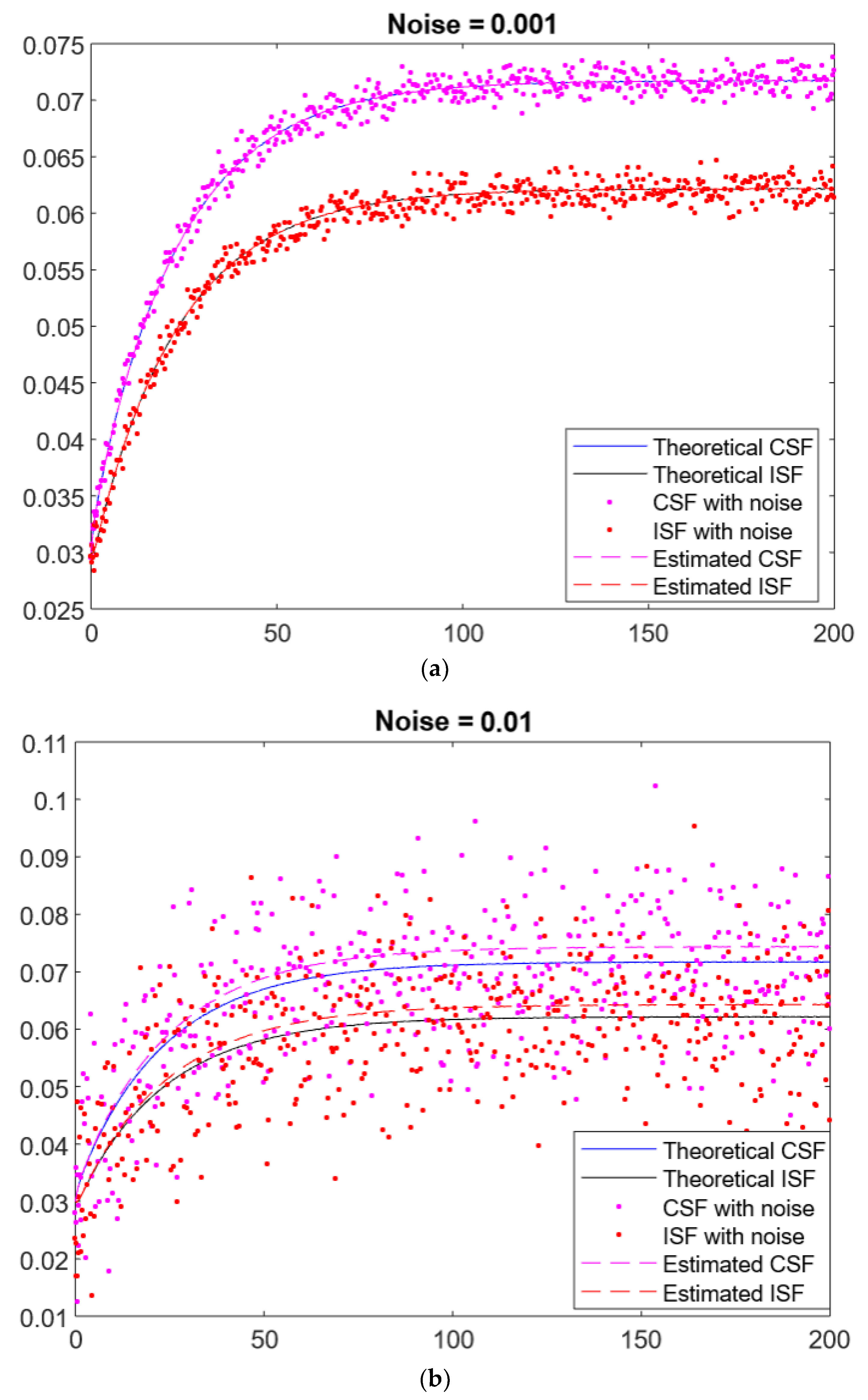
3.1. Estimation of One Parameter
3.2. Estimation of Two Parameters
3.3. Estimation of Three Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ndayisaba, A.; Kaindlstorfer, C.; Wenning, G.K. Iron in Neurodegeneration—Cause or Consequence? Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, A.; So, P.-W. Spotlight on Ferroptosis: Iron-Dependent Cell Death in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficiarà, E.; Munir, Z.; Boschi, S.; Caligiuri, M.E.; Guiot, C. Alteration of Iron Concentration in Alzheimer’s Disease as a Possible Diagnostic Biomarker Unveiling Ferroptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, C.M.; Jain, S.; Cook, A.D.; Packard, L.E.; Mullin, H.A.; Chen, N.; Liu, C.; Song, A.W.; Madden, D.J. Cortical Iron Mediates Age-Related Decline in Fluid Cognition. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2022, 43, 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, R.C.; Kosman, D.J. Iron Transport across the Blood-Brain Barrier: Development, Neurovascular Regulation and Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moos, T.; Morgan, E.H. Transferrin and Transferrin Receptor Function in Brain Barrier Systems. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2000, 20, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Aschner, M.; Ghersi-Egea, J.-F. Brain Barrier Systems: A New Frontier in Metal Neurotoxicological Research. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2003, 192, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Monnot, A.D. Regulation of Brain Iron and Copper Homeostasis by Brain Barrier Systems: Implication in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 133, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorefeldt, A.; Illes, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Hanse, E. Neuromodulation via the Cerebrospinal Fluid: Insights from Recent in Vitro Studies. Front. Neural. Circuits 2018, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boespflug, E.L.; Iliff, J.J. The Emerging Relationship Between Interstitial Fluid-Cerebrospinal Fluid Exchange, Amyloid-β, and Sleep. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes-Hampton, G.P.; Chakrabarti, M.; Cockrell, A.L.; McCormick, S.P.; Abbott, L.C.; Lindahl, L.S.; Lindahl, P.A. Changing Iron Content of the Mouse Brain during Development. Metallomics 2012, 4, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-H.; Singh, N.; Tay, H.; Walczyk, T. Imbalance of Iron Influx and Efflux Causes Brain Iron Accumulation over Time in the Healthy Adult Rat. Metallomics 2014, 6, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, T.J.; Luganskaja, T.; Vujić Spasić, M.; Hentze, M.W.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Schümann, K.; Reich, J.G. Systems Analysis of Iron Metabolism: The Network of Iron Pools and Fluxes. BMC Syst. Biol. 2010, 4, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berzuini, C.; Franzone, P.C.; Stefanelli, M.; Viganotti, C. Iron Kinetics: Modelling and Parameter Estimation in Normal and Anemic States. Comput. Biomed. Res. 1978, 11, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollycove, M.; Mortimer, R. The Quantitative Determination Of Iron Kinetics And Hemoglobin Synthesis In Human Subjects. J. Clin. Invest. 1961, 40, 753–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.I.; Liu, J.; Dutta, P. Iron Transport Kinetics through Blood-Brain Barrier Endothelial Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2018, 1862, 1168–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficiarà, E.; D’Agata, F.; Ansari, S.; Boschi, S.; Rainero, I.; Priano, L.; Cattaldo, S.; Abollino, O.; Cavalli, R.; Guiot, C. A Mathematical Model for the Evaluation of Iron Transport across the Blood-Cerebrospinal Fluid Barrier in Neurodegenerative Diseases. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 2270–2273. [Google Scholar]
- Ficiarà, E.; D’Agata, F.; Cattaldo, S.; Priano, L.; Mauro, A.; Guiot, C. A Compartmental Model for the Iron Trafficking Across the Blood-Brain Barriers in Neurodegenerative Diseases. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine Biology Society (EMBC), Virtual Conference, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 4200–4203. [Google Scholar]
- Ficiarà, E.; Boschi, S.; Ansari, S.; D’Agata, F.; Abollino, O.; Caroppo, P.; Di Fede, G.; Indaco, A.; Rainero, I.; Guiot, C. Machine Learning Profiling of Alzheimer’s Disease Patients Based on Current Cerebrospinal Fluid Markers and Iron Content in Biofluids. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R.C. Particle Swarm Optimization. Proc. 1995 IEEE Int. Conf. Neural Netw. 1995, 1, 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, M.E.H.; Chipperfield, A.J. Simplifying Particle Swarm Optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2010, 10, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Eberhart, R.C. A Modified Particle Swarm Optimizer. Proc. 1998 IEEE Int. Conf. Evol. Comput. 1998, 1, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Perracchione, E.; Stura, I. RBF Kernel Method and Its Applications to Clinical Data. Dolomites Res. Notes Approx. 2016, 9, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Massa, P.; Perracchione, E.; Garbarino, S.; Battaglia, A.F.; Benvenuto, F.; Piana, M.; Hurford, G.; Krucker, S. Imaging from STIX Visibility Amplitudes. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 656, A25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.; Nocedal, J. Numerical Optimization. Springer Sci. 1999, 35, 67–68. [Google Scholar]
- Stura, I.; Perracchione, E.; Migliaretti, G.; Cavallo, F. A New Numerical Method for Processing Longitudinal Data: Clinical Applications. Epidemiol. Biostat. Public Health 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecca, L.; Youdim, M.B.H.; Riederer, P.; Connor, J.R.; Crichton, R.R. Iron, Brain Ageing and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficiarà, E.; Stura, I.; Guiot, C. Iron Deposition in Brain: Does Aging Matter? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahnke, J.; Langer, O.; Krohn, M. Alzheimer’s and ABC Transporters--New Opportunities for Diagnostics and Treatment. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 72 Pt A, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Description | Normal Value | High Rate Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| E | Iron intake into the blood from food (mg/L) | 0.22 | 0.22 |
| k | Iron consumption from blood and excretion mechanisms | 0.23 | 0.23 |
| Kinetic constant rate for iron entering from blood to CSF across BCSFB | 0.0002 | 0.001 | |
| Kinetic constant rate for iron returning from CSF and brain to blood | 0.05 | 0.08 | |
| Kinetic constant rate for iron passing from CSF to ISF | 0.8 | 0.8 | |
| Kinetic constant rate for iron passing from ISF to CSF | 1 | 1 | |
| Kinetic constant rate for iron entering from blood to brain (consequently ISF), across BBB | 0.002 | 0.005 | |
| Kinetic constant rate for iron returning from the brain to blood | 1 × 10−6 | 5 × 10−6 |
| N° of Estimated Parameters | Noise | Parameter | Estimation for PC | Estimation for HRC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0.0500 | 4.2689 × 10−15 | 0.0800 | 3.8223 × 10−15 | |
| 1.0000 | 1.1465 × 10−15 | 1.0000 | 7.0460 × 10−13 | |||
| 0.8000 | 2.3891 × 10−11 | 0.8000 | 8.4539 × 10−15 | |||
| 0.0020 | 0.6540 | 0.0050 | 0.9318 | |||
| 0.001 | 0.0501 | 5.8056 × 10−6 | 0.0799 | 1.9159 × 10−6 | ||
| 1.0014 | 1.2567 × 10−6 | 1.0041 | 2.8066 × 10−5 | |||
| 0.7926 | 3.5431 × 10−5 | 0.7977 | 1.0568 × 10−5 | |||
| 0.0020 | 0.5723 | 0.0050 | 0.4659 | |||
| 0.01 | 0.0491 | 4.9117 × 10−4 | 0.0818 | 0.0011 | ||
| 0.9356 | 0.0023 | 0.9647 | 0.0019 | |||
| 0.7457 | 0.0024 | 0.7780 | 0.0010 | |||
| 0.0020 | 0.4909 | 0.0050 | 0.9318 | |||
| 2 | 0 | 0.0500 | 3.3379 × 10−14 | 0.0800 | 7.9000 × 10−15 | |
| 1.0000 | 1.0000 | |||||
| 0.0500 | 3.4623 × 10−15 | 0.0800 | 1.2001 × 10−4 | |||
| 0.8000 | 0.8000 | |||||
| 0.8000 | 0.0079 | 0.5998 | 0.0013 | |||
| 1.0000 | 0.7692 | |||||
| 0.0930 | 0.0542 | 0.0800 | 0.0428 | |||
| 0.0037 | 0.0050 | |||||
| 1.0000 | 0.3967 | 0.9909 | 0.5573 | |||
| 0.0020 | 0.0050 | |||||
| 0.001 | 0.0503 | 3.5199 × 10−5 | 0.0800 | 1.2536 × 10−5 | ||
| 0.9900 | 1.0007 | |||||
| 0.0499 | 5.0687 × 10−6 | 0.0798 | 1.0124 × 10−5 | |||
| 0.7968 | 0.7967 | |||||
| 0.0865 | 0.0324 | 0.6639 | 0.2220 | |||
| 0.1594 | 0.8440 | |||||
| 0.0503 | 0.2401 | 0.0861 | 0.1399 | |||
| 0.0020 | 0.0054 | |||||
| 1.0223 | 0.1548 | 0.9963 | 0.5516 | |||
| 0.0020 | 0.0050 | |||||
| 0.01 | 0.0530 | 0.0052 | 0.0824 | 0.0044 | ||
| 0.9310 | 0.9339 | |||||
| 0.0505 | 0.0232 | 0.0791 | 0.1628 | |||
| 0.7411 | 0.7824 | |||||
| 0.0036 | 1.0892 × 10−4 | 0.0767 | 5.0163 × 10−4 | |||
| 0.0610 | 0.1621 | |||||
| 0.1105 | 0.1275 | 0.0850 | 0.0238 | |||
| 0.0043 | 0.0053 | |||||
| 0.8054 | 0.2116 | 0.9838 | 0.4631 | |||
| 0.0019 | 0.0049 | |||||
| 3 | 0 | 1.4080 | 6.4164 × 10−4 | 1.5710 | 0.0920 | |
| 2.6049 | 2.7064 | |||||
| 0.0620 | 0.1121 | |||||
| 0.0500 | 0.1364 | 0.0800 | 0.0157 | |||
| 1.2887 | 0.9199 | |||||
| 1.0443 | 0.7302 | |||||
| 0.001 | 0.8329 | 41.6743 | 0.6466 | 0.1379 | ||
| 1.9264 | 1.6499 | |||||
| 0.0366 | 0.0459 | |||||
| 0.0500 | 4.5772 × 10−5 | 0.0799 | 0.4450 | |||
| 1.3334 | 0.3549 | |||||
| 1.0806 | 0.2391 | |||||
| 0.01 | 1.9090 | 9.6464 | 1.0405 | 0.0699 | ||
| 3.1090 | 2.0884 | |||||
| 0.0844 | 0.0743 | |||||
| 0.0486 | 0.0030 | 0.0809 | 0.5067 | |||
| 0.1231 | 2.2613 | |||||
| 0.0451 | 1.9322 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ficiarà, E.; Stura, I.; Guiot, C. Iron Transport across Brain Barriers: Model and Numerical Parameter Estimation. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10234461
Ficiarà E, Stura I, Guiot C. Iron Transport across Brain Barriers: Model and Numerical Parameter Estimation. Mathematics. 2022; 10(23):4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10234461
Chicago/Turabian StyleFiciarà, Eleonora, Ilaria Stura, and Caterina Guiot. 2022. "Iron Transport across Brain Barriers: Model and Numerical Parameter Estimation" Mathematics 10, no. 23: 4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10234461
APA StyleFiciarà, E., Stura, I., & Guiot, C. (2022). Iron Transport across Brain Barriers: Model and Numerical Parameter Estimation. Mathematics, 10(23), 4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10234461






