Nonlinear Frequency-Modulated Waveforms Modeling and Optimization for Radar Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modeling and Optimization of NLFM Waveform
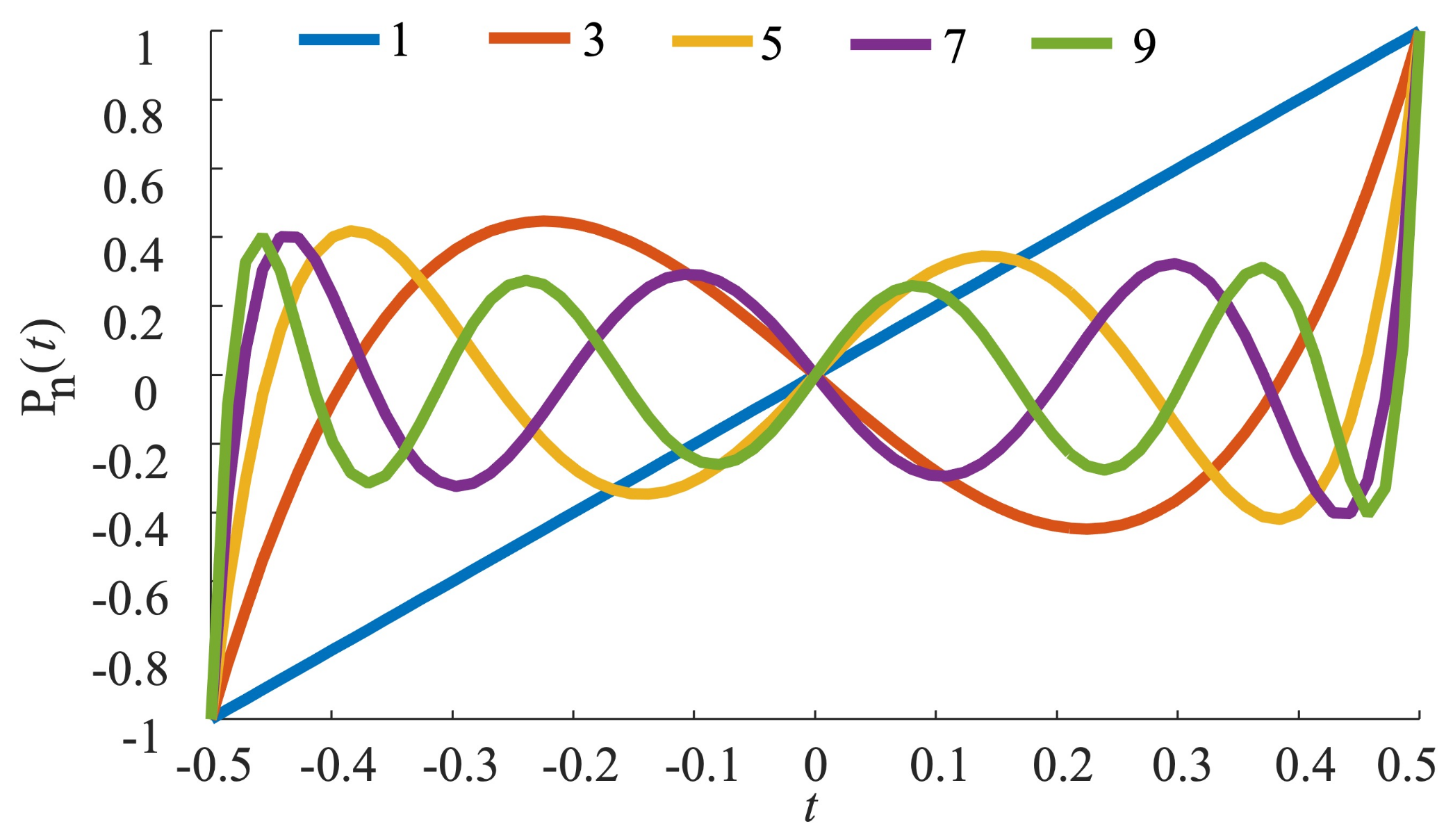
2.1. Modeling of NLFM Waveforms
- Step 1:
- Input the coefficient vector of the Legendre polynomial ;
- Step 2:
- Define a frequency function of time based on the coefficient vector of the Legendre polynomial using Equation (1);
- Step 3:
- Integrate the frequency function to obtain the phase function using Equation (2);
- Step 4:
- Output the NLFM signal waveform using Equation (3);
- Step 5:
- Assess the signal performance.
2.2. Optimization of NLFM Waveform
- Step 1:
- Initialize each firefly as
- Step 2:
- Step 3:
- Rank the fireflies by light intensity and find the current global best solution (corresponding to the brightest one).
- Step 4:
- Move all fireflies toward the brighter ones by Equation (8).
- Step 5:
- Repeat Steps 2–5 until the iteration times reach the threshold of the objective function.
3. Numerical Results
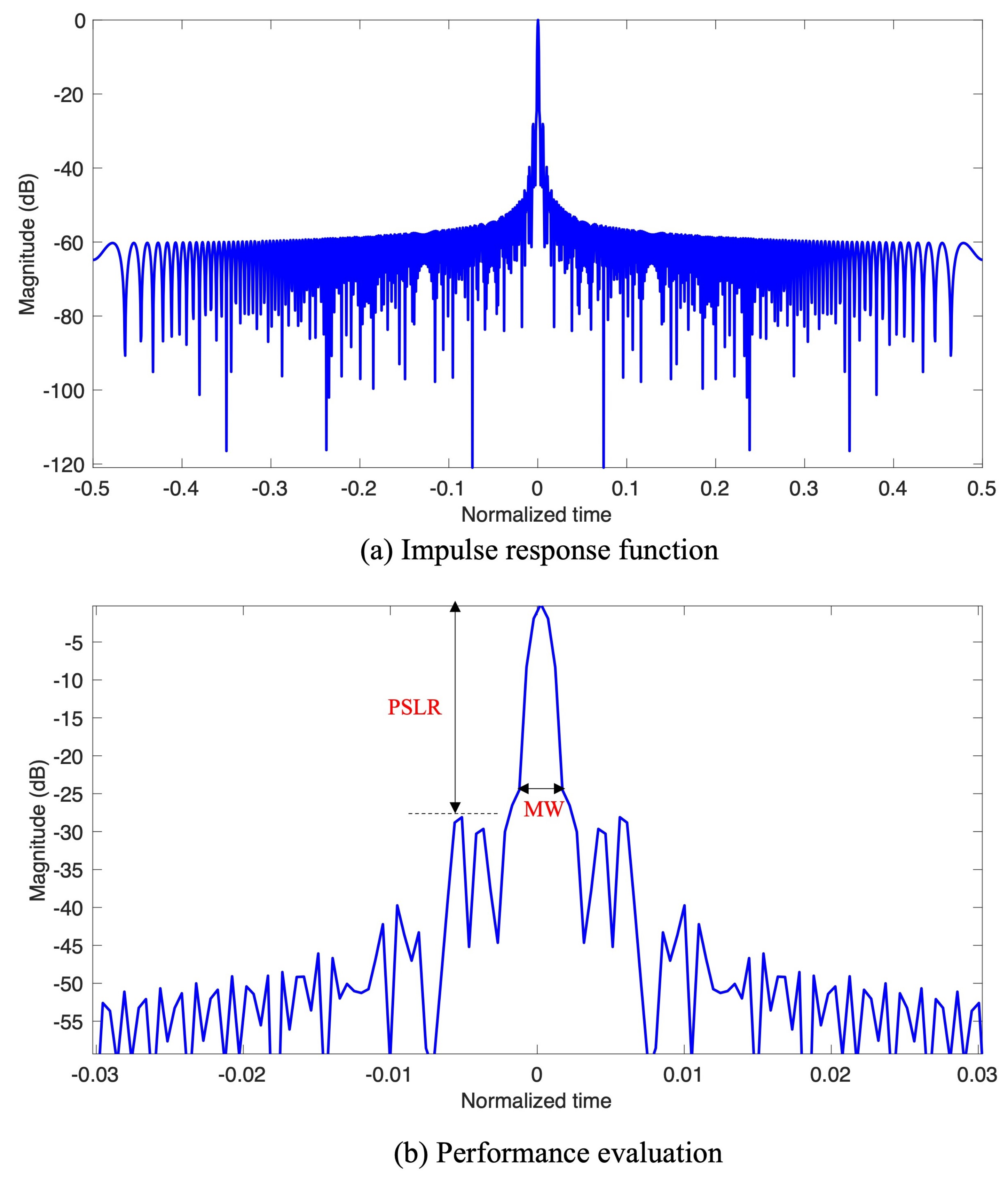
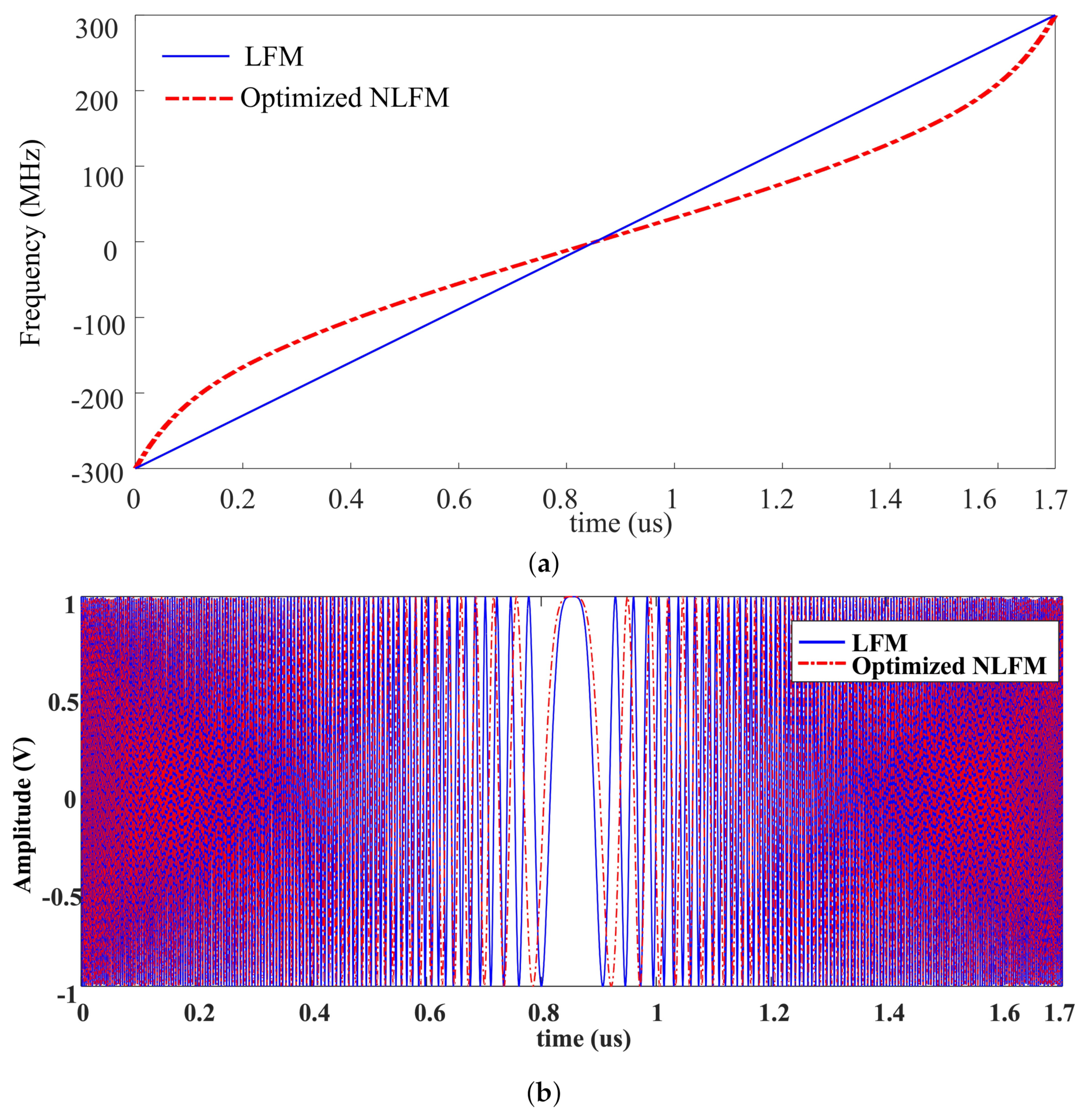
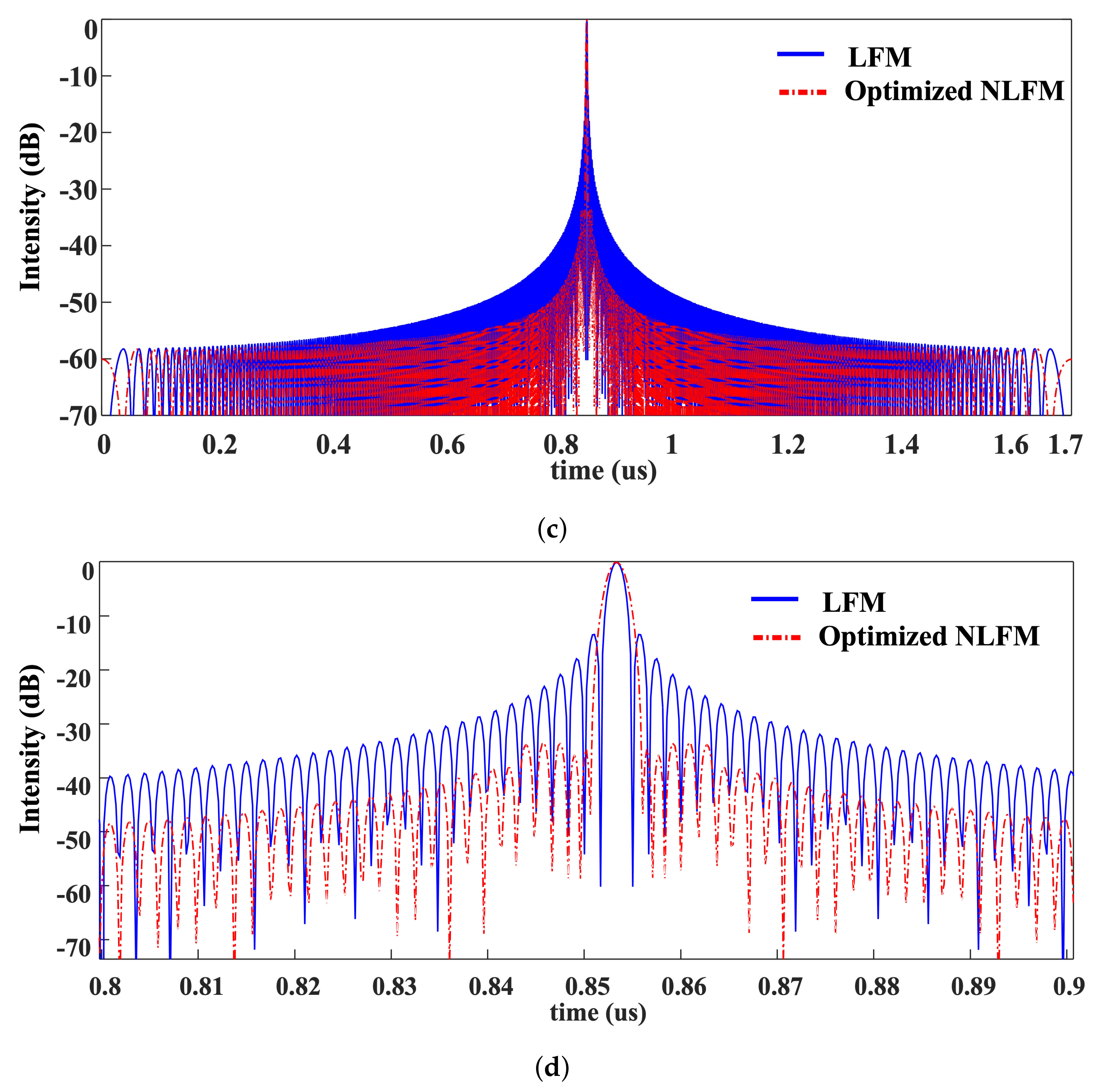
3.1. Numerical Results of the NLFM Signal
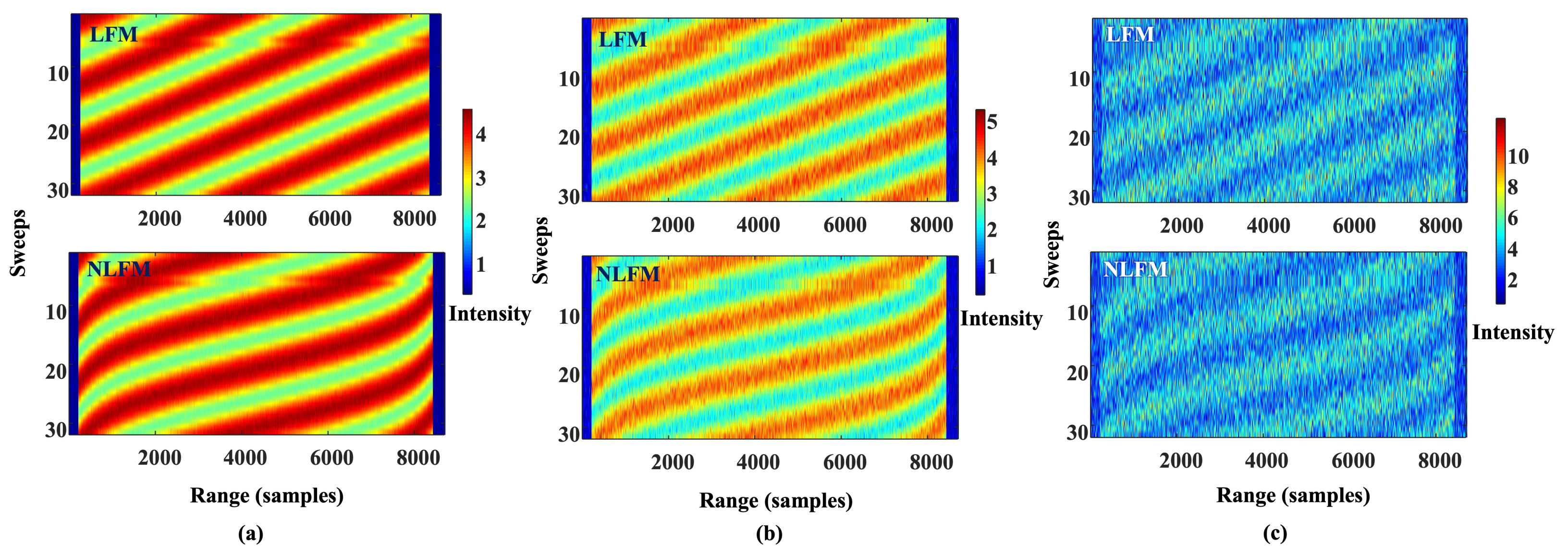
3.2. Application of the Optimized NLFM Signal for Radar-Target Range and Velocity Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Curlander, J.C.; McDonough, R.N. Synthetic Aperture Radar Systems and Signal processing; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.H.; Baker, C.J.; Pooni, S. Range and Doppler Cell Migration in Wideband Automotive Radar. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 5527–5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Xue, S.; Wang, Y. Incoherent Interference Detection and Mitigation for Millimeter-Wave FMCW Radars. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdzo, J.M.; Cheong, B.L.; Palmer, R.D.; Zhang, G.; Meier, J.B. A pulse compression waveform for improved-sensitivity weather radar observations. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 2713–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Richards, M.A. Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Milczarek, H.; Leśnik, C.; Djurović, I.; Kawalec, A. Estimating the Instantaneous Frequency of Linear and Nonlinear Frequency Modulated Radar Signals—A Comparative Study. Sensors 2021, 21, 2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, G.; Deng, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, W.; Wang, P.; Long, Y.; Zhang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y. An advanced nonlinear frequency modulation waveform for radar imaging with low sidelobe. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6155–6168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Li, N.; Hou, L.; Xu, Z. First demonstration of airborne SAR with nonlinear FM chirp waveforms. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.H.; Shi, Q. Interference Mitigation for Automotive Radar Using Orthogonal Noise Waveforms. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.H.; Shi, Q.; Sun, L. Novel Orthogonal Random Phase-Coded Pulsed Radar for Automotive Application. J. Radars 2018, 7, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.H.; Wang, R.; Ye, K.; Wang, W.; Quan, S.; Wei, M. Simultaneous range ambiguity mitigation and sidelobe reduction using orthogonal non-linear frequency-modulated (ONLFM) signals for satellite SAR Imaging. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 9, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ritchie, M.; Lu, X.; Su, W.; Gu, H. Non-continuous piecewise nonlinear frequency modulation pulse with variable sub-pulse duration in a MIMO SAR radar system. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 11, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.H.; Deng, Y.k.; Wang, Y. A novel optimization framework for classic windows using bio-inspired methodology. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 35, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levanon, N.; Mozeson, E. Radar Signals; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Li, H.C.; Shi, Q.; Wang, H.; Wei, M.; Shi, J.; Shao, Y. Effect analysis and spectral weighting optimization of sidelobe reduction on SAR image understanding. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 3434–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, I.G.; Wong, F.H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]




| SNR (dB) | LFM | WLFM | NLFM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 7.302 | 1.441 | 0.665 |
| 15 | 7.254 | 1.378 | 0.641 |
| 30 | 7.249 | 1.365 | 0.630 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Nonlinear Frequency-Modulated Waveforms Modeling and Optimization for Radar Applications. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3939. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10213939
Xu Z, Wang X, Wang Y. Nonlinear Frequency-Modulated Waveforms Modeling and Optimization for Radar Applications. Mathematics. 2022; 10(21):3939. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10213939
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zhihuo, Xiaoyue Wang, and Yuexia Wang. 2022. "Nonlinear Frequency-Modulated Waveforms Modeling and Optimization for Radar Applications" Mathematics 10, no. 21: 3939. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10213939
APA StyleXu, Z., Wang, X., & Wang, Y. (2022). Nonlinear Frequency-Modulated Waveforms Modeling and Optimization for Radar Applications. Mathematics, 10(21), 3939. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10213939








