Abstract
The increase in air pollution levels in recent decades around the world has caused a negative impact on human health. A recent investigation by the World Health Organization indicates that nine out of ten people on the planet breathe air containing high levels of pollutants and seven million people die each year from this cause. This problem is present in several cities in South America due to dangerous levels of particulate matter present in the air, particularly in the winter period, making it a public health problem. Santiago in Chile and Lima in Peru are among the ten cities with the highest levels of air pollution in South America. The location, climate, and anthropogenic conditions of these cities generate critical episodes of air pollution, especially in the coldest months. In this context, we developed a semiparametric model to predict particulate matter levels as a function of meteorological variables. For this, we discuss estimation and diagnostic procedures using a Student’s -based partially varying coefficient model. Parameter estimation is performed through the penalized maximum likelihood method using smoothing splines. To obtain the parameter estimates, we present a weighted back-fitting algorithm implemented in R-project and Matlab software. In addition, we developed local influence techniques that allowed us to evaluate the potential influence of certain observations in the model using four different perturbation schemes. Finally, we applied the developed model to real data on air pollution and meteorological variables in Santiago and Lima.
Keywords:
air pollution; local influence measure; maximum penalized likelihood estimates; partial varying coefficient model; Student t distribution; weighted back-fitting algorithm MSC:
62J20
1. Introduction
Particulate matter (PM) with an aerodynamic diameter of less than 2.5 μm (PM 2.5) is composed of small particles, and is capable of entering the respiratory system, reaching the lungs and even the alveoli; see [1]. For more than three decades, the city of Santiago in Chile has presented particulate levels that exceed national and international air quality regulations. Its location, topography, and meteorology cause conditions that can have critical effects on human health. During the coldest months of autumn and winter, pollutants become concentrated in the Santiago valley, producing air pollution in the city; see [2].
Peru is a highly urban country, with a high density in Lima, which is considered one of the most polluted cities in Latin America [3]. In this context, the need arises to propose cutting-edge methodologies that can support environmental management [4] with the aim of making more precision estimates and diagnostic analyses to support decision-making and establish policies for adequate mitigation and prevention.
Periodical episodes of extreme air pollution can occur with certain contaminants. These contaminants and their high concentrations vary according to meteorological and geographical fluctuations, which depend on the source and type of emission changes. Because of this variation, atmospheric contaminant concentrations are treated as random variables, which can be modeled by probability distributions; see [2]. Weather conditions are a key uncontrollable factor in determining air pollution variability. In certain cases, this can overcome the influence of certain anthropogenic effects, such as those caused by vehicle traffic; see [5]. Furthermore, the relationship between meteorological variables and PM has been analyzed worldwide [6]; several of these variables are considered as explanatory variables in the model proposed in this study. The relationship between meteorological parameters and PM has been studied using different statistical techniques, including multiple linear regression, generalized additive models, multivariate adaptive regression splines, multivariate regression, neural networks, and support vector machine regression; see [7].
In recent years, there have been several attempts to improve the flexibility of linear regression models, leading to new advances, such as the approach of replacing linear models and parametric functions of regressors with nonparametric smooth functions, such as in the additive models proposed by Hastie and Tibshirani [8]. This concept has lead to the varying coefficient model (VCM), which allows for special interactions between regressor variables by means of smooth functions, permitting the dynamic characteristics that may be present in certain datasets to be explored; see [9]. In the context of the semiparametric model, different works have been developed with interesting applications in various research areas. For example, Ibacache-Pulgar et al. [10] extended normal semiparametric additive models to the symmetric case. In [11], Ibacache-Pulgar et al. proposed the elliptic semiparametric mixed effects model and illustrated its applicability with two real data sets from the medical field. Ibacache-Pulgar and Reyes [9] introduced elliptic partially varying coefficient models showing, through an application with real data, the importance of this class of models in modeling dynamic trends present in the data. Recently, Lira et al. [12] studied partially varying coefficient generalized linear models and showed, through an application involving air pollution data, the advantages of these models in relation to others proposed in the literature.
The main goal of the present research is to study the estimation and diagnostic analysis for Student’s PVCM (called Student- PVCM hereafter) in order to model pollution data, addressing specific points such as the study of the theory of the PVCM model, the derivation of an interactive process to obtain the parameter estimates, and the development of a diagnostic analysis. It is important to mention that local influence offers a look at how the action of a small perturbation in the model can cause a crucial change in the results. There is a vast literature on this topic, starting with [13], who integrated the approach of assessing the sensitivity of parameter estimators when small perturbations are introduced in the model assumptions or in the data. Works related to this diagnostic technique include the following. Zhang et al. [14] and Ibacache-Pulgar and Reyes [9] developed local influence measures for normal and elliptical PVCM, respectively. Ferreira and Paula [15] extended the local influence technique for different perturbation schemes considering a skew-normal partially linear model, while Emami [16] applied local influence analysis to Liu’s penalized least squares estimators. Ibacache-Pulgar et al. [17] derived the normal curvature for the semiparametric additive beta regression model. Moraga et al. [18] studied the estimation and inference problem in elliptical thin-plate spline PVCM and performed a diagnostic analysis based on the residuals. Ibacache-Pulgar et al. [19] studied various diagnostic measures, both global and local, for the nonparametric regression model with symmetric random errors, obtaining evidence that the maximum penalized likelihood estimator (MPLE) derived from the iterative process under the Student- distribution with small degrees of freedom are less sensitive than those obtained under the normal model. Cárcamo et al. [20] incorporated a semiparametric additive term in the link function of the Birnbaum–Saunders regression model and extended the sensitivity analysis of maximum penalized likelihood estimators. Cavieres et al. [21] proposed a thin-plate spline regression model assuming that random errors follow a skew-normal distribution for spatial data, and extended the local influence method to assess the sensitivity of the estimators derived from the EM algorithm.
As mentioned above, VCM models are extensions of other models; however, for this research we focus on the PVCM with Student- distributional assumption. The main goal of this research is to study the estimation and diagnostic analysis for Student- PVCM in order to model pollution data, addressing specific points such as the study of the theory of the PVCM model, the derivation of an iterative process to obtain the parameter estimates, and the development of a diagnostic analysis. We introduce two applications where PVCM is used to model real-world PM data and meteorological variables during critical episodes management (CEM) in Santiago, Chile and Lima, Peru. In the first study, the data were obtained from the automatic monitoring network of atmospheric pollutants of the Metropolitan network (MACAM in Spanish) of the official website of the Chilean Ministry of Environment (MMA in Spanish), and in the second from the official website of the SENAMHI (Servicio Nacional de Meteorología e Hidrología del Peru in Spanish). Our main motivation was to study the association between the PM levels, temperature, and relative humidity, which can generate knowledge for the better monitoring of air quality management in Santiago and Lima. The datasets were analyzed with R-project (www.r-project.org) and Matlab (www.mathworks.com) software (accessed on 15 July 2021).
This research is organized as follows. Section 2 presents Student’s PVCM and considers a penalized log-likelihood function for parameter estimation. Section 3 discusses the process of obtaining MPLEs and the derivation of a back-fitting algorithm. In addition, this section contains inferential aspects of the studied model, among them the obtaining of confidence bands, a discussion of the estimation of the degrees of freedom, and the selection of the smoothing parameter. Section 4 considers the main concepts of local influence and derives the normal curvatures for perturbation schemes. Section 5 presents an illustration of the proposed model as applied to environmental datasets obtained from the official website of the Chilean MMA and from the official website of the SENAMHI, carried out using Matlab and R-project software. Specifically, we use Matlab to implement the parameter estimation algorithm and diagnostic techniques and R-project for data visualization. Finally, in Section 6, concluding remarks, limitations, and future research prospects are presented.
2. The Proposed Model
This section presents the PVCM and the distributional assumption considered for random errors. In addition, the penalized log-likelihood function used to carry out the model fit is presented.
2.1. The Model
The PVCM represents the relationship between the response variable and the explanatory variables, as follows:
where denotes the response value associated with the i-th individual or experimental unit, is the vector of an explanatory variable, is a unknown parameter vector, () are the unknown smooth arbitrary functions of explanatory variable and are associated with explanatory variable , and is a random error. From the point of view of statistical modeling, this model allows the coefficients to vary smoothly over the group stratified by , allowing nonlinear interactions between and . Note that the interaction between explanatory variables and allows, for a level different from explanatory variable , a different regression model around . The model provided in Equation (1) can be written in matrix form as
where is an random vector of observed responses, is an design matrix with rows , , , is an incidence matrix with the th element equal to the indicator , where denotes the distinct and ordered values of the explanatory variable is an vector, and is an errors vector.
2.2. Distributional Assumption
Usually, the PVCM assumes that the random errors follow a normal distribution. However, it is known that there are cases where a normal distribution is not appropriate, and thus the estimates could be wrong. One possible option to deal with this deficiency is to assume heavy-tailed distributions for the errors. One class of distributions containing such characteristics is the Student- distribution, which allows for more flexibility when analyzing heavier-tailed data sets. Thus, we assume that are independent random variables such that follows a Student- distribution with a mean of zero, dispersion parameter . and degrees of freedom, namely, . Therefore, has a probability density function provided by
where denotes the gamma function, with as the Mahalanobis distance, is the i-th row of , and denotes the degrees of freedom. Here, and for all .
2.3. Penalized Log-Likelihood Function
The log-likelihood function for where with can be expressed as follows:
where
A problem with using direct maximization of without imposing restrictions over the functions is that it leads to overfitting. An alternative route for determining the estimators of the functions is to incorporate a penalty function over each function . If we assume that belongs to the Sobolev function space [22], that is, belongs to the set of all continuously differentiable functions on with square integrable second derivatives, then the estimator of maximizes the penalized log-likelihood function
over all functions in this set, with the subscript p denoting the penalty of the function , a being a non-negative definite matrix, and . The first term on the right side of Equation (2) measures the goodness of fit, whereas the second term penalizes the roughness of each with a fixed parameter . In this case, the estimation of leads to a natural cubic spline with knots at points , that is, it is a piecewise polynomial of degree 3 in each interval ; see Green and Silverman [23]. It should be noted that the choice of , known in the literature as the smoothing parameters, is crucial in the estimation process, as they control the tradeoff between goodness of fit and the smoothness (regularity) estimated function. A more extensive discussion on the methods of selecting such parameters is presented later.
3. Parameter Estimation and Inference
In this section, we consider parameter estimation and inferential aspects associated with the Student- PVCM. In Section 3.1, we derive an iterative process to estimate the model parameters. In Section 3.2, we derive the variance–covariance matrix of the MPLEs from the inverse of the Fisher information matrix and propose approximate confidence bands for the smooth functions of the model. In Section 3.3, we present a discussion concerning the selection of smoothing parameters and the effective degrees of freedom associated with the nonparametric components. Finally, in Section 3.4, a method for selecting a model is presented.
3.1. Resolving the Estimation Equations
Assume that the function provided in Equation (2) is regular with respect to and . Then, the penalized score function of is
the elements of which can be written in the form
where , with , and . The natural procedure to determine the estimator of based on the maximization of the penalized likelihood function is equivalent to solving the equation . However, the estimating equations are nonlinear and require an iterative method. In this case, the determination of can be performed using, for example, the Fisher scoring algorithm, which is equivalent to solving the following estimating equation system
which leads to the following back-fitting (Gauss–Seidel) iterations:
and the solution for provided by
where and , with and . The system of Equation (3) is consistent and the back-fitting algorithm provided in Equation (4) converges to a solution for any starting values if the weight matrix is symmetric and positively defined [24]. Additionally, this solution is unique with no concurvity in the data. The estimation procedure for obtaining the maximum penalized likelihood estimator (MPLE) of iterates between a weighed back-fitting algorithm with weight matrix and a maximum likelihood estimation of the scale parameter.
3.2. Approximate Standard Errors
According to Ibacache-Pulgar et al. [10], the asymptotic variance–covariance matrix of can be obtained from the inverse Fisher information matrix, which in turn is calculated considering the penalized likelihood function as a likelihood function usual; see, for instance, Wahba [25] and Segal et al. [26]. For the purpose of computing the inverse matrix, denoted by , we consider and
where with . Note that this last matrix corresponds to the block of matrix associated with the nonparametric component of the model. Then, assuming that all the necessary inverses exist, the inverse matrix of assumes the following block diagonal form:
where and , with . Then, the asymptotic variance–covariance matrix of is provided by
We can consider an approximate pointwise standard error band (SEB) for nonparametric functions in order to evaluate the accuracy of the estimators for different locations within the range of interest. In our case, these approximate pointwise SEBs are provided by
where is the lth principal diagonal element of the matrix provided in Equation (5) for . Note that correspond to the knots associated with each variable with a contribution to the model that is nonparametric.
3.3. On Degrees of Freedom and Smoothing Parameters
The degrees of freedom (df) associated with the parametric component are defined as , where p is the rank of , while the df values for the nonparametric component are provided by . Previously, the smoothing parameters s were assumed to be fixed. However, in practical situations the smoothing parameters should be selected from the data. One way to select the smoothing parameters is when depends only on , and therefore the corresponding smoothing parameter can be specified. In other words, we pre-specify a target for a function and then find the value that achieves this target. This approach is used for the Generalized Additive Model and VCM in Hastie and Tibshirani [8,27], respectively; see Buja et al. [28] and Rigby and Stasinopoulos [29] as well.
3.4. Selecting an Appropriate Model
For Student- PVCM, the Akaike information criterion (AIC) or Bayes information criterion can be used to select an appropriate model for different degrees of freedom . The idea is to minimize the function
where denotes the penalized log-likelihood function available at for a fixed and denotes approximately the number of effective parameters involved in modeling of the smooth functions. A grid for different values of the degrees of freedom and its corresponding is useful for choosing the best model from the Student’s family.
4. Diagnostics
In this section, we perform a diagnostic analysis for the Student- PVCM. In Section 4.1, we propose a residual analysis based on closed expressions of the estimators of the parameters. In Section 4.2, we provide a general description of the local influence method and derive the normal curvature for three perturbation schemes.
4.1. Residual Analysis
In order to detect misspecification of the error distribution as well the presence of outlying observations, we propose a residual analysis approach. According to Opsomer [30] and Ibacache-Pulgar et al. [10], the system of equations provided in (3) can be written in matrix terms as follows:
if and are fixed and the inverse of exists. From this last equation, we obtain , where is the smoother matrix obtained when fitting the j-th explanatory variable only by smoothing spline, with being a partitioned matrix provided by
The estimators provide a useful tool to construct diagnostic techniques based on the residuals. Let . Then, the fitted values vector, denoted here by , is provided by , where the matrix is equivalent to the hat matrix defined in the class of parametric regression models. The leverage points obtained in the last iteration of the iterative process, denoted by , play an important role in the construction of diagnostic techniques in the class of nonparametric and semiparametric regression models. As is known, the residual vector is the difference between the observed data and estimated mean vectors, that is, . As is not a projection operator, that is, , we can find that the approximate variance of the residual vector is provided by , where . Then, we find that the lth Studentized residual takes the form
where , with denoting an vector with 1 at the lth position and 0 elsewhere for .
4.2. Local Influence Method
Let be the penalized log-likelihood function, where . Consider a perturbation in the model induced by an n-dimensional vector , and denote the perturbed penalized log-likelihood function by . We assume that there is a non-perturbation vector such that is verified. The likelihood displacement , where is the MPLE under , can be used to assess the influence of minor perturbations on the MPLE . The idea proposed by Cook [13] consists of studying the local behavior of around , selecting a unit direction , and then considering the plot of against a, where . We recommended studying the direction of , which corresponds to the greatest curvature . The index plot of eventually reveals the presence of observations that under small perturbations can exert a significant influence on . Cook [13] defined the normal curvature in the unit direction ℓ provided by , where and . The elements of matrix are presented in the Appendix A. Here, denotes the local influence on the estimate after perturbing the model or data. Poon and Poon [31] derived a normal curvature that remains invariant against changes in scale. This curvature is called the conformal normal curvature, and is defined as follows:
This curvature, unlike those defined above, admits that for any unit vector ℓ one has . The idea is to consider the direction corresponding to the largest curvature , or alternatively, considering the normal curvature at the direction and observing the index plot of , where is an n-dimensional vector with zero at the i-th position and zeros at the remaining positions. Next, we consider the calculation of the matrix for four perturbations schemes: weight, scale perturbation, explanatory variable perturbation, and response perturbation.
The weight perturbation case considers , where denotes the vector of weights, with , , and the matrix is provided by
where , and , with , and , with denoting an n-dimensional vector of ones.
Now, we consider the perturbation of the scale parameter, where , with . In this scheme, and the matrix take the form
where , with (). The third perturbation scheme consists of incorporating an additive-type perturbation to the response variable, that is, , where represents the non-perturbation vector. In this case, the perturbed penalized log-likelihood function is obtained from the expression provided in (2), with replaced by , obtaining the following structure for matrix :
where , with , (). The fourth and final perturbation scheme involves the perturbation of an explanatory variable. Here, it is assumed that the d-th explanatory variable is continuous and that the additive perturbation scheme considers , where and the matrix is provided by , where , and , with
where denotes a vector with 1 at the dth position and zero elsewhere, and denotes the dth element of .
5. Applications and Results
In this section, we present two applications to real datasets of environmental pollution from Santiago, Chile and Lima, Peru.
5.1. Chile Air Pollution
In this application, data collected from the Pudahuel MACAM during the year 2015 in the CEM period (1 April 2015 to 31 August 2015) were used. These data were obtained from the National Air Quality Information System (SINCA in Spanish) website of the Chilean MMA, which provides air quality data for the entire country (http://sinca.mma.gob.cl, accessed on 15 June 2020). The Pudahuel station registered the highest concentrations of PM during 2015. This station is the most influential monitoring station in Santiago, informing administrative decisions based on predicted critical episodes; see [32]. Meteorological and air pollutant data for this station were obtained from the SINCA website of the Chilean MMA.
The explanatory variables used in PVCM are (i) the maximum level of PM in g/Nm (PM); (ii) the average wind speed in meters per second (WIND); (iii) the average relative humidity as a percentage (RH); and (iv) the average temperature in degrees Celsius (TEMP). The response variable considered is maximum level of PM in g/Nm (PM). We started our study with an exploratory analysis of the response variable, PM. Table 1 reports a descriptive summary of the data, including maximum, minimum, range, mean, median, standard deviation (SD), coefficient of variation (CV), and kurtosis (CK) for the response variable. The primary air quality regulation for PM is 50 g/Nm, on a 24 h level. According to Table 1, the primary air quality regulation are exceeded for the response variable.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics for PM recorded for the Pudahuel monitoring station during the CEM period in 2015 in Santiago, Chile.
Figure 1a shows a boxplot with identification of possible atypical data. In this figure, the data {65, 73, 74, 75} have been highlighted as possibly atypical, indicating the need to use distributions with heavy tails. In Figure 1b, a correlation plot of the explanatory variables and the response variable is shown. From this figure, a high positive correlation can be identified between PM and PM (correlation coefficient 0.82), while the other explanatory variables show moderate or low correlation with the response variable PM, i.e., with WIND (−0.53), TEMP (−0.22) and RH (−0.49).
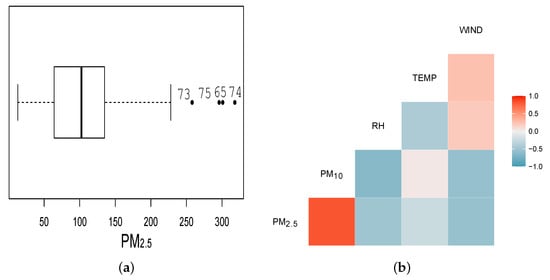
Figure 1.
(a) Boxplot for PM levels recorded by the Pudahuel monitoring station in Santiago, Chile, during 2015 and (b) scatter plot with the corresponding correlations for the indicated explanatory variables and response variable.
In Figure 2, scatter plots of the explanatory variables, response variable, and possible interactions between explanatory variables are shown. In this figure, the relationship between PM and the explanatory variable PM is linear (Figure 2a), while that of the relationship between PM and WIND is nonlinear (Figure 2b). In addition, Figure 2c,d suggests that the RH and TEMP explanatory variables could be interacting with the WIND variable in a nonlinear way.
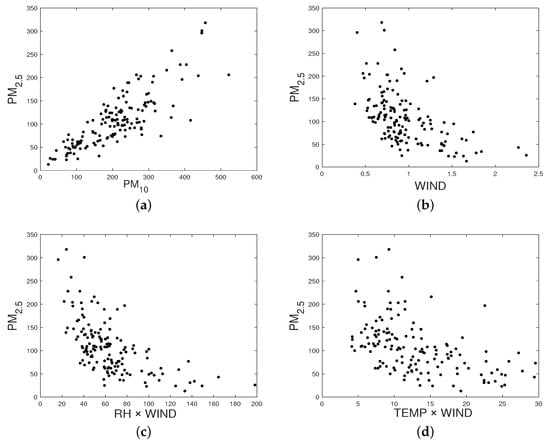
Figure 2.
Scatter plots for (a) PM v/s PM, (b) PM v/s WIND, (c) PM v/s RH × WIND, and (d) PM v/s TEMP × WIND.
These trends suggest a PVCM between PM and the explanatory variables. Specifically, we assume the following model:
where denotes the response value associated with the i-th PM level, is the i-th PM level, are unknown smooth arbitrary functions of explanatory variable (WIND) associated with the explanatory variables (RH and TEMP), and is a random error that follows Student’s -distribution. To verify the distributional assumption established in the model, we performed a quantil-quantil (QQ) plot for the standardized residuals. From Figure 3a, the good fit of the Student- PVCM can be seen. Figure 3b identifies {13, 32, 33, 37, 65, 73, 74, 75, 145} observations as possible outliers. We apply the procedure described in Section 3.3 on smoothing parameters. Subsequently, we use the AIC method to select the value of that maximizes the penalized log-likelihood function for the Student- PVCM. For this, a grid of was considered to find the value that maximizes the penalized log-likelihood function, obtaining as optimal. Table 2 shows the parameter estimates, penalized log-likelihood evaluated at , SE estimates, and AIC value.
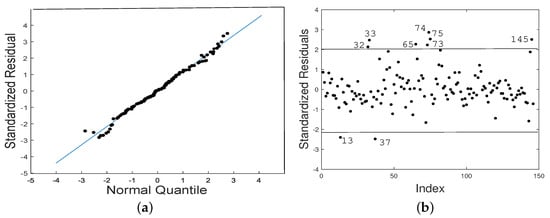
Figure 3.
QQ plot for standardized residuals (a) and plot of index values versus standardized residuals (b) for Student- PCVM (Santiago data).

Table 2.
Maximum penalized likelihood estimates with corresponding estimated SE and AIC value under Student- ( = 4) model.
Figure 4 shows the estimated functions and their corresponding confidence bands based on the approximate SE (discontinuous curves). These plots suggests that the curves of the estimated functions vary with the explanatory variable WIND.
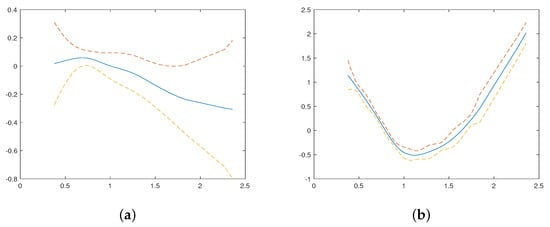
Figure 4.
Plots of (a) and (b) and their approximate SE bands indicated by the discontinuous lines.
Figure 5 shows plot of the observed versus predicted PM values for the Student- PVCM. Analyzing this graph, the predictions are good because the Student- PVCM is capable of following the overall trend of the observed PM levels.
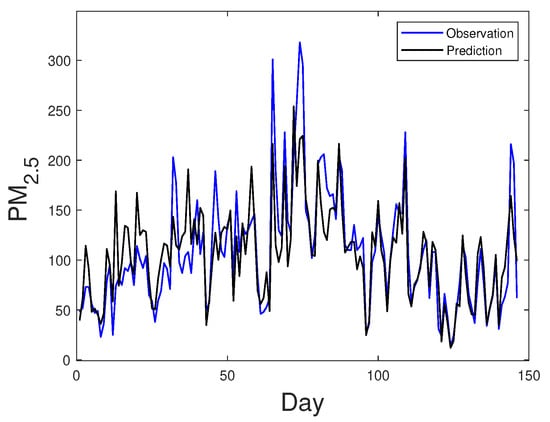
Figure 5.
Plot of observed versus predicted PM levels for Student- PVCM (Santiago data).
Figure 6 displays index plots of the Mahanalobis distance under Student- PVCM (Figure 6a), while Figure 6b shows the estimated weights of Student- PVCM. In these figures, possible outliers and/or influential values under the pre-adjusted model can be observed. In Figure 6a, {13, 37, 65, 73, 74, 82} cases are highlighted as possible outliers. In Figure 6b, it can be observed that the estimated weights for the observations described above take the smallest values, confirming the robust aspects of MPLEs against outlier observations under Student- PVCM. With respect to the values detected in Figure 6a, these correspond to the days 20 April, 14 April, 11 June, 19 June, 20 June, and 28 June, respectively.
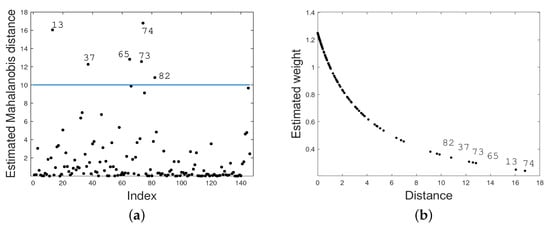
Figure 6.
Index plots of the Mahalanobis distance (a) and the estimated weights (b) for Student- PVCM (Santiago data).
The local influence allows for detection of the effect of perturbations on parameter estimation. To identify possible influential cases under the fitted model, diagnostic plots for the local influence are presented below. We present index plots of for and . In this application, we use the approach (cutoff line) to determine whether an observation is influential or not. In addition, we present a confirmatory analysis that allows analysis of the behavior of the estimates by eliminating those that have been highlighted as possibly influential under local influence techniques.
In Figure 7a, the observations highlighted as influential under case-weight perturbation for for the Student- PVCM correspond to the observations , which were registered on 27 April and 16 June, while in Figure 7b the observations highlighted as influential in correspond to the observations , which were registered on 4 June, 16 June 16, and 21 June.
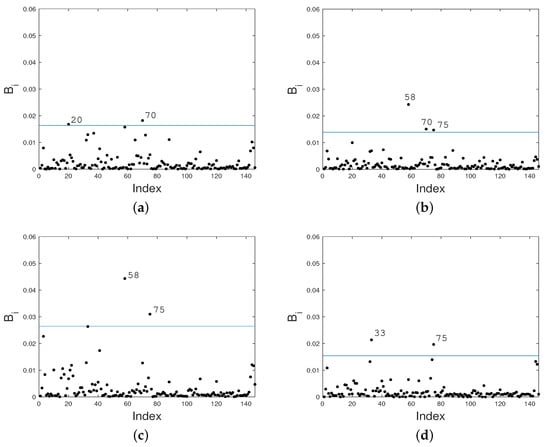
Figure 7.
Index plots of for assessing local influence on (a); (b); (c); and (d) under case-weight perturbation for fitted Student- PVCM (Santiago data).
In Figure 7c, the observations highlighted as influential in for the Student- PVCM correspond to the observations {58, 75}, which were registered on 4 June and 21 June. In Figure 7d, the observations highlighted as influential in for the Student- PVCM correspond to the observations {33, 75}, which were registered on 10 May and 21 June.
Next, we analyze how model parameter estimation behaves when the explanatory variable PM is modified. In Figure 8a–d, no observations are highlighted as influential for , , , or under Student- PVCM.
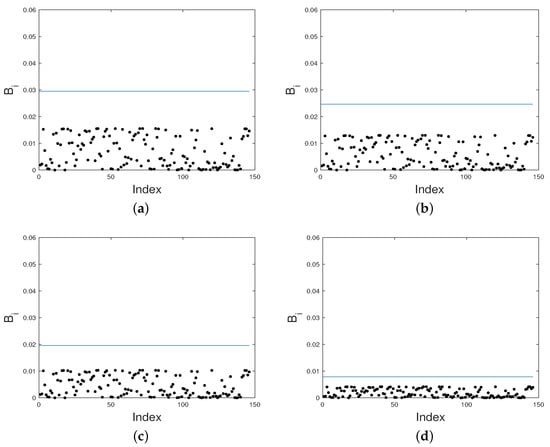
Figure 8.
Index plots of for assessing local influence on (a); (b); (c); and (d) under explanatory variable perturbation for Student- PVCM (Santiago data).
Considering the results obtained from the local influence plots, we mention here that under explanatory variable perturbation, , , , and are less sensitive for small degrees of freedom.
Now, we address the relative changes (in %) of the estimates of , and considering the removal of highlighted observations as possible outliers and/or influential data present in local influence plots. From the above, we work with to later be eliminated. The relative change of each estimated parameter is obtained using
where and denote the MPLE of and the MPLE of after removing the i-th observation, respectively, for with , and . The results obtained for set I are displayed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Relative changes (%) on , and Student- PVCM.
Note that in the local influence analysis the observations that were detected as possibly influential in the parametric component are not necessarily detected in the nonparametric component. For example, in the case-weight perturbation, observations #20 and #70 were detected as potentially influential for the parametric component. However, of these two observations only #70 is indicated as possibly influential in the nonparametric component of the first smooth function. In Table 3, the individual elimination of observations #20 and #75 produces a relative change in of 10% and 6.7%, respectively, identified as potentially influential cases. On these days, 27 April and 21 June, high concentrations of PM and PM were recorded, being higher for observation #75, while the wind speed was very close to the minimum recorded throughout the period for observation #75. The elimination of the set I, the observations of which were detected as potentially influential in both the nonparametric and parametric components, generates significant changes in and on the order of 22% and 33%.
In Santiago, Chile, according to the MMA, an environmental alert was decreed for #58 and pre-emergency for #70 and #75. Thus, we can consider that there is a relationship between the official air quality alerts and the influential observations detected by our model.
In addition, in Table 3, even though some RC values are large, inferential changes are not observed (i.e., p-values remain below 0.01). Note that the elimination of observations detached in the diagnostic plots causes larger changes in the parameter estimates on this account. Thus, the well-known robust aspects of the maximum likelihood estimates from Student- models are not necessarily extended to other perturbation schemes, indicating the need for diagnostic examination in each case.
5.2. Lima Air Pollution
In this application, the dataset comprises a period of two years (from 1 January 2017 to 31 December 2018) and includes PM (g/Nm) concentrations for year, month, day, and hour, ambient temperature in degrees Celsius, relative air humidity in percent, and wind speed in meters per second. The+ is dataset is based on data from five air quality monitoring stations of the SENAMHI: (i) Ate (ATE), (ii) Jesús María (CDM), (iii) Carabayllo (CRB), (iv) Huachipa (HCH), and (v) San Martín de Porres (SMP), with two located in North Lima, two in East Lima, and one in Central Lima; see [4,33]. The primary air quality regulation for PM is 100 g/m as the 24-h level; see [34].
For this illustration, we use validated datasets from 2017 and 2018 during the CEM period, provided by SENAMHI. This allows us to obtain valid results. We analyze only the HCH monitoring station, as it is the station that presents the most critical pollution levels in Lima.
In this illustration, we consider the following explanatory variables: (i) maximum level of PM in g/Nm (MAXPM); (ii) maximum wind speed in meters per second (WIND); (iii) minimum temperature in degrees Celsius (TEMP); and (iv) maximum relative humidity in percentage (RH). For these data, the response variable considered is average PM concentration in g/Nm (PM). Table 4 provides descriptive statistics for PM levels. According to this table, the behavior of the data describes an empirical probability distribution with heavy tails in HCH. PM concentration levels are high, with great variability. These critical pollution levels occur at HCH monitoring station due to the intense activity of the automotive fleet, and factories lead to further increase [4,33].

Table 4.
Descriptive statistics for PM recorded for the HCH monitoring station (CEM period 2017–2018) Lima, Peru.
In Figure 9a, #212 has been highlighted as possibly atypical. In Figure 9b, a correlation plot of the explanatory variables and the response variable is shown, observing a high positive correlation between PM and MAXPM (correlation coefficient 0.91), while the other explanatory variables show moderate or low correlation with the response variable PM, i.e., with WIND (0.36), RH (−0.52) and TEMP (0.47).
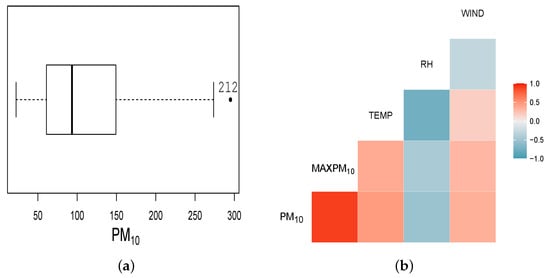
Figure 9.
Boxplot for PM levels recorded by the HCH monitoring station in Lima, Peru. (a) Boxplot for PM10 levels recorded by the HCH monitoring station in Lima, Peru, during 2017–2018 and (b) scatter plot with the corresponding correlations for the indicated explanatory variables and response variable.
In Figure 10, scatter plots of the explanatory variables, response variable, and possible interactions between explanatory variables are shown. For example, it can be seen that the relationship between PM and the explanatory variable MAXPM is linear (Figure 10a), while that of the trend between PM and WIND is nonlinear (Figure 10b). In addition, Figure 10c,d suggests that the TEMP and TEMP explanatory variables could be interacting with the WIND variable in a nonlinear way.
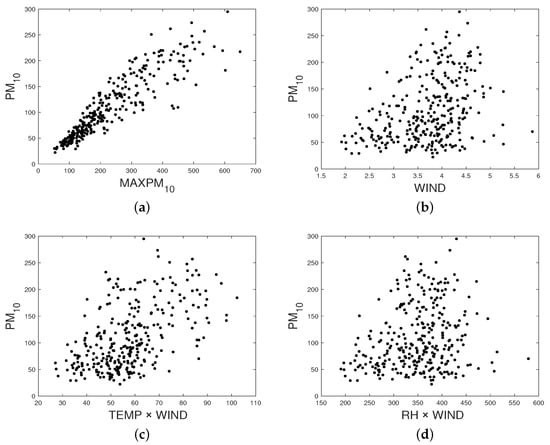
Figure 10.
Scatter plots for (a) PM v/s MAXPM, (b) PM v/s WIND, (c) PM v/s TEMP × WIND, and (d) PM v/s RH × WIND.
Based on the trends observed in the previous graphs, it is suggested that the PVCM be fitted between PM and the explanatory variables. Specifically, we assume that
where denotes the PM concentrations, denotes the maximum PM concentration, is the minimum temperature, is the maximum air relative humidity, is the maximum wind speed from the i-th experimental unit, , are unknown functions, and are independent random errors that follow a Student’s -distribution with . In Figure 11a, which shows the QQ plot for the standardized residuals, an adequate fit of the Student- PVCM is observed, whereas Figure 11b identifies the observations {39, 51, 54, 155, 156, 160, 165, 167, 178, 188, 211} as possible outliers. Table 5 shows the parameter estimates, the penalized log-likelihood evaluated at , SE estimates, and AIC value.
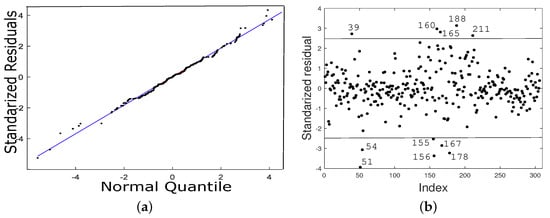
Figure 11.
QQ plot for standardized residuals (a) and plot of index values versus standardized residuals (b) for the indicated model.

Table 5.
Maximum penalized likelihood estimates with corresponding estimated SE and AIC values under Student- ( = 4) model.
In relation to the estimated smooth functions and their corresponding confidence bands, these are shown in Figure 12. Both graphs confirm the non-linear trend noted in the exploratory analysis of the data. In other words, the smooth functions and vary with the explanatory variable WIND.
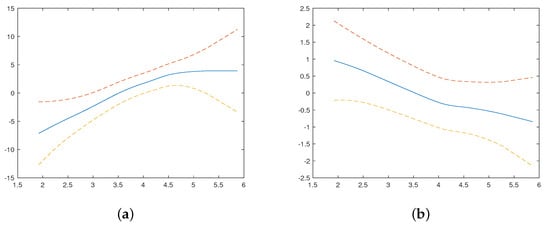
Figure 12.
Plots of (a) and (b) and their approximate SE band, indicated by the discontinuous lines.
Figure 13 shows the plot of the observed PM versus the values predicted by the Student- PVCM. From the trend observed in the graph, we can conclude that the estimates obtained under the model seem to be optimal, as they generate reasonable estimated mean values.
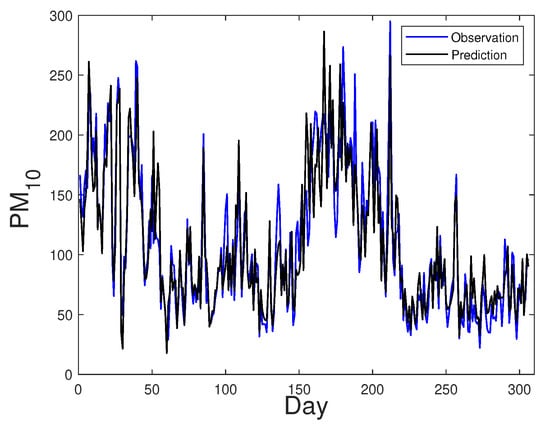
Figure 13.
Plot of observed versus predicted PM levels for Student- PVCM (Lima data).
Figure 14 displays index plots of the Mahanalobis distance under Student- PVCM (Figure 14a), while Figure 14b shows the estimated weights of Student- PVCM. In these figures, we can see possible outliers and/or influential values under the already-adjusted model. In Figure 14a, {39, 51, 54, 155, 156, 160, 165, 167, 178, 188, 211} cases are highlighted as possible outliers. In Figure 14b, we can observe that the estimated weights for the observations described above take the smallest values, confirming the robust aspects of MPLEs against outlier observations under Student- PVCM. With respect to the values detected in Figure 14a, these correspond to the days 9 May 2017, 21 May 2017, 24 May 2017, 2 April 2018, 3 April 2018, 7 April 2018, 12 April 2018, 14 April 2018, 25 April 2018, 5 May 2018, and 28 May 2018, respectively.
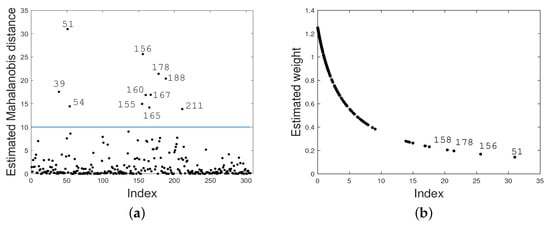
Figure 14.
Index plots of the Mahalanobis distance (a) and the estimated weights (b) for Student- PVCM (Lima data).
In Figure 15a, the observations highlighted as influential under case-weight perturbation for correspond to the observations , which were registered on 14 April 2018, 18 April 2018, 25 April 2018, 28 April 2018, and 29 May 2018, while in Figure 15b, the observations highlighted as influential in correspond to the observations , which were registered on 17 April 2017, 29 April 2017, and 30 April 2017. In Figure 15c, the observations highlighted as influential in correspond to the observations {29, 30}, which were registered on 29 April 2017 and 30 April 2017. In Figure 15d, the observations highlighted as influential in correspond to the observations {51, 54, 160, 165}, which were registered on 21 May 2017, 24 May 2017, 07 April 2018, and 12 April 2018.
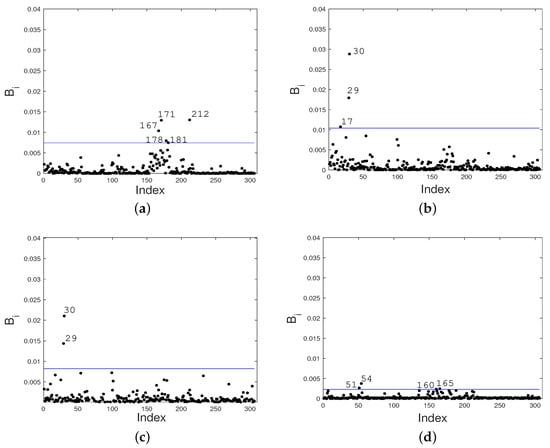
Figure 15.
Index plots of for assessing local influence on (a); (b); (c); and (d) under case-weight perturbation for fitted Student- PVCM (Lima data).
Now, we analyze how the estimators behave when the explanatory variable MAXPM is modified. In Figure 16a–d, no observations are highlighted as influential for , , , or .
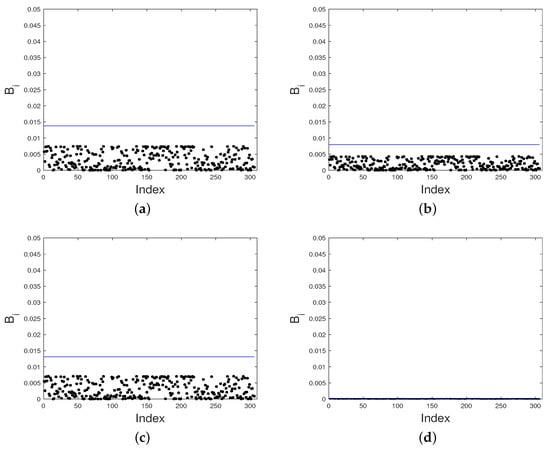
Figure 16.
Index plots of for assessing local influence on (a); (b); (c); and (d) under explanatory variable perturbation for Student- PVCM (Lima data).
Considering the results obtained from the local influence plots, we mention here that under explanatory variable perturbation, , , , and are less sensitive for small degrees of freedom of Student’s -distribution. Note that this robust aspect of the estimators was observed in the previous application as well.
Here, we address the (in %) of the estimates of , and considering the removal of highlighted observations as possible outliers and/or influential data present in local influence plots. The results obtained for set are displayed in Table 6.

Table 6.
Relative changes (%) in MPLE and of Student- PVCM.
As in the previous application, this influence analysis shows that the influential data in the parametric part are not necessarily the same in the non-parametric component. To illustrate this, in the case-weight perturbation scheme, the observations {167, 171, 178, 181, 212} are detected as influencing the parametric component and not the nonparametric one. In Table 6, we note that the individual removal of observation #167 and #178 produces a relative change on the order of 7.53% and 8.42% on , respectively, identified as potentially influential cases. These correspond to 25 April 2018 and 14 April 2018 of the CEM period. Analyzing these observations, a high concentration of PM and wind speed were recorded in #167, while observation #212 corresponds to the maximum PM recorded, which was detected as an outlier in Section 5.2. Finally, the elimination of the set of observations I = {165, 167, 171, 178, 181, 212}, observations which were detected as potentially influential in both the non-parametric and parametric components, leads to significant changes in the MPL estimate of and on the order of 23.1% and 16.3%, respectively.
In summary, the diagnostic analysis based on the local influence method and residuals confirms that the proposed model is suitable for modeling pollution data, even if there are outliers and potentially influential observations.
6. Conclusions, Limitations, and Future Research
In this work, we have studied the estimation problem for the partially varying coefficient model with Student’s -random errors under the penalized likelihood approach. In addition, we have developed local influence techniques for the proposed model under case-weight and PM explanatory variable perturbations and applied the developed methodology to two real datasets consisting of air pollution data from Santiago, Chile and Lima, Peru. We selected the smoothing parameters by setting the effective degrees of freedom of each nonparametric component and applied the Akaike information criterion to select the better model. This study provides evidence on the robustness of the maximum penalized likelihood estimators derived from the Student’s partially varying coefficient model with small degrees of freedom and presence of atypical observations. To conclude, we suggest the Student’s partially varying coefficient model as a good option for modeling datasets with heavy tails and nonlinear interaction effects between the explanatory variables.
It is important to mention that this work pioneers the exploration of air pollution data from Lima, Peru using the partially varying coefficient model approach with heavy tails; there has been no previous such analysis in the literature. However, access to this type of data is limited, constituting one of the main limitations of this study. Data on variables that could be related to air pollution, such as atmospheric pressure, precipitation, evaporation, solar radiation, and dew point, were not available. We believe that our results would be more robust if data on these variables were included. Additionally, the considered data were obtained from data equally spaced in time. A correlation structure between the lags was not considered. This could be addressed with an error approach, that is, by developing an extension of the model able to consider random errors through an autoregressive structure. Another limitation in this study is that the degrees of freedom are fixed in the model after a search through a grid of values. For this, the incorporation of the estimation of this parameter in the modeling process could be explored. Finally, the model does not consider the joint effects of certain covariates, only the interaction effect. In this case, a surface can be incorporated to model the joint effects using thin-plate spline smoothing, for example.
In future work, a package in R could be implemented to ensure that various users have this model computationally available for practical applications. Currently, the R and Matlab codes are available from the authors upon request. Furthermore, Student’s partially varying coefficient models can be extended to the case of heteroscedastic random errors . In addition, other types of more flexible distributions could be considered in order to improve the modeling.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.J. and G.I.-P.; methodology, C.M. and G.I.-P.; software, N.J., C.M. and G.I.-P.; validation, N.J.; formal analysis, N.J., C.M. and G.I.-P.; investigation, C.M. and G.I.-P.; resources, C.M., G.I.-P. and J.L.L.-G.; data curation, N.J. and C.M.; writing—original draft preparation, C.M. and G.I.-P.; writing—review and editing, N.J., G.I.-P., C.M. and J.L.L.-G.; visualization, N.J. and C.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was partially funded by FONDECYT, project grant number 11190636 (C. Marchant) from the National Agency for Research and Development (ANID) of the Chilean government under the Ministry of Science, Technology, Knowledge, and Innovation.
Data Availability Statement
Data and computational codes are available upon request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Penalized Hessian Matrix
Let and be the matrix with -element provided by for , and , with . The elements of the matrix can be written as
where , , , and for . For further details on this matrix, see Lange et al. [35] and Ibacache-Pulgar et al. [10].
References
- MMA. Establishment of Primary Quality Guideline for Inhalable Fine Particulate Matter PM2.5; Technical Report Decree 12; Ministry of Environment of the Chilean Government: Santiago, Chile, 2021.
- Puentes, R.; Marchant, C.; Leiva, V.; Figueroa-Zuñiga, J.; Ruggeri, F. Predicting PM2.5 and PM10 Levels During Critical Episodes Management in Santiago, Chile, with a bivariate Birnbaum-Saunders Log-Linear Model. Mathematics 2021, 9, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, V.; Carbajal, L.; Vásquez, V.; Espinoza, R.; Vásquez-Velásquez, C.; Steenland, K.; Gonzales, G. Traffic regulation and environmental pollution by particulate material (2.5 and 10), sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen dioxide in Metropolitan Lima, Peru. Rev. Peru. De Med. Exp. Y Salud Pública 2018, 35, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordova, C.H.; Portocarrero, M.N.L.; Salas, R.; Torres, R.; Rodrigues, P.C.; López-Gonzales, J.L. Air quality assessment and pollution forecasting using artificial neural networks in Metropolitan Lima-Peru. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez, M.; Baettig, R.; Cornejo, J.; Zamudio, F.; Guajardo, J.; Fica, R. Urban airborne matter in central and southern Chile: Effects of meteorological conditions on fine and coarse particulate matter. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 161, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, N.; Hannigan, M.; Miller, S.; Peel, J.; Milford, J. Comparisons of urban and rural PM10-2.5 and PM2.5 mass levels and semi-volatile fractions in northeastern Colorado. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 7469–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño, G.; López-Cortés, X.A.; Marchant, C. Machine Learning Models to Predict Critical Episodes of Environmental Pollution for PM2.5 and PM10 in Talca, Chile. Mathematics 2022, 10, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Generalized Additive Models; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ibacache-Pulgar, G.; Reyes, S. Local influence for elliptical partially varying-coefficient model. Stat. Model. 2018, 18, 149–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibacache-Pulgar, G.; Paula, G.; Cysneiros, F. Semiparametric additive models under symmetric distributions. Test 2013, 22, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibacache-Pulgar, G.; Paula, G.A.; Galea, M. Influence diagnostics for elliptical semiparametric mixed models. Stat. Model. 2012, 12, 165–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira, V.; Ibacache-Pulgar, G.; Villegas, C. Assessing influence in the varying-coefficient generalized linear model. REVSTAT-Stat. J. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, R.D. Assessment of local influence (with discussion). J. R. Soc. 1986, 48, 133–169. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H.; Zhiya, C. Local influence analysis of varying-coefficient linear model. J. Interdiscip. Math. 2015, 3, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.S.; Paula, G.A. Estimation and diagnostic for skew-normal partially linear models. J. Appl. Stat. 2017, 44, 3033–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, H. Local influence for Liu estimators in semiparametric linear models. Stat. Pap. 2017, 19, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibacache-pulgar, G.; Figueroa-Zúñiga, J.; Marchant, C. Semi-parametric additive beta regression models: Inference and local influence diagnostics. REVSTAT-Stat. J. 2021, 19, 255–274. [Google Scholar]
- Moraga, M.; Ibacache-Pulgar, G.; Nicolis, O. On Elliptical Thin-Plate Spline Partially Varying-Coefficient Model. Chil. J. Stat. 2021, 12, 205–227. [Google Scholar]
- Ibacache-Pulgar, G.; Villegas, C.; López-Gonzales, J.L.; Moraga, M. Influence Measures in Symmetric Nonparametric Regression Model. Stat. Methods Appl. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárcamo, E.; Marchant, C.; Ibacache-Pulgar, G.; Leiva, V. Birnbaum-Saunders semi-parametric additive modelling: Estimation, smoothing, diagnostics, and application. REVSTAT-Stat. J. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Cavieres, J.; Ibacache-Pulgar, G.; Contreras-Reyes, J. Smoothing Thin-Plate Spline under Skew Normal setting using Laplace Approximation and Influence Diagnostics Analysis. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2022, in press.
- Adams, R.; Fournier, J. Sobolev Spaces; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Green, P.; Silverman, B. Nonparametric Regression and Generalized Linear Models: A Roughness Penalty; Chapman and Hall/CRC: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Berhane, K.; Tibshirani, J. Generalized additive models for longitudinal data. Can. J. Stat. 1998, 26, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahba, G. Bayesian confidence intervals for the cross-validated smoothing spline. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1983, 45, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, M.; Bacchetti, P.; Jewell, P. Variances for maximum penalized likelihood estimates obtained via the EM algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1994, 56, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Varying-Coefficient Models. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1993, 55, 757–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buja, A.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Linear smoothers and additive models. Ann. Stat. 1989, 17, 453–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, R.A.; Stasinopoulos, D.M. Generalized additive models for location, scale and shape. Appl. Stat. 2005, 54, 507–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opsomer, D. Asymptotic Properties of Backfitting Estimators. J. Multivar. Anal. 2000, 73, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, W.; Poon, Y.S. Conformal normal curvature and assessment of local influence. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1999, 61, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MMA. Establishes a Prevention and Atmospheric Decontamination Plan for the Santiago Metropolitan Region; Technical Report Decree 31; Ministry of Environment of the Chilean Government: Santiago, Chile, 2017.
- Encalada-Malca, A.A.; Cochachi-Bustamante, J.D.; Rodrigues, P.C.; Salas, R.; López-Gonzales, J.L. A Spatio-Temporal Visualization Approach of PM10 Concentration Data in Metropolitan Lima. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MINAM. Approval of Environmental Quality Standards for Air and Establish Complementary Provisions; Supreme Decree N 003-2017; MINAM: Lima, Peru, 2017.
- Lange, K.L.; Little, R.J.A.; Taylor, J.M.G. Robust statistical modeling using the t distribution. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1989, 84, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).