Abstract
Access plan recommendation is a query optimization approach that executes new queries using prior created query execution plans (QEPs). The query optimizer divides the query space into clusters in the mentioned method. However, traditional clustering algorithms take a significant amount of execution time for clustering such large datasets. The MapReduce distributed computing model provides efficient solutions for storing and processing vast quantities of data. Apache Spark and Apache Hadoop frameworks are used in the present investigation to cluster different sizes of query datasets in the MapReduce-based access plan recommendation method. The performance evaluation is performed based on execution time. The results of the experiments demonstrated the effectiveness of parallel query clustering in achieving high scalability. Furthermore, Apache Spark achieved better performance than Apache Hadoop, reaching an average speedup of 2x.
Keywords:
access plan recommendation; parallel processing; Apache Hadoop; Apache Spark; big data; artificial intelligence; soft computing; cloud computing; data science; MapReduce MSC:
68U35
1. Introduction
A query’s cost model includes local processing costs and communication costs between nodes in distributed query processing [1,2,3]. The search space of possible query execution plans (QEPs) can be fairly ample based on the complexity of the query. The query optimizer cannot efficiently search through all possible QEPs to find the most efficient QEP. The access plan recommendation method is introduced to decrease the query optimization costs by reusing the previously generated QEPs [4,5,6]. The access plan recommendation technique looks for textual similarities between the novel query and prior ones in order to reuse prior executed query plans for future ones. In the presented process, the query optimizer makes use of the likeness of query statements to execute new queries. However, clustering large query sets becomes a problem for traditional clustering algorithms due to the high processing time [7,8]. Various query plan prediction techniques are introduced [5,6] to identify the similarity between the queries using traditional clustering algorithms. For instance, Zahir, et al. [6] proposed an approach for recommending query plans that is efficient and effective. The SQL semantics are used for similarity detection. The expectation-maximization (EM) and K-means algorithms are applied in the proposed method. In addition, association rule (AR), naive Bayes (NB), and support vector machine (SVM) classification algorithms have been used in another study [5] for query plan prediction. The findings demonstrate that the AR algorithm is more accurate than the SVM and NB techniques in forecasting. It can be observed that the presented approaches reduce the expenses related to optimizing. Azhir, et al. [7] also presented a novel query plan recommendation technique depending on DBSCAN and NSGA-II algorithms for enhancing prediction accuracy. The outcomes related to the suggested method are compared to traditional K-means and DBSCAN. Based on the obtained outcomes, the presented approach achieves better performance in terms of accuracy. These papers aim to reuse previous query plans. However, clustering large query sets is one of the major challenges for such conventional clustering methods, due to the required processing time.
MapReduce is a distributed programming model for processing massive amounts of data [9,10]. MapReduce is an efficient method for clustering large query sets in a reasonable amount of time. Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark [11] are two of the most popular frameworks used for executing MapReduce programs. Apache Hadoop is a framework that is mainly used for scalable and distributed processing in the cloud [10,12]. Hadoop processes huge quantities of data by dividing tasks into smaller tasks [9]. It frequently writes and reads data from the disk. It can decrease the performance of the system. However, Apache Spark provides in-memory computations for reducing the number of the read/write cycle to disk [13]. We will go through a few clustering approaches that are built on parallel structures in the following sections. Elsayed, et al. [14] proposed a novel model to cluster intensive data documents. The WordNet ontology is used with bisecting K-means in order to utilize the semantic relations between words. The proposed model is based on distributed implementation for the bisecting K-means using the MapReduce programming model to improve document clustering results. The trial results have revealed that lexical categories for nouns enhanced internal evaluation measures of document clustering and decreased the document’s features. According to the trial outcomes, the proposed approach obtained better results in text clustering than the typical K-means approach. Zewen and Yao [15] presented a parallel text clustering algorithm for the cloud environment. In this paper, the classical Jarvis–Patrick (JP) algorithm is implemented using the MapReduce programming model. In the proposed method, the shared nearest neighbor (SNN) table of the JP algorithm is created using MapReduce parallel processing. The results indicate the efficiency of the parallelization of the JP algorithm. Furthermore, high scalability is a key benefit of the technique. In addition, Li, et al. [16] suggested a new parallel method for clustering the text documents. The proposed algorithm is a parallel form of sequential K-means based on neighbors (SKBN). This parallel method, called PKBN, uses data parallelism in its three main phases, which are as follows: creating the neighbor matrix, choosing the primary centroids grounded on ranks, and repeating the loop of the assignment phase and the update phase. The neighbor matrix of the proposed algorithm is generated using a novel parallel pair-generating technique called PG-New. The results proved that the decrease in communication overheads is accorded to the PG-New. Furthermore, the scalability of PKBN is improved using the proposed parallelism.
This paper aims to enhance the recommendation time of the access plan recommendation method. The term frequency (TF) method [17] and cosine measure with a feature representation of SQL query language are used in the presented access plan recommendation method. In the present article, a parallel MapReduce model is applied to sped up the query clustering operation in Apache Hadoop [18]. Furthermore, the performance of the presented access plan recommendation method [18] is improved using the implementation in Apache Spark, which is a in-memory distributed data processing engine. The following list underlines the article’s key contributions:
- (i)
- Presenting a parallel query plan recommendation method using the MapReduce model.
- (ii)
- Implementing the parallel query plan recommendation technique using Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark distributed frameworks.
- (iii)
- Evaluating the performance of the implemented algorithm with multiple-query datasets.
In Section 2, Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark distributed processing frameworks are presented. The parallel query plan recommendation method is introduced in Section 3. Our test environment is illustrated in Section 4. The findings of the simulation results are provided in Section 5. Finally, Section 6 reviews the main points and recommends some suggestions for future research.
2. Overview and Background
In this part, two commonly used cloud frameworks are presented. Hadoop is a framework for storing and processing large quantities of data. It is based on the MapReduce programming model for parallel processing. However, Spark is used for real-time data analysis and can achieve higher performance than Hadoop MapReduce using the main memory.
2.1. Apache Hadoop
Apache Hadoop is an effective open-source platform for reliable, scalable, and distributed processing of large amounts of data. This framework can work with thousands of nodes and several petabytes of data. Generally, Hadoop has a set of modules for processing large quantities of distributed data on different nodes across the Hadoop cluster. Therefore, Hadoop is considered a collection that includes data gathering, storage, analysis, and maintenance services. There are two key parts in the core of Hadoop [19]: (1) the storage part is called the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), which is responsible for partitioning, storing, and retrieving large files on a Hadoop cluster, and (2) the processing part is called MapReduce, which is responsible for analyzing and processing distributed data. Hadoop is based on master-worker architecture for data storage and distributed processing using HDFS and MapReduce. In the Hadoop cluster, there are a master node and several worker nodes. In addition, a layered architecture is also used in Hadoop, with HDFS on the bottom layer and the MapReduce layer on it. Hadoop offers parallel and distributed processing on big data sets through the MapReduce model [10]. MapReduce is a programming model for parallel data processing that provides great scalability on a Hadoop cluster [9].
2.2. MapReduce
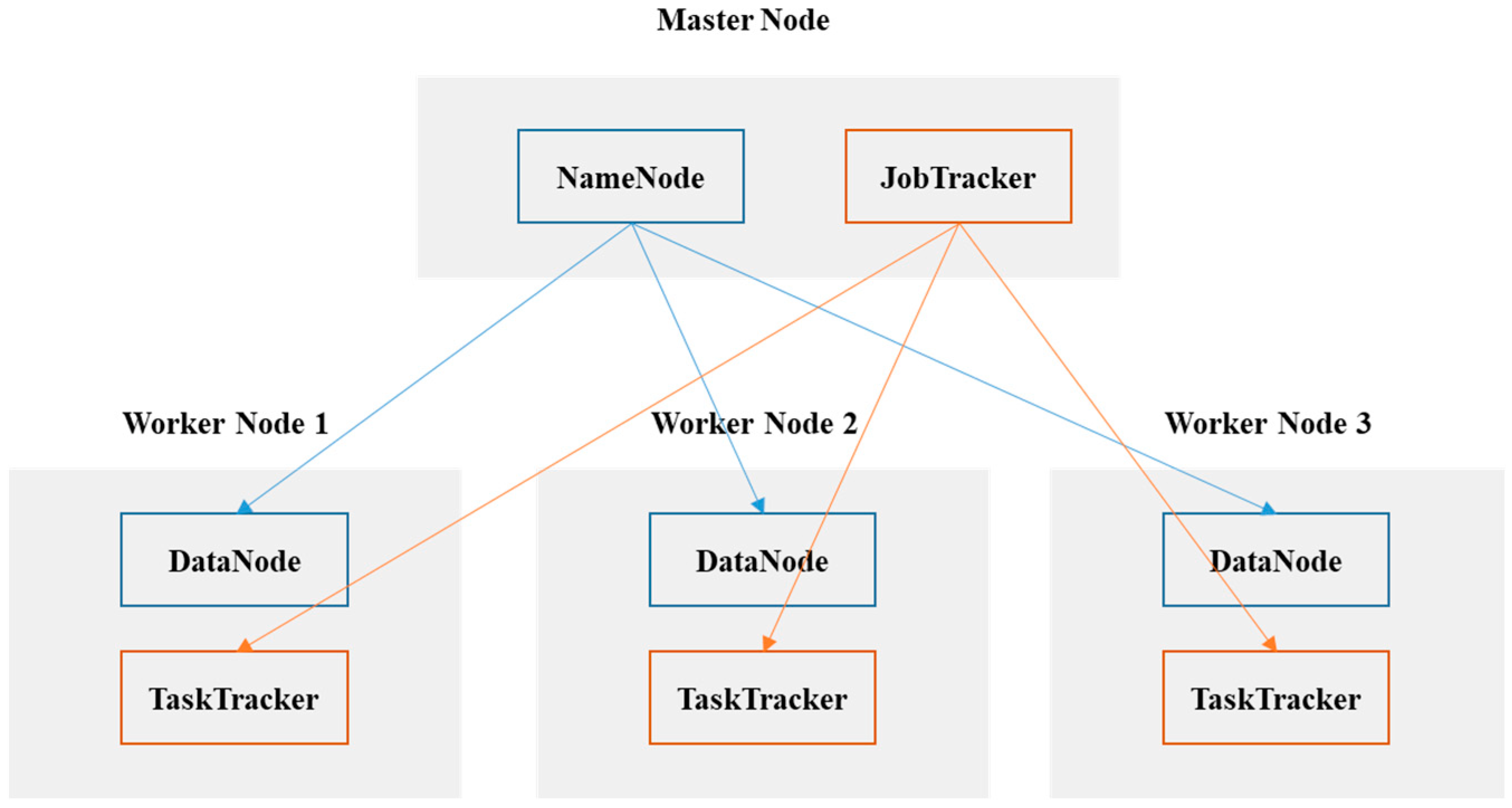
MapReduce distributes input data across different machines. In the MapReduce model, the processing operation is divided between several nodes. Therefore, MapReduce helps process big data through distribution. Data are processed in parallel by several machines instead of one machine. This means that the data processing time is greatly reduced. Figure 1 illustrates the MapReduce process. First, the client sends MapReduce execution requests to the JobTracker. JobTracker splits jobs into tasks among the cluster nodes. Furthermore, the JobTracker talks to the NameNode to find the DataNodes that contain the data to be used in processing. TaskTrackers perform processing independently and in parallel (Mapper).
Figure 1.
The MapReduce process in Hadoop.
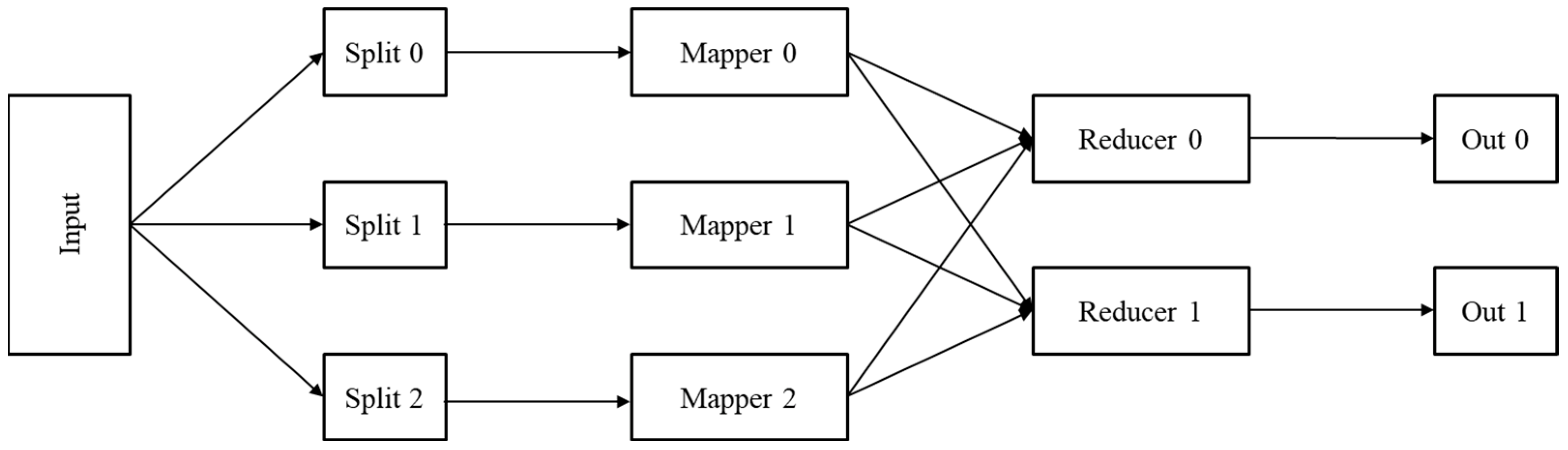
The MapReduce processing model includes the following two key phases: the map phase and the reduce phase. As shown in Figure 2, the map phase takes key-value pairs as input and implements some processing on this input. The results of the map phase are passed to the reduce phase in the form of key/value pairs. Finally, the map phase’s findings are processed in the reduce phase.
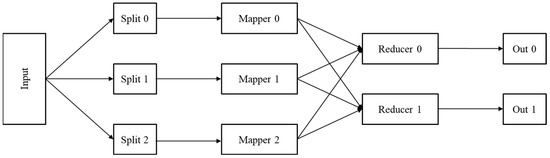
Figure 2.
Hadoop MapReduce framework.
2.3. Apache Spark
Apache Spark is a framework for processing batch and stream data in a distributed computing manner. The Spark is introduced to increase processing speed and enhance complex processing. Spark uses in-memory computing to speed up data processing, which is more efficient than the Hadoop model. Spark speed is nearly 100 times faster than Hadoop when data are stored in memory and up to tens of times faster than when all the data are not in memory. Apache Spark combines various modules, such as MLib machine learning libraries, GraphX for large-scale graph analytics, Spark SQL for relational data analysis, and Spark Streaming for streaming data analysis [20]. Iterative algorithms, graph analytics, and interactive data analysis algorithms all perform better. Spark uses Hadoop YARN or Apache Mesos as a cluster manager and it has a distributed storage system. Spark supports a wide variety of distributed storage, including HDFS, Cassandra, OpenStack Swift, and Amazon S3. The resilient distributed dataset (RDD) and directed acyclic graph (DAG) execution engine are two key concepts in Spark [11]. RDD is the first distributed memory abstraction provided by Spark. It provides in-memory computation on large distributed clusters with high fault-tolerance. The Spark driver program creates RDD and divides it among different nodes. Transformations and actions are two kinds of operations executed by RDD. Transformations generated new datasets from the input RDD (map), and actions return a value after performing calculations on the dataset (reduce). Spark can cache RDDs on memory and repeat the MapReduce operation without performance overhead. Therefore, Spark has a performance advantage for recursive algorithms. When an action is executed on an RDD by a user, a DAG is created according to the transformation dependencies. This enhances the performance and eliminates the multistage execution model of MapReduce.
3. Methodology
The access plan recommendation method uses earlier query plans for new queries. Initially, optimal QEPs are generated for a query group in the system log. The output of the query optimizer is a set of optimal QEPs of the existing queries. This technique transforms query statements into feature vectors, which are then compared to verify how similar they are. Therefore, when a new query is created, the query vector is produced using the query statement. Then, the similarity degree between the novel query and the other ones placed in the clusters is calculated, and the ideal query plan is extracted. If the query is not similar to the existing clusters, the optimizer generates the optimal query plan to update the clustering. Query preprocessing, tokenizing, feature weighting based on TF, similarity measurement, and plan recommendation are the five key stages of the access plan recommendation method. Accordingly, various stages are presented in Figure 3, and the way the presented method is converted to reduce/map flows is explained in the following section.

Figure 3.
The map-reduce-based access plan recommendation.
3.1. Query Preprocessing
In the presented method, the SQL statements are manipulated using the JSQL parser. In order to enhance the clustering quality, a custom JSQL parser library (http://jsqlparser.sourceforge.net/, accessed on 23 February 2022) and different normalization rules to increase the clustering quality are applied to queries’ expressions [7]. The JSQL parser rewrites the queries’ text to eliminate string constants, table aliases, column aliases, syntax sugar, and namespaces [21].
3.2. Query Tokenizing
The clustering algorithms divide data into different groups using a feature space. In the tokenization, the queries are represented in a feature space. Therefore, the tokenization process split the queries’ texts into words. The words’ frequencies are also calculated as the queries’ features for clustering in the next part. In the tokenizing stage, the parser breaks the query text into tokens. In addition, the parser qualifies tokens by utilizing the SQL clauses, including FROM, SELECT, GROUP BY, WHERE, and ORDER BY (Table 1).

Table 1.
An example of SQL query tokenization.
3.3. Feature Weighting based on TF using MapReduce
The frequency of a word in a document is calculated using the TF method. In this paper, the TF method assesses the importance of a feature in a query. In the presented access plan recommendation method, the created tokens (features) are weighted by frequency. The number of times the feature f appears in query q is shown as tf (f,q) [17]. In this stage, the term frequency algorithm computes the weight of the word in the query vector using the frequency of each word [22]. Table 2 describes an example of the TF calculation for a simple query. As shown in Table 1 and Table 2, to calculate the weight of the term “WHERE salary,” it appears twice in the query [17].

Table 2.
An example of a feature vector.
The parallelized feature weighting algorithm in MapReduce is presented in Algorithms 1–3. First, Algorithm 1 counts the number of each term in each query. Algorithm 2 calculates the whole terms of each query. Then, Algorithm 3 calculates the weights of each feature by using the TF method.
| Algorithm 1: The number of each term in every query |
| Input: query Output: The total number of occurrences of each token (term) in every query (queryID); ((term, queryID), sum) 1: class Mapper: A key/value pair is generated for each query. 2: function map (query) 3: for all term query.split() do//The query is divided into smaller units (term) 4: emit ((term, queryID), 1) //The number 1 is assigend as the value to each term. 5: end for 6: end function 7: end class |
| 1: class Reducer: The total number of occurrences of each term in a query is counted. 2: function reduce ((term, queryID), counts [ c1, c2, …]) 3: sum = 0 4: for all count counts do 5: sum += count 6: end for 7: emit ((term, queryID), sum)//Key: term and queryID, Value:The number of repetitions of a term in a query. 8: end function 9: end class |
| Algorithm 2: The total terms of each query |
| Input: The number of each token in each query ((term, queryID), sum) Output: The total number of terms (sum) in a query ((queryID, N), (term, sum)) 1: class Mapper: All terms in each query are grouped. 2: function map ((term, queryID), sum) 3: for all element (term, queryID) do 4: emit (queryID, (term, sum)) //Key: queryID, Value: The term and the number of repetitions of each term in a query. 5: end for 6: end function 7: end class |
| 1: class Reducer: The total number of terms in a query is computed. 2: function reduce (queryID, (term, sum)) 3: N = 0 //N is the total number of terms in a query. 4: for all tuple (term, sum) do 5: N = N + sum 6: end for 7: emit ((queryID, N), (term, sum)) 8: end function 9: end class |
| Algorithm 3: The weights of each feature |
| Input: The total number of terms in a query ((queryID, N), (term, sum)) Output: The weights of each feature ((queryID), (term, tf)) 1: class Mapper: 2: function map (queryID, N), (term, sum)) 3: for all element (term, sum) do 4: emit ((term, (queryID, sum, N)) 5: end for 6: end function 7: end class |
| 1: class Reducer: The term frequency is calculated. 2: function reduce ((term, (queryID, sum, N)) 3: for all element in (queryID, sum, N) do 5: tf = sum/N; 6: end for 7: emit ((queryID), (term, tf)); 8: end function 9: end class |
3.4. Similarity Measurement using MapReduce
In the presented method, the Cosine similarity [23] is applied to find similar queries. To measure the similarity between the two query vectors and , the cosine of the angle between and is calculated using (2) [23].
where the weight of the words in each query vector is divided by the length of the words in that query.
Algorithm 4 may be used to compute the Cosine similarity between the produced query vectors in parallel [22].
| Algorithm 4: The Cosine similarity of the produced query vectors |
| Input: query vectors Output: The Cosine similarity between the produced query vectors 1: class Mapper: The key/value pair is formed. 2: function map (queries) 3: for i = 0 to n //Where n is the total number of queries. 4: for j = i + 1 to n 5: emit ((q [i].id, q[j].id), (q[i].tf, q[j].tf))//The term frequency values are assigned as the value. 6: end for 7: end for 8: end function 9: end class |
| 1: class Reducer: The Cosine similarity is calculated for each pair of queries. 2: function reduce ((q1, q2), (q1.tf, q2.tf)) 3: 4: emit ((q1, q2), cosine) 5: end function 6: end class |
3.5. Plan Recommendation
In this part, the recommendation process is performed; for a new query, the query is assigned to one cluster according to its detected similarity. The recommendation is made using the identified similarities between the novel query and the old ones whose access plans are accessible in the memory. If a similarity is identified, the recommender system suggests that the query optimizer reuses the old query execution plan to execute the new incoming query. DBSCAN is a clustering method based on density that can find clusters of any shape. In the introduced recommender system, DBSCAN clustering is performed from the precomputed distance matrix. A few main definitions of DBSCAN are [24] as follows:
Definition 1.
Theneighborhood of a point is a set of points within distance from point . It can be expressed as .
Definition 2.
is directly density-reachable from the point if is in the radius of (i.e., ) and is a center object (i.e., ).
Definition 3.
is density reachable from the point q if there is a directly density reachable connection between two points.
The DBSCAN clustering technique starts by choosing a random point p and then retrieving density-reachable points from point p. The algorithm creates a cluster if p is a core object. If no point can be reached using density from point p, the algorithm moves on to the subsequent point in the given dataset. This technique is carried out for each of the points. To divide queries into similar clusters, the R DBSCAN package is used [25].
4. Experimental Set Up
Several experiments are conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of the presented parallel access plan recommender system. The employed set-up for experiments is presented in this part. Virtualbox 6.1.16 was used to create the virtual environment in a physical system, with 16 GB of RAM and a 2.8 GHz Intel Core i7 processor. The tests were carried out on a Hadoop cluster with varying numbers of virtual nodes. One node is the master, while the others are workers. On the master and worker nodes, the Red Hat (64bit) Linux Operating System (OS) is installed. The master node has four virtual cores and eight gigabytes of memory. Each worker node has two virtual cores and three gigabytes of RAM. In addition, Hadoop 2.8.0 was installed. The IIT Bombay dataset [26] is also used to create simple selection query sets. Therefore, the bind variables of the queries are substituted with different data values. Table 3 contains three query sets. A distinct hash value is assigned to a query’s QEP when it is run in Oracle. Each query set is manually classified based on the distinctive value of its QEPs. The S2 query set, for instance, has 593 queries divided into 14 classes.

Table 3.
Features of the generated query sets.
5. Results
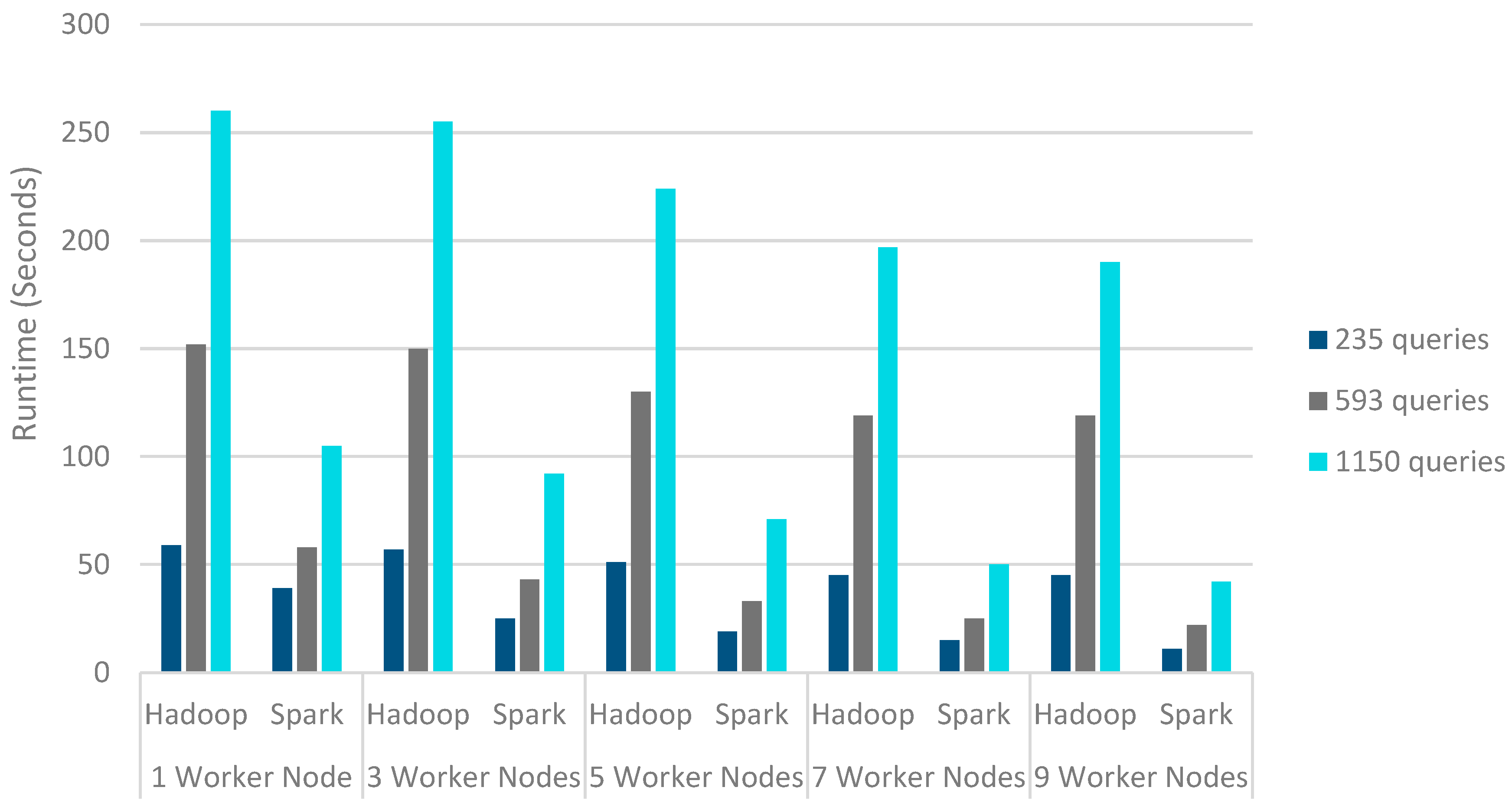
The performance of the presented parallel access plan recommendation method is evaluated using both Hadoop [18] and Spark frameworks in terms of execution time. The presented algorithm is evaluated on the three created query sets described in Table 3. Table 4 demonstrated the presented technique’s implementation time for various numbers of queries with diverse worker nodes. As shown in Table 4, Hadoop took a long time on the data sets with large query sizes. However, it performs better when the number of queries is reduced. Similar results were also obtained from Spark. In Spark’s case, the results were not significantly different when we reduced the number of queries.

Table 4.
Run-time (Seconds) of Hadoop and Spark with the change in number of queries.
Because of Hadoops’ inherent nature of using disk I/O for its computation, which increases Hadoop execution time as the data size increases, it is more beneficial to use Spark instead of Hadoop for large datasets. Figure 4 shows that multi-node cluster implementation always outperforms the stand-alone implementation. Therefore the MapReduce model performs better in the distributed mode rather than on a single machine. Furthermore, it is obvious that memory-based Spark performs better than disk-based MapReduce for all query sets. The outcomes revealed that the speedup value is enhanced along with the number of nodes in Hadoop and Spark. However, Apache Spark scales performed better than Hadoop when the number of nodes was enhanced.
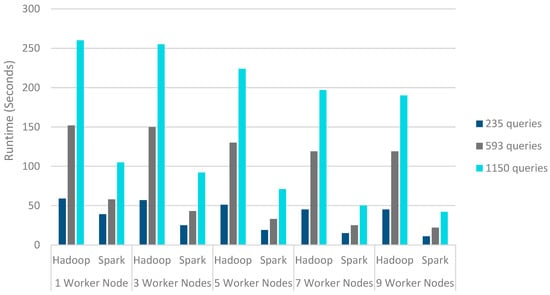
Figure 4.
Run-time of Hadoop on different nodes.
The query optimization problem in large-scale and distributed databases is NP-hard in nature. The query optimizer’s complexity increases with the complexity of the query. Therefore, the large space of alternative query plans should be explored by the query optimizer to generate optimal QEPs. Recommendation-based methods help the query optimizer to recognize similarities between old and future queries. An efficient parallel processing method based on MapReduce is used in this paper to increase the efficiency of the proposed access plan recommendation method [7]. The presented MapReduce algorithm is executed on different query sets. The trial outcomes have shown that the presented parallel recommendation method can process large query sets with time-efficiency. As shown in Figure 4, as the number of queries increases, the efficiency of parallel computing will be higher. The results have shown that the speedup increases with the number of queries. It was also concluded that the proposed method in the Spark platform could more effectively solve the large-scale query set processing with reasonable processing time.
6. Conclusions
This paper aimed to enhance the recommendation time in the access plan recommendation method. For this purpose, the access plan recommendation method was implemented with two common cloud-based frameworks, Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark. First, the query expression was standardized, and query vectors were generated. Then, parallelized feature weighting and similarity measurement algorithms were designed to create the queries’ weight matrix. At last, the recommendation was made using the DBSCAN clustering algorithm. The performances of Hadoop and Spark were compared by investigating the execution time. Several experiments were performed with different cluster nodes and query sets. The experiments showed that Spark outperforms Hadoop in all cases due to its efficient utilization of main memory. However, Apache Hadoop was more cost-effective. Future work is recommended to investigate the performance of other clustering and classification algorithms for query plan recommendations regarding execution time and accuracy. Furthermore, additional tests will be beneficial in evaluating the suggested strategy’s performance for more complicated query sets. Finally, the optimization of the MapReduce process using the partitioning and indexing techniques can be addressed by future works.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.A. and M.H.; Methodology, E.A. and M.H.; Software, E.A.; Validation, E.A., F.K. and A.M.; Resources, E.A.; Data Curation, E.A. and A.M.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, E.A.; Writing—Review and Editing, E.A. and F.K.; Visualization, E.A.; Supervision, A.M.; Project Administration, F.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Singh, V. Multi-objective Parametric Query Optimization for Distributed Database Systems. In Proceedings of Fifth International Conference on Soft Computing for Problem Solving; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 219–233. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.; Youn, J.; Lee, S.-G. Efficient query processing on distributed stream processing engine. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication, Beppu, Japan, 5–7 January 2017; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Panahi, V.; Navimipour, N.J. Join query optimization in the distributed database system using an artificial bee colony algorithm and genetic operators. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2019, 31, e5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Parikh, J.; Sengar, V.S.; Haritsa, J.R. Plan selection based on query clustering. In Proceedings of the VLDB’02: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Very Large Databases, Hong Kong, China, 20–23 August 2002; pp. 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Zahir, J.; El Qadi, A. A recommendation system for execution plans using machine learning. Math. Comput. Appl. 2016, 21, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahir, J.; El Qadi, A.; Mouline, S. Access plan recommendation: A clustering based approach using queries similarity. In Proceedings of the 2014 Second World Conference on Complex Systems (WCCS), Agadir, Morocco, 10–12 November 2014; pp. 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Azhir, E.; Navimipour, N.J.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Sharifi, A.; Darwesh, A. An automatic clustering technique for query plan recommendation. Inf. Sci. 2021, 545, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhir, E.; Navimipour, N.J.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Sharifi, A.; Darwesh, A. An efficient automated incremental density-based algorithm for clustering and classification. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 114, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, J.; Ghemawat, S. MapReduce: Simplified data processing on large clusters. Commun. ACM 2008, 51, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabestari, F.; Rahmani, A.M.; Navimipour, N.J.; Jabbehdari, S. A taxonomy of software-based and hardware-based approaches for energy efficiency management in the Hadoop. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2019, 126, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, M.; Xin, R.S.; Wendell, P.; Das, T.; Armbrust, M.; Dave, A.; Meng, X.; Rosen, J.; Venkataraman, S.; Franklin, M.J. Apache spark: A unified engine for big data processing. Commun. ACM 2016, 59, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Rathi, V.K.; Chaudhary, B. Big data and cloud computing: Challenges and opportunities. Int. J. Innov. Eng. Technol. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Zaharia, M.; Chowdhury, M.; Franklin, M.J.; Shenker, S.; Stoica, I. Spark: Cluster computing with working sets. HotCloud 2010, 10, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Elsayed, A.; Mokhtar, H.M.; Ismail, O. Ontology based document clustering using mapreduce. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.02891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewen, C.; Yao, Z. Parallel text clustering based on mapreduce. In Proceedings of the 2012 Second International Conference on Cloud and Green Computing, Xiangtan, China, 1–3 November 2012; pp. 226–229. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Luo, C.; Chung, S.M. A parallel text document clustering algorithm based on neighbors. Clust. Comput. 2015, 18, 933–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makiyama, V.H.; Raddick, J.; Santos, R.D. Text Mining Applied to SQL Queries: A Case Study for the SDSS SkyServer; SIMBig: Cusco, Peru, 2015; pp. 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- Azhir, E.; Navimipour, N.J.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Sharifi, A.; Darwesh, A. A technique for parallel query optimization using MapReduce framework and a semantic-based clustering method. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basha, S.A.K.; Basha, S.M.; Vincent, D.R.; Rajput, D.S. Challenges in storing and processing big data using Hadoop and Spark. In Deep Learning and Parallel Computing Environment for Bioengineering Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 179–187. [Google Scholar]
- Ryza, S.; Laserson, U.; Owen, S.; Wills, J. Advanced Analytics with Spark: Patterns for Learning from Data at Scale; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kul, G.; Luong, D.T.A.; Xie, T.; Chandola, V.; Kennedy, O.; Upadhyaya, S. Similarity metrics for sql query clustering. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2018, 30, 2408–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, G.-S.; Antonia, P.; Spyros, S. Csmr: A scalable algorithm for text clustering with cosine similarity and mapreduce. In Proceedings of the IFIP International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations, Rhodes, Greece, 19–21 September 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; pp. 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, L.; Amer, A.A. Advanced Cosine Measures for Collaborative Filtering. Adapt. Pers. 2019, 1, 21–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.-P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A Density-Based Algorithm for Discovering Clusters in Large Spatial Databases with Noise; Kdd: Portland, OR, USA, 1996; Volume 96, pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Hahsler, M.; Piekenbrock, M.; Doran, D. dbscan: Fast density-based clustering with R. J. Stat. Softw. 2019, 91, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, B.; Chawda, B.; Kar, B.; Reddy, K.M.; Shah, S.; Sudarshan, S. Data generation for testing and grading SQL queries. VLDB J. 2015, 24, 731–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).