Dynamics of a Stochastic HIV Infection Model with Logistic Growth and CTLs Immune Response under Regime Switching
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model and Preliminaries
- for any , ;
- is symmetric for each , and satisfieswith some constant for all ;
- there is a nonempty open set with compact closure and a twice continuously differential function such that, for positive constant α and ,
3. Global Positive Solutions and Boundedness
4. Existence of an Ergodic Stationary Distribution
- If , it then follows thatIn view of (6), we arrive at for all
- If , one hasBy condition of (6), we can get for all
- If , it can be easily obtained thatAccording to of (6), is implied for all
- If , this shows thatOn the basis of (6), we achieve that for all
- If , we can get thatIn line with of (6), we have for all
- IfIf , we obtain
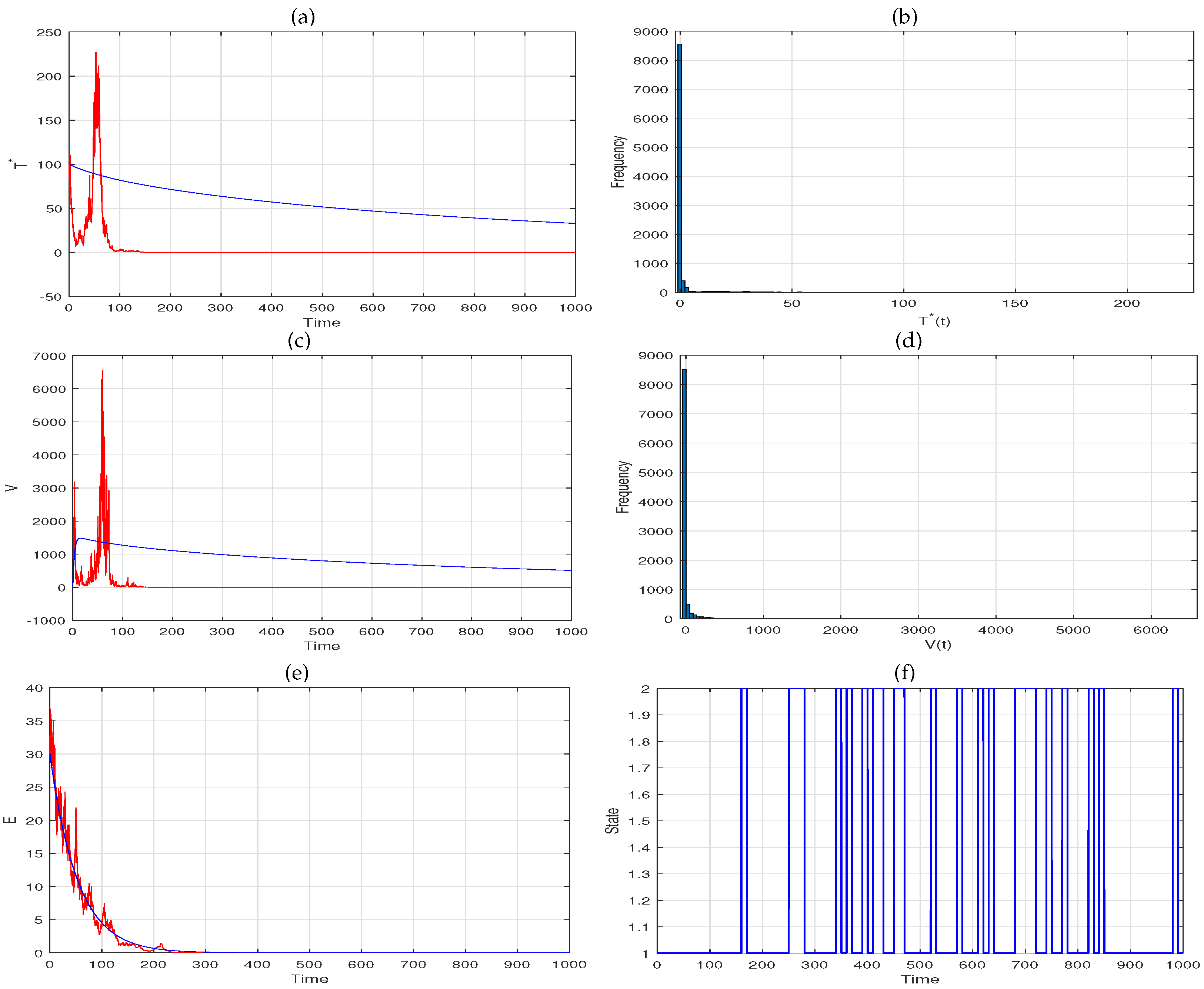
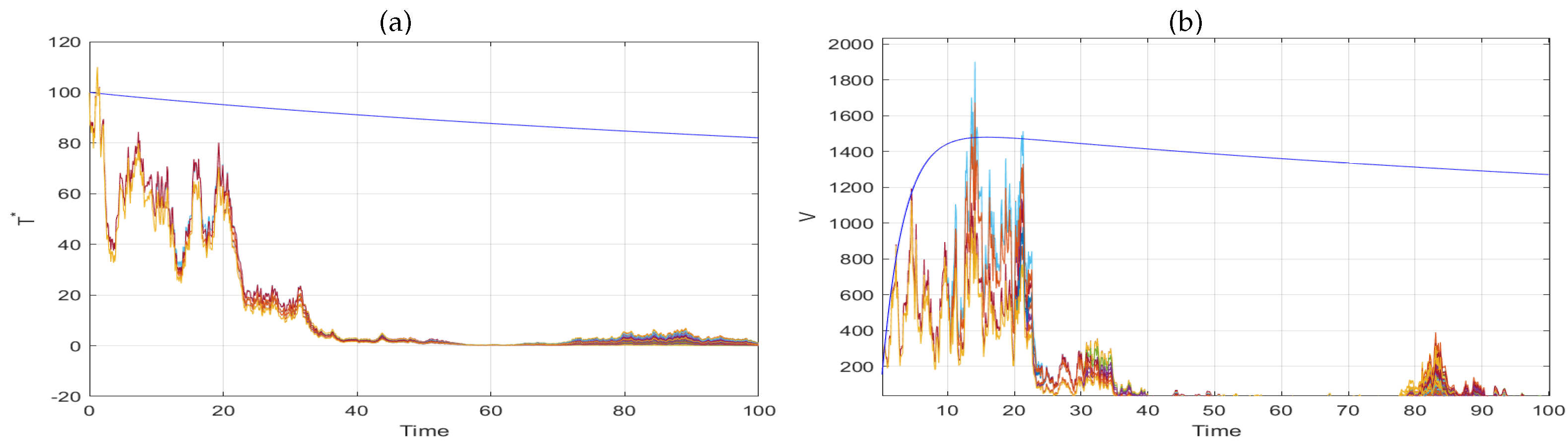
5. Extinction
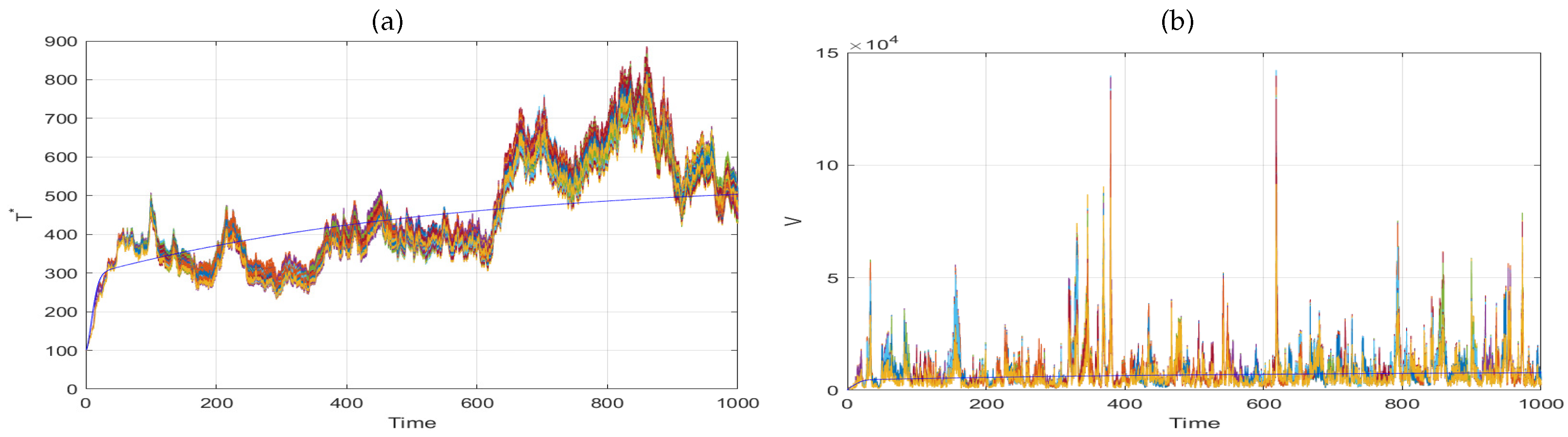
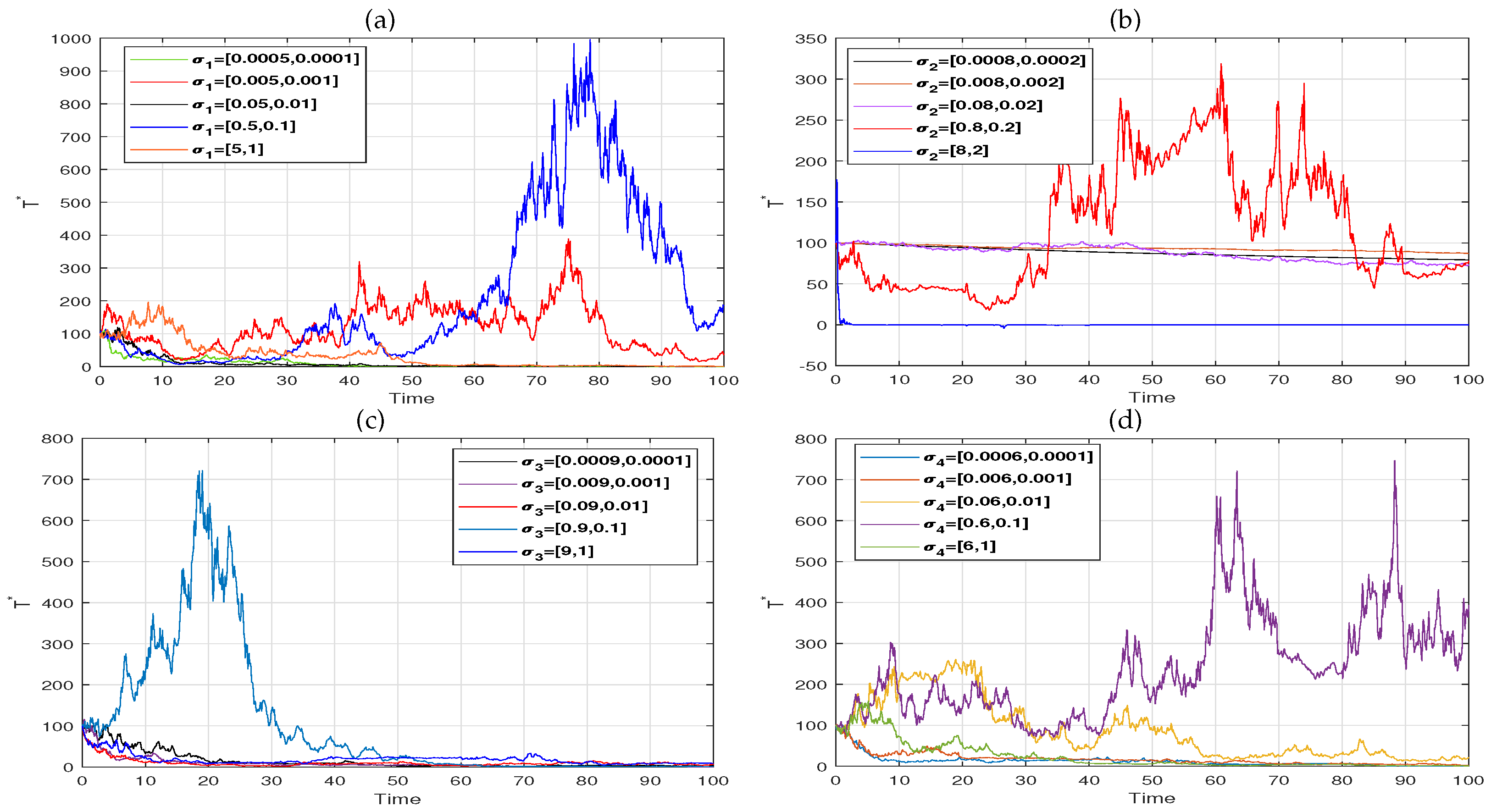
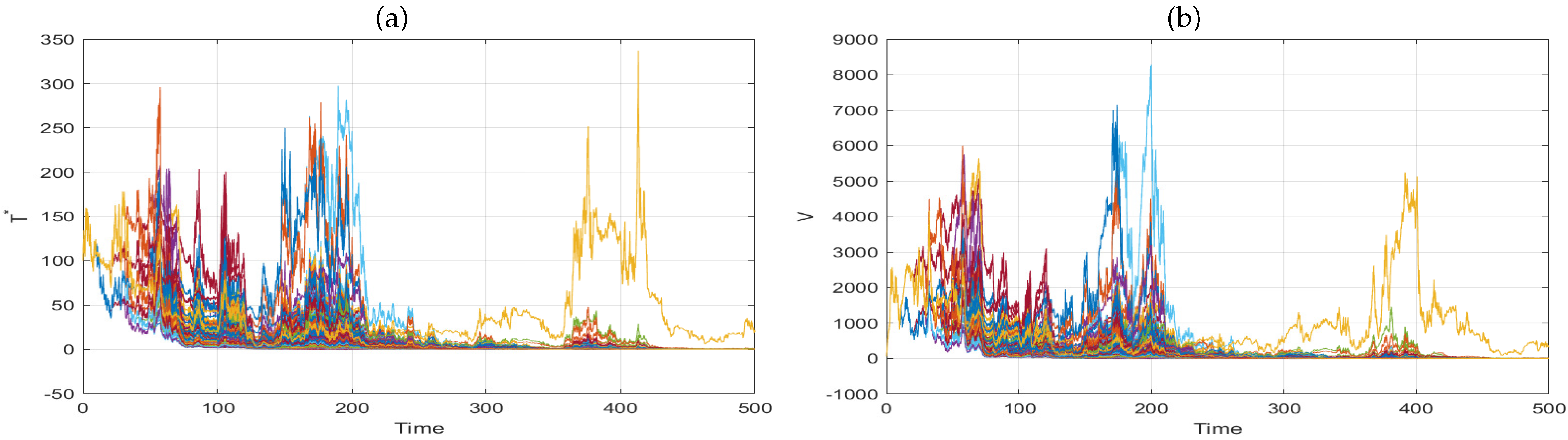
6. Numerical Simulation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. HIV/AIDS. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hiv-aids (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Nowak, M.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Shaw, G.; May, R. Anti-viral drug treatment: Dynamics of resistance in free virus and infected cell populations. J. Theor. Biol. 1997, 184, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Onofrio, A. A note on the global behaviour of the network-based SIS epidemic model. Nonlinear Anal.-Real 2008, 9, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Zhang, S.; Meng, X.; Dong, H. Periodic solution and ergodic stationary distribution of two stochastic SIQS epidemic systems. Physica A 2018, 508, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culshaw, R.; Ruan, S. A delay-differential equation model of HIV infection of CD4+ T-cells. Math. Biosci. 2000, 165, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, N.; Greenhalgh, D.; Mao, X. A stochastic model for internal HIV dynamics. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2008, 341, 1084–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, H.; Nie, L.F. Analysis of a stochastic HBV infection model nonlinear incidence rate. J. Biol. Syst. 2019, 27, 399–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhao, T. A stochastic HIV infection model with latent infection and antiretroviral therapy. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2018, 2018, 5175383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yves, E.; Bongor, D.; Rodoumta, K. Mathematical analysis of HIV/AIDS stochastic dynamic models. Appl. Math. Model. 2016, 40, 9131–9151. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Hoffmann, A. A stochastic spatio-temporal (SST) model to study cell-to-cell variability in HIV-1 infection. J. Theor. Biol. 2016, 395, 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.; Dong, L. Dynamical behaviors of stochastic virus dynamic models with saturation responses. Math. Biosci. 2019, 308, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C. The threshold for a stochastic HIV-1 infection model with Beddington-DeAngelis incidence rate. Appl. Math. Model. 2018, 64, 168–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.; Jung, I.H.; Zaman, G. A stochastic model for the transmission dynamics of hepatitis B virus. J. Biol. Dynam. 2019, 13, 328–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahrouz, A.; Settati, A. Asymptotic properties of switching diffusion epidemic model with varying population size. Appl. Math. Comput. 2013, 219, 11134–11148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Wang, K. Optimal harvesting for a stochastic regime-switching logistic diffusion system with jumps. Nonlinear Anal.-Hybri. 2014, 13, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C. Permanence of a regime-switching malaria transmission model. Physica A 2019, 523, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.; Greenhalgh, D.; Mao, X.; Pan, J. The SIS epidemic model with Markovian switching. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2012, 394, 496–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, D.; Liang, Y.; Mao, X. Modelling the effect of telegraph noise in the SIRS epidemic model using markovian switching. Physica A 2016, 462, 684–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, D.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T. Stationary distribution of stochastic SIS epidemic model with vaccination under regime switching. Appl. Math. Lett. 2016, 59, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omame, A.; Abbas, M.; Din, A. Global asymptotic stability, extinction and ergodic stationary distribution in a stochastic model for dual variants of SARS-CoV-2. Math. Comput. Simulat. 2023, 204, 302–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settati, A.; Lahrouz, A. Stationary distribution of stochastic population systems under regime switching. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 244, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Luo, J. Stationary distribution and extinction of SIR model with nonlinear incident rate under Markovian switching. Physica A 2018, 505, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xu, X.; Jiang, D.; Hayat, T.; Ahmad, B. Stationary distribution and extinction of the DS-I-A model disease with periodic parameter function and Markovian switching. Appl. Math. Comput. 2017, 311, 66–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Wang, L.; Watmough, J. Global stability of a nonlinear viral infection model with inifinitely distributed intracellular delays and CTL immune response. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2013, 73, 1280–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, D.; Rong, L.; Neumann, A.U.; Dahari, H. Mathematical modeling of viral kinetics under immune control during primary HIV-1 infection. J. Theor. Biol. 2009, 259, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaout, R.; Nowak, M.; Wodarz, D. HIV-1 dynamics revisited: Biphasic decay by cytotoxic lymphocyte killing? Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2000, 265, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Yuan, C. Stochastic Differential Equation with Markovian Switching; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Skorokhod, A.V. Asymptotic Methods in the Theory of Stochastic Differential Equations; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Yin, G. Asymptotic properties of hybrid diffusion systems. SIAM J. Control. Optim. 2007, 46, 1155–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Marion, G.; Renshaw, E. Environmental Brownian noise suppresses explosions in population dynamics. Stoch. Proc. Appl. 2002, 97, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, B.; Teng, Z. The global dynamics for a stochastic SIS epidemic model with isolation. Physica A 2018, 492, 1604–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasminskii, R.; Zhu, C.; Yin, C. Stability of regime-switching diffusions. Stoch. Proc. Appl. 2007, 117, 1037–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Liu, Q.; Shi, N.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Xia, P. Dynamics of a stochastic HIV-1 infection model with logistic growth. Physica A 2017, 469, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, N.; Watanabe, S. A comparison theorem for solutions of stochastic differential equations and its applications. Osaka J. Math. 1977, 14, 619–633. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X. Stochastic Differential Equations and Applications, 2nd ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Higham, D. An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations. SIAM Rev. 2001, 43, 525–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Param. | Description | Range | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rate of creation of new cells (cells/mm3/day) | ∼50 | [25] | |
| d | Natural mortality rate of uninfected cell (day−1) | ∼0.2 | [25] |
| r | Proliferation rate of uninfected cell (cells/mm3/day) | 0.03∼3 | [5] |
| Maximal level of CD T-cells (cells/mm3/day) | [5] | ||
| Viral infection rate (virions mm3/day) | ∼ | [25] | |
| Natural mortality rate of infected cell (day−1) | 0.1∼1 | [25] | |
| q | Rate at which infected cells are killed by CTLs (day−1) | 0.001∼1 | [26] |
| N | Burst size of the infected cell (virions/cell) | 1∼ | [25] |
| c | Natural death rate of virus (day−1) | ∼1 | [25] |
| p | Immune response activation rate (day−1) | 0.001∼1 | [26] |
| Natural death rate of CTLs (day−1) | 0.05∼0.15 | [26] |
| d | r | N | c | q | q | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| state 1 | 10 | 0.02 | 0.1 | 180 | 2500 | 0.0185 | 3.0 | 0.00020 | 0.00012 | 0.00012 | 0.20 |
| state 2 | 15 | 0.035 | 0.05 | 160 | 3500 | 0.0195 | 2.5 | 0.00015 | 0.00010 | 0.00010 | 0.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, L.; Nie, L.-F. Dynamics of a Stochastic HIV Infection Model with Logistic Growth and CTLs Immune Response under Regime Switching. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3472. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193472
Hu L, Nie L-F. Dynamics of a Stochastic HIV Infection Model with Logistic Growth and CTLs Immune Response under Regime Switching. Mathematics. 2022; 10(19):3472. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193472
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Lin, and Lin-Fei Nie. 2022. "Dynamics of a Stochastic HIV Infection Model with Logistic Growth and CTLs Immune Response under Regime Switching" Mathematics 10, no. 19: 3472. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193472
APA StyleHu, L., & Nie, L.-F. (2022). Dynamics of a Stochastic HIV Infection Model with Logistic Growth and CTLs Immune Response under Regime Switching. Mathematics, 10(19), 3472. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193472






