An Extended Multi-Attributive Border Approximation Area Comparison Method for Emergency Decision Making with Complex Linguistic Information
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Preliminaries
- (1)
- ;
- (2)
- ;
- (3)
- (1)
- If, then;
- (2)
- If, then
- (a)
- If, then;
- (b)
- If, then.
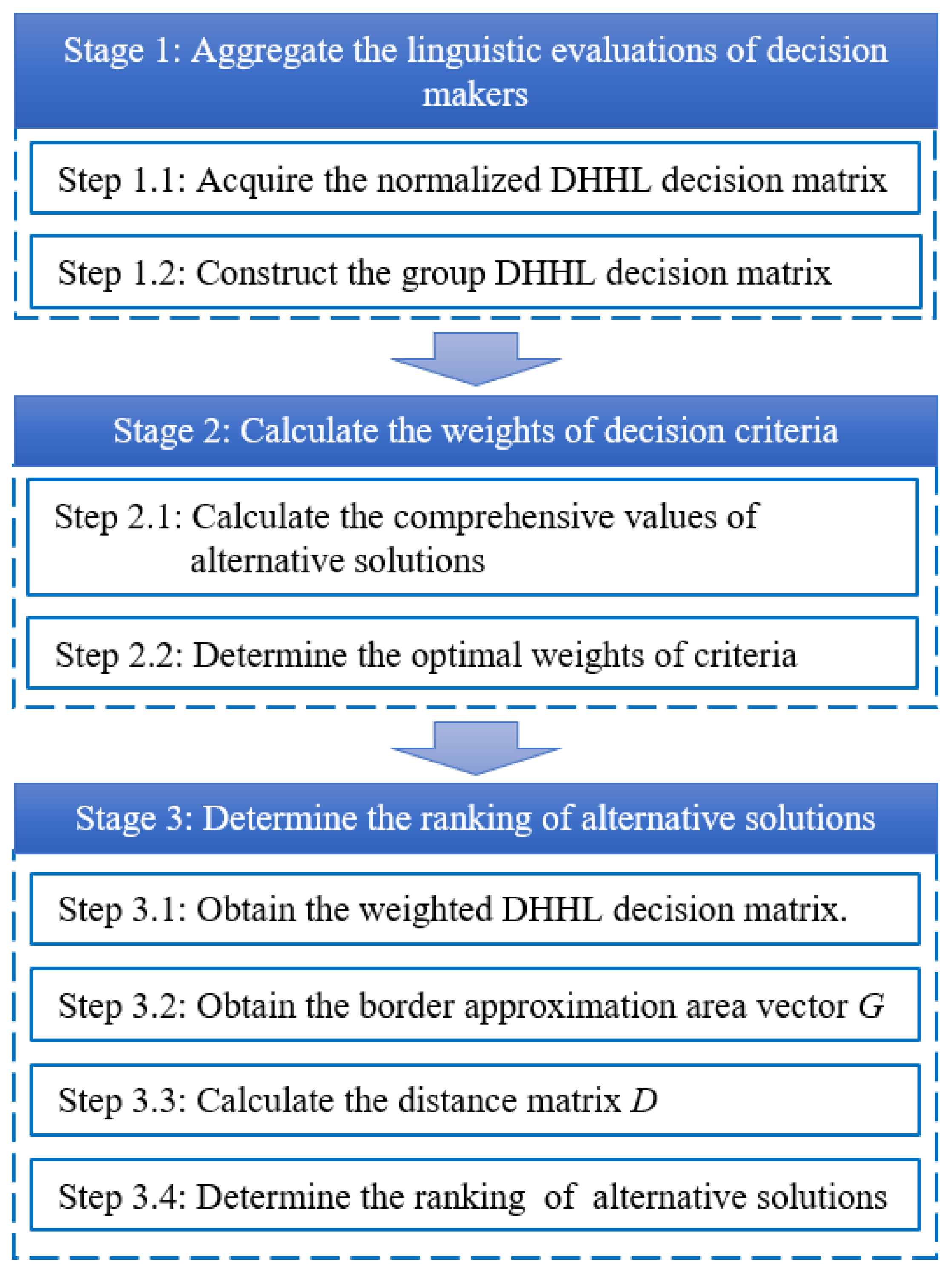
4. The Proposed EDM Model
4.1. Aggregate the Linguistic Evaluations of Decision Makers
4.2. Calculate the Weights of Decision Criteria
- (1)
- A weak raking: ;
- (2)
- A strict ranking: ;
- (3)
- A ranking of difference: ;
- (4)
- A ranking with multiples: ;
- (5)
- An interval form: .
4.3. Determine the Ranking of Alternative Solutions
5. Illustrative Example
5.1. Implementation and Results
5.2. Comparison Analysis
- (1)
- The proposed EDM model can express complex linguistic decision information in a more prominent manner and reduce the loss of information in fusing multiple-expert evaluations. This enables decision makers to express their judgments more realistically and easily.
- (2)
- The proposed EDM model is able to assign the weights of decision criteria when their weighting information is partially known. This is particularly useful for EDM since precise data is usually unavailable or unreliable under strong time constraints.
- (3)
- The proposed EDM model is more efficient in the EDM process and can assist decision makers in achieving more reasonable and credible ranking results of alternative solutions. This makes the proposed DHHL-MABAC method more realistic and practical.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qi, K.; Chai, H.; Duan, Q.; Du, Y.; Wang, Q.; Sun, J.; Liew, K.M. A collaborative emergency decision making approach based on BWM and TODIM under interval 2-tuple linguistic environment. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2022, 13, 383–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, G.; Liu, H.; Xu, L. Group decision making for internet public opinion emergency based upon linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy information. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2022, 13, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Goh, M.; Wang, Y.M. Interval-valued hesitant fuzzy TODIM method for dynamic emergency responses. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 8263–8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Wang, Y.M.; Goh, M. An extended TODIM approach for group emergency decision making based on bidirectional projection with hesitant triangular fuzzy sets. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 151, 106959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Xu, Z.; Mi, X.; Ren, Z. Dynamic reference point method with probabilistic linguistic information based on the regret theory for public health emergency decision-making. Econ. Res.—Ekon. Istraz. 2021, 34, 3355–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.X.; Liu, R.; Mou, X.; Liu, H.C. New approach for quality function deployment using linguistic Z-numbers and EDAS method. Informatica 2021, 32, 565–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wu, X.; Xu, Z.; Fujita, H. Emergency decision making for natural disasters: An overview. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2018, 27, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Qin, J.; Chai, J.; Gómez Muñoz, C.Q. Emergency rescue planning under probabilistic linguistic information: An integrated FTA-ANP method. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 37, 101170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xu, Z.; Liang, Z.; Liao, H. Expected consistency-based emergency decision making with incomplete probabilistic linguistic preference relations. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2019, 176, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Mao, L.X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.C. New method for emergency decision making with an integrated regret theory-EDAS method in 2-tuple spherical linguistic environment. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 13296–13309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Ma, X. An IT2FS-PT3 based emergency response plan evaluation with MULTIMOORA method in group decision making. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 122, 108812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pei, Z. A novel multiple attribute decision-making approach for evaluation of emergency management schemes under picture fuzzy environment. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2022, 13, 633–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.F.; Liu, H.C.; Shi, H. A dynamic approach for emergency decision making based on prospect theory with interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy linguistic variables. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 131, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Tu, Y.; Ju, Y.; Shen, W. A multi-granularity proportional hesitant fuzzy linguistic TODIM method and its application to emergency decision making. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 36, 101081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Fujita, H. A dynamic weight determination approach based on the intuitionistic fuzzy Bayesian network and its application to emergency decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 26, 1893–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.F.; Liu, H.C. A new approach for emergency decision-making based on zero-sum game with Pythagorean fuzzy uncertain linguistic variables. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2019, 34, 1667–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Ma, W.; Li, B.; Li, X. Three-way decisions approach to multiple attribute group decision making with linguistic information-based decision-theoretic rough fuzzy set. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2018, 93, 424–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhang, K.; Gao, J.Q.; Yang, L.H. A heterogeneous multi-attribute case retrieval method for emergency decision making based on bidirectional projection and TODIM. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 203, 117382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.F.; Liu, H.C. An extended prospect theory–VIKOR approach for emergency decision making with 2-dimension uncertain linguistic information. Soft Comput. 2019, 23, 12139–12150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Wang, Y.M. A dynamic multi-attribute group emergency decision making method considering experts’ hesitation. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2018, 11, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.; Liao, H.; Xu, Z.; Herrera, F. Double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set and MULTIMOORA method: A case of study to evaluate the implementation status of haze controlling measures. Inf. Fusion 2017, 38, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Shen, M.; Teng, F.; Zhu, B.; Rong, L.; Geng, Y. Double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic entropy-based TODIM approach using evidential theory. Inf. Sci. 2021, 547, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishankumar, R.; Ravichandran, K.S.; Kar, S.; Gupta, P.; Mehlawat, M.K. Double-hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set-based decision framework for multi-attribute group decision-making. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 2665–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.; Xu, Z.; Liao, H.; Herrera, F. Multiple criteria decision making based on distance and similarity measures under double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic environment. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 126, 516–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.; Xu, Z. Double hierarchy linguistic term set and its extensions: The state-of-the-art survey. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 36, 832–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.; Xu, Z.; Liao, H.; Herrera, F. Probabilistic double hierarchy linguistic term set and its use in designing an improved VIKOR method: The application in smart healthcare. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2021, 72, 2611–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, Z.; Gou, X. ELECTRE II method based on the cosine similarity to evaluate the performance of financial logistics enterprises under double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic environment. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Mak. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; He, Y.; Xu, Z. Evaluate public-private-partnership’s advancement using double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic promethee with subjective and objective information from stakeholder perspective. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2019, 25, 386–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.Y.; Chen, X.Q.; Shi, H.; Liu, H.C. A new model for failure mode and effects analysis based on k-means clustering within hesitant linguistic environment. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2022, 69, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, R.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.C. Passenger satisfaction evaluation of public transport using alternative queuing method under hesitant linguistic environment. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 26, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishankumar, R.; Pamucar, D.; Pandey, A.; Kar, S.; Ravichandran, K.S. Double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic information based framework for personalized ranking of sustainable suppliers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 65371–65390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.X.; Mao, L.X.; Liu, H.C.; Zhang, L. Decades on emergency decision-making: A bibliometric analysis and literature review. Complex Intell. Syst. 2021, 7, 2819–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.C. Emergency decision making with extended axiomatic design approach under picture fuzzy environment. Expert Syst. 2020, 37, e12482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamučar, D.; Ćirović, G. The selection of transport and handling resources in logistics centers using multi-attributive border approximation area comparison (MABAC). Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 3016–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.R.; Saha, A.; Rani, P.; Pamucar, D.; Dutta, D.; Hezam, I.M. Sustainable supplier selection using HF-DEA-FOCUM-MABAC technique: A case study in the Auto-making industry. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 8821–8840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatina, N.; Tadić, D.; Aleksić, A.; Jovanović, A.D. The assessment and selection of suppliers using AHP and MABAC with type-2 fuzzy numbers in automotive industry. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part O J. Risk Reliab. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ju, Y.; Dong, P.; Gonzalez, E.D.R.S. A hybrid decision making aided framework for multi-criteria decision making with R-numbers and preference models. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 111, 104777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.W.; Li, Q.; Yin, L.; Liu, H.C. Undergraduate teaching audit and evaluation using an extended MABAC method under q-rung orthopair fuzzy environment. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2020, 35, 1912–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, D. A 2-dimensional uncertain linguistic MABAC method for multiattribute group decision-making problems. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Liu, Y.; Senapati, T.; Garg, H.; Rong, Y. An extended MABAC method based on prospect theory with unknown weight information under Fermatean fuzzy environment for risk investment assessment in B&R. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamucar, D.; Petrovic, I.; Ćirović, G.; Stević, Ž. An extension of the MABAC and OS model using linguistic neutrosophic numbers: Selection of unmanned aircraft for fighting forest fires. Transport 2022, 37, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.; Roy, S.K. Application of Choquet integral in interval type-2 Pythagorean fuzzy sustainable supply chain management under risk. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2022, 37, 217–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Xiao, L.; Pedrycz, W.; Pamucar, D.; Zhang, G.; Martínez, L. Design alternative assessment and selection: A novel Z-cloud rough number-based BWM-MABAC model. Inf. Sci. 2022, 603, 149–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Hou, L.X.; Liu, H.C.; Lin, W. Occupational health and safety risk assessment using an integrated SWARA-MABAC model under bipolar fuzzy environment. Comput. Appl. Math. 2020, 39, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadikolaei, A.S.; Parkouhi, S.V.; Saloukolaei, D.D. Extension of a hybrid MABAC-DANP method under gray environment for green supplier selection. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2022, 21, 755–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning—I. Inf. Sci. 1975, 8, 199–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Xu, Z.; Hao, Z. Hesitant fuzzy thermodynamic method for emergency decision making based on prospect theory. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 47, 2531–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Sun, B.; Zhang, X. PF-TOPSIS method based on CPFRS models: An application to unconventional emergency events. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 139, 106192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.; Abdullah, S. Emergency decision support modeling for COVID-19 based on spherical fuzzy information. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2020, 35, 1601–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Zeng, S.; Zhou, J.; Li, T.; Koe, A.S.V. Interval-valued Pythagorean fuzzy linguistic KPCA model based on TOPSIS and its application for emergency group decision making. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2022, 37, 6415–6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.P.; Xu, G.L.; Wang, F.K.; Dong, J.Y. A new method for Atanassov’s interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy MAGDM with incomplete attribute weight information. Inf. Sci. 2020, 316, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; You, J.X.; Duan, C.Y. An integrated approach for failure mode and effect analysis under interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 207, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.; Abdullah, S.; Aslam, M.; Qiyas, M.; Kutbi, M.A. Spherical fuzzy sets and its representation of spherical fuzzy t-norms and t-conorms. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 36, 6089–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yager, R.R. Pythagorean membership grades in multicriteria decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 22, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P. An approach to group decision making based on 2-dimension uncertain linguistic information. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2012, 18, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J. Fuzzy linear programming based on statistical confidence interval and interval-valued fuzzy set. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 129, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Decision Makers | Alternative Solutions | Criteria | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | ||
| D1 | A1 | |||||
| A2 | ||||||
| A3 | ||||||
| A4 | ||||||
| D2 | A1 | |||||
| A2 | ||||||
| A3 | ||||||
| A4 | ||||||
| D3 | A1 | |||||
| A2 | ||||||
| A3 | ||||||
| A4 | ||||||
| D4 | A1 | |||||
| A2 | ||||||
| A3 | ||||||
| A4 | ||||||
| D5 | A1 | |||||
| A2 | ||||||
| A3 | ||||||
| A4 | ||||||
| Alternative solutions | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | |||||
| A2 | |||||
| A3 | |||||
| A4 |
| Alternatives | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | |||||
| A2 | |||||
| A3 | |||||
| A4 |
| Alternatives | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | |||||
| A2 | |||||
| A3 | |||||
| A4 |
| Alternatives | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 0.073 | 0.137 | 0.013 | 0.060 | −0.044 |
| A2 | 0.012 | −0.044 | 0.005 | −0.024 | 0.029 |
| A3 | 0.033 | −0.057 | 0.007 | −0.004 | 0.033 |
| A4 | −0.101 | −0.014 | −0.024 | −0.027 | −0.013 |
| Characteristics | The Spherical Fuzzy GRA | The Pythagorean Fuzzy TOPSIS | The Linguistic VIKOR | The Interval TODIM | The Proposed DHHL-MABAC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whether model uncertainty more powerful | No | No | YES | No | Yes |
| Whether considers quantity of both gains and losses | No | YES | No | No | Yes |
| Whether handles partial weighting information | No | No | No | No | Yes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, H.; Huang, L.; Li, K.; Wang, X.-H.; Liu, H.-C. An Extended Multi-Attributive Border Approximation Area Comparison Method for Emergency Decision Making with Complex Linguistic Information. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3437. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193437
Shi H, Huang L, Li K, Wang X-H, Liu H-C. An Extended Multi-Attributive Border Approximation Area Comparison Method for Emergency Decision Making with Complex Linguistic Information. Mathematics. 2022; 10(19):3437. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193437
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Hua, Lin Huang, Ke Li, Xiang-Hu Wang, and Hu-Chen Liu. 2022. "An Extended Multi-Attributive Border Approximation Area Comparison Method for Emergency Decision Making with Complex Linguistic Information" Mathematics 10, no. 19: 3437. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193437
APA StyleShi, H., Huang, L., Li, K., Wang, X.-H., & Liu, H.-C. (2022). An Extended Multi-Attributive Border Approximation Area Comparison Method for Emergency Decision Making with Complex Linguistic Information. Mathematics, 10(19), 3437. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10193437






