Effectiveness of a Multimodal Intervention on Social Climate (School and Family) and Performance in Mathematics of Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- The school climate and family climate of a group of children with ADHD (multimodal group) compared to a group of children who only received stimulant medication (control group).
- -
- The mathematical performance of students with ADHD in the multimodal group compared to children in the control group.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Sample of Children
2.3. Sample of Parents
2.4. Sample of Teachers
2.5. Measures
2.6. Procedure
2.7. Teacher Training Programme
2.8. Parent Training Programme
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
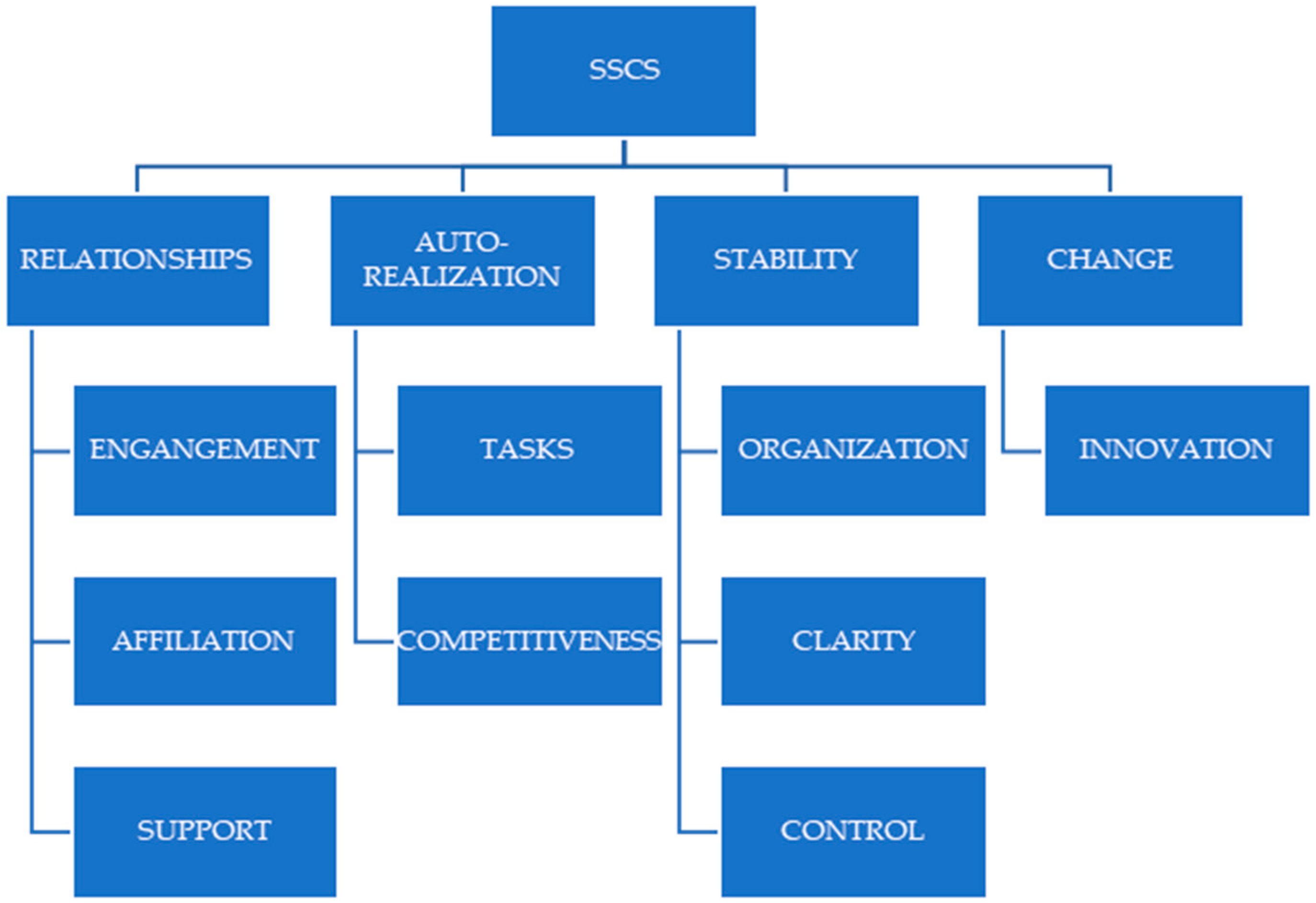
School Climate
4. Family Climate
Academic Performance in Mathematics
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohammadi, M.R.; Zarafshan, H.; Khaleghi, A.; Ahmadi, N.; Hooshyari, Z.; Mostafavi, S.A.; Ahmadi, A.; Alavi, S.S.; Shakiba, A.; Salmanian, M. Prevalence of ADHD and Its Comorbidities in a Population-Based Sample. J. Atten. Disord. 2021, 25, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, M.J.; Soutullo, C.; Díez, A.; Figueroa, A. TDAH y su comorbilidad psiquiátrica. In Todo Sobre el TDAH. Guía Para la Vida Diaria; Martínez Martín, M.A., Ed.; Altaria: Tarragona, Spain, 2013; pp. 81–130. [Google Scholar]
- López, J. Estudio Descriptivo del Trastorno por Déficit de Atención con Hiperactividad (TDAH): Perfil Psicoeducativo y Comorbilidad en los Diferentes Subtipos. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Murcia, Murcia, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Montoya, E.; Herrera-Gutiérrez, E. Manifestaciones del TDAH en la etapa de educación infantil y cómo afrontarlas. In Claves para una Educación Diversa; Navarro, J., Gracia, M.D., y Lineros, R., Soto, F.J., Eds.; Consejería de Educación, Cultura y Universidades: Murcia, Spain, 2014; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Avaria, M.A.; Kleinsteuber, K. Dificultad de aprendizaje en el niño. Rev. Esp. Pediatr. 2014, 11, 18–35. [Google Scholar]
- DuPaul, G.J.; Volpe, R.J. ADHD and learning disabilities: Research findings and clinical implications. Curr. Atten. Disord. Rep. 2009, 1, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meliá de Alba, A. Dificultades en el Aprendizaje de las Matemáticas en Niños con TDAH: Comparación de los Perfiles Cognitivos y Metacognitivos. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Valencia, Valencia, Spain, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rosich, N.; Casajús, A. El alumnado con déficit de atención e hiperactividad (TDAH) en el aprendizaje de las matemáticas en los niveles obligatorios. Rev. Mat. Iberoam. 2008, 16, 63–83. [Google Scholar]
- Mayes, S.D.; Calhoun, S.L. Frequency of reading, math, and writing disabilities in children with clinical disorders. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2006, 16, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kercood, S.; Zentall, S.; Vinh, M.; Wright, K.T. Attentional cuing in math word problems for girls at-risk for ADHD and their peers in general education settings. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 2012, 37, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosto, M.G.; Momi, S.; Asherson, P.; Malki, K. A systematic review of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and mathematical ability: Current findings and future implications. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslau, J.; Miller, E.; Breslau, N.; Bohnert, K.; Lucia, V.; Schweitzer, J. The impact of early behavior disturbances on academic achievement in high school. Pediatrics 2009, 123, 1472–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calub, C.; Rapport, M.; Friedman, L.; Eckrich, S. IQ and academic achievement in children with ADHD: The differential effects of specific cognitive functions. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess 2019, 41, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, G.J.; Dowsett, C.J.; Claessens, A.; Magnuson, K.; Huston, A.C.; Klebanov, P.; Pagani, L.S.; Feinstein, L.; Engel, M.; Brooks-Gunn, J.; et al. School Readiness and Later Achievement. Dev. Psychol. 2007, 43, 1428–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogel, Y.; Rosenblum, S.; Josman, N. Environmental factors and daily functioning levels among adolescents with executive function deficits. Br. J. Occup. Ther. 2020, 83, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, A.; Grau, M.D.; Roselló, B.; Marco, R. Estilos de disciplina en familias con hijos con trastorno por déficit de atención/hiperactividad: Influencia en la evolución del trastorno. Rev. Neurol. 2007, 44, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robledo, P.; García, J.N. Contexto familiar del alumnado con dificultades de aprendizaje o TDAH, percepciones de padres e hijos, ESE. Estud. Sobre Educ. 2014, 26, 149–173. [Google Scholar]
- González, R.; Bakker, L.; Rubiales, J. Estilos parentales en niños y niñas con TDAH. Rev. Latinoam. Cienc. Soc. Ninez Juv. 2014, 12, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselló, B.; García, R.; Tárraga, R.; Mulas, F. El papel de los padres en el desarrollo y aprendizaje de los niños con TDAH. Rev. Neurol. 2003, 36 (Suppl. S1), 79. [Google Scholar]
- Theule, J.; Wiener, J.; Tannock, R.; Jenkins, J.M. Parenting Stress in Families of Children With ADHD: A Meta-Analysis. J. Emot. Behav. Disord. 2013, 21, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, D.P.; Harrison, C.A. Parenting practices of mothers of children with ADHD: The role of maternal and child factors. Child Adolesc. Ment. Health 2006, 11, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, A.; Presentación, M.J.; Colomer, C.; Roselló, B. Satisfacción con la vida de niños con trastorno por déficit de atención/hiperactividad: Estudio de posibles factores de riesgo y de protección. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 52 (Suppl. S1), 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, G.; Sheerin, D.; Carr, A.; Dooley, B.; Barton, V.; Marshall, D.; Mulligan, A.; Lawlor, M.; Belton, M.; Doyle, M. Family factors associated with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and emotional disorders in children. J. Fam. Ther. 2005, 27, 76–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keown, L.J.; Woodward, L.J. Early parent-child relations and family functioning of preschool boys with pervasive hyperactivity. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2002, 30, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, D.J. Discrepancia Educativa Parental y TDAH: Intervención Psicoeducativa a Través de un Programa de Entrenamiento a Padres. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Murcia, Murcia, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wolraich, M.L.; Hagan, J.F.; Allan, C.; Chan, E.; Davison, D.; Earls, M.; Evans, S.W.; Flinn, S.K.; Froehlich, T.; Frost, J.; et al. Subcommittee on children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactive disorder. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics 2019, 144, e20192528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkley, R.A. Defiant Children: A Clinicians’ Manual for Assessment and Parent Training; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Aghebati, A.; Gharraee, B.; Hakim, M.; Gohari, M.R. Triple p-positive parenting program for mothers of ADHD children. Iran J. Psychiatry Behav. Sci. 2014, 8, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Bor, W.; Sanders, M.R.; Markie-Dadds, C. The effects of the Triple P-Positive Parenting Program on preschool children with co-occurring disruptive behavior and attentional/hyperactive difficulties. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2002, 30, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaf, I.; Speetjens, P.; Smit, F.; de Wolff, M.; Tavecchio, L. Effectiveness of the Triple P Positive Parenting Program on behavioral problems in children: A meta-analysis. Behav. Modif. 2008, 32, 714–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ireland, J.L.; Sanders, M.R.; Markie-Dadds, C. The impact of parent training on marital functioning: A comparison of two group versions of the Triple P-Positive Parenting Program for parents of children with early-onset conduct problems. Behav. Cogn. Psychother. 2003, 31, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharreri, F.; Soltanifar, A.; Khalesi, H.; Eslami, N. The evaluation of efficacy of the positive parenting for parents in order improvement of relationship with their adolescents. Iran J. Basic Med. Sci. 2012, 55, 116–123. [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf, Ö.; Gonka, Ö.; Pekcanlar, A. The effects of the triple P-positive parenting programme on parenting, family functioning and symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. A randomized controlled trial. Psychiatr. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.; Daley, D.; Hutchings, J.; Bywater, T.; Eames, C. Efficacy of the Incredible Years Programme as an early intervention for children with conduct problems and ADHD: Long-term follow-up. Child Care Health Dev. 2008, 34, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, D.W.; Rabiner, D.L.; Kuhn, L.; Pan, Y.; Sabet, R.F. Investigating teacher and student effects of the Incredible Years Classroom Management Program in early elementary school. Sch. Psychol. 2018, 67, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trillingsgaard, T.; Trillingsgaard, A.; Webster-Stratton, C. Assessing the effectiveness of the ‘Incredible Years® parent training’to parents of young children with ADHD symptoms—A preliminary report. Scand. J. Psychol. 2014, 55, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, A.; Grau, D.; Melià, A.; Roselló, B. Fundamentación de un programa multicomponencial de asesoramiento a familias con TDAH [Multicomponent counselling programme rationale for families with ADHD]. Rev. Neurol. 2008, 46 (Suppl. S1), 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Smit, S.; Mikami, A.Y.; Normand, S. Effects of the Parental Friendship Coaching Intervention on Parental Emotion Socialization of Children with ADHD. Res. Child Adolesc. Psychopathol. 2022, 50, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronis, A.; Chacko, A.; Fabiano, B.; Wymbs, B.; Pelham, W. Enhancements to the behavioral parent training paradigm for families of children with ADHD: Review and future directions. Clin. Child Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2004, 7, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, B.P.; Creed, T.A.; Xanthopoulos, M.; Brown, R.T. Psychosocial treatments for children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2007, 17, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, J.; Hornstra, R.; Van der Oord, S.; Luman, M.; Hoekstra, P.J.; Groenman, A.P.; van den Hoofdakker, B.J. Meta-analysis: Which components of parent training work for children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder? J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. 2022, 61, 478–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiano, G.; Pelham, W.E.; Coles, E.; Gnagy, E. A meta-analysis of behavioral treatments for ADHD. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2009, 29, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, T.A.; Rooney, M.; Chronis-Tuscano, A.; Tariq, N. Preliminary efficacy of a behavioral parent training program for children with ADHD in Pakistan. J. Atten. Disord. 2017, 21, 390–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonuga-Barke, E.J.; Daley, D.; Thompson, M.; Laver-Bradbury, C.; Weeks, A. Parent-based therapies for preschool attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A randomized, controlled trial with a community sample. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. 2001, 40, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solan, M.; Brunstein, A.; Ankori, G.; Bloch, A.; Apter, A.; Plishty, S. Impact of a new parent behavioral-schema training on children with ADHD: A pragmatic control trial. J. Atten. Disord. 2021, 25, 2048–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwel, S.; Reynolds, K.J.; Lee, E.; Subasic, E.; Bromhead, D. The impact of school climate and school identification on academic achievement: Multilevel modeling with student and teacher data. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, A.; Cohen, J.; Guffey, S.; Higgins, A. A review of school climate research. Rev. Educ. Res. 2013, 83, 257–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newland, L.A.; De Cino, D.A.; Mourlam, D.J.; Strouse, G.A. School climate, emotions, and relationships: Children’s experiences of well-being in the Midwestern US. Int. J. Emot. Educ. 2019, 11, 67–83. [Google Scholar]
- Varela, J.J.; Sirlopú, D.; Melipillán, R.; Espelage, D.; Green, J.; Guzmán, J. Exploring the influence of school climate on the relationship between school violence and adolescent subjective well-being. Child Indic. Res. 2019, 12, 2095–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, S.M.; Mann, M.J.; Kristjansson, A.L.; Smith, M.L.; Zullig, K.J. School climate and academic achievement in middle and high school students. J. Sch. Health 2019, 89, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-González, L.; Oriol, X. La relación entre competencia emocional, clima de aula y rendimiento académico en estudiantes de secundaria. Cult. Educ. 2016, 28, 130–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, K.; Rico, R. El clima escolar como elemento fundamental de la convivencia en la escuela. Escenarios 2014, 12, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, I.; Reynolds, K.J.; Lee, E.; Subasic, E.; Bromhead, D. Well-being, school climate, and the social identity process: A latent growth model study of bullying perpetration and peer victimization. Sch. Psychol. 2014, 29, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuperminc, G.P.; Leadbeater, B.J.; Blatt, S.J. School Social Climate and Individual Differences in Vulnerability to Psychopathology among Middle School Students. Sch. Psychol. 2001, 39, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, G.; Gras, M. Atribuciones del comportamiento antisocial en el alumnado de educación secundaria: Aspectos destacables frente a la intervención. In Las Conductas de Riesgo del Adolescente. Investigación y Soluciones; Palacios, R., Ed.; Centro de Investigación e Innovación Biopsicosocial: Madrid, Spain, 2011; pp. 141–162. [Google Scholar]
- Somersalo, H.; Solantaus, T.; Almqvist, F. Classroom climate and the mental health of primary school children. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2002, 56, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Both, F.; Schmiedeler, S.; Abelein, P.; Schneider, W. Wirksamkeit eines Workshops für Lehrkräfte über die Aufmerksamkeitsdefizit-/Hyperaktivitätsstörung (ADHS) [Effectiveness of an educator training about the Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)]. Prax. Kinderpsychol. Kinderpsychiatr. 2016, 65, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelemy, L.; Harvey, K.; Waite, P. Supporting students’ mental health in schools: What do teachers want and need? Emot. Behav. Diffic. 2019, 24, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, A.P.; Kieling, R.R.; Costa, A.C.; Chardosim, N.; Dorneles, B.V.; Almeida, M.R.; Mazzuca, A.C.; Kieling, C.; Rohde, L.A. Increasing teachers’ knowledge about ADHD and learning disorders. J. Atten. Disord. 2014, 18, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anto, M.R.; Jacob, M.V. Effectiveness of self-instructional module on knowledge of teachers regarding childhood attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J. Nurs. Healthc. 2014, 3, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casajús, A.M. Resolución de Problemas Aritmético-Verbales por Alumnos con Déficit de Atención con Hiperactividad (TDAH). Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Froelich, J.; Breuer, D.; Doepfner, M.; Amonn, F. Effects of a Teacher Training Programme on Symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Spec. Educ. 2012, 27, 76–87. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, A.; Jarque, S.; Rosel, J. Treatment of children with ADHD: Psychopedagogical program at school versus psychostimulant medication. Psicothema 2006, 18, 335–341. [Google Scholar]
- Syed, E.U.; Hussein, S.A. Increase in teachers’ knowledge about ADHD after a week-long training program: A pilot study. J. Atten. Disord. 2010, 13, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.J.; Bristow, S.J.; Kovshoff, H.; Cortese, S.; Kreppner, J. The Effects of ADHD Teacher Training Programs on Teachers and Pupils: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Atten. Disord. 2022, 26, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuPaul, G.J.; Stoner, G. ADHD in the Schools: Assessment and Intervention Strategies, 3rd ed.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, S.W.; Owens, J.S.; Wymbs, B.T.; Ray, A.R. Evidence-Based Psychosocial Treatments for Children and Adolescents With Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2018, 47, 157–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Diagnosis and Management; Guidance and Guidelines; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pelham, W.E.; Burrows-MacLean, L.; Gangy, E.M.; Fabiano, G.A.; Coles, E.K.; Wymbs, B.T.; Waschbusch, D.A. A Dose-Ranging Study of Behavioral and Pharmacological Treatment in Social Settings for Children with ADHD. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2014, 42, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfiffner, L.J.; DePaul, G.J. Treatment of ADHD in school settings. In Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook for Diagnosis and Treatment, 4th ed.; Barkley, R.A., Ed.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 596–629. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus, A.A. The Practice of Multimodal Therapy: Systematic, Comprehensive and Effective Psychotherapy; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Amado, L.; Jarque, S.; Ceccato, R. Differential impact of a multimodal versus pharmacological therapy on the core symptoms of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in childhood. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2016, 59, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dahl, V.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Spears, A.P.; Jorge, A.; Lu, J.; Bigio, N.; Chacko, A. Psychoeducation Interventions for Parents and Teachers of Children and Adolescents with ADHD: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Dev. Phys. Disabil. 2020, 32, 257–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The MTA Cooperative Group; Multimodal Treatment Study of Children with ADHD. A 14-month randomized clinical trial of treatment strategies for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1999, 56, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.S.; Hinshaw, S.P.; Swanson, J.M.; Greenhill, L.L.; Conners, C.K.; Arnold, L.E.; Abikoff, H.B.; Elliott, B.; Hechtman, L.; Hoza, B.; et al. Findings from the NIMH Multimodal Treatment Study of ADHD (MTA): Implications and applications for primary care providers. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2001, 22, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Hechtman, L. The Multimodal Treatment of Children with ADHD (MTA) follow-up study: Outcomes and their predictors. In Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Adult Outcome and Its Predictors; Hechtman, L., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 231–260. [Google Scholar]
- Ostberg, M.; Rydell, A.M. An efficacy study of a combined parent and teacher management training programme for children with ADHD. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2012, 66, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pfiffner, L.J.; Hinshaw, S.P.; Owens, E.; Zalecki, C.; Kaiser, N.M.; Villodas, M.; McBurnett, K. A two-site randomized clinical trial of integrated psychosocial treatment for ADHD-inattentive type. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2014, 82, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wang, C.; Tian, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, G. Effects of Parent-Teacher Training on Academic Performance and Parental Anxiety in School-Aged Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial in Shanghai, China. Front. Psychol. 2021, 9, 733450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villodas, M.T.; McBurnett, K.; Kaiser, N.; Rooney, M.; Pfiffner, L.J. Additive Effects of Parent Adherence on Social and Behavioral Outcomes of a Collaborative School–Home Behavioral Intervention for ADHD. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2014, 45, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ballesteros, R.; Sierra, B. Escalas de Clima Social: Familia, Trabajo, Instituciones Penitenciarias, Centro Escolar. In Manual: Investigación y Publicaciones Psicológicas; TEA Ediciones: Madrid, Spain, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Mena, B.; Nicolau, R.; Salat, L.; Tort, P.; Romero, B. El Alumno con TDAH. Guía Práctica para Educadores; Mayo Ediciones: Madrid, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jarque, S.; Amado, L.; Oporto, M.; Fernández, M. Effectiveness of a Long-Term Training Programme for Teachers in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder on Knowledge and Self-Efficacy. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1414. [Google Scholar]
- Amado, L.; Jarque, S.; Signes, M.T.; Acereda, A.; López, A. Propuesta de un programa de intervención psicosocial para maestros de niños con TDAH. Rev. Int. Evaluación Med. Calid. Educ. 2014, 1, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Montague, M. Solve It! A Practical Approach to Teaching Mathematical Problem Solving Skills; Exceptional Innovations: Westville, OH, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Montague, M.; Warger, C.; Morgan, T.H. Solve It! Strategy Instruction to Improve Mathematical Problem Solving. Learn. Disabil. Res. Pract. 2010, 15, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronis, A.; Jones, H.; Raggi, V. Evidence-based psychosocial treatments for children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2006, 26, 486–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoza, B.; Kaiser, N.M.; Hurt, E. Multimodal treatment for childhood attention-defict/hyperactivity disorder: Interpreting outcomes in the context of study designs. Clin. Child Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2007, 10, 318–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcia, E.; Frank, R.; Sánchez-Lacay, A.; Fernández, M.C. Teacher understanding of ADHD as reflected in attibutions and classroom strategies. J. Atten. Disord. 2000, 4, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Oord, S.; Prins, P.J.; Oosterlaan, J.; Emmelkamp, P.M. Does brief, clinically based, intensive multimodal behavior therapy enhance the effects of methylphenidate in children with ADHD? Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2007, 16, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langberg, J.M.; Arnold, L.E.; Flowers, A.M.; Epstein, J.N.; Altaye, M.; Hinshaw, S.P.; Swanson, J.M.; Kotkin, R.; Simpson, S.; Molina, B.; et al. Parent-Reported Homework Problems in the MTA Study: Evidence for Sustained Improvement with Behavioral Treatment. J. Clin. Child Psychol. 2010, 39, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langberg, J.M.; Becker, S.P. Does long-term medication use improve the academic outcomes of youth with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder? Clin. Child Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2012, 15, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baweja, R.; Mattison, R.E.; Waxmonsky, J.G. Impact of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder on school performance: What are the effects of medication? Pediatric Drugs 2015, 17, 459–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, B.S.G.; Hinshaw, S.P.; Swanson, J.M.; Arnold, L.E.; Vitiello, B.; Jensen, P.S.; Epstein, J.N.; Hoza, B.; Hechtman, L.; Abikoff, H.B.; et al. The MTA at 8 years: Prospective follow-up of children treated for combined-type ADHD in a multisite study. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2009, 48, 484–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronis, A.M.; Pelham, W.E.; Gnagy, E.M., Jr.; Roberts, J.E.; Aronoff, H.R. The impact of late-afternoon stimulant dosing for children with ADHD on parent and parent-child domains. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2003, 32, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaray, M.P.; Malecky, C.K. The relationship between perceived social support and maladjustment for students at risk. Psychol. Sch. 2002, 39, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.F.; Cashwell, C.S. Preteens talking to parents: Perceived communication and school-based aggression. Fam. J. 2004, 12, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, M.M.; Nigg, J.T. Child ADHD and personality/temperament traits of reactive and effortful control, resiliency, and emotionality. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2006, 47, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigg, J.T.; Nikolas, M.; Friderici, K.; Park, L.; Zucher, R.A. Genotype and Neuropsychological Response Inhibition as Resilience Promoters for ADHD, ODD, and CD under Conditions of Psychosocial Adversity. Dev. Psychopathol. 2007, 19, 767–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regalla, M.A.; Rodrigues, G.P.; Serra-Pinheiro, M.A. Resiliência e transtorno do déficit de atenção/hiperatividade. J. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2007, 56, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

| Characteristics | Control Group | Multimodal Group |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| 7 years 8 years 9 years | 3 (30%) 4 (40%) 3 (30%) | 3 (30%) 4 (40%) 3 (30%) |
| Mean age | 7.6 | 7.8 |
| Sex | ||
| Male Female | 8 (80%) 2 (20%) | 9 (90%) 1 (10%) |
| Characteristics | Control Group | Multimodal Group |
|---|---|---|
| Mean age | 37.5 | 39.3 |
| Sex | ||
| Male Female | 10 (50%) 10 (50%) | 10 (50%) 10 (50%) |
| Mean number of children | 2.1 | 2.5 |
| Educational level | ||
| Basic Studies Secondary University | 2 (10%) 5 (25%) 13 (65%) | 4 (20%) 8 (40%) 8 (40%) |
| Characteristics | Control Group | Multimodal Group |
|---|---|---|
| Mean age | 40.3 | 38.4 |
| Sex | ||
| Males Females | 4 (20%) 16 (80%) | 7 (35%) 13 (65%) |
| Mean experience as a teacher | 2.5 | 19.1 |
| Mean experience with children with ADHD | 9 (45%) | 12 (60%) |
| Attendance of ADHD courses | 0 | 1 (5%) |
| Month | Session | Parents | Session | Teachers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| September | 0 | Presentation and organization | 0 | ADHD seminar |
| October | 1 | INTRODUCE MYSELF: My child and I | 1 2 | INTRODUCE MYSELF: My student and I |
| November | 2 | I KNOW IT AND I UNDERSTAND: Knowledge about ADHD | 3 4 | I KNOW IT AND I UNDERSTAND: Knowledge about ADHD |
| December | 3 | ADHD IN SCHOOL: Difficulties in learning how to relate | 5 6 | WHAT WE CAN DO |
| January | 4 | ADHD IN MY FAMILY: Emotional implications | 7 8 | I VALUE HIM/HER POSITIVELY, she values and reinforces him/herself |
| February | 5 | ADHD IN MY FAMILY: Educational implications | 9 10 | I ORGANIZE HIM/HER, s/he organizes 10 him/herself and s/he listens |
| March | 6 | 11 12 | I ADAPT the classroom and activities | |
| April | 7 | I IMPROVE MY COMMUNICATION | 13 | WE BUILD BRIDGES |
| May | 8 | I IMPROVE MY SELF CONTROL | 14 15 | I IMPROVE MY SELF CONTROL |
| June | 9 | FAREWELL: what I take with me | 16 17 | FAREWELL: what I take with me |
| Hours | 18 | 34 |
| Pre Treatment | Post Treatment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | z | p | r | ||
| Relationships | EN | 42.6 | 2.96 | 42.5 | 3.26 | −0.142 | 0.887 | −0.022 |
| AF | 45 | 4.63 | 45.7 | 4.32 | −1.19 | 0.234 | −0.188 | |
| SU | 22.45 | 6.12 | 25.25 | 5.95 | −2.309 | 0.021 * | −0.365 | |
| Auto-Realization | TA | 61.95 | 5.38 | 62.35 | 4.57 | −0.73 | 0.465 | −0.115 |
| CO | 57.25 | 4.72 | 58.5 | 4.61 | −1.387 | 0.166 | −0.219 | |
| Stabilility | OR | 46.75 | 4.6 | 46.5 | 4.72 | −0.108 | 0.914 | −0.017 |
| CL | 37.9 | 4.3 | 37.75 | 3.5 | −0.172 | 0.863 | −0.027 | |
| CN | 59.15 | 6.19 | 57.85 | 4.76 | −1.387 | 0.165 | −0.219 | |
| Change | IN | 50.35 | 4.79 | 50.2 | 5.16 | −0.187 | 0.851 | −0.029 |
| Pre Treatment | Post Treatment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | z | p | r | ||
| Relationships | EN | 48.1 | 3.8 | 52.2 | 2.66 | −2.997 | 0.003 ** | −0.473 |
| AF | 48.9 | 4.1 | 48.4 | 4.2 | −1 | 0.317 | −0.158 | |
| SU | 23.5 | 6.2 | 39.5 | 5.2 | −3.953 | 0.000 ** | −0.625 | |
| Auto-Realization | TA | 63.7 | 4.3 | 53.6 | 4.6 | −3.772 | 000 ** | −0.596 |
| CO | 58 | 4.7 | 63.75 | 2.44 | −3.331 | 0.001 ** | −0.526 | |
| Stability | OR | 45.7 | 4.6 | 54.7 | 2.44 | −3.785 | 0.000 ** | −0.598 |
| CL | 36.4 | 3.9 | 46.5 | 2.56 | −3.847 | 0.000 ** | −0.608 | |
| CN | 57.8 | 5.1 | 65.7 | 2.55 | −3.745 | 0.000 ** | −0.592 | |
| Change | IN | 50.9 | 5.2 | 50.3 | 3.21 | −0.612 | 0.541 | −0.096 |
| Control Group | Multimodal Group | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | z | p | r | ||
| Relationships | EN | 42.50 | 3.26 | 52.2 | 2.66 | −5.402 | 0.000 ** | −0.854 |
| AF | 45.70 | 4.32 | 48.4 | 4.2 | −1.945 | 0.052 * | −0.307 | |
| SU | 25.25 | 5.95 | 39.5 | 5.2 | −5.256 | 0.000 ** | −0.8310 | |
| Auto-Realization | TA | 62.35 | 4.57 | 53.6 | 4.6 | −4.370 | 0.000 ** | −0.690 |
| CO | 58.50 | 4.61 | 63.75 | 2.44 | −3.706 | 0.000 ** | −0.585 | |
| Stability | OR | 46.50 | 4.72 | 54.7 | 2.44 | −4.796 | 0.000 ** | −0.758 |
| CL | 37.75 | 3.50 | 46.5 | 2.56 | −5.156 | 0.000 | −0.815 | |
| CN | 57.85 | 4.76 | 65.7 | 2.55 | −4.120 | 0.000 ** | −0.651 | |
| Change | IN | 50.2 | 5.16 | 50.3 | 3.21 | −0.072 | 0.942 | −0.011 |
| Control Group | Multimodal Group | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | z | p | r | ||
| Relationships | EN | 42.6 | 2.96 | 48.1 | 3.8 | −4.016 | 0.000 ** | −0.634 |
| AF | 45 | 4.63 | 48.9 | 4.1 | −2.628 | 0.009 ** | −0.415 | |
| SU | 22.45 | 6.12 | 23.5 | 6.2 | −0.358 | 0.72 | −0.056 | |
| Auto-Realization | TA | 61.95 | 5.38 | 63.7 | 4.3 | −0.775 | 0.439 | −0.122 |
| CO | 57.25 | 4.72 | 58 | 4.7 | −0.625 | 0.532 | −0.098 | |
| Stability | OR | 46.75 | 4.6 | 45.7 | 4.6 | −0.803 | 0.422 | −0.126 |
| CL | 37.9 | 4.3 | 36.4 | 3.9 | −0.779 | 0.436 | −0.123 | |
| CN | 59.15 | 6.19 | 57.8 | 5.1 | −0.584 | 0.559 | −0.092 | |
| Change | IN | 50.35 | 4.79 | 50.9 | 5.2 | −0.412 | 0.681 | −0.065 |
| Pre-Treatment | Post-Treatment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | z | p | r | ||
| Relationships | CH | 45.25 | 3.58 | 43.45 | 3.51 | −1.916 | 0.055 * | −0.302 |
| EX | 41.95 | 8.77 | 44.55 | 5.5 | −1.768 | 0.077 | −0.279 | |
| CT | 67.75 | 8.2 | 66.85 | 15.48 | −1.200 | 0.230 | −0.189 | |
| Development | AU | 46.65 | 8.82 | 45.9 | 8.73 | −0.478 | 0.633 | −0.075 |
| AC | 53.3 | 7.4 | 52.7 | 6.44 | −0.343 | 0.732 | −0.054 | |
| IC | 50.15 | 7.87 | 49.45 | 7.66 | −0.517 | 0.605 | −0.081 | |
| SR | 49.75 | 3.27 | 49.45 | 3.13 | −0.577 | 0.564 | −0.091 | |
| MR | 56.8 | 6.1 | 57.1 | 5.59 | −0.447 | 0.655 | −0.070 | |
| Stability | OR | 33.1 | 5.59 | 32.5 | 4.71 | −0.632 | 0.527 | −0.099 |
| CN | 52 | 4.12 | 50.8 | 2.82 | −2.000 | 0.046 * | −0.316 | |
| Pre-Treatment | Post-Treatment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | z | p | r | ||
| Relationships | CH | 44.8 | 4.7 | 57.8 | 4.8 | −3.931 | 0.000 ** | −0.621 |
| EX | 41.9 | 9.4 | 55.1 | 5.9 | −3.842 | 0.000 ** | −0.607 | |
| CT | 68 | 8.3 | 73.5 | 4.3 | −2.397 | 0.017 * | −0.378 | |
| Development | AU | 50.1 | 9.5 | 64.6 | 5.2 | −3.742 | 0.000 * | −0.591 |
| AC | 54.3 | 7.7 | 55.6 | 4.8 | −1.224 | 0.221 | −0.193 | |
| IC | 51.3 | 6.3 | 52.8 | 4.09 | −0.956 | 0.339 | −0.151 | |
| SR | 54.2 | 5.7 | 64.8 | 6.1 | −3.865 | 0.000 ** | −0.611 | |
| MR | 53.5 | 7.5 | 53.2 | 6.1 | −0.378 | 0.705 | −0.059 | |
| Stabilility | OR | 36.1 | 6.2 | 49.8 | 4.5 | −3.741 | 0.000 ** | −0.591 |
| CN | 56.9 | 5.6 | 64.8 | 5 | −3.213 | 0.001 ** | −0.508 | |
| Control Group | Multimodal Group | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | z | p | r | ||
| Relationships | CH | 43.45 | 3.51 | 57.8 | 4.8 | −5.383 | 0.000 ** | −0.851 |
| EX | 44.55 | 5.5 | 55.1 | 5.9 | −4.503 | 0.000 ** | −0.711 | |
| CT | 66.85 | 15.48 | 73.5 | 4.3 | −1.772 | 0.076 | −0.280 | |
| Development | AU | 45.9 | 8.73 | 64.6 | 5.2 | −5.057 | 0.000 ** | −0.799 |
| AC | 52.7 | 6.44 | 55.6 | 4.8 | −1.579 | 0.114 | −0.249 | |
| IC | 49.45 | 7.66 | 52.8 | 4.09 | −1.175 | 0.240 | −0.185 | |
| SR | 49.45 | 3.13 | 64.8 | 6.1 | −5.435 | 0.000 ** | −0.859 | |
| MR | 57.1 | 5.59 | 53.2 | 6.1 | −1.835 | 0.067 | −0.290 | |
| Stability | OR | 32.5 | 4.71 | 49.8 | 4.5 | −5.454 | 0.000 ** | −0.862 |
| CN | 50.8 | 2.82 | 64.8 | 5 | −5.426 | 0.000 ** | −0.857 | |
| Control Group | Multimodal Group | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | z | p | r | ||
| Relationships | CH | 45.25 | 3.58 | 44.8 | 4.7 | −0.255 | 0.799 | −0.040 |
| EX | 41.95 | 8.77 | 41.9 | 9.4 | −0.042 | 0.967 | −0.006 | |
| CT | 67.75 | 8.2 | 68 | 8.3 | −0.138 | 0.890 | −0.021 | |
| Development | AU | 46.65 | 8.82 | 50.1 | 9.5 | −1.173 | 0.241 | −0.185 |
| AC | 53.3 | 7.4 | 54.3 | 7.7 | −0.420 | 0.675 | −0.066 | |
| IC | 50.15 | 7.87 | 51.3 | 6.3 | −0.321 | 0.749 | −0.050 | |
| SR | 49.75 | 3.27 | 54.2 | 5.7 | −2.814 | 0.005 * | −0.444 | |
| MR | 56.8 | 6.1 | 53.5 | 7.5 | −1.274 | 0.203 | −0.201 | |
| Stability | OR | 33.1 | 5.59 | 36.1 | 6.2 | −1.401 | 0.161 | −0.221 |
| CN | 52 | 4.12 | 56.9 | 5.6 | −2.842 | 0.004 * | −0.449 | |
| Control Group | Multimodal Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mathematics | M | SD | M | SD | z | p | r |
| Performance | 4.7 | 1.05 | 5.1 | 0.99 | −1.088 | 0.277 | 0.192 |
| Control Group | Multimodal Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mathematics | M | SD | M | SD | z | p | r |
| Performance | 4.4 | 0.51 | 5.4 | 0.96 | −2.408 | 0.016 * | 0.545 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amado, L.; Jarque, S. Effectiveness of a Multimodal Intervention on Social Climate (School and Family) and Performance in Mathematics of Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10173133
Amado L, Jarque S. Effectiveness of a Multimodal Intervention on Social Climate (School and Family) and Performance in Mathematics of Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Mathematics. 2022; 10(17):3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10173133
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmado, Laura, and Sonia Jarque. 2022. "Effectiveness of a Multimodal Intervention on Social Climate (School and Family) and Performance in Mathematics of Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder" Mathematics 10, no. 17: 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10173133
APA StyleAmado, L., & Jarque, S. (2022). Effectiveness of a Multimodal Intervention on Social Climate (School and Family) and Performance in Mathematics of Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Mathematics, 10(17), 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10173133





