Dynamics Analysis of a Predator–Prey Model with Hunting Cooperative and Nonlinear Stochastic Disturbance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
3. Extinction and Persistence in Mean
4. Stationary Distribution
5. Numerical Simulations
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- If holds, the predator can be extinct.
- (2)
- When holds, the prey can be persistent and have a unique ergodic stationary distribution.
- (3)
- When , the predator can be persistent in the mean.
- (4)
- When , then model has a unique ergodic stationary distribution.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lotka, A.J. Elements of Physical Biology; Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1925. [Google Scholar]
- Volterra, V. Fluctuations in the abundance of a species considered mathematically. Nature 1926, 118, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegeling, A.; Kooij, R.E. Singular perturbations of the Holling I predator-prey system with a focus. J. Differ. Equ. 2020, 269, 5434–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y. Global stability of a delayed predator-prey system with fear and Holling-type II functional response in deterministic and stochastic environments. Math. Comput. Simul. 2022, 200, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sang, B. Four limit cycles in a predator-prey system of Leslie type with generalized Holling type III functional response. Nonlinear Anal.-Real World Appl. 2019, 50, 218–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C. Dynamical analysis and numerical simulations on a crowley-Martin predator-prey model in stochastic environment. Appl. Math. Comput. 2022, 413, 126641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Li, Q.; Lv, J. Stochastic bifurcations, a necessary and sufficient condition for a stochastic beddington-deangelis predator-prey model. Appl. Math. Lett. 2021, 117, 107069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosner, C.; DeAngelis, D.L.; Ault, J.S.; Olson, D.B. Effects of spatial grouping on the functional response of predators. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1999, 56, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.; Sabyasachi, B.; Sudip, S. Spatiotemporal dynamics of Leslie-Gower predator-prey model with Allee effect on both populations. Math. Comput. Simul. 2022, 200, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D.; Maji, C. Bifurcation analysis of a Holling type II predator-prey model with refuge. Chin. J. Phys. 2020, 65, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Meng, X.; Chen, L. A new stage structured predator-prey Gomportz model with time delay and impulsive perturbations on the prey. Appl. Math. Comput. 2008, 196, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, F.; Gao, S. Global analysis and numerical simulations of a novel stochastic eco-epidemiological model with time delay. Appl. Math. Comput. 2018, 339, 701–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How, M.J.; Santon, M. Cuttlefish camouflage: Blending in by matching background features. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, R523–R525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, S.; Laurent, G. Visual perception and cuttlefish camouflage. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2020, 60, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Sun, H.; Stevens, M. Plant camouflage: Ecology, evolution, and implications. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, H.; Sarwardi, S.; Haque, M. Dynamics of adding variable prey refuge and an Allee effect to a predator-prey model. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 4175–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.P.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, A.K. Impact of fear effect on plankton-fish system dynamics incorporating zooplankton refuge. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 143, 110563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salti, N.; Al-Musalhi, F.; Gandhi, V.; Al-Moqbali, M.; Elmojtaba, I. Dynamical analysis of a prey-predator model incorporating a prey refuge with variable carrying capacity. Ecol. Complex. 2021, 45, 100888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheel, D.; Packer, C. Group hunting behaviour of lions: A search for cooperation. Anim. Behav. 1991, 41, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinsohn, R.; Packer, C. Complex cooperative strategies in group-territorial African lions. Science 1995, 269, 1260–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, P.A.; Mech, L.D. Wolf pack size and food acquisition. Am. Nat. 1997, 269, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Zhang, H. Effect of hunting cooperation on the dynamic behavior for a diffusive Holling type II predator-prey model. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2021, 99, 105807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Pal, N.; Samanta, S.; Chattopadhyay, J. Fear effect in prey and hunting cooperation among predators in a Leslie-Gower model. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2019, 16, 5146–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sk, N.; Tiwari, P.K.; Pal, S. A delay nonautonomous model for the impacts of fear and refuge in a three species food chain model with hunting cooperation. Math. Comput. Simul. 2022, 192, 136–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Meng, X.; Hayat, T.; Hobiny, A. Stationary distribution of a stochastic predator-prey model with hunting cooperation. Appl. Math. Lett. 2022, 124, 107662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, T. A predator-prey model with different response functions to juvenile and adult prey in deterministic and stochastic environments. Appl. Math. Comput. 2022, 413, 126598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, X. The dynamics of stochastic predator-prey models with non-constant mortality rate and general nonlinear functional response. J. Nonlinear Model. Anal. 2020, 2, 495–511. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, N.; Li, M. Stochastically permanent analysis of a non-autonomous holling II predator-prey model with a complex type of noises. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 2022, 12, 479–496. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, H.; Meng, X. Threshold behavior of a stochastic predator-prey system with prey refuge and fear effect. Appl. Math. Lett. 2021, 113, 106846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Meng, X. Mathematical modeling, analysis and numerical simulation of HIV: The influence of stochastic environmental fluctuations on dynamics. Math. Comput. Simul. 2021, 187, 700–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jiang, D.; Hayat, T.; Ahmad, B. Stationary distribution and extinction of a stochastic predator-prey model with additional food and nonlinear perturbation. Appl. Math. Comput. 2018, 320, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Jiang, D. The threshold of a stochastic SIS epidemic model with vaccination. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 243, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jiang, D. Influence of the fear factor on the dynamics of a stochastic predator-prey model. Appl. Math. Lett. 2021, 112, 106756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asamoah, J.K.K.; Jin, Z.; Sun, G.Q. Non-seasonal and seasonal relapse model for Q fever disease with comprehensive cost-effectiveness analysis. Results Phys. 2021, 22, 103889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasminskii, R. Stochastic Stability of Differential Equations, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, M.A.; Aboul-Hassan, A.; Rabia, S.I. The composite Milstein methods for the numerical solution of Ito stochastic differential equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2011, 235, 2277–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
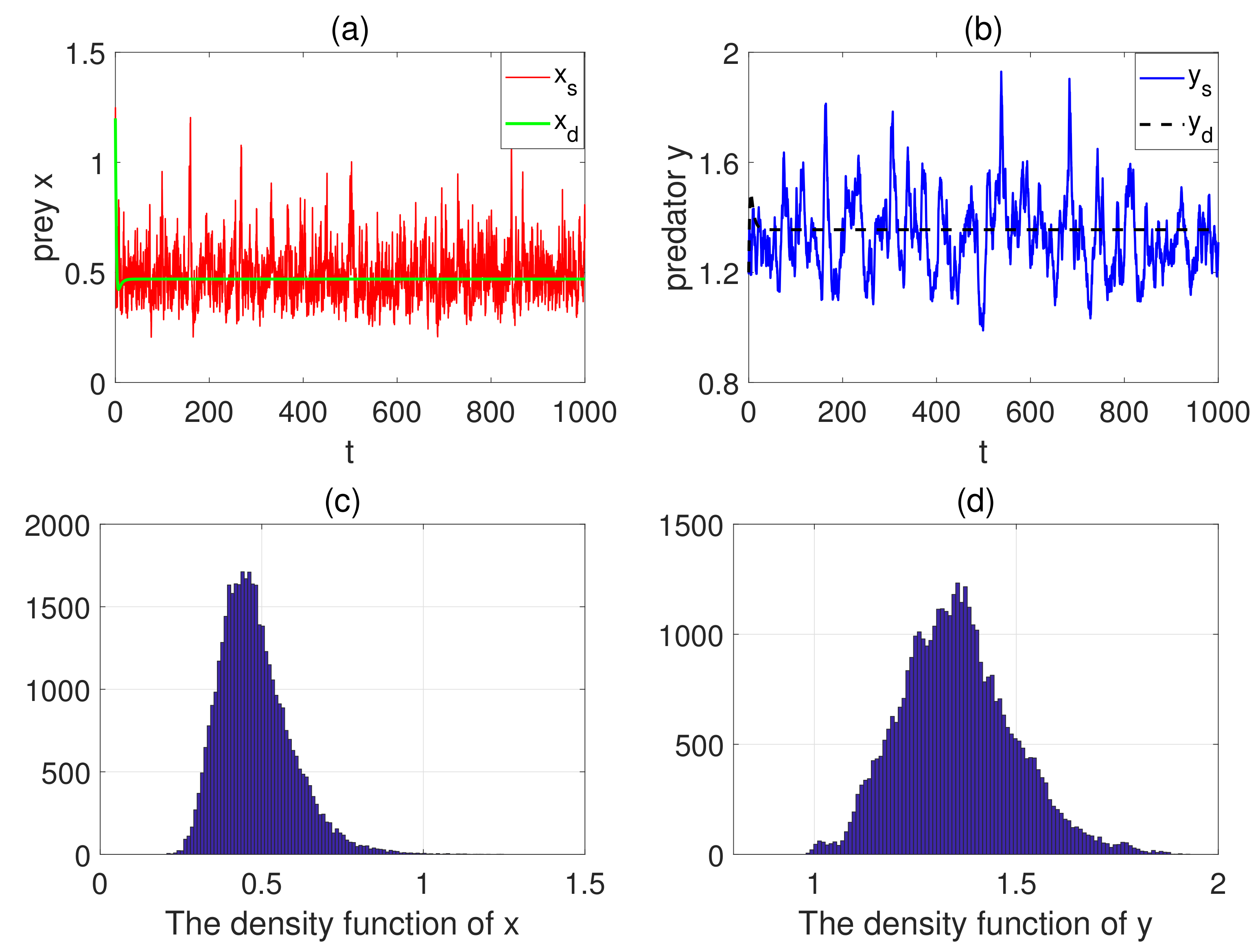

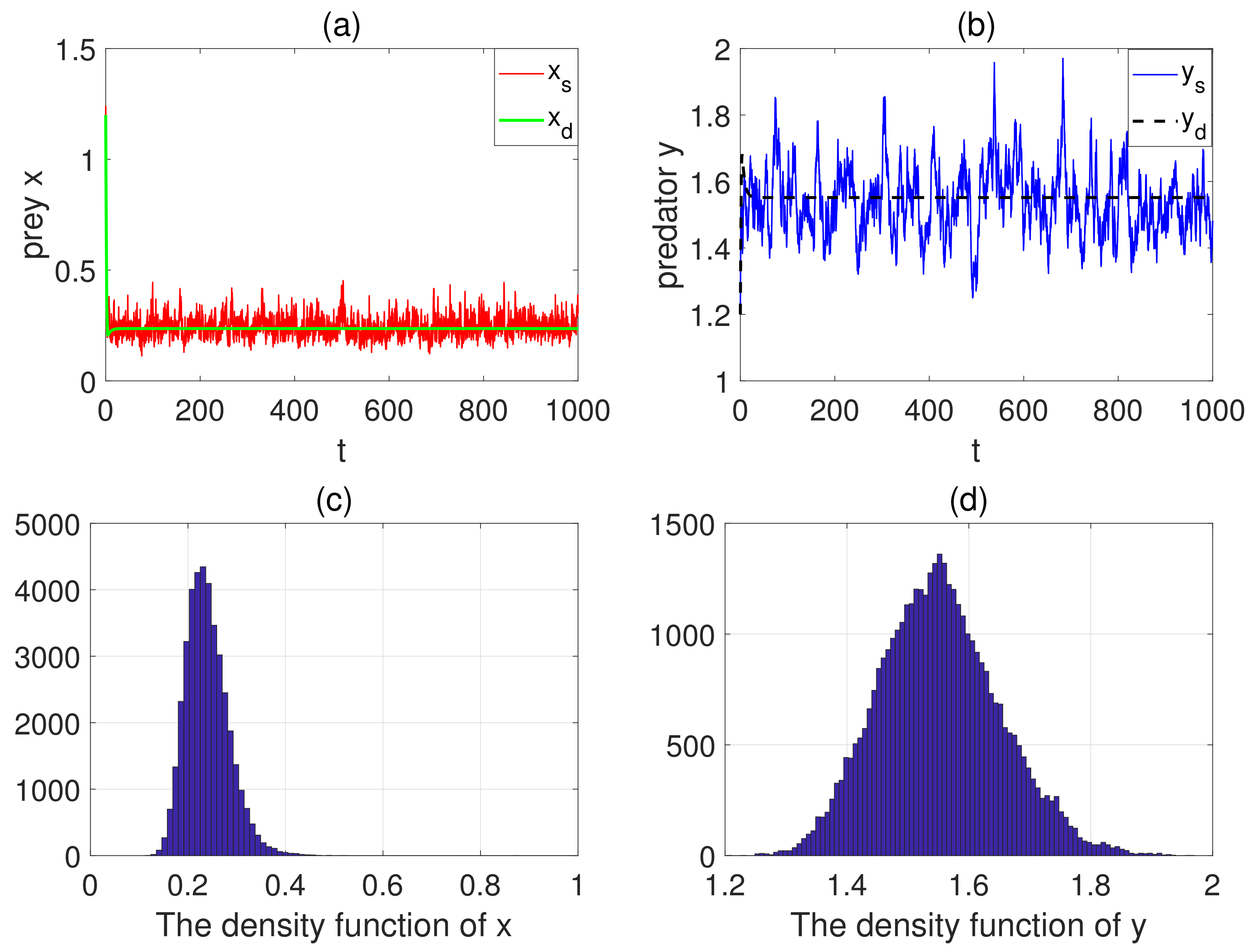
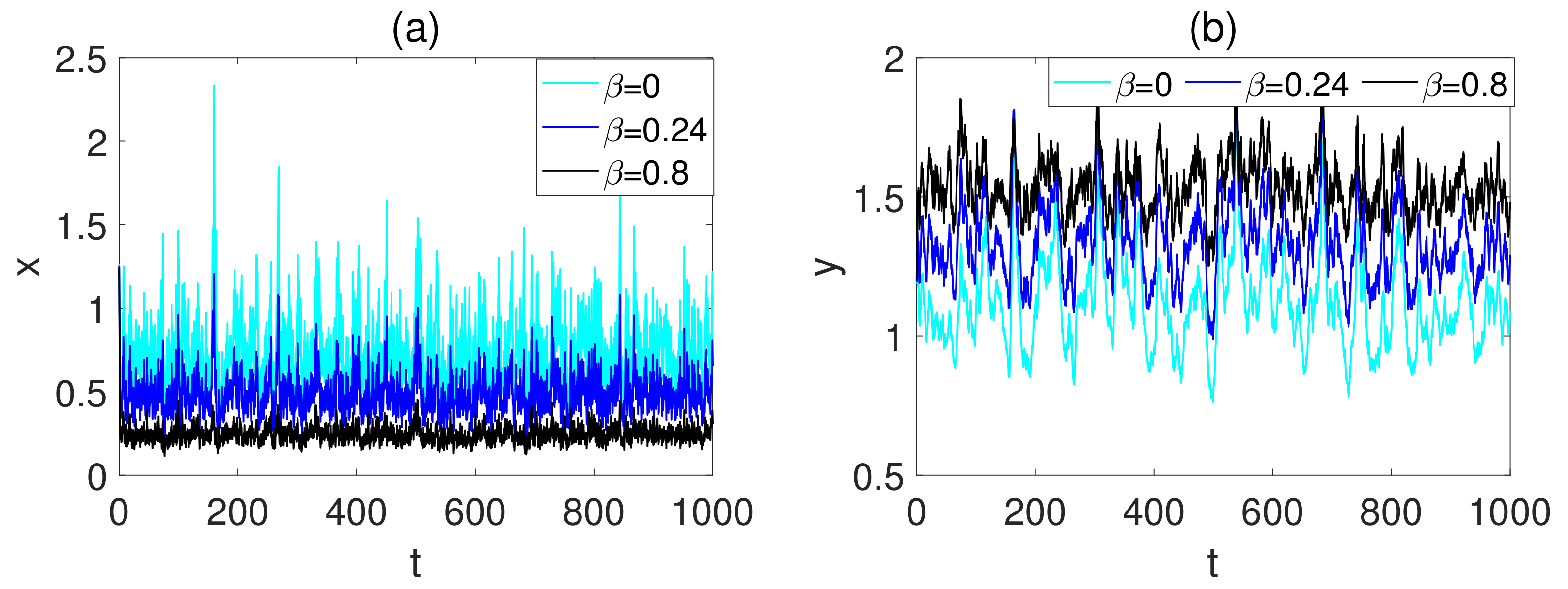
| Parameters | Biological Significance |
|---|---|
| The birth rate of prey. | |
| The natural death rate of prey. | |
| d | The natural death rate of predator. |
| The attack rate per predator to prey. | |
| The predator’s handing time of prey. | |
| k | Conversion efficiency. |
| Parameter of predator in hunting cooperation. |
| Parameter Values | Case 1 | Case 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 0.24 | 0.8 | |
| 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| 0.24 | 0.24 | |
| d | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| 1.2 | 1.2 | |
| k | 0.7 | 0.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Meng, X. Dynamics Analysis of a Predator–Prey Model with Hunting Cooperative and Nonlinear Stochastic Disturbance. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10162890
Zhang Y, Meng X. Dynamics Analysis of a Predator–Prey Model with Hunting Cooperative and Nonlinear Stochastic Disturbance. Mathematics. 2022; 10(16):2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10162890
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuke, and Xinzhu Meng. 2022. "Dynamics Analysis of a Predator–Prey Model with Hunting Cooperative and Nonlinear Stochastic Disturbance" Mathematics 10, no. 16: 2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10162890
APA StyleZhang, Y., & Meng, X. (2022). Dynamics Analysis of a Predator–Prey Model with Hunting Cooperative and Nonlinear Stochastic Disturbance. Mathematics, 10(16), 2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10162890







