Double Features Zeroing Neural Network Model for Solving the Pseudoninverse of a Complex-Valued Time-Varying Matrix
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- For solving complex-valued time-varying issues, the design of the DFZNN model constructs a mechanism to deal with both convergence and robustness, which enriches the usage of complex-valued ZNN;
- The convergence rate is improved; specifically, the DFZNN model can converge in the predefine time. Moreover, the convergence rate is not affected by the initial value;
- Robustness is better, compared with the existing ZNNs, and the DFZNN model has stronger stability in noise situation;
- The simulation example and an application further illustrate the reliability of the proposed DFZNN model.
2. Problem Formulation and ZNN Models
2.1. Problem Formulation
2.2. Design Process of ZNN Model
3. Theoretical Analysis
3.1. Global Stability
3.2. Predefined Time Convergence
3.3. Robustness
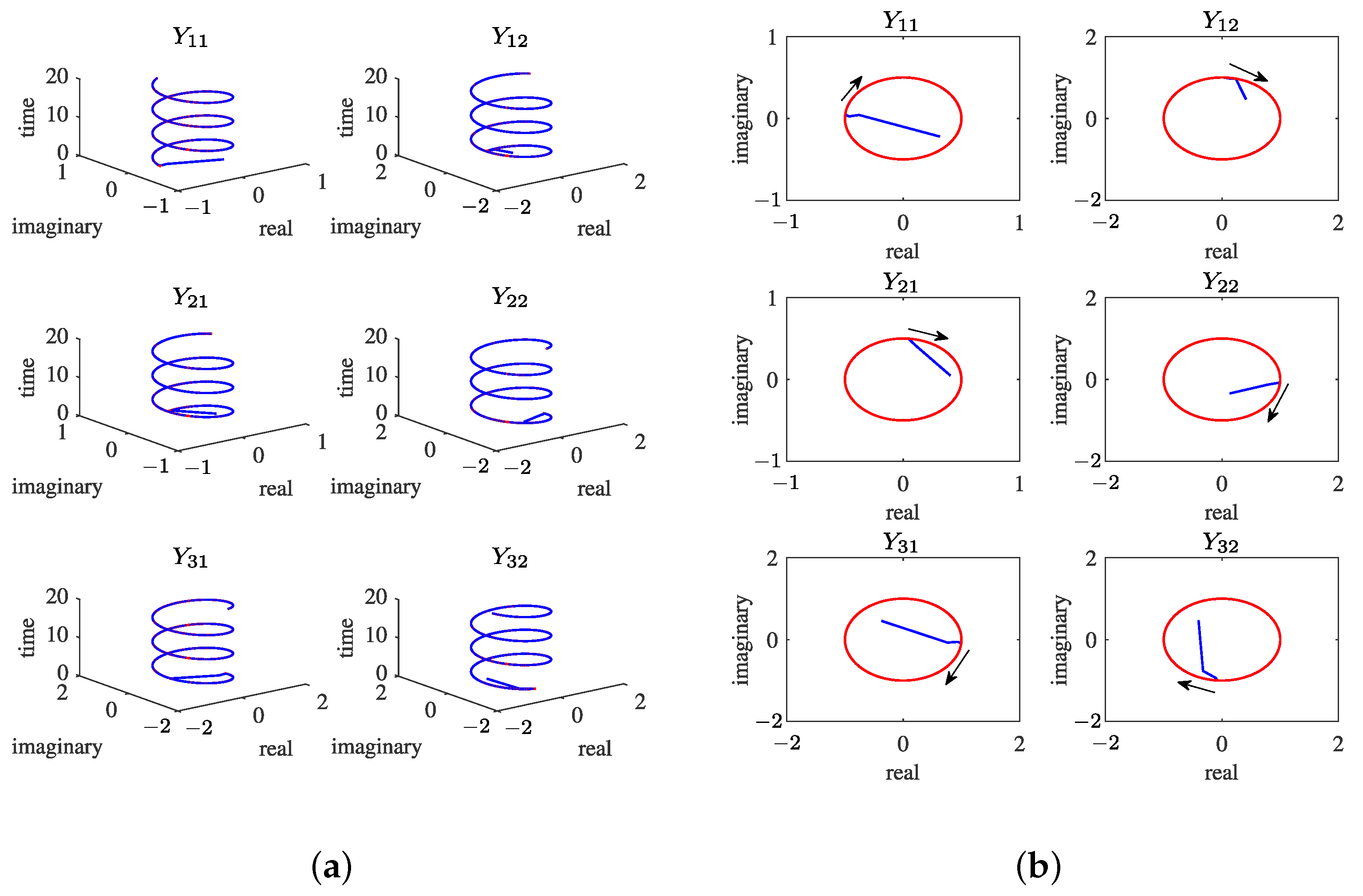
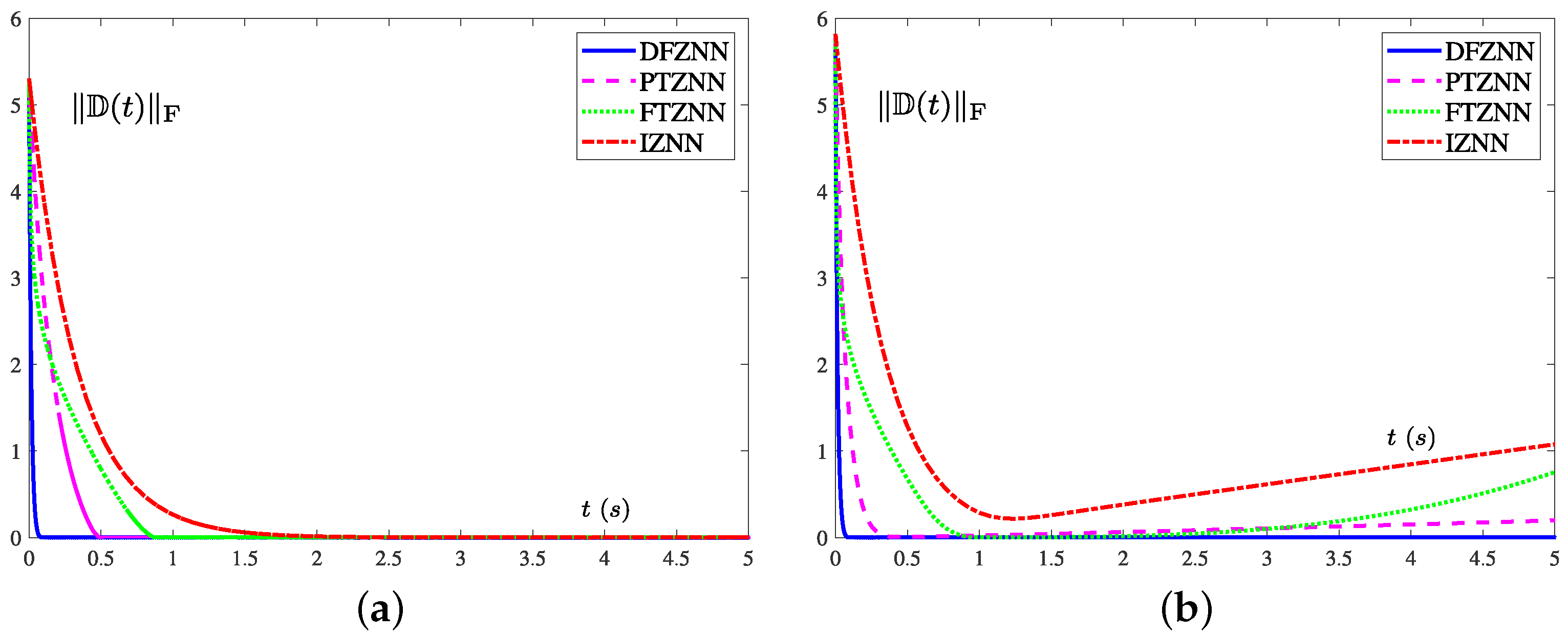
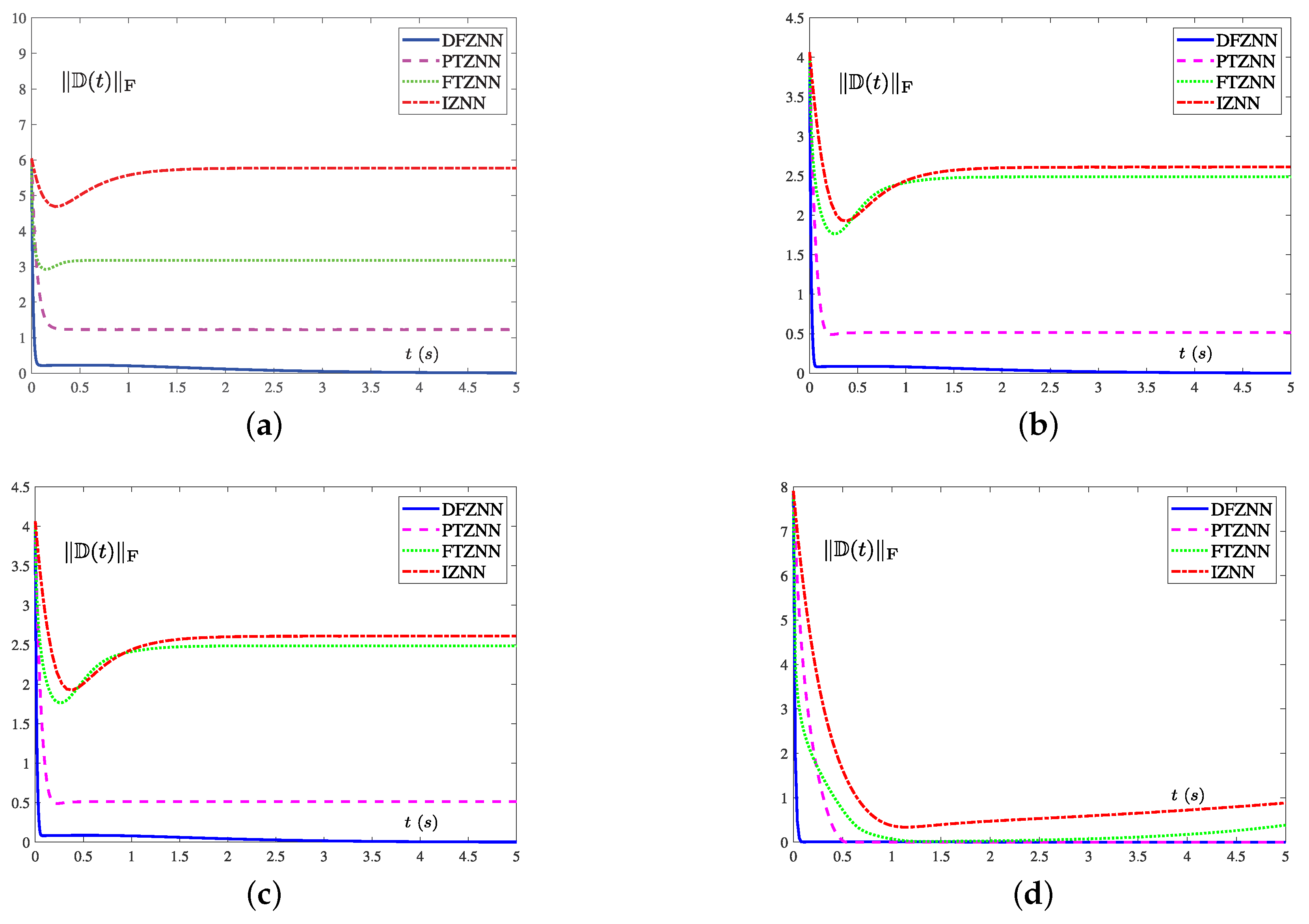
4. Numerical Experiments
5. Application
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ZNN | zeroing neural network |
| IZNN | initial ZNN |
| RNN | recurrent neural network |
| GNN | gradient-based RNN |
| LTCZNN | limited time convergence ZNN |
| PTCZNN | predefined time convergence ZNN |
| VPZNN | varying-time parameter ZNN |
| DFZNN | double features ZNN |
References
- Kulikov, G.Y.; Kulikova, M.V. Moore–Penrose-pseudo-inverse-based Kalman-like filtering methods for estimation of stiff continuous-discrete stochastic systems with ill-conditioned measurements. IET Control Theory Appl. 2018, 12, 2205–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.; Zhang, J.; Chakrabortty, A. Distributed optimization algorithms for wide-area oscillation monitoring in power systems using interregional PMU-PDC architectures. IEEE Trans. Smart. Grid. 2015, 6, 2529–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, F.X.; Sierra, H.; Arzuaga, E. Improving execution time for supervised sparse representation classification of hyperspectral images using the Moore–Penrose pseudoinverse. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2019, 13, 026512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Xu, F.; Yan, L. New pseudoinverse-based path-planning scheme with PID characteristic for redundant robot manipulators in the presence of noise. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2017, 26, 2008–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filelis-Papadopoulos, C.K.; Kyziropoulos, P.E.; Morrison, J.P.; O’Reilly, P. Modelling and forecasting based on recurrent pseudoinverse matrices. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Science, Krakow, Poland, 16–18 June 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 229–242. [Google Scholar]
- Sayevand, K.; Pourdarvish, A.; Machado, J.A.T.; Erfanifar, R. On the calculation of the Moore–Penrose and Drazin inverses: Application to fractional calculus. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanimirović Predrag, S.; Tasić Milan, B. Computing generalized inverses using LU factorization of matrix product. Int. J Comput. Math. 2008, 85, 1865–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyrchei, I.I. Analogs of the adjoint matrix for generalized inverses and corresponding Cramer rules. Linear Multilinear Algebra 2008, 56, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artidiello, S.; Cordero, A.; Torregrosa, J.R.; Vassileva, M.P. Generalized inverses estimations by means of iterative methods with memory. Mathematics 2019, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Li, K.; Ouyang, A.; Tang, Z.; Li, K. Gpu-accelerated parallel hierarchical extreme learning machine on flink for big data. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2017, 47, 2740–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.E.; Hu, Y.T. Using machine learning classifiers to recognize the mixture control chart patterns for a multiple-input multiple-output process. Mathematics 2020, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, L.; Lu, R. A finite-time recurrent neural network for computing quadratic minimization with time-varying coefficients. Chin. J. Electron. 2019, 28, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, K.; Tan, H.Z. Performance analysis of gradient neural network exploited for online time-varying matrix inversion. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2009, 54, 1940–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long Jin, S.L.; Hu, B. RNN models for dynamic matrix inversion: A control-theoretical perspective. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 14, 189–199. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Li, K.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, B.; Chen, K.; Jin, L.; Li, S. Nonlinear gradient neural network for solving system of linear equations. Inf. Process. Lett. 2019, 142, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Wang, J. A recurrent neural network for solving Sylvester equation with time-varying coefficients. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2002, 13, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Zhang, Y. From different ZFs to different ZNN models accelerated via Li activation functions to finite-time convergence for time-varying matrix pseudoinversion. Neurocomputing 2014, 133, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Li, Z.; Nie, Z.; Shao, H.; Guo, D. Zeroing neural network for solving time-varying linear equation and inequality systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 30, 2346–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Zhang, Y. Zhang neural network for online solution of time-varying linear matrix inequality aided with an equality conversion. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2013, 25, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Li, S.; Liao, B.; Zhang, Z. Zeroing neural networks: A survey. Neurocomputing 2017, 267, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Y. Nonlinearly activated neural network for solving time-varying complex Sylvester equation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 44, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, X.; Liao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Y. Z-type control of populations for Lotka–Volterra model with exponential convergence. Math. Biosci. 2016, 272, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Peng, C.; Xiang, Q. Prescribed-time convergent and noise-tolerant Z-type neural dynamics for calculating time-dependent quadratic programming. Neural Comput. Applic. 2021, 33, 5327–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, X.; Kong, L.; Li, S. A circadian rhythms learning network for resisting cognitive periodic noises of time-varying dynamic system and applications to robots. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2019, 12, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S. Integration-enhanced Zhang neural network for real-time-varying matrix inversion in the presence of various kinds of noises. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 27, 2615–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Dai, J.; Li, J.; Tang, W. A noise-tolerant zeroing neural network for time-dependent complex matrix inversion under various kinds of noises. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 3757–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Chen, S.; Liu, B. Accelerating a recurrent neural network to finite-time convergence for solving time-varying Sylvester equation by using a sign-bi-power activation function. Neural Process Lett. 2013, 37, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Liao, B.; Li, S.; Chen, K. Nonlinear recurrent neural networks for finite-time solution of general time-varying linear matrix equations. Neural Netw. 2018, 98, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Liu, L.; Xiao, L.; Li, K.; Cai, S. A robust and fixed-time zeroing neural dynamics for computing time-variant nonlinear equation using a novel nonlinear activation function. Neurocomputing 2019, 350, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, M.; Donoho, D.; Pauly, J.M. Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 58, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loesch, B.; Yang, B. Cramér-Rao bound for circular complex independent component analysis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Latent Variable Analysis and Signal Separation, Tel Aviv, Israel, 12–15 March 2012; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Bobrovnikova, E.Y.; Vavasis, S.A. A norm bound for projections with complex weights. Linear Algebra Appl. 2000, 307, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Xia, Y.; Zheng, W. A complex-valued neural dynamical optimization approach and its stability analysis. Neural Netw. 2015, 61, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed Ali, M.; Narayanan, G.; Orman, Z.; Shekher, V.; Arik, S. Finite time stability analysis of fractional-order complex-valued memristive neural networks with proportional delays. Neural Process Lett. 2020, 51, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, N.; Zhai, G. Sampled-data state-estimation of delayed complex-valued neural networks. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2020, 51, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, N.; Zhai, G. Stability analysis for uncertain switched delayed complex-valued neural networks. Neurocomputing 2019, 367, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakkiyappan, R.; Cao, J.; Velmurugan, G. Existence and uniform stability analysis of fractional-order complex-valued neural networks with time delays. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2014, 26, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z.; Stanimirović, P.S.; Wei, Y. Complex ZFs for computing time-varying complex outer inverses. Neurocomputing 2018, 275, 983–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, X. Complex-valued neural network for hermitian matrices. Eng. Lett. 2017, 25, 312–320. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, S.; Wang, X.Z.; Wei, Y. Two finite-time convergent Zhang neural network models for time-varying complex matrix Drazin inverse. Linear Algebra Appl. 2018, 542, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Weng, J.; Mao, Y.; Lu, W.; Xiao, L. A new varying-parameter recurrent neural-network for online solution of time-varying Sylvester equation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 48, 3135–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanimirović Predrag, S.; Katsikis Vasilios, N.; Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Zhou, M. Varying-parameter Zhang neural network for approximating some expressions involving outer inverses. Optim. Methods Softw. 2020, 35, 1304–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; He, Y. A noise-suppression ZNN model with new variable parameter for dynamic Sylvester equation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 7513–7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z. Three recurrent neural networks and three numerical methods for solving a repetitive motion planning scheme of redundant robot manipulators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Number | Influencing Parameter | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero Noise | Time-Varying Noise | |||
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.1694 | 1.2766 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.1664 | 0.6436 |
| 3 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 0.1640 | 0.6388 |
| 4 | 0.5 | 2 | 0.1592 | 0.6338 |
| 5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.0822 | 0.6384 |
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 0.0774 | 0.6326 |
| 7 | 1 | 1.5 | 0.0758 | 0.6284 |
| 8 | 1 | 2 | 0.0750 | 0.6284 |
| 9 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.1694 | 1.2766 |
| 10 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.0822 | 0.6384 |
| 11 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.0374 | 0.6286 |
| 12 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.0170 | 0.0168 |
| 13 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.1640 | 0.6436 |
| 14 | 1 | 1 | 0.0774 | 0.6326 |
| 15 | 1.5 | 1 | 0.0368 | 0.6256 |
| 16 | 2 | 1 | 0.0168 | 0.0168 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, Y.; Dai, Z.; Liao, B.; Xia, G.; He, Y. Double Features Zeroing Neural Network Model for Solving the Pseudoninverse of a Complex-Valued Time-Varying Matrix. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10122122
Lei Y, Dai Z, Liao B, Xia G, He Y. Double Features Zeroing Neural Network Model for Solving the Pseudoninverse of a Complex-Valued Time-Varying Matrix. Mathematics. 2022; 10(12):2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10122122
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Yihui, Zhengqi Dai, Bolin Liao, Guangping Xia, and Yongjun He. 2022. "Double Features Zeroing Neural Network Model for Solving the Pseudoninverse of a Complex-Valued Time-Varying Matrix" Mathematics 10, no. 12: 2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10122122
APA StyleLei, Y., Dai, Z., Liao, B., Xia, G., & He, Y. (2022). Double Features Zeroing Neural Network Model for Solving the Pseudoninverse of a Complex-Valued Time-Varying Matrix. Mathematics, 10(12), 2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10122122






