Coupling Effect Suppressed Compact Surgical Robot with 7-Axis Multi-Joint Using Wire-Driven Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mechanical Design
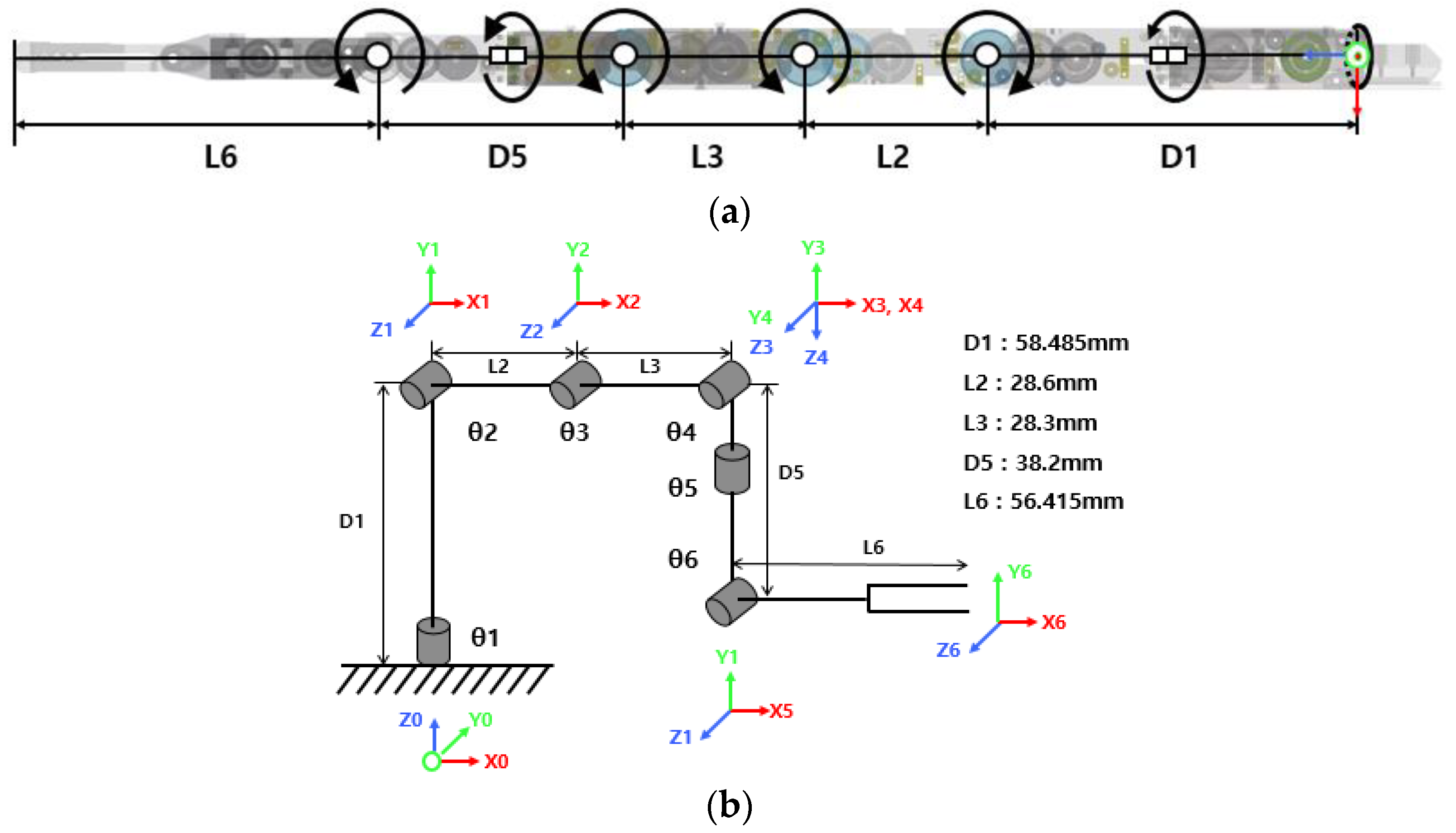
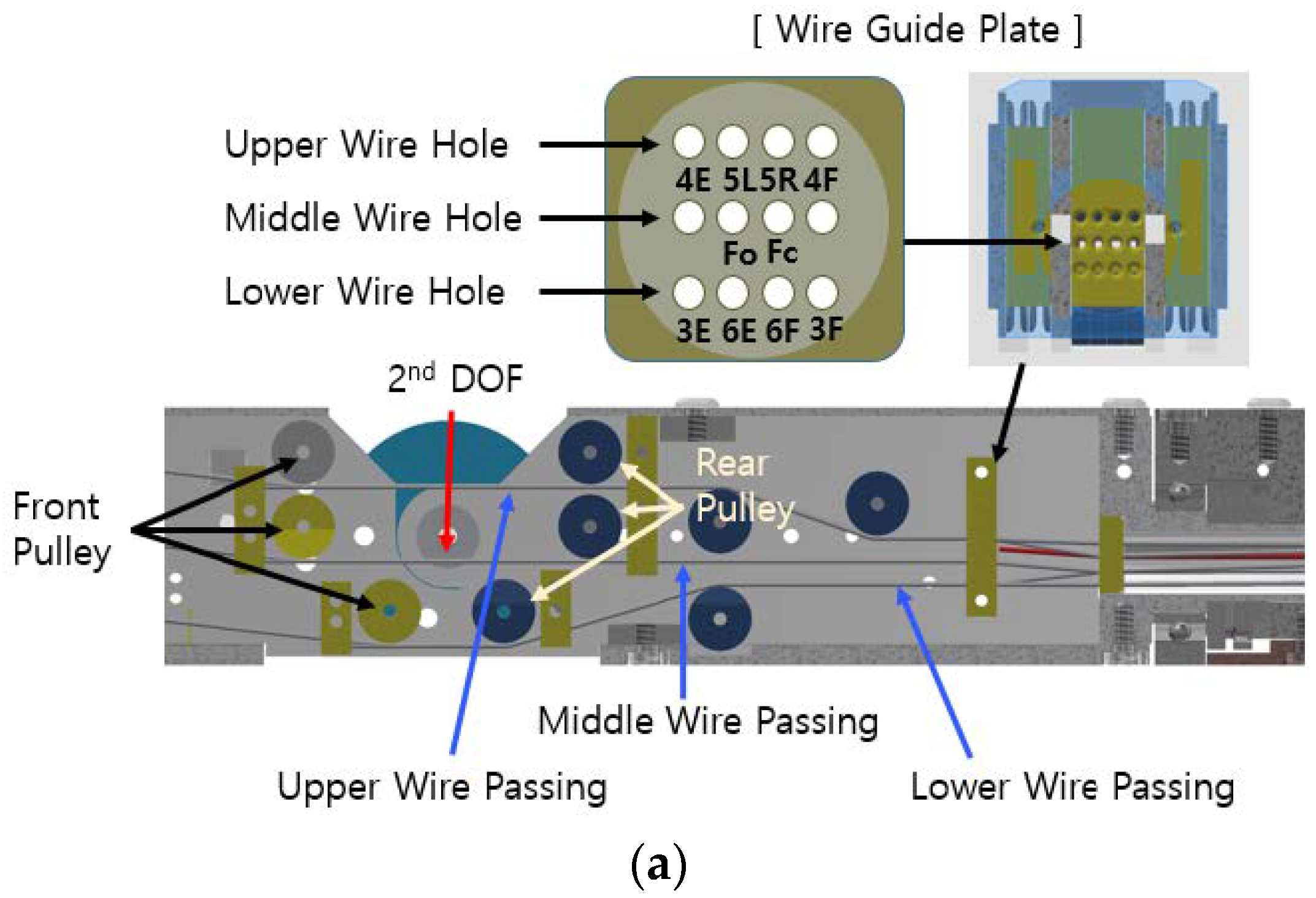
2.1. 7-Axis Vertical Multi-Joint Robot
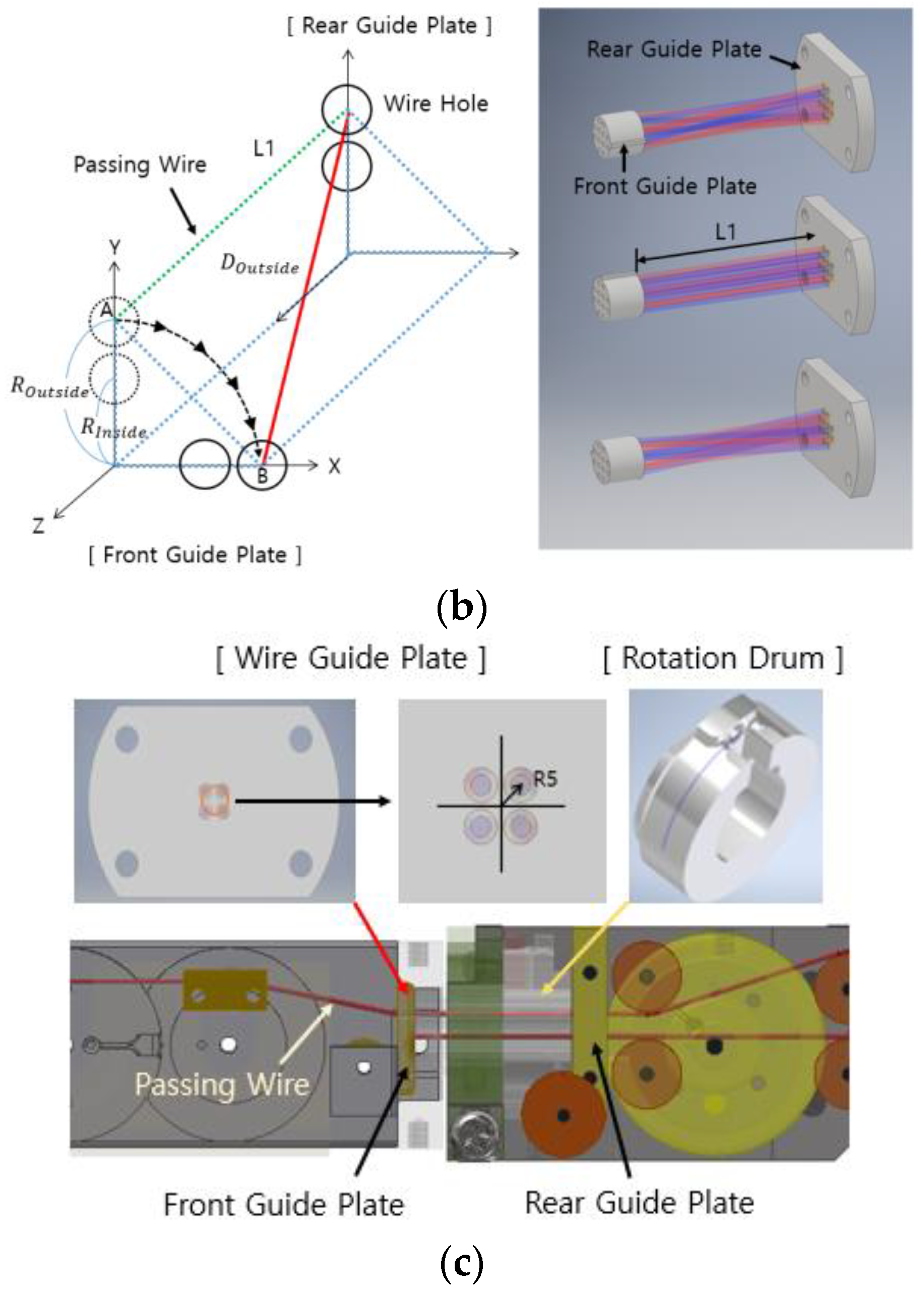
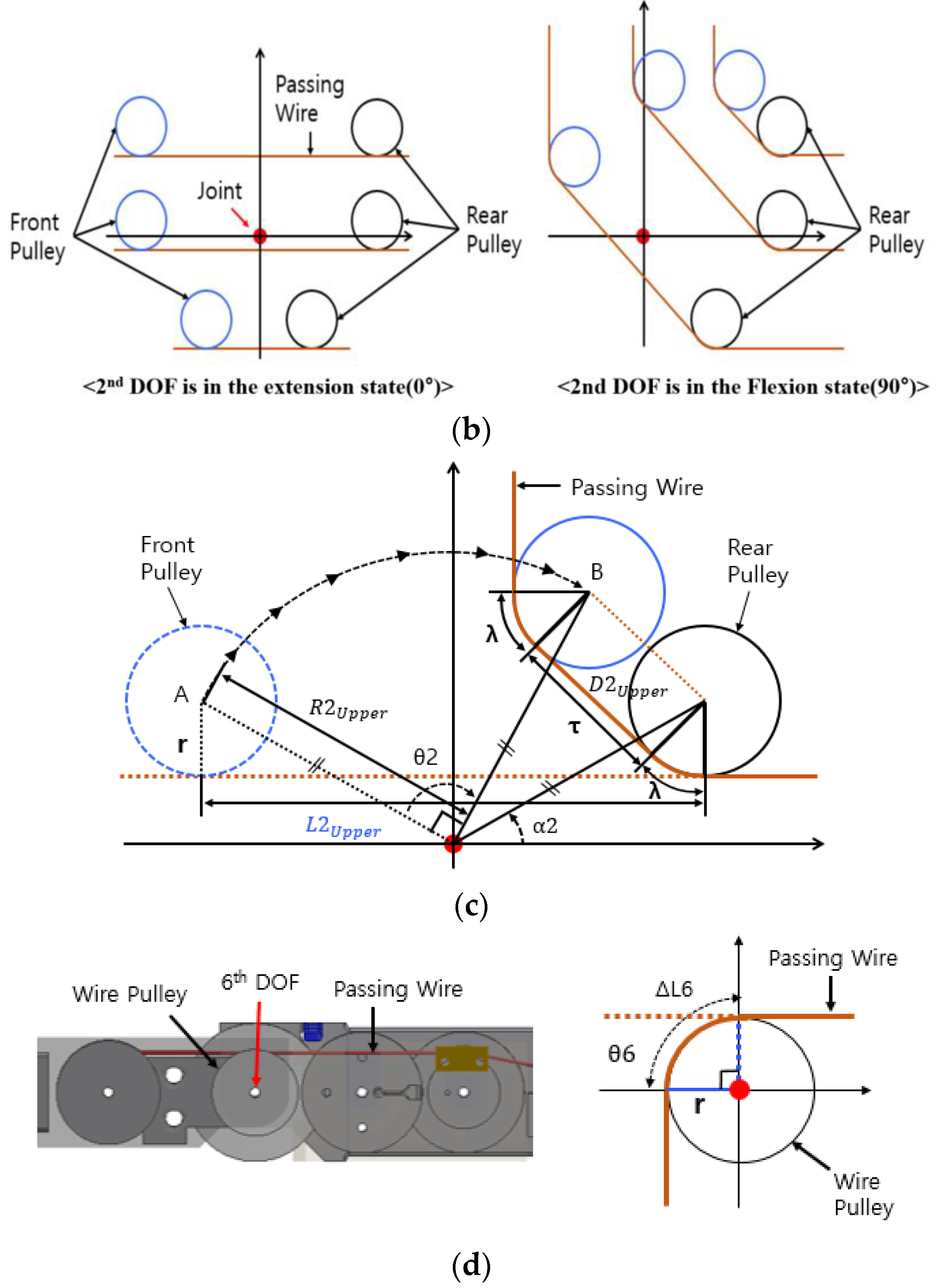
2.2. Relationship between Motor Length Change and Surgical Robot Joint Angle
3. Analysis of Wire-Driven Robot Arm
3.1. Forward Kinematics
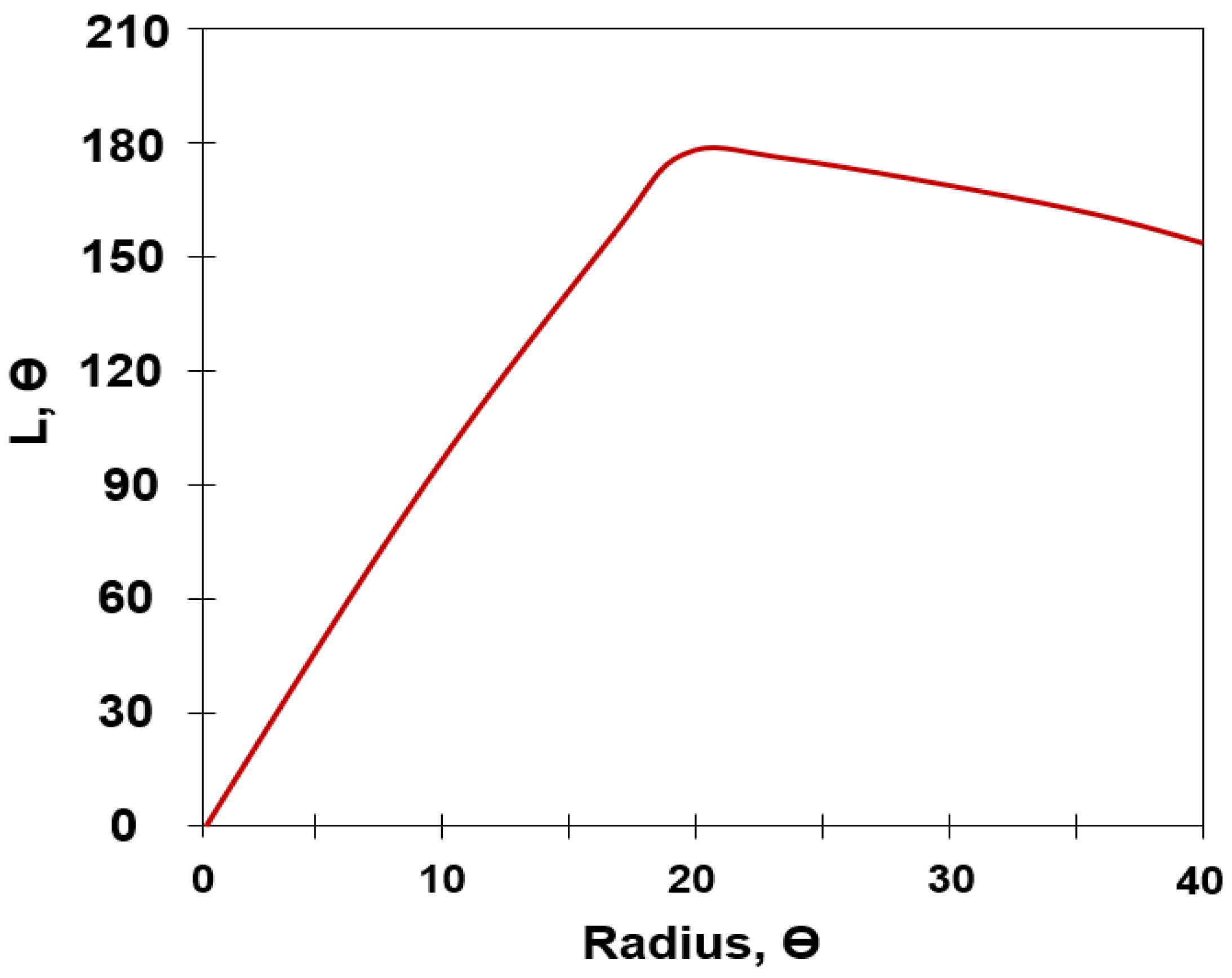
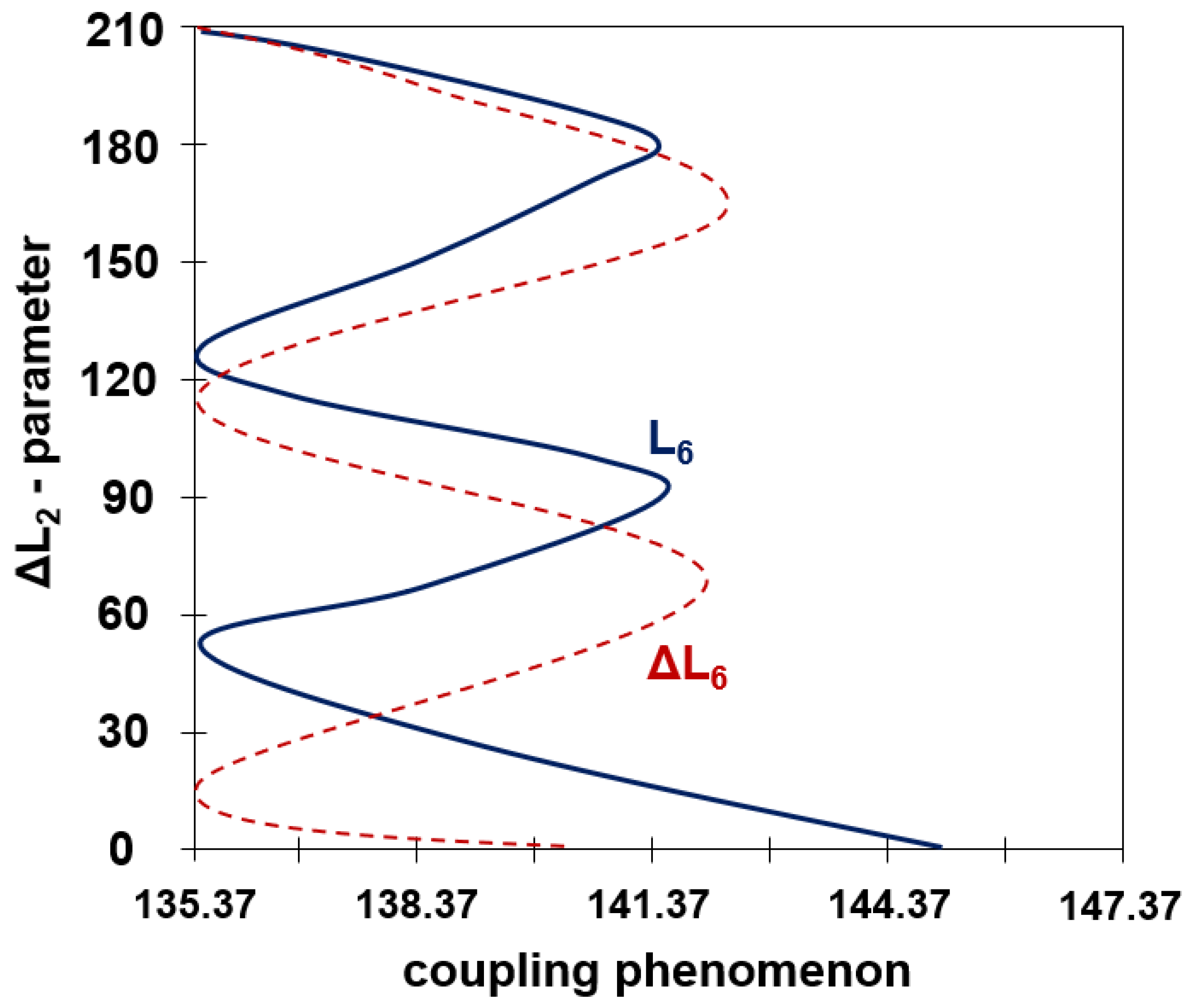
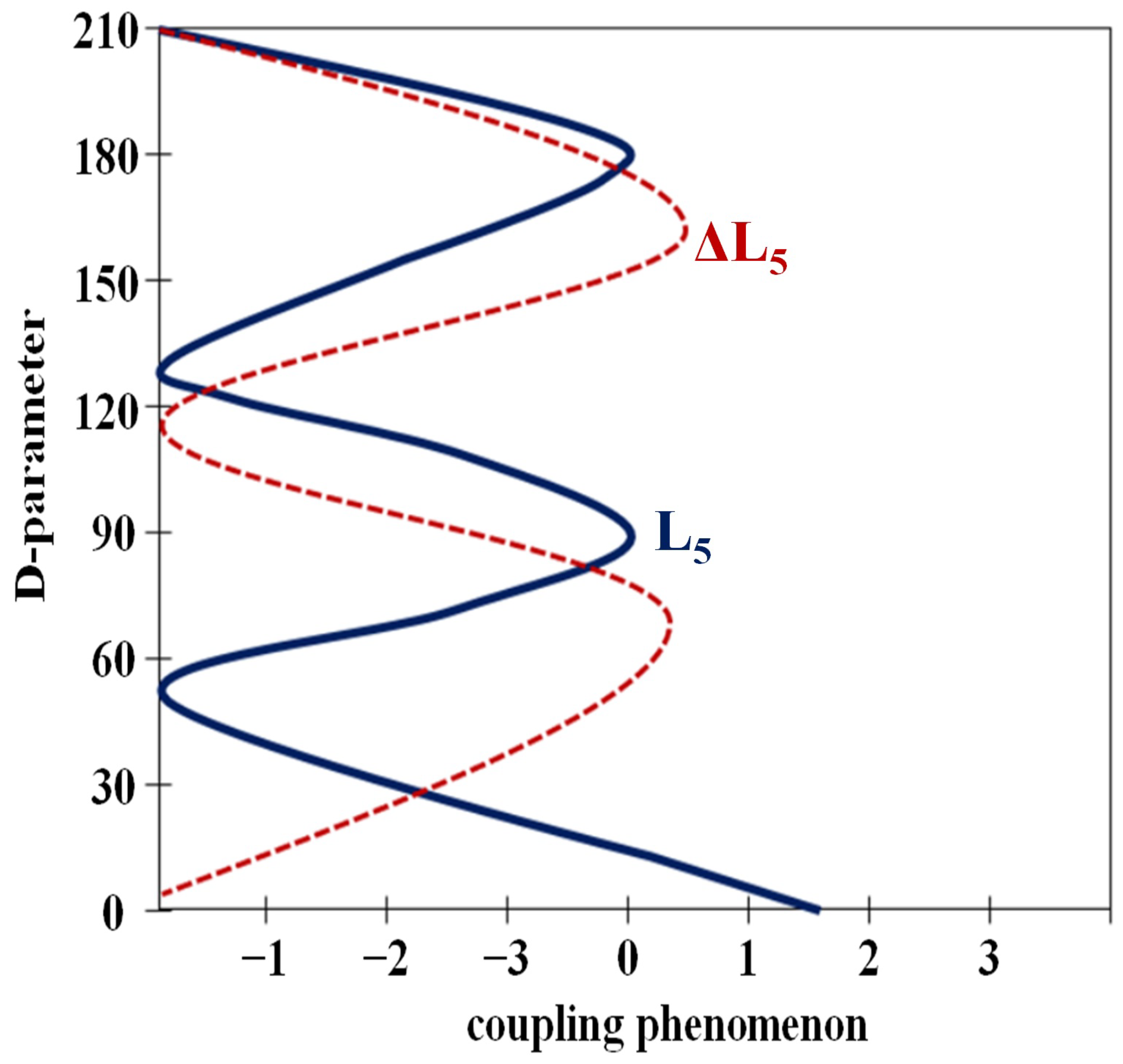
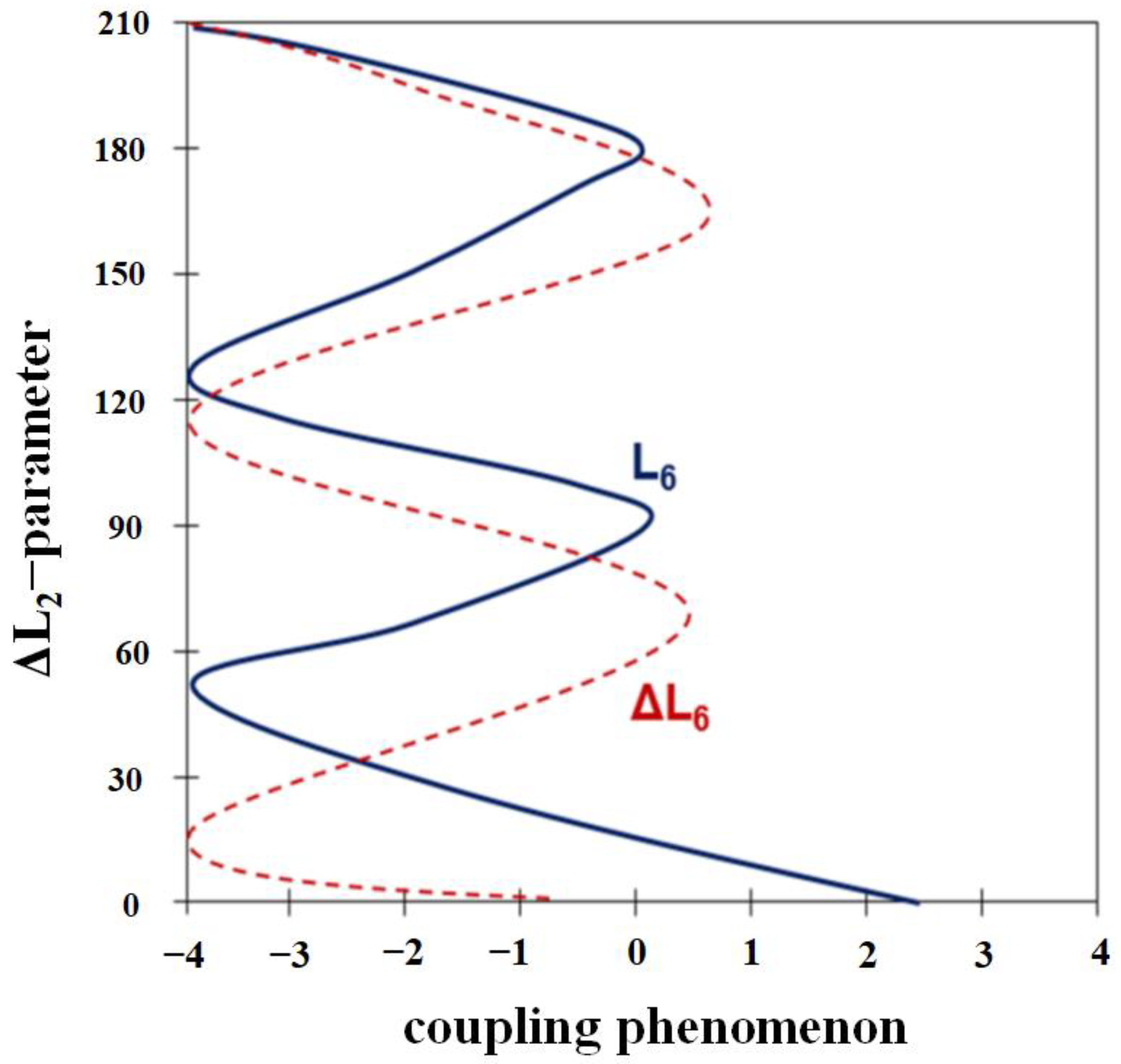
3.2. Coupling Analysis of Rotation Joint
3.3. Coupling Analysis of Angulation Joint
4. Experiment Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, Y.-J.; Lee, E.-S.; Choi, S.-B. A Cylindrical Grip Type of Tactile Device Using Magneto-Responsive Materials Integrated with Surgical Robot Console: Design and Analysis. Sensors 2022, 22, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, S.; Chen, T.; Chen, X.; Chen, B. A Wearable Hands-Free Human-Robot Interface for Robotized Flexible Endoscope. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 3953–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Wang, J.; Song, S.; Li, B.; Meng, M.Q.-H. A Modular Lockable Mechanism for Tendon-Driven Robots: Design, Modeling and Characterization. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 2023–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.M.; Ducko, C.T.; Stephenson, E.R.; Chambers, C.E.; Damiano, R.J. Prospective clinical trial of robotically assisted endoscopic coronary grafting with 1-year follow-up. Ann Surg. 2001, 233, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, G.R.; McBeth, P.B.; Louw, D.F. NeuroArm: An MR compatible robot for microsurgery. Int. Congr. Ser. 2003, 1256, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Rogers, A.J.; Light, E.D.; Allmen, D.; Smith, S.W. Three-dimentsional ultrasound guidance of autonomous robotic breast biopsy: Feasibility study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2010, 36, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, M.; Liu, H.; Tao, G. A stereo-fluoroscopic image-guided robotic biopsy scheme. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2002, 10, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Dohi, T.; Hashizume, M.; Konishi, K.; Hata, N. An ultrasound-driven needle-insertion robot for percutaneous cholecystostomy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2004, 49, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, K.; Zigmund, B.; Banovac, F.; White, C.; Stoianovici, D. Robotically assisted lung biopsy under CT fluoroscopy: Lung cancer screening and phantom study. Int. Congr. Ser. 2005, 1281, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, S.R.H.; Hanumara, N.C.; Walsh, C.J.; Slocum, A.H.; Gupta, R.; Shepard, J.O. A remote needle guidance system for percutaneous biopsies. In Proceedings of the ASME 2005 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Long Beach, CA, USA, 24–28 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, C.J.; Hanumara, N.C.; Slocum, A.H.; Shepard, J.-A.; Gupta, R. A Patient-Mounted, Telerobotic Tool for CT-Guided Percutaneous Interventions. J. Med. Devices 2008, 2, 011007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Col, T.; Caccianiga, G.; Catellani, M.; Mariani, A.; Ferro, M.; Cordima, G.; De Momi, E.; Ferrigno, G.; de Cobelli, O. Automating Endoscope Motion in Robotic Surgery: A Usability Study on da Vinci-Assisted Ex Vivo Neobladder Reconstruction. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapsalyamov, A.; Hussain, S.; Jamwal, P.K. A novel compliant surgical robot: Preliminary design analysis. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2020, 17, 1944–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.; Wei, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Dong, J.; Huo, H.; Li, Y. Development of the X-Perce—A Universal FBG-Based Force Sensing Kit for Laparoscopic Surgical Robot. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 2022, 4, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Choi, P.; Hui, C.-W.V.; Taylor, R.H.; Au, K.W.S. A Task Space Virtual Fixture Architecture for Teleoperated Surgical System with Slave Joint Limit Constraints. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2022, 27, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, R.E.; Khan, S.; Troisi, R.I.; Montalti, R.; Vanlander, A.; Fong, Y.; Kingham, T.P.; Boerner, T.; Berber, E.; Kahramangil, B.; et al. Long-Term and Oncologic Outcomes of Robotic Versus Laparoscopic Liver Resection for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Multicenter, Propensity Score Matching Analysis. World J. Surg. 2020, 44, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, D.G.; Hosseinabadi, A.H.H.; Salcudean, S.E. 6-DOF Force Sensing for the Master Tool Manipulator of the da Vinci Surgical System. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 2264–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Song, C.; Chiu, P.W.-Y.; Li, Z. Visual Servo of a 6-DOF Robotic Stereo Flexible Endoscope Based on da Vinci Research Kit (dVRK) System. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildan Gifari, M.; Naghibi, H.; Stramigioli, S.; Abayazid, M. A review on recent advances in soft surgical robots for endoscopic applications. Int. J. Med. Robotics Comput. Assist. Surg. 2019, 15, e2010. [Google Scholar]
- Berthet-Rayne, P.; Leibrandt, K.; Gras, G.; Fraisse, P.; Crosnier, A.; Yang, G.-Z. Inverse Kinematics Control Methods for Redundant Snakelike Robot Teleoperation during Minimally Invasive Surgery. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 2501–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Song, C.; Chiu, P.W.; Li, Z. Autonomous flexible endoscope for minimally invasive surgery with enhanced safety. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 2607–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, J.; Han, S. Kinematic model and real-time path generator for a wire-driven surgical robot arm with articulated joint structure. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Zuo, S. Development of Visible Manipulator with Multi-Gear Array Mechanism for Laparoscopic Surgery. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3090–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, S.; Hameed, A.; Kamal, N.; Hasan, O.; Matsuno, F. Design and Realization of a Robotic Manipulator for Minimally Invasive Surgery with Replaceable Surgical Tools. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2020, 25, 2754–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, M.; Saleem, M.M.; Tiwana, M.I.; Shakoor, R.I.; Cheung, R. A Soft Multi-Axis High Force Range Magnetic Tactile Sensor for Force Feedback in Robotic Surgical Systems. Sensors 2022, 22, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, M.; Kwon, D.S. K-FLEX: A flexible robotic platform for scar-free endoscopic surgery. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2020, 16, e2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, M.; Thananjeyan, B.; Paradis, S.; Seita, D.; Ichnowski, J.; Fer, D.; Low, T.; Goldberg, K. Efficiently Calibrating Cable-Driven Surgical Robots With RGBD Fiducial Sensing and Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 5937–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, P.-L.; Chen, Y.-J. Contact Compliance Based Visual Feedback for Tool Alignment in Robot Assisted Bone Drilling. Sensors 2022, 22, 3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zi, B.; Wang, D.; Qian, J.; You, W.; Yu, L. External Force Self-Sensing Based on Cable-Tension Disturbance Observer for Surgical Robot End-Effector. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 5274–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Direkwatana, C.; Suthakorn, J.; Wilasrusmee, C. Development of wire-driven laparoscopic surgical robotic system, “MU-LapaRobot”. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Karon Beach, Thailand, 7–11 December 2011; pp. 485–490. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, M.; Fu, Y.; Pan, B.; Liu, C. A medical robot system for celiac minimally invasive surgery. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Shenzhen, China, 6–8 June 2011; pp. 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Du, R.; Lei, M.C.; Yuan, S.M. Design and analysis of a biomimetic wire-driven robot arm. In Proceedings of the ASME 2011 International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition, Denver, CO, USA, 11–17 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, R.J., III; Jones, B.A. Design and Kinematic Modeling of Constant Curvature Continuum Robots: A Review. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2010, 29, 1661–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trochimczuk, R.; Łukaszewicz, A.; Mikołajczyk, T.; Aggogeri, F.; Borboni, A. Finite element method stiffness analysis of a novel telemanipulator for minimally invasive surgery. Med. Simul. 2019, 95, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, S.M.; Chung, T.; Lee, J.S.; Yoon, K.C.; Kim, K.G. For end effector of surgical robot 5 axis master system development. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on BioMedical Technology (ICBMT 2019), Da Nang, Vietnam, 20–23 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, K.W.; Park, J.; Kim, I.Y.; Kim, K.G. Application of Stereo-Imaging Technology to Medical Field. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2012, 18, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashuri, T.; Armani, A.; Hamidi, R.J.; Reasnor, T.; Ahmadi, S.; Iqbal, K. Biomedical soft robots: Current status and perspective. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2020, 10, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
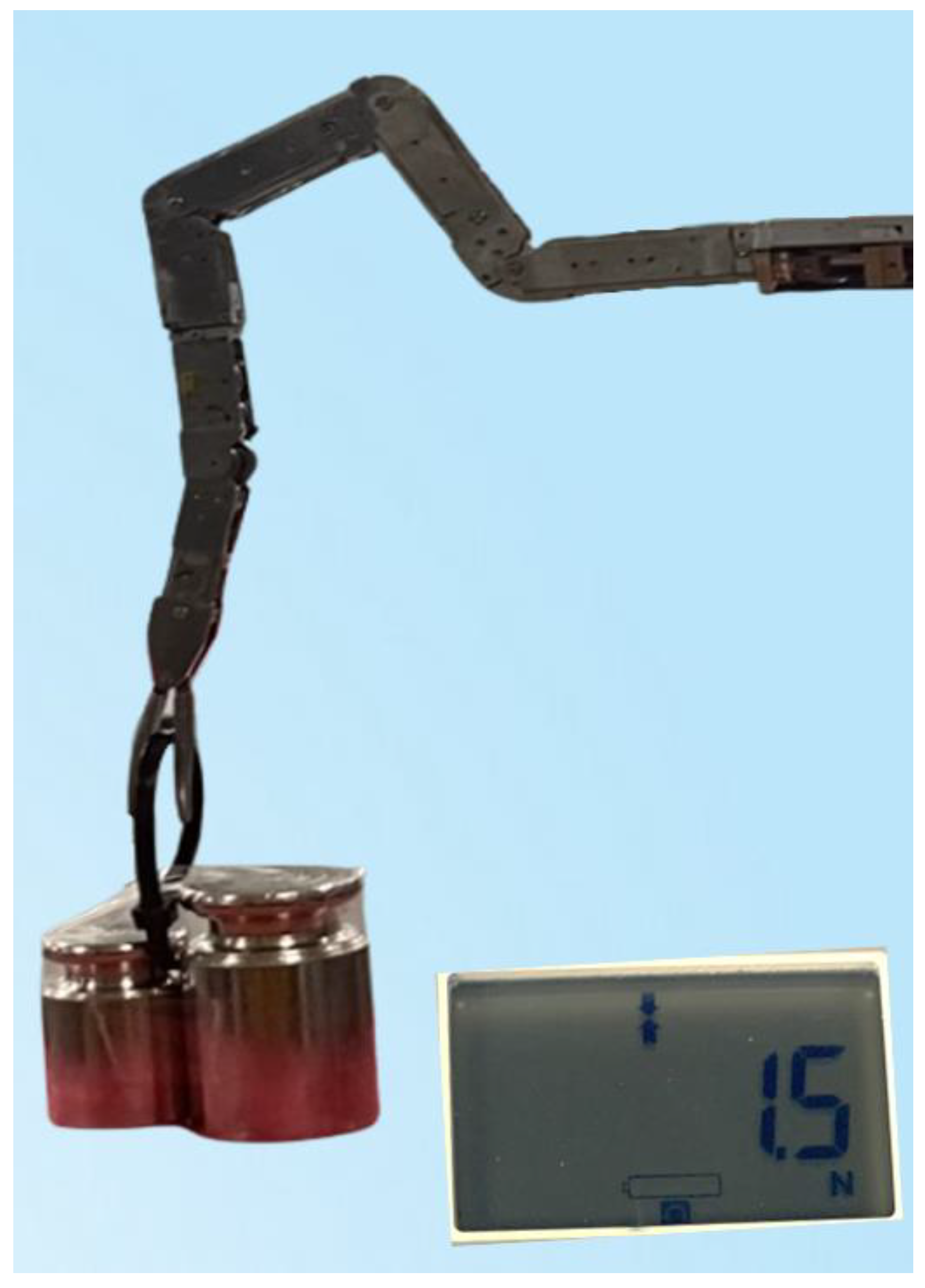





| Gear Ratio | Encoder Value (Pulse) | Pulley D (mm) | L/Rotation (mm) | Joint-Angle Range | LT (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| axis #1, #5 | 150:1 | 4096 | 15 | 47.124 | 120° | 150.71 |
| axis #2,3,4,6 | 150:1 | 4096 | 15 | 47.124 | 90° | 11.78 |
| axis #7 | 150:1 | 4096 | 15 | 47.124 | 71.9° | 9.41 |
| Joint No. | Joint Angle (θ-Rad) | Joint Offset (Di-mm) | Link Length (Li-mm) | Twist Angle (α-Rad) | Motion Range (R) (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | θ1 | D1 | 0 | +π/2 | −60° to +60° |
| 2 | θ2 | 0 | L2 | 0 | +90° to +180° |
| 3 | θ3 | 0 | L3 | 0 | −90° to 0° |
| 4 | θ4 | 0 | 0 | +π/2 | 0° to +90° |
| 5 | θ5 | D5 | 0 | +π/2 | −60° to +60° |
| 6 | θ6 | 0 | L6 | 0 | −180° to −90° |
| DOF | Preset | Measured | Error | DOF | Preset | Measured | Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2nd | 90° | 89.7° | 0.3° | 3rd | 90° | 89.2° | 0.8° |
| (a) When 1st DOF = 120° | (b) When 1st DOF = 120° and 2nd DOF = 90° | ||||||
| DOF | Preset | Measured | Error | DOF | Preset | Measured | Error |
| 4th | 90° | 89.5° | 0.5° | 5th | 120° | 118.3° | 1.7° |
| (c) When 1st DOF = 120°, 2nd DOF = 90°, and 3rd DOF = 90° | (d) When 1st DOF = 120°, 2nd DOF = 90°, 3rd DOF = 90°, and 4th DOF = 90° | ||||||
| DOF | Preset | Measured | Error | DOF | Preset | Measured | Error |
| 6th | 90° | 86.8° | 3.2° | 7th | 120° | 115.7° | 4.3° |
| (e) When 1st DOF = 120°, 2nd DOF = 90°, 3rd DOF = 90°, 4th DOF = 90°, and 5th DOF = 120° | (f) When 1st DOF = 120°, 2nd DOF = 90°, 3rd DOF = 90°, 4th DOF = 90°, 5th DOF = 120°, and 6th DOF = 90° | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, K.; Cho, S.-M.; Kim, K.G. Coupling Effect Suppressed Compact Surgical Robot with 7-Axis Multi-Joint Using Wire-Driven Method. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1698. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10101698
Yoon K, Cho S-M, Kim KG. Coupling Effect Suppressed Compact Surgical Robot with 7-Axis Multi-Joint Using Wire-Driven Method. Mathematics. 2022; 10(10):1698. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10101698
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Kicheol, Sung-Min Cho, and Kwang Gi Kim. 2022. "Coupling Effect Suppressed Compact Surgical Robot with 7-Axis Multi-Joint Using Wire-Driven Method" Mathematics 10, no. 10: 1698. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10101698
APA StyleYoon, K., Cho, S.-M., & Kim, K. G. (2022). Coupling Effect Suppressed Compact Surgical Robot with 7-Axis Multi-Joint Using Wire-Driven Method. Mathematics, 10(10), 1698. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10101698







