Geometric Metric Learning for Multi-Output Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Multi-Output Learning
2.2. Metric Learning
3. The Proposed Method
3.1. Background
3.2. Proposed Formulation
| Algorithm 1: GCMoL. |
|
3.3. Prediction
3.4. Complexity Analysis
3.4.1. Training Time
3.4.2. Testing Time
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
- BR [16] is the most intuitive solution to multi-label learning. It works by decomposing the multi-label learning task into multiple independent binary learning tasks, so it is a problem transformation method. In order to be fair in the experiment, we use the kNN model as the base classifier and set .
- LMMO [9] is a recently proposed large-margin metric learning method for multi-output tasks. It projects both input and output into the same embedding space, and then learns a distance metric to keep instances with the same output close and instances with very different outputs farther away. Its formulation is presented in Equation (2) and can only be used for multi-label learning task. Parameter is selected from .
4.2. Experimental Results
4.3. Analysis
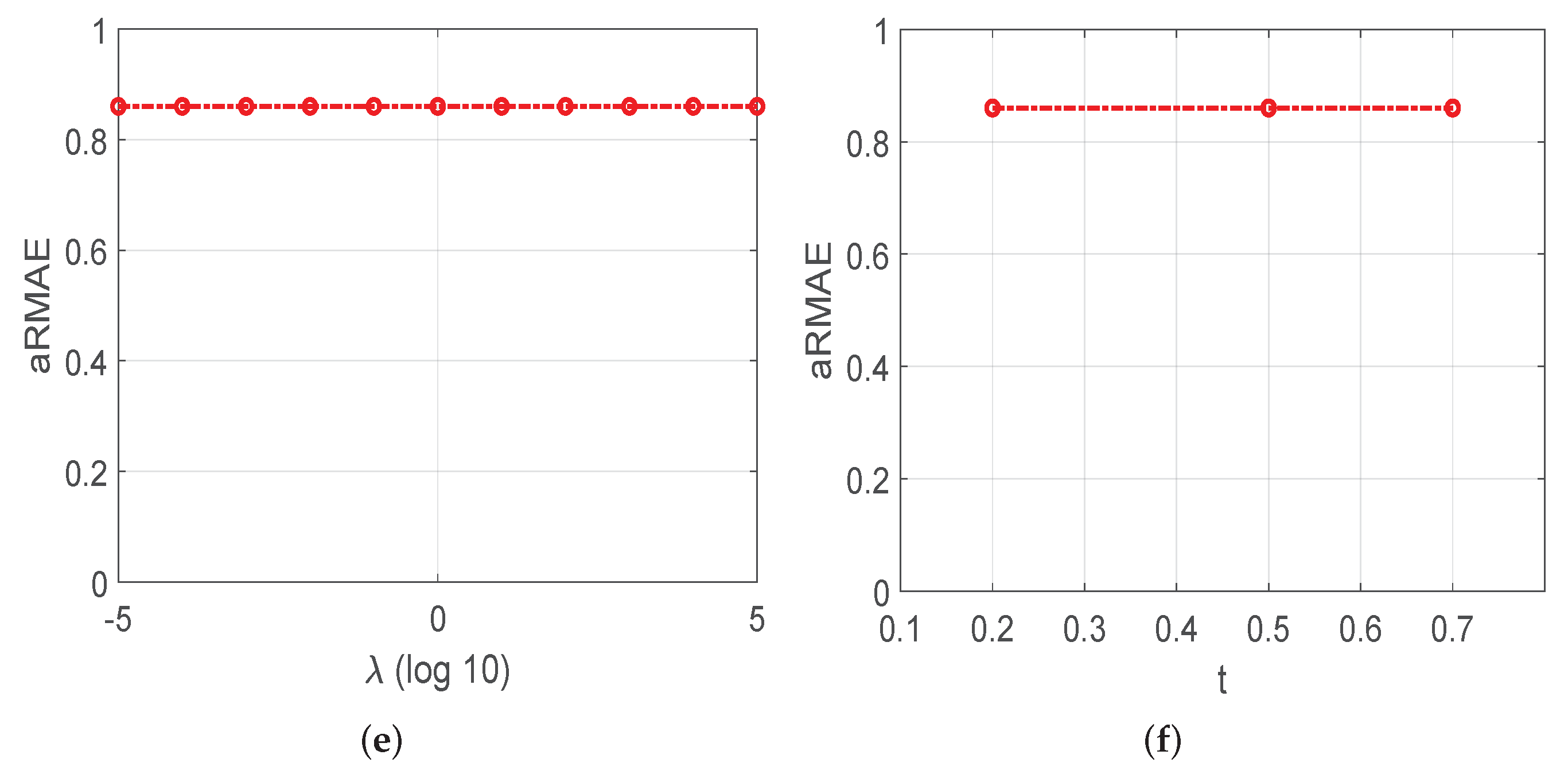
4.3.1. Hyper-Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
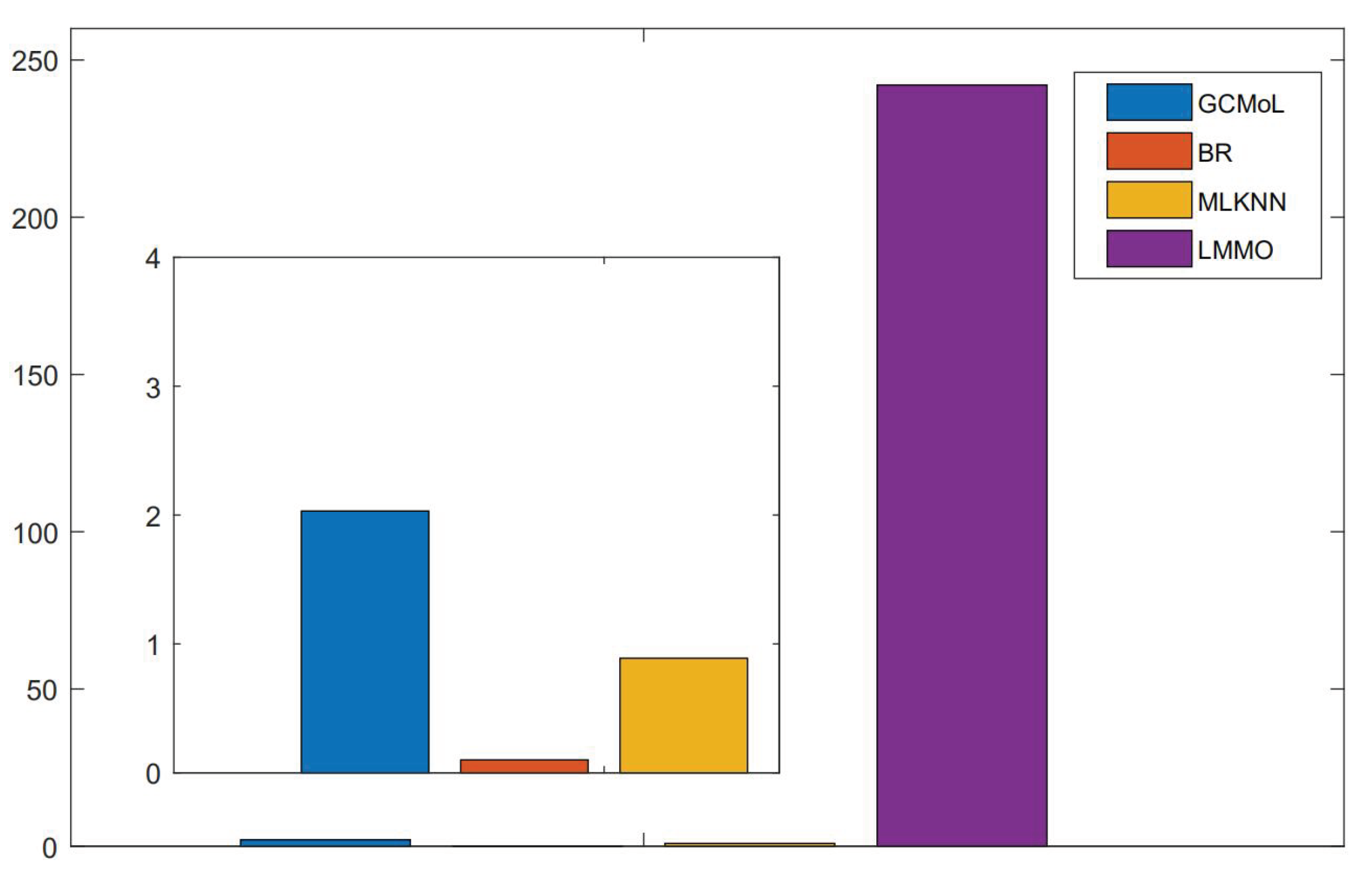
4.3.2. Time-Comsuming Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, D.; Shi, Y.; Tsang, I.W.; Ong, Y.S.; Gong, C.; Shen, X. Survey on Multi-Output Learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 31, 2409–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.L.; Zhou, Z.H. A review on multi-label learning algorithms. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2013, 26, 1819–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchani, H.; Varando, G.; Bielza, C.; Larrañaga, P. A survey on multi-output regression. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2015, 5, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gou, J.; Qiu, W.; Yi, Z.; Shen, X.; Zhan, Y.; Ou, W. Locality constrained representation-based K-nearest neighbor classification. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2019, 167, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Sun, L.; Du, L.; Ma, H.; Xiong, T.; Ou, W.; Zhan, Y. A representation coefficient-based k-nearest centroid neighbor classifier. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 194, 116529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Schneider, J. Maximum margin output coding. In Proceedings of the 29th International Coference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Edinburgh, UK, 26 June–1 July 2012; pp. 379–386. [Google Scholar]
- Tsochantaridis, I.; Joachims, T.; Hofmann, T.; Altun, Y. Large margin methods for structured and interdependent output variables. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2005, 6, 1453–1484. [Google Scholar]
- BakIr, G.; Hofmann, T.; Schölkopf, B.; Smola, A.J.; Taskar, B.; Vishwanathan, S. Generalization Bounds and Consistency for Structured Labeling; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Xu, D.; Tsang, I.W.; Zhang, W. Metric learning for multi-output tasks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 408–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, T.N.; Chambers, A.; Smyth, P.; Steyvers, M. Statistical topic models for multi-label document classification. Mach. Learn. 2012, 88, 157–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, Y.; Jawahar, C. Image annotation by propagating labels from semantic neighbourhoods. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2017, 121, 126–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Zhan, D.C.; Zhou, Z.H. Multi-modal image annotation with multi-instance multi-label LDA. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Third International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Beijing, China, 3–9 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.L.; Zhou, Z.H. ML-KNN: A lazy learning approach to multi-label learning. Pattern Recognit. 2007, 40, 2038–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clare, A.; King, R.D. Knowledge discovery in multi-label phenotype data. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Principles of Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, Freiburg, Germany, 3–5 September 2001; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 42–53. [Google Scholar]
- Elisseeff, A.; Weston, J. A kernel method for multi-labelled classification. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 681–687. [Google Scholar]
- Boutell, M.R.; Luo, J.; Shen, X.; Brown, C.M. Learning multi-label scene classification. Pattern Recognit. 2004, 37, 1757–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsoumakas, G.; Vlahavas, I. Random k-labelsets: An ensemble method for multilabel classification. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Machine Learning, Warsaw, Poland, 17–21 September 2007; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 406–417. [Google Scholar]
- Fürnkranz, J.; Hüllermeier, E.; Mencía, E.L.; Brinker, K. Multilabel classification via calibrated label ranking. Mach. Learn. 2008, 73, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Read, J.; Pfahringer, B.; Holmes, G.; Frank, E. Classifier chains for multi-label classification. Mach. Learn. 2011, 85, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spyromitros-Xioufis, E.; Sechidis, K.; Vlahavas, I. Multi-target regression via output space quantization. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.09896. [Google Scholar]
- Spyromitros-Xioufis, E.; Tsoumakas, G.; Groves, W.; Vlahavas, I. Multi-target regression via input space expansion: Treating targets as inputs. Mach. Learn. 2016, 104, 55–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Jin, R. Distance metric learning: A comprehensive survey. Mich. State Univ. 2006, 2, 4. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; King, O.; Ma, W.Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.J. Learning a semantic space from user’s relevance feedback for image retrieval. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2003, 13, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Ma, W.Y.; Zhang, H.J. Learning an image manifold for retrieval. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual ACM International Conference on Multimedia, New York, NY, USA, 10–16 October 2004; pp. 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.J.; Tong, H.; Zhang, C. Manifold-ranking based image retrieval. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual ACM International Conference on Multimedia, New York, NY, USA, 10–16 October 2004; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger, K.Q.; Saul, L.K. Distance metric learning for large margin nearest neighbor classification. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2009, 10, 207–244. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, E.P.; Jordan, M.I.; Russell, S.J.; Ng, A.Y. Distance metric learning with application to clustering with side-information. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Heisterkamp, D.R.; Dai, H. Adaptive kernel metric nearest neighbor classification. In Proceedings of the 2002 International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 11–15 August 2002; Volume 3, pp. 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, P.; Hosseini, R.; Sra, S. Geometric mean metric learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; pp. 2464–2471. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Tsang, I.W. Large margin metric learning for multi-label prediction. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015. [Google Scholar]


| Dataset | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLC | emotions | 593 | 72 | 6 | 1.869 |
| scene | 2407 | 294 | 6 | 1.074 | |
| cal500 | 502 | 68 | 174 | 26.044 | |
| genbase | 662 | 1186 | 27 | 1.252 | |
| MTR | edm | 154 | 16 | 2 | - |
| enb | 768 | 8 | 2 | - | |
| jura | 359 | 15 | 3 | - | |
| scpf | 1137 | 23 | 3 | - |
| Task | Criteria | Dataset | Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BR | MLkNN | LMMO | GCMoL | |||
| MLC | Micro-F1 | emotions | 0.4905 | 0.4918 | 0.6753 | 0.6774 |
| genbase | 0.9607 | 0.9505 | 0.9697 | 0.9791 | ||
| yeast | 0.6330 | 0.6392 | 0.5600 | 0.6376 | ||
| CAL500 | 0.3131 | 0.3185 | 0.3339 | 0.3709 | ||
| Macro-F1 | emotions | 0.4170 | 0.3811 | 0.6563 | 0.6634 | |
| genbase | 0.5683 | 0.5321 | 0.5877 | 0.6258 | ||
| yeast | 0.3892 | 0.3697 | 0.3748 | 0.4056 | ||
| CAL500 | 0.0738 | 0.0534 | 0.0689 | 0.1049 | ||
| MTR | aRMAE | edm | 0.9335 | - | 0.9010 | 0.8591 |
| enb | 0.2230 | - | 0.2488 | 0.1538 | ||
| jura | 0.6030 | - | 0.7158 | 0.5704 | ||
| wq | 0.8628 | - | 0.9933 | 0.8713 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, H.; Ma, Z. Geometric Metric Learning for Multi-Output Learning. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10101632
Gao H, Ma Z. Geometric Metric Learning for Multi-Output Learning. Mathematics. 2022; 10(10):1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10101632
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Huiping, and Zhongchen Ma. 2022. "Geometric Metric Learning for Multi-Output Learning" Mathematics 10, no. 10: 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10101632
APA StyleGao, H., & Ma, Z. (2022). Geometric Metric Learning for Multi-Output Learning. Mathematics, 10(10), 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10101632





