Small Mass but Strong Information: Diagnostic Ions Provide Crucial Clues to Correctly Identify Histone Lysine Modifications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Acid Extraction and Proteolysis by Trypsin of Histones from Whole Mouse Testis
2.2. LC-MS/MS Analyses of Digested Endogenous Histones and Synthetic Peptides
2.3. Interpretation of Proteomics Data
3. Results
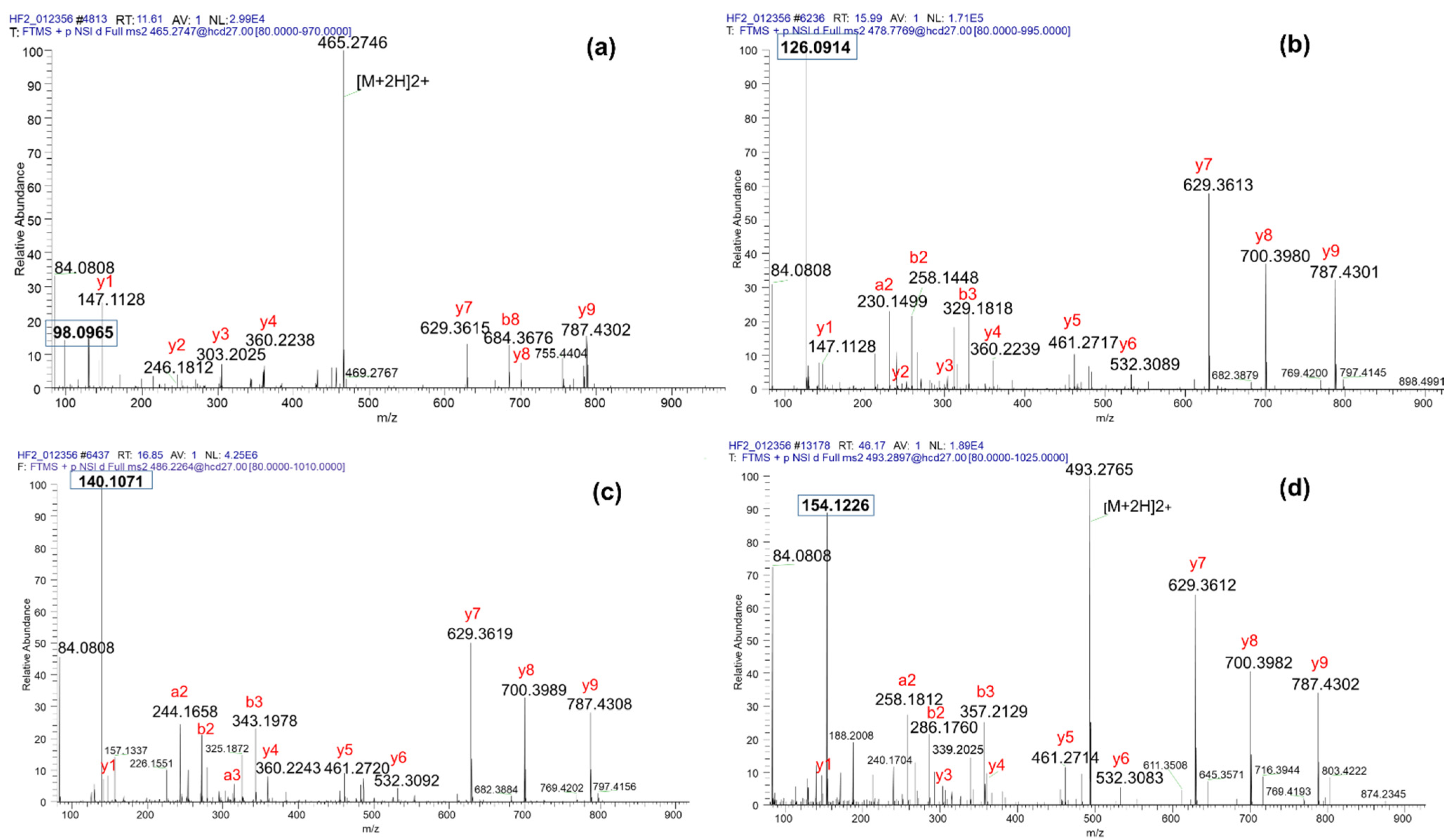
3.1. Diagnostic Ions and Neutral Losses Reveal the Nature of PTMs on Lysine Residues of Fragmented Peptides
3.2. Formylation or Acetylation at the N-Terminal of Peptides Does Not Prevent Production of the Diagnostic ion of K1PTM
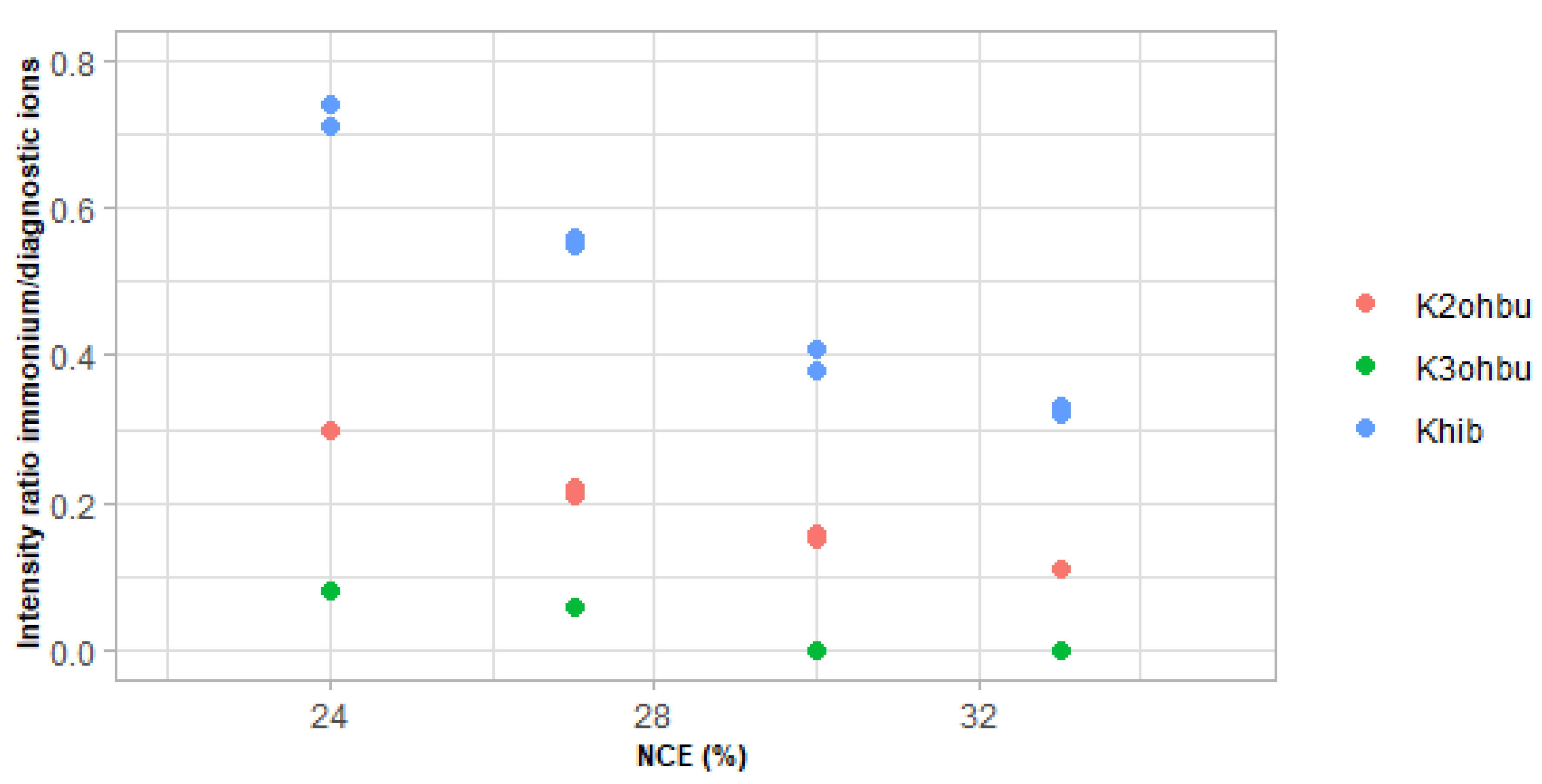
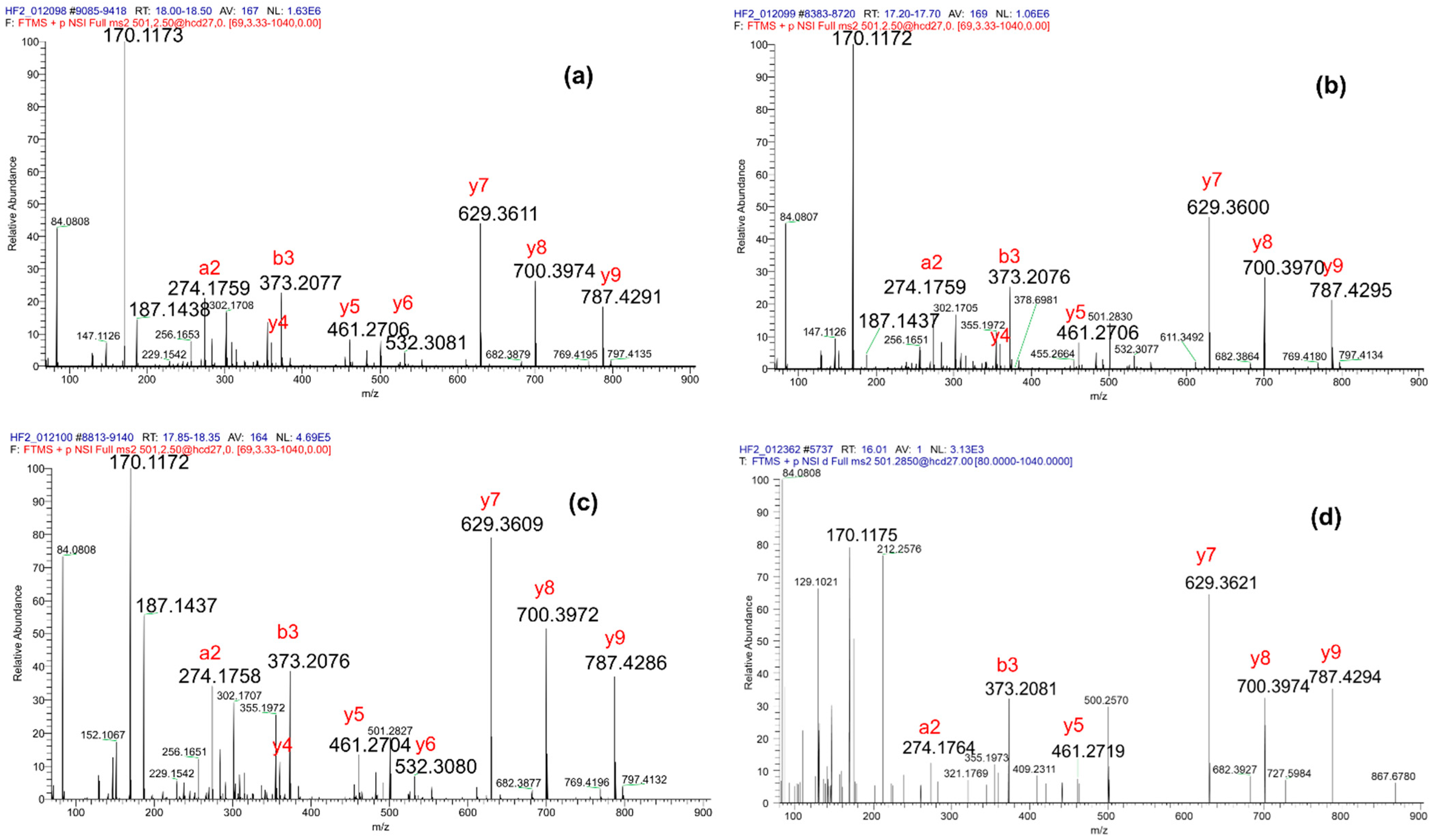
3.3. Usefulness of the Immonium and Diagnostic Ions to Discriminate Positional Isomers of Lysine Hydroxybutyrylation
3.4. Adjusting Normalized Collision Energy (NCE) Values on the Longer Peptide KPTMSAPATGGVKme2KPHR
3.5. When In Vitro Propionylation Is Performed before Trypsin Digestion
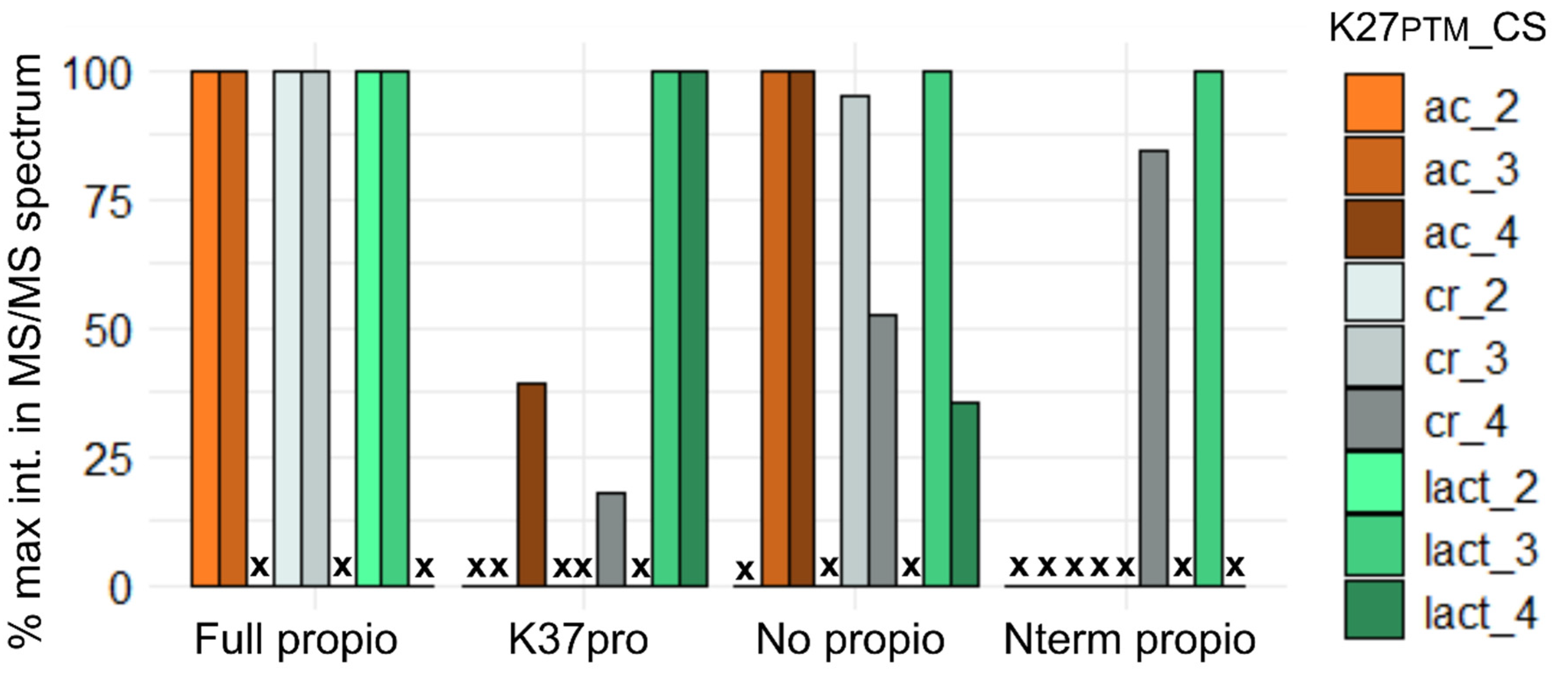
3.6. Testing the Production of Diagnostic Ions for K27PTM from Synthetic Peptides KPTMSAPATGGVKme2KPHR with Variable Levels of In Vitro Propionylation
3.7. Can Retention Times Be Useful to Differentiate Variably Modified KPTMS(A/V)P(A/S)TGGVK?
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Phillips, D.M. The Presence of Acetyl Groups of Histones. Biochem. J. 1963, 87, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Sprung, R.; Tang, Y.; Ball, H.; Sangras, B.; Kim, S.C.; Falck, J.R.; Peng, J.; Gu, W.; Zhao, Y. Lysine Propionylation and Butyrylation Are Novel Post-Translational Modifications in Histones. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2007, 6, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Dai, J.; Dai, L.; Tan, M.; Cheng, Z.; Wu, Y.; Boeke, J.D.; Zhao, Y. Lysine Succinylation and Lysine Malonylation in Histones. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2012, 11, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tan, M.; Xie, Z.; Dai, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y. Identification of Lysine Succinylation as a New Post-Translational Modification. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Luo, H.; Lee, S.; Jin, F.; Yang, J.S.; Montellier, E.; Buchou, T.; Cheng, Z.; Rousseaux, S.; Rajagopal, N.; et al. Identification of 67 Histone Marks and Histone Lysine Crotonylation as a New Type of Histone Modification. Cell 2011, 146, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Peng, C.; Montellier, E.; Lu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ishii, H.; Debernardi, A.; Buchou, T.; Rousseaux, S.; Jin, F.; et al. Lysine 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation Is a Widely Distributed Active Histone Mark. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhang, D.; Chung, D.; Tang, Z.; Huang, H.; Dai, L.; Qi, S.; Li, J.; Colak, G.; Chen, Y.; et al. Metabolic Regulation of Gene Expression by Histone Lysine β-Hydroxybutyrylation. Mol. Cell 2016, 62, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Perez-Neut, M.; Han, Z.; Zheng, Y.G.; Hao, Q.; Zhao, Y. Lysine Benzoylation Is a Histone Mark Regulated by SIRT2. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Tang, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhou, G.; Cui, C.; Weng, Y.; Liu, W.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Perez-Neut, M.; et al. Metabolic Regulation of Gene Expression by Histone Lactylation. Nature 2019, 574, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, M.; Damont, A.; Blanco, M.; Lastrucci, E.; Kennani, S.E.; Ialy-Radio, C.; Khattabi, L.E.; Terrier, S.; Louwagie, M.; Kieffer-Jaquinod, S.; et al. Multi-Omic Analysis of Gametogenesis Reveals a Novel Signature at the Promoters and Distal Enhancers of Active Genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 4115–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kennani, S.; Crespo, M.; Govin, J.; Pflieger, D. Proteomic Analysis of Histone Variants and Their PTMs: Strategies and Pitfalls. Proteomes 2018, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maehara, K.; Harada, A.; Sato, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Nakayama, K.I.; Kimura, H.; Ohkawa, Y. Tissue-Specific Expression of Histone H3 Variants Diversified after Species Separation. Epigenetics Chromatin 2015, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Williams, K.; Huang, L.; Yau, P.; Siino, J.; Bradbury, E.; Jones, P.; Minch, M.; Burlingame, A. Histone Acetylation and Deacetylation: Identification of Acetylation and Methylation Sites of HeLa Histone H4 by Mass Spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2002, 1, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couttas, T.A.; Raftery, M.J.; Bernardini, G.; Wilkins, M.R. Immonium Ion Scanning for the Discovery of Post-Translational Modifications and Its Application to Histones. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 2632–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Tian, B.; Brasier, A.R.; Sowers, L.C.; Zhang, K. Measurement of Histone Methylation Dynamics by One-Carbon Metabolic Isotope Labeling and High-Energy Collisional Dissociation Methylation Signature Ion Detection. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Fang, H.; Yin, E.; Brasier, A.R.; Sowers, L.C.; Zhang, K. Multiplexed Parallel Reaction Monitoring Targeting Histone Modifications on the QExactive Mass Spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5526–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lin, Y.; Darwanto, A.; Song, X.; Xu, G.; Zhang, K. Identification and Characterization of Propionylation at Histone H3 Lysine 23 in Mammalian Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 32288–32295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolg, D.P.; Wilhelm, M.; Schmidt, T.; Médard, G.; Zerweck, J.; Knaute, T.; Wenschuh, H.; Reimer, U.; Schnatbaum, K.; Kuster, B. ProteomeTools: Systematic Characterization of 21 Post-Translational Protein Modifications by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) Using Synthetic Peptides. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2018, 17, 1850–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muroski, J.M.; Fu, J.Y.; Nguyen, H.H.; Loo, R.R.O.; Loo, J.A. Leveraging Immonium Ions for Targeting Acyl-Lysine Modifications in Proteomic Datasets. Proteomics 2021, 21, 2000111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathke, C.; Baarends, W.; Awe, S.; Renkawitz-Pohl, R. Chromatin Dynamics during Spermiogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gene Regul. Mech. 2014, 1839, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maile, T.M.; Izrael-Tomasevic, A.; Cheung, T.; Guler, G.D.; Tindell, C.; Masselot, A.; Liang, J.; Zhao, F.; Trojer, P.; Classon, M.; et al. Mass Spectrometric Quantification of Histone Post-Translational Modifications by a Hybrid Chemical Labeling Method. Mol. Cell. Proteomics MCP 2015, 14, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kennani, S.; Adrait, A.; Shaytan, A.K.; Khochbin, S.; Bruley, C.; Panchenko, A.R.; Landsman, D.; Pflieger, D.; Govin, J. MS_HistoneDB, a Manually Curated Resource for Proteomic Analysis of Human and Mouse Histones. Epigenetics Chromatin 2017, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, T.; Harrison, A.G. Ion Chemistry of Protonated Lysine Derivatives. J. Mass Spectrom. 1996, 31, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenaille, F.; Tabet, J.-C.; Guy, P.A. Study of Peptides Containing Modified Lysine Residues by Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Precursor Ion Scanning of Hexanal-Modified Peptides. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Yau, P.M.; Chandrasekhar, B.; New, R.; Kondrat, R.; Imai, B.S.; Bradbury, M.E. Differentiation between Peptides Containing Acetylated or Tri-Methylated Lysines by Mass Spectrometry: An Application for Determining Lysine 9 Acetylation and Methylation of Histone H3. Proteomics 2004, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shek, P.Y.I.; Zhao, J.; Ke, Y.; Siu, K.W.M.; Hopkinson, A.C. Fragmentations of Protonated Arginine, Lysine and Their Methylated Derivatives: Concomitant Losses of Carbon Monoxide or Carbon Dioxide and an Amine. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 8282–8296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brame, C.J.; Moran, M.F.; McBroom-Cerajewski, L.D.B. A Mass Spectrometry Based Method for Distinguishing between Symmetrically and Asymmetrically Dimethylated Arginine Residues. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldi, M.; Cuomo, A.; Bonaldi, T. Quantitative Assessment of Chemical Artefacts Produced by Propionylation of Histones Prior to Mass Spectrometry Analysis. Proteomics 2016, 16, 1952–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paternoster, V.; Edhager, A.V.; Sibbersen, C.; Nielsen, A.L.; Børglum, A.D.; Christensen, J.H.; Palmfeldt, J. Quantitative Assessment of Methyl-Esterification and Other Side Reactions in a Standard Propionylation Protocol for Detection of Histone Modifications. Proteomics 2016, 16, 2059–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meert, P.; Dierickx, S.; Govaert, E.; Clerck, L.D.; Willems, S.; Dhaenens, M.; Deforce, D. Tackling Aspecific Side Reactions during Histone Propionylation: The Promise of Reversing Overpropionylation. Proteomics 2016, 16, 1970–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kennani, S.; Adrait, A.; Permiakova, O.; Hesse, A.-M.; Ialy-Radio, C.; Ferro, M.; Brun, V.; Cocquet, J.; Govin, J.; Pflieger, D. Systematic Quantitative Analysis of H2A and H2B Variants by Targeted Proteomics. Epigenetics Chromatin 2018, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
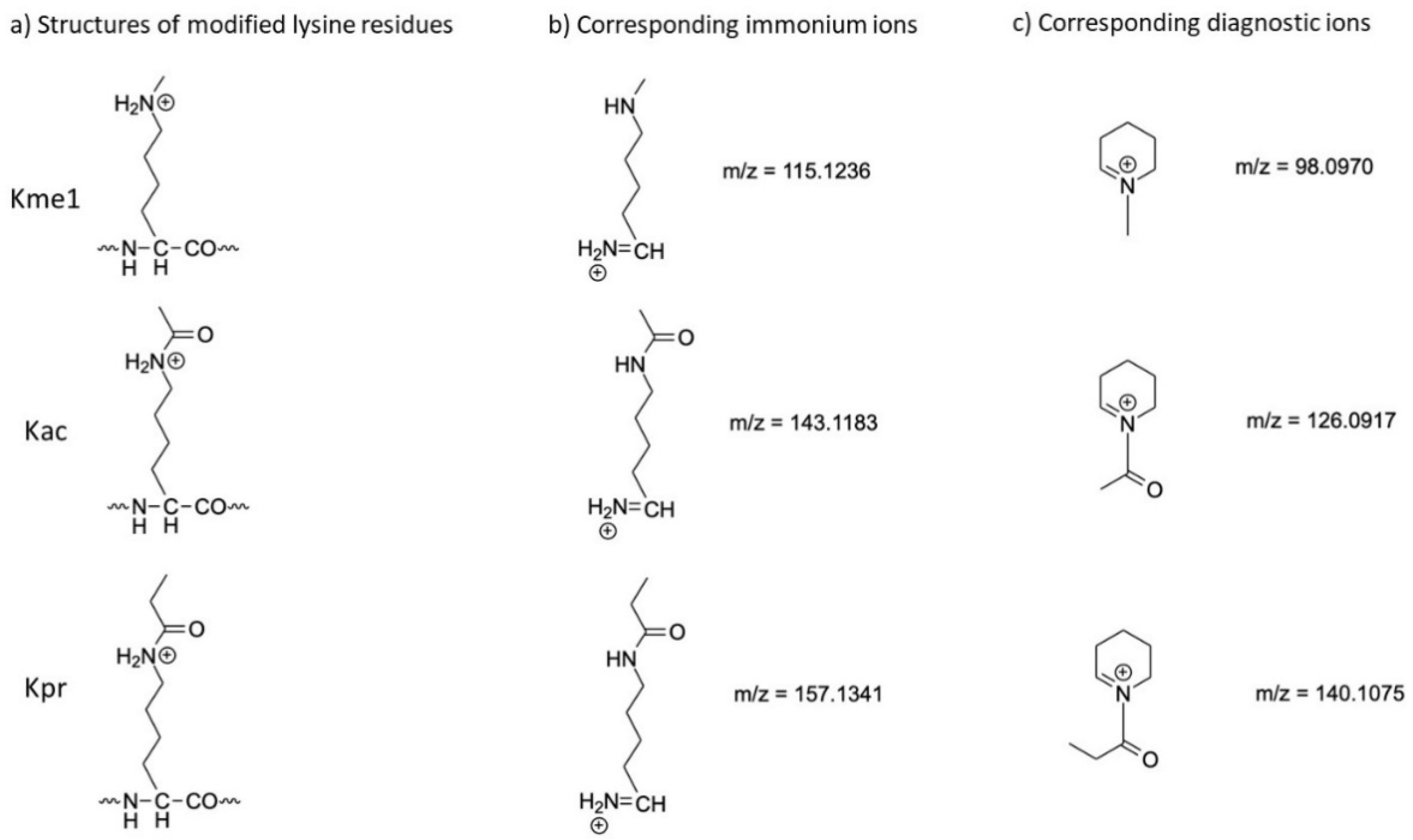
| Lysine Modification | M (Diagnostic Ion) | M (Immonium Ion) |
|---|---|---|
| non-modified | 84.0813 | 101.1079 |
| methyl | 98.0970 | 115.1236 |
| formyl | 112.0757 | 129.1023 |
| acetyl | 126.0917 | 143.1183 |
| propionyl | 140.1075 | 157.1341 |
| butyryl | 154.1226 | 171.1492 |
| crotonyl | 152.1070 | 169.1336 |
| hydroxybutyryl | 170.1176 | 187.1442 |
| lactyl | 156.1019 | 173.1285 |
| Mass | PTM | Isobaric PTM Combination 1 | Isobaric PTM Combination 2 | Isobaric PTM Combination 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 42.0106 | acetyl | formyl + methyl | -- | -- |
| 56.0262 | propionyl | acetyl + methyl | formyl + dimethyl | -- |
| 70.0419 | butyryl | propionyl + methyl | formyl + trimethyl | acetyl + dimethyl |
| 100.0160 | succinyl | malonyl + methyl | ||
| 114.0317 | glutaryl | hydroxybutyryl + formyl | malonyl + dimethyl | succinyl + methyl |
| Histone | Probable Identified Sequence | CSprec | Int (diagK27PTM) | Int (diagKpro) | Int (diagK27PTM)/Int (diagKpro) | %Max Int (diagKpro) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cano H3 | Kme1SAPATGGVKproKproPHR | 3 or 4 | 10.4 | 100 | 0.10 | 100 |
| Cano H3 | Kme3SAPATGGVKproKproPHR | 3 or 4 | N.A. (a) | 90 or 75 | ||
| H3.3 | Kme3SAPSTGGVKproKproPHR | 3 | N.A. (a) | 95 | ||
| Cano H3 | KacSAPATGGVKproKproPHR | 3 | 100 | 75 | 1.25 | 75 |
| H3.3 | KacSAPSTGGVKproKproPHR | 2 | 100 | 31 | 3.2 | 25 |
| H3mm13 | KacSVPSTGGVKproKproPHR | 3 | 3.1 | 100 | 0.03 | 97 |
| H3mm13 | KacSVPSTGGVKme2KproPHR | 4 | 95 | 100 | 0.95 | 10 |
| H3mm13 | KproSVPSTGGVKproKproPHR | 3 | N.A. | 100 | ||
| H3.3 | K(me1pro)SAPSTGGVKproKproPHR | 3 | 23 | 100 | 0.23 | 100 |
| H3.3 | K(me1pro)SAPSTGGVK(me1pro)KproPHR | 2 | 100 | 80 | 1.25 | 12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hseiky, A.; Crespo, M.; Kieffer-Jaquinod, S.; Fenaille, F.; Pflieger, D. Small Mass but Strong Information: Diagnostic Ions Provide Crucial Clues to Correctly Identify Histone Lysine Modifications. Proteomes 2021, 9, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes9020018
Hseiky A, Crespo M, Kieffer-Jaquinod S, Fenaille F, Pflieger D. Small Mass but Strong Information: Diagnostic Ions Provide Crucial Clues to Correctly Identify Histone Lysine Modifications. Proteomes. 2021; 9(2):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes9020018
Chicago/Turabian StyleHseiky, Alaa, Marion Crespo, Sylvie Kieffer-Jaquinod, François Fenaille, and Delphine Pflieger. 2021. "Small Mass but Strong Information: Diagnostic Ions Provide Crucial Clues to Correctly Identify Histone Lysine Modifications" Proteomes 9, no. 2: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes9020018
APA StyleHseiky, A., Crespo, M., Kieffer-Jaquinod, S., Fenaille, F., & Pflieger, D. (2021). Small Mass but Strong Information: Diagnostic Ions Provide Crucial Clues to Correctly Identify Histone Lysine Modifications. Proteomes, 9(2), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes9020018







