The Constitutive Proteome of Human Aqueous Humor and Race Specific Alterations
Abstract
1. Introduction
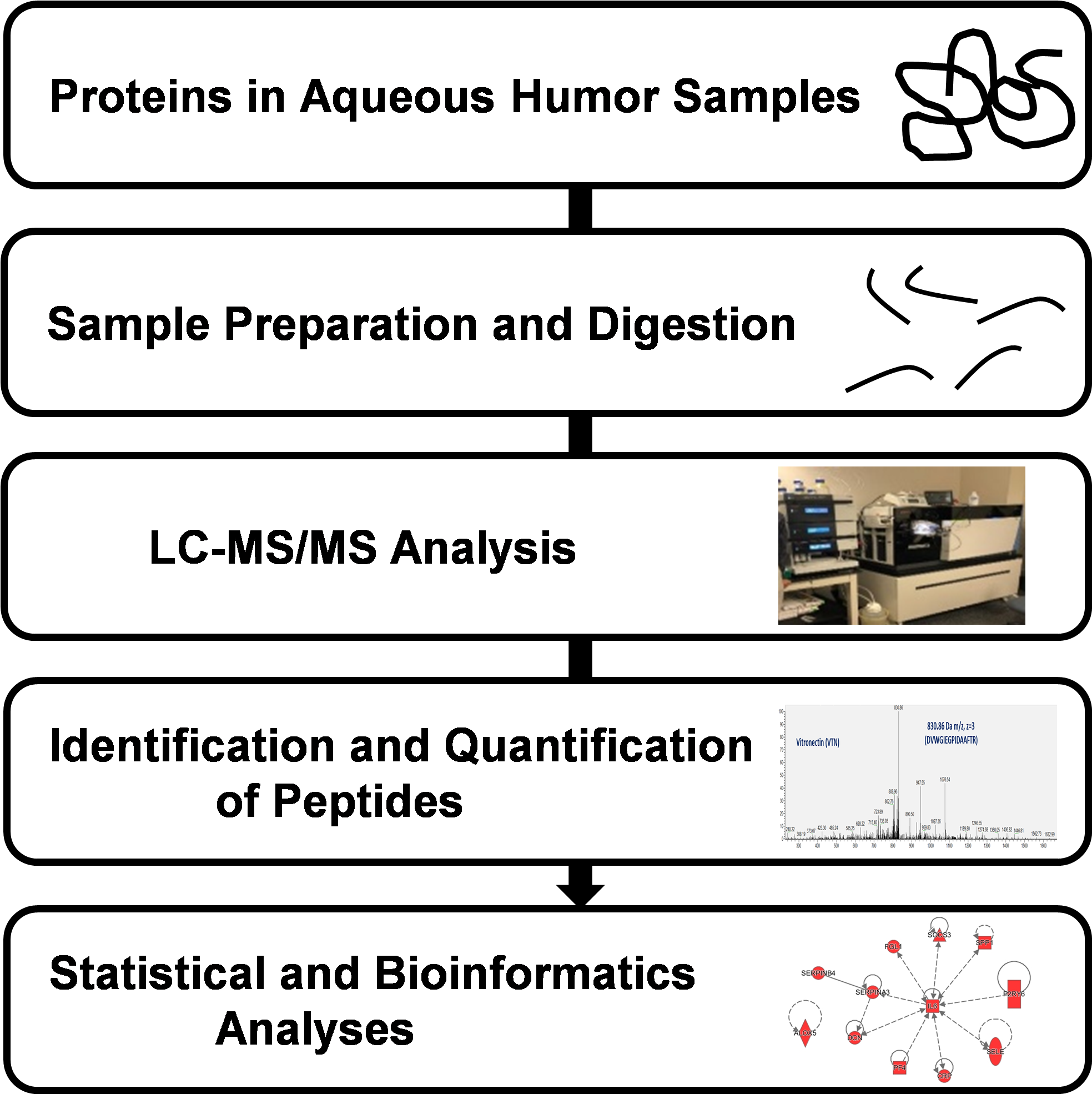
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Subjects and Sample Collection
2.2. Aqueous Humor Sample Preparation
2.3. LC-MS/MS Analysis
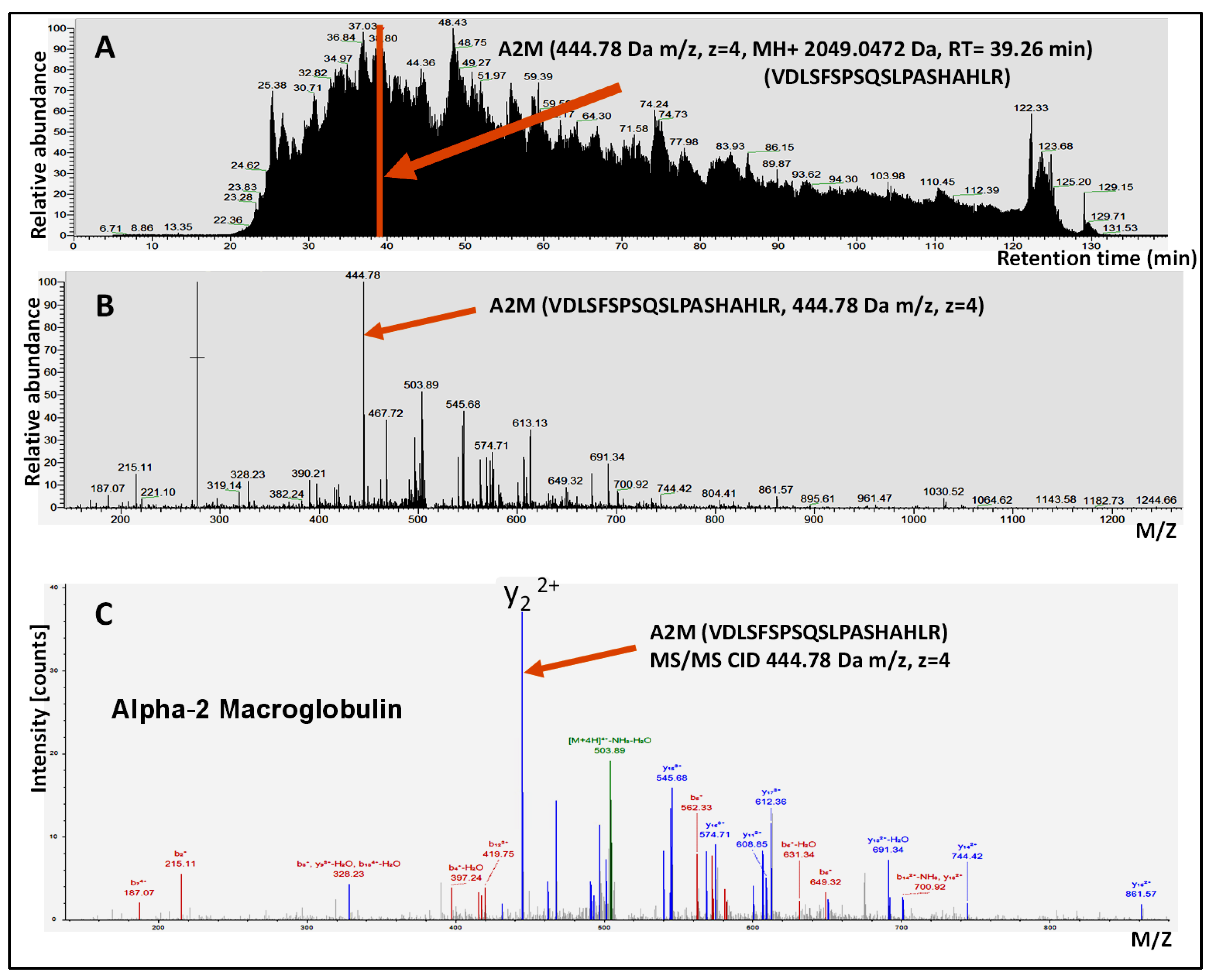
2.4. Protein Identification and Quantification
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
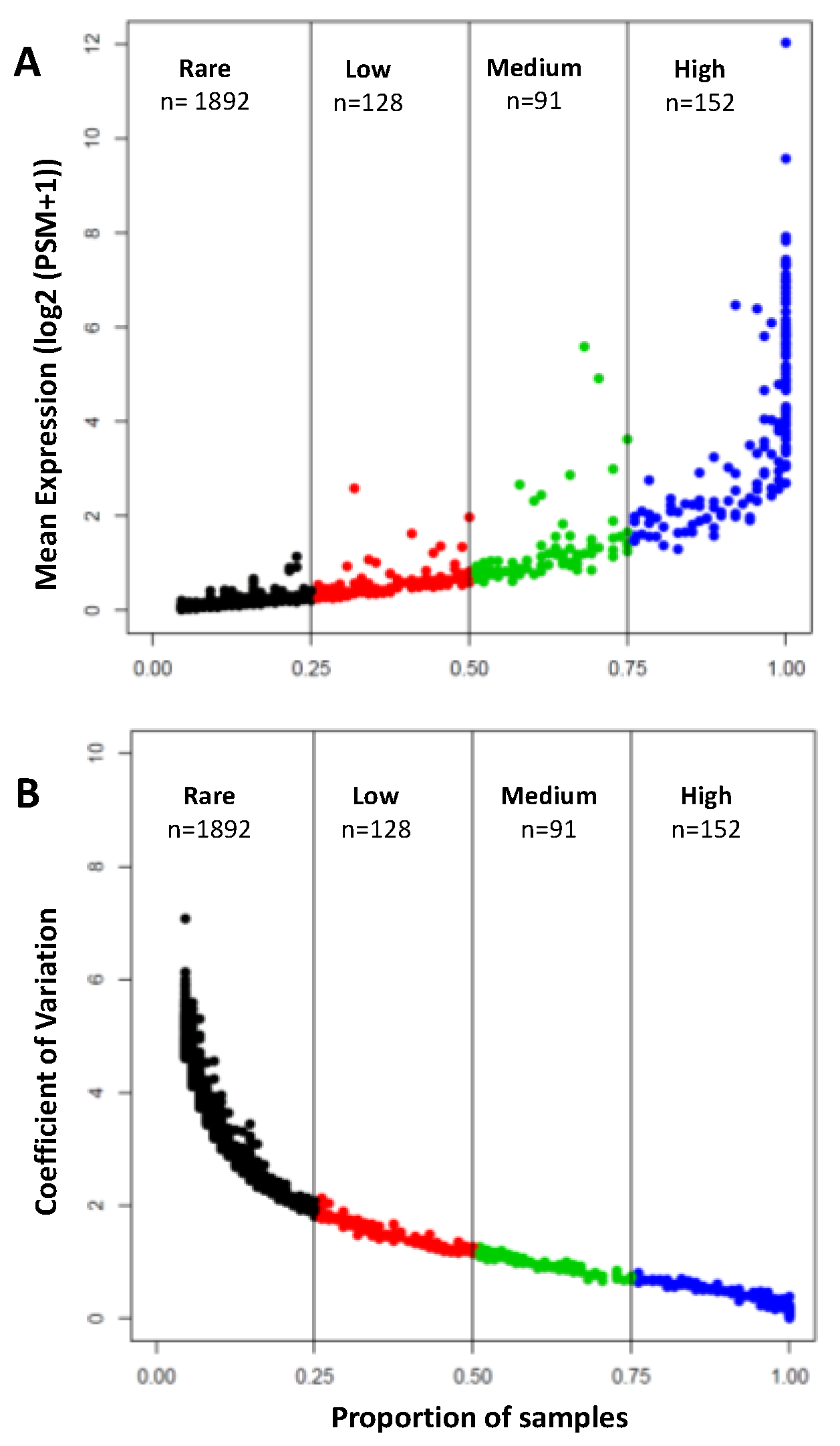
3.1. Protein Content of the Human Aqueous Humor
3.2. Major Protein Families Detected in the Human Aqueous Humor
3.3. Gene Ontology Enrichment Analysis
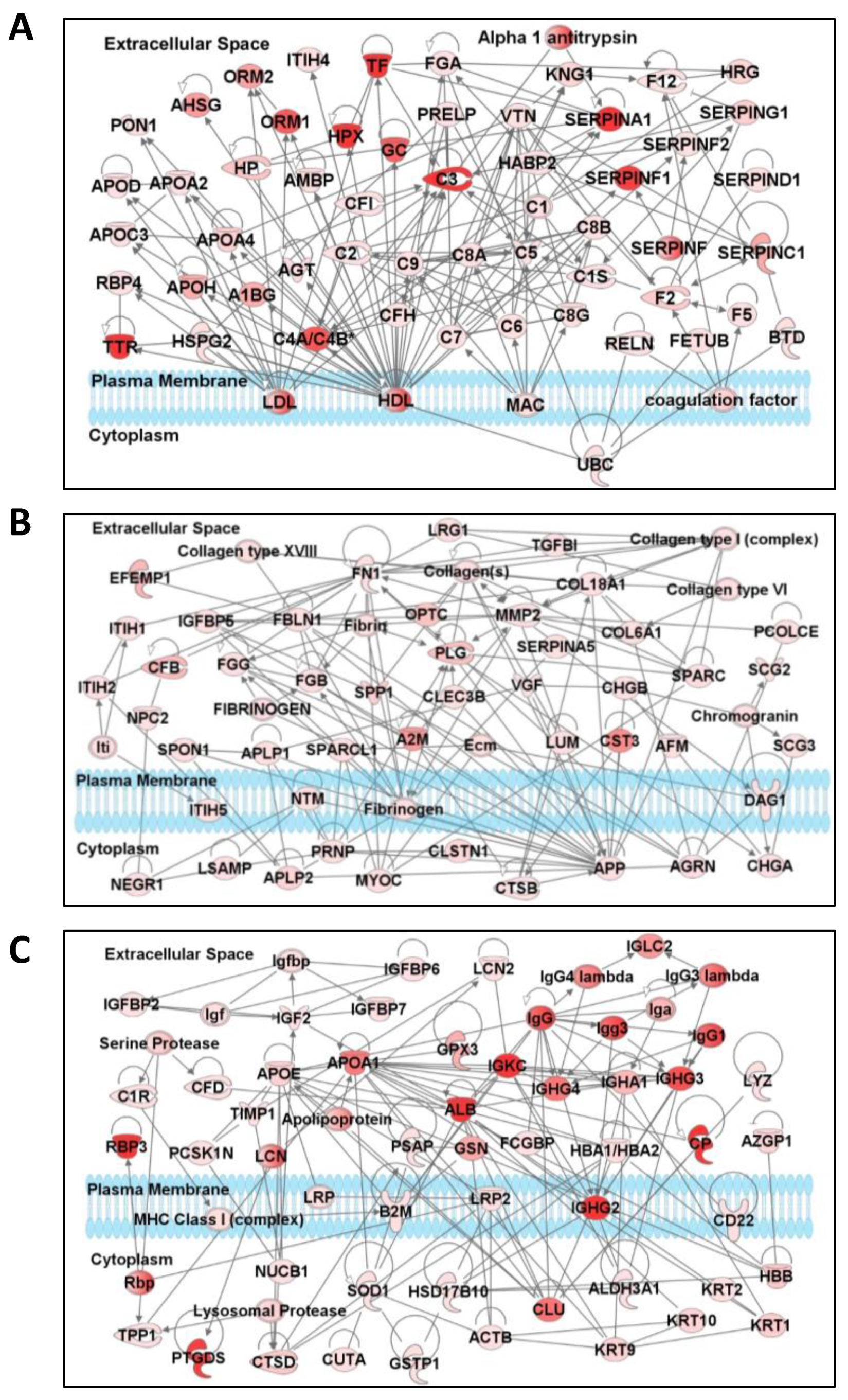
3.4. Network and Pathway Analysis
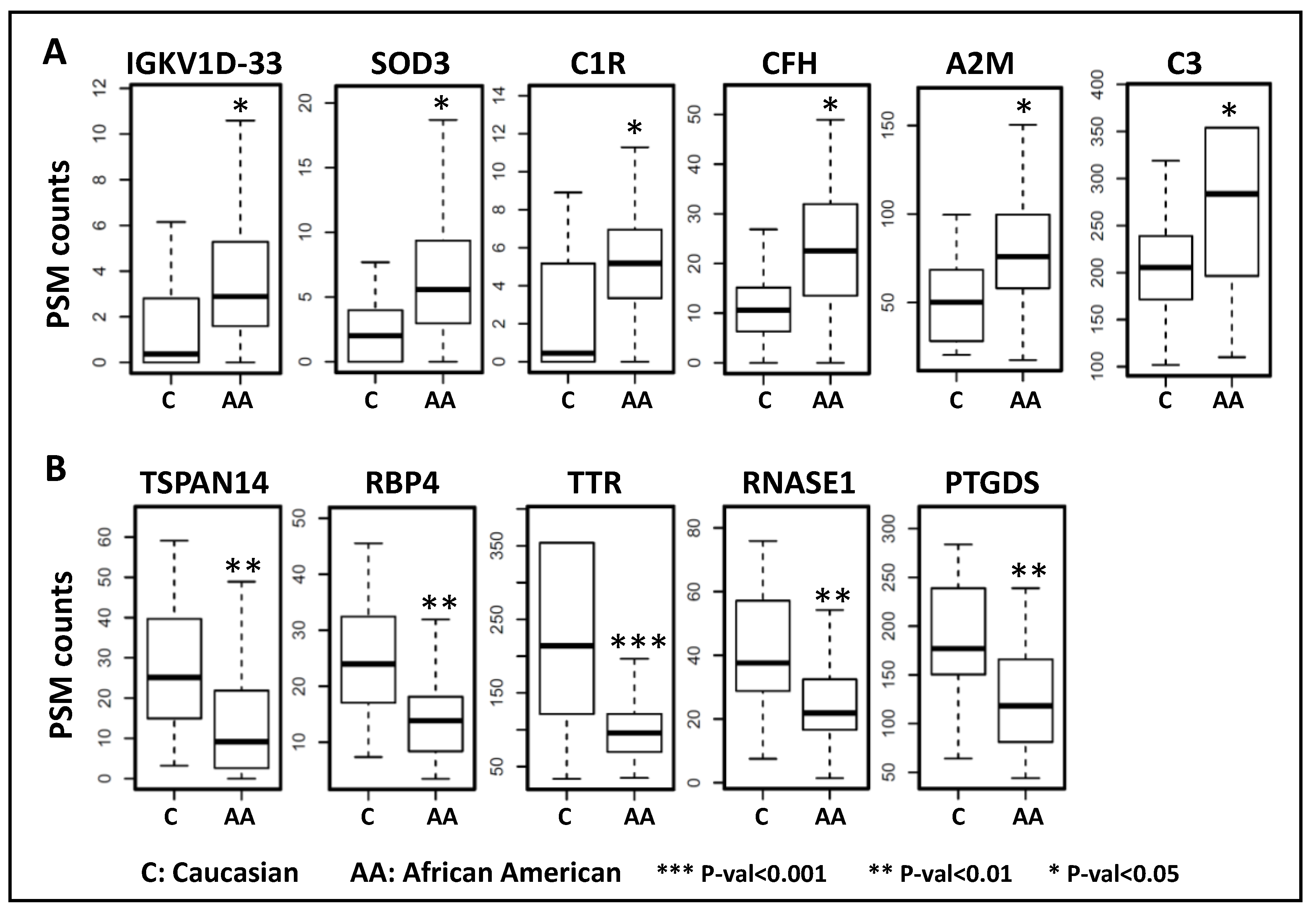
3.5. Aqueous Humor Proteins Associated with Race
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carreon, T.; Van Der Merwe, E.; Fellman, R.L.; Johnstone, M.; Bhattacharya, S.K. Aqueous Outflow—A Continuum from Trabecular Meshwork to Episcleral Veins. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2017, 57, 108–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, U.R.; Madden, B.J.; Charlesworth, M.C.; Fautsch, M.P. Proteome Analysis of Human Aqueous Humor. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 4921–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, C.-H.; Bsc, C.-W.K.; Bsc, C.-Y.C.; Shahidullah, M.; Do, C.; Shahidullah, M.; To, C. The Mechanism of Aqueous Humour Formation. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2002, 85, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, K.; Pederson, J.E. Contribution of Secretion and Filtration to Aqueous Humor Formation. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1972, 222, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fautsch, M.P.; Johnson, D.H. Aqueous Humor Outflow: What Do We Know? Where Will It Lead Us? Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 4181–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.; Goldenberg-Cohen, N.; Axer-Siegel, R.; Weinberger, V.; Cohen, Y.; Monselise, Y. Inflammatory Reaction in Acute Retinal Artery Occlusion: Cytokine Levels in Aqueous Humor and Serum. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2005, 13, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, K.R.; Rajagopalan, P.; Pinto, S.M.; Advani, J.; Murthy, P.R.; Goel, R.; Subbannayya, Y.; Balakrishnan, L.; Dash, M.; Anil, A.K.; et al. Proteomics of Human Aqueous Humor. OMICS 2015, 19, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grus, F.H.; Joachim, S.C.; Pfeiffer, N. Proteomics in Ocular Fluids. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2007, 1, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barsotti, M.F.; Bartels, S.P.; Freddo, T.F.; Kamm, R.D. The Source of Protein in the Aqueous Humor of the Normal Monkey Eye. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1992, 33, 581–595. [Google Scholar]
- Freddo, T.F.; Bartels, S.P.; Barsotti, M.F.; Kamm, R.D. The Source of Proteins in the Aqueous Humor of the Normal Rabbit. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1990, 31, 125–137. [Google Scholar]
- McLaren, J.W.; Ziai, N.; Brubaker, R.F. A Simple Three-compartment Model of Anterior Segment Kinetics. Exp. Eye Res. 1993, 56, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kliuchnikova, A.A.; Samokhina, N.I.; Ilina, I.Y.; Karpov, D.; Pyatnitskiy, M.A.; Kuznetsova, K.G.; Toropygin, I.Y.; Kochergin, S.A.; Alekseev, I.B.; Zgoda, V.G.; et al. Human Aqueous Humor Proteome in Cataract, Glaucoma, and Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome. Proteomics 2016, 16, 1938–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funke, S.; Perumal, N.; Bell, K.; Pfeiffer, N.; Grus, F.H. The Potential Impact of Recent Insights Into Proteomic Changes Associated With Glaucoma. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2017, 14, 311–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaeslin, M.A.; Killer, H.E.; Fuhrer, C.A.; Zeleny, N.; Huber, A.R.; Neutzner, A. Changes to the Aqueous Humor Proteome during Glaucoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzotti, A.; Longobardi, M.; Cartiglia, C.; Saccà, S.C. Proteome Alterations in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Aqueous Humor. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 4831–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Lu, Q.; Xue, P.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Z.; Yang, F.; Wang, N. Proteomic Analysis of Aqueous Humor From Patients With Myopia. Mol. Vis. 2008, 14, 370–377. [Google Scholar]
- Semba, R.D.; Enghild, J.J.; Venkatraman, V.; Dyrlund, T.F.; Van Eyk, J.E. The Human Eye Proteome Project: Perspectives on an Emerging Proteome. Proteomics 2013, 13, 2500–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.-Y.; Tsai, M.-L.; Wang, C.-Y.; Chen, A.; Chou, Y.-C.; Hsia, C.-W.; Wu, Y.-F.; Chen, H.-M.; Huang, T.-H.; Chen, P.-H.; et al. Proteomic Analysis and Identification of Aqueous Humor Proteins With a Pathophysiological Role in Diabetic Retinopathy. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 2950–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Kang, J.W.; Ahn, J.; Lee, E.K.; Cho, K.-C.; Han, B.N.R.; Hong, N.Y.; Park, J.; Kim, K.P. Proteomic Analysis of the Aqueous Humor in Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) Patients. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 4034–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Bollinger, K.E.; Kodeboyina, S.K.; Zhi, W.; Patton, J.; Bai, S.; Edwards, B.; Ulrich, L.; Bogorad, D.; Sharma, A. Proteomic Alterations in Aqueous Humor From Patients With Primary Open Angle Glaucoma. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 2635–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Xue, P.; Wang, N.; Dong, Z.; Lu, Q.; Yang, F. Proteomic Analysis of Aqueous Humor from Patients with Primary Open Angle Glaucoma. Mol. Vis. 2010, 16, 2839–2846. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhuang, M.; Wang, F.; Chen, X.; Hang, H.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Q. Proteomic Analysis of the Aqueous Humor in Patients With Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2013, 7, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Määttä, M.; Tervahartiala, T.; Harju, M.; Airaksinen, J.; Autio-Harmainen, H.; Sorsa, T. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Tissue Inhibitors in Aqueous Humor of Patients With Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma, Exfoliation Syndrome, and Exfoliation Glaucoma. J. Glaucoma 2005, 14, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcan, A.A.; Ozdemir, N.; Canataroglu, A. The Aqueous Levels of TGF- 2 in Patients with Glaucoma. Int. Ophthalmol. 2004, 25, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.-H.; Lim, D.; Park, K.H.; Chae, J.-B.; Jang, H.; Lee, J.; Chung, H. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Aqueous Humor From Patients With Drusen and Reticular Pseudodrusen in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018, 18, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, M.A. Protein Identification by Mass Spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2003, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Girolamo, F.; Lante, I.; Muraca, M.; Putignani, L. The Role of Mass Spectrometry in the “Omics” Era. Curr. Org. Chem. 2013, 17, 2891–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Csordas, A.; Bai, J.; Bernal-Llinares, M.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Inuganti, A.; Griss, J.; Mayer, G.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The Pride Database and Related Tools and Resources in 2019: Improving Support for Quantification Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D442–D450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Kawaji, T.; Tanihara, H. Elevated Levels of Multiple Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease in the Aqueous Humor of Eyes With Open-Angle Glaucoma. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 5353–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Z.; Ke, M.; Chen, X. Identification of Proteins in the Aqueous Humor Associated With Cataract Development Using iTRAQ Methodology. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 3111–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, D.K.; Sarin, G.S.; Saha, K. Immunoglobulins in Human Aqueous Humour. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1977, 61, 216–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, I.; Kaur, J.; Sooraj, K.; Goswami, S.; Saxena, R.; Chauhan, V.S.; Sihota, R. Comparative Evaluation of the Aqueous Humor Proteome of Primary Angle Closure and Primary Open Angle Glaucomas and Age-Related Cataract Eyes. Int. Ophthalmol. 2018, 39, 69–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoen, T.J.; Waldbillig, R.J.; Searcy, G.; Gaudet, S.J.; Jones, B.E.; Chader, G.J.; Moshyedi, P. Identification and Partial Characterization of a Proteinase Specific for Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 in Aqueous and Vitreous Humors. Curr. Eye Res. 1995, 14, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Safieh, L.; Abboud, E.B.; Alkuraya, H.; Shamseldin, H.; Al-Enzi, S.; Al-Abdi, L.; Hashem, M.; Colak, D.; Jarallah, A.; Ahmad, H.; et al. Mutation of IGFBP7 Causes Upregulation of BRAF/MEK/ERK Pathway and Familial Retinal Arterial Macroaneurysms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 89, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.V.; Calzi, S.L.; Shaw, L.C.; Kielczewski, J.L.; Korah, H.E.; Grant, M.B. An Ocular View of the IGF–IGFBP System. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2013, 23, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-H.; Lin, S.-T.; Chou, H.-C.; Lee, Y.-R.; Chan, H.-L. Proteomic Analysis of Retinopathy-Related Plasma Biomarkers in Diabetic Patients. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 529, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Mo, J.S.; Kaplan, H.; Cooper, N.G. Early Involvement of Immune/Inflammatory Response Genes in Retinal Degeneration in DBA/2J Mice. Ophthalmol. Eye Dis. 2010, 2010, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescosolido, N.; Barbato, A.; Pascarella, A.; Giannotti, R.; Genzano, M.; Nebbioso, M. Role of Protease-Inhibitors in Ocular Diseases. Molecules 2014, 19, 20557–20569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhli-Hattenbach, C.; Jochmans, K.; Scharrer, I.; Lüchtenberg, M.; Hattenbach, L.O. Retinal Vein Occlusion Associated with Antithrombin Deficiency Secondary to a Novel G9840C Missense Mutation. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2006, 124, 1165–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, N.; Imaizumi, M.; Miyashiro, M.; Arichi, M.; Matsuoka, M.; Ando, A.; Matsumura, M. Low Levels of Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor in Highly Myopic Eyes with Chorioretinal Atrophy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 140, 937–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filleur, S.; Nelius, T.; De Riese, W.; Kennedy, R. Characterization of PEDF: A Multi-Functional Serpin Family Protein. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 106, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becerra, S.; Sagasti, A.; Spinella, P.; Notario, V. Pigment Epithelium-derived Factor Behaves Like a Noninhibitory Serpin: Neurotrophic Activity Does Not Require the Serpin Reactive Loop. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 25992–25999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rychli, K.; Huber, K.; Wojta, J. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor (PEDF) as a Therapeutic Target in Cardiovascular Disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2009, 13, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno-Matsui, K.; Morita, I.; Tombran-Tink, J.; Mrazek, D.; Onodera, M.; Uetama, T.; Hayano, M.; Murota, S.-I.; Mochizuki, M. Novel Mechanism for Age-Related Macular Degeneration: An Equilibrium Shift Between the Angiogenesis Factors VEGF and PEDF. J. Cell. Physiol. 2001, 189, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, J.-P.; Yao, Y.-F. Contribution of VEGF and PEDF to Choroidal Angiogenesis: A Need for Balanced Expressions. Clin. Biochem. 2006, 39, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, R.; Shimizu, T.; Yamagishi, S.-I.; Shibaki, A.; Amano, S.; Inagaki, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Sugawara, H.; Nakamura, H.; Takeuchi, M.; et al. Overexpression of Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor Decreases Angiogenesis and Inhibits the Growth of Human Malignant Melanoma Cells In Vivo. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funatsu, H.; Yamashita, H.; Nakamura, S.; Mimura, T.; Eguchi, S.; Noma, H.; Hori, S. Vitreous Levels of Pigment Epithelium–Derived Factor and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Are Related to Diabetic Macular Edema. Ophthalmology 2006, 113, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.E.; Mejia, P.; Lu, F. Biological Activities of C1 Inhibitor. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 4057–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, R.N.; Buckle, A.M.; Le Bonniec, B.F.; Church, F.C. Control of the coagulation system by serpins. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 4842–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, M.G. Eye-Opening Potential for Tetraspanin Tspan12 as a Therapeutic Target for Diseases of the Retinal Vasculature. Circulation 2017, 136, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.M.; Nelson, C.; Tarlé, S.A.; Pribila, J.T.; Bardakjian, T.; Woods, S.; Schneider, A.; Glaser, T. Biochemical Basis for Dominant Inheritance, Variable Penetrance, and Maternal Effects in RBP4 Congenital Eye Disease. Cell 2015, 161, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaiya, S.; Zhou, Z.; Chalam, K. Characterization of Vitreous and Aqueous Proteome in Humans With Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy and Its Clinical Correlation. Proteom. Insights 2017, 8, 1178641816686078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | Count |
|---|---|
| Subjects, (n) | 88 |
| Sex: F/M | 55/33 |
| Age (years) | 67.0 ± 9.56 |
| Race: AA/Caucasian | 66/22 |
| Hypertension, N/Y | 41/47 |
| Smoking, N/Y | 56/32 |
| Cardiovascular disease, N/Y | 81/7 |
| Cerebrovascular disease, N/Y | 87/1 |
| Collagen vascular disease, N/Y | 75/13 |
| Intraocular Pressure (IOP) | 19.5 ± 7.01 |
| Uniprot ID | Gene Symbol | Description | Detected in Proportion of Samples (%) | Mean PSM Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P02768 | ALB | Albumin | 100.00 | 4202.61 |
| P02787 | TF | Serotransferrin | 100.00 | 765.31 |
| P01024 | C3 | Complement C3 | 100.00 | 255.00 |
| P01009 | SERPINA1 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin | 100.00 | 233.24 |
| P02790 | HPX | Hemopexin | 100.00 | 176.64 |
| P01859 | IGHG2 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 2 | 100.00 | 168.92 |
| P10745 | RBP3 | Retinol-binding protein 3 | 100.00 | 166.25 |
| P00450 | CP | Ceruloplasmin | 100.00 | 165.20 |
| P01834 | IGKC | Immunoglobulin kappa constant | 100.00 | 161.42 |
| P02766 | TTR | Transthyretin | 100.00 | 156.30 |
| P41222 | PTGDS | Prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase | 100.00 | 142.25 |
| P36955 | SERPINF1 | Pigment epithelium-derived factor | 100.00 | 141.33 |
| P01860 | IGHG3 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 3 | 100.00 | 127.65 |
| P02763 | ORM1 | Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 1 | 100.00 | 119.16 |
| P02774 | GC | Vitamin D-binding protein | 100.00 | 115.89 |
| P0DOX7 | N/A | Immunoglobulin kappa light chain | 100.00 | 108.22 |
| P10909 | CLU | Clusterin | 100.00 | 102.33 |
| P02647 | APOA1 | Apolipoprotein A-I | 100.00 | 96.78 |
| P01034 | CST3 | Cystatin-C | 100.00 | 82.73 |
| P02765 | AHSG | Alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein | 100.00 | 73.27 |
| P01023 | A2M | Alpha-2-macroglobulin | 100.00 | 72.77 |
| P19652 | ORM2 | Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 2 | 100.00 | 68.70 |
| P06396 | GSN | Gelsolin | 100.00 | 62.66 |
| P01008 | SERPINC1 | Antithrombin-III | 100.00 | 62.65 |
| P02749 | APOH | Beta-2-glycoprotein 1 | 100.00 | 59.09 |
| P04217 | A1BG | Alpha-1B-glycoprotein | 100.00 | 59.04 |
| P22352 | GPX3 | Glutathione peroxidase 3 | 100.00 | 58.23 |
| Q9UBP4 | DKK3 | Dickkopf-related protein 3 | 100.00 | 56.91 |
| P01011 | SERPINA3 | Alpha-1-antichymotrypsin | 100.00 | 53.15 |
| P01876 | IGHA1 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant alpha 1 | 100.00 | 51.83 |
| Q12805 | EFEMP1 | EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 1 | 100.00 | 50.79 |
| P00751 | CFB | Complement factor B | 100.00 | 50.35 |
| Q13822 | ENPP2 | Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 2 | 100.00 | 45.77 |
| P00747 | PLG | Plasminogen | 100.00 | 45.45 |
| Q9UBM4 | OPTC | Opticin | 100.00 | 43.07 |
| P07339 | CTSD | Cathepsin D | 100.00 | 39.10 |
| P00734 | F2 | Prothrombin | 100.00 | 38.21 |
| P05155 | SERPING1 | Plasma protease C1 inhibitor | 100.00 | 35.94 |
| P10451 | SPP1 | Osteopontin | 100.00 | 35.94 |
| P06727 | APOA4 | Apolipoprotein A-IV | 100.00 | 33.93 |
| P02649 | APOE | Apolipoprotein E | 100.00 | 32.43 |
| P01042 | KNG1 | Kininogen-1 | 100.00 | 30.10 |
| P04196 | HRG | Histidine-rich glycoprotein | 100.00 | 29.90 |
| P25311 | AZGP1 | Zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein | 100.00 | 29.67 |
| P07998 | RNASE1 | Ribonuclease pancreatic | 100.00 | 29.30 |
| O94985 | CLSTN1 | Calsyntenin-1 | 100.00 | 27.54 |
| P01019 | AGT | Angiotensinogen | 100.00 | 26.00 |
| P02760 | AMBP | Protein AMBP | 100.00 | 24.23 |
| P02652 | APOA2 | Apolipoprotein A-II | 100.00 | 20.83 |
| P36222 | CHI3L1 | Chitinase-3-like protein 1 | 100.00 | 20.03 |
| P23142 | FBLN1 | Fibulin-1 | 100.00 | 19.91 |
| P02750 | LRG1 | Leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein | 100.00 | 18.87 |
| P05156 | CFI | Complement factor I | 100.00 | 18.82 |
| P02753 | RBP4 | Retinol-binding protein 4 | 100.00 | 17.09 |
| P04004 | VTN | Vitronectin | 100.00 | 16.58 |
| Q16270 | IGFBP7 | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 | 100.00 | 15.10 |
| P51884 | LUM | Lumican | 100.00 | 13.89 |
| P00746 | CFD | Complement factor D | 100.00 | 13.10 |
| P05090 | APOD | Apolipoprotein D | 100.00 | 12.66 |
| O43505 | B4GAT1 | Beta-1,4-glucuronyltransferase 1 | 100.00 | 12.09 |
| P24592 | IGFBP6 | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 6 | 100.00 | 11.28 |
| Q96PD5 | PGLYRP2 | N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase | 100.00 | 11.19 |
| Q14515 | SPARCL1 | SPARC-like protein 1 | 100.00 | 11.01 |
| P61916 | NPC2 | NPC intracellular cholesterol transporter 2 | 100.00 | 9.57 |
| Q99969 | RARRES2 | Retinoic acid receptor responder protein 2 | 100.00 | 8.03 |
| P61769 | B2M | Beta-2-microglobulin | 100.00 | 7.77 |
| Q99714 | HSD17B10 | 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase type-2 | 100.00 | 7.61 |
| Q06481 | APLP2 | Amyloid-like protein 2 | 98.86 | 30.95 |
| P43652 | AFM | Afamin | 98.86 | 17.18 |
| Q8IZJ3 | CPAMD8 | C3 and PZP-like alpha-2-macroglobulin domain-containing protein 8 | 98.86 | 17.14 |
| Q14767 | LTBP2 | Latent-transforming growth factor beta-binding protein 2 | 98.86 | 15.82 |
| Q15582 | TGFBI | Transforming growth factor-beta-induced protein ig-h3 | 98.86 | 14.68 |
| Q9Y5W5 | WIF1 | Wnt inhibitory factor 1 | 98.86 | 14.39 |
| Q08629 | SPOCK1 | Testican-1 | 98.86 | 8.93 |
| P07602 | PSAP | Prosaposin | 98.86 | 7.48 |
| Q08380 | LGALS3BP | Galectin-3-binding protein | 98.86 | 6.67 |
| P00748 | F12 | Coagulation factor XII | 98.86 | 6.06 |
| P0DOY2 | IGLC2 | Immunoglobulin lambda constant 2 | 97.73 | 75.13 |
| P16870 | CPE | Carboxypeptidase E | 97.73 | 18.17 |
| Q9HCB6 | SPON1 | Spondin-1 | 97.73 | 10.63 |
| P06312 | IGKV4-1 | Immunoglobulin kappa variable 4-1 | 97.73 | 6.06 |
| P51888 | PRELP | Prolargin | 97.73 | 5.19 |
| P0DOX8 | N/A | Immunoglobulin lambda-1 light chain | 96.59 | 64.10 |
| P00738 | HP | Haptoglobin | 96.59 | 43.35 |
| P08603 | CFH | Complement factor H | 96.59 | 20.12 |
| Q8NG11 | TSPAN14 | Tetraspanin-14 | 96.59 | 17.09 |
| Q14624 | ITIH4 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4 | 96.59 | 14.89 |
| Q99972 | MYOC | Myocilin | 96.59 | 8.76 |
| Q9NQ79 | CRTAC1 | Cartilage acidic protein 1 | 96.59 | 8.24 |
| P01861 | IGHG4 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 4 | 95.45 | 99.95 |
| P35555 | FBN1 | Fibrillin-1 | 95.45 | 12.27 |
| Q9BSG5 | RTBDN | Retbindin | 95.45 | 6.64 |
| P05452 | CLEC3B | Tetranectin | 95.45 | 6.41 |
| Q92520 | FAM3C | Protein FAM3C | 95.45 | 5.67 |
| Q86UP8 | GTF2IRD2 | General transcription factor II-I repeat domain-containing protein 2A | 95.45 | 5.51 |
| P02748 | C9 | Complement component C9 | 94.32 | 13.93 |
| O14773 | TPP1 | Tripeptidyl-peptidase 1 | 94.32 | 5.24 |
| P01033 | TIMP1 | Metalloproteinase inhibitor 1 | 94.32 | 3.64 |
| Q15113 | PCOLCE | Procollagen C-endopeptidase enhancer 1 | 94.32 | 3.45 |
| P01700 | IGLV1-47 | Immunoglobulin lambda variable 1-47 | 93.18 | 4.61 |
| P0C0L5 | C4B | Complement C4-B | 92.05 | 124.58 |
| P08697 | SERPINF2 | Alpha-2-antiplasmin | 92.05 | 9.18 |
| A0A0C4DH25 | IGKV3D-20 | Immunoglobulin kappa variable 3D-20 | 92.05 | 6.28 |
| P10643 | C7 | Complement component C7 | 92.05 | 4.08 |
| P19022 | CDH2 | Cadherin-2 | 92.05 | 3.83 |
| P19823 | ITIH2 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H2 | 90.91 | 10.06 |
| Q5T3U5 | ABCC10 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 7 | 90.91 | 5.73 |
| P51693 | APLP1 | Amyloid-like protein 1 | 89.77 | 4.08 |
| P07357 | C8A | Complement component C8 alpha chain | 89.77 | 3.88 |
| P20273 | CD22 | B-cell receptor CD22 | 88.64 | 15.02 |
| P98160 | HSPG2 | Basement membrane-specific heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein | 88.64 | 5.82 |
| Q5T8P6 | RBM26 | RNA-binding protein 26 | 88.64 | 4.68 |
| Q9Y287 | ITM2B | Integral membrane protein 2B | 88.64 | 3.43 |
| P39060 | COL18A1 | Collagen alpha-1(XVIII) chain | 88.64 | 2.36 |
| P18065 | IGFBP2 | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2 | 87.50 | 3.78 |
| P10645 | CHGA | Chromogranin-A | 87.50 | 3.71 |
| P05067 | APP | Amyloid-beta precursor protein | 86.36 | 10.08 |
| P08294 | SOD3 | Extracellular superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] | 86.36 | 5.86 |
| Q92765 | FRZB | Secreted frizzled-related protein 3 | 86.36 | 4.79 |
| Q96S96 | PEBP4 | Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 4 | 86.36 | 3.76 |
| P01780 | IGHV3-7 | Immunoglobulin heavy variable 3-7 | 85.23 | 4.97 |
| Q9HCJ0 | TNRC6C | Trinucleotide repeat-containing gene 6C protein | 85.23 | 3.70 |
| O15240 | VGF | Neurosecretory protein VGF | 85.23 | 2.74 |
| P02675 | FGB | Fibrinogen beta chain | 84.09 | 6.75 |
| P55083 | MFAP4 | Microfibril-associated glycoprotein 4 | 84.09 | 2.81 |
| P22914 | CRYGS | Gamma-crystallin S | 82.95 | 6.40 |
| P00441 | SOD1 | Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] | 82.95 | 2.84 |
| P34096 | RNASE4 | Ribonuclease 4 | 82.95 | 1.81 |
| Q9Y6R7 | FCGBP | IgGFc-binding protein | 81.82 | 6.89 |
| O75326 | SEMA7A | Semaphorin-7A | 81.82 | 5.49 |
| P00736 | C1R | Complement C1r subcomponent | 81.82 | 4.49 |
| Q9BZV3 | IMPG2 | Interphotoreceptor matrix proteoglycan 2 | 80.68 | 3.07 |
| A0A087WSY6 | IGKV3D-15 | Immunoglobulin kappa variable 3D-15 | 80.68 | 2.17 |
| P61626 | LYZ | Lysozyme C | 79.55 | 4.83 |
| P43251 | BTD | Biotinidase | 79.55 | 2.71 |
| P06733 | ENO1 | Alpha-enolase | 78.41 | 12.05 |
| P29622 | SERPINA4 | Kallistatin | 78.41 | 5.03 |
| P05546 | SERPIND1 | Heparin cofactor 2 | 78.41 | 5.03 |
| P08185 | SERPINA6 | Corticosteroid-binding globulin | 78.41 | 3.86 |
| Q7Z7G0 | ABI3BP | Target of Nesh-SH3 | 78.41 | 2.72 |
| P04406 | GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 77.27 | 5.63 |
| P01593 | IGKV1D-33 | Immunoglobulin kappa variable 1D-33 | 77.27 | 2.93 |
| P02679 | FGG | Fibrinogen gamma chain | 76.14 | 4.92 |
| Q66K66 | TMEM198 | Transmembrane protein 198 | 76.14 | 4.40 |
| P02656 | APOC3 | Apolipoprotein C-III | 76.14 | 3.19 |
| P13671 | C6 | Complement component C6 | 76.14 | 2.96 |
| Q99574 | SERPINI1 | Neuroserpin | 76.14 | 2.38 |
| P04264 | KRT1 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1 | 75.00 | 36.86 |
| Q9UHG2 | PCSK1N | ProSAAS | 75.00 | 3.28 |
| P08571 | CD14 | Monocyte differentiation antigen CD14 | 75.00 | 2.48 |
| Q86UD1 | OAF | Out at first protein homolog | 75.00 | 2.12 |
| P98164 | LRP2 | Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 2 | 75.00 | 1.84 |
| Family | Level | Proteins | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apolipoproteins | High | APOA1 | APOA2 | APOA4 | APOC3 | APOD |
| APOE | APOH | |||||
| Medium | ||||||
| Low | ||||||
| Rare | APOB | APOC1 | APOF | APOL1 | APOLD1 | |
| Complement Proteins | High | C1R | C3 | C4B | C6 | C7 |
| C8A | C9 | CFB | CFD | CFH | ||
| CFI | ||||||
| Medium | C1S | C2 | C4A | C5 | C8B | |
| C8G | ||||||
| Low | C1QC | CFHR1 | CFHR2 | |||
| Rare | C1QB | C1QTNF6 | C1QTNF7 | C1RL | CD55 | |
| Immunoglobulins | High | IGHA1 | IGHG2 | IGHG3 | IGHG4 | IGHV3-7 |
| IGKC | IGKV1D-33 | IGKV3D-15 | IGKV3D-20 | IGKV4-1 | ||
| IGLC2 | IGLV1-47 | |||||
| Medium | IGHV3-49 | IGHV5-51 | IGHV6-1 | IGKV1-8 | IGKV2-28 | |
| IGLV1-40 | IGLV3-9 | |||||
| Low | IGHG1 | IGHM | IGHV3-66 | IGHV4-59 | IGKV1-6 | |
| IGKV1D-13 | IGKV3D-11 | IGLV6-57 | ||||
| Rare | IGDCC4 | IGHA2 | IGHV1-2 | IGHV1-3 | IGHV1-18 | |
| IGHV1-46 | IGHV1-69 | IGHV2-26 | IGHV2-70D | IGHV3-9 | ||
| IGHV3-15 | IGHV3-64D | IGHV3-72 | IGHV3-74 | IGKV1-5 | ||
| IGKV1-16 | IGKV1-17 | IGKV1-27 | IGKV3-11 | IGKV3-20 | ||
| IGLV1-44 | IGLV1-51 | IGLV2-11 | IGLV2-14 | IGLV2-18 | ||
| IGLV3-10 | IGLV3-19 | IGLV3-21 | IGSF10 | IGSF21 | ||
| IGSF22 | ILDR1 | ISLR | JCHAIN | |||
| Insulin Growth Factor (IGF) Family | High | IGFBP2 | IGFBP6 | IGFBP7 | ||
| Medium | IGF2 | IGFBP5 | ||||
| Low | IGFALS | IGFBP3 | ||||
| Rare | IGF1R | IGF2BP1 | IGFBP4 | |||
| Serine Protease Inhibitors (SERPINs) | High | SERPINA1 | SERPINA3 | SERPINA4 | SERPINA6 | SERPINC1 |
| SERPIND1 | SERPINF1 | SERPINF2 | SERPING1 | SERPINI1 | ||
| Medium | SERPINA5 | SERPINA7 | ||||
| Low | ||||||
| Rare | SERPINB3 | SERPINB13 | SERPINE3 | SERPINH1 |
| Canonical Pathway | p-Value | # of Proteins |
|---|---|---|
| Acute Phase Response Signaling | 5.01 × 10−42 | 40 |
| LXR/RXR Activation | 5.01 × 10−38 | 33 |
| FXR/RXR Activation | 1.00 × 10−35 | 32 |
| Complement System | 1.00 × 10−24 | 17 |
| Coagulation System | 2.00 × 10−19 | 14 |
| Clathrin-mediated Endocytosis Signaling | 1.58 × 10−12 | 18 |
| Atherosclerosis Signaling | 3.98 × 10−12 | 15 |
| IL-12 Signaling and Production in Macrophages | 1.00 × 10−10 | 14 |
| Extrinsic Prothrombin Activation Pathway | 1.15 × 10−10 | 7 |
| Intrinsic Prothrombin Activation Pathway | 3.55 × 10−10 | 9 |
| Production of Nitric Oxide and Reactive Oxygen Species in Macrophages | 1.02 × 10−8 | 14 |
| Hepatic Fibrosis/Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation | 6.92 × 10−8 | 13 |
| Maturity Onset Diabetes of Young (MODY) Signaling | 1.74 × 10−7 | 8 |
| Airway Pathology in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | 3.63 × 10−6 | 9 |
| Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Signaling | 4.68 × 10−6 | 12 |
| Neuroprotective Role of THOP1 in Alzheimer’s Disease | 2.63 × 10−5 | 8 |
| GP6 Signaling Pathway | 2.29 × 10−4 | 7 |
| Iron homeostasis signaling pathway | 5.37 × 10−4 | 7 |
| Actin Cytoskeleton Signaling | 0.002 | 8 |
| Role of Macrophages, Fibroblasts and Endothelial Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis | 0.016 | 8 |
| Glucocorticoid Receptor Signaling | 0.021 | 10 |
| UniProt ID | Gene Symbol | Description | Fold Change | Adj. p-Value | Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upregulated in African American subjects | |||||
| P01593 | IGKV1D-33 | Immunoglobulin kappa variable 1D-33 | 2.191 | 0.024 | Complement activation |
| P08294 | SOD3 | Extracellular superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] | 2.190 | 0.017 | Antioxidant, Heparin binding |
| P00736 | C1R | Complement C1r subcomponent | 2.182 | 0.014 | Complement activation, classical pathway |
| P08603 | CFH | Complement factor H | 1.865 | 0.021 | Complement activation, alternative pathway |
| P01023 | A2M | Alpha-2-macroglobulin | 1.489 | 0.047 | Blood coagulation |
| P01024 | C3 | Complement C3 | 1.289 | 0.047 | Endopeptidase inhibitor activity |
| Downregulated in African American subjects | |||||
| Q8NG11 | TSPAN14 | Tetraspanin-14 | −2.089 | 0.005 | Cellular protein metabolic process |
| P02753 | RBP4 | Retinol-binding protein 4 | −1.753 | 0.002 | Retinal and retinol binding |
| P02766 | TTR | Transthyretin | −1.751 | <0.001 | Hormone activity |
| P07998 | RNASE1 | Ribonuclease pancreatic | −1.636 | 0.002 | Nucleic acid binding |
| P41222 | PTGDS | Prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase | −1.435 | 0.002 | Fatty acid binding |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kodeboyina, S.K.; Lee, T.J.; Churchwell, L.; Ulrich, L.; Bollinger, K.; Bogorad, D.; Estes, A.; Zhi, W.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, A. The Constitutive Proteome of Human Aqueous Humor and Race Specific Alterations. Proteomes 2020, 8, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes8040034
Kodeboyina SK, Lee TJ, Churchwell L, Ulrich L, Bollinger K, Bogorad D, Estes A, Zhi W, Sharma S, Sharma A. The Constitutive Proteome of Human Aqueous Humor and Race Specific Alterations. Proteomes. 2020; 8(4):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes8040034
Chicago/Turabian StyleKodeboyina, Sai Karthik, Tae Jin Lee, Lara Churchwell, Lane Ulrich, Kathryn Bollinger, David Bogorad, Amy Estes, Wenbo Zhi, Shruti Sharma, and Ashok Sharma. 2020. "The Constitutive Proteome of Human Aqueous Humor and Race Specific Alterations" Proteomes 8, no. 4: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes8040034
APA StyleKodeboyina, S. K., Lee, T. J., Churchwell, L., Ulrich, L., Bollinger, K., Bogorad, D., Estes, A., Zhi, W., Sharma, S., & Sharma, A. (2020). The Constitutive Proteome of Human Aqueous Humor and Race Specific Alterations. Proteomes, 8(4), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes8040034





