Cellular and Extracellular Proteome of the Animal Pathogen Corynebacterium silvaticum, a Close Relative of Zoonotic Corynebacterium ulcerans and Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Growth Conditions
2.2. Sample Preparation for Mass Spectrometric Analyses
2.3. Mass Spectrometric Analyses
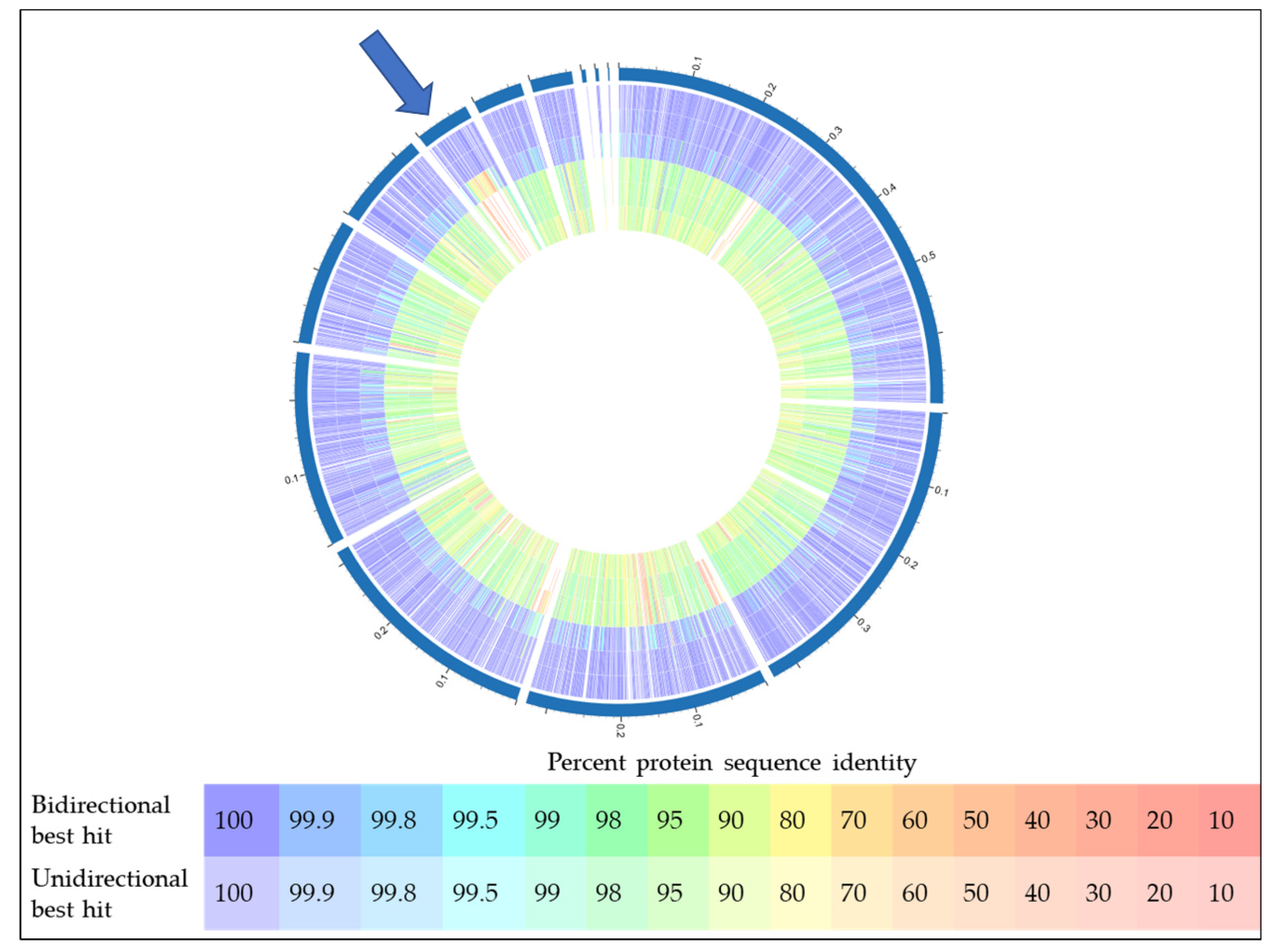
2.4. Bioinformatic Analyses
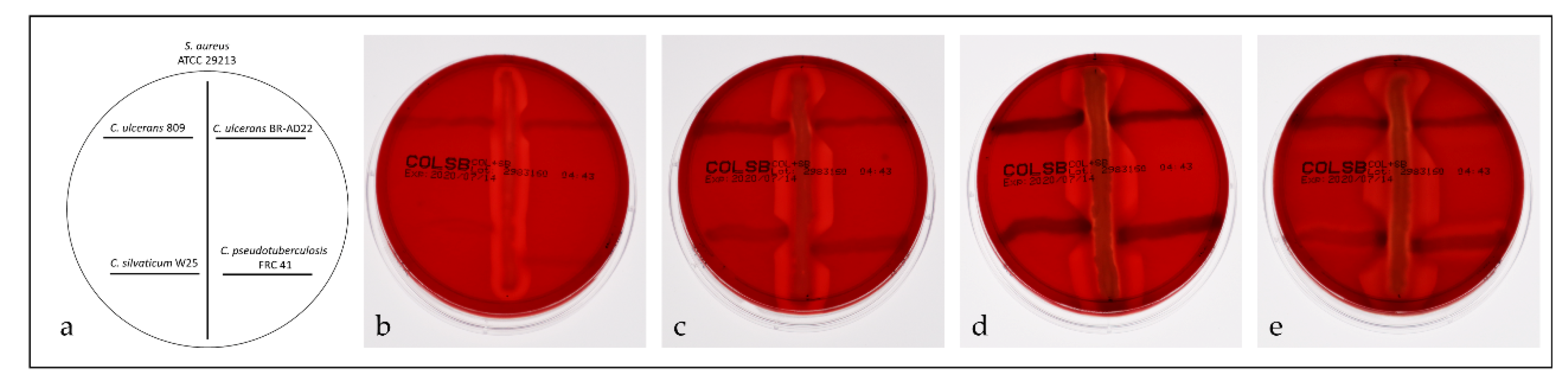
2.5. Reverse CAMP Test
2.6. Data Availability Statement
3. Results
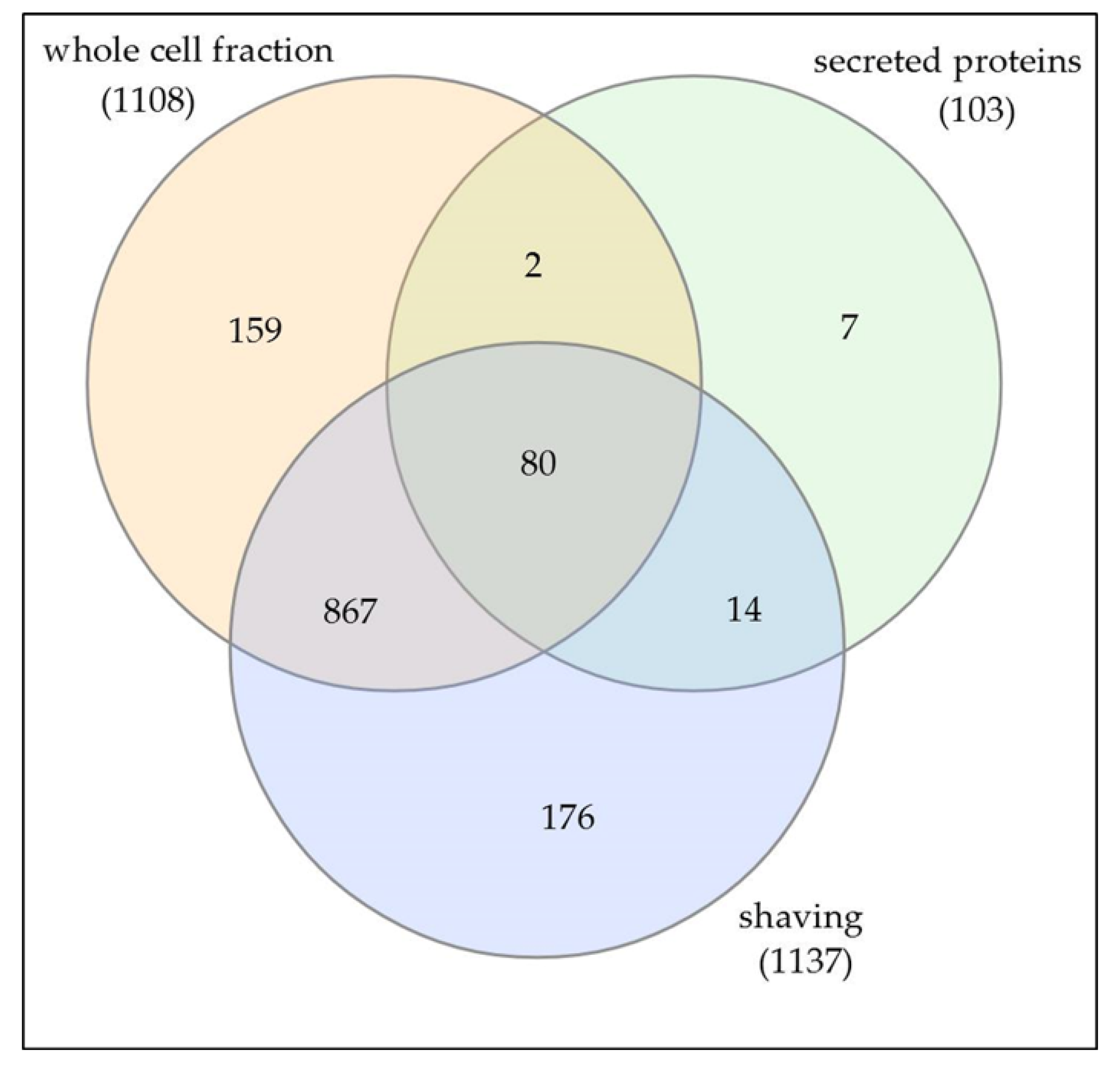
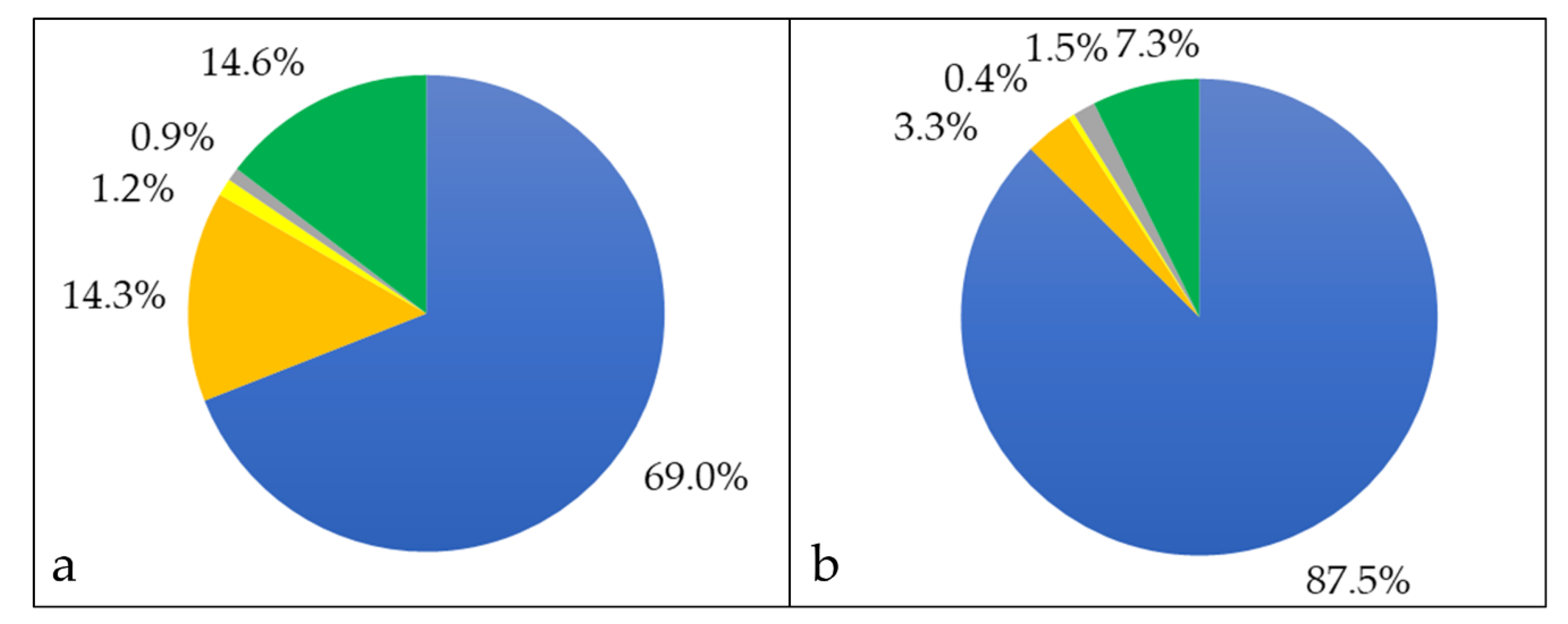
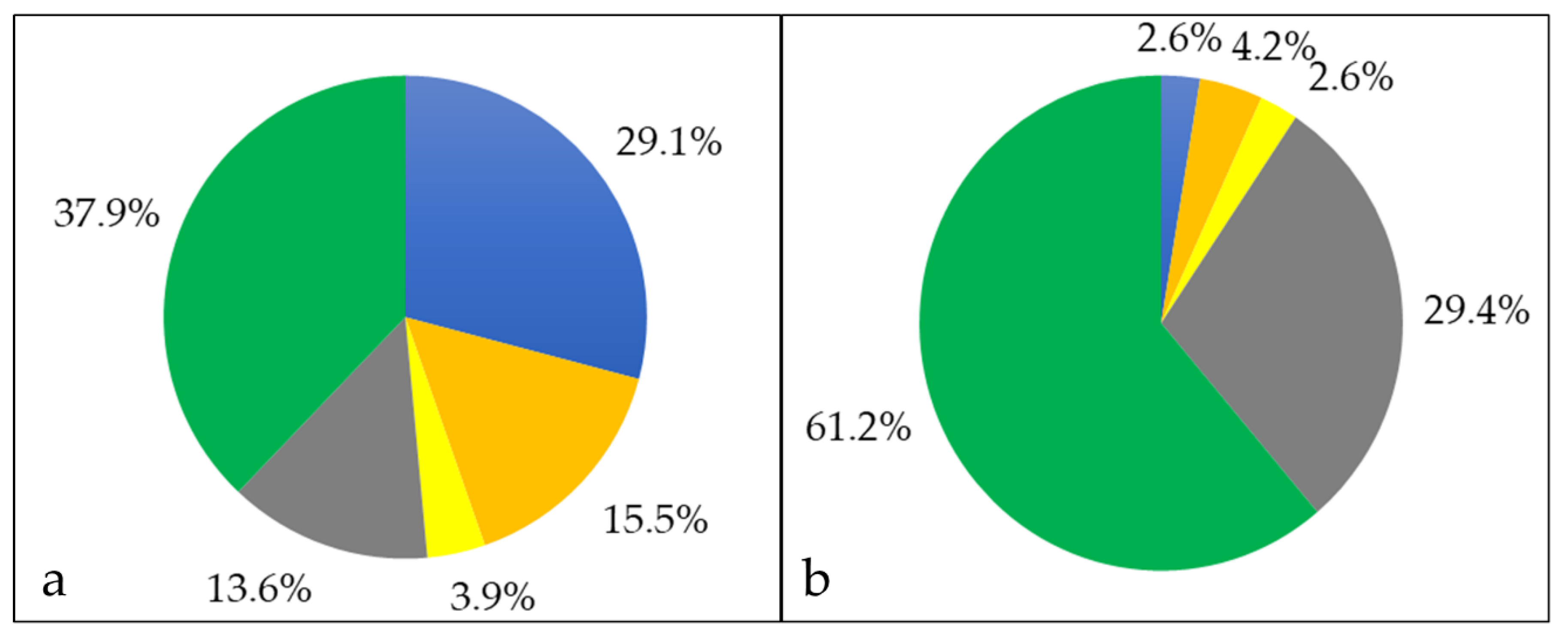
3.1. Analysis of Cellular Proteins
3.2. Characterization of Whole Cell and Shaving Fraction
3.3. Analysis of Extracellular Proteins
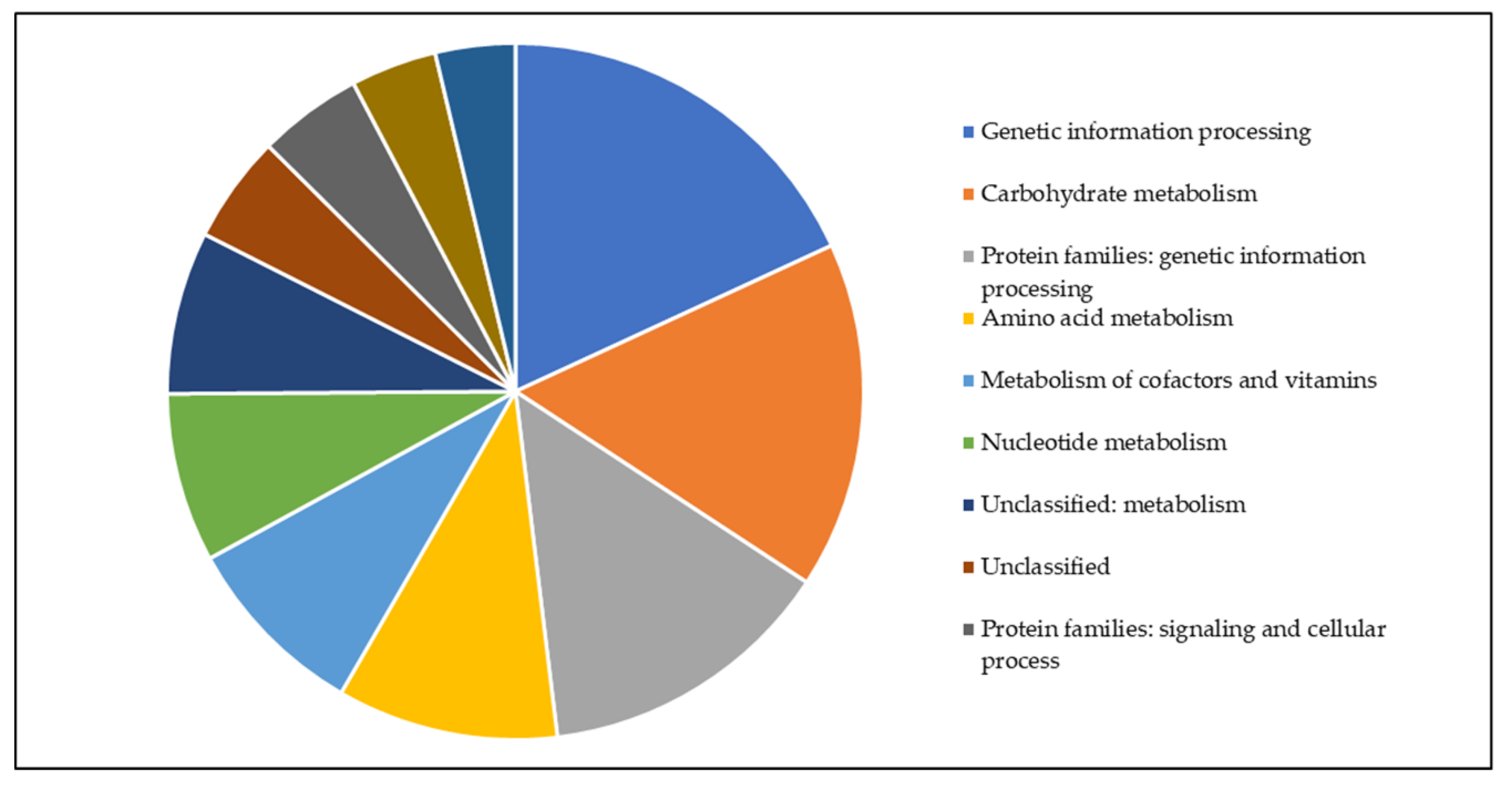
3.4. Metabolic Pathway Analysis
3.5. Analysis of Virulence Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lehmann, K.B.; Neumann, R.O. Atlas und Grundriss der Bakteriologie und Lehrbuch der Speziellen Bakteriologischen Diagnostik, 1st ed.; J.F. Lehmanns Verlag: München, Germany, 2010; ISBN 1141578476. [Google Scholar]
- Genus Corynebacterium. Available online: www.bacterio.net/corynebacterium.html (accessed on 2 June 2020).
- Dangel, A.; Berger, A.; Rau, J.; Eisenberg, T.; Kämpfer, P.; Margos, G.; Contzen, M.; Busse, H.-J.; Konrad, R.; Peters, M.; et al. Corynebacterium silvaticum sp. nov., a unique group of NTTB corynebacteria in wild boar and roe deer. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 3614–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauch, A.; Sandbote, J. The family Corynebacteriaceae. In The Prokaryotes; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Lory, S., Stackenbrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 239–277. ISBN 9783642301384. [Google Scholar]
- Bernard, K.A.; Funke, G. Corynebacterium. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Whitman, W.B., DeVos, P., Dedysh, S., Hedlund, B., Kämpfer, P., Rainey, F., Trujillo, M.E., Bowman, J.P., Brown, D.R., Glöckner, F.O., et al., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–70. ISBN 9781118960608. [Google Scholar]
- Burkovski, A. Diphtheria. In The Prokaryotes, 4th ed.; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; Volume 5, pp. 237–246. [Google Scholar]
- Burkovski, A. Diphtheria and its etiological agents. In Corynebacterium Diphtheriae and Related Toxigenic Species; Burkovski, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, N.C.; Efstratiou, A.; Mokrousov, I.; Mutreja, A.; Das, B.; Ramamurthy, T. Diphtheria. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessling, M.; Feiertag, J.; Hoenes, K. Pathogens provoking most deaths worldwide: A review. Heal. Sci. Commun. Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 2017, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Loeffler, F. Untersuchungen über die Bedeutung der Mikroorganismen für die Entstehung der Diphtherie beim Menschen, bei der Taube und beim Kalbe. In Mitteilungen an dem Kaiserlichen Gesundheitsamte; Norddeutsche Buchdruckerei und Verlaganstalt: Berlin, Germany, 1884; pp. 421–499. [Google Scholar]
- Roux, E.; Yersin, A. Contribution à l’étude de la diphtérie. Ann. Inst. Pasteur 1888, 2, 629–661. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, B.; Özerman Edis, B.; Bektas, M. Toxin structure, delivery and action. In Corynebacterium Diphtheriae and Related Toxigenic Species; Burkovski, A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, R.; Stewart, F.C. Corynebacterium ulcerans: A pathogenic microorganism resembling Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1927, 12, 756–761. [Google Scholar]
- Zakikhany, K.; Efstratiou, A. Diphtheria in Europe: Current problems and new challenges. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkovski, A. Pathogenesis of Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Corynebacterium ulcerans. In Human Emerging and Re-Emerging Infections; Singh, S.K., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA; Wiley Blackwell Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 697–708. [Google Scholar]
- Hacker, E.; Antunes, C.A.; Mattos-Guaraldi, A.L.; Burkovski, A.; Tauch, A. Corynebacterium ulcerans, an emerging human pathogen. Future Microbiol. 2016, 11, 1191–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.; Dangel, A.; Peters, M.; Mühldorfer, K.; Braune, S.; Eisenberg, T. Tox-positive Corynebacterium ulcerans in hedgehogs, Germany. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riegel, P.; Ruimy, R.; De Brie, D.; Prkost, G.; Jehl, F.; Christen, R. Taxonomy of Corynebacterium diphtheriae and related taxa, with recognition of Corynebacterium ulcerans sp. nov. nom. rev. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1995, 126, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangal, V.; Hoskisson, P.A. Corynephages: Infections of the infectors. In Corynebacterium Diphtheriae and Related Toxigenic Species; Burkovski, A., Ed.; Springer: Dobrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 67–81. ISBN 9789400776241. [Google Scholar]
- Dorella, F.A.; Pacheco, L.G.C.; Oliveira, S.C.; Miyoshi, A.; Azevedo, V. Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis: Microbiology, biochemical properties, pathogenesis and molecular studies of virulence. Vet. Res. 2006, 37, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, A.; Möller, J.; Burkovski, A.; Hotzel, H. Genome sequence of a pathogenic Corynebacterium ulcerans strain isolated from a wild boar with necrotizing lymphadenitis. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.; Barroco, C.; Mottola, C.; Santos, R.; Lemsaddek, A.; Tavares, L.; Semedo-Lemsaddek, T. First report of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis from caseous lymphadenitis lesions in Black Alentejano pig (Sus scrofa domesticus). BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Möller, J.; Musella, L.; Melnikov, V.; Geißdörfer, W.; Burkovski, A.; Sangal, V. Phylogenomic characterisation of a novel corynebacterial species pathogenic to animals. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1225–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauch, A.; Burkovski, A. Molecular armory or niche factors: Virulence determinants of Corynebacterium species. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnv185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangal, V.; Blom, J.; Sutcliffe, I.C.; von Hunolstein, C.; Burkovski, A.; Hoskisson, P.A. Adherence and invasive properties of Corynebacterium diphtheriae strains correlates with the predicted membrane-associated and secreted proteome. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkovski, A. Cell envelope of corynebacteria: Structure and influence on pathogenicity. ISRN Microbiol. 2013, 2013, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkovski, A. The role of corynomycolic acids in Corynebacterium-host interaction. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, T.; Wersch, G.; Uhlemann, E.; Schmid, R.; Burkovski, A. Mapping and identification of Corynebacterium glutamicum proteins by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and microsequencing. Electrophoresis 1998, 19, 3217–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, T.; Finkemeier, M.; Wersch, G.; Krämer, R.; Burkovski, A.; Ag, D. Two-dimensional electrophoretic analysis of Corynebacterium glutamicum membrane fraction and surface proteins. Electrophoresis 2000, 21, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiery, E.; Poetsch, A.; Moosbauer, T.; Amin, B.; Hofmann, J.; Burkovski, A. A proteomic study of Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. michiganensis culture supernatants. Proteomes 2015, 3, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittel, M.; Gastiger, S.; Amin, B.; Hofmann, J.; Burkovski, A. Surface and extracellular proteome of the emerging pathogen Corynebacterium ulcerans. Proteomes 2018, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, J.; Kraner, M.E.; Burkovski, A. More than a toxin: Protein inventory of Clostridium tetani toxoid vaccines. Proteomes 2019, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, J.; Kraner, M.; Sonnewald, U.; Sangal, V.; Tittlbach, H.; Winkler, J.; Winkler, T.H.; Melnikov, V.; Lang, R.; Sing, A.; et al. Proteomics of diphtheria toxoid vaccines reveals multiple proteins that are immunogenic and may contribute to protection of humans against Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Vaccine 2019, 37, 3061–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, J.; Kraner, M.E.; Burkovski, A. Proteomics of Bordetella pertussis whole-cell and acellular vaccines. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, T.; Pfefferle, W.; Baumann, C.; Busker, E.; Schaffer, S.; Bott, M.; Sahm, H.; Dusch, N.; Kalinowski, J.; Pühler, A.; et al. Proteome analysis of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Electrophoresis 2001, 22, 1712–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendt, A.K.; Burkovski, A.; Schaffer, S.; Bott, M.; Farwick, M.; Hermann, T.; Ag, D. Towards a phosphoproteome map of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Proteomics 2003, 3, 1637–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, S.; Burkovski, A. Handbook of Corynebacterium glutamicum. In Handbook of Corynebacterium Glutamicum; Bott, M., Eggeling, L., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 99–118. ISBN 9781420039696. [Google Scholar]
- Silberbach, M.; Scha, M.; Hu, A.T.; Pu, A.; Kra, R.; Burkovski, A. Adaptation of Corynebacterium glutamicum to ammonium limitation: A global analysis using transcriptome and proteome techniques. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2391–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, R.; Kübler, D.; Pallisse, R.; Burkovski, A.; Lehmann, W.D. Protein and proteome phosphorylation analysis by element mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 1987–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkovski, A. Proteomics of Corynebacterium glutamicum: Essential industrial bacterium. Methods Biochem. Anal. 2006, 49, 137–147. [Google Scholar]
- Lüdke, A.; Krämer, R.; Burkovski, A.; Schluesener, D.; Poetsch, A. A proteomic study of Corynebacterium glutamicum AAA+ protease FtsH. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poetsch, A.; Haußmann, U.; Burkovski, A. Proteomics of corynebacteria: From biotechnology workhorses to pathogens. Proteomics 2011, 11, 3244–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisniewski, J.R.; Zougman, A.; Nagaraj, N.; Mann, M. Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraner, M.E.; Müller, C.; Sonnewald, U. Comparative proteomic profiling of the choline transporter-like1 (CHER1) mutant provides insights into plasmodesmata composition of fully developed Arabidopsis thaliana leaves. Plant. J. 2017, 92, 696–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjalsma, H.; Lambooy, L.; Hermans, P.W.; Swinkels, D.W. Shedding & shaving: Disclosure of proteomic expressions on a bacterial face. Proteomics 2008, 8, 1415–1428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, W.; Eckart, R.A.; Schmid, B.; Cagköylü, H.; Hof, K.; Muller, Y.A. Nuclear trafficking of the anti-apoptotic Coxiella burnetii effector protein AnkG requires binding to p32 and Importin-α 1. Cell. Microbiol. 2017, 19, e12634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: A worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, M.R.; Melli, G.; Sahinalp, S.C.; Yu, N.Y.; Lo, R.; Dao, P.; Brinkman, F.S.L.; Wagner, J.R.; Ester, M.; Foster, L.J.; et al. PSORTb 3.0: Improved protein subcellular localization prediction with refined localization subcategories and predictive capabilities for all prokaryotes. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski, J.R.; Hein, M.Y.; Cox, J.; Mann, M. A “Proteomic Ruler” for protein copy number and concentration estimation without spike-in standards. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2014, 13, 3497–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. BlastKOALA and GhostKOALA: KEGG tools for functional characterization of genome and metagenome sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattam, A.R.; Davis, J.J.; Assaf, R.; Brettin, T.; Bun, C.; Conrad, N.; Dietrich, E.M.; Disz, T.; Gabbard, J.L.; Gerdes, S.; et al. Improvements to PATRIC, the all-bacterial bioinformatics database and analysis resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D535–D542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Csordas, A.; Bai, J.; Bernal-llinares, M.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Inuganti, A.; Griss, J.; Mayer, G.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: Improving support for quantification data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkovski, A. Rapid detection of bacterial surface proteins using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay system. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 1997, 34, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfanzagl, V.; Holcik, L.; Maresch, D.; Gorgone, G.; Michlits, H.; Paul, G. Coproheme decarboxylases—Phylogenetic prediction versus biochemical experiments. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 640, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Goldberger, A.C.; Tompkins, L.S.; Plorde, J.J. Infections caused by nondiphtheria corynebacteria. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1982, 4, 1220–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, A.L.M.; Krywult, J.; Corner, L.A.; Rothel, J.S.; Radford, A.J. Rational attenuation of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis: Potential cheesy gland vaccine and live delivery vehicle. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 2900–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansmeier, N.; Chao, T.C.; Kalinowski, J.; Pühler, A.; Tauch, A. Mapping and comprehensive analysis of the extracellular and cell surface proteome of the human pathogen Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Proteomics 2006, 6, 2465–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, L.; Höller, M.; Gerlach, R.G.; Hensel, M.; Rheinlaender, J.; Schäffer, T.E.; Burkovski, A. Corynebacterium diphtheriae invasion-associated protein (DIP1281) is involved in cell surface organization, adhesion and internalization in epithelial cells. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, E.; Al-Dilaimi, A.; Papavasiliou, P.; Schneider, J.; Viehoever, P.; Burkovski, A.; Soares, S.C.; Almeida, S.S.; Dorella, F.A.; Miyoshi, A.; et al. Comparative analysis of two complete Corynebacterium ulcerans genomes and detection of candidate virulence factors. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, E.; Ott, L.; Schneider, J.; Schröder, J.; Jaenicke, S.; Goesmann, A.; Husemann, P.; Stoye, J.; Dorella, F.A.; Rocha, F.S.; et al. The complete genome sequence of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis FRC41 isolated from a 12-year-old girl with necrotizing lymphadenitis reveals insights into gene- regulatory networks contributing to virulence. BMC Genomics 2010, 11, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Protein | Gene | Whole Cell | Secreted | Shaving |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phospholipase D | pld | − | − | + |
| Neuraminidase (sialidase) | nanH | + | + | + |
| Trypsin-like serine protease | vsp1 | − | − | − |
| Peptidoglycan endopeptidase | ripA | + | + | + |
| Hydrolase (cell wall peptidase) | cwlH | + | + | + |
| Protease | vsp2 | + | + | − |
| Protease (endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F2) | cpp | − | − | − |
| Type VII secretion-associated serine protease mycosin | cpfrc_00397 | + | − | − |
| AccD5-3 acyl-CoA carboxylase beta | dtsR2 | + | − | + |
| AccD5-2 propionyl-CoA carboxylase beta chain 2 | dtsR1 | + | − | + |
| AccD5-1 acyl-CoA carboxylase subunit beta | accD3 | + | − | + |
| Hydrolase | cpfrc_00536 | + | − | + |
| Non-ribosomal peptide synthetase | nrpS1 | − | − | − |
| Resuscitation-promoting factor | rpfA | + | + | + |
| Resuscitation-promoting factor | rpfB | + | + | + |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Möller, J.; Schorlemmer, S.; Hofmann, J.; Burkovski, A. Cellular and Extracellular Proteome of the Animal Pathogen Corynebacterium silvaticum, a Close Relative of Zoonotic Corynebacterium ulcerans and Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis. Proteomes 2020, 8, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes8030019
Möller J, Schorlemmer S, Hofmann J, Burkovski A. Cellular and Extracellular Proteome of the Animal Pathogen Corynebacterium silvaticum, a Close Relative of Zoonotic Corynebacterium ulcerans and Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis. Proteomes. 2020; 8(3):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes8030019
Chicago/Turabian StyleMöller, Jens, Svenja Schorlemmer, Jörg Hofmann, and Andreas Burkovski. 2020. "Cellular and Extracellular Proteome of the Animal Pathogen Corynebacterium silvaticum, a Close Relative of Zoonotic Corynebacterium ulcerans and Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis" Proteomes 8, no. 3: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes8030019
APA StyleMöller, J., Schorlemmer, S., Hofmann, J., & Burkovski, A. (2020). Cellular and Extracellular Proteome of the Animal Pathogen Corynebacterium silvaticum, a Close Relative of Zoonotic Corynebacterium ulcerans and Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis. Proteomes, 8(3), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes8030019







