In Silico Identification of Antimicrobial Peptides in the Proteomes of Goat and Sheep Milk and Feta Cheese
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
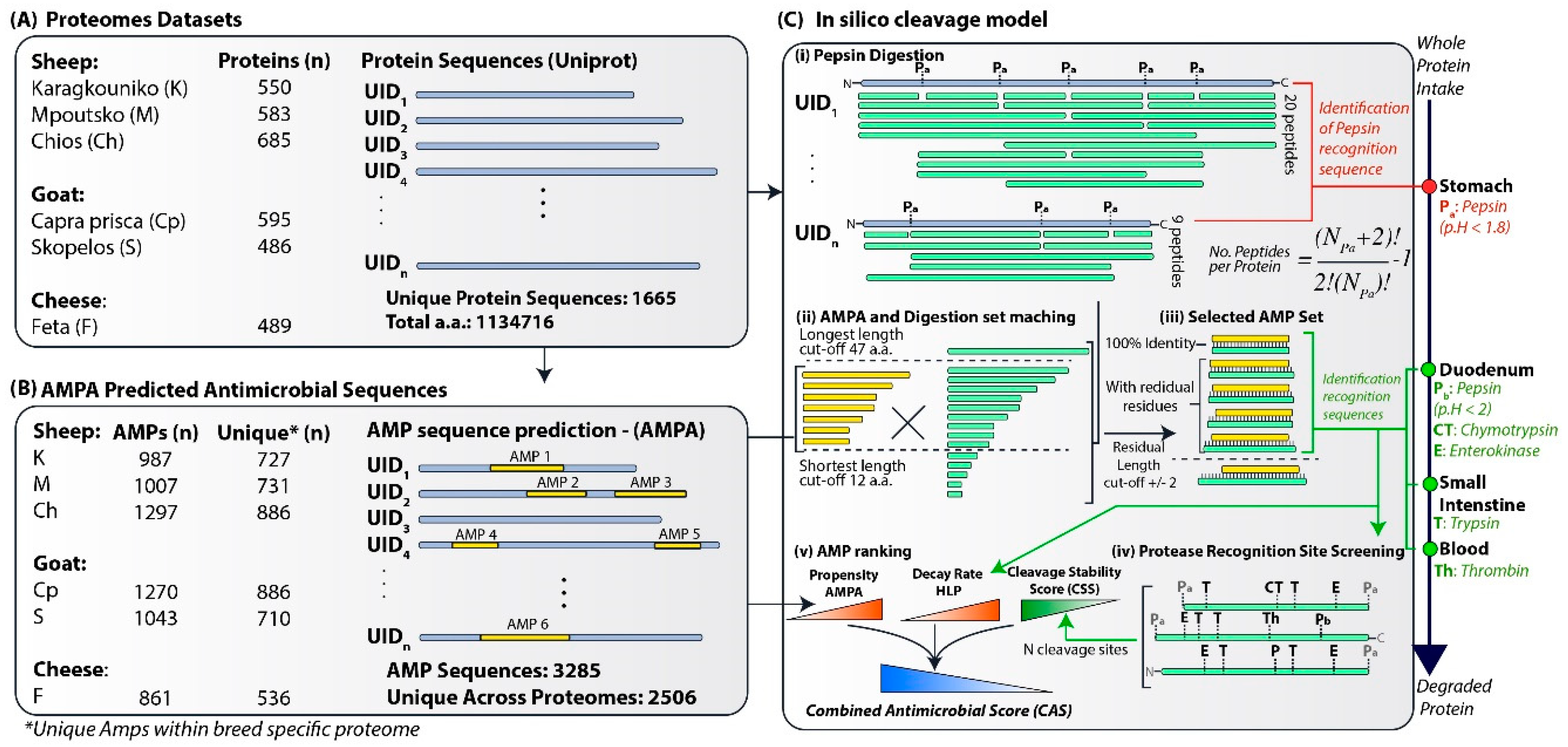
2.1. Protein Datasets
2.2. Prediction of Antimicrobial Peptides
2.3. Protein Cleavage Model
2.4. Stability Assessment
2.5. AMP Ranking
2.6. Informatics
2.7. Physicochemical Properties
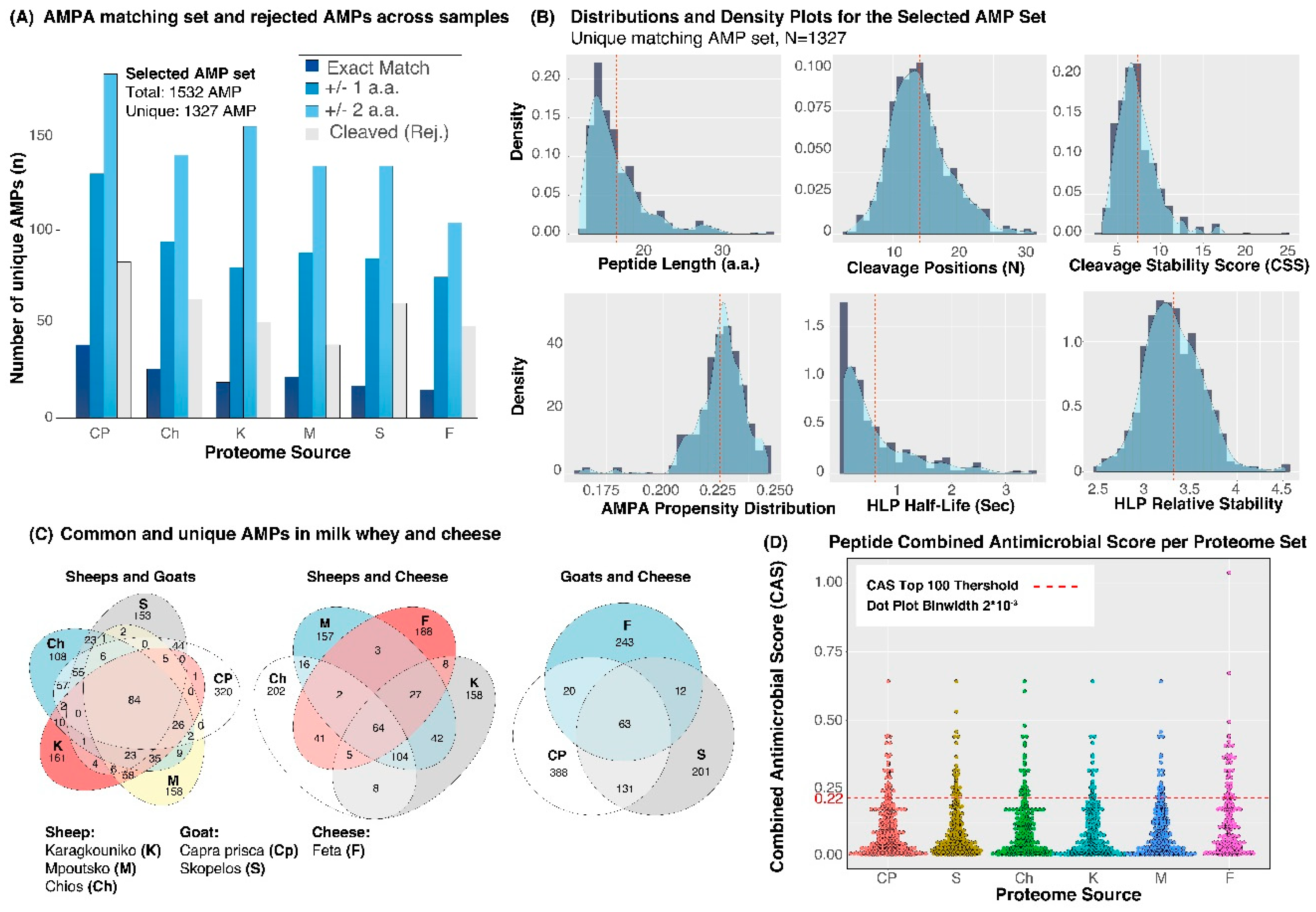
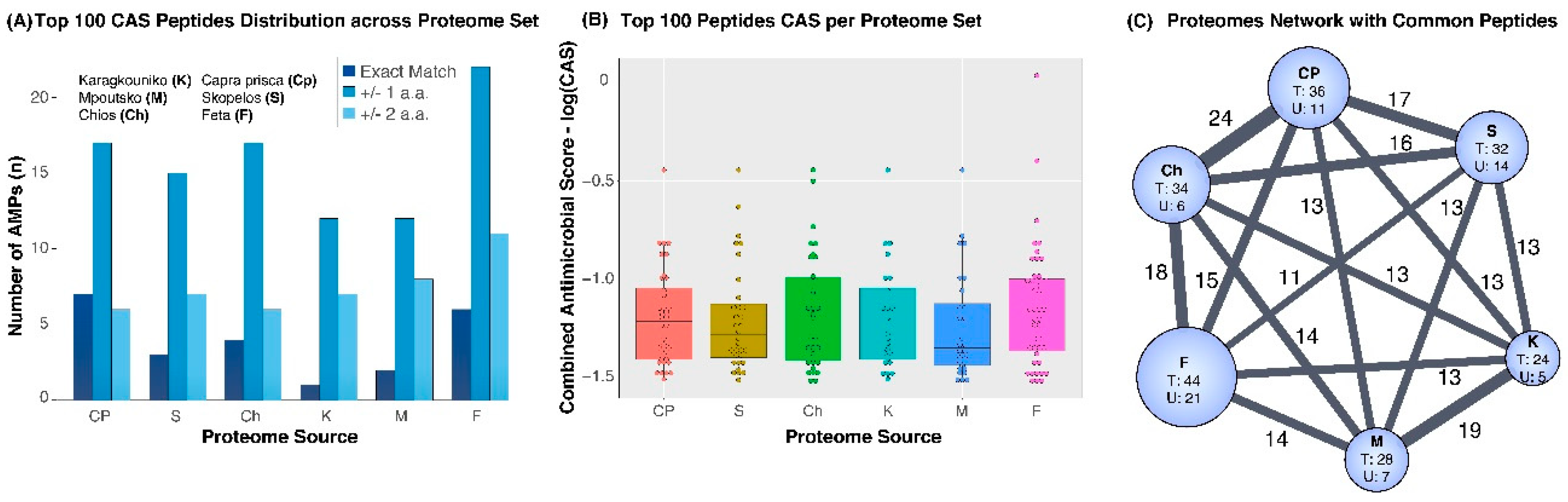
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Availability of Resources
References
- Pellegrini, A. Antimicrobial Peptides from Food Proteins. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 9, 1225–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, T.B.; Wong, J.H.; Almahdy, O.; El-Fakharany, E.M.; El-Dabaa, E.; Redwan, E.R.M. Antimicrobial activities of casein and other milk proteins. In Casein: Production, Uses and Health Effects; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 233–241. ISBN 9781621001294. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, E.; Chand, R.; Kapila, S. Biofunctional properties of bioactive peptides of milk origin. Food Rev. Int. 2009, 25, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miner-Williams, W.M.; Stevens, B.R.; Moughan, P.J. Are intact peptides absorbed from the healthy gut in the adult human? Nutr. Res. Rev. 2014, 27, 308–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Lai, R.; Zou, Q. An antimicrobial peptide with antimicrobial activity against Helicobacter pylori. Peptides 2007, 28, 1527–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallas, D.C.; Guerrero, A.; Khaldi, N.; Castillo, P.A.; Martin, W.F.; Smilowitz, J.T.; Bevins, C.L.; Barile, D.; German, J.B.; Lebrilla, C.B. Extensive in vivo human milk peptidomics reveals specific proteolysis yielding protective antimicrobial peptides. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 2295–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zeng, X.; Yang, Q.; Qiao, S. Antimicrobial peptides as potential alternatives to antibiotics in food animal industry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Kizhakkedathu, J.; Straus, S. Antimicrobial Peptides: Diversity, Mechanism of Action and Strategies to Improve the Activity and Biocompatibility In Vivo. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulm, H.; Wilmes, M.; Shai, Y.; Sahl, H.G. Antimicrobial host defensins specific antibiotic activities and innate defense modulation. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrent, M.; Di Tommaso, P.; Pulido, D.; Nogués, M.V.; Notredame, C.; Boix, E.; Andreu, D. AMPA: An automated web server for prediction of protein antimicrobial regions. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 130–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrent, M.; Nogués, V.M.; Boix, E. A theoretical approach to spot active regions in antimicrobial proteins. BMC Bioinforma. 2009, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadaei, V. Milk Proteins-derived antibacterial peptides as novel functional food ingredients. Ann. Biol. Res. 2012, 3, 2520–2526. [Google Scholar]
- Atanasova, J.; Ivanova, I. Antibacterial peptides from goat and sheep milk proteins. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2010, 24, 1799–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.W.; Nam, M.S. Bioactive Peptides in Milk and Dairy Products: A Review. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2015, 35, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostopoulos, A.K.; Katsafadou, A.I.; Pierros, V.; Kontopodis, E.; Fthenakis, G.C.; Arsenos, G.; Karkabounas, S.C.; Tzora, A.; Skoufos, I.; Tsangaris, G.T. Milk of Greek sheep and goat breeds; characterization by means of proteomics. J. Proteomics 2016, 147, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandelli, A.; Daroit, D.J.; Corrêa, A.P.F. Whey as a source of peptides with remarkable biological activities. Food Res. Int. 2015, 73, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hati, S.; Patel, N.; Sakure, A.; Mandal, S. Influence of Whey Protein Concentrate on the Production of Antibacterial Peptides Derived from Fermented Milk by Lactic Acid Bacteria. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2018, 24, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, A.K.; Tsangaris, G.T. Feta cheese proteins: Manifesting the identity of Greece’s National Treasure. Data Br. 2018, 19, 2037–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Singla, D.; Rashid, M.; Raghava, G.P.S. Designing of peptides with desired half-life in intestine-like environment. BMC Bioinforma. 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, A. UniProt: A worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, A.; Chaudhary, K.; Kumar, R.; Raghava, G.P.S. Computer-aided virtual screening and designing of cell-penetrating peptides. In Cell-Penetrating Peptides: Methods and Protocols; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 59–69. ISBN 9781493928064. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, A.; Chaudhary, K.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, A.; Kapoor, P.; Tyagi, A.; Raghava, G.P.S. In silico approaches for designing highly effective cell penetrating peptides. J. Transl. Med. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria, 2018. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org (accessed on 12 June 2019).
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Anekthanakul, K.; Hongsthong, A.; Senachak, J.; Ruengjitchatchawalya, M. SpirPep: An in silico digestion-based platform to assist bioactive peptides discovery from a genome-wide database. BMC Bioinforma. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H. R: Package ‘stringr.’ CRAN. 2017. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/stringr/stringr.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2019).
- Larsson, J.; Gustafsson, P. A case study in fitting area-proportional euler diagrams with ellipses using eulerr. In Proceedings of the CEUR Workshop Proceedings, Edinburgh, UK, 2018; Volume 2116, pp. 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A. ggpubr: “ggplot2” Based Publication Ready Plots. R package version 0.1.7. 2018. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ggpubr/ggpubr.pdf. (accessed on 5 July 2019).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2011, 3, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.E.; Cohen, S.H. Package: igraph. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2007, 29, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Francois, R. The dplyr package. R Core Team 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jhong, J.H.; Chi, Y.H.; Li, W.C.; Lin, T.H.; Huang, K.Y.; Lee, T.Y. DbAMP: An integrated resource for exploring antimicrobial peptides with functional activities and physicochemical properties on transcriptome and proteome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirtskhalava, M.; Gabrielian, A.; Cruz, P.; Griggs, H.L.; Squires, R.B.; Hurt, D.E.; Grigolava, M.; Chubinidze, M.; Gogoladze, G.; Vishnepolsky, B.; et al. DBAASP v.2: An enhanced database of structure and antimicrobial/cytotoxic activity of natural and synthetic peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. APD: the Antimicrobial Peptide Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghu, F.H.; Gopi, L.; Barai, R.S.; Ramteke, P.; Nizami, B.; Idicula-Thomas, S. CAMP: Collection of sequences and structures of antimicrobial peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, H.; Lu, H.; Li, G.; Huang, Q. LAMP: A Database Linking Antimicrobial Peptides. PLoS ONE 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boöttger, R.; Hoffmann, R.; Knappe, D. Differential stability of therapeutic peptides with different proteolytic cleavage sites in blood, plasma and serum. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimi, S.; Zirah, S.; Hammami, R.; Fernandez, B.; Rebuffat, S.; Fliss, I. Fate and biological activity of the antimicrobial lasso peptide microcin J25 under gastrointestinal tract conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renukuntla, J.; Vadlapudi, A.D.; Patel, A.; Boddu, S.H.S.; Mitra, A.K. Approaches for enhancing oral bioavailability of peptides and proteins. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 447, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessione, E.; Cirrincione, S. Bioactive molecules released in food by lactic acid bacteria: Encrypted peptides and biogenic amines. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Mao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zou, H.; Ye, M. Enzyme Kinetics for Complex System Enables Accurate Determination of Specificity Constants of Numerous Substrates in a Mixture by Proteomics Platform. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2017, 16, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorris, H.H.; Bade, S.; Röckendorf, N.; Albers, E.; Schmidt, M.A.; Fránek, M.; Frey, A. Rapid profiling of peptide stability in proteolytic environments. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Proteome | Proteins (n) | AMPs (n) | Ratio to Proteome | Mean Propensity | Mean dx (s−1) | Mean CSS | Mean CAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP | 595 | 602 | 1.012 | 0.224 | 1.270 | 7.08 | 0.062 |
| S | 486 | 407 | 0.837 | 0.224 | 1.155 | 7.156 | 0.069 |
| Ch | 685 | 442 | 0.645 | 0.225 | 1.120 | 6.891 | 0.069 |
| K | 550 | 416 | 0.756 | 0.225 | 1.238 | 6.989 | 0.063 |
| M | 583 | 415 | 0.712 | 0.224 | 1.199 | 6.869 | 0.064 |
| F | 489 | 338 | 0.691 | 0.224 | 0.968 | 7.382 | 0.086 |
| Proteome | Proteins (n) | AMPs (n) | Ratio to proteome | Mean Propensity | Mean dx (s−1) | Mean CSS | Mean CAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP | 595 | 36 | 0.061 | 0.229 | 0.288 | 9.895 | 0.312 |
| S | 486 | 32 | 0.066 | 0.231 | 0.310 | 10.31 | 0.311 |
| Ch | 685 | 34 | 0.050 | 0.229 | 0.283 | 9.713 | 0.326 |
| K | 550 | 24 | 0.044 | 0.231 | 0.301 | 10.304 | 0.311 |
| M | 583 | 28 | 0.048 | 0.228 | 0.296 | 9.632 | 0.3 |
| F | 489 | 44 | 0.090 | 0.229 | 0.271 | 10.045 | 0.338 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomazou, M.; Oulas, A.; Anagnostopoulos, A.K.; Tsangaris, G.T.; Spyrou, G.M. In Silico Identification of Antimicrobial Peptides in the Proteomes of Goat and Sheep Milk and Feta Cheese. Proteomes 2019, 7, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes7040032
Tomazou M, Oulas A, Anagnostopoulos AK, Tsangaris GT, Spyrou GM. In Silico Identification of Antimicrobial Peptides in the Proteomes of Goat and Sheep Milk and Feta Cheese. Proteomes. 2019; 7(4):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes7040032
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomazou, Marios, Anastasis Oulas, Athanasios K. Anagnostopoulos, George Th. Tsangaris, and George M. Spyrou. 2019. "In Silico Identification of Antimicrobial Peptides in the Proteomes of Goat and Sheep Milk and Feta Cheese" Proteomes 7, no. 4: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes7040032
APA StyleTomazou, M., Oulas, A., Anagnostopoulos, A. K., Tsangaris, G. T., & Spyrou, G. M. (2019). In Silico Identification of Antimicrobial Peptides in the Proteomes of Goat and Sheep Milk and Feta Cheese. Proteomes, 7(4), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes7040032







