Mitochondrial Proteomics of Antimony and Miltefosine Resistant Leishmania infantum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Culture and Resistance Selection
2.3. Extraction and Purification of Mitochondria
2.4. Protein Extraction
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS)-PAGE
2.7. Two Dimensional Protein Gels
2.8. Protein In-Gel Digestion and Spot Identification
3. Results
3.1. Extracting and Analysing Purified Mitochondria
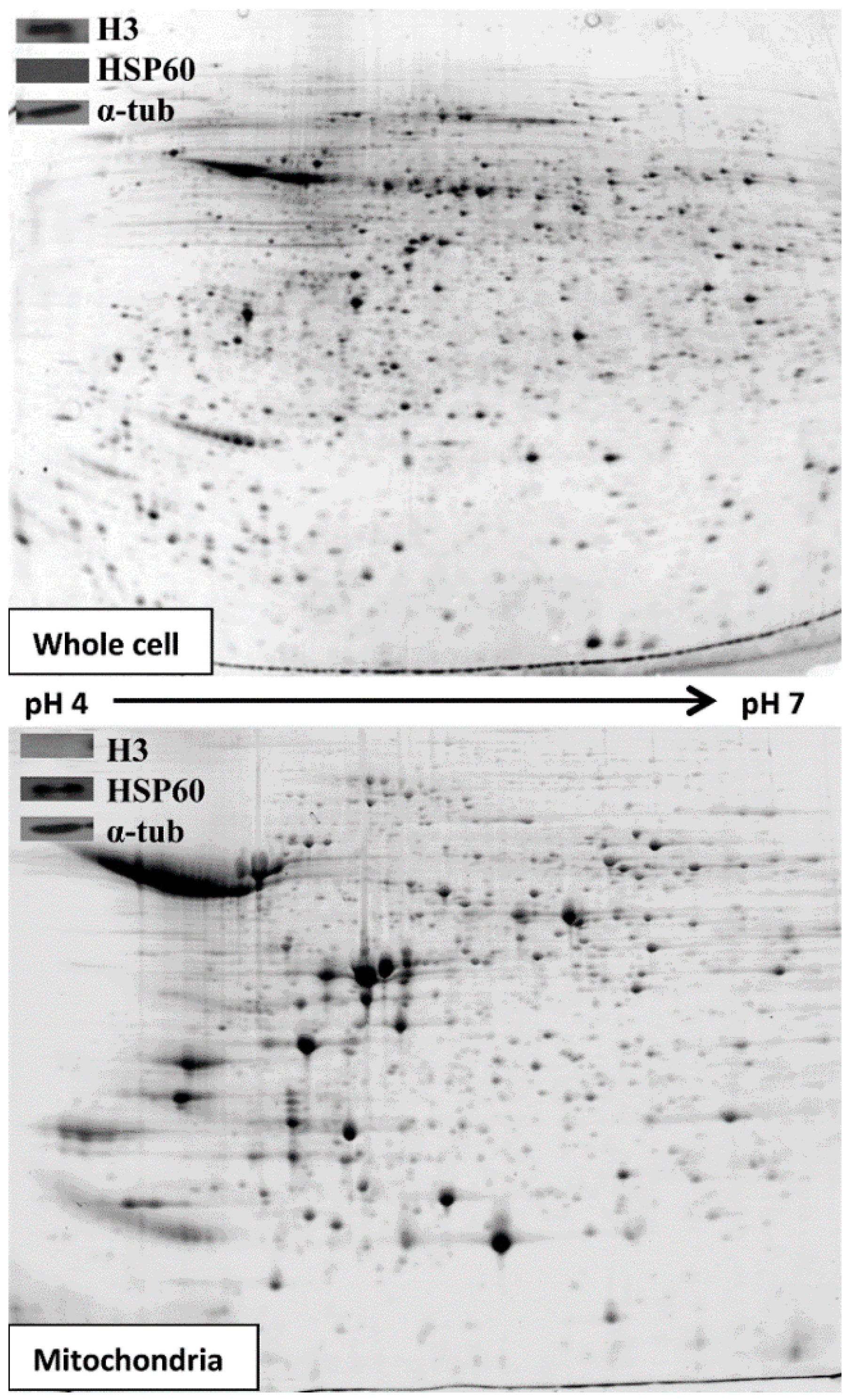
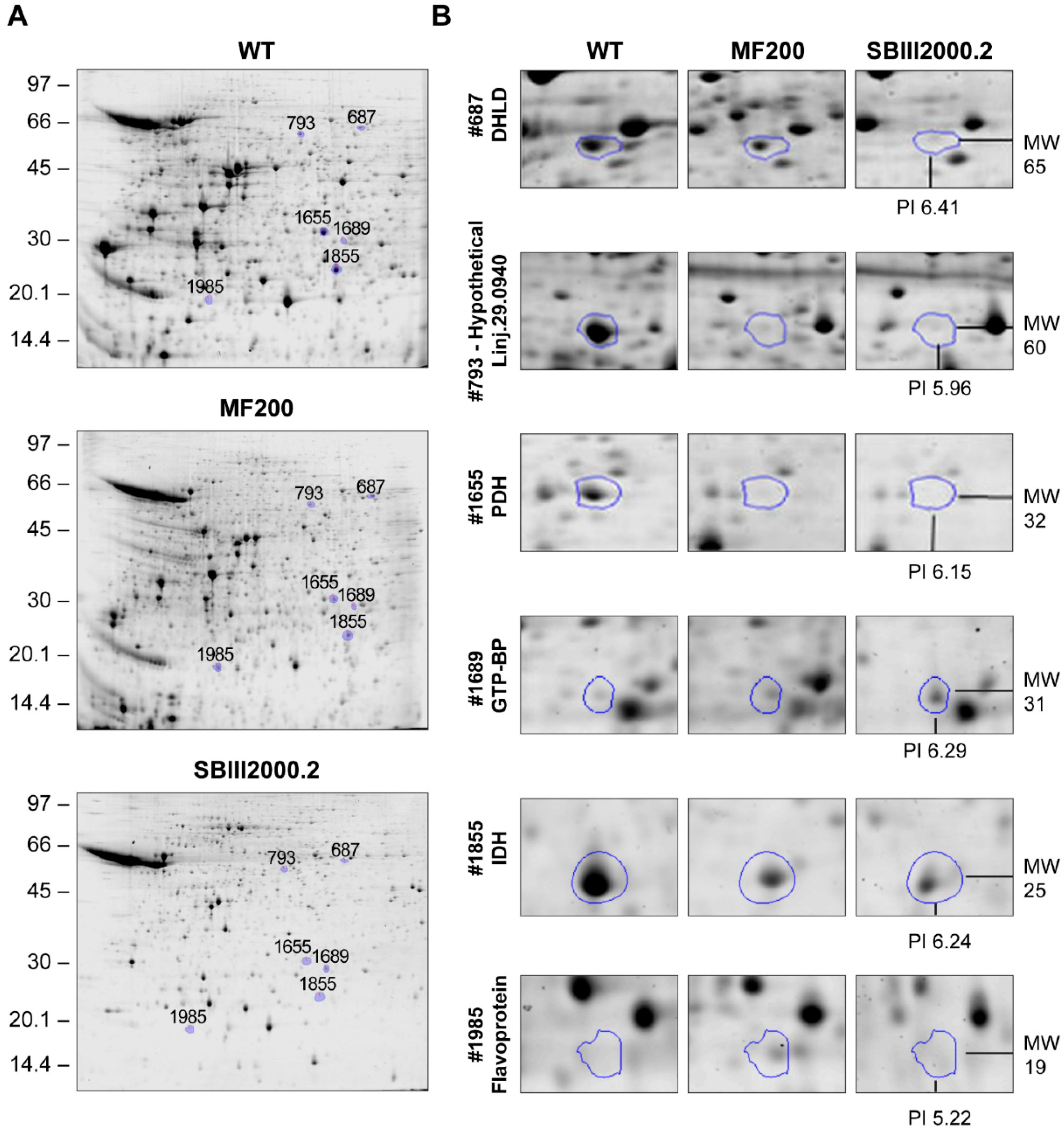
3.2. Comparative 2D Gels
| Progenesis 2D Spot # | ID 1 | Accession Number | Probability of Export to Mitochondrion 2 | Total Spectrum Count | % Sequence Coverage | Fold Change c.f. WT | Molecular Weight 3 (KDa) | Isoelectric Oint 3 | Secondary ID 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MF200 | SbIII 2000.2 | Th/Exp | Th/Exp | |||||||
| 687 | Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase, putative | LinJ.32.3510 | 0.0841 | 63 | 32 | 0.77 | 0.36 * | 51/65 | 6.87/6.41 | LinJ.33.2570 |
| 702 | Hypothetical protein, conserved | LinJ.29.0940 | 0.9761 | 70 | 34 | 2.90 * | 1.91 * | 53/64 | 7.8/6.54 | LinJ.35.1390 |
| 721 | Axoneme central apparatus protein, putative | LinJ.20.1450 | 0.3102 | 410 | 68 | 1.80 | 5.56 * | 55/63 | 5.72/5.91 | LinJ.12.0580 (ALAT) |
| 765 | Hypothetical | LinJ.30.3740 | 0.0665 | 7 | 9.5 | 0.28 * | 0.18 * | 51/61 | 5.98/6.13 | None |
| 793 | Hypothetical protein, conserved | LinJ.29.0940 | 0.9761 | 418 | 43 | 0.30 * | 0.21 * | 53/60 | 7.8/5.96 | LinJ.34.3460 |
| 921 | Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase, putative | LinJ.32.3510 | 0.0841 | 223 | 55 | 0.46 * | 0.22 * | 51/55 | 6.87/6.39 | LinJ.36.5380 |
| 1018 | Hypothetical | LinJ.29.0940 | 0.9761 | 186 | 36 | 0.56 * | 0.47 * | 53/51 | 7.8/6.27 | LinJ.34.0560 |
| 1313 | Hypothetical protein containing WD repeats and a STRAP motif | LinJ.27.1140 | 0.0772 | 64 | 60 | 2.75 * | 1.38 | 35/41 | 6.18/6.06 | LinJ.28.2950 |
| 1499 | GTP-binding protein, putative, Probable dynamin-1-like protein | LinJ.29.2310 | 0.0951 | 8 | 8.40 | 0.20 * | 0.16 * | 78/36 | 7.49/5.86 | LinJ.25.1210 |
| 1524 | Hypothetical (first half) | LinJ.36.5380 | 0.9460 | 168 | 25 | 0.25 * | 0.16 * | 71/35 | 5.69/5.73 | None |
| 1655 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 beta subunit, putative | LinJ.25.1790 | 0.9909 | 833 | 52 | 0.29 | 0.14 * | 38/32 | 5.72/6.15 | None |
| 1664 | Calcium binding protein, putative | LinJ.30.1300 | 0.1494 | 19 | 16 | 0.22 * | 0.22 * | 59/32 | 7.42/5.66 | LinJ.25.1790 |
| 1689 | GTP-binding protein (putative) | LinJ.25.1460 | 0.0197 | 117 | 53 | 2.06 | 3.09 * | 24/31 | 6.51/6.29 | None |
| 1690 | Hypothetical (second half) | LinJ.36.5380 | 0.9460 | 80 | 21 | 2.68 * | 1.30 | 71/30 | 5.69/5.85 | LinJ.30.1920 |
| 1757 | Hypothetical | LinJ.25.1720 | 0.9632 | 22 | 25 | 2.51 * | 2.52 | 26/28 | 8.62/6.29 | LinJ.16.1510 |
| 1809 | Hypothetical | LinJ.36.7070 | 0.8229 | 108 | 36 | 0.57 | 0.22 ** | 29/27 | 5.56/5.81 | None |
| 1855 | isocitrate dehydrogenase [NADP], mitochondrial precursor, putative | LinJ.10.0310 | 0.8889 | 3 | 8 | 0.25 | 0.12 * | 48/25 | 8.51/6.24 | None |
| 1904 | Hypothetical | LinJ.25.2520 | 0.0044 | 146 | 7.5 | 0.37 * | 0.40 | 109/23 | 7.36/5.15 | None |
| 1918 | orotidine-5-P decarboxylase/orotate phosphoribosyltransferase, putative | LinJ.16.0560 | 0.4661 | 14 | 14 | 0.26 * | 0.23 ** | 50/22 | 9.41/5.62 | None |
| 1921 | orotidine-5-P decarboxylase/orotate phosphoribosyltransferase, putative | LinJ.16.0560 | 0.4661 | 11 | 15 | 0.19 * | 0.11 ** | 50/22 | 9.41/6.00 | None |
| 1985 | Flavoprotein subunit-like protein | LinJ.07.0910 | 0.5405 | 12 | 17 | 2.43 * | 1.69 | 61/19 | 8.84/5.32 | LinJ.15.0320 |
| 2036 | Hypothetical | LinJ.21.1560 | 0.7471 | 19 | 13 | 0.59 * | 0.31 * | 39/18 | 4.94/6.33 | None |
| 2042 | pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 beta subunit, putative | LinJ.25.1790 | 0.9909 | 25 | 39 | 0.68 | 0.38 * | 38/17 | 5.72/5.5 | LinJ.22.0900 |
| 2108 | Hypothetical | LinJ.35.3770 | 0.0528 | 12 | 13 | 0.27 * | 0.20 * | 51/<14 | 7.51/5.12 | None |
| 2145 | Hypothetical | LinJ.26.1020 | 0.1396 | 37 | 6.9 | 0.36 * | 0.25 * | 60/<14 | 6.87/5.32 | LinJ.29.0940 |
| 2540 | Hypothetical protein containing an EF-hand calcium binding domain | LinJ.34.2780 | 0.0227 | 309 | 60 | 1.28 | 2.61 * | 47/56 | 5.35/5.66 | None |
| 2605 | i/6 autoantigen-like protein | LinJ.22.1310 | 0.1369 | 199 | 59 | 2.67 * | 2.2 * | 23/30 | 5.53/6.08 | None |
| 2625 | Succinyl-coa:3-ketoacid-coenzyme a transferase like protein | LinJ.30.1920 | 0.9835 | 371 | 49 | 1.48 | 3.10 * | 53/68 | 7.15/6.61 | LinJ.32.3510 |
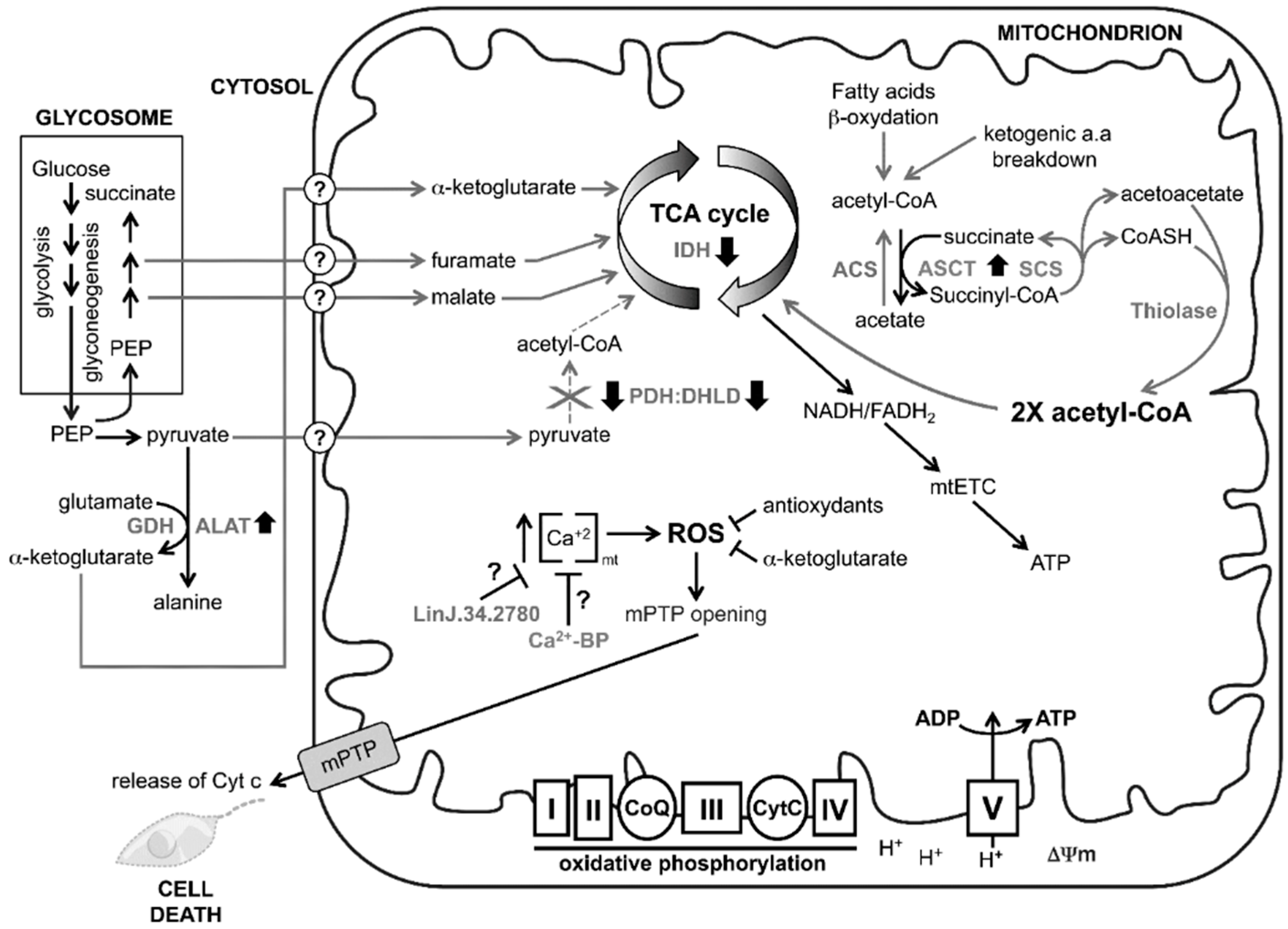
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. The World Health Organization, World Health Report; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette, M.; Drummelsmith, J.; Papadopoulou, B. Leishmaniasis: Drugs in the clinic, resistance and new developments. Drug Resist. Updat. 2004, 7, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira Cdos, S.; Martins, P.S.; Demicheli, C.; Brochu, C.; Ouellette, M.; Frézard, F. Thiol-induced reduction of antimony(V) into antimony(III): A comparative study with trypanothione, cysteinyl-glycine, cysteine and glutathione. Biometals 2003, 16, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, R.; Dey, S.; Xu, N.; Gage, D.; Lightbody, J.; Ouellette, M.; Rosen, B.P. Trypanothione overproduction and resistance to antimonials and arsenicals in Leishmania. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 10383–10387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Li, F.; Ding, K.; Sun, H. Reduction of pentavalent antimony by trypanothione and formation of a binary and ternary complex of antimony(III) and trypanothione. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 8, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El Fadili, K.; Messier, N.; Leprohon, P.; Roy, G.; Guimond, C.; Trudel, N.; Saravia, N.G.; Papadopoulou, B.; Légaré, D.; Ouellette, M. Role of the ABC transporter MRPA (PGPA) in antimony resistance in Leishmania infantum axenic and intracellular amastigotes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 1988–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haimeur, A.; Guimond, C.; Pilote, S.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Rosen, B.P.; Poulin, R.; Ouellette, M. Elevated levels of polyamines and trypanothione resulting from overexpression of the ornithine decarboxylase gene in arsenite-resistant Leishmania. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 34, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.; Padmanabhan, P.K.; Singh, S.; Roy, G.; Girard, I.; Chatterjee, M.; Ouellette, M.; Madhubala, R. Role of ABC transporter MRPA, gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase and ornithine decarboxylase in natural antimony-resistant isolates of Leishmania donovani. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 59, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haimeur, A.; Brochu, C.; Genest, P.; Papadopoulou, B.; Ouellette, M. Amplification of the ABC transporter gene PGPA and increased trypanothione levels in potassium antimonyl tartrate (SbIII) resistant Leishmania tarentolae. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2000, 108, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leprohon, P.; Legare, D.; Raymond, F.; Madore, E.; Hardiman, G.; Corbeil, J.; Ouellette, M. Gene expression modulation is associated with gene amplification, supernumerary chromosomes and chromosome loss in antimony-resistant Leishmania infantum. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mookerjee Basu, J.; Mookerjee, A.; Banerjee, R.; Saha, M.; Singh, S.; Naskar, K.; Tripathy, G.; Sinha, P.K.; Pandey, K.; Sundar, S.; et al. Inhibition of ABC transporters abolishes antimony resistance in Leishmania Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mandal, G.; Wyllie, S.; Singh, N.; Sundar, S.; Fairlamb, A.H.; Chatterjee, M. Increased levels of thiols protect antimony unresponsive Leishmania donovani field isolates against reactive oxygen species generated by trivalent antimony. Parasitology 2007, 134, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, W.; Leprohon, P.; Ouellette, M. Tolerance to drug-induced cell death favours the acquisition of multidrug resistance in Leishmania. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Victoria, F.J.; Gamarro, F.; Ouellette, M.; Castanys, S. Functional cloning of the miltefosine transporter. A novel P-type phospholipid translocase from Leishmania involved in drug resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 49965–49971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, A.C.; Boisvert, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Leprohon, P.; Corbeil, J.; Ouellette, M. Multiple mutations in heterogeneous miltefosine-resistant Leishmania major population as determined by whole genome sequencing. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cojean, S.; Houze, S.; Haouchine, D.; Huteau, F.; Lariven, S.; Hubert, V.; Michard, F.; Bories, C.; Pratlong, F.; le Bras, J.; et al. Leishmania resistance to miltefosine associated with genetic marker. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 704–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, S.L.; Coombs, G.H. Leishmaniasis—Current chemotherapy and recent advances in the search for novel drugs. Trends Parasitol. 2003, 19, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, J.; Saxena, A.; Singh, S. Chemotherapy of leishmaniasis: Past, present and future. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 1153–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, I.M.; Weidt, S.; Rivas, L.; Burgess, K.; Smith, T.K.; Ouellette, M. Untargeted metabolomic analysis of miltefosine action in Leishmania infantum reveals changes to the internal lipid metabolism. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2014, 4, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, C.; Loiseau, P.M.; Bories, C.; Breard, J. Miltefosine induces apoptosis-like death in Leishmania donovani promastigotes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sereno, D.; Holzmuller, P.; Mangot, I.; Cuny, G.; Ouaissi, A.; Lemesre, J.-L. Antimonial-mediated DNA fragmentation in Leishmania infantum amastigotes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 2064–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhandiran, G.; Shaha, C. Antimonial-induced increase in intracellular Ca2+ through non-selective cation channels in the host and the parasite is responsible for apoptosis of intracellular Leishmania donovani amastigotes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 25120–25132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, N.K.; Singh, G.; Dey, C.S. Miltefosine induces apoptosis in arsenite-resistant leishmania donovani promastigotes through mitochondrial dysfunction. Exp. Parasitol. 2007, 116, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proto, W.R.; Coombs, G.H.; Mottram, J.C. Cell death in parasitic protozoa: Regulated or incidental? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getachew, F.; Gedamu, L. Leishmania donovani mitochondrial iron superoxide dismutase A is released into the cytosol during miltefosine induced programmed cell death. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2012, 183, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mookerjee Basu, J.; Mookerjee, A.; Sen, P.; Bhaumik, S.; Sen, P.; Banerjee, S.; Naskar, K.; Choudhuri, S.K.; Saha, B.; Raha, S.; et al. Sodium antimony gluconate induces generation of reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide via phosphoinositide 3-kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in Leishmania donovani-infected macrophages. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1788–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panigrahi, A.K.; Ogata, Y.; Zikova, A.; Anupama, A.; Dalley, R.A.; Acestor, N.; Myler, P.J.; Stuart, K.D. A comprehensive analysis of Trypanosoma brucei mitochondrial proteome. Proteomics 2009, 9, 434–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, R.; Pypaert, M.; Hausler, T.; Horn, E.K.; Schneider, A. In vitro import of proteins into mitochondria of Trypanosoma brucei and Leishmania tarentolae. J. Cell Sci. 1996, 109 Pt 2, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horvath, A.; Nebohacova, M.; Lukes, J.; Maslov, D.A. Unusual polypeptide synthesis in the kinetoplast-mitochondria from Leishmania tarentolae. Identification of individual de novo translation products. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 7222–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, V.L.; Gabriel, K.; Traven, A. The ins and outs of the intermembrane space: Diverse mechanisms and evolutionary rewiring of mitochondrial protein import routes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claros, M.G.; Vincens, P. Computational method to predict mitochondrially imported proteins and their targeting sequences. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 241, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soumya, N.; Kumar, I.S.; Shivaprasad, S.; Gorakh, L.N.; Dinesh, N.; Swamy, K.K.; Singh, S. Amp-acetyl coa synthetase from leishmania donovani: Identification and functional analysis of “px4gk” motif. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 75, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummelsmith, J.; Brochu, V.; Girard, I.; Messier, N.; Ouellette, M. Proteome mapping of the protozoan parasite Leishmania and application to the study of drug targets and resistance mechanisms. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2003, 2, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, K.J.; Griffiths, M.W. Impact of hydroxyl- and superoxide anion-based oxidative stress on logarithmic and stationary phase Escherichia coli O157:H7 stress and virulence gene expression. Food Microbiol. 2012, 29, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomas, A.M.; Castro, H. Redox metabolism in mitochondria of trypanosomatids. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, J.; Singh, S. Miltefosine resistance in leishmania donovani involves suppression of oxidative stress-induced programmed cell death. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 135, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canuto, G.A.; Castilho-Martins, E.A.; Tavares, M.F.; Rivas, L.; Barbas, C.; López-Gonzálvez, Á. Multi-analytical platform metabolomic approach to study miltefosine mechanism of action and resistance in Leishmania. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 3459–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Chiang, S.C.; Lee, S.T. Divergence of trypanothione-dependent tryparedoxin cascade into cytosolic and mitochondrial pathways in arsenite-resistant variants of Leishmania amazonensis. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2008, 157, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessarollo, N.G.; Andrade, J.M.; Moreira, D.S.; Murta, S.M. Functional analysis of iron superoxide dismutase-A in wild-type and antimony-resistant Leishmania braziliensis and Leishmania infantum lines. Parasitol. Int. 2015, 64, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, L.; Luque-Ortega, J.R.; Manzano, J.I.; Castanys, S.; Rivas, L.; Gamarro, F. Tafenoquine, an antiplasmodial 8-aminoquinoline, targets leishmania respiratory complex III and induces apoptosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 5344–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathuria, M.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Sashidhara, K.V.; Singh, S.P.; Mitra, K. Induction of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in Leishmania donovani by orally active clerodane diterpene. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5916–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, N.; Das, B.B.; Ganguly, A.; Mukherjee, T.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Majumder, H.K. Camptothecin-induced imbalance in intracellular cation homeostasis regulates programmed cell death in unicellular hemoflagellate Leishmania donovani. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 52366–52375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Martin, X.; Garcia-Marchan, Y.; Fernandez, A.; Rodriguez, N.; Rojas, H.; Visbal, G.; Benaim, G. Amiodarone destabilizes intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis and biosynthesis of sterols in leishmania mexicana. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, S.N.; Ayong, L.; Pace, D.A. Calcium storage and function in apicomplexan parasites. Essays Biochem. 2011, 51, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Z.H.; Ridgley, E.L.; Enis, D.; Olness, F.; Ruben, L. Selective transfer of calcium from an acidic compartment to the mitochondrion of Trypanosoma brucei. Measurements with targeted aequorins. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 31022–31028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailloux, R.J.; Beriault, R.; Lemire, J.; Singh, R.; Chénier, D.R.; Hamel, R.D.; Appanna, V.D. The tricarboxylic acid cycle, an ancient metabolic network with a novel twist. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bringaud, F.; Riviere, L.; Coustou, V. Energy metabolism of trypanosomatids: Adaptation to available carbon sources. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2006, 149, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tielens, A.G.; van Grinsven, K.W.; Henze, K.; van Hellemond, J.J.; Martin, W. Acetate formation in the energy metabolism of parasitic helminths and protists. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazet, M.; Harijan, R.K.; Kiema, T.R.; Haapalainen, A.M.; Morand, P.; Morales, J.; Bringaud, F.; Wierenga, R.K.; Michels, P.A. The characterization and evolutionary relationships of a trypanosomal thiolase. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, G.W.; Goulding, D.; Field, M.C. The single dynamin-like protein of Trypanosoma brucei regulates mitochondrial division and is not required for endocytosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 10692–10701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanez, A.L.; Hehl, A.B.; Engstler, M.; Schneider, A. Ablation of the single dynamin of T. brucei blocks mitochondrial fission and endocytosis and leads to a precise cytokinesis arrest. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 2968–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vincent, I.M.; Racine, G.; Légaré, D.; Ouellette, M. Mitochondrial Proteomics of Antimony and Miltefosine Resistant Leishmania infantum. Proteomes 2015, 3, 328-346. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes3040328
Vincent IM, Racine G, Légaré D, Ouellette M. Mitochondrial Proteomics of Antimony and Miltefosine Resistant Leishmania infantum. Proteomes. 2015; 3(4):328-346. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes3040328
Chicago/Turabian StyleVincent, Isabel M., Gina Racine, Danielle Légaré, and Marc Ouellette. 2015. "Mitochondrial Proteomics of Antimony and Miltefosine Resistant Leishmania infantum" Proteomes 3, no. 4: 328-346. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes3040328
APA StyleVincent, I. M., Racine, G., Légaré, D., & Ouellette, M. (2015). Mitochondrial Proteomics of Antimony and Miltefosine Resistant Leishmania infantum. Proteomes, 3(4), 328-346. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes3040328





