Temporal and Spatial Profiling of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Surface Proteome: Insights into Intestinal Colonisation Dynamics In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Growth Conditions
2.2. Mice Ileal Loop Assay
2.3. Ethics Statement
2.4. Animals
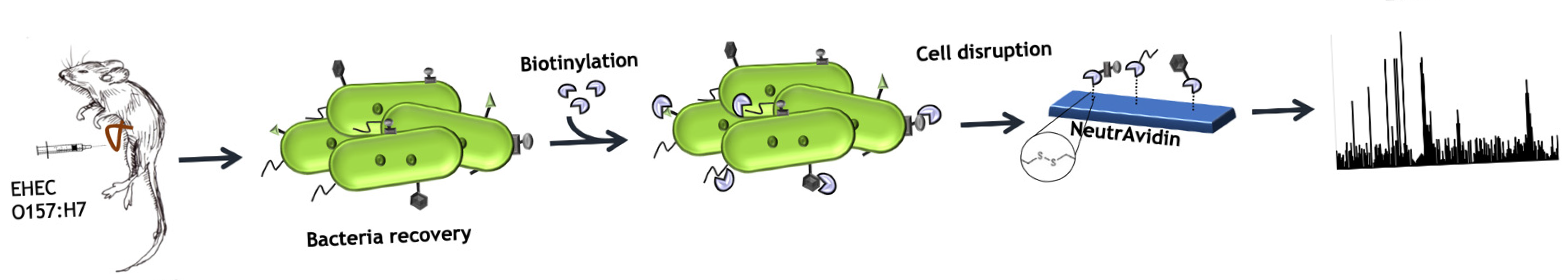
2.5. Biotinylation of Bacterial Cell Surface Proteins and Protein Affinity Purification
2.6. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.7. Protein Identification and Comparison
2.8. Secretome Prediction and Gene Ontology Enrichment
3. Results
3.1. Intestinal Profiling of E. coli O157:H7 Surface Proteins
3.2. Expression of Specific Surface Proteins of E. coli O157:H7 EDL933 Is Modified Depending on the Environment and the Stage of Infection
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, J.Y.; Yoon, J.; Hovde, C.J. A brief overview of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and its plasmid O157. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferens, W.A.; Hovde, C.J. Escherichia coli O157:H7: Animal reservoir and sources of human infection. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 465–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambushe, S.M.; Zishiri, O.T.; El Zowalaty, M.E. Review of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Prevalence, Pathogenicity, Heavy Metal and Antimicrobial Resistance, African Perspective. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 4645–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpman, D.; Stahl, A.L. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli Pathogenesis and the Host Response. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxen, M.A.; Finlay, B.B. Molecular mechanisms of Escherichia coli pathogenicity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, J.C.; Paton, A.W. Pathogenesis and diagnosis of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 450–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.P.; Frankel, G.M. The Locus of Enterocyte Effacement and Associated Virulence Factors of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, EHEC-0007-2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ageorges, V.; Monteiro, R.; Leroy, S.; Burgess, C.M.; Pizza, M.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F.; Desvaux, M. Molecular determinants of surface colonisation in diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli (DEC): From bacterial adhesion to biofilm formation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 314–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordonnier, C.; Etienne-Mesmin, L.; Thévenot, J.; Rougeron, A.; Rénier, S.; Chassaing, B.; Darfeuille-Michaud, A.; Barnich, N.; Blanquet-Diot, S.; Livrelli, V. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli pathogenesis: Role of Long polar fimbriae in Peyer’s patches interactions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, R.; Ageorges, V.; Rojas-Lopez, M.; Schmidt, H.; Weiss, A.; Bertin, Y.; Forano, E.; Jubelin, G.; Henderson, I.R.; Livrelli, V.; et al. A secretome view of colonisation factors in Shiga toxin-encoding Escherichia coli (STEC): From enterohaemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) to related enteropathotypes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363, fnw179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.; Chafsey, I.; Ageorges, V.; Leroy, S.; Chambon, C.; Hébraud, M.; Livrelli, V.; Pizza, M.; Pezzicoli, A.; Desvaux, M. The Secretome landscape of Escherichia coli O157:H7: Deciphering the cell-surface, outer membrane vesicle and extracellular subproteomes. J. Proteom. 2021, 232, 104025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.G.; Kaper, J.B. Multiple elements controlling adherence of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 to HeLa cells. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 4985–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.G.; Li, Y.; Tutt, C.B.; Xin, L.; Eaves-Pyles, T.; Soong, L. Outer membrane protein A of Escherichia coli O157:H7 stimulates dendritic cell activation. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 2676–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cookson, A.L.; Woodward, M.J. The role of intimin in the adherence of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) O157:H7 to HEp-2 tissue culture cells and to bovine gut explant tissues. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 292, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, F.; Batisson, I.; Frankel, G.M.; Harel, J.; Fairbrother, J.M. Interaction of enteropathogenic and Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli and porcine intestinal mucosa: Role of intimin and Tir in adherence. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 6005–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVinney, R.; Stein, M.; Reinscheid, D.; Abe, A.; Ruschkowski, S.; Finlay, B.B. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 produces Tir, which is translocated to the host cell membrane but is not tyrosine phosphorylated. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 2389–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, K.; Hilliard, G.M.; Hamilton, D.J.; Luo, J.; Ostmann, M.M.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli EtpA mediates adhesion between flagella and host cells. Nature 2009, 457, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, M.L.; Sanna, M.G.; Fontaine, A.; Sansonetti, P.J. OmpC is involved in invasion of epithelial cells by Shigella flexneri. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 3625–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, S.W.; Schirmer, T.; Rummel, G.; Steiert, M.; Ghosh, R.; Pauptit, R.A.; Jansonius, J.N.; Rosenbusch, J.P. Crystal structures explain functional properties of two E. coli porins. Nature 1992, 358, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.; Chafsey, I.; Caccia, N.; Ageorges, V.; Leroy, S.; Viala, D.; Hébraud, M.; Livrelli, V.; Pizza, M.; Pezzicoli, A.; et al. Specific Proteomic Identification of Collagen-Binding Proteins in Escherichia coli O157:H7: Characterisation of OmpA as a Potent Vaccine Antigen. Cells 2023, 12, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pore, D.; Chakrabarti, M.K. Outer membrane protein A (OmpA) from Shigella flexneri 2a: A promising subunit vaccine candidate. Vaccine 2013, 31, 3644–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Lopez, M.; Monteiro, R.; Pizza, M.; Desvaux, M.; Rosini, R. Intestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli: Insights for Vaccine Development. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolhion, N.; Carvalho, F.A.; Darfeuille-Michaud, A. OmpC and the sigma(E) regulatory pathway are involved in adhesion and invasion of the Crohn’s disease-associated Escherichia coli strain LF82. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 63, 1684–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, J.; Schulz, G.E. The structure of the outer membrane protein OmpX from Escherichia coli reveals possible mechanisms of virulence. Structure 1999, 7, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.Q.; Carychao, D.; Lindsey, R.L. Conditional expression of flagellar motility, curli fimbriae, and biofilms in Shiga toxin- producing Escherichia albertii. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1456637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, R.; Chafsey, I.; Leroy, S.; Chambon, C.; Hébraud, M.; Livrelli, V.; Pizza, M.; Pezzicoli, A.; Desvaux, M. Differential biotin labelling of the cell envelope proteins in lipopolysaccharidic diderm bacteria: Exploring the proteosurfaceome of Escherichia coli using sulfo-NHS-SS-biotin and sulfo-NHS-PEG4-bismannose-SS-biotin. J. Proteom. 2018, 181, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Sangiao, E.; Giddey, A.D.; Rodriguez, C.L.; Tang, Z.; Liu, X.; Soares, N.C. Proteomic Approaches to Unravel Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance and Immune Evasion of Bacterial Pathogens. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 850374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, C.; Rappuoli, R. Reverse vaccinology in the 21st century: Improvements over the original design. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1285, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, L.W.; Remis, R.S.; Helgerson, S.D.; McGee, H.B.; Wells, J.G.; Davis, B.R.; Hebert, R.J.; Olcott, E.S.; Johnson, L.M.; Hargrett, N.T.; et al. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983, 308, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, G. Biotinylation reagents for the study of cell surface proteins. Proteomics 2008, 8, 4012–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romine, M.F. Genome-wide protein localization prediction strategies for gram negative bacteria. BMC Genom. 2011, 12 (Suppl. S1), S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, N.Y.; Wagner, J.R.; Laird, M.R.; Melli, G.; Rey, S.; Lo, R.; Dao, P.; Sahinalp, S.C.; Ester, M.; Foster, L.J.; et al. PSORTb 3.0: Improved protein subcellular localization prediction with refined localization subcategories and predictive capabilities for all prokaryotes. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufel, F.; Armenteros, J.J.A.; Johansen, A.R.; Gíslason, M.H.; Pihl, S.I.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 6.0 predicts all five types of signal peptides using protein language models. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendtsen, J.D.; Kiemer, L.; Fausbøll, A.; Brunak, S. Non-classical protein secretion in bacteria. BMC Microbiol. 2005, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yuan, Z.; Ma, Z.; Song, J.; Xie, X.; Chen, Y. KEGG-PATH: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes-based pathway analysis using a path analysis model. Mol. Biosyst. 2014, 10, 2441–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagnot, C.; Zorgani, M.A.; Astruc, T.; Desvaux, M. Proteinaceous determinants of surface colonization in bacteria: Bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation from a protein secretion perspective. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, H.; Zabad, S.; Rivera, N.; Rowin, E.; Hassan, M.; De Jesus, S.M.G.; Santos, P.S.L.; Kravchenko, K.; Mikhova, M.; et al. MoonProt 3.0: An update of the moonlighting proteins database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D368–D372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.D.; Ebert, D.; Muruganujan, A.; Mushayahama, T.; Albou, L.; Mi, H. PANTHER: Making genome-scale phylogenetics accessible to all. Protein Sci. 2022, 31, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiberson, E.R.; Weiss, A.; Ryan, D.J.; Monteith, A.J.; Sharman, K.; Gutierrez, D.B.; Perry, W.J.; Caprioli, R.M.; Skaar, E.P.; Spraggins, J.M. Spatially Targeted Proteomics of the Host-Pathogen Interface during Staphylococcal Abscess Formation. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumaran, A.; Woroszchuk, E.; Ross, T.; Geddes-McAlister, J. Proteomics of host-bacterial interactions: New insights from dual perspectives. Can. J. Microbiol. 2021, 67, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, T.M.; Cristea, I.M. Proteomics Tracing the Footsteps of Infectious Disease. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2017, 16 (Suppl. S1), S5–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.; Kakar, N.; Meyer, T.C.; Depke, M.; Masouris, I.; Burchhardt, G.; Gómez-Mejia, A.; Dhople, V.; Håvarstein, L.S.; Sun, Z.; et al. In vivo proteomics identifies the competence regulon and AliB oligopeptide transporter as pathogenic factors in pneumococcal meningitis. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruh, N.A.; Troudt, J.; Izzo, A.; Prenni, J.; Dobos, K.M. Portrait of a pathogen: The Mycobacterium tuberculosis proteome in vivo. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, A.; Bobonis, J.; Kurzawa, N.; Stein, F.; Helm, D.; Hevler, J.; Typas, A.; Savitski, M.M. Thermal proteome profiling in bacteria: Probing protein state in vivo. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2018, 14, e8242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, T.; Vorwerk, S.; Liss, V.; Chao, T.-C.; Hensel, M.; Hansmeier, N. Proteomic Analysis of Salmonella-modified Membranes Reveals Adaptations to Macrophage Hosts. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2020, 19, 900–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markoutsa, S.; Bahr, U.; Papasotiriou, D.G.; Häfner, A.-K.; Karas, M.; Sorg, B.L. Sulfo-NHS-SS-biotin derivatization: A versatile tool for MALDI mass analysis of PTMs in lysine-rich proteins. Proteomics 2014, 14, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langó, T.; Kuffa, K.; Tóth, G.; Turiák, L.; Drahos, L.; Tusnády, G.E. Comprehensive Discovery of the Accessible Primary Amino Group-Containing Segments from Cell Surface Proteins by Fine-Tuning a High-Throughput Biotinylation Method. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Nakayama, D.; Shima, K.; Kuyama, H.; Ando, E.; Okamura, T.; Ueyama, N.; Nakazawa, T.; Norioka, S.; Nishimura, O.; et al. Selective isolation of N-terminal peptides from proteins and their de novo sequencing by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry without regard to unblocking or blocking of N-terminal amino acids. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 3313–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Chavez, F.; Baumler, A.J. The Pyromaniac Inside You: Salmonella Metabolism in the Host Gut. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 69, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinaud, L.; Ferrari, M.L.; Friedman, R.; Jehmlich, N.; von Bergen, M.; Phalipon, A.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Campbell-Valois, F.-X. Identification of novel substrates of Shigella T3SA through analysis of its virulence plasmid-encoded secretome. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaar, E.P. The battle for iron between bacterial pathogens and their vertebrate hosts. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000949. [Google Scholar]
- Hooker-Romero, D.; Mettert, E.; Schwiesow, L.; Balderas, D.; Alvarez, A.P.; Kicin, A.; Gonzalez, A.L.; Plano, G.V.; Kiley, P.J.; Auerbuch, V. Iron availability and oxygen tension regulate the Yersinia Ysc type III secretion system to enable disseminated infection. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008001. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, E.D.; Wyckoff, E.E.; Mey, A.R.; Fisher, C.R.; Payne, S.M. Nonredundant Roles of Iron Acquisition Systems in Vibrio cholerae. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Dai, X. Shaping of microbial phenotypes by trade-offs. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, M.; Yu, K.; Fu, J.; Zhou, F.; Liu, X. Proteomic Analyses of Intracellular Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Reveal Extensive Bacterial Adaptations to Infected Host Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 2897–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fourie, K.R.; Wilson, H.L. Understanding GroEL and DnaK Stress Response Proteins as Antigens for Bacterial Diseases. Vaccines 2020, 8, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, C.J. Protein moonlighting: What is it, and why is it important? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20160523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, B.; Martin, A. Bacterial moonlighting proteins and bacterial virulence. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 358, 155–213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

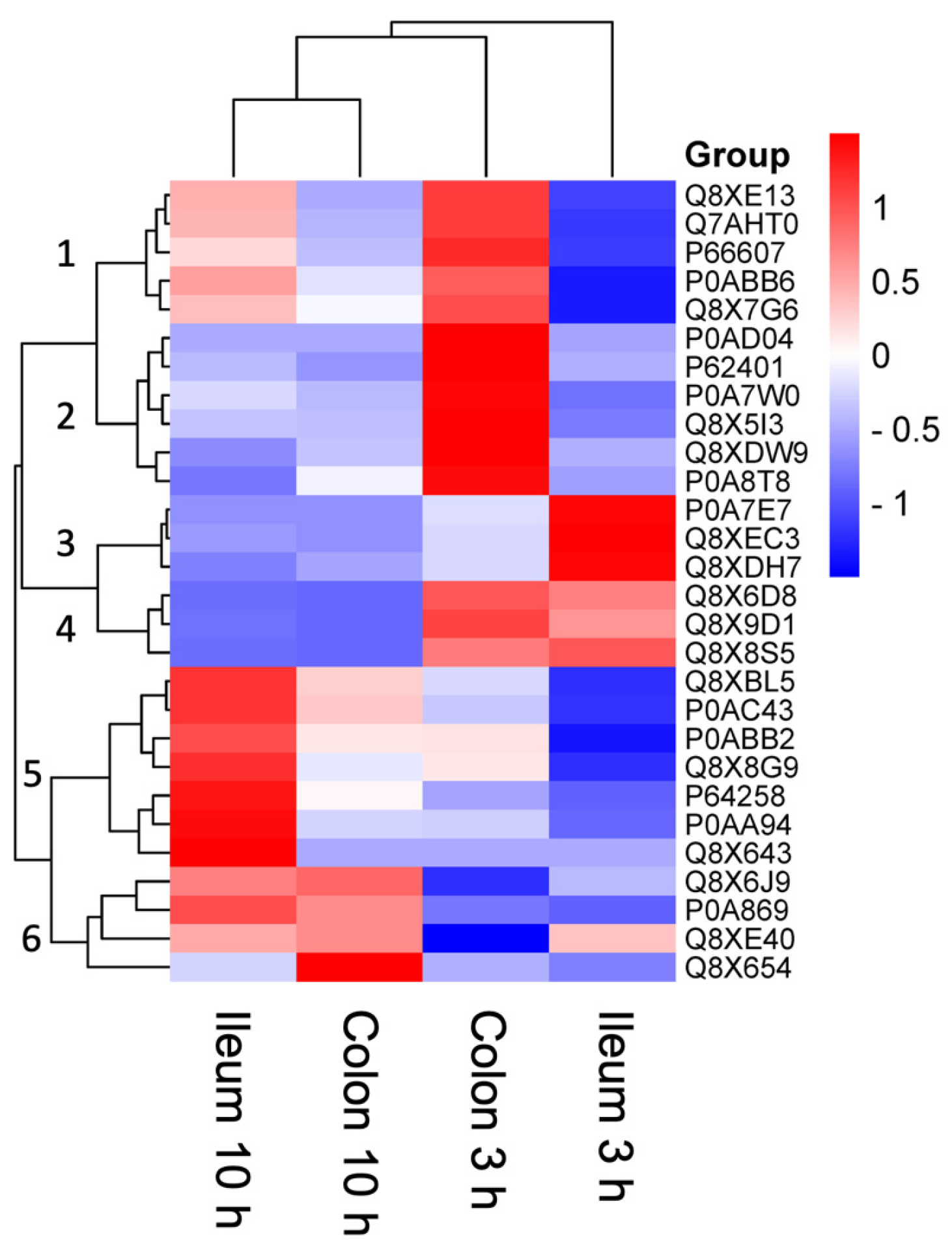
| Uniprot ID | Protein Name (Gene) | Function | Highest Abundance Conditions | Lowest Abundance Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q8XE13 | GlpB (Z3500) | Conversion of glycerol 3-phosphate to dihydroxyacetone. Uses fumarate or nitrate as electron acceptor. | Colon 3 h | Ileum 3 h |
| Q7AHT0 | FixC (Z0049) | Could be part of an electron transfer system required for anaerobic carnitine reduction. | Colon 3 h | Ileum 3 h |
| P66607 | RpsG (Z4699) | One of the primary rRNA binding proteins, it binds directly to 16S rRNA where it nucleates assembly of the head domain of the 30S subunit. Is located at the subunit interface close to the decoding center, probably blocks exit of the E-site tRNA. | Colon 3 h | Ileum 3 h |
| P0ABB6 | AtpD (Z5230) | Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. The catalytic sites are hosted primarily by the beta subunits. | Colon 3 h | Ileum 3 h |
| A0A9Q6ZIS0 | PuuC (Z2488) | Catalyses the aminotransferase reaction from putrescine to 2-oxoglutarate, leading to glutamate and 4-aminobutanal, which spontaneously cyclises to form 1-pyrroline. | Colon 3 h | Ileum 3 h |
| P0AD04 | LetA (Z2880) | Lipophilic envelope-spanning tunnel protein AComponent of a transport pathway that contributes to membrane integrity. | Colon 3 h | Ileum 3 h |
| P62401 | RplE (Z4678) | This is one of the proteins that bind and probably mediate the attachment of the 5S RNA into the large ribosomal subunit, where it forms part of the central protuberance. In the 70S ribosome it contacts protein S13 of the 30S subunit (bridge B1b), connecting the 2 subunits; this bridge is implicated in subunit movement. Contacts the P site tRNA; the 5S rRNA and some of its associated proteins might help stabilise positioning of ribosome-bound tRNAs. | Colon 3 h | Colon 10 h |
| P0A7W0 | RpsD (Z4666) | Functions as a rho-dependent antiterminator of rRNA transcription, increasing the synthesis of rRNA under conditions of excess protein, allowing a more rapid return to homeostasis. Binds directly to RNA polymerase | Colon 3 h | Ileum 3 h |
| A0A5Q2ENA4 | CydC (Z1230) | Maintain the reduced state of cytoplasmic L-cysteine, thereby providing an important connection between sulfur metabolism, oxidative stress and resistance to antibiotics | Colon 3 h | Ileum 3 h |
| A0A9Q7EDA9 | GdhA (Z2793) | Catalyses the reversible oxidative deamination of glutamate to alpha-ketoglutarate and ammonia. | Colon 3 h | Ileum 10 h |
| P0A8T8 | RpoC (Z5561) | DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyses the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. | Colon 3 h | Ileum 10 h |
| P0A7E7 | PyrG (Z4095) | Catalyses the ATP-dependent amination of UTP to CTP with either L-glutamine or ammonia as the source of nitrogen. Regulates intracellular CTP levels through interactions with the four ribonucleotide triphosphates. | Ileum 3 h | Ileum 10 h |
| Q8XEC3 | UbiC (Z5638) | Removes the pyruvyl group from chorismate, with concomitant aromatisation of the ring, to provide 4-hydroxybenzoate (4HB) for the ubiquinone pathway. | Ileum 3 h | Colon 10 h |
| Q8XDH7 | TreA (Z1968) | Provides the cells with the ability to utilise trehalose at high osmolarity by splitting it into glucose molecules that can subsequently be taken up by the phosphotransferase-mediated uptake system. | Ileum 3 h | Ileum 10 h |
| A0A9Q7EEZ3 | EivE (Z4196) | Encoded within the type III secretion system (SPI-1 T3SS), it is essential for the translocation of protein effectors into host cells. Forms a complex with SipB and SipC in the presence of their chaperone SicA. Positively regulates the secretion of SPI-1 T3SS effector proteins SipB, SipC and SipD and negatively influences the secretion of SipA, SopA and SptP. | Ileum 3 h Colon 3 h | Colon 10 h |
| A0A9Q6Z841 | MreC (Z4609) | Involved in formation and maintenance of cell shape. Responsible for formation of rod shape. May also contribute to regulation of formation of penicillin-binding proteins. | Ileum 3 h Colon 3 h | Colon 10 h |
| Q8X8S5 | Csm (Z2389) | DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase activity, acting on CpNpG substrates. | Ileum 3 h Colon 3 h | Colon 10 h |
| Q8XBL5 | LigA (Z3677) | DNA ligase that catalyses the formation of phosphodiester linkages between 5′-phosphoryl and 3′-hydroxyl groups in double-stranded DNA using NAD as a coenzyme and as the energy source for the reaction. It is essential for DNA replication and repair of damaged DNA. | Ileum 10 h | Ileum 3 h |
| P0AC43 | SdhA (Z0877) | Two distinct, membrane-bound, FAD-containing enzymes are responsible for the catalysis of fumarate and succinate interconversion; the fumarate reductase is used in anaerobic growth, and the succinate dehydrogenase is used in aerobic growth. | Ileum 10 h | Ileum 3 h |
| P0ABB2 | AtpA (Z5232) | Produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane. The alpha chain is a regulatory subunit. | Ileum 10 h | Ileum 3 h |
| Q8X8G9 | YihI (Z5402) | A GTPase-activating protein (GAP) that modifies Der/EngA GTPase function. May play a role in ribosome biogenesis. | Ileum 10 h | Ileum 3 h |
| P64258 | MraY (Z0097) | Catalyses the initial step of the lipid cycle reactions in the biosynthesis of the cell wall peptidoglycan: transfers peptidoglycan precursor phospho-MurNAc-pentapeptide from UDP-MurNAc-pentapeptide onto the lipid carrier undecaprenyl phosphate, yielding undecaprenyl-pyrophosphoryl-MurNAc-pentapeptide, known as lipid I. | Ileum 10 h | Ileum 3 h |
| P0AA94 | YpdA (Z3645) | Member of the two-component regulatory system YpdA/YpdB. YpdA activates YpdB by phosphorylation in response to high concentrations of extracellular pyruvate. | Ileum 10 h | Ileum 3 h |
| Q8X643 | PreA (Z3402) | Involved in pyrimidine base degradation. Catalyses physiologically the reduction in uracil to 5,6-dihydrouracil (DHU) by using NADH as a specific cosubstrate. It also catalyses the reverse reaction and the reduction in thymine to 5,6-dihydrothymine (DHT). | Ileum 10 h | Ileum 3 h |
| Q8X6J9 | LysRA (Z0346) | Regulates the expression of the nodABCFE genes which encode other nodulation proteins. | Ileum 10 h Colon 10 h | Colon 3 h |
| P0A869 | TalA (Z3720) | Transaldolase is important for the balance of metabolites in the pentose-phosphate pathway. | Ileum 10 h Colon 10 h | Ileum 3 h |
| A0A9Q7ED38 | RcsD (Z3475) | Component of the Rcs signaling system, which controls transcription of numerous genes. RcsD is a phosphotransfer intermediate between the sensor kinase RcsC and the response regulator RcsB. It acquires a phosphoryl group from RcsC and transfers it to RcsB. | Ileum 10 h Colon 10 h | Colon 3 h |
| Q8X654 | LysRB (Z3395) | Regulatory gene, a lysR homologue, which regulates the level of chvE | Ileum 10 h Colon 10 h | Ileum 3 h |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monteiro, R.; Chafsey, I.; Cordonnier, C.; Ageorges, V.; Viala, D.; Hébraud, M.; Livrelli, V.; Pezzicoli, A.; Pizza, M.; Desvaux, M. Temporal and Spatial Profiling of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Surface Proteome: Insights into Intestinal Colonisation Dynamics In Vivo. Proteomes 2025, 13, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes13040052
Monteiro R, Chafsey I, Cordonnier C, Ageorges V, Viala D, Hébraud M, Livrelli V, Pezzicoli A, Pizza M, Desvaux M. Temporal and Spatial Profiling of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Surface Proteome: Insights into Intestinal Colonisation Dynamics In Vivo. Proteomes. 2025; 13(4):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes13040052
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonteiro, Ricardo, Ingrid Chafsey, Charlotte Cordonnier, Valentin Ageorges, Didier Viala, Michel Hébraud, Valérie Livrelli, Alfredo Pezzicoli, Mariagrazia Pizza, and Mickaël Desvaux. 2025. "Temporal and Spatial Profiling of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Surface Proteome: Insights into Intestinal Colonisation Dynamics In Vivo" Proteomes 13, no. 4: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes13040052
APA StyleMonteiro, R., Chafsey, I., Cordonnier, C., Ageorges, V., Viala, D., Hébraud, M., Livrelli, V., Pezzicoli, A., Pizza, M., & Desvaux, M. (2025). Temporal and Spatial Profiling of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Surface Proteome: Insights into Intestinal Colonisation Dynamics In Vivo. Proteomes, 13(4), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes13040052








