Role of LIN28B in the Regulation of Ribosomal Biogenesis and Lipid Metabolism in Medulloblastoma Brain Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. siRNA-Mediated Knockdown Transfection
2.3. Immunoblotting
2.4. WST-1 Assay and Protein Content
2.5. Proteomic Analysis
2.5.1. Protein Extraction and Sample Preparation
2.5.2. Protein Reduction, Alkylation, and Digestion
2.5.3. Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics Data Analysis
2.6. Nucleolar Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.7. Assessment of Intracellular Lipid Droplets
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
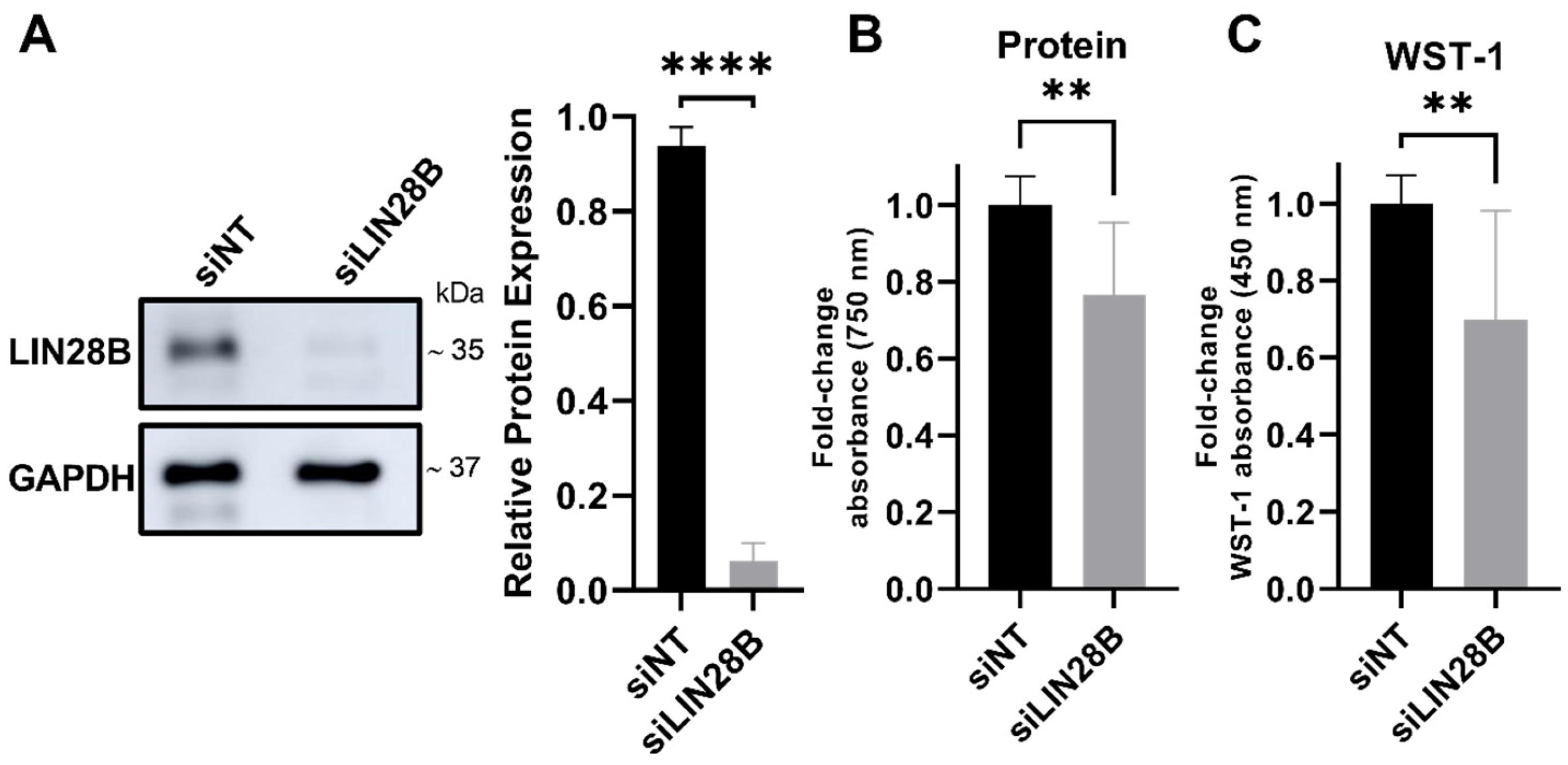
3.1. LIN28B Silencing Reduces Viability of MB Cells
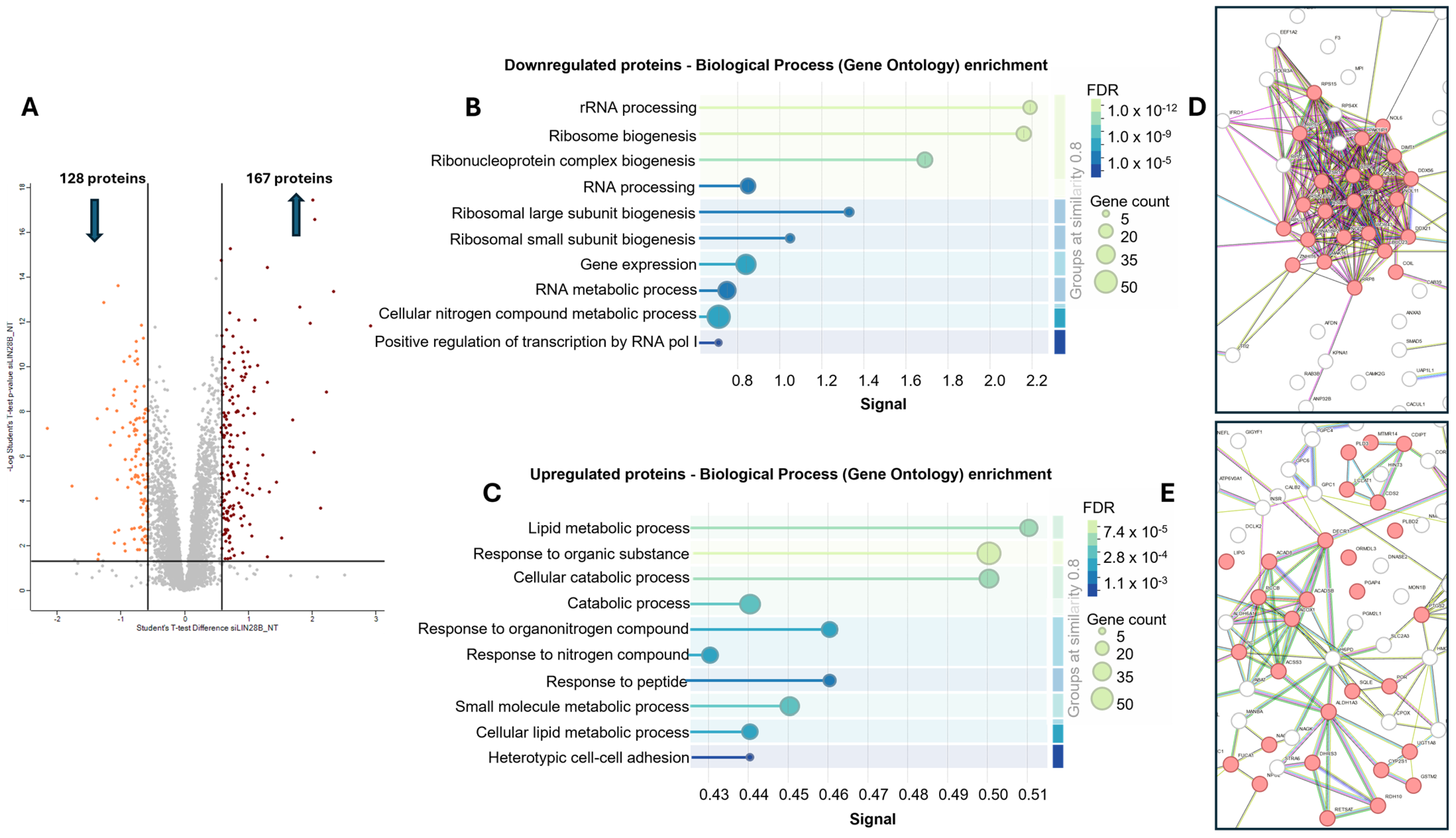
3.2. LIN28B Knockdown Regulates Expression of Proteins Associated with RNA Biogenesis and Different Metabolic Pathways
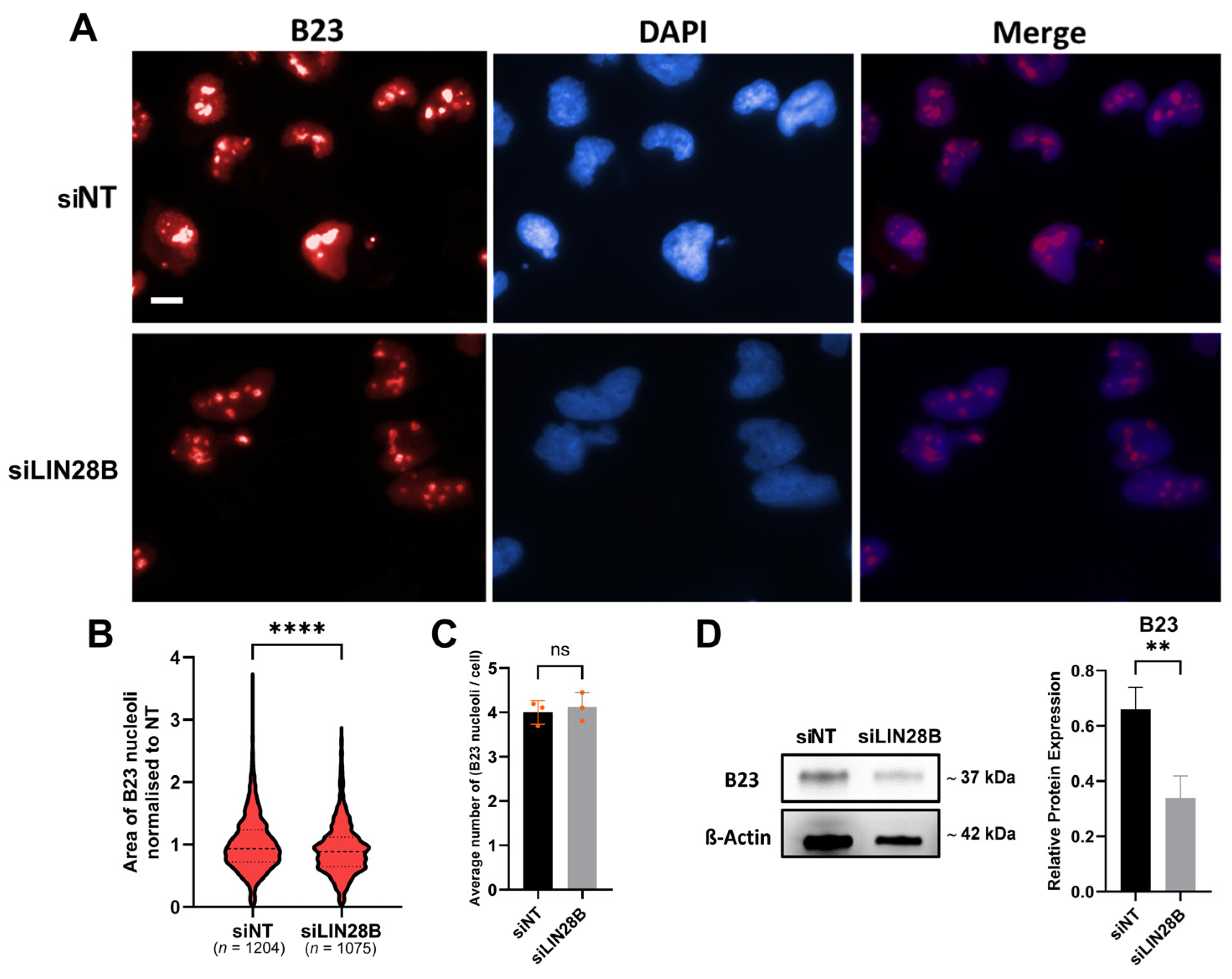
3.3. LIN28B Promotes Expression of Proteins Involved in Ribosomal Biogenesis
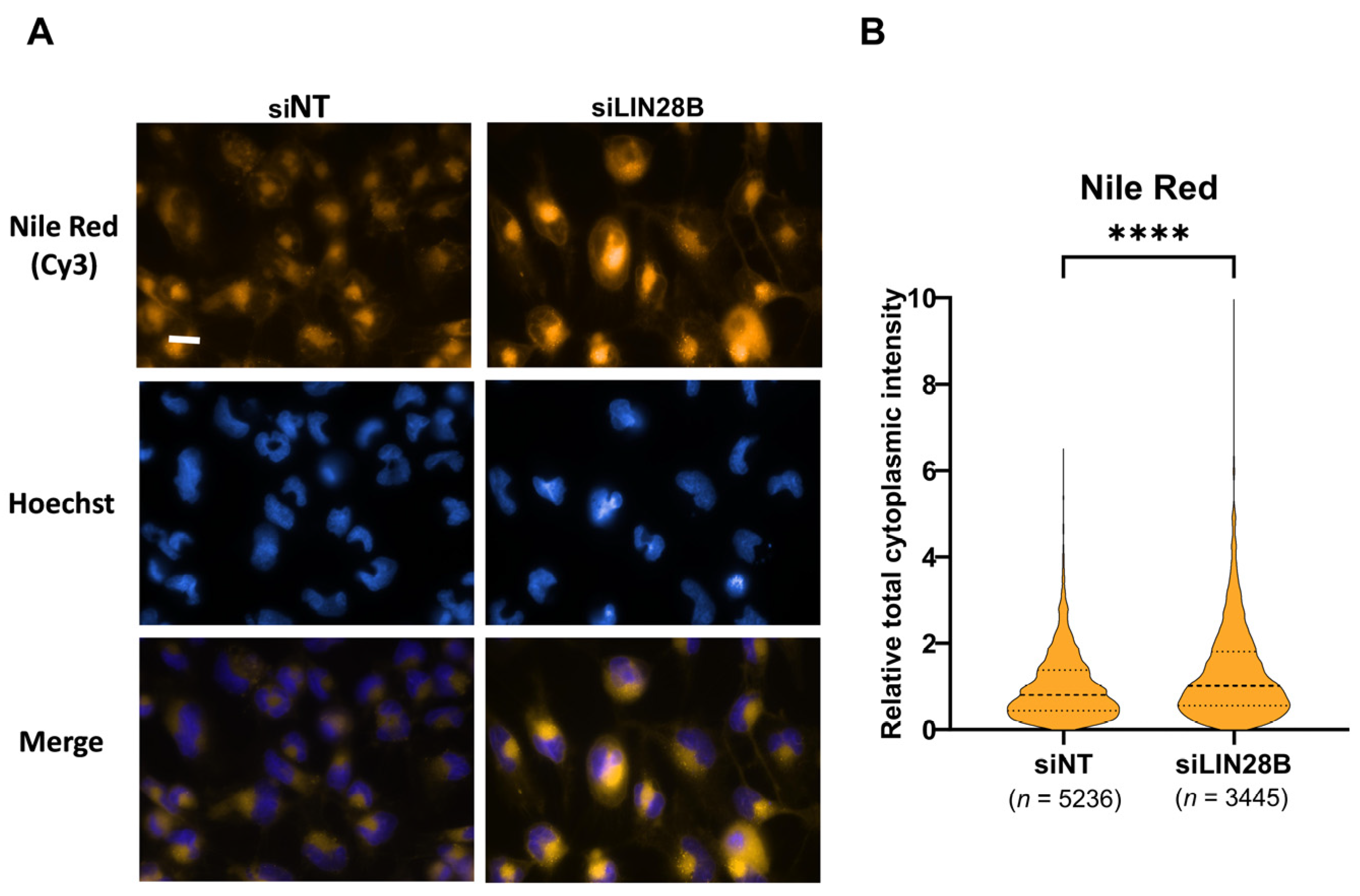
3.4. LIN28B Inhibits Lipid Accumulation in Daoy Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Northcott, P.A.; Robinson, G.W.; Kratz, C.P.; Mabbott, D.J.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Clifford, S.C.; Rutkowski, S.; Ellison, D.W.; Malkin, D.; Taylor, M.D.; et al. Medulloblastoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbertson, R.J. Medulloblastoma: Signalling a change in treatment. Lancet Oncol. 2004, 5, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, A.; Caracciolo, V.; Russo, G.; Reiss, K.; Giordano, A. Medulloblastoma: From molecular pathology to therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, D.M.; Merchant, T.E.; Strother, D.; Zhou, T.; Duffner, P.; Burger, P.C.; Miller, D.C.; Lyon, N.; Bonner, M.J.; Msall, M.; et al. Induction chemotherapy and conformal radiation therapy for very young children with nonmetastatic medulloblastoma: Children’s Oncology Group study P9934. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3181–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddrey, A.M.; Bergeron, J.A.; Lombardo, E.R.; McDonald, N.K.; Mulne, A.F.; Barenberg, P.D.; Bowers, D.C. Neuropsychological performance and quality of life of 10 year survivors of childhood medulloblastoma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2005, 72, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maklad, A.; Sedeeq, M.; Wilson, R.; Heath, J.A.; Gueven, N.; Azimi, I. LIN28 expression and function in medulloblastoma. J. Cell Physiol. 2023, 238, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ito, H.; Watanabe, A.; Ge, X.; Kodama, T.; Aburatani, H. Identification and characterization of lin-28 homolog B (LIN28B) in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Gene 2006, 384, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, E.G.; Tang, L. Conservation of the heterochronic regulator Lin-28, its developmental expression and microRNA complementary sites. Dev. Biol. 2003, 258, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, E.G.; Lee, R.C.; Ambros, V. The Cold Shock Domain Protein LIN-28 Controls Developmental Timing in C. elegans and Is Regulated by the lin-4 RNA. Cell 1997, 88, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambros, V.; Horvitz, H. Heterochronic mutants of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 1984, 226, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yang, S.L.; Herrlinger, S.; Liang, C.; Dzieciatkowska, M.; Hansen, K.C.; Desai, R.; Nagy, A.; Niswander, L.; Moss, E.G.; et al. Lin28 promotes the proliferative capacity of neural progenitor cells in brain development. Development 2015, 142, 1616–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.A.; Viswanathan, S.R.; Yabuuchi, A.; Cunniff, K.; Takeuchi, A.; Park, I.H.; Sero, J.E.; Zhu, H.; Perez-Atayde, A.; Frazier, A.L.; et al. A role for Lin28 in primordial germ-cell development and germ-cell malignancy. Nature 2009, 460, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzer, E.; Heine, C.; Jiang, Q.; Lee, V.M.; Moss, E.G. LIN28 alters cell fate succession and acts independently of the let-7 microRNA during neurogliogenesis in vitro. Development 2010, 137, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polesskaya, A.; Cuvellier, S.; Naguibneva, I.; Duquet, A.; Moss, E.G.; Harel-Bellan, A. Lin-28 binds IGF-2 mRNA and participates in skeletal myogenesis by increasing translation efficiency. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 1125–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, R.; Zhou, J.; Chen, C.; Xu, T.; Yan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Shen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Fu, D.; et al. LIN28 Is Involved in Glioma Carcinogenesis and Predicts Outcomes of Glioblastoma Multiforme Patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Rajeswarie, R.T.; Chickabasaviah Yasha, T.; Nandeesh, B.N.; Arivazhagan, A.; Santosh, V. LIN28A, a sensitive immunohistochemical marker for Embryonal Tumor with Multilayered Rosettes (ETMR), is also positive in a subset of Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor (AT/RT). Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2017, 33, 1953–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Shim, K.-W.; Han, J.W.; Choi, J.; Kim, D.-S.; Lyu, C.J.; Kim, J.W.; Suh, C.-O.; Cho, J. Treatment Outcome and Prognostic Molecular Markers of Supratentorial Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumors. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshunov, A.; Ryzhova, M.; Jones, D.T.W.; Northcott, P.A.; Van Sluis, P.; Volckmann, R.; Koster, J.; Versteeg, R.; Cowdrey, C.; Perry, A.; et al. LIN28A immunoreactivity is a potent diagnostic marker of embryonal tumor with multilayered rosettes (ETMR). Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 124, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diskin, S.J.; Capasso, M.; Schnepp, R.W.; Cole, K.A.; Attiyeh, E.F.; Hou, C.; Diamond, M.; Carpenter, E.L.; Winter, C.; Lee, H.; et al. Common variation at 6q16 within HACE1 and LIN28B influences susceptibility to neuroblastoma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.S.; Moggridge, S.; Müller, T.; Sorensen, P.H.; Morin, G.B.; Krijgsveld, J. Single-pot, solid-phase-enhanced sample preparation for proteomics experiments. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chear, S.; Perry, S.; Wilson, R.; Bindoff, A.; Talbot, J.; Ware, T.L.; Grubman, A.; Vickers, J.C.; Pébay, A.; Ruddle, J.B.; et al. Lysosomal alterations and decreased electrophysiological activity in CLN3 disease patient-derived cortical neurons. Dis. Model. Mech. 2022, 15, dmm049651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Csordas, A.; Bai, J.; Bernal-Llinares, M.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Inuganti, A.; Griss, J.; Mayer, G.; Eisenacher, M. The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: Improving support for quantification data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D442–D450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Ebert, D.; Muruganujan, A.; Mills, C.; Albou, L.P.; Mushayamaha, T.; Thomas, P.D. PANTHER version 16: A revised family classification tree-based classification tool enhancer regions extensive, A.P.I. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D394–D403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, L.J.; Kuhn, M.; Stark, M.; Chaffron, S.; Creevey, C.; Muller, J.; Doerks, T.; Julien, P.; Roth, A.; Simonovic, M.; et al. STRING 8—A global view on proteins and their functional interactions in 630 organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D412–D416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, M.O.J.; Hingorani, K.; Szebeni, A. Conventional and nonconventional roles of the nucleolus. In International Review of Cytology; Jeon, K.W., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 199–266. [Google Scholar]
- Boisvert, F.M.; van Koningsbruggen, S.; Navascués, J.; Lamond, A.I. The multifunctional nucleolus. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savkur, R.S.; Olson, M.O. Preferential cleavage in pre-ribosomal RNA by protein B23 endoribonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 4508–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itahana, K.; Bhat, K.P.; Jin, A.; Itahana, Y.; Hawke, D.; Kobayashi, R.; Zhang, Y. Tumor Suppressor ARF Degrades B23, a Nucleolar Protein Involved in Ribosome Biogenesis and Cell Proliferation. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.; Wang, Y.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Backlund, P.; Kolli, N.; Yergey, A.; Wilkinson, K.D.; Dasso, M. Nucleolar protein B23/nucleophosmin regulates the vertebrate SUMO pathway through SENP3 and SENP5 proteases. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 183, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.E. Developmental regulation of nucleolus size during Drosophila eye differentiation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derenzini, M.; Trerè, D.; Pession, A.; Govoni, M.; Sirri, V.; Chieco, P. Nucleolar size indicates the rapidity of cell proliferation in cancer tissues. J. Pathol. 2000, 191, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanaro, L.; Treré, D.; Derenzini, M. Nucleolus, ribosomes, and cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrlinger, S.; Shao, Q.; Yang, M.; Chang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Pan, X.; Yin, H.; Xie, L.-W.; Chen, J.-F. Lin28-mediated temporal promotion of protein synthesis is crucial for neural progenitor cell maintenance and brain development in mice. Development 2019, 146, dev173765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Robinton, D.A.; Seligson, M.T.; Wu, L.; Li, L.; Rakheja, D.; Comerford, S.A.; Ramezani, S.; Sun, X.; Parikh, M.S.; et al. Lin28b Is Sufficient to Drive Liver Cancer and Necessary for Its Maintenance in Murine Models. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molenaar, J.J.; Domingo-Fernández, R.; E Ebus, M.; Lindner, S.; Koster, J.; Drabek, K.; Mestdagh, P.; van Sluis, P.; Valentijn, L.J.; van Nes, J.; et al. LIN28B induces neuroblastoma and enhances MYCN levels via let-7 suppression. Nat Genet. 2012, 44, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corallo, D.; Donadon, M.; Pantile, M.; Sidarovich, V.; Cocchi, S.; Ori, M.; De Sarlo, M.; Candiani, S.; Frasson, C.; Distel, M.; et al. LIN28B increases neural crest cell migration and leads to transformation of trunk sympathoadrenal precursors. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 1225–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missios, P.; da Rocha, E.L.; Pearson, D.S.; Philipp, J.; Aleman, M.M.; Pirouz, M.; Farache, D.; Franses, J.W.; Kubaczka, C.; Tsanov, K.M.; et al. LIN28B alters ribosomal dynamics to promote metastasis in MYCN-driven malignancy. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e145142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Bai, L.; Cao, F.; Wang, S.; He, H.; Song, M.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Si, Q.; et al. Targeting LIN28B reprograms tumor glucose metabolism and acidic microenvironment to suppress cancer stemness and metastasis. Oncogene 2019, 38, 4527–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, R.; Chatterji, P.; Andres, S.; Hamilton, K.; Simon, L.; Foley, S.W.; Jeganathan, A.; Gregory, B.D.; Madison, B.; Rustgi, A.K. Differential Regulation of LET-7 by LIN28B Isoform–Specific Functions. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turi, Z.; Lacey, M.; Mistrik, M.; Moudry, P. Impaired ribosome biogenesis: Mechanisms and relevance to cancer and aging. Aging 2019, 11, 2512–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley-Barnes, K.I.; McCann, K.L.; Ogawa, L.M.; Merkel, J.; Surovtseva, Y.V.; Baserga, S.J. Diverse Regulators of Human Ribosome Biogenesis Discovered by Changes in Nucleolar Number. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 1923–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskounova, E.; Polytarchou, C.; Thornton, J.E.; Lapierre, R.J.; Pothoulakis, C.; Hagan, J.P.; Iliopoulos, D.; Gregory, R.I. Lin28A and Lin28B Inhibit let-7 MicroRNA Biogenesis by Distinct Mechanisms. Cell 2011, 147, 1066–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, H.; Lazareva-Ulitsky, B.; Loo, R.; Kejariwal, A.; Vandergriff, J.; Rabkin, S.; Guo, N.; Muruganujan, A.; Doremieux, O.; Campbell, M.J.; et al. The PANTHER database of protein families, subfamilies, functions and pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D284–D288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.D.; Kejariwal, A.; Campbell, M.J.; Mi, H.; Diemer, K.; Guo, N.; Ladunga, I.; Ulitsky-Lazareva, B.; Muruganujan, A.; Rabkin, S.; et al. PANTHER: A browsable database of gene products organized by biological function, using curated protein family and subfamily classification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekka, E.; Kokanovic, A.; Mosole, S.; Civenni, G.; Schmidli, S.; Laski, A.; Ghidini, A.; Iyer, P.; Berk, C.; Behera, A.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of Lin28 promotes ketogenesis and restores lipid homeostasis in models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Hu, C.; Wu, Q.; Cai, Y.; Xing, S.; Lu, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, D.; Sun, L.; et al. Lin28 enhances de novo fatty acid synthesis to promote cancer progression via SREBP-1. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e48115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewalt, T.; Noh, K.W.; Meder, L. The role of LIN28B in tumor progression and metastasis in solid tumor entities. Oncol Res. 2023, 31, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.E.; Cuatrecasas, M.; Castells, A.; Sepulveda, A.R.; Lee, J.S.; Rustgi, A.K. LIN28B Promotes Colon Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4260–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Katsaros, D.; Shaverdashvili, K.; Qian, B.; Wu, Y.; de la Longrais, I.A.R.; Preti, M.; Menato, G.; Yu, H. Pluripotent factor, l.i.n.-2.8.; its homologue lin-28b in epithelial ovarian cancer their associations with disease outcomes expression of let-7a, I.G.F.-I.I. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 2212–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, G.; Hao, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Ning, N.; Li, X. Aberrant regulation of the LIN28A/LIN28B and let-7 loop in human malignant tumors and its effects on the hallmarks of cancer. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Shen, J.; Peng, D.; He, X.; Xu, C.; Chen, X.; Tanyi, J.L.; Montone, K.; Fan, Y.; Huang, Q.; et al. RNA-binding protein LIN28B inhibits apoptosis through regulation of the AKT2/FOXO3A/BIM axis in ovarian cancer cells. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Peng, J.; Liu, W.; He, X.; Cui, L.; Chen, X.; Yang, M.; Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, H. Lin28B is a novel prognostic marker in gastric adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 5083–5092. [Google Scholar]
- Corre, C.; Shinoda, G.; Zhu, H.; Cousminer, D.L.; Crossman, C.; Bellissimo, C.; Goldenberg, A.; Daley, G.Q.; Palmert, M.R. Sex-specific regulation of weight and puberty by the Lin28/let-7 axis. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 228, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Jia, J.; Xiong, X.; He, H.; Bu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, C.; Zhang, W. Increased Expression of Lin28B Associates with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maklad, A.; Sedeeq, M.; Chan, K.M.; Gueven, N.; Azimi, I. Exploring Lin28 proteins: Unravelling structure and functions with emphasis on nervous system malignancies. Life Sci. 2023, 335, 122275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radaeva, M.; Ho, C.H.; Xie, N.; Zhang, S.; Lee, J.; Liu, L.; Lallous, N.; Cherkasov, A.; Dong, X. Discovery of Novel Lin28 Inhibitors to Suppress Cancer Cell Stemness. Cancers 2022, 14, 5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias-Barrios, V.M.; Radaeva, M.; Rosellinny, G.; Jia, Q.; Xie, N.; Villanueva, M.; Ibrahim, H.; Smith, J.; Gleave, M.; Lallous, N.; et al. Developing novel Lin28 inhibitors by computer aided drug design. Cell Death Discov. 2025, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maklad, A.; Sedeeq, M.; Baghaei, K.; Wilson, R.; Heath, J.A.; Gueven, N.; Azimi, I. Role of LIN28B in the Regulation of Ribosomal Biogenesis and Lipid Metabolism in Medulloblastoma Brain Cancer Cells. Proteomes 2025, 13, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes13020014
Maklad A, Sedeeq M, Baghaei K, Wilson R, Heath JA, Gueven N, Azimi I. Role of LIN28B in the Regulation of Ribosomal Biogenesis and Lipid Metabolism in Medulloblastoma Brain Cancer Cells. Proteomes. 2025; 13(2):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes13020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaklad, Ahmed, Mohammed Sedeeq, Kaveh Baghaei, Richard Wilson, John A. Heath, Nuri Gueven, and Iman Azimi. 2025. "Role of LIN28B in the Regulation of Ribosomal Biogenesis and Lipid Metabolism in Medulloblastoma Brain Cancer Cells" Proteomes 13, no. 2: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes13020014
APA StyleMaklad, A., Sedeeq, M., Baghaei, K., Wilson, R., Heath, J. A., Gueven, N., & Azimi, I. (2025). Role of LIN28B in the Regulation of Ribosomal Biogenesis and Lipid Metabolism in Medulloblastoma Brain Cancer Cells. Proteomes, 13(2), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes13020014





