Urine Peptidome Analysis Identifies Common and Stage-Specific Markers in Early Versus Advanced CKD
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
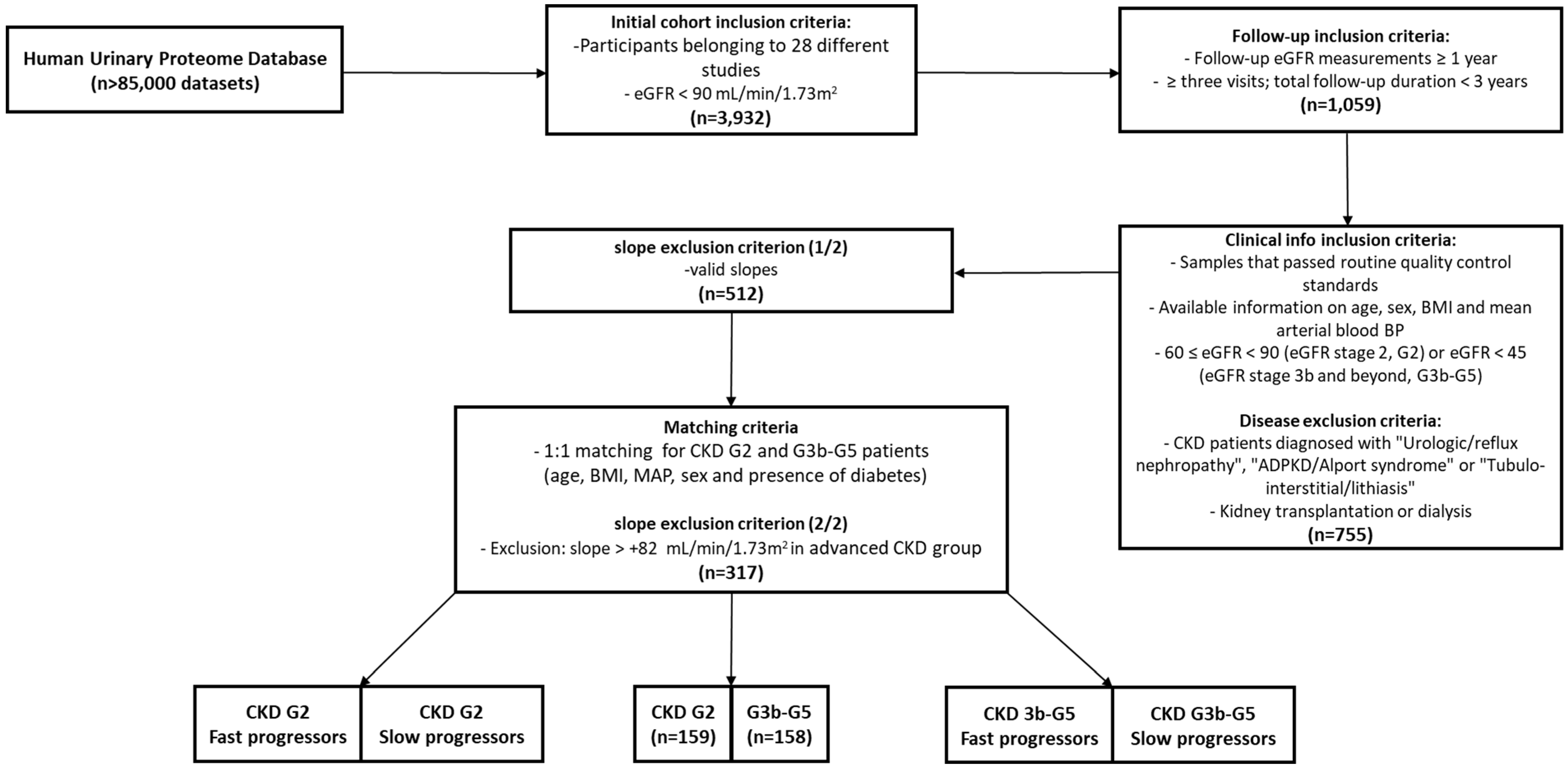
2.1. Initial Patient Population
2.2. CKD Progression
2.3. Matching
2.4. Peptide Differential Abundance Analyses
2.5. Processing of Peptides/CE-MS Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Protease Analysis
2.8. Pathway Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Determination and Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Comparison between Early and Advanced CKD Stages
3.3. Comparison Based on Progression within Early and Advanced CKD Stages
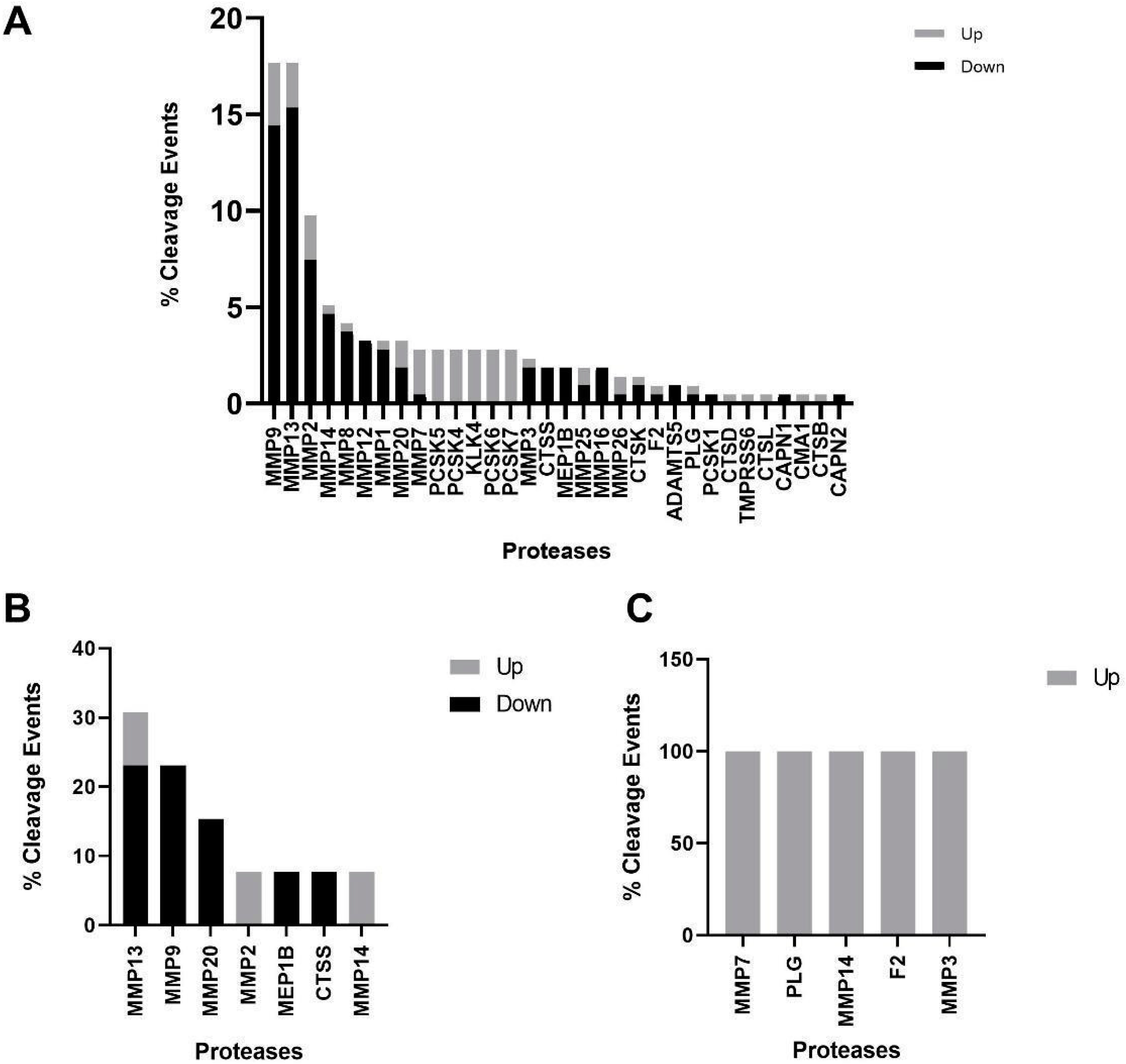
3.4. Protease Analysis between Different CKD Stages and Progressor Types
3.5. Functional Pathway Analysis between Different CKD Stages and Progressor Types
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anonymous. Chapter 1: Definition and Classification of CKD. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 19–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovesdy, C.P. Epidemiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: An Update 2022. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2022, 12, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikbov, B.; Purcell, C.A.; Levey, A.S.; Smith, M.; Abdoli, A.; Abebe, M.; Adebayo, O.M.; Afarideh, M.; Agarwal, S.K.; Agudelo-Botero, M.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, J.; Floege, J.; Fliser, D.; Böhm, M.; Marx, N. Cardiovascular Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease: Pathophysiological Insights and Therapeutic Options. Circulation 2021, 11, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.; James, M.; Wiebe, N.; Hemmelgarn, B.; Manns, B.; Klarenbach, S.; Tonelli, M. Alberta Kidney Disease Network Cause of Death in Patients with Reduced Kidney Function. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2504–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendrick, J.; Chonchol, M.B. Nontraditional Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2008, 4, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccali, C.; Tripepi, G.; Dounousi, E.; Mallamaci, F. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) as a Systemic Disease: Whole Body Autoregulation and Inter-Organ Cross-Talk. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2014, 39, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petra, E.; He, T.; Lygirou, V.; Latosinska, A.; Mischak, H.; Vlahou, A.; Jankowski, J. Urine Peptidome Analysis in Cardiorenal Syndrome Reflects Molecular Processes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, T.; Ninomiya, T.; Jha, V.; Neal, B.; Patrice, H.M.; Okpechi, I.; Zhao, M.; Lv, J.; Garg, A.X.; Knight, J.; et al. Worldwide Access to Treatment for End-Stage Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review. Lancet 2015, 385, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mischak, H.; Kolch, W.; Aivaliotis, M.; Bouyssié, D.; Court, M.; Dihazi, H.; Dihazi, G.H.; Franke, J.; Garin, J.; de Peredo, A.G.; et al. Comprehensive Human Urine Standards for Comparability and Standardization in Clinical Proteome Analysis. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2010, 4, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogeorgis, E.; Mischak, H.; Latosinska, A.; Siwy, J.; Jankowski, V.; Jankowski, J. Reproducibility Evaluation of Urinary Peptide Detection Using CE-MS. Molecules 2021, 26, 7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Good, D.M.; Zürbig, P.; Argilés, À.; Bauer, H.W.; Behrens, G.; Coon, J.J.; Dakna, M.; Decramer, S.; Delles, C.; Dominiczak, A.F.; et al. Naturally Occurring Human Urinary Peptides for Use in Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010, 9, 2424–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnaper, H.W. The Tubulointerstitial Pathophysiology of Progressive Kidney Disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017, 24, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudnicki, M.; Siwy, J.; Wendt, R.; Lipphardt, M.; Koziolek, M.J.; Maixnerova, D.; Peters, B.; Kerschbaum, J.; Leierer, J.; Neprasova, M.; et al. Urine Proteomics for Prediction of Disease Progression in Patients with IgA Nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, T.; Mischak, H.; Mullen, W.; Staessen, J.A. Urinary Proteome Analysis in Hypertensive Patients with Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 2342–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhardt, M.; Persson, F.; Zürbig, P.; Stalmach, A.; Mischak, H.; de Zeeuw, D.; Lambers Heerspink, H.; Klein, R.; Orchard, T.; Porta, M.; et al. Urinary Proteomics Predict Onset of Microalbuminuria in Normoalbuminuric Type 2 Diabetic Patients, a Sub-Study of the DIRECT-Protect 2 Study. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2017, 32, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markoska, A.; Mendoza, L.C.; Valaiyapathi, R.; Thorn, C.; Dornhorst, A. Insulin Sensitivity Assessed Using Urine C Peptide Creatinine Ratio (UCPCR) in Pregnancy: Cross-Sectional Analysis of an English Multiethnic Cohort. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e020029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, D.S.; Thijs, L.; Latosinska, A.; Trenson, S.; Siwy, J.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Wang, C.; Beige, J.; Vlahou, A.; Janssens, S.; et al. Urinary Peptidomic Profiles to Address Age-Related Disabilities: A Prospective Population Study. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2021, 2, e690–e703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packham, D.K.; Wolfe, R.; Reutens, A.T.; Berl, T.; Heerspink, H.L.; Rohde, R.; Ivory, S.; Lewis, J.; Raz, I.; Wiegmann, T.B.; et al. Sulodexide Fails to Demonstrate Renoprotection in Overt Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, M.J.; Mischak, H.; Heerspink, H.J.L. Proteomics for Prediction of Disease Progression and Response to Therapy in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snell-Bergeon, J.K.; Chartier-Logan, C.; Maahs, D.M.; Ogden, L.G.; Hokanson, J.E.; Kinney, G.L.; Eckel, R.H.; Ehrlich, J.; Rewers, M. Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Eat a High-Fat Atherogenic Diet That Is Associated with Coronary Artery Calcium. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tofte, N.; Lindhardt, M.; Adamova, K.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Beige, J.; Beulens, J.W.J.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Currie, G.; Delles, C.; Dimos, I.; et al. Early Detection of Diabetic Kidney Disease by Urinary Proteomics and Subsequent Intervention with Spironolactone to Delay Progression (PRIORITY): A Prospective Observational Study and Embedded Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.; Castro, A.F., III; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A New Equation to Estimate Glomerular Filtration Rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jantos-Siwy, J.; Schiffer, E.; Brand, K.; Brand, K.; Schumann, G.; Schumann, G.; Rossing, K.; Delles, C.; Mischak, H.; Metzger, J. Quantitative Urinary Proteome Analysis for Biomarker Evaluation in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zürbig, P.; Renfrow, M.B.; Schiffer, E.; Novak, J.; Walden, M.; Wittke, S.; Just, I.; Pelzing, M.; Neusüss, C.; Theodorescu, D.; et al. Biomarker Discovery by CE-MS Enables Sequence Analysis via MS/MS with Platform-Independent Separation. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 2111–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Fundation for Statistcal Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, D.; Imai, K.; King, G.; Stuart, E.A. MatchIt: Nonparametric Preprocessing for Parametric Causal Inference. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 42, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koncevičius, K. MatrixTests: Fast Statistical Hypothesis Tests on Rows and Columns of Matrices 2023. Available online: https://github.com/karoliskoncevicius/matrixTests (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Klein, J.; Eales, J.; Zürbig, P.; Vlahou, A.; Mischak, H.; Stevens, R. Proteasix: A Tool for Automated and Large-Scale Prediction of Proteases Involved in Naturally Occurring Peptide Generation. Proteomics 2013, 13, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M. Toward Understanding the Origin and Evolution of Cellular Organisms. Protein Sci. 2019, 28, 1947–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG for Taxonomy-Based Analysis of Pathways and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D587–D592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontillo, C.; Jacobs, L.; Staessen, J.A.; Schanstra, J.P.; Rossing, P.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Siwy, J.; Mullen, W.; Vlahou, A.; Mischak, H.; et al. A Urinary Proteome-Based Classifier for the Early Detection of Decline in Glomerular Filtration. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 1510–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanstra, J.P.; Zürbig, P.; Alkhalaf, A.; Argiles, A.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Beige, J.; Bilo, H.J.G.; Chatzikyrkou, C.; Dakna, M.; Dawson, J.; et al. Diagnosis and Prediction of CKD Progression by Assessment of Urinary Peptides. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1999–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goek, O.-N.; Köttgen, A.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Coresh, J.; Astor, B.C. Association of Apolipoprotein A1 and B with Kidney Function and Chronic Kidney Disease in Two Multiethnic Population Samples. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2012, 27, 2839–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, P.; Zürbig, P.; Mischak, H.; Schleicher, E. Urinary Fetuin-A Peptides as a New Marker for Impaired Kidney Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provenzano, M.; Andreucci, M.; Garofalo, C.; Faga, T.; Michael, A.; Ielapi, N.; Grande, R.; Sapienza, P.; de Franciscis, S.; Mastroroberto, P.; et al. The Association of Matrix Metalloproteinases with Chronic Kidney Disease and Peripheral Vascular Disease: A Light at the End of the Tunnel? Biomolecules 2020, 10, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petra, E.; Siwy, J.; Vlahou, A.; Jankowski, J. Urine Peptidome in Combination with Transcriptomics Analysis Highlights MMP7, MMP14 and PCSK5 for Further Investigation in Chronic Kidney Disease. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Early Stage CKD (G2) | Advanced Stage CKD (G3b–G5) |
|---|---|---|
| n | 159 | 158 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 78.6 (8.7) | 31.1 (7.4) |
| Age | 62.8 (6.2) | 63.1 (9.4) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.5 (4.3) | 30.2 (5.4) |
| MAP (mmHg) | 96.5 (7.6) | 96.1 (8.6) |
| Male (%) | 47.8 | 58.9 |
| Diabetic (%) | 98.7 | 99.4 |
| Protein Symbol | Protein Name | Sequence | Fold Change | Adj. p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upregulated | ||||
| COL1A1 | Collagen alpha-1(I) | RGPpGPpGKNGDDGEAGKPGRpGERGPpGP | 339.2 | 4.14 × 10−24 |
| MUC19 | Mucin-19 | GVTGKSGLSAGVTGKTGLSAGVTGTTGPS | 223.5 | 2.49 × 10−17 |
| APOA4 | Apolipoprotein A-IV | RQKLGPHAGDVEGHLS | 179.2 | 1.88 × 10−26 |
| APOA1 | Apolipoprotein A-I | LEEYTKKLNTQ | 161.8 | 7.66 × 10−24 |
| HBB | Hemoglobin subunit beta | FESFGDLSTPDAVMGNPKVKAHGKKVLG | 105.4 | 3.33 × 10−25 |
| COL1A1 | Collagen alpha-1(I) | PGPAGPPGEAGKPGEQGVPGDLGAPGPSGARG | 95.6 | 1.79 × 10−21 |
| APOA2 | Apolipoprotein A-II | FVELGTQPATQ | 87.6 | 1.35 × 10−31 |
| TTR | Transthyretin | LSPYSYSTTAVVTNPKE | 84.6 | 1.56 × 10−25 |
| HBB | Hemoglobin subunit beta | VHLTPEEKSAVTALWGKVNVDEV | 80.8 | 6.30 × 10−22 |
| SERPINA1 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin | SEGLKLVDKFLEDVKKL | 71.3 | 7.52 × 10−17 |
| SERPINA1 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin | EDPQGDAAQKTDTSHHDQDHPTFNKITPN | 69.2 | 4.61 × 10−20 |
| SERPINA1 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin | MIEQNTKSPLFMGKVVNPTQK | 67.8 | 1.36 × 10−27 |
| APOA1 | Apolipoprotein A-I | ALEEYTKKLNTQ | 67.2 | 2.06 × 10−18 |
| COL19A1 | Collagen alpha-1(XIX) | GPEGPSGKpGINGKDGIPGAQGImGKpGDRGpKGERGDQGIP | 67.0 | 3.40 × 10−35 |
| COL3A1 | Collagen alpha-1(III) | GEPGRDGVPGGPGMRGMPGSPGGPGSDGKPGPpGSQGESGRpGpP | 65.4 | 2.54 × 10−17 |
| B2M | Beta-2-microglobulin | NGERIEKVEHSDLSFSKDWS | 62.7 | 1.96 × 10−17 |
| APOA1 | Apolipoprotein A-I | DEPPQSPWDRVKDL | 62.7 | 7.95 × 10−14 |
| B2M | Beta-2-microglobulin | LKNGERIEKVEHSDLSFSKDWS | 61.1 | 4.84 × 10−22 |
| SERPINA1 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin | EAIPMSIPPEVKFNKP | 59.4 | 4.72 × 10−27 |
| B2M | Beta-2-microglobulin | YVSGFHPSDIEVD | 58.9 | 3.69 × 10−15 |
| Downregulated | ||||
| COL21A1 | Collagen alpha-1(XXI) | pGYPGQpGQDGKPGYQGIAGTpGVpGSPG | 0.0196 | 3.44 × 10−27 |
| COL1A1 | Collagen alpha-1(I) | PpGpAGFAGpPGADGQPGAKGEPGDAGAKGDAGPPGPAGP | 0.0245 | 3.75 × 10−27 |
| COL5A3 | Collagen alpha-3(V) | IDGSpGEKGDPGDVGGPGPPGASGEPGAPGPPGKRGPS | 0.0287 | 2.83 × 10−18 |
| SEMA7A | Semaphorin-7A | FREAQHWQLLPEDGIM | 0.0341 | 1.03 × 10−36 |
| COL1A1 | Collagen alpha-1(I) | GADGQpGAKGEpGDAGAKGDAGPpGPAGPAGPpGPIG | 0.0364 | 2.69 × 10−32 |
| PIGR | Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor | AVADTRDQADGSRASVDSGSSEEQGGSSRALVSTLVPLG | 0.0392 | 2.03 × 10−15 |
| COL1A1 | Collagen alpha-1(I) | pPGADGQPGAKGEpGDAGAKGDAGPpGPAGPAGPPGPIG | 0.0406 | 1.14 × 10−25 |
| CADPS | Calcium-dependent secretion activator 1 | GGAGAGAGVGAGGGGGSGASSGGGAGGL | 0.0423 | 4.16 × 10−24 |
| COL1A1 | Collagen alpha-1(I) | TGPIGpPGPAGAPGDKGESGpSGPAGPTG | 0.0426 | 6.30 × 10−34 |
| CD99 | CD99 antigen | DGVSGGEGKGGSDGGGSHRKEGEEADAPGVIPGIVGA | 0.0511 | 1.73 × 10−25 |
| CD99 | CD99 antigen | DLADGVSGGEGKGGSDGGGSHRKEGEEADAPGVIPG | 0.0571 | 4.35 × 10−23 |
| COL2A1 | Collagen alpha-1(II) | GpAGpPGEKGEPGDDGPSGAEGpPGPQ | 0.0627 | 1.14 × 10−18 |
| COL1A2 | Collagen alpha-2(I) | GEPGSAGPQGPPGPSGEEGKRGPNGEAGSAGPPGpPGL | 0.0644 | 7.72 × 10−44 |
| COL1A1 | Collagen alpha-1(I) | GADGQpGAKGEpGDAGAKGDAGPPGPAGPAGPpGPIG | 0.0652 | 1.96× 10−33 |
| COL15A1 | Collagen alpha-1(XV) | VSFVTGYGGFPAYSFGPGANVGR | 0.0662 | 2.04 × 10−20 |
| UMOD | Uromodulin | IDQSRVLNLGPITR | 0.0686 | 4.16 × 10−18 |
| C4A | Complement C4-A | DELPAKDDPDAPLQPVTP | 0.0688 | 1.11 × 10−29 |
| CD99 | CD99 antigen | DGGFDLSDALPDNENKKPtAIP | 0.0701 | 4.64 × 10−36 |
| COL1A1 | Collagen alpha-1(I) | pPGADGQpGAKGEpGDAGAKGDAGPpGPAGP | 0.0729 | 1.07 × 10−22 |
| COL1A2 | Collagen alpha-2(I) | PAGSRGDGGPpGMTGFpGAAGRTGpPGPSGISGPPGPPGPAG | 0.0738 | 5.55 × 10−19 |
| Protein Symbol | Protein Name | Sequence | Fold Change | Adj. p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upregulated | ||||
| COL5A2 | Collagen alpha-2(V) | GSPGTSGppGSAGpPGSpG | 6.6238 | 2.43 × 10−2 |
| HSPG2 | Basement membrane-specific heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein | LAFPGHVFSRSLPEVPETIEL | 5.3553 | 3.57 × 10−2 |
| COL5A3 | Collagen alpha-3(V) | GPpGPpGFpGDPGPPG | 4.5915 | 3.24 × 10−2 |
| COL5A3 | Collagen alpha-3(V) | GPpGPpGFPGDpGPpG | 4.1514 | 1.51 × 10−2 |
| COL4A1 | Collagen alpha-1(IV) | GPpGFTGppGPPGPPGP | 3.9258 | 2.43 × 10−2 |
| COL1A1 | Collagen alpha-1(I) | GEPGSPGENGApGQMGp | 3.6261 | 2.43 × 10−2 |
| COL11A1 | Collagen alpha-1(XI) | GPpGDDGMRGEDGEIGpRGLp | 3.6150 | 6.51 × 10−3 |
| COL3A1 | Collagen alpha-1(III) | AGIpGVpGAKGEDGKDGSpGEpGANG | 3.2461 | 4.07 × 10−2 |
| COL1A1 | Collagen alpha-1(I) | ADGQPGAKGEPGDAGAKGDAGpPGPA | 2.8850 | 2.43 × 10−2 |
| COL3A1 | Collagen alpha-1(III) | pGARGLpGpPGSNGNPGpP | 2.8372 | 6.51 × 10−3 |
| Downregulated | ||||
| COL9A3 | Collagen alpha-3(IX) | GpAGPpGpPGPpG | 0.2119 | 3.24 × 10−2 |
| COL1A2 | Collagen alpha-2(I) | TGPPGPSGISGPpGpPGPAG | 0.2423 | 3.69 × 10−2 |
| COL22A1 | Collagen alpha-1(XXII) | pGVpGPPGPGGSPGLPGE | 0.2741 | 2.43 × 10−2 |
| COL3A1 | Collagen alpha-1(III) | PpGENGKpG | 0.3418 | 3.90 × 10−2 |
| COL4A3 | Collagen alpha-3(IV) | GPPGTpGEpGMQGEpGPP | 0.3592 | 1.60 × 10−2 |
| FXYD2 | Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit gamma | TGLSMDGGGSPKGDVDP | 0.3857 | 3.24 × 10−2 |
| CD99 | CD99 antigen | DGVSGGEGKGGSDGGGSHRKEGEEADAPGVIPGIVGAVV | 0.3898 | 1.00 × 10−2 |
| COL3A1 | Collagen alpha-1(III) | SpGERGETGPpGPA | 0.3976 | 2.43 × 10−2 |
| POTEF | POTE ankyrin domain family member F | RVAPEEHPV | 0.3984 | 1.51 × 10−2 |
| COL3A1 | Collagen alpha-1(III) | KNGETGPQGppGPTGPGGDKGDTGPpGPQG | 0.4087 | 2.43 × 10−2 |
| Protein Symbol | Protein Name | Sequence | Fold Change | Adj. p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| APOA1 | Apolipoprotein A-I | ALEEYTKKLNTQ | 8.4493 | 1.94 × 10−2 |
| AHSG | Alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein | LGSPSGEVSHPRKT | 7.6154 | 4.51 × 10−3 |
| FGA | Fibrinogen alpha chain | SGEGDFLAEGGGVR | 2.1838 | 1.94 × 10−2 |
| COL1A1 | Collagen alpha-1(I) | NSGEpGApGSKGDTGAkGEpGPVG | 0.4708 | 4.35 × 10−2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hobson, S.; Mavrogeorgis, E.; He, T.; Siwy, J.; Ebert, T.; Kublickiene, K.; Stenvinkel, P.; Mischak, H. Urine Peptidome Analysis Identifies Common and Stage-Specific Markers in Early Versus Advanced CKD. Proteomes 2023, 11, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes11030025
Hobson S, Mavrogeorgis E, He T, Siwy J, Ebert T, Kublickiene K, Stenvinkel P, Mischak H. Urine Peptidome Analysis Identifies Common and Stage-Specific Markers in Early Versus Advanced CKD. Proteomes. 2023; 11(3):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes11030025
Chicago/Turabian StyleHobson, Sam, Emmanouil Mavrogeorgis, Tianlin He, Justyna Siwy, Thomas Ebert, Karolina Kublickiene, Peter Stenvinkel, and Harald Mischak. 2023. "Urine Peptidome Analysis Identifies Common and Stage-Specific Markers in Early Versus Advanced CKD" Proteomes 11, no. 3: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes11030025
APA StyleHobson, S., Mavrogeorgis, E., He, T., Siwy, J., Ebert, T., Kublickiene, K., Stenvinkel, P., & Mischak, H. (2023). Urine Peptidome Analysis Identifies Common and Stage-Specific Markers in Early Versus Advanced CKD. Proteomes, 11(3), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes11030025







