Non-Specific Signal Peptidase Processing of Extracellular Proteins in Staphylococcus aureus N315
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Bacterial Growth and Culture Conditions
2.3. Chemical Labeling of Extracellular Proteins with SMTA
2.4. Chemical Labeling of S. aureus Cell Lysate with SMTA
2.5. LC-MS/MS Bottom-up Protein Analysis
2.6. Orbitrap Fusion Lumos Tribrid Mass Spectrometry and Database Search
2.7. LC-MS/MS Top-down Protein Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Non-Specific SPase Cleavages in the Secretory Proteins
3.2. Random Cleavages in the Secreted Proteins
3.3. Non-Specific Cleavages Confirmed through Native and Top-down Proteomic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Green, E.R.; Mecsas, J. Bacterial Secretion Systems: An Overview. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusch, H.; Engelmann, S. Secrets of the secretome in Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merriman, J.A.; Klingelhutz, A.J.; Diekema, D.J.; Leung, D.Y.; Schlievert, P.M. Novel Staphylococcus aureus Secreted Protein Alters Keratinocyte Proliferation and Elicits a Proinflammatory Response In Vitro and In Vivo. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 4855–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongerius, I.; von Kockritz-Blickwede, M.; Horsburgh, M.J.; Ruyken, M.; Nizet, V.; Rooijakkers, S.H. Staphylococcus aureus virulence is enhanced by secreted factors that block innate immune defenses. J. Innate Immun. 2012, 4, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallenberger, M.A.; Niessen, S.; Shao, C.; Fowler, B.J.; Romesberg, F.E. Type I signal peptidase and protein secretion in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 2677–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravipaty, S.; Reilly, J.P. Comprehensive characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus COL secretome by two-dimensional liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. Mol. Cell Proteomics. 2010, 9, 1898–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, A.; van Dijl, J.M.; Hecker, M.; Becher, D. The Staphylococcus aureus proteome. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjalsma, H.; Antelmann, H.; Jongbloed, J.D.; Braun, P.G.; Darmon, E.; Dorenbos, R.; Dubois, J.-Y.F.; Westers, H.; Zanen, G.; Quax, W.J.; et al. Proteomics of protein secretion by Bacillus subtilis: Separating the “secrets” of the secretome. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 207–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjalsma, H.; Bolhuis, A.; Jongbloed, J.D.; Bron, S.; van Dijl, J.M. Signal peptide-dependent protein transport in Bacillus subtilis: A genome-based survey of the secretome. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000, 64, 515–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Keyzer, J.; van der Does, C.; Driessen, A.J. The bacterial translocase: A dynamic protein channel complex. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2003, 60, 2034–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, P.; Bruser, T.; Driessen, A.J. Sec- and Tat-mediated protein secretion across the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane--distinct translocases and mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 1735–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibbald, M.J.; Ziebandt, A.K.; Engelmann, S.; Hecker, M.; de Jong, A.; Harmsen, H.J.; Raangs, G.C.; Stokroos, I.; Arends, J.P.; Dubois, J.Y.F.; et al. Mapping the pathways to staphylococcal pathogenesis by comparative secretomics. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2006, 70, 755–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Casabona, M.G.; Kneuper, H.; Chalmers, J.D.; Palmer, T. The type VII secretion system of Staphylococcus aureus secretes a nuclease toxin that targets competitor bacteria. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 2, 16183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S.; He, H.; Dalbey, R.E. Bacterial Signal Peptides- Navigating the Journey of Proteins. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 933153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emr, S.D.; Hanley-Way, S.; Silhavy, T.J. Suppressor mutations that restore export of a protein with a defective signal sequence. Cell 1981, 23, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cregg, K.M.; Wilding, I.; Black, M.T. Molecular cloning and expression of the spsB gene encoding an essential type I signal peptidase from Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 5712–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, R.A.; Allen, W.J.; Komar, J.; Masiulis, S.; Menzies, S.; Robson, A.; Collinson, I. Unlocking the Bacterial SecY Translocon. Structure 2016, 24, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Lindemann, C.; Young, B.C.; Muller, J.; Osterreich, B.; Ternette, N.; Winkler, A.-C.; Paprotka, K.; Reinhardt, R.; Förstner, K.U.; et al. Natural mutations in a Staphylococcus aureus virulence regulator attenuate cytotoxicity but permit bacteremia and abscess formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E3101-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craney, A.; Romesberg, F.E. Stable Signal Peptides and the Response to Secretion Stress in Staphylococcus aureus. Mbio 2017, 8, e01507-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbort, M.; Klein, M.; Manting, E.H.; Driessen, A.J.; Freudl, R. Temporal expression of the Bacillus subtilis secA gene, encoding a central component of the preprotein translocase. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misal, S.A.; Li, S.; Tang, H.; Radivojac, P.; Reilly, J.P. Identification of N-terminal protein processing sites by chemical labeling mass spectrometry. Rapid. Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 33, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, A.G. To b or not to b: The ongoing saga of peptide b ions. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2009, 28, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Dabir, A.; Misal, S.A.; Tang, H.; Radivojac, P.; Reilly, J.P. Impact of Amidination on Peptide Fragmentation and Identification in Shotgun Proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 3656–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thumm, M.; Hoenes, J.; Pfleiderer, G. S-Methylthioacetimidate is a new reagent for the amidination of proteins at low pH. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 1987, 923, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karty, J.A.; Running, W.E.; Reilly, J.P. Two dimensional liquid phase separations of proteins using online fractionation and concentration between chromatographic dimensions. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed Life Sci. 2007, 847, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Pevzner, P.A. MS-GF+ makes progress towards a universal database search tool for proteomics. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Sonderby, C.K.; Petersen, T.N.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; Von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, T.N.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 4.0: Discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammel, M.; Sfyroera, G.; Ricklin, D.; Magotti, P.; Lambris, J.D.; Geisbrecht, B.V. A structural basis for complement inhibition by Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Mishra, M.; Wu, L.F.; Yin, Z.C.; Balasubramanian, M.K. The bacterial cell division protein FtsZ assembles into cytoplasmic rings in fission yeast. Gene Dev. 2008, 22, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huecas, S.; Ramirez-Aportela, E.; Vergonos, A.; Nunez-Ramirez, R.; Llorca, O.; Diaz, J.F.; Juan-Rodríguez, D.; Oliva, M.A.; Castellen, P.; Andreu, J.M. Self-Organization of FtsZ Polymers in Solution Reveals Spacer Role of the Disordered C-Terminal Tail. Biophys. J. 2017, 113, 1831–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, E.F.; Lutkenhaus, J. FtsZ ring structure associated with division in Escherichia coli. Nature 1991, 354, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, K.A.J.A.; Moore, D.A.; Erickson, H.P. The C-terminal linker of Escherichia coli FtsZ functions as an intrinsically disordered peptide. Molecular. Microbiol. 2013, 89, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buske, P.J.; Levin, P.A. A flexible C-terminal linker is required for proper FtsZ assembly in vitro and cytokinetic ring formation in vivo. Molecular. Microbiol. 2013, 89, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huecas, S.; Canosa-Valls, A.J.; Araujo-Bazan, L.; Ruiz, F.M.; Laurents, D.V.; Fernandez-Tornero, C.; Andreu, J.M. Nucleotide-induced folding of cell division protein FtsZ from Staphylococcus aureus. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 4048–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroni, M.; Franke, K.B.; Maurer, M.; Jager, J.; Hantke, I.; Gloge, F.; Linder, D.; Gremer, S.; Turgay, K.; Bukau, B.; et al. Regulatory coiled-coil domains promote head-to-head assemblies of AAA+ chaperones essential for tunable activity control. Elife 2017, 6, e30120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazmanian, S.K.; Liu, G.; Ton-That, H.; Schneewind, O. Staphylococcus aureus Sortase, an Enzyme that Anchors Surface Proteins to the Cell Wall. Science 1999, 285, 760–763. [Google Scholar]
- Mazmanian, S.K.; Ton-That, H.; Schneewind, O. Sortase-catalysed anchoring of surface proteins to the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 40, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craney, A.; Dix, M.M.; Adhikary, R.; Cravatt, B.F.; Romesberg, F.E. An Alternative Terminal Step of the General Secretory Pathway in Staphylococcus aureus. Mbio 2015, 6, e01178-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojkova, P.; Spidlova, P.; Stulik, J. Nucleoid-Associated Protein HU: A Lilliputian in Gene Regulation of Bacterial Virulence. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavanaugh, J.S.; Flack, C.E.; Lister, J.; Ricker, E.B.; Ibberson, C.B.; Jenul, C.; Moormeier, D.E.; Delmain, E.A.; Bayles, K.W.; Horswill, A.R. Identification of Extracellular DNA-Binding Proteins in the Biofilm Matrix. Mbio 2019, 10, e01137-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craney, A.; Romesberg, F.E. The inhibition of type I bacterial signal peptidase: Biological consequences and therapeutic potential. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 4761–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneewind, O.; Missiakas, D.M. Protein secretion and surface display in Gram-positive bacteria. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 1123–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folz, R.J.; Nothwehr, S.F.; Gordon, J.I. Substrate specificity of eukaryotic signal peptidase. J Biol Chem. 1988, 263, 2070–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Heijne, G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J. Mol. Biol. 1985, 184, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, H.; Engelbrecht, J.; Brunak, S.; vonHeijne, G. Identification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic signal peptides and prediction of their cleavage sites. Protein Eng. 1997, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.M.; Lee, J.I.; Cheng, S.; Jutte, H.; Kuhn, A.; Dalbey, R.E. Use of site-directed mutagenesis to define the limits of sequence variation tolerated for processing of the M13 procoat protein by the Escherichia coli leader peptidase. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 11775–11781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
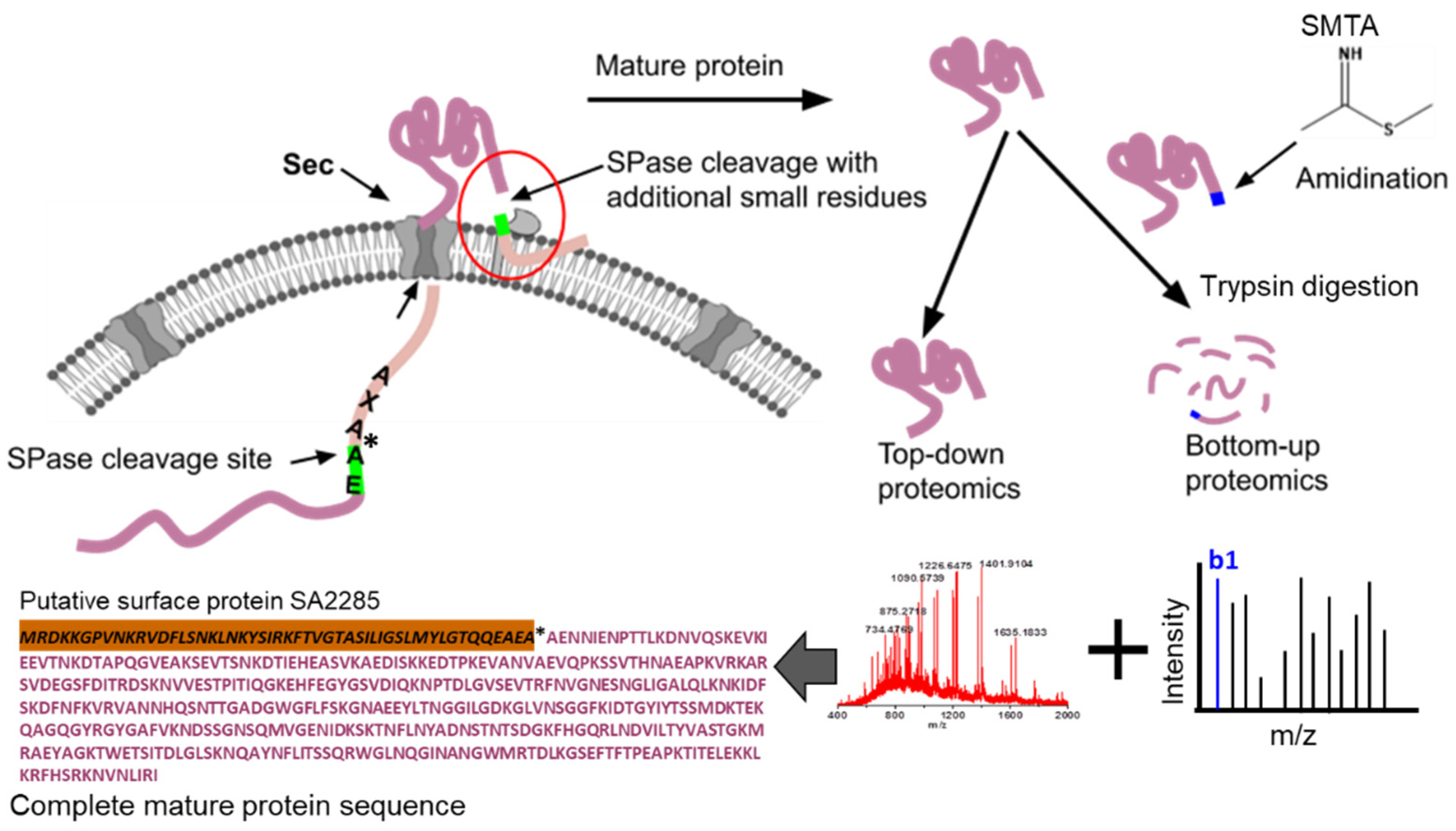
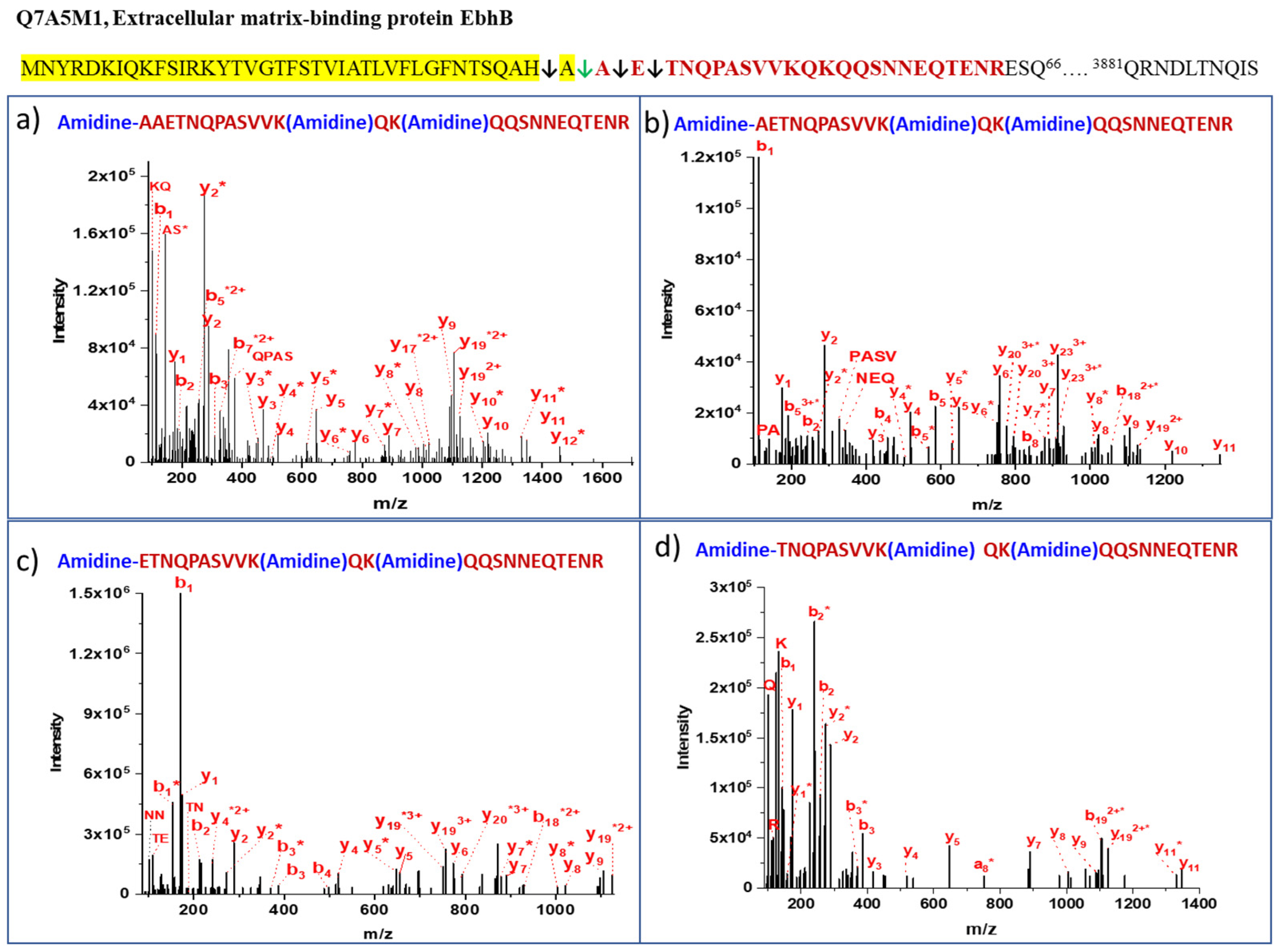
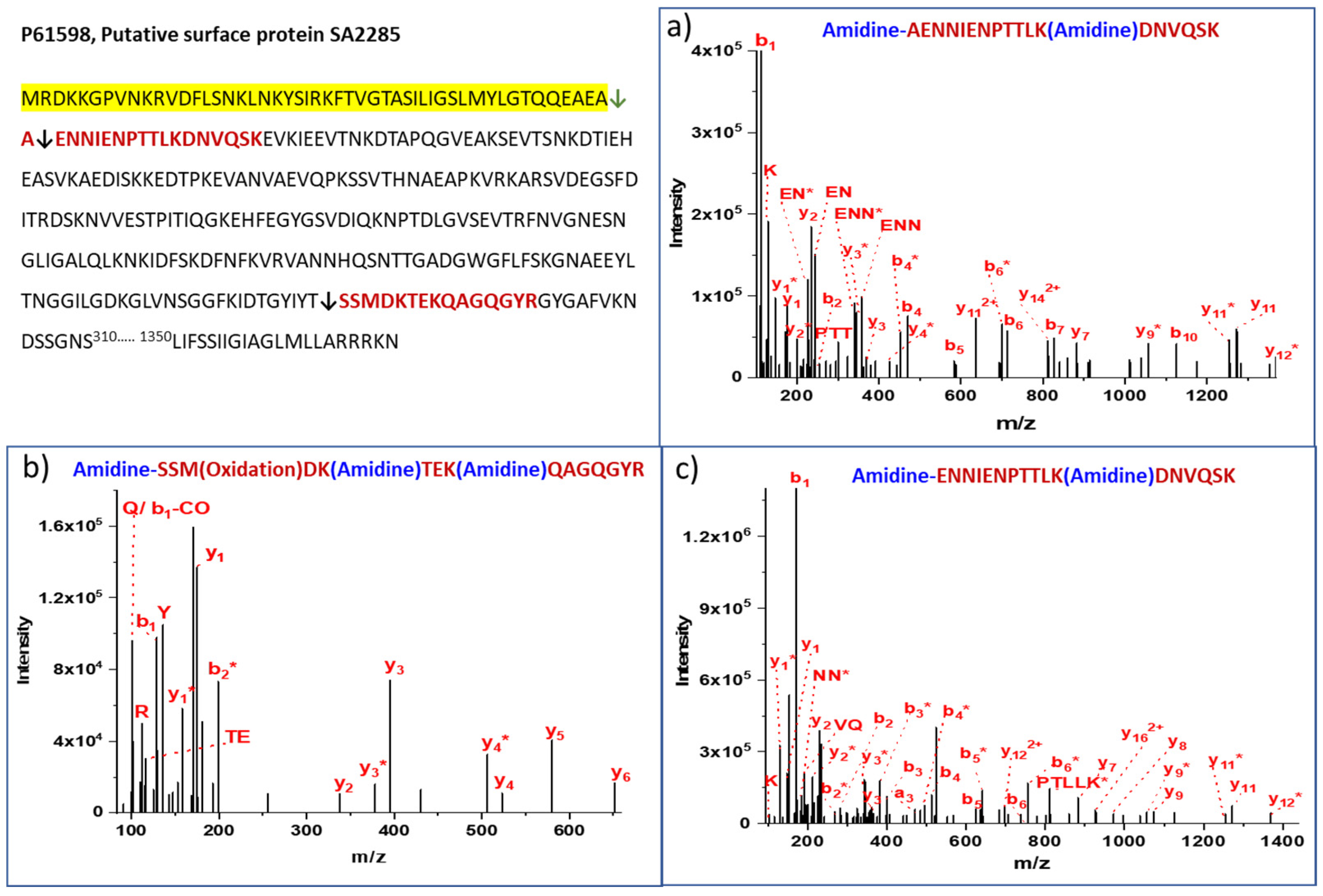
| No. | Protein | Peptide | Cleavage Pattern | % b1 ion Abundance * | Total Peptides | Amidinated | Non-Amidinated | % Cleavage Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Q7A5M1 Extracellular matrix-binding protein EbhB | AAETNQPASVVKQKQQSNNEQTENR | QAH↓AAET | 46 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 10 |
| 2 | Q7A5M1 Extracellular matrix-binding protein EbhB | AETNQPASVVKQKQQSNNEQTENR | AHA↓AET | 100 | 21 | 21 | 0 | 68 |
| 3 | Q7A5M1 Extracellular matrix-binding protein EbhB | ETNQPASVVKQKQQSNNEQTENR | HAA↓ETN | 100 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 23 |
| 4 | Q7A5M1 Extracellular matrix-binding protein EbhB | TNQPASVVKQKQQSNNEQTENR | AAE↓TNQ | 35 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 6 |
| 5 | P99134 Immunoglobulin G binding protein A | AAQHDEAQQNAFYQVLNMPNLNADQR | AAN↓AAQ | 30 | 0 | 30 | 39 | |
| 6 | P99134 Immunoglobulin G binding protein A | AQHDEAQQNAFYQVLNMPNLNADQR | ANA↓AQH | 47 | 41 | 38 | 3 | 53 |
| 7 | P99134 Immunoglobulin G binding protein A | QHDEAQQNAFYQVLNMPNLNADQR | ANAA↓QHD | 38 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 8 |
| 8 | P61598 Putative surface protein SA2285 | AENNIENPTTLKDNVQSK | AEA↓AEN | 100 | 71 | 40 | 31 | 86 |
| 9 | P61598 Putative surface protein SA2285 | ENNIENPTTLKDNVQSK | EAA↓ENN | 100 | 12 | 10 | 2 | 14 |
| 10 | A0A0H3JNG8 Staphylocoagulase | IVTKDYSKESR | ADA↓IVT | 100 | 17 | 17 | 0 | 59 |
| 11 | A0A0H3JNG8 Staphylocoagulase | VTKDYSKESR | ADAI↓VTK | 82 | 12 | 13 | 0 | 41 |
| 12 | Q7A4V3 UPF0342 protein SA1663 | VKANEESKKLFDEFR | AFAN↓VKA | 16 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 43 |
| 13 | Q7A4V3 UPF0342 protein SA1663 | ANVKANEESKKLFDEFR | EAF↓ANV | 20 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 57 |
| 14 | Q99SU9 Staphylococcal complement inhibitor | STSLPTSNEYQNEKLANELK | AQA↓STS | 100 | 24 | 20 | 4 | 77 |
| 15 | Q99SU9 Staphylococcal complement inhibitor | TSLPTSNEYQNEK | AQAS↓TSL | 4 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 23 |
| 16 | Q7A6A6 Glutamyl endopeptidase | SSKAMDNHPQQTQSSKQQTPK | ANAL↓SSK | 100 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 |
| 17 | A0A0H3JNR9 Uncharacterized protein | SETNQKVSTNQESK | AEA↓SET | 45 | 20 | 18 | 2 | 100 |
| No. | Protein | Peptide | Location in Protein | Cleavage Pattern | Subcellular Location | % b1 Ion Abundance * | Total PSMs | Amidinated | Non-Amidinated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A0A0H3JPH2 Uncharacterized protein | GTLLGVTYK | N-term | FVSSCIASTILF16↓17GTL | Extracellular | 50 | 20 | 20 | 0 |
| 2 | A0A0H3JPH2 Uncharacterized protein | TILFGTLLGVTYK | N-term | KKFVSSCIAS12↓13TIL | Extracellular | 100 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 3 | A0A0H3JM99 SA1477 Uncharacterized protein | IILIALLVILLFRVGLSILR | N-term | MSILT5↓6IIL | Predicted/transmembrane | 50 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 4 | P65986 DNA repair protein RecO | DVHAVILSNK | Middle | DGAISRQEASK181↓182DVH | Cytoplasm | 20 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 5 | P99160 Probable transglycosylase IsaA | APTYHNYSTSTTSSSVR | Middle | SSNSNVEAVS130↓131APT | Extracellular | 100 | 47 | 28 | 19 |
| 6 | P68800 Fibrinogen-binding protein | IVEYNDGTFKYQSR | Middle | EKKPVSINHN46↓47IVE | Extracellular | 100 | 9 | 4 | 5 |
| 7 | P65289 Lipase 1 | NPNIVYKTYTGEATHK | Middle | ATDLNRKTSL548↓549NPN | Extracellular | 80 | 9 | 9 | 0 |
| 8 | Q99RL2 Immunoglobulin-binding protein sbi | LKGITEEQR | Middle | QQKAFYQVLH60↓61LKG | Extracellular | 30 | 54 | 39 | 15 |
| 9 | Q7A6A6 Glutamyl endopeptidase | LKPLEQR | Middle | QTPKIKKGGN57↓58LKP | Extracellular | 40 | 24 | 24 | 0 |
| 10 | A0A0H3JP98 SA0743 protein | APSKKPTTPTTYTETTTQVPMPTVER | Middle | DNENDRQLVVS344↓345APS | Extracellular | 100 | 7 | 7 | 0 |
| 11 | P61598 Putative surface protein SA2285 | SSMDKTEKQAGQGYR | Middle | FKIDTGYIYT281↓282SSM | Extracellular/Cell wall | 40 | 14 | 10 | 4 |
| 12 | P61598 Putative surface protein SA2285 | SVDIQKNPTDLGVSEVTR | Middle | QGKEHFEGYG178↓179SVD | Extracellular/Cell wall | 100 | 97 | 16 | 81 |
| 13 | P61598 Putative surface protein SA2285 | EVTSNKDTIEHEASVK | Middle | TAPQGVEAKS88↓89EVT | Extracellular/Cell wall | 30 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| 14 | P99134 Immunoglobulin G-binding protein A | IKPGQELVVDKK | Middle | ADNKLADKNM390↓391IKP | Extracellular/Cell wall | 30 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 15 | Q7A6P2 Thermonuclease | SQTDNGVNR | Middle | VSSLSSSANA60↓61SQT | Extracellular | 100 | 22 | 22 | 0 |
| 16 | Q7A6U1 Lipoteichoic acid synthase | SEDDLTKVLNYTKQR | Middle | IENNQQKALA217↓218SED | Cell membrane/Extracellular | 100 | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| 17 | A0A0H3JKR2 Penicillin binding protein 2 prime | EKLYDKKLQHEDGYR | Middle | DDAVIGKKGL283↓284EKL | Membrane | 20 | 7 | 4 | 3 |
| 18 | A0A0H3JTB6 Uncharacterized protein | SEVNENVEKQNHFKHR | Middle | DILNIHTAKA67↓68SEV | Predicted membrane | 20 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| 19 | A0A0H3JNE5 SA0173 protein | ANTLVYR | Middle | GTEQMLGMF1266↓1267ANT | predicted/not known | yn−1 | 9 | 9 | 0 |
| 20 | P64416 histidine ammonia-lyase | LQVNLIR | Middle | SDVRIDQYNE74 ↓75LQV | Cytoplasm/membrane | 20 | 520 | 432 | 88 |
| 21 | A0A0H3JQ77 Penicillin-binding protein 3 | GETMVDEPLHFQGGLTKR | Middle | AGYQNKAIKV410↓411GET | Predicted/transmembrane | 60 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| 22 | A0A0H3JKY5 SA1224 protein | LKILSGELDSQTGHVSLGKNER | Middle | GANGAGKSTF43↓44LKI | Predicted/ABC transporter | 30 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 23 | Q7A600 Probable dual-specificity RNA methyltransferase RlmN | STLGGLK | Middle | GCRIGCTFCA135↓136STL | Cytoplasm | 10 | 6 | 6 | 0 |
| 24 | P99135 Phosphoglycerate kinase | IKDLKEGDVLLVENTR | Middle | ETRGEKLEAA103↓104IKD | Cytoplasm | 30 | 6 | 5 | 1 |
| 25 | A0A0H3JLW4 Uncharacterized protein | PENIVEKYQYQDFDDMFKHYQQLINQCKVQFDNYVTGK | Middle | ADYEGWWLFSDW20↓21PEN | Predicted | 100 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 26 | A0A0H3JNR9 Uncharactrized protein | SINNKFINFEER | Middle | HTSVKGKVAL221↓222SIN | Predicted | 20 | 107 | 27 | 80 |
| 27 | P99134 Immunoglobulin G binding protein A | GEENPFIGTTVFGGLSLALGAALLAGR | Near C-term | LPET419↓420GEE | Extracellular | 100 | 123 | 123 | 0 |
| 28 | P99108 Cell division protein Ftsz | SNSSNAQATDSVSER | Near C-term | SNATSKDESFT349↓350SNS | Cytoplasm | 90 | 28 | 28 | 0 |
| 29 | A0A0H3JNV0 SA2202 protein | AKIKAIKGNAEQSR | Near C-term | LSYLDYKKQKPN199↓200AKI | Predicted membrane/Signal | 30 | 18 | 15 | 3 |
| 30 | Q7A7P2 Lipase 2 | IINDLLR | Near C-term | RKGAELANFYTG670↓671IIN | Extracellular | 20 | 9 | 9 | 0 |
| 31 | A0A0H3JMK9 SA1273 protein | ALSAGQR | Near C-term | YQSVENVVENID222↓223ALS | not Known | 100 | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| 32 | Q7A423 Staphylococcal secretory antigen ssaA2 | GPGVVTSR | Near C-term | NGSVRVSEMNYGY245↓246GPG | Extracellular | 100 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| 332 | A0A0H3JK15 Uncharacterized protein | SKVAGNFGYIEKGK | Near C-term | YVGKAVTHTEY131↓132SKV | Predicted/Signal | 10 | 13 | 11 | 2 |
| 34 | A0A0H3JKR2 Penicillin binding protein 2 prime | LKMKQGETGR | Near C-term | YANLIGKSGTAE602↓603LKM | Predicted/transmembrane/signal | 30 | 8 | 7 | 1 |
| 35 | A0A0H3JM43 Uncharacterized protein | GMIMATINSKSEGMTEWER | Near C-term | TINKNYADDQTYYLS407↓408GMI | Predicted/membrane | 100 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 36 | A0A0H3JTW9 Cell division protein FtsL | SLENDNVKVVR | Near C-term | IYEKAKKQGM115↓116SLE | Cell membrane | 10 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 37 | P68800 Fibrinogen-binding protein | LKQGLVR | Near C-term | LQERIDNV158↓159LKQ | Extracellular | 20 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 38 | A0A0H3JKR2 Penicillin binding protein 2 | VNKTHKEDIYR | Near C-term | LTDGMQQV578↓579VNK | Predicted/transmembrane | 100 | 6 | 6 | 0 |
| 39 | A0A0H3JPQ1 SA1000 Fibrinogen-binding protein | LKYNTLK | Near C-term | SYEKKKLQRQIDLV↓103LKY | Predicted Extracellular | 20 | 32 | 32 | 0 |
| 40 | A0A0H3JPH2 Uncharacterized protein | SGVARPGVQSKASAPK | Near C-term | STAVGKYSSF69↓70SGV | Extracellular | 20 | 6 | 1 | 5 |
| 41 | P60432 Ribosomal protein L2 | SVMNPNDHPHGGGEGR | Near C-term | SRWKGIRPTVRG222↓223SVMNPN | Cytoplasm | 10 | 623 | 623 | 0 |
| 42 | P99152 Elongation factor Tu | APGSITPHTEFKAEVYVLSKDEGGR | Near C-term | GVAREDVQRGQVLA294↓295APG | Cytoplasm | 100 | 6 | 6 | 0 |
| 43 | P60185 Adapter protein MecA | NVTAQVR | Near C-term | YLNDYAKIIMSH224↓225NVT | Cytoplasm | 100 | 21 | 21 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Misal, S.A.; Ovhal, S.D.; Li, S.; Karty, J.A.; Tang, H.; Radivojac, P.; Reilly, J.P. Non-Specific Signal Peptidase Processing of Extracellular Proteins in Staphylococcus aureus N315. Proteomes 2023, 11, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes11010008
Misal SA, Ovhal SD, Li S, Karty JA, Tang H, Radivojac P, Reilly JP. Non-Specific Signal Peptidase Processing of Extracellular Proteins in Staphylococcus aureus N315. Proteomes. 2023; 11(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes11010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleMisal, Santosh A., Shital D. Ovhal, Sujun Li, Jonathan A. Karty, Haixu Tang, Predrag Radivojac, and James P. Reilly. 2023. "Non-Specific Signal Peptidase Processing of Extracellular Proteins in Staphylococcus aureus N315" Proteomes 11, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes11010008
APA StyleMisal, S. A., Ovhal, S. D., Li, S., Karty, J. A., Tang, H., Radivojac, P., & Reilly, J. P. (2023). Non-Specific Signal Peptidase Processing of Extracellular Proteins in Staphylococcus aureus N315. Proteomes, 11(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes11010008





