Comprehensive Kinase Activity Profiling Revealed the Kinase Activity Patterns Associated with the Effects of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Sensitizing EGFR Mutations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Assessments
2.4. EGFR-mutation Analysis
2.5. Comprehensive Tyrosine Kinase Activity Assay
2.6. Identification of Upstream Kinases
2.7. STRING Analysis
2.8. Pathway Analysis, Network Analysis, and Reactome Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Comprehensive Kinase Activity Analysis in NSCLC Patients with Sensitizing EGFR Mutations
3.3. Identification of Peptides Showing Significant Activation of Phosphorylation in Advanced NSCLC with Sensitizing EGFR Mutations
3.4. Putative Upstream Kinases
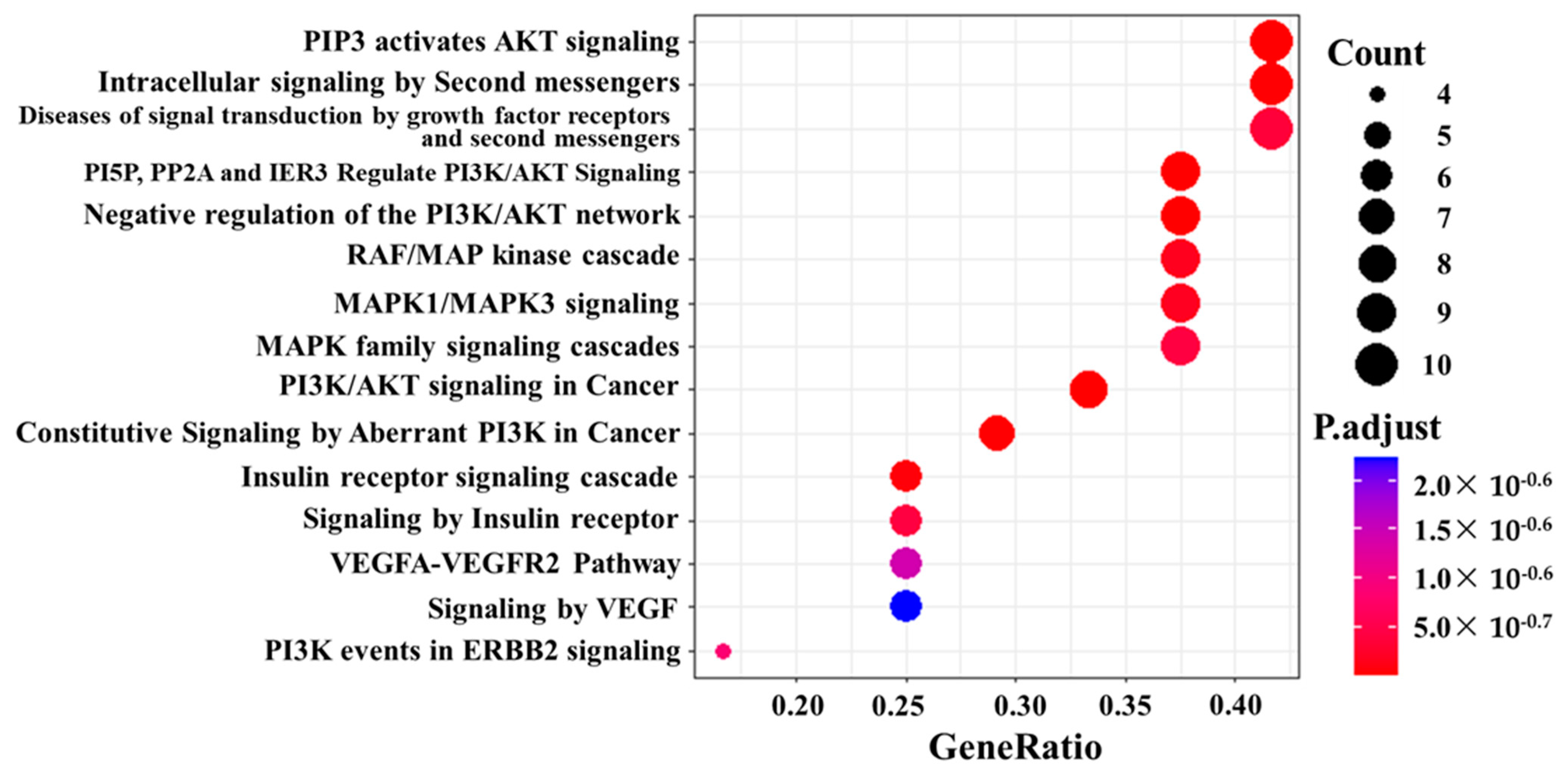
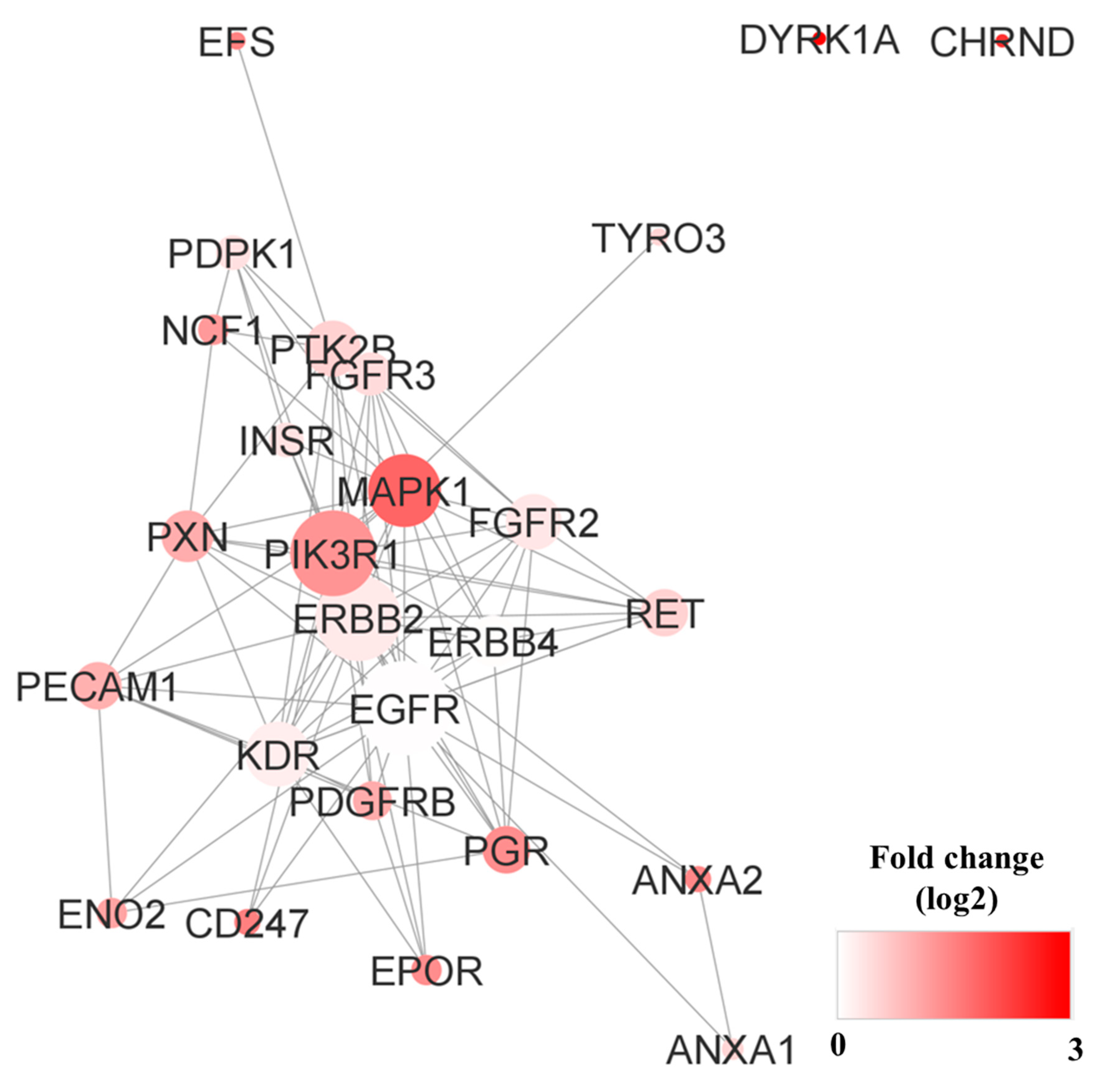
3.5. Pathway Analysis and Network Analysis
3.6. Kinase Profile Different between Highly Phosphorylated and Lower Phosphorylated Group
3.7. Pathway Analysis, Reactome Analysis, and Network Analysis between Highly Phosphorylated Group and Low Phosphorylated Group
3.8. Disease Free Survival (DFS) and Overall Survival (OS)
4. Discussion
4.1. Common Activated Kinases in NSCLC with Sensitizing EGFR Mutations
4.2. Activated Kinases in NSCLC Patients with Poor Prognosis
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H. Overview of gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer: An Asian perspective. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 39, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group, N.M.-A.C. Chemotherapy in addition to supportive care improves survival in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data from 16 randomized controlled trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 4617–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.J.; Stinchcombe, T.E.; Der, C.J.; Socinski, M.A. Personalized medicine in non-small-cell lung cancer: Is KRAS a useful marker in selecting patients for epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy? J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4769–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Guerra, H.; Waddell, T.K.; Salvarrey, M.A.; Joshua, A.M.; Chung, C.T.; Paul, N.; Boerner, S.; Sakurada, A.; Ludkovski, O.; Ma, C.; et al. Phase II study of preoperative gefitinib in clinical stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 6229–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, T.J.; Bell, D.W.; Sordella, R.; Gurubhagavatula, S.; Okimoto, R.A.; Brannigan, B.W.; Harris, P.L.; Haserlat, S.M.; Supko, J.G.; Haluska, F.G.; et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paez, J.G.; Janne, P.A.; Lee, J.C.; Tracy, S.; Greulich, H.; Gabriel, S.; Herman, P.; Kaye, F.J.; Lindeman, N.; Boggon, T.J.; et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004, 304, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindeman, N.I.; Cagle, P.T.; Beasley, M.B.; Chitale, D.A.; Dacic, S.; Giaccone, G.; Jenkins, R.B.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Saldivar, J.S.; Squire, J.; et al. Molecular testing guideline for selection of lung cancer patients for EGFR and ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Guideline from the College of American Pathologists, International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and Association for Molecular Pathology. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2013, 137, 828–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazdar, A.F. Activating and resistance mutations of EGFR in non-small-cell lung cancer: Role in clinical response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncogene 2009, 28 (Suppl. S1), S24–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.V.; Bell, D.W.; Settleman, J.; Haber, D.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintala, L.; Kurzrock, R. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation and diverse tumors: Case report and concise literature review. Mol. Oncol. 2010, 4, 306–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.K.; Brown, C.; Gralla, R.J.; Hirsh, V.; Thongprasert, S.; Tsai, C.M.; Tan, E.H.; Ho, J.C.; da Chu, T.; Zaatar, A.; et al. Impact of EGFR inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer on progression-free and overall survival: A meta-analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riely, G.J.; Pao, W.; Pham, D.; Li, A.R.; Rizvi, N.; Venkatraman, E.S.; Zakowski, M.F.; Kris, M.G.; Ladanyi, M.; Miller, V.A. Clinical course of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and epidermal growth factor receptor exon 19 and exon 21 mutations treated with gefitinib or erlotinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawson, T.; Scott, J.D. Protein phosphorylation in signaling—50 years and counting. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005, 30, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, G.; Plowman, G.D.; Hunter, T.; Sudarsanam, S. Evolution of protein kinase signaling from yeast to man. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.J.; Linley, A.; Hammond, D.E.; Hood, F.E.; Coulson, J.M.; MacEwan, D.J.; Ross, S.J.; Slupsky, J.R.; Smith, P.D.; Eyers, P.A.; et al. New Perspectives, Opportunities, and Challenges in Exploring the Human Protein Kinome. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleuren, E.D.; Zhang, L.; Wu, J.; Daly, R.J. The kinome ‘at large’ in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.W.; Chien, C.H.; Sung, M.I.; Chen, C.W.; Chen, Y.T. dBMHCC: A comprehensive hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) biomarker database provides a reliable prediction system for novel HCC phosphorylated biomarkers. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0234084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolch, W.; Pitt, A. Functional proteomics to dissect tyrosine kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giamas, G.; Stebbing, J.; Vorgias, C.E.; Knippschild, U. Protein kinases as targets for cancer treatment. Pharmacogenomics 2007, 8, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannaiyan, R.; Mahadevan, D. A comprehensive review of protein kinase inhibitors for cancer therapy. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2018, 18, 1249–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.C.; Duarte, C.W.; Welaya, K.; Rohrbach, T.D.; Bredel, M.; Yang, E.S.; Choradia, N.V.; Thottassery, J.V.; Yancey Gillespie, G.; Bonner, J.A.; et al. Kinomic exploration of temozolomide and radiation resistance in Glioblastoma multiforme xenolines. Radiother. Oncol. 2014, 111, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbeck, P.V.; Zhang, B.; Murray, B.; Kornhauser, J.M.; Latham, V.; Skrzypek, E. PhosphoSitePlus, 2014: Mutations, PTMs and recalibrations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D512–D520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: A worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Ding, W. Support vector machine classifier for prediction of the metastasis of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Morris, J.H.; Cook, H.; Kuhn, M.; Wyder, S.; Simonovic, M.; Santos, A.; Doncheva, N.T.; Roth, A.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D362–D368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindea, G.; Galon, J.; Mlecnik, B. CluePedia Cytoscape plugin: Pathway insights using integrated experimental and in silico data. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; He, Q.Y. ReactomePA: An R/Bioconductor package for reactome pathway analysis and visualization. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Wang, Y.; Broaddus, R.; Sun, L.; Xue, F.; Zhang, W. Exon 3 mutations of CTNNB1 drive tumorigenesis: A review. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 5492–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, S.; Sng, N.; Carretero, J.; Welner, R.; Hayashi, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Tan, A.J.; Yamaguchi, N.; Yasuda, H.; Li, D.; et al. beta-catenin contributes to lung tumor development induced by EGFR mutations. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5891–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, S.M. Crk family adaptors-signalling complex formation and biological roles. Oncogene 2001, 20, 6348–6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birge, R.B.; Kalodimos, C.; Inagaki, F.; Tanaka, S. Crk and CrkL adaptor proteins: Networks for physiological and pathological signaling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2009, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosser, S.; Sorokina, E.; Pratt, P.; Sorokin, A. CrkIII: A novel and biologically distinct member of the Crk family of adaptor proteins. Oncogene 2003, 22, 4799–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.T.; Chen, G.; Gharib, T.G.; Wang, H.; Thomas, D.G.; Misek, D.E.; Giordano, T.J.; Yee, J.; Orringer, M.B.; Hanash, S.M.; et al. Increased C-CRK proto-oncogene expression is associated with an aggressive phenotype in lung adenocarcinomas. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7950–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rettig, M.; Trinidad, K.; Pezeshkpour, G.; Frost, P.; Sharma, S.; Moatamed, F.; Tamanoi, F.; Mortazavi, F. PAK1 kinase promotes cell motility and invasiveness through CRK-II serine phosphorylation in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One 2012, 7, e42012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Kamath, A.; Joseph, A.M.; Rajala, M.S. PLCgamma1dependent invasion and migration of cells expressing NSCLCassociated EGFR mutants. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neel, B.G.; Gu, H.; Pao, L. The ‘Shp’ing news: SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatases in cell signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003, 28, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiganis, T.; Bennett, A.M. Protein tyrosine phosphatase function: The substrate perspective. Biochem. J. 2007, 402, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentires-Alj, M.; Paez, J.G.; David, F.S.; Keilhack, H.; Halmos, B.; Naoki, K.; Maris, J.M.; Richardson, A.; Bardelli, A.; Sugarbaker, D.J.; et al. Activating mutations of the noonan syndrome-associated SHP2/PTPN11 gene in human solid tumors and adult acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 8816–8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomon, D.S.; Brandt, R.; Ciardiello, F.; Normanno, N. Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 1995, 19, 183–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennis, B.W.; Lippman, M.E.; Dickson, R.B. The EGF receptor system as a target for antitumor therapy. Cancer Invest. 1991, 9, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavelic, K.; Banjac, Z.; Pavelic, J.; Spaventi, S. Evidence for a role of EGF receptor in the progression of human lung carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 1993, 13, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohsaki, Y.; Tanno, S.; Fujita, Y.; Toyoshima, E.; Fujiuchi, S.; Nishigaki, Y.; Ishida, S.; Nagase, A.; Miyokawa, N.; Hirata, S.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression correlates with poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients with p53 overexpression. Oncol. Rep. 2000, 7, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volm, M.; Rittgen, W.; Drings, P. Prognostic value of ERBB-1, VEGF, cyclin A, FOS, JUN and MYC in patients with squamous cell lung carcinomas. Br. J. Cancer 1998, 77, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabender, J.; Danenberg, K.D.; Metzger, R.; Schneider, P.M.; Park, J.; Salonga, D.; Holscher, A.H.; Danenberg, P.V. Epidermal growth factor receptor and HER2-neu mRNA expression in non-small cell lung cancer Is correlated with survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 1850–1855. [Google Scholar]
- Rikova, K.; Guo, A.; Zeng, Q.; Possemato, A.; Yu, J.; Haack, H.; Nardone, J.; Lee, K.; Reeves, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell 2007, 131, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappuzzo, F.; Ligorio, C.; Toschi, L.; Rossi, E.; Trisolini, R.; Paioli, D.; Magrini, E.; Finocchiaro, G.; Bartolini, S.; Cancellieri, A.; et al. EGFR and HER2 gene copy number and response to first-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2007, 2, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristics | n (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Median age, years | 73.0 (46.0–88.0) | |
| Age | <70 | 7 (36.8) |
| ≧70 | 12 (63.2) | |
| Gender | Male | 6 (31.6) |
| Female | 13 (68.4) | |
| Smoking history | Never | 6 (31.6) |
| Current or former | 13 (68.4) | |
| ECOG performance status | 0 | 6 (31.6) |
| 1 | 13 (68.4) | |
| 2 | 2 (10.5) | |
| Histology | Adenocarcinoma | 18 (94.7) |
| NOS | 1 (5.3) | |
| Stage | IV | 19 (100) |
| EGFR mutation | Del19 | 11 (57.9) |
| L858R | 8 (42.1) | |
| EGFR TKI therapy | Gefitinib | 2 (10.5) |
| Afatinib | 3 (15.8) | |
| Osimertinib | 14 (73.7) | |
| Response | PR | 15 (78.9) |
| SD | 1 (5.3) | |
| PD | 1 (5.3) | |
| NE | 2 (10.5) | |
| ORR | 88.24% | |
| DCR | 94.12% | |
| Median MTS | 44.1 (−36.0–80.0) | |
| Proteome analysis | Cluster 1 | 9 (47.4) |
| Cluster 2 | 9 (47.4) | |
| Unanalyzable | 1 (5.3) |
| Peptide ID | Uniprot Accession | Protein Name | Sequence | Tyr | Type of Cluster | UniProt | Phosphosite Plus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PGFRB_1002_1014 | P09619 | PDGFRB | LDTSSVLYTAVQP | (1009) | Cluster A | PDGFRB | PDGFRB |
| MET_1227_1239 | P08581 | MET | RDMYDKEYYSVHN | (1230, 1234, 1235) | Cluster A | MET | MET, Ron |
| RAF1_332_344 | P04049 | RAF1 | PRGQRDSSYYWEI | (340, 341) | Cluster A | SRC | SRC |
| ERBB2_1241_1253 | P04626 | ERBB2 | PTAENPEYLGLDV | (1248) | Cluster A | ERBB2 | ERBB2 |
| FGFR2_762_774 | P21802 | FGFR2 | TLTTNEEYLDLSQ | (769) | Cluster A | FGFR2 | FGFR2 |
| LCK_387_399 | P06239 | LCK | RLIEDNEYTAREG | (394) | Cluster A | Lck | Lck, AXL, yopH |
| PDPK1_369_381 | O15530 | PDPK1 | DEDCYGNYDNLLS | (373, 376) | Cluster A | SRC, INSR | SRC |
| CBL_693_705 | P22681 | CBL | EGEEDTEYMTPSS | (700) | Cluster A | ABl1 | Abl, Fyn, INSR |
| FAK1_569_581 | Q05397 | PTK2 | RYMEDSTYYKASK | (570, 576, 577) | Cluster A | RET, SRC | FAK, FGR, Met, RET |
| PGFRB_771_783 | P09619 | PDGFRB | YMAPYDNYVPSAP | (771, 775, 778) | Cluster A | PDGFRB | PDGFRB |
| KSYK_518_530 | P43405 | SYK | ALRADENYYKAQT | (525, 526) | Cluster A | SYK | SYK, Lyn |
| PGFRB_768_780 | P09619 | PDGFRB | SSNYMAPYDNYVP | (771, 775, 778) | Cluster A | PDGFRB | PDGFRB |
| VGFR2_1168_1180 | P35968 | KDR | AQQDGKDYIVLPI | (1175) | Cluster A | VEGFR2 | Src, VEGFR2 |
| VGFR2_1052_1064 | P35968 | KDR | DIYKDPDYVRKGD | (1054, 1059) | Cluster A | VEGFR2 | VEGFR2 |
| PLCG1_764_776 | P19174 | PLCG1 | IGTAEPDYGALYE | (771, 775) | Cluster B | SYK | Abl, EGFR, SYK |
| PAXI_111_123 | P49023 | PXN | VGEEEHVYSFPNK | (118) | Cluster B | PTK6 | Abl, FAK |
| FES_706_718 | P07332 | FES | REEADGVYAASGG | (713) | Cluster B | FES | FES |
| PGFRB_572_584 | P09619 | PDGFRB | VSSDGHEYIYVDP | (579, 581) | Cluster B | PDGFRB | PDGFRB |
| CDK2_8_20 | P24941 | CDK2 | EKIGEGTYGVVYK | (15, 19) | Cluster B | WEE1 | WEE1 |
| VGFR2_989_1001 | P35968 | KDR | EEAPEDLYKDFLT | (996) | Cluster B | VEGFR2 | VEGFR2 |
| PGFRB_1014_1028 | P09619 | PDGFRB | PNEGDNDYIIPLPDP | (1021) | Cluster B | PDGFRB | PDGFRB |
| FER_707_719 | P16591 | FER | RQEDGGVYSSSGL | (714) | Cluster B | FER | FER, Src |
| VGFR2_1046_1058 | P35968 | KDR | DFGLARDIYKDPD | (1054) | Cluster C | VEGFR2 | VEGFR2 |
| INSR_992_1004 | P06213 | INSR | YASSNPEYLSASD | (992, 999) | Cluster C | INSR | INSR |
| EGFR_1165_1177 | P00533 | EGFR | ISLDNPDYQQDFF | (1172) | Cluster C | EGFR | EGFR |
| ERBB4_1277_1289 | Q15303 | ERBB4 | IVAENPEYLSEFS | (1284) | Cluster C | ERBB4 | HER4 |
| EGFR_1190_1202 | P00533 | EGFR | STAENAEYLRVAP | (1197) | Cluster C | EGFR | EGFR |
| FGFR1_761_773 | P11362 | FGFR1 | TSNQEYLDLSMPL | (766) | Cluster C | FGFR1 | FGFR1 |
| CRK_214_226 | P46108 | CRK | GPPEPGPYAQPSV | (221) | Cluster C | ABL1 | ABL1 |
| VGFR3_1061_1073 | P35916 | FLT4 | DIYKDPDYVRKGS | (1063, 1068) | Cluster C | SRC, FLT4 | SRC |
| ANXA2_17_29 | P07355 | ANXA2 | HSTPPSAYGSVKA | (24) | Cluster C | SRC | SRC, IGF1R, Yes |
| EGFR_1103_1115 | P00533 | EGFR | GSVQNPVYHNQPL | (1110) | Cluster C | EGFR | EGFR |
| VGFR2_944_956 | P35968 | KDR | RFRQGKDYVGAIP | (951) | Cluster C | VEGFR2 | VEGFR2 |
| MK14_173_185 | Q16539 | MAPK14 | RHTDDEMTGYVAT | (182) | Cluster C | MAP2K3, MAP2K4, MAP14, MAP2K6 | MAP2K3, MAP2K4, MAP2K6, MAP3K6 |
| EPHA4_589_601 | P54764 | EPHA4 | LNQGVRTYVDPFT | (596) | Cluster C | EPHA4 | EPHA4 |
| MK01_180_192 | P28482 | MAPK1 | HTGFLTEYVATRW | (187) | Cluster C | MAP2K1, MAP2K2 | JAK2, EGFR, MAP2K2, Ret, MAP2K1 |
| #term ID | Term Description | Observed Gene Count | Background Gene Count | Strength | False Discovery Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa04151 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 26 | 350 | 1.27 | 4.27 × 10 −23 |
| hsa04014 | Ras signaling pathway | 21 | 226 | 1.37 | 2.53 × 10 −20 |
| hsa04015 | Rap1 signaling pathway | 20 | 202 | 1.4 | 6.04 × 10 −20 |
| hsa05200 | Pathways in cancer | 26 | 517 | 1.1 | 1.29 × 10 −19 |
| hsa04010 | MAPK signaling pathway | 21 | 288 | 1.26 | 1.12 × 10 −18 |
| hsa05205 | Proteoglycans in cancer | 17 | 196 | 1.34 | 4.08 × 10 −16 |
| hsa01521 | EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance | 13 | 78 | 1.62 | 1.54 × 10 −15 |
| hsa05235 | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | 13 | 88 | 1.57 | 5.55 × 10 −15 |
| hsa04510 | Focal adhesion | 16 | 198 | 1.31 | 7.92 × 10 −15 |
| hsa04360 | Axon guidance | 15 | 177 | 1.33 | 3.50 × 10 −14 |
| hsa05215 | Prostate cancer | 12 | 96 | 1.5 | 3.99 × 10 −13 |
| hsa05230 | Central carbon metabolism in cancer | 11 | 69 | 1.6 | 4.38 × 10 −13 |
| hsa04660 | T cell receptor signaling pathway | 12 | 101 | 1.47 | 5.90 × 10 −13 |
| hsa04722 | Neurotrophin signaling pathway | 12 | 114 | 1.42 | 2.07 × 10 −12 |
| hsa04012 | ErbB signaling pathway | 11 | 83 | 1.52 | 2.21 × 10 −12 |
| hsa04658 | Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | 11 | 87 | 1.5 | 3.32 × 10 −12 |
| hsa05167 | Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection | 13 | 187 | 1.24 | 2.08 × 10 −11 |
| hsa04670 | Leukocyte transendothelial migration | 11 | 109 | 1.4 | 2.85 × 10 −11 |
| hsa05161 | Hepatitis B | 12 | 159 | 1.28 | 5.99 × 10 −11 |
| hsa05135 | Yersinia infection | 11 | 125 | 1.34 | 1.02 × 10 −10 |
| ID | Kinase | Uniprot ID | Betweenness Centrality | Closeness Centrality | Degree | Stress |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CTNNB1 | P35222 | 0.180455356 | 0.768421053 | 51 | 4522 |
| 2 | EGFR | P00533 | 0.100566651 | 0.760416667 | 51 | 3226 |
| 3 | PIK3R1 | P27986 | 0.061532117 | 0.688679245 | 42 | 1996 |
| 4 | ERBB2 | P04626 | 0.043504506 | 0.688679245 | 41 | 1742 |
| 5 | PTPN11 | Q06124 | 0.036477003 | 0.688679245 | 41 | 1594 |
| 6 | PLCG1 | P19174 | 0.04424585 | 0.651785714 | 39 | 1566 |
| 7 | CRK | P46108 | 0.03378544 | 0.646017699 | 36 | 1354 |
| Peptide Site | Phosphorylation Site | Signal Intensity | Fold Change | p Value | FDR q Value | PhosphoPlus | Uniprot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DYR1A_312_324 | (19, 321) | 13.52805 | 3.116532 | 9.83 × 10 −8 | 3.34 × 10 −6 | EGFR | - |
| VINC_815_827 | (822) | 6.042773 | 3.077846 | 1.55 × 10 −5 | 0.000144 | KARS | - |
| ACHD_383_395 | (383, 390) | 6.138561 | 2.551585 | 0.00015 | 0.001174 | - | - |
| MK01_180_192 | (187) | 9.516106 | 2.024014 | 5.80 × 10 −6 | 6.58 × 10 −5 | EGFR | MAP2K1, MAP2K2 |
| CD3Z_116_128 | (123) | 42.36624 | 1.731 | 0.001188 | 0.006731 | - | - |
| EFS_246_258 | (253) | 1559.662 | 1.719715 | 0.013831 | 0.04551 | - | Src |
| ANXA2_17_29 | (24) | 20.03061 | 1.659909 | 0.009685 | 0.036588 | Src, IGF1R | Src |
| EGFR_1103_1115 | (1110) | 21.06897 | 1.621966 | 0.01073 | 0.03774 | EGFR | EGFR |
| EPOR_419_431 | (368) | 59.07756 | 1.599058 | 0.001489 | 0.007994 | JAK2 | JAK2 |
| PRGR_786_798 | (795) | 14.26506 | 1.579949 | 0.002504 | 0.012161 | - | - |
| SRC8_CHICK_476_488 | (477, 483) | 1262.13 | 1.566668 | 1.80 × 10 −6 | 3.01 × 10 −5 | - | Src |
| P85A_600_612 | (607) | 419.0784 | 1.515741 | 0.000528 | 0.00359 | EGFR, INSR, CSFR | - |
| #Term ID | Term Description | Observed Gene Count | Background Gene Count | Strength | False Discovery Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa04151 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 26 | 348 | 1.27 | 2.74 × 10 −23 |
| hsa04014 | Ras signaling pathway | 20 | 228 | 1.34 | 5.64 × 10 −19 |
| hsa04015 | Rap1 signaling pathway | 19 | 203 | 1.37 | 1.28 × 10 −18 |
| hsa04010 | MAPK signaling pathway | 21 | 293 | 1.25 | 1.32 × 10 −18 |
| hsa05200 | Pathways in cancer | 25 | 515 | 1.08 | 1.32 × 10 −18 |
| hsa05205 | Proteoglycans in cancer | 18 | 195 | 1.36 | 8.99 × 10 −18 |
| hsa04510 | Focal adhesion | 17 | 197 | 1.33 | 2.40 × 10 −16 |
| hsa01521 | EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance | 13 | 78 | 1.62 | 8.07 × 10 −16 |
| hsa04360 | Axon guidance | 15 | 173 | 1.33 | 1.74 × 10 −14 |
| hsa05230 | Central carbon metabolism in cancer | 11 | 65 | 1.62 | 1.69 × 10 −13 |
| hsa05215 | Prostate cancer | 12 | 97 | 1.49 | 2.64 × 10 −13 |
| hsa04670 | Leukocyte transendothelial migration | 12 | 112 | 1.42 | 1.17 × 10 −12 |
| hsa04012 | ErbB signaling pathway | 11 | 83 | 1.52 | 1.48 × 10 −12 |
| hsa04658 | Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | 11 | 88 | 1.49 | 2.47 × 10 −12 |
| hsa04660 | T cell receptor signaling pathway | 11 | 99 | 1.44 | 7.54 × 10 −12 |
| hsa04722 | Neurotrophic signaling pathway | 11 | 116 | 1.37 | 3.49 × 10 −11 |
| hsa04380 | Osteoclast differentiation | 11 | 124 | 1.34 | 6.45 × 10 −11 |
| hsa04370 | VEGF signaling pathway | 9 | 59 | 1.58 | 6.57 × 10 −11 |
| hsa04068 | FoxO signaling pathway | 11 | 130 | 1.32 | 9.30 × 10 −11 |
| hsa01522 | Endocrine resistance | 10 | 95 | 1.42 | 1.10 × 10 −10 |
| Kinase | Uniprot ID | Degree | Betweenness Centrality | Closeness Centrality | Stress |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR | P00533 | 19 | 0.230237725 | 0.851851852 | 306 |
| PIK3R1 | P27986 | 17 | 0.183294549 | 0.793103448 | 248 |
| ERBB2 | P04626 | 17 | 0.120685682 | 0.793103448 | 218 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noguchi, R.; Yoshimura, A.; Uchino, J.; Takeda, T.; Chihara, Y.; Ota, T.; Hiranuma, O.; Gyotoku, H.; Takayama, K.; Kondo, T. Comprehensive Kinase Activity Profiling Revealed the Kinase Activity Patterns Associated with the Effects of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Sensitizing EGFR Mutations. Proteomes 2023, 11, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes11010006
Noguchi R, Yoshimura A, Uchino J, Takeda T, Chihara Y, Ota T, Hiranuma O, Gyotoku H, Takayama K, Kondo T. Comprehensive Kinase Activity Profiling Revealed the Kinase Activity Patterns Associated with the Effects of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Sensitizing EGFR Mutations. Proteomes. 2023; 11(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes11010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoguchi, Rei, Akihiro Yoshimura, Junji Uchino, Takayuki Takeda, Yusuke Chihara, Takayo Ota, Osamu Hiranuma, Hiroshi Gyotoku, Koichi Takayama, and Tadashi Kondo. 2023. "Comprehensive Kinase Activity Profiling Revealed the Kinase Activity Patterns Associated with the Effects of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Sensitizing EGFR Mutations" Proteomes 11, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes11010006
APA StyleNoguchi, R., Yoshimura, A., Uchino, J., Takeda, T., Chihara, Y., Ota, T., Hiranuma, O., Gyotoku, H., Takayama, K., & Kondo, T. (2023). Comprehensive Kinase Activity Profiling Revealed the Kinase Activity Patterns Associated with the Effects of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Sensitizing EGFR Mutations. Proteomes, 11(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes11010006









