Investigating Engineering Student Learning Style Trends by Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Learning Styles
2.1. Myers–Briggs-Based Type Indicator
- Extraverts: They try things out; introverts: They think things through.
- Sensors: Practical; intuitors: Imaginative.
- Thinkers: They tend to make decisions based on facts; feelers: They tend to make decisions based on feelings and personal hunches.
- Judgers: They follow agendas; perceivers: They adapt to change.
2.2. The Felder–Silverman Model
- What type of information the student preferentially perceives: Sensory or intuitive.
- What type of sensory information is most effectively perceived: Visual or verbal.
- How students prefer to process the information: Actively or reflectively.
- How the student characteristically progresses toward understanding: Sequentially or globally.
3. Current Practice
4. Proposed Evaluation of Students
5. Clustering Algorithms Based on Similarity Coefficients
- a: The number of parts that visit both machines,
- b: The number of parts that visit machine i but not j,
- c: The number of parts that visit machine j but not i.
- Start with M cluster containing a M × M symmetric matrix of distance/similarities in .
- Find the smallest distances/similarities in .
- Merge the corresponding objects, U and V, to obtain the cluster, .
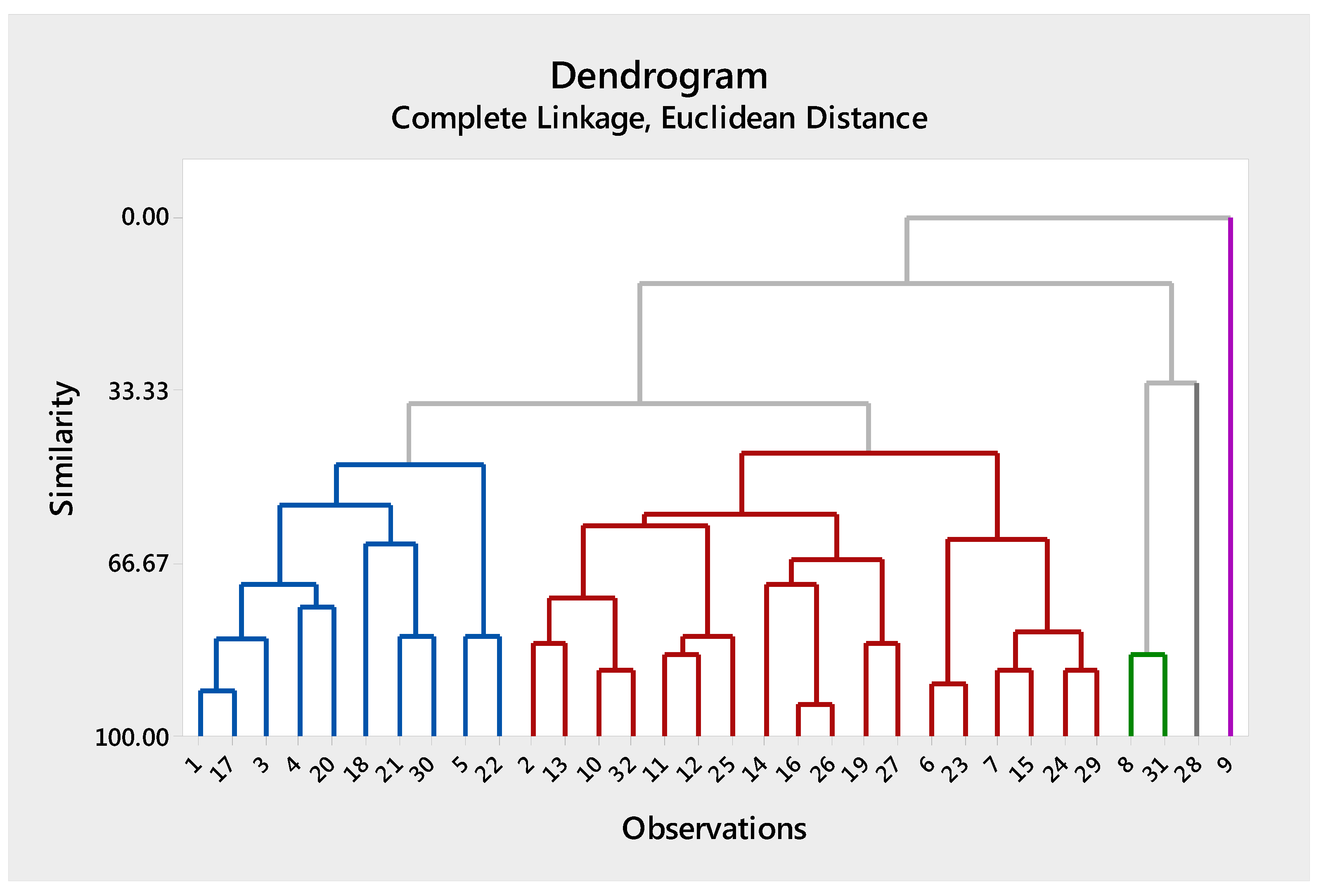
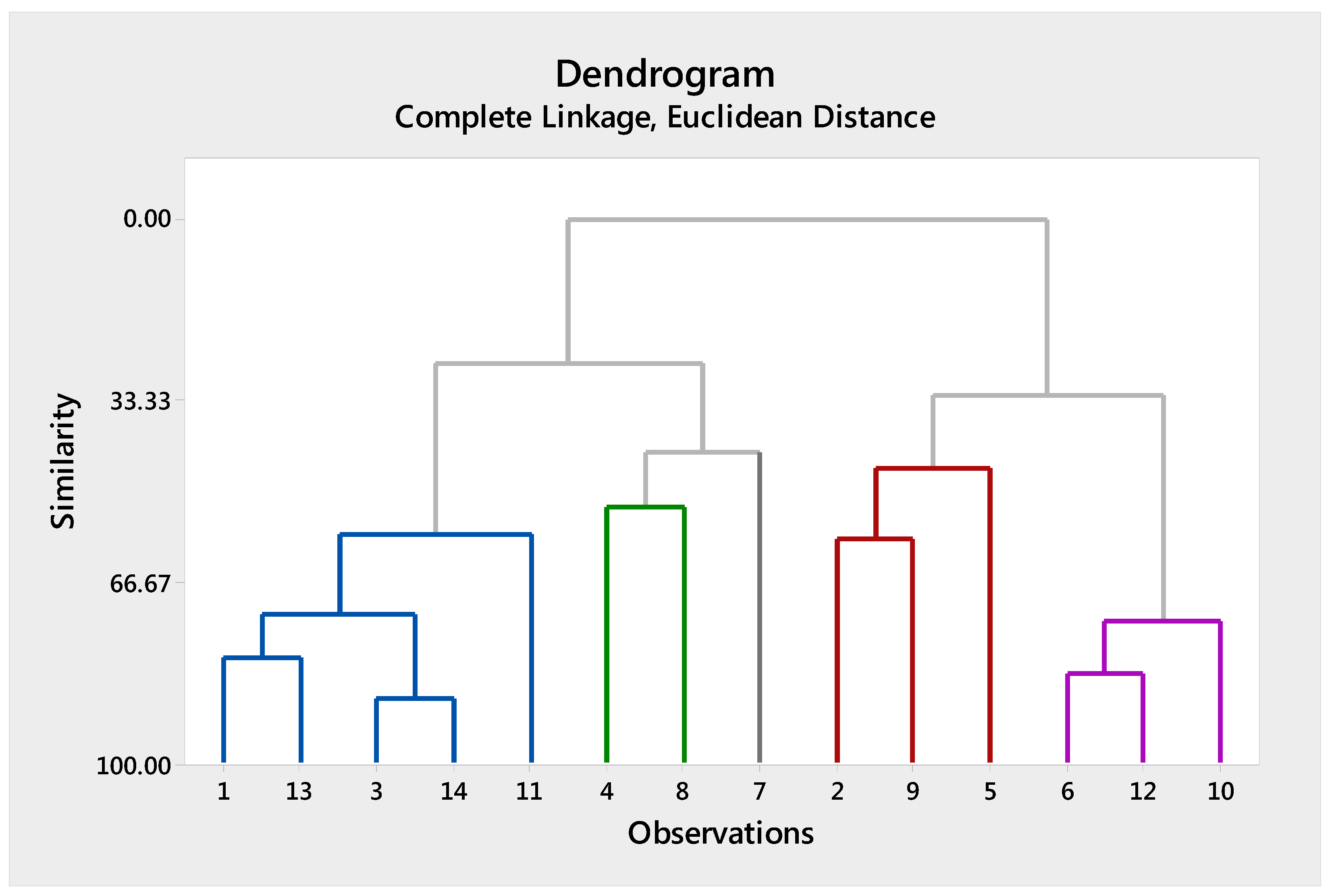
- The distance/similarities between and any other cluster, Q, is computed by:The values, dUQ and dVQ, are the distances/similarities between the clusters, U and Q, and V and Q, respectively. The result is graphically shown in the form of a tree diagram (dendrogram). The tree diagram representing the machine cells/part-families at different levels of similarity is created by using the similarity coefficient matrix.
6. Data Collection
7. Data Analysis
7.1. Data Analysis for the First Sample of Students
7.2. Data Analysis for the Second Sample of Students
8. Observations and Results
9. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeung, A.; Read, J.; Schmid, S. Students’ learning styles and academic performance in first year chemistry. In Proceedings of the Australian Conference on Science and Mathematics Education (formerly Uni. Serve Science Conference), Sydney, Australia, 26–28 September 2012; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Khurshid, F.; Mahmood, N. Learning styles of natural sciences, social sciences and humanities students at graduate level. Interdiscip. J. Contemp. Res. Bus. 2012, 3, 672–678. [Google Scholar]
- Abidin, M.J.Z.; Rezaee, A.A.; Abdullah, H.N.; Singh, K.K.B. Learning styles and overall academic achievement in a specific educational system. Int. J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2011, 1, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Christou, N.; Dinov, I.D. A study of students’ learning styles, discipline attitudes and knowledge acquisition in technology-enhanced probability and statistics education. MERLOT J. Online Learn. Teach. 2010, 6, 546–572. [Google Scholar]
- Komarraju, M.; Karau, S.J.; Schmeck, R.R.; Avdic, A. The big five personality traits, learning styles, and academic achievement. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2011, 51, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsh, A.A.; Kusangaya, R.S.; Siddiquil, H.T.; Syed, H.; Khan, S.; Bilal, I.; Shaikh, R.B. Learning styles and teaching/learning preferences of pre-clinical medical students in Ajman, UAE. In Gulf Medical Journal, Proceedings of the 6th Annual Scientific Meeting Oral Proceedings; Gulf Medical University: Ajman, United Arab Emirates, 2014; Volume 3, pp. 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Yousef, D.A. Learning style preferences of undergraduate business students: A study in the faculty of business and economics at the UAE university (UAEU). J. Int. Bus. Educ. 2014, 9, 211–223. [Google Scholar]
- Yousef, D.A. Learning styles preferences of managers at local government departments: A study in the emirate of Ras Al Khaimah (UAE). J. Int. Bus. Educ. 2015, 10, 137–154. [Google Scholar]
- Sugahara, S.; Boland, G. The role of cultural factors in the learning style preferences of accounting students: A comparative study between Japan and Australia. Account. Educ. Int. J. 2010, 19, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtbrügge, D.; Mohr, A.T. Cultural determinants of learning style preferences. Acad. Manag. Learn. Educ. 2010, 9, 622–637. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, C.Y.R.; Teo, T.C. Understanding Asian students learning styles, cultural influence and learning strategies. J. Educ. Soc. Policy 2017, 7, 194–210. [Google Scholar]
- Bachman, C.H. Using Learning Styles as a Group Selection Technique; Center for Teaching Excellence, United States Military Academy: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Massey, M.G.; Kim, S.H.; Mitchell, C. A study of the learning styles of undergraduate social work students. J. Evid. Based Soc. Work 2011, 8, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, T.; Kreiner, S. Course evaluation for the purpose of development: What can learning styles contribute? Stud. Educ. Eval. 2017, 54, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simelane, S.; Mji, A. Impact of Technology-Engagement Teaching Strategy with the Aid of Clickers on Student’s Learning. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 136, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulbure, C. Learning Styles, Teaching Strategies and Academic Achievement in Higher Education: A Cross-Sectional Investigation. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 33, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadden, C. Making Connections: Instructional Strategies 2005. Available online: http://education.uregina.ca/iteachered/modules/preservice/module3.html (accessed on 10 December 2018).
- Giles, J.; Ryan, D.A.J.; Belliveau, G.; De Freitas, E.; Casey, R. Teaching style and learning in a quantitative classroom. Act. Learn. High. Educ. 2006, 7, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhar, N.; Strong, R.D. Toward dynamic modeling of a teaching learning system Part 2: A new theory on types of learners. Int. J. Eng. Educ. 1988, 16, 368–406. [Google Scholar]
- Dembo, M.H.; Howard, K. Advice about the use of learning styles: A major myth in education. J. Coll. Read. Learn. 2007, 37, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, D.P.; Kelly, M.; Wong, W.S.S. Chinese conceptions of ‘effective teaching’ in Hong Kong: Towards culturally sensitive evaluation of teaching. Int. J. Lifelong Educ. 1999, 18, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywood, J. Assessment in Higher Education Student Learning, Teaching, Programs and Institutions; Jessica Kingsley: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Corno, L.; Snow, R.E. Adapting Teaching to Individual Differences among Learners. In Handbook of Research on Teaching, 3rd ed.; Wittrock, M.C., Ed.; Macmillan and Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Schmeck, R.R. Learning Strategies and Learning Styles; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Stice, J.E. Using Kolb’s Learning Cycle to Improve Student Learning. Eng. Educ. 1987, 77, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Felder, R.M.; Silverman, L.K. Learning and Teaching Styles in Engineering Education. Eng. Educ. 1988, 7, 674–681. Available online: http://www.ncsu.edu/felder-public/Papers/LS-1988.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2017).
- Felder, R.M. Matters of Style. ASEE Prism 1996, 6, 18–23. Available online: www.ncsu.edu/felder-public/Papers/LSPrism.htm (accessed on 10 June 2017).
- Lawrence, G. People Types and Tiger Stripes: A Practical Guide to Learning Styles, 3rd ed.; Enter for Applications of Psychological Type: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Yokomoto, C.E.; Ware, J.R. Improving Problem Solving Performance Using the MBTI. In Proceedings of the 1982 ASEE Conference and Exposition, American Society for Engineering Education, Washington, DC, USA, 28 June 1982. [Google Scholar]
- McCaulley, M.H.; Godleski, E.S.; Yokomoto, C.F.; Harrisberger, L.; Sloan, E.D. Applications of Psychological Type in Engineering Education. Eng. Educ. 1983, 73, 394–400. [Google Scholar]
- Godleski, E.S. Learning Style Compatibility of Engineering Students and Faculty. In Proceedings of the 1984 ASEE/IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 24 June 1984. [Google Scholar]
- McCaulley, M.H.; Macdaid, G.P.; Granade, J.G. ASEEMBTI Engineering Consortium: Report of the First Five Years. In Proceedings of the 1985 ASEE Annual Conference, American Society for Engineering Education, Washington, DC, USA, 23 June 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Lumsdaine, M.; Lumsdaine, E. Thinking Preferences of Engineering Students: Implications for Curriculum Restructuring. J. Eng. Educ. 1995, 84, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.; Beaudry, J.S.; Klavas, A. Survey of Research on Learning Styles. Educ. Leadersh. 1989, 46, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, R. Understanding the Dunn and Dunn Learning Styles Model and the Need for Individual Diagnosis and Prescription. Read. Writ. Learn. Disabil. 1990, 6, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, J.E.; Harb, J.N.; Terry, R.E. Combining Kolb Learning Styles and Writing to Learn in Engineering Classes. J. Eng. Educ. 1997, 86, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, J.E. Learning Styles and Technical Communication: Improving Communication and Teamwork Skills. In Proceedings of the 1998 ASEE/IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 20 June 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rosati, P.A. Specific Differences and Similarities in the Learning Preferences of Engineering Students. In Proceedings of the 1999 ASEE/IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 19 June 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zywno, M.S.; Waalen, J.K. The Effect of Hypermedia Instruction on Achievement and Attitudes of Students with Different Learning Styles. In Proceedings of the 2001 ASEE Conference and Exposition, American Society for Engineering Education, Washington, DC, USA, 23 June 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Livesay, G.A.; Dee, K.C.; Nauman, E.A.; Hites, L.S. Engineering Student Learning Styles: A Statistical Analysis Using Felder’s Index of Learning Styles. In Proceedings of the 2002 ASEE Conference and Exposition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 16–19 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zywno, M.S. Instructional Technology, Learning Styles, and Academic Achievement. In Proceedings of the 2002 ASEE Conference and Exposition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 16–19 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ashford, T.S.; Shehab, R.L.; Rhoads, T.R.; Court, M.C. A Survey of Learning Styles of Engineering Students. In Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2003; Volume 47, pp. 870–874. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, K.G. Student Perceptions of Internet-Based Learning Tools in Environmental Engineering Education. J. Eng. Educ. 1999, 88, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, S.; Viola, S.R.; Tommaso, L. In-Depth Analysis of the Felder-Silverman Learning Style Dimensions. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 2007, 40, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangineto, E.; Capuano, N.; Gaeta, M.; Micarelli, A. Adaptive course generation through learning styles representation. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2008, 7, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felder, R.M.; Spurlin, J.E. Applications, Reliability, and Validity of the Index of Learning Styles. Int. J. Eng. Educ. 2005, 21, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, A.Y. The use of the learning styles questionnaire (LSQ) in the United Arab Emirates. Quality Assur. Educ. 2016, 24, 227–243. [Google Scholar]
- Felder, R.M.; Brent, R. Understanding Student Differences. J. Engr. Educ. 2005, 94, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhadi, A. Preventive Maintenance Grouping Using Similarity Coefficient Methodology. Ph.D. Thesis, Industrial Engineering Department, University of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.A.; Wichern, D.W. Applied Multivariate Statistical Analysis, 6th ed.; Pearson Education: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Minitab. Minitab Corporation. 2016. Available online: https://www.minitab.com (accessed on 20 August 2018).
| Student # | ACT | REF | SEN | INT | VIS | VRB | SEQ | GLO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 9 | 3 | 3 | ||||
| 2 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 1 | ||||
| 3 | 9 | 9 | 4 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 3 | ||||
| 5 | 3 | 9 | 3 | 3 | ||||
| 6 | 5 | 5 | 9 | 2 | ||||
| 7 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 | ||||
| 8 | 9 | 7 | 11 | 7 | ||||
| 9 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 7 | ||||
| 10 | 3 | 1 | 7 | 3 | ||||
| 11 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5 | ||||
| 12 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | ||||
| 13 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 3 | ||||
| 14 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 1 | ||||
| 15 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 3 | ||||
| 16 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 1 | ||||
| 17 | 5 | 9 | 5 | 3 | ||||
| 18 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 3 | ||||
| 19 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | ||||
| 20 | 5 | 9 | 3 | 3 | ||||
| 21 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 3 | ||||
| 22 | 3 | 9 | 3 | 3 | ||||
| 23 | 5 | 3 | 9 | 1 | ||||
| 24 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 7 | ||||
| 25 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 5 | ||||
| 26 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 1 | ||||
| 27 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 28 | 11 | 5 | 7 | 9 | ||||
| 29 | 1 | 5 | 9 | 5 | ||||
| 30 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 3 | ||||
| 31 | 7 | 5 | 9 | 7 | ||||
| 32 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| Student # | ACT | REF | SEN | INT | VIS | VRB | SEQ | GLO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | ||||
| 2 | 5 | 5 | 9 | 3 | ||||
| 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | ||||
| 4 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 9 | ||||
| 5 | 9 | 1 | 11 | 9 | ||||
| 6 | 9 | 7 | 9 | 3 | ||||
| 7 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 11 | ||||
| 8 | 3 | 9 | 9 | 9 | ||||
| 9 | 1 | 5 | 9 | 7 | ||||
| 10 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 3 | ||||
| 11 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||||
| 12 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 1 | ||||
| 13 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | ||||
| 14 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Step | Similarity Level % | Student Number Joined | New Cluster | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 93.5 | 16 | 26 | 16 |
| 2 | 90.9 | 1 | 17 | 1 |
| 3 | 89.8 | 6 | 23 | 6 |
| 4 | 87.1 | 10 | 32 | 10 |
| 5 | 87.1 | 24 | 29 | 24 |
| 6 | 87.1 | 7 | 15 | 7 |
| 7 | 84.2 | 8 | 31 | 8 |
| 8 | 84.2 | 11 | 12 | 11 |
| 9 | 81.7 | 19 | 27 | 19 |
| 10 | 81.7 | 2 | 13 | 2 |
| 11 | 81.2 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| 12 | 80.6 | 21 | 30 | 21 |
| 13 | 80.6 | 11 | 25 | 11 |
| 14 | 80.6 | 5 | 22 | 5 |
| 15 | 79.6 | 7 | 24 | 7 |
| 16 | 75 | 4 | 20 | 4 |
| 17 | 73.4 | 2 | 10 | 2 |
| 18 | 70.7 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| 19 | 70.4 | 14 | 16 | 14 |
| 20 | 65.8 | 14 | 19 | 14 |
| 21 | 62.9 | 18 | 21 | 18 |
| 22 | 61.8 | 6 | 7 | 6 |
| 23 | 59.2 | 2 | 11 | 2 |
| 24 | 57.2 | 2 | 14 | 2 |
| 25 | 55.3 | 1 | 18 | 1 |
| 26 | 47.4 | 1 | 5 | 1 |
| 27 | 45.2 | 2 | 6 | 2 |
| 28 | 35.6 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 29 | 31.7 | 8 | 28 | 8 |
| 30 | 12.7 | 1 | 8 | 1 |
| 31 | 0 | 1 | 9 | 1 |
| Step | Similarity Level % | Student Number Joined | New Cluster | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 88.2 | 3 | 14 | 3 |
| 2 | 83.3 | 6 | 12 | 6 |
| 3 | 80.7 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| 4 | 73.6 | 6 | 10 | 6 |
| 5 | 72.7 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| 6 | 56.5 | 2 | 9 | 2 |
| 7 | 579 | 1 | 11 | 1 |
| 8 | 52.7 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| 9 | 45.8 | 2 | 5 | 2 |
| 10 | 42.9 | 4 | 7 | 4 |
| 11 | 32.5 | 2 | 6 | 2 |
| 12 | 26.2 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| 13 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Learning Style | Engineering Economy Class | Reinforced Concert Class |
|---|---|---|
| ACT | 3.25 | 3.29 |
| REF | 1.13 | 1.43 |
| SEN | 3.69 | 2.93 |
| INT | 1.00 | 0.93 |
| VIS | 4.56 | 5.50 |
| VRB | 0.41 | 0.07 |
| SEQ | 2.34 | 2.86 |
| GLO | 1.25 | 1.86 |
| Student # | ACT | REF | SEN | INT | VIS | VRB | SEQ | GLO | Group ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 1 | ||||
| 3 | 9 | 9 | 4 | 3 | |||||
| 4 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 3 | |||||
| 5 | 3 | 9 | 3 | 3 | |||||
| 17 | 5 | 9 | 5 | 3 | |||||
| 18 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 3 | |||||
| 20 | 5 | 9 | 3 | 3 | |||||
| 21 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 3 | |||||
| 22 | 3 | 9 | 3 | 3 | |||||
| 30 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelhadi, A.; Ibrahim, Y.; Nurunnabi, M. Investigating Engineering Student Learning Style Trends by Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Educ. Sci. 2019, 9, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci9010058
Abdelhadi A, Ibrahim Y, Nurunnabi M. Investigating Engineering Student Learning Style Trends by Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Education Sciences. 2019; 9(1):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci9010058
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelhadi, Abdelhakim, Yasser Ibrahim, and Mohammad Nurunnabi. 2019. "Investigating Engineering Student Learning Style Trends by Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis" Education Sciences 9, no. 1: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci9010058
APA StyleAbdelhadi, A., Ibrahim, Y., & Nurunnabi, M. (2019). Investigating Engineering Student Learning Style Trends by Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Education Sciences, 9(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci9010058







