Abstract
The use of mobile technologies has recently received great attention in language learning. Most research evaluates the effects of employing mobile devices in language learning and explores the design of mobile-learning interventions that can maximize the benefits of new technologies. However, it is still unclear whether the use of mobile devices in language learning is more effective than other instructional approaches. It is also not clear whether the effects of mobile-device use vary in different settings. Our meta-analysis will explore these questions about mobile technology use in language learning. Based on the specific inclusion and exclusion criteria, 22 d-type effect sizes from 20 studies were calculated for the meta-analysis. We adopted the random-effects model, and the estimated average effect was 0.51 (se = 0.10). This is a moderate positive overall effect of using mobile devices on language acquisition and language-learning achievement. Moderator analyses under the mixed-effects model examined six features; effects varied significantly only by test type and source of the study. The overall effect and the effects of these moderators of mobile-device use on achievement in language learning are discussed.
1. Introduction
With the rapid growth of mobile technologies as well as the explosion in the number of educational applications and mobile devices, a large number of studies have been conducted about the use of mobile devices in education [1,2,3,4]. Widespread ownership of mobile devices has cued researchers to pay attention to mobile devices as potential media to deliver learning content [5,6,7], and to consider how to use mobile devices as pedagogical support tools [8,9]. Educators have not only begun to use mobile technologies in formal classroom settings but have also integrated such technologies into informal education settings in daily life [7,9].
Language learning is one area in which the use of mobile technologies has been well researched [10]. Previous studies have identified advantages of mobile devices including their portability, versatility of features, connectivity, and individuality [6,11,12]. Their portability, combined with the pervasive presence of mobile devices in daily life, enables learners to use handheld devices anytime they want [9,13,14,15]. In addition, research on language learning can be conducted not only in formal classrooms but also in informal settings such as during language use at home and in social communication. Therefore, language learning is a domain in which mobile devices can play an important role in educational activities [1,16,17].
1.1. Definition of Mobile Learning
Mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets are becoming ubiquitous. Unlike other forms of e-learning that deliver educational content via the internet, mobile learning or m-learning has one certain benefit: learner mobility [18,19,20,21,22,23]. Mobile learning combines student support tools from e-learning with mobile technology, thus allowing access to educational content or information without the limitations of physical location or time [9]. That is, mobile learning can be defined as any sort of learning in which content or facilitated educational activities are delivered using mobile technologies as mediating tools, whenever and wherever the learner desires [9].
1.2. Trends in Mobile Learning in Education
Mobile learning is increasingly being recognized as a potential learning environment in education [1,7]. The adoption of mobile technologies is rapidly expanding in higher education, in primary and secondary schools, and in training contexts [9]. According to a report by the Pew Research Center [24], 73% of Advanced Placement and National Writing Project teachers reported that they and/or their students used cell phones for educational purposes in the classroom or when they worked on assignments. In addition, 45% of teachers and students reported use of e-readers, and 43% of teachers or students indicated use of tablet computers in the classroom or for assignments.
Why do both teachers and students rely on mobile technologies? Three potential answers are (1) mobile phones are nearly always present in daily life, (2) smartphones can be used as hand-held computers to support learning activities with integrated technologies such as voice recorder/player, camera/camcorder, web browser, and personal computing [23], and (3) numerous mobile applications are being developed for educational activities. With these features of mobile devices and their potential capabilities as pedagogical support tools, the landscape of technology-supported learning highlights mobile learning as a critical emerging area [23,25,26]. According to reviews of trends in mobile-learning research [4,7], studies of mobile learning have examined a diversity of disciplines including the humanities, social sciences, health sciences, and natural sciences. Language and linguistics, a sub-discipline of the humanities, has the largest number of studies on mobile learning. In addition, five reviews [1,4,7,18,19] have synthesized general mobile-learning trends. Wu et al. [4] (2012) noted that, from 2003 to 2010, many researchers focused on the effectiveness of mobile learning (i.e., 58% of mobile-learning studies). These reviews reported valuable information on how different types of mobile-device use and mobile-device-based learning environments hold benefits for other mobile-learning settings. In addition, those aforementioned reviews represented the overall research trends related to the use of mobile technology in the field of education.
1.3. Mobile-Assisted Language Learning
Researchers in language learning and linguistics have attempted to use technology-supported learning to enhance learning outcomes and learner performance in numerous ways [7,14,15,27,28]. Mobile-Assisted Language Learning (MALL) is a technology-supported approach to language learning, which focuses on acquisition of linguistic knowledge and skills as well as providing assistance with communication using emerging mobile technology [29].
The use of mobile technologies has recently received great attention in language learning [4,9,14,30,31]. Language learning is defined as the process of development in language ability. For example, current mobile-learning trends indicate that the largest numbers of studies on mobile learning have focused on language and linguistic disciplines [4]. In MALL studies, scholars evaluate the effects of employing mobile devices in language learning and explore the design of mobile-learning interventions that can maximize the benefits of new technologies [14,32,33].
A variety of language skills may be considered under the umbrella of language learning. One of course is the learning of a new language. Learning a language requires one to learn vocabulary words, to recognize them when listening and reading, and to pronounce them properly. As well, one needs to understand and be able to independently produce the grammatical structures of the language being learned [34]. More mundane and concrete skills such as spelling and using proper punctuation are also parts of language learning. However, these skills are not only needed when learning a second language, they are relevant to one’s first-language skill improvement as well. Learning more words, and more complex words, is an important part of being an advanced reader [16]. Reading itself is a language skill [35,36].
Some of these component skills in language learning are thought to be particularly suitable to mobile learning. Vocabulary accumulation [37] and pronunciation [38] appear ideally suited for the mobile-learning context.
However, it is still unclear whether the use of mobile devices in language learning is more effective than other instructional approaches such as language learning with computers or print-based materials. It is also not clear whether the effects of mobile-device use vary in different settings. Our meta-analysis will explore these questions about mobile-technology use in language learning.
In this review, we synthesize the results of experimental studies that measure the effects of using mobile devices on language learning. We investigate the effects of using mobile devices in language learning using the methods of meta-analysis. We offer a systematic review and synthesize the findings of relevant documents (e.g., published articles, dissertations, reports, etc.) from the language-learning and linguistics disciplines. Specifically, the goal of our meta-analysis is to answer the following two research questions:
Research question 1. What is the average effect of using mobile devices on language learning?
Research question 2. How do the effects of using mobile devices vary when language achievement is measured in different research settings and contexts, at different school levels, in different types of study, and for different target language-learning skills, types of test, and target language learners?
2. Methods
2.1. Data Search Strategy and Study Selection
A systematic literature search was conducted to explore relevant publications on MALL. Electronic databases including ERIC, EBSCOhost (Academic Search Complete), PsycINFO, JSTOR, and ProQuest Dissertations & Theses were used for the literature search. The key words (“language learning” AND “achievement”) AND (“mobile” OR “m-learning”) were used as distinct search terms. We located 337 articles in ERIC and 776 articles in EBSCOhost. In addition, we found 264 articles from PsycINFO and 1345 articles from JSTOR. For unpublished studies, ProQuest Dissertations & Theses was used, and 147 studies were found (see Figure 1). The research results were limited to have publication dates between 2005 and 2017 because most mobile learning studies have been conducted since 2005. We found no study results from conference papers and books suitable for inclusion in our meta-analysis.
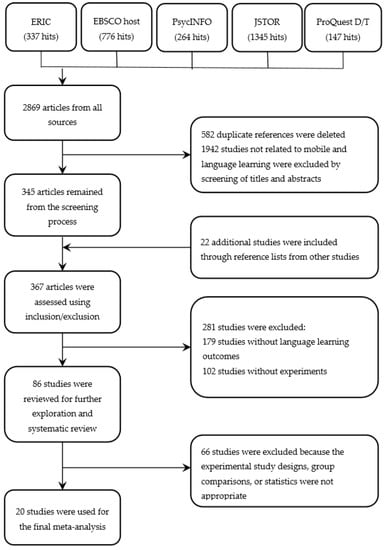
Figure 1.
Flow chart of the literature search.
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Rules
The results of the literature search and study exclusions were shown in Figure 1. A total of 2869 articles was found after conducting the first exploratory searches through the electronic databases. After a series of screening decisions, 345 potentially relevant articles were identified. The following criteria were used for inclusion of the studies: the study had (1) included mobile learning as a treatment plus some control condition, (2) used an experimental design to compare mobile learning and some other intervention, (3) included educational activities delivered via mobile devices, (4) included a clear description of participants, and (5) provided sufficient statistical information to allow computation of d-type effect sizes. In addition, collected sources were excluded if the studies (1) were not related to mobile learning and language-learning, (2) did not measure language learning achievement as a learning outcome, (3) were published before 2005, or (4) showed unusually large effect sizes as outliers. Based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 367 articles were excluded, and 86 studies were retained for further exploration and coding. Finally, 20 studies remained for the meta-analysis.
2.3. Data Evaluation
A total of 20 studies provided 22 effect sizes. A list of studies and coded features is presented in Table 1. The coded features included: (1) participant information, (2) treatment and setting characteristics, and (3) statistics used, including sample size, means, and standard deviations.

Table 1.
List of selected studies with key features.
2.3.1. Initial Coding
The first coding category, study information, included school level, total sample size, and publication type. Treatment and setting characteristics included features such as the context of the study, type of mobile device, intervention components, and representation of content. In addition to these two major categories, information to calculate effect sizes was collected. Because the main research questions were related to the effects of mobile-device use versus other conventional learning interventions, means and standard deviations or other statistics were used to compute d-type effect sizes; these are listed in Table 1.
2.3.2. Moderators
Six potential moderator variables—school level, source of study, context of study, target language-learning skill, type of test, and target language learner–were identified as shown in Table 1. School level was divided into three categories: (1) primary, (2) secondary, and (3) post-secondary. Source of study classified the publication outlet of the research, as either (1) journal or (2) dissertation. Context of study identified whether the research was conducted in a formal or informal learning environment. Formal learning was defined as the act of acquiring knowledge or skills in highly structured, classroom-based, or institutionalized settings [49,50]. Thus, formal learning in this review referred to the use of mobile devices in structured classroom instruction, or during homework. Informal learning was intentional but not highly structured [50]. Here, informal learning referred to the use of mobile devices for learning in social activities or field trips which were not part of classroom-based instruction. Target language-learning skill was divided into four categories: (1) vocabulary, (2) pronunciation, (3) reading, and (4) language arts. Type of test had two categories: (1) commercial standardized tests and (2) researcher-made scales which were developed for each specific study. Target language learner in this review represented the focus group for English language learning: (1) English as a Second Language (ESL) learner group vs. (2) English as a First Language (EFL) learner group.
2.4. Extraction and Calculation of Effect Sizes
Twenty-two effect sizes were extracted from the 20 studies that remained after applying the inclusion/exclusion rules. If a study included results of multiple experiments or subgroups, the effect sizes were calculated separately for each sample. For example, Wang [3] studied the effects of using mobile devices on comprehensive reading with three different majors in post-secondary school: business administration, information management, and tourism management. In this case, three independent effect sizes were extracted. On the other hand, multiple outcomes from a study were averaged due to the dependency that exists when examining the same participants repeatedly. To avoid the overestimation of variance when the dependency of effect sizes occurred, the robust variance estimation (RVE) method [51] was applied to calculate the corresponding variances of effect sizes.
Our main research questions related to the effects of mobile devices versus those of other learning interventions. Thus, effect sizes (d) were obtained by calculating the difference between the means of the experimental (mobile) and control (other treatment) groups, divided by the pooled standard deviation as shown in Equation (1):
Also, nT and nC are the sample sizes for the mobile learning and control groups, respectively, and m = nT + nC − 2.
The variance of the effect size was calculated using
In the case of different study designs or analyses of the primary studies, such as analysis of covariance, the effect size (d) was calculated by using the adjusted means in the numerator, assuming the adjustments were reasonable, and using the pooled unadjusted standard deviation for the calculation [52].
2.5. Coding and Effect Size Reliabilities
All 22 effect sizes from 20 studies and six moderators were coded independently at least twice by three of the authors, and then their results were compared to assess inter-coder reliability. For effect sizes, the reliability was calculated as a Pearson correlation. The reliabilities of other key variables were calculated using the proportion of agreement. All disagreements were discussed until any discrepancies were fully resolved. The reliabilities of initial codes for the effect sizes and moderators are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Inter-coder reliability.
2.6. Data Analysis
2.6.1. Applications Used for the Meta-Analysis
To assess the heterogeneity of our effect sizes and potential for publication bias, we drew confidence interval (CI) plots and the funnel plot [53], using Excel and R. To explore possible moderators for the effect size of the impact of mobile devices on language learning, SPSS macros developed by David Wilson, including MeanES and MetaF, were used to compute Q statistics including QB (i.e., the Q value for testing between groups differences) and QW (i.e., the Q value for remaining within groups variability). These macros were available at http://mason.gmu.edu/~dwilsonb/ma.html.
2.6.2. Publication Bias
Publication bias is defined as “the state of affairs when published research on a topic is systematically unrepresentative of the population of completed studies on that topic” [53] (p. 61). Rothstein and Dickersin [54] listed several sources of publication bias, including editorial policies, unpublished or delayed reports of statistically non-significant studies, and over-representation of large results for overall effect size due to sample size. Rothstein and Dickersin argued that publication bias was a potential threat to the validity of meta-analytic results. In the current review, the funnel plot, trim-and-fill method, and Egger’s test were employed for evaluating publication bias. In the funnel plot, effects from larger more precise studies appear at the top of the plot, whereas those from smaller, less precise studies appear more dispersed at the bottom of the graph. If publication bias does not exist and the effects are from a single population, the effects will be distributed symmetrically and form the shape of an upside-down funnel. The plot typically will be skewed to one side in the presence of publication bias [53]. The trim-and-fill method is used to estimate the number of studies missing from a meta-analysis in a funnel plot and to adjust the mean accordingly. Egger’s test checks for asymmetry of the funnel plot; both it and the funnel plot are good indices for checking for publication bias.
2.6.3. Model Specification
Borenstein, Hedges, Higgins, and Rothstein [55] described two statistical models for meta-analysis: the fixed-effects model and the random-effects model. In the simplest fixed-effects model perspective, one true effect size exists for all studies, and all differences between effect sizes are assumed to be due to sampling error. The random-effects model consists of a common effect with two sources of variance: between studies variation and sampling error.
The effect sizes in this review were inspected to see whether they came from the same population. First, an overall homogeneity test was conducted using Hedges’ formula for Q based on inverse variance weighting (using w = 1/Var(d)). Second, I-squared and the Birge ratio were computed, and CIs for the effect sizes [52] were plotted in order to assess the variability between studies.
When the homogeneity test verified that the effect sizes were not from a single homogeneous population, then it would be sensible to explore the variation in effects, to determine whether some of the between studies variance was explained by our moderator variables [52].
Based on both QB and QW statistics in our moderator analysis, we employed the random-effects model and the analysis-of-variance or ANOVA-like mixed-effects model. The weight was the inverse of the sum of the effect variance Var(dij) and the within-group random-effects variance, specifically.
for study i in group j.
2.6.4. Moderator Analysis
We considered six variables as moderators of effect size: school level, source of study, context of study, target language learning skill of study, type of test, and target language-learner. All these variables were categorical.
3. Results
3.1. Publication Bias Analysis
The funnel plot showing the effect-size standard error (on the vertical axis) versus effect size (on the horizontal axis) allowed us to assess potential publication bias and is shown in Figure 2. This asymmetrical funnel plot reflected some potential publication bias. The funnel plot showed more positive effects than negative ones; also several very large effects (above 2) were seen. The reference line showed the mean of the observed effects, which is 0.51.
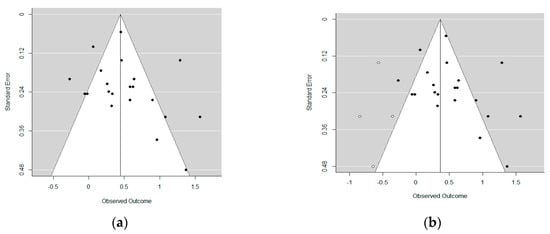
Figure 2.
Funnel plots. (a) Funnel plots for effect sizes in this meta-analysis (left); (b) Funnel plots adding possible missing effects as open circles (right).
We next conducted Egger’s regression test for asymmetry [56]. Egger’s test evaluates the intercept of the regression of the standard normal deviate of each effect on the precision, 1/Var. The standard normal deviate was calculated as the effect size divided by the standard error of the effect size or . This regression test for funnel-plot asymmetry under the mixed-effects meta-regression model with the predictor of standard error was not statistically significant with z = 1.83 at alpha level 0.05. Therefore, the intercept for this test suggested no evidence of funnel-plot asymmetry. In the funnel plot, most missing studies (i.e., the four estimated missing studies) were to the left of the mean. After applying the trim-and-fill method, the adjusted mean was decreased to d = 0.36, (se = 0.03) from the original overall effect size of d = 0.51, (se = 0.10) in Figure 2.
3.2. Overall Effect Size
As shown in the forest plot in Figure 3, no common effect size seemed evident given the wide array of the twenty-five confidence intervals. This result was consistent with heterogeneity of the effect-size data. The overall homogeneity test suggested that the data were not homogeneous (Q = 103.27, df = 21, p < 0.05). In addition, the values of Birge’s ratio (4.92) and I-squared (79.66%) also supported the view that the effect sizes were not homogeneous. Based on the results of the homogeneity test, it was not reasonable to estimate a common effect. Any overall effect would represent an average of the set of population effect sizes. The next steps were to estimate the degree of heterogeneity of the effect sizes from different populations and to examine the effects of the moderator variables.
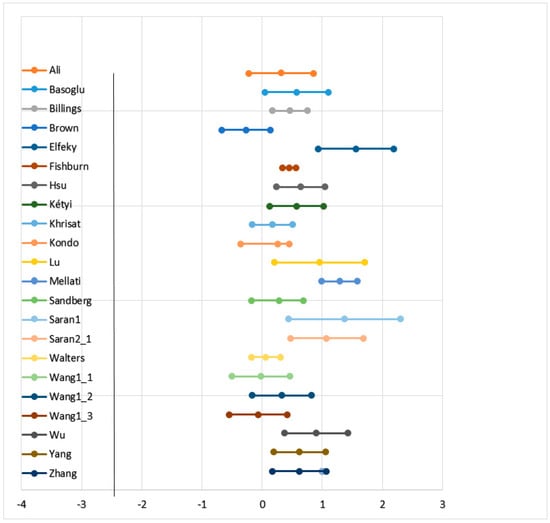
Figure 3.
The confidence interval plot of effect sizes. The x-axis represents the standardized-mean-difference effect size (d) and the y-axis shows the names of the first authors of the primary studies.
Table 3 shows the overall weighted mean and homogeneity test for the 22 independent effect sizes. Because of the heterogeneity of effect sizes, we first proceeded with a random-effects model overall analysis. The overall mean effect size was strong (d = 0.51) with a random effects variance component of 0.10. This was used to estimate the interval within which 95% of all population effects might fall (assuming normality). This interval was from 0.32 to 0.70, indicating mobile learning was significantly more effective than the other interventions for language learning.

Table 3.
Weighted mean effect sizes for mobile language-learning achievement under various conditions.
3.3. Moderator Variable Analysis
We next inspected the six potential moderators of our effect sizes. According to the ANOVA-like mixed-effects model with moderators (Table 4), only source of study and type of test were significant moderators. Table 4 shows the weighted mean effect sizes for language-learning achievement under various conditions.

Table 4.
The results of moderator analyses with QB and QW.
3.3.1. School Level
We compared the effect sizes across school levels. As shown in Table 4, studies done in primary and post-secondary schools both showed significant detectable effect sizes, d = 0.52 (se = 0.16) and d = 0.54 (se = 0.13), respectively. Studies of learners in secondary school showed a mean effect size that was not significantly different from zero. However, because of high degrees of variation within each of the school levels, school level was not a moderator that could explain all the population variance in the effects (QB = 0.35, p > 0.05).
3.3.2. Source of Study
Studies in the current review were from two sources: journal articles and dissertations. A finding that larger effects were reported in journal articles led us to suspect publication bias may be at play. As shown in Table 4, mean effect sizes from journal articles were significantly larger than the mean effect sizes from dissertations (QB = 4.07, p < 0.05). Mobile-learning studies that were reported in journal articles also showed non-zero effects (d = 0.59, se = 0.10), whereas results based on dissertations showed virtually no effect with a mean of 0.11 (se = 0.22).
3.3.3. Context of Study
The context-of-study predictor included two categories: formal and informal learning. As shown in Table 4, mean effect sizes were significantly detectable from zero for the mobile-learning studies conducted in both formal-learning settings and informal-learning settings. The means of 0.54 (se = 0.10) and 0.38 (se = 0.21) represented moderate to large effects in both settings. However, the value of QB was not significant at α = 0.05 (QB = 0.49). Therefore, we determined that the study context was not a moderator explaining the effect-size differences.
3.3.4. Target Language-Learning Skill
Four learning outcomes were examined in the mobile-learning studies we gathered: vocabulary, language arts, reading, and pronunciation. As shown in Table 4, learning outcomes for vocabulary, language arts, and pronunciation had strong positive effects. Only the reading learning outcome showed a weak effect. Thus, use of mobile devices appeared effective for language-learning achievement across most target language-learning skills. However, the value of QB was again not significant at α = 0.05 (QB = 1.41, p > 0.05), so that the target language-learning skill predictor did not moderate the effects of mobile device use on language learning in this mixed-effects model.
3.3.5. Type of Test
The test-type predictor included two types of test: commercial standardized tests and researcher-made scales. The results demonstrated that mobile-learning outcomes that were measured with researcher-made scales were significantly different from those from the studies conducted with commercial standardized tests. Researcher-made scales showed much higher effect sizes (d = 0.70, se = 0.10) than standardized commercial tests (d = 0.19, se = 0.13).
3.3.6. Target Language Learner
The target language-learner predictor includes two types of student who participated in the studies: ESL and EFL. In this review, nearly all the studies in language-learning achievement were conducted with English as second language learners, except for two studies. In addition, larger effects were reported for ESL learners than for EFL learners. Mobile-learning studies which focused on ESL also showed non-zero effects (d = 0.56, se = 0.11), whereas results for EFL showed virtually no effect with a mean of 0.12 (se = 0.31). However, due to the very great uncertainty associated with the EFL mean, the target participant predictor was not a significant moderator, with QB value of 1.80 (p > 0.05).
4. Discussion
This study synthesized 22 effect sizes from 20 studies and investigated the effects of using mobile devices on students’ achievement in language learning. Specifically, language-learning achievement was examined in different research settings and circumstances, including different school levels and study contexts. Also, studies varied in their target language-learning skills, type of tests used, and target language-learner populations. Results included were both published and unpublished (i.e., from dissertations).
4.1. Overall Effects of Using Mobile Devices on Achievement in Language Learning
The result of a medium sized overall positive effect of using mobile devices on language acquisition and language-learning achievement confirmed that the use of mobile devices could facilitate language learning. These results were consistent with other research findings regarding the effects of mobile devices on subsequent language-learning skills, such as vocabulary [27,28,37,57] and general language acquisition [30,58]. In addition, the result connected with recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses [2,7,59].
4.2. The Effects of Using Mobile Devices under Various Conditions
School Level. Finding large effect sizes for using mobile devices in all school levels indicated employing mobile devices with students can influence language acquisition and achievement.
Context of Study. Both formal and informal learning contexts were settings where positive effects of using mobile devices on language learning were found [7]. This implies mobile devices were functional to deliver language-learning materials and activities directly, such as for collaborative speaking and listening activities [14] as well as serving as learning supports.
Type of Test. Results indicated that positive treatment effects differed from zero only when language-learning achievement was assessed using researcher-made scales. Researcher-made scales were likely constructed to fit study goals and might measure specific areas that the researcher targeted and wanted to assess. Commercial standardized tests might assess broader areas of language achievement that students might not have learned from/on their mobile devices [60]. In contrast, researchers who create their own scales likely closely target the specific skills or vocabulary terms that were covered in their own m-learning applications. This could reflect the phenomenon of teaching to the test [61].
4.3. Significance of the Study
Similar to other reviews or meta-analysis studies that showed strong positive effects of mobile learning [4], this review also found medium sized positive effects of using mobile devices on language learning. Also in spite of the fact that effects varied between studies, in conditions similar to those in our studies, students receiving mobile-learning language instruction will almost always outscore others on average. In addition, the current review employed a comprehensive set of moderators to investigate the effects of various potential conditions on language-learning achievement which could lead to heterogeneity in the population. Only study source and type of test explained between studies differences. It is disconcerting that the effects of mobile learning were minimal when measured via standardized tests because, in many school settings, those are the tests of choice for assessment. School level, context of study, target language learning skill, type of test, and target language-learner group did not reach significance. This comprehensive moderator analysis contributed to understanding the various conditions for effective mobile-device use in language learning.
4.4. Limitations and Suggestions for Future Study
First, the results of our analysis for source of study showed that the mean effect size of journal articles (d = 0.59, se = 0.10) was significantly different from the mean effect size of dissertations (d = 0.11, se = 0.22). We suspect publication bias may have played a role in this result. Researchers have observed that publication bias arises from the tendency of journals to reject insignificant findings [62,63]. Therefore, using only journal articles as resources in prior meta-analyses may have led to skewed interpretations if their published studies were more likely to include significant results [64,65]. This was clearly the case for our studies. In future reviews, unpublished studies and reports should be included to ensure that conclusions that are more appropriate. When we applied the trim-and-fill technique to estimate the adjusted mean for the hypothetical full set of studies (including studies missing from the funnel plot), the estimated mean was still positive, but showed a smaller (and not significant) effect of using mobile devices for language learning (d = 0.36, se = 0.03).
Second, it might be useful to address more potential moderators in a meta-analysis study. For example, we would like to investigate the specifications of mobile devices such as screen size and operational system (i.e., OSX vs. Android). Sung et al. [7] found hardware specifications (e.g., handheld devices and laptops vs. mixed devices) influenced the heterogeneity of the effect sizes in their review. In addition, the effects of type of mobile application (e.g., commercial training vs. educational purposes) or additional target language skills such as language acquisition and language skill improvement can be addressed.
Third, this review investigated the effectiveness of mobile devices on the cognitive domain (i.e., language-learning achievement) across various moderators. In future studies, it may be fruitful to conduct research on the effects of using mobile devices in the affective domain, such as on learners’ motivational status or attitudes toward language learning; and in the meta-cognitive domain, such as on learners’ self-regulation and use of intellectual strategies [10].
Author Contributions
Joo and Lee conceived of the presented idea, collected the papers and wrote the initial draft. Cho verified the analytical methods, conducted analyses, wrote method and result and contributed to the interpretation of the results. Becker: provided advice about analyses, wrote parts of the text, edited text. All authors discusses the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
References
- Hwang, G.-J.; Tsai, C.-C. Research trends in mobile and ubiquitous learning: A review of publications in selected journals from 2001 to 2010. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2011, 42, E65–E70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.-T.; Chang, K.-E.; Yang, J.-M. Review: How effective are mobile devices for language learning? A meta-analysis. Educ. Res. Rev. 2015, 16, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H. Integrating self-paced mobile learning into language instruction: Impact on reading comprehension and learner satisfaction. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2017, 25, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-H.; Wu, Y.-C.J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Kao, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Huang, S.-H. Review of trends from mobile learning studies: A meta-analysis. Comput. Educ. 2012, 59, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.; Uther, M. Mobile language learning with multimedia and multi-modal interfaces. In Proceedings of the 2006 Fourth IEEE International Workshop on Wireless, Mobile and Ubiquitous Technology in Education, Athens, Greece, 16–17 November 2006; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2006; p. 124. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, P.H. Action research approach on mobile learning design for the underserved. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2009, 57, 415–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.-T.; Chang, K.-E.; Liu, T.-C. The effects of integrating mobile devices with teaching and learning on students’ learning performance: A meta-analysis and research synthesis. Comput. Educ. 2016, 94, 252–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera Díaz, L.E.; Cruz Ramos, M.d.l.M.; Sandoval Sánchez, M.A. Using personal portable devices as learning tools in the english class. How 2014, 21, 74–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traxler, J.; Kukulska-Hulme, A. Mobile Learning: A Handbook for Educators and Trainers; Routledge: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Viberg, O.; Grönlund, Å. Mobile assisted language learning: A literature review. In Proceedings of the 11th World Conference on Mobile and Contextual Learning, (mLearn 2012), Helsinki, Finland, 16–18 October 2012; Volume 955. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.-K.; Hwang, G.-J.; Chang, C.-K. A personalized recommendation-based mobile learning approach to improving the reading performance of EFL students. Comput. Educ. 2013, 63, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopfer, E.; Squire, K. Environmental detectives—The development of an augmented reality platform for environmental simulations. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2008, 56, 203–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfeky, A.I.M.; Masadeh, T.S.Y. The effect of mobile learning on students' achievement and conversational skills. Int. J. High. Educ. 2016, 5, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukulska-Hulme, A.; Shield, L. An overview of mobile assisted language learning: From content delivery to supported collaboration and interaction. ReCall 2008, 20, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, J.; Maris, M.; de Geus, K. Mobile english learning: An evidence-based study with fifth graders. Comput. Educ. 2011, 57, 1334–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-C.; Hwang, G.-J.; Hung, C.-M.; Tseng, S.-S. An evaluation of the learning effectiveness of concept map-based science book reading via mobile devices. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2013, 16, 167–178. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, P.; Houser, C. Using mobile phones in English education in Japan. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2005, 21, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, J.L.; Zhang, K. Examining mobile learning trends 2003–2008: A categorical meta-trend analysis using text mining techniques. J. Comput. High. Educ. 2012, 24, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingir, S.; Cavlazoglu, B.; Caliskan, O.; Koklu, O.; Intepe-Tingir, S. Effects of mobile devices on K-12 students’ achievement: A meta-analysis. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2017, 33, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemaja, M.; Taamallah, A. Towards situation driven mobile tutoring system for learning languages and communication skills: Application to users with specific Needsneeds. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2016, 19, 113–128. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Y.-F.; Sie, Y.-S. Using RSS to support mobile learning based on media richness theory. Comput. Educ. 2010, 55, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisey, S.H.; Ramteke, P.L.; Burghate, B.R. Mobile learning transforming education & training. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Sci. 2012, 3, 827–831. [Google Scholar]
- Sharples, M. Big Issues in Mobile Learning; University of Nottingham: Nottingham, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, K.; Heaps, A.; Buchanan, J.; Friedrich, L. How Teachers Are Using Technology at Home and in Their Classroom. Pew Research Center, 2013. Available online: http://pewinternet.org/Reports/2013/teachers-and-technology (accessed on 20 March 2013).
- Huang, C.S.J.; Yang, S.J.H.; Chiang, T.H.C.; Su, A.Y.S. Effects of situated mobile learning approach on learning motivation and performance of EFL students. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2016, 19, 263–276. [Google Scholar]
- Kukulska-Hulme, A. Will mobile learning change language learning? ReCALL 2009, 21, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavus, N.; Ibrahim, D. m-Learning: An experiment in using SMS to support learning new English language words. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2009, 40, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M. Effectiveness of vocabulary learning via mobile phone. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2008, 24, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnery, G.M. Going to the MALL: Mobile assisted language learning. Lang. Learn. Technol. 2006, 10, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-M.; Chung, C.-J. Personalized mobile English vocabulary learning system based on item response theory and learning memory cycle. Comput. Educ. 2008, 51, 624–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Miri, S.S. The impact of mobile dictionary use on language learning. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 98, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.-C.; Hsieh, S.-W.; Sun, P.-C.; Chen, C.-M. To activate English learning: Listen and speak in real life context with an AR featured u-learning system. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2017, 20, 176–187. [Google Scholar]
- Kenning, M.M. ICT and Language Learning: From Print to the Mobile Phone; Palgrave Macmillan: Basingstoke, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Saffran, J.R.; Senghas, A.; Trueswell, J.C. The acquisition of language by children. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12874–12875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L. Using Mobile Learning to Teach Reading to Ninth-Grade Students. Ph.D. Dissertation, Capella University, Minneapolis, MN, USA, November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Fishburn, T.A. Mobile Device Reading Interventions in the Kindergarten Classroom. Ph.D. Dissertation, Wilmington University (Delaware), Ann Arbor, MI, USA, November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Song, W.; Burston, J. Reexamining the effectiveness of vocabulary learning via mobile phones. Turk. Online J. Educ. Technol. TOJET 2011, 10, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Murat, S.; Gölge, S.; Kürşat, Ç. Mobile assisted language learning: English pronunciation at learners' fingertips. Eurasian J. Educ. Res. 2009, 34, 97–114. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad Zamzuri Mohamad, A.; Kogilathah, S.; Tan Wee, H. Effects of verbal components in 3D talking-head on pronunciation learning among non-native speakers. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2015, 18, 313–322. [Google Scholar]
- Basoglu, E.B.; Akdemir, O. A comparison of undergraduate students’ English vocabulary learning: Using mobile phones and flash cards. Turk. Online J. Educ. Technol. TOJET 2010, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Billings, E.; Mathison, C. I get to use an iPod in school? Using technology-based advance organizers to support the academic success of English learners. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 2012, 21, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kétyi, A. Practical evaluation of a mobile language learning tool in higher education. In Proceedings of the 2015 EUROCALL Conference, Padova, Italy, 26–29 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Khrisat, A.A.; Mahmoud, S.S. Integrating mobile phones into the EFL foundation year classroom in King Abdulaziz University/KSA: Effects on achievement in general English and students’ attitudes. Eng. Lang. Teach. 2013, 6, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, M.; Ishikawa, Y.; Smith, C.; Sakamoto, K.; Shimomura, H.; Wada, N. Mobile assisted language learning in university EFL courses in Japan: Developing attitudes and skills for self-regulated learning. ReCALL 2012, 24, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellati, M.; Khademi, M. The impacts of distance interactivity on learners’ achievements in online mobile language learning: Social software and participatory learning. Int. J. Web Based Learn. Teach. Technol. 2015, 10, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murat, S.; Gölge, S.; Kürşat, Ç. Mobile language learning: Contribution of multimedia messages via mobile phones in consolidating vocabulary. Asia Pac. Educ. Res. Salle Univ. Manila 2012, 21, 181–190. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, J.L. English Language Learners’ Reading Self-Efficacy and Achievement Using 1:1 Mobile Learning Devices. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of California, San Diego, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.T.; Huang, Y.M. Mobile game-based english vocabulary practice system based on portfolio analysis. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2017, 20, 265–277. [Google Scholar]
- Comas-Quinn, A.; Mardomingo, R.; Valentine, C. Mobile blogs in language learning: Making the most of informal and situated learning opportunities. ReCALL 2009, 21, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsick, V.J.; Watkins, K.E. Informal and incidental learning. New Dir. Adult Contin. Educ. 2001, 89, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidik, K.; Jonkman, J.N. Robust variance estimation for random effects meta-analysis. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2006, 50, 3681–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsey, M.W.; Wilson, D.B. Practical Meta-Analysis; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein, H.R. Publication bias as a threat to the validity of meta-analytic results. J. Exp. Criminol. 2008, 4, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothstein, H.R.; Sutton, A.J.; Borenstein, M. Publication bias: Recognizing the problem, understanding its origins and scope, and preventing harm. In Publication Bias in Meta-Analysis: Prevention, Assessment & Adjustments; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Rothstein, H.R. A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 2010, 1, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effer, M.; Davey Smith, G.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ Br. Med. J. 1997, 315, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, G. Using mobile phones for vocabulary activities: Examining the effect of the platform. Lang. Learn. Technol. 2010, 14, 95–110. [Google Scholar]
- De Jong, T.; Specht, M.; Koper, R. A study of contextualised mobile information delivery for language learning. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2010, 13, 110–125. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdi, H.S. Effectiveness of mobile devices on vocabulary learning: A meta-analysis. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 2018, 56, 134–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braus, J.A.; Wood, D.S. Environmental Education in the Schools: Creating a Program that Works! NAAEE: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Phakiti, A. Experimental Research Methods in Language Learning; Bloomsbury Academic: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sterne, J.A.; Gavaghan, D.; Egger, M. Publication and related bias in meta-analysis: Power of statistical tests and prevalence in the literature. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2000, 53, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, A.; Lee, P. Original articles: Publication bias in meta-analysis. its causes and consequences. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2000, 53, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesope, O.O.; Lavin, T.; Thompson, T.; Ungerleider, C. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the cognitive correlates of bilingualism. Rev. Educ. Res. 2010, 80, 207–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Hooper, L.; Loke, Y.K. Publication bias: What is it? How do we measure it? How do we avoid it? Open Access J. Clin. Trials 2013, 2013, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).