Abstract
The flipped classroom is an approach to incorporate active learning that is being used in secondary education, higher education, and professional schools. This study investigates its impact on student learning and confidence in a professional degree program course. A quasi-experimental study was conducted to evaluate pharmacy students enrolled in a semester-long didactic traditional classroom course compared to students learning the same material using a flipped model through online self-study modules in a hands-on experiential learning course. Before and after each learning experience, students of each group completed a 16-item knowledge assessment on four topic areas and rated their level of confidence with each topic area on a Likert scale. There was a significant difference in knowledge with students in the traditional course scoring higher than students using flipped approach in the experiential course. Furthermore, the flipped experiential course students did not improve assessment scores from pre-test to post-test. For confidence rating, the traditional course group ranked confidence higher than the flipped experiential group for all topics. These findings challenge the notion that the flipped model using self-study in an experiential setting can be a substitution for didactic delivery of pharmacy education.
1. Introduction
1.1. The Flipped Classroom in Health Professional Schools
The flipped classroom is gaining momentum across a variety of educational institutions. This approach has been cited in health professional programs such as medicine, nursing, dentistry, and pharmacy [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. Studies in these fields focus on student perception, satisfaction, and some on academic test scores. Most studies show positive perception yet neutral performance results for the flipped classroom method. Two recent systematic reviews of flipped classrooms in medical and nursing education suggest mixed results. In medical education, the flipped classroom lacked evidence for knowledge and skill acquisition compared to traditional methods even though students liked the flipped method [8]. In nursing, they found neutral or positive academic performance outcomes, but mixed results in student satisfaction [9]. In these healthcare programs, it is paramount for students to transcend the material itself and use it to problem-solve, reason, and apply concepts and skills into practice. To achieve this, many programs use experiential learning labeled as rotations or clerkships in addition to the didactic curriculum. Using the flipped model in these learning experiences is unknown and it is unclear if this is effective for all topics within the healthcare field. A flipped model used during an emergency medicine clinical clerkship showed no difference on a multiple-choice exam, and authors noted several challenges using this method within the clinical setting [10]. This paper describes our effort to understand if the flipped model can be used during these clinical experiences to impart new material in pharmacy education.
1.2. Pharmacy Education
In the United States, students entering pharmacy school have completed at least two years of university-level courses or have already attained a four-year degree in higher education. The professional pharmacy degree takes four years to obtain and the degree requires students to complete didactic and experiential coursework. One competency in the coursework is ability to triage, treat, and provide patient education in the realm of self-care and nonprescription medications [11]. A variety of course andragogy are employed at pharmacy schools to ensure that students are sufficiently knowledgeable in self-care and nonprescription medications. Methods cited in the literature include integration of self-care topics into therapeutic courses or experiential experiences and required or elective semester-long courses designated to self-care [11]. While a thorough review of literature demonstrates an inconsistency between teaching methods used for self-care topics, inclusion of these self-care and nonprescription medications is required for pharmacy school accreditation in the United States.
1.3. Curriculum Transformation in a Pharmacy School
In 2015, a School of Pharmacy transformed its curriculum [12]. This curriculum change resulted in increased time in experiential education, which meant didactic course content was reduced. Thus, a three-credit stand-alone didactic course, “Self-Care and Non-Prescription Medications” was removed from the curriculum. Students entering pharmacy school prior to fall 2015 took the didactic course in their second year and then enrolled in an experiential course in community pharmacy practice. It was decided that students entering pharmacy school in fall 2015 would learn self-care topics using a flipped approach during the experiential course only. Web-based modules were developed for students’ self-study and, simultaneously, students could reinforce and apply the self-care knowledge and skills during their experiential experience. The modules were developed using content from the stand-alone course as well as the Handbook of Nonprescription Drugs [13]. Support for the effectiveness of online modules for the purpose of teaching self-care and nonprescription topics has not been studied.
The aim of this study was to compare teaching methods of self-care topics as delivered via the traditional didactic course versus the flipped experiential course using online self-study modules. While numerous pharmacy education studies have focused on student confidence and preference, this study focuses on the impact of student learning by quantifying academic success [13,14]. Our hypothesis was that students in the flipped experiential course would learn self-care topics as thoroughly as students who took the traditional course. Additionally, as the professional program is responsible for ensuring that knowledge is translated to patient care, we also wanted to study if confidence in these topics varied by the teaching method.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sampling and Questionnaire
This study employed a quasi-experimental design to evaluate the change between a traditional classroom course to a self-paced, flipped experiential course. The primary assessment was comparison of knowledge scores and confidence on a pre-post survey between the traditional course group and flipped experiential group. These methods were reviewed and approved by the institutional review board (IRB) as well as the educational research and review committee. Self-care content knowledge and student confidence were compared between the two educational methods. The first educational method included second-year students enrolled in the traditional self-care course who also completed an experiential course in community practice. The second educational method included students completing the flipped experiential course in community practice only, without the didactic course.
A 24-item questionnaire was designed to collect demographic information, experience with self-care information, student confidence, and an assessment for self-care knowledge. The questionnaire consisted of 16 knowledge assessment questions on the following self-care topics: heartburn, constipation, allergic rhinitis, and dermatitis. The knowledge assessment questions were multiple-choice questions developed by the course director. The multiple-choice questions had been used and tested for reliability and consistency in the stand-alone course. The questionnaire was reviewed by post-graduate trainees and consulting staff on survey methodology at the host institution. A system was used to track if students in the flipped experiential course logged onto view the modules.
Student confidence was asked as “How confident do you feel in your ability to counsel patients on the following subjects?” and was measured using a Likert scale for each self-care topic. The questionnaire was optional for students, distributed via email using Qualtrics, and did not affect overall course grades. Each group was given one week to complete the questionnaire. A total of three follow-up reminders were sent to those who had not completed the survey. Both cohorts of students completed the survey twice. The traditional course group completed the questionnaire at the end of the course and at the end of their experiential course. The flipped experiential group completed the questionnaire at the beginning and end of the flipped experiential course.
2.2. Statistical Analyses
We initially examined the characteristics of the sample to assess the distribution of demographics and previous experience with self-care information. Data were analyzed in STATA version 13.0 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA). The mean, standard deviation, and the shape of distribution were calculated for any continuous variables and frequencies were tabulated for categorical variables. Student confidence was measured using a four-point Likert scale (very confident, moderately confident, a little confident, or not confident at all) for each self-care topic and medians were compared for each group. For the primary objective, the mean knowledge assessment scores were compared using a two-sided t test for the pre- and post-assessment between both groups. We also compared results using all survey responses to those who completed the entire questionnaire. Due to wide standard deviations using all responses, we reported results based on fully completed questionnaires only. Then, a paired and unpaired t test was used to compare the change in knowledge scores within each group. Due to the small sample size, we also examined the mean score differences using Wilcoxon rank sum test, and the results were similar to the t-test. Finally, we examined the Likert scale medians on confidence for each topic between the two groups using Wilcoxon rank sum test.
3. Results
3.1. Demographics of Pharmacy Students
The response rate for the pre-test for the traditional course group was 34% (54/159) and 33% (26/78) for the flipped experiential group. Table 1 lists the baseline characteristics of the student population. Among baseline characteristics of the cohorts of students enrolled in the traditional and flipped educational techniques, prior experience with self-care topics was the only one of significance. Student gender, age, cumulative grade point average (GPA), and educational level were not significant.

Table 1.
Demographic information of survey respondents.
3.2. Knowledge Assessment Results
The pre-test knowledge assessment scores were significantly higher in the traditional course group compared to the flipped experiential group (66% vs. 43%, p < 0.001) as seen in Table 2. This result was expected, as the traditional course group completed a semester of learning with the self-care material and the flipped experiential group had yet to be exposed to self-care material. For post-test knowledge assessment scores, there was a significant effect (p < 0.001) with the traditional course receiving higher post-test scores than the flipped experiential group (74% vs. 55%). This result could be explained because students in the traditional course group had two exposures to self-care material, whereas the flipped experiential group had one exposure. However, at the end traditional course alone, prior to experiential rotation experience, students performed better (66% vs. 55%) than students at the end of their flipped rotation experience (p = 0.009). This result proves our hypothesis to be untrue. Students in both groups had one exposure to the self-care material; however, the knowledge of the self-care material was not similar with their performance. It was determined through the tracking software that all students in the flipped experiential course logged onto the modules a minimum of three times.

Table 2.
Knowledge Assessment Scores Among Students in Flipped Experiential Course vs. Traditional Course.
3.3. Confidence Results
The Wilcoxon rank sum test indicated that the traditional course group ranked confidence statistically higher than the flipped experiential group for all topics: dermatology (p = 0.007), allergic rhinitis (p = 0.033), constipation (p = 0.003), and heartburn (p = 0.004). The traditional group had significantly more students report that they were “very confident” or “moderately confident” in all four categories (Figure 1). Only one student in the traditional course reported, “not feeling confident at all” in one topic. There were 14 reports of feeling “not confident at all” in multiple topics by the flipped experiential group.
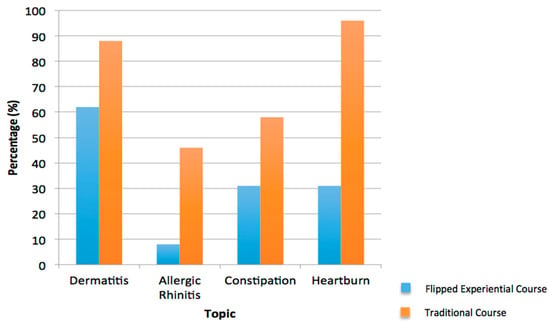
Figure 1.
Very high or moderate confidence in counseling patients on self-care topics.
4. Discussion
The results from this study demonstrate that learners who were exposed to online modules using the flipped experiential course did not perform the same as students who completed the 12-week didactic course. Previous studies indicated the use of online modules has been positively received by both students and faculty [10]. Benefits include increased enrollment rates for courses with online modules, increased student confidence, and reduced burden on faculty long-term [7]. Common issues that were reported included frustration with technological issues and the amount of time faculty must invest in the creation of the online modules [12]. However, many of these issues (especially time burden on faculty) were resolved after years of the course being taught [12]. In this study, student confidence of those enrolled in the traditional coursework was higher than those enrolled in the flipped experiential course. Thus, our study does not support what has been previously reported in the literature.
Support for the effectiveness of online self-study modules for the purpose of teaching self-care and nonprescription topics in lieu of a traditional didactic course had not been previously studied. While numerous pharmacy education studies have focused on student confidence and preference of various flipped approaches, this study also focuses on quantifying academic success [8,9]. In examining student knowledge, it is important to note that our survey relied on only four multiple-choice questions in four selected self-care topics to quantify knowledge. The length of the survey was kept short in order to encourage completion. The thought was that the scores of the students in the flipped experiential course would improve from the time of the pre-test to the post-test as the students completed their modules. In contrast, students taking the traditional course took the pre-test survey at the end of the course. These students also had a month-long experience following the course to re-enforce their self-care knowledge. Therefore, the hypothesis was that the students’ scores would not change from pre-test to post-test. However, the main hypothesis was that there would be no significant difference between the post-test scores of the traditional and flipped experiential courses. The results support that pharmacy students do not learn information just as effectively in flipped experiential rotation as they do in a traditional didactic course.
There are limitations to this study, with characteristics of the students and nonresponse bias being the most prevalent. It may be debated that comparing first-year and second-year students is not a fair research design; however, we accounted for this difference when looking at knowledge results. Our hypothesis was that the knowledge of the second-year students prior to their experiential course, but after the didactic course, would be equivalent to the first-year students after the experiential course alone. As curricula shift to become more experiential, we need to be mindful to ensure that knowledge can be properly learned and assessed. It was also anticipated that the second-year students would be more confident than first-year students. Our results demonstrate this, allowing us to defend our study design with differing student characteristics.
In regards to nonresponse bias, the completion of the survey was optional for students and did not count toward or against their course grade. In addition, students in the traditional didactic course were more motivated to look at the pre-test survey questions because it was advertised that the questions would serve as a good review for their final exam. Once their final exam was taken, there was not an incentive for them to take the post-test survey. Also of note is that, for the post-test, students were recruited individually by email and some experienced a long lag time between the pre- and post-test, ranging from four weeks to 12 weeks, depending on their scheduled experiential rotation. Hence, there was a dramatic decrease in the post-test completion for this group. In contrast, the flipped experiential course did not have a final exam. In addition, the students in the traditional course were in their second year of pharmacy school, while the flipped experiential students were in their first year of pharmacy school.
The implications of this study include expanding the use of online modules in the pharmacy school curriculum to reduce burden on faculty and to maximize finite class time. Given that we had mixed results in confidence and knowledge, a blended model of teaching may be a better approach. Literature cites that blended learning using online modules with in-class learning achieves better academic performance [15,16,17]. Also, because students are able to practice clinical skills in the hands-on experiential learning course using a blended model may assist with increasing student confidence.
5. Conclusions
Schools of pharmacy may consider a flipped approach using online modules to acquire knowledge of self-care and nonprescription products; however, the use of online modules alone lessens student confidence in making self-care recommendations.
Acknowledgments
No funding was sought for this research.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study design and manuscript preparation. Colleen McCabe submitted to IRB, distributed survey and reminders. Megan G. Smith ran statistical analysis and Stefanie P. Ferreri provided expert oversight of the project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Persky, A.M.; Dupuis, R.E. An eight-year retrospective study in “flipped” pharmacokinetics courses. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2014, 78, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, J.E.; Griffin, L.M.; Esserman, D.A.; Davidson, C.A.; Glatt, D.M.; Roth, M.T.; Gharkholonarehe, N.; Mumper, R.J. Pharmacy student engagement, performance, and perception in a flipped satellite classroom. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2013, 77, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubbiyappa, K.S.; Barua, A; Das, B; Murthy, C.V.; Baloch, H.Z. Effectiveness of flipped classroom with Poll Everywhere as a teaching-learning method for pharmacy students. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, S41–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossaer, J.B.; Panus, P.; Stewart, D.W.; Hagemeier, N.E.; George, J. Student Performance in a Pharmacotherapy Oncology Module Before and After Flipping the Classroom. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2016, 80, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, C.L.; Demps, E.L.; Farris, C.; Bowman, J.D.; Panahi, L.; Boyle, P. Impact of Flipped Classroom Design on Student Performance and Perceptions in a Pharmacotherapy Course. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2016, 80, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, D.A.; Colbert-Getz, J. Measuring the impact of the flipped anatomy classroom: The importance of categorizing an assessment by bloom’s taxonomy. Anat. Sci. Educ. 2016, 10, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presti, C.R. The Flipped Learning Approach in Nursing Education: A Literature Review. J. Nurs. Educ. 2016, 55, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Lui, A.M.; Martinelli, S.M. A systematic review of the effectiveness of flipped classrooms in medical education. Med. Educ. 2017, 51, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betihavas, V.; Bridgman, H.; Kornhaber, R.; Cross, M. The evidence for ‘flipping out’: A systematic review of the flipped classroom in nursing education. Nurse Educ. Today 2016, 38, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitz, C.; Prusakowski, M.; Willis, G.; Franck, C. Does the Concept of the “Flipped Classroom” Extend to the Emergency Medicine Clinical Clerkship? West. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 16, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambizas, E.; Bastianelli, K.; Ferreri, S.; Haines, S.; Orr, K.; Stutz, M.; van Amburgh, J.; Wilhelm, M. Evolution of self-care education. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2014, 78, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, M.; Mumper, R.; Singleton, S.; Lee, C.; Rodgers, P.; Cox, W.; McLaughlin, J.E.; Joyner, P.; Blouin, R.A. A Renaissance in Pharmacy Education at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. NC Med. J. 2014, 75, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krinsky, D.L. Handbook of Nonprescription Drugs, 18th ed.; American Pharmacists Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ochs, J.H. Online or In-Class: Evaluating an Alternative Online Pedagogy for Teaching Transcultural Nursing. J. Nurs. Educ. 2017, 56, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, J.E.; Roth, M.T.; Glatt, D.M.; Gharkholonarehe, N.; Davidson, C.A.; Griffin, L.M.; Esserman, D.A.; Mumper, R.J. The flipped classroom: a course redesign to foster learning and engagement in a health professions school. Acad. Med. 2014, 89, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruehter, V.; Lindsey, C.; Graham, M.; Garavalia, L. Use of online modules to enhance knowledge and skills application during an introductory pharmacy practice experience. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2012, 76, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanova, J.; McLaughlin, J.E.; Rhoney, D.H.; Roth, M.T.; Harris, S. Student Perceptions of a Flipped Pharmacotherapy Course. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2015, 79, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).