Abstract
This study explores the potential of Intelligent Geographic Information Systems (GISs) in advancing educational practices through the integration of real-time data models. The objective is to investigate how GIS technology can enhance teaching and learning by providing interactive and dynamic learning environments. The research employs a bibliometric analysis based on the Scopus database, covering the period from 2000 to 2024, to identify key trends, the evolution of GIS applications in education, and their pedagogical impact. Findings reveal that GISs, particularly when incorporating real-time data, enable a more immersive learning experience, facilitate data-driven decision-making, and promote student engagement through project-based learning. However, challenges such as the lack of specialized training for educators and limitations in technological infrastructure remain significant barriers to widespread adoption. The study concludes that Intelligent GISs have the potential to transform education by fostering personalized, interdisciplinary learning and enhancing educational management. It emphasizes the need for further research aimed at developing user-friendly systems and addressing ethical concerns to ensure the benefits of GIS technology are accessible to all students. Future studies should examine the long-term effects of GISs on student outcomes and explore their integration into diverse educational contexts.
1. Introduction
Education has undergone a significant transformation in recent decades, driven by technological advances and the growing need to improve the quality of learning at all levels. Among these innovations, Geographic Information Systems (GISs) have emerged as powerful tools for teaching and learning in various disciplines. These systems enable the collection, analysis, and visualization of geospatial data, facilitating access to a deeper understanding of spatial phenomena and patterns (Chen et al., 2022). Although GISs have traditionally been used in areas such as geography and urban planning, their potential in the educational field has greatly expanded with the incorporation of real-time data (RTD) models, also known as GISs (Tinker, 1992).
The concept of GISs refers to advanced platforms that integrate the ability to manage, analyze, and visualize data in real time. These systems provide interactive maps and allow users to perform complex, dynamic analyses that reflect real-world situations continuously and accurately. The integration of GISs into education has been particularly promising, offering students and teachers tools to study and analyze spatial data in real time, enhancing the understanding of key concepts in fields such as geography, environmental sciences, social sciences, and urban planning. As education adapts to the new demands of the 21st century, the use of these technologies presents a unique opportunity to enhance traditional pedagogical approaches and promote more active, interactive, and project-based learning (Liu, 2003).
The purpose of this study is to conduct a comprehensive review of the current state of research on the integration of GISs into education, with a particular focus on RTD. In recent years, numerous studies have emerged that have examined the applications of GISs in education, but there are still several areas that require further research, especially in relation to recent advances in the field of GISs. Despite the wide adoption of these technologies in various academic disciplines, certain controversies persist regarding their implementation and effectiveness in the classroom (Rutkofske et al., 2022).
Through a detailed literature review, this paper aims to address current applications of GIS in the educational context, as well as the advances and challenges associated with their implementation. The main platforms used in classrooms, such as ArcGIS, QGIS, Google Earth, and GIS Cloud, are analyzed, and the various disciplines in which they have been successfully implemented will be examined. The impact of GIS on educational practices will be discussed, assessing both their benefits and limitations (Peter et al., 2020; Rutkofske et al., 2022). Particular attention will be paid to how RTD have transformed learning experiences, providing examples of recent studies that demonstrate the effectiveness of these tools in educational settings.
Previous studies have shown that integrating GISs in the classroom positively impacts the development of analytical and problem-solving skills, as well as student motivation and engagement. However, despite these advances, researchers agree that significant obstacles remain to the widespread adoption of these technologies in education (Carrión Montalván et al., 2024; González-Zamar et al., 2020a). Lack of specialized training for teachers, technological barriers, and infrastructure limitations in some educational institutions are common challenges that prevent a broader implementation of GISs in classrooms. Despite these obstacles, the available evidence suggests that the benefits far outweigh the difficulties, justifying the need to further analyze the potential of GISs in education (Karl et al., 2012).
The importance of this work lies in its ability to provide a comprehensive view of how GISs are revolutionizing education and how RTD are changing the way disciplines that require spatial understanding are taught and learned. This study reviews existing literature, and identifies key areas of future research, proposing questions and objectives that can guide the development of new research in this field. A key finding of this study is the impact of GISs on active and project-based learning. These tools allow students to actively engage in the learning process, developing valuable skills like complex problem solving and informed decision-making. By working with real-time data, students can engage in learning experiences that reflect real-world situations, enhancing their understanding and preparing them for future professional challenges.
Likewise, this study builds upon previous research on the application of artificial intelligence (AI) in educational data mining and human-in-the-loop approaches, where the interplay between machine learning and human teaching was examined in depth (López-Meneses et al., 2025). Expanding on those findings, the present work shifts the focus toward GISs, exploring their potential to integrate real-time educational data through advanced analytical models. This enables territorially contextualized, data-driven educational innovation grounded in dynamic evidence.
This study aims to provide an in-depth insight into the most recent advances in the use of GISs in education, focusing on RTD and their impact on educational practices. By reviewing the existing literature and addressing the main areas of future research, we seek to shed light on the transformative potential of these technologies and how they can contribute to a more dynamic, interactive, and student-centered education. Through this work, we hope to stimulate interest in further examining the possibilities that GIS offer in teaching and learn how to navigate the complexities of their implementation in diverse educational environments.
In line with the aim of exploring how GISs contribute to the advancement of educational practices through real-time data integration, the present study addresses the following research questions:
- RQ1: How has scientific production evolved between 2000 and 2024 in relation to the use of GISs for promoting educational practices supported by real-time data (RTD)?
- RQ2: What are the main thematic trends and research clusters associated with the integration of GISs in education, as revealed through keyword co-occurrence analysis?
- RQ3: What emerging lines of research and future directions are identified in the scientific literature concerning the application of intelligent GISs in education?
The structure of the article is organized as follows: Section 2 presents the literature review, analyzing the key concepts related to GISs in education and their integration with RTD. Section 3 describes the methodology employed, which combines a bibliometric analysis with a systematic review to examine the evolution of scientific production in the area. Section 4 presents the quantitative and qualitative results obtained from the analysis, highlighting key trends and term co-occurrence networks. Section 5 discusses the findings in relation to existing literature, identifying challenges and opportunities for future research. Finally, Section 6 presents the conclusions and highlights the educational implications derived from the study.
2. Theoretical Framework
The integration of GISs in education has been the subject of growing interest in recent decades, due to its potential to transform teaching and learning practices into various disciplines. GISs enable the visualization and analysis of spatial data, offering students a deeper understanding of the geographic, environmental, and social phenomena that shape the world. Their application is not limited to geography alone but spans areas such as environmental sciences, urban planning, social sciences, and beyond, making GISs key tools for promoting interactive, problem-based learning.
This section examines the most relevant advances in the integration of GISs in education, addressing both their technological evolution and the various pedagogical applications that have been derived from their use. At the same time, the benefits and challenges associated with their implementation in the classroom are examined, considering both the most common tools and the emerging platforms that have facilitated their adoption globally.
2.1. Integrating GISs into Education
The integration of GISs in education has proven to be a powerful tool for improving the teaching–learning process in various disciplines. It facilitates the understanding of spatial and geographic concepts, as well as fostering the development of critical skills such as data analysis, problem solving, and collaborative work. With continued technological advancement and the availability of more accessible platforms, the use of GISs in education continues to expand, opening up new possibilities for students and teachers. As RTD and emerging technologies continue to improve, the influence of GISs in the educational field will likely continue to grow, enriching pedagogical practices and preparing students to face global challenges (Augusiak et al., 2024).
GISs have thus evolved from being specialized tools for experts in geography and urban planning to becoming accessible and highly valuable resources in a variety of fields, including education. The integration of GISs into education has transformed the way concepts related to space, geography, social sciences, environmental science, and other disciplines are taught and learned (Lei et al., 2023; Tedyyana et al., 2024).
2.1.1. Definition and Components of GISs
A GIS can be defined as a technology that enables the collection, storage, analysis, visualization, and dissemination of geospatial data. These systems are composed of four main components: hardware, software, data, and users. Hardware includes input and output devices such as computers and workstations, while software is the set of applications that allow data to be manipulated. Data, in the context of GISs, is geographic and spatial information, which can include maps, satellite images, and other location-related data sets (Barcus & Smith, 2016; Duncan et al., 2010). Finally, users are the people who interact with the system to extract useful information for decision-making.
In education, the use of GISs allows students to understand spatial phenomena more deeply and to analyze data related to different aspects of the physical and social world. The concept of “space” in education, particularly in disciplines such as geography, environmental sciences, social sciences, and urban planning, has been expanded by the possibilities offered by GISs. By incorporating this technology, educators provide students with the ability to interactively examine geographic data, increasing their understanding of the topics covered (Hawthorne & Kwan, 2012; Rutkofske et al., 2022).
2.1.2. History and Evolution of the Use of GISs in Education
The integration of GISs in education has transformed the way in which different academic disciplines are approached. This technology is not limited to the simple teaching of maps and coordinates but offers a multidisciplinary approach, allowing students to interact with geospatial data in real time, which enriches their understanding and analysis of complex phenomena (Brown et al., 2024). Across various areas of knowledge, GISs have given rise to innovative applications that go beyond basic concepts, expanding the way in which we understand the phenomena and processes that affect our environment.
In the field of Geography and Social Sciences, GISs have established themselves as an indispensable tool for teaching fundamental concepts related to mapping, geolocation, and spatial analysis. Through these tools, students can access visual representations of the geographic distribution of phenomena such as population, land use, climate change, migration, or socioeconomic inequalities (González-Zamar et al., 2020b). Using GISs allows students to analyze how natural factors interact with human activities, fostering a deeper understanding of how societies are structured and how their interactions impact the physical environment. These tools provide the possibility of dynamically visualizing changes over time, which is particularly useful for studying the evolution of urban or rural landscapes, the expansion of infrastructures or the displacement of communities (Barcus & Smith, 2016; Duncan et al., 2010).
In the area of Environmental Sciences, GISs play a key role by allowing students to carry out spatial analysis of environmental phenomena such as deforestation, air and water pollution, or climate change. Using real-time geospatial data, students can observe the spread of pollutants, the impact of human activity on ecosystems, or the distribution of natural resources, all within a global and local context. This ability to analyze data in real time offers students a closer experience to field research, allowing them to generate hypotheses, conduct research, and propose solutions to environmental problems (Hallak & Polat, 2021; Hawthorne & Kwan, 2012).
In the field of Urban Planning and Sustainable Development, GISs are fundamental tools for teaching how cities are developed and how key decisions are made about land use, the distribution of public services, and the planning of sustainable infrastructure. Students can analyze urban growth patterns, identify areas with limited access to resources or services, and assess accessibility to transport and recreational areas. This ability to visualize the urban environment allows them to understand the dynamics of urban space and to question development models and propose alternatives that promote equity and sustainability. GISs allow students to examine the impact of urban planning policies on the quality of life of inhabitants and how urban design can contribute to improving energy efficiency and reducing the carbon footprint (Hallak & Polat, 2021; Morgan et al., 2022).
2.1.3. GIS Tools and Platforms in Education
Over the years, various GIS tools and platforms that are specifically designed for the educational environment have emerged, giving students and teachers the ability to interact with spatial data intuitively and in real time. These tools allow for the analysis and visualization of geospatial data, and the creation of interactive maps that facilitate the learning of complex concepts. Among the most widely used platforms in the educational field, several stand out that have gained popularity for their accessibility, educational resources, and ease of teaching (Morgan et al., 2022; Rutkofske et al., 2022).
One of the most prominent tools in this field is ArcGIS for Education, developed by ESRI. ArcGIS is considered one of the most widely used GIS programs globally due to its robustness and variety of functions. In its educational version, ArcGIS allows students to perform advanced spatial analysis, create interactive maps, and analyze geographic phenomena from different perspectives. The interface is intuitive, making it easy to use even for those with little prior experience in GISs. ArcGIS offers specialized educational resources, including tutorials, lessons, and support materials for teachers, making it a comprehensive tool for teaching a variety of disciplines, from geography to social and environmental sciences (Bédard et al., 2007).
On the other hand, QGIS (Quantum GIS 3.28 Firenze) is an open-source software that has gained popularity especially in the educational field due to its accessibility and advanced features. Being free and open-source, QGIS is an attractive option for institutions with limited resources or for those looking for a flexible alternative to commercial programs. Despite being free, QGIS offers powerful tools for spatial analysis, map creation, and geospatial data visualization, making it an ideal choice for both students and researchers. Being based on the open source community, QGIS has a large number of plugins and extensions that allow the platform to be customized to the user’s needs, increasing its versatility in the educational environment (Giski & Ebrahimzadeh, 2019). In addition, there are numerous tutorials and training materials available online, making it easy to learn and implement in classrooms.
Google Earth, although not a traditional GIS in the strict sense, has been a widely used tool in classrooms to teach basic concepts of geography, social sciences, and environmental sciences. Through its 3D map interface, Google Earth allows students to interactively examine the world, observing the geographic distribution of phenomena and locating points of interest on a global scale. The platform also offers access to a wealth of geospatial data that students can use to conduct simple research and analysis. Google Earth has proven to be a useful tool for teaching physical and human geography, as well as for studying changes in the environment, such as global warming or deforestation. Its ease of use and the ability to access interactive visual information make Google Earth an ideal choice to complement educational materials in the classroom (Merry et al., 2016).
Another platform that has gained relevance in the educational field is GIS Cloud, a cloud-based tool that allows the creation of interactive maps and the analysis of geospatial data in real time. Being hosted in the cloud, GIS Cloud offers the advantage that students and teachers can access its tools and data from anywhere with Internet access, facilitating collaborative work and the integration of technology in the classroom. This platform is especially useful for projects that require real-time data analysis, as it allows for continuous visualization and updating of maps and geospatial data. GIS Cloud is also known for its ease of use and intuitive interface, making it a great choice for those who want to incorporate GISs into the classroom without requiring in-depth technical training (Jiménez-Espada et al., 2022).
2.2. Advances in GISs: Real-Time Data Models
Advances in GISs have led to a significant evolution in their ability to collect, analyze, and visualize geospatial data, especially with the integration of AI and the use of RTD. The combination of these technologies has generated what is known as a GIS, which allows static geospatial information to be visualized, and provides dynamic and predictive analysis, considering data that is constantly changing in real time. This integration of real-time data allows GISs to provide more accurate and up-to-date information, which is particularly useful for decision-making, research, and teaching (Rutkofske et al., 2022).
The concept of GISs encompasses a variety of technologies that, by integrating AI and real-time data analysis, transform traditional GIS tools. Rather than simply being visualization tools, GISs can analyze large volumes of data and provide predictive information about geographic and environmental phenomena (Liu, 2003). This is achieved by incorporating machine learning and predictive analytics algorithms, which allow systems to “learn” from data, identifying patterns and making predictions based on the information that is continuously received. The difference from traditional GISs is that these systems serve to display historical or static information and are able to adapt to changes in real time, which significantly improves their usefulness in planning and decision-making applications (Agrawal et al., 2014).
The use of RTD has become one of the most notable advances within GISs. These models allow data to be processed and analyzed as it is generated, which is key for situations where time is a determining factor, such as in monitoring natural disasters, urban traffic management, air quality, or predicting meteorological phenomena (Bearman et al., 2016; Ramezan et al., 2024). In the specific case of education, the use of RTD offers students the opportunity to interact with data that reflects current environmental conditions, which enriches the teaching–learning process and fosters a deeper understanding of geospatial phenomena.
One of the key technologies that has enabled the development of RTD in GISs is the Internet of Things (IoT). Through IoT, connected devices and sensors enable the capture of real-time environmental and geospatial data. These devices include remote sensors, weather stations, cameras, and a variety of other instruments that measure various parameters, such as air quality, temperature, humidity levels, and more (Milson & Earle, 2007; Sofias & Pierrakeas, 2023). This data is transmitted to GIS platforms that process and present it in interactive visual formats, allowing users to access accurate and up-to-date information. In conjunction with remote sensors, such as satellites and drones, that collect large-scale geospatial data, GISs can provide a detailed, real-time picture of what is happening in various areas of the world. This is especially useful in emergency situations, such as early detection of forest fires, floods, or earthquakes, where the speed and accuracy of information is essential for making quick and effective decisions (Milson & Earle, 2007; Rutkofske et al., 2022).
Another essential component in the development of RTD is the analysis of large volumes of data, known as big data. Processing large amounts of geospatial data in real time allows GISs to identify patterns, perform predictive analysis, and make informed decisions. For example, predictive algorithms can anticipate the behavior of a natural phenomenon, such as a storm or earthquake, based on the data that is being received in real time. In the educational context, this opens the door to more interactive and practical learning experiences, where students can use current data to analyze geographic or environmental events that are happening at that very moment, reinforcing their understanding of the topics covered (Morgan et al., 2022; Rutkofske et al., 2022).
RTD allows students to engage in research projects using current data, which increases the relevance and applicability of the projects. For example, a group of students could use real-time data on urban traffic to investigate how city planning decisions affect traffic congestion and air quality. Other students could analyze data on water quality in a river or the behavior of animals in a nature reserve. These types of real-data-based investigations are more engaging, and provide a deeper understanding of concepts, as students work with data that is directly related to their environment (Bédard et al., 2007; Rutkofske et al., 2022).
2.3. Impact of GISs on Educational Practices
The impact of GISs on educational practices has been profound and transformative, extending to diverse disciplines and educational levels. Going beyond their simple use in geography and cartography, these systems have been effectively integrated into educational environments to offer new teaching, learning and assessment opportunities. The ability of GISs to integrate real-time data, use predictive analytics tools, and apply dynamic models has enabled educators and students to interact with content more efficiently and with greater engagement. In particular, AI, IoT sensors and the ability to model geospatial phenomena in real time have improved both theoretical and practical teaching, providing a number of benefits in the educational domain (Jesus et al., 2021; March & Scarletto, 2017).
In this context, the impact of GISs on educational practices has been significant, transforming both teaching methods and learning approaches. Through their ability to integrate real-time data, facilitate predictive analytics and enhance classroom interactivity, GIS have enabled a more dynamic and participatory approach to learning. These technological advances enhance the student experience, and foster research, innovation, and the development of valuable technical skills for students’ future careers (Klooster et al., 2022; Liu & Satur, 1999).
One of the most prominent ways that GISs impact educational practices is by enhancing the learning experience, transforming traditional methods into more dynamic and interactive approaches. These systems allow students to learn about abstract concepts and visualize and manipulate geospatial data in a hands-on way, facilitating deeper and more lasting understanding (Aladaǧ, 2010).
This interactivity, fueled by RTD, makes students feel more engaged in the learning process by allowing them to actively examine concepts and experiment with live information. Through simulations, interactive visualizations, and predictive analytics, students can observe how various factors affect a phenomenon and see the results in real time (Jakab et al., 2017; Milson & Earle, 2007). For example, in the field of geography, GISs can be used to model and analyze the impact of natural phenomena such as earthquakes, storms, or floods, allowing students to observe how these events affect communities, ecosystems, and infrastructure.
3. Materials and Methods
The study focuses on an analysis of how GISs have enhanced educational practices through RTD. The aim is to provide a comprehensive overview of the trends that have marked the development of this topic from 2000 to 2024. To achieve this, a methodology combining a qualitative systematic review with a detailed bibliometric analysis was utilized, allowing the identification of the most researched topics and the directions that future research might take.
To ensure methodological rigor and transparency, this study applied the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) methodology. The aim was to identify, screen, and select relevant literature for a bibliometric analysis focused on the integration of Geographic Information Systems (GISs) and data models in educational innovation. The search was conducted in Scopus in January 2025, using the terms “education”, Geographic Information System”, and “data”, which were applied simultaneously in the fields of Article Title, Abstract, and Keywords. This initial query yielded a total of 109,339 contributions. To refine the data set, several inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied. These included limiting the period of analysis to publications from 2000 to 2024, selecting only peer-reviewed journal articles (excluding conference proceedings, book chapters, editorials, and reviews), and filtering by subject areas related to education, geoinformation science, computer science, and environmental sciences. Additionally, only articles published in English were considered. After removing duplicates and screening for thematic relevance, the final sample consisted of 889 articles, which served as the basis for the bibliometric analysis carried out using tools such as VOSviewer.
Scopus was selected as the primary database for this study due to its comprehensive coverage of academic journals, conference papers, and other peer-reviewed publications across a wide range of disciplines. As one of the largest and most reputable databases for scientific literature, Scopus provides a reliable and standardized source of information, ensuring the accuracy and validity of bibliometric analysis. Furthermore, Scopus offers robust indexing and citation tracking features, allowing for a detailed and systematic review of trends in GIS education research. While other valuable sources, such as conference proceedings, books, and technical reports, were excluded, the decision to focus on Scopus was made to maintain consistency and rigor in the selection of scholarly articles. Future research could extend the analysis by incorporating additional sources to provide a more holistic view of the field.
To further analyze the data, VOSviewer (version 1.6.20, Leiden University, Leiden, The Netherlands) was used to create network maps that visualize the frequency and co-occurrence of terms across different publications. These maps also depict the intensity of relationships between concepts, with link strength indicating the number of articles that present terms together (Van Eck et al., 2010; van Eck & Waltman, 2010). This co-occurrence analysis facilitated the identification of dominant and emerging research lines, providing insights into the academic discourse surrounding GIS in education.
A key finding from this PRISMA-guided analysis is the emergence of real-time data integration as a transformative trend, significantly influencing educational methodologies. Terms such as “real-time monitoring”, “spatial analysis”, and “interactive learning environments” have become increasingly prevalent, highlighting a growing shift towards data-driven education strategies. Furthermore, the study notes a rising interest in the integration of GISs with AI technologies, pointing to a multidisciplinary approach that has gained momentum in recent years (Moher et al., 2011).
Following the PRISMA framework, relevance scoring was applied to rank key terms based on their frequency in titles and abstracts, ensuring transparency and consistency in the identification of the most representative concepts for each analyzed period. This scoring facilitates the prediction of future research directions, highlighting areas such as AI-enhanced GIS, immersive learning experiences, and adaptive educational technologies as emerging focal points (van Eck & Waltman, 2007; Waltman et al., 2010).
The scope of this study is limited to articles indexed in Scopus, excluding other valuable research forms like conference proceedings, books, and technical reports. Including these sources in future analyses could provide a more comprehensive understanding of trends in GIS education research (González-Zamar & Abad-Segura, 2024). This analysis reveals that GISs, coupled with RTD, have become a pivotal element in advancing educational practices. The integration of AI amplifies the impact of GISs in education, positioning them as fundamental tools for the real-time management and analysis of geospatial data, driving future pedagogical innovations (López-Meneses et al., 2025). By mapping the evolution of this field, the study highlights current research trends, and outlines possible directions for future research, emphasizing the need for interdisciplinary approaches to fully exploit the potential of GIS in education.
4. Results
The Results section is structured to directly address the research questions formulated in the Introduction. Specifically, the analysis of the evolution of scientific output, the identification of thematic clusters through keyword co-occurrence, and the projection of future research trends provide a comprehensive response to the three guiding questions of this study. This structure ensures coherence between the study’s objectives and its empirical findings, reinforcing the validity of the conclusions drawn.
4.1. Evolution of Scientific Research (2000–2024)
Analysis of data on academic production related to the promotion of educational practices through GISs in the context of RTD reveals a progressive and interesting evolution of this research field (Figure 1). Over the 24 years covered, from 2000 to 2024, the number of annual publications has shown an increasing trend that reflects the rise in the interest and application of GISs in the educational field. This growth is related to both technological advances and the growing recognition of the potential of GISs to improve educational decision-making, optimize management, and offer innovative solutions to current educational challenges.
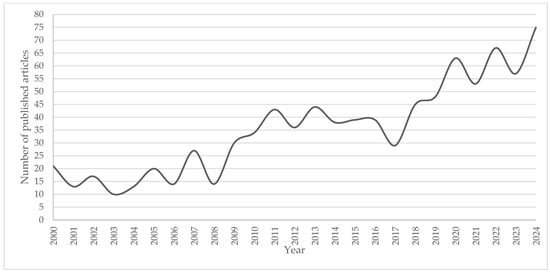
Figure 1.
Development of Scientific Publications (2000–2024).
- Initial period (2000–2009)
Looking at the early years of the period, it can be noted that the number of publications was relatively low, reflecting a field in its early stages of development. In 2000, 2.36% of the cumulative publications were recorded, indicating that, although the use of GISs in education was already being considered, it was still in its infancy. During the first years of the 21st century, the number of publications was limited, and in 2001 and 2002, the figures were even lower, with only 1.46% and 1.91%, respectively. These values suggest that, although GISs were recognized as a valuable tool in other fields, such as urban planning or environmental management, its use in education was not yet widely studied or applied. The period from 2003 to 2007 showed a modest increase in publications, but the figures remained low, with 1.12% in 2003, 2.25% in 2005, and 3.04% in 2007. During these years, GISs were mainly used in research areas related to geography and environmental sciences, and their integration into the educational field was not yet a priority. However, the progressive expansion of information and communication technologies (ICTs) in the 2000s was a factor that, in the long term, would contribute to a greater interest in GISs in education.
- Progressive growth (2010–2015)
From 2010 onwards, the number of publications began to increase more clearly. In 2010, publications represented 3.82% of the total accumulated, which already indicated a growing interest in the use of GISs in education. This increase coincides with the period when technologies began to be more intensively integrated into educational institutions, driven by digitalization policies and improvements in technological infrastructure. During this decade, GISs began to be recognized as useful tools in geography, and in areas of higher education, curriculum planning, educational resource management, and learning enhancement through geospatial analysis.
In 2011, publications increased to 4.84%, and in 2012 they reached 4.05%. This moderate growth was maintained throughout the following years, with 4.39% in 2013, 4.95% in 2014, and 4.39% in 2015. During these years, GISs began to be applied in the analysis and management of educational data, using geospatial models to improve resource allocation, classroom planning, and the identification of academic performance patterns in different regions. The integration of GISs, which enables real-time analysis, began to be seen as an opportunity to address specific challenges in education, such as managing student performance and optimizing resource allocation.
- Expansion (2016–2020)
Starting in 2016, the number of publications related to GISs in education experienced a more notable growth. In 2016, publications accounted for 4.39%, and in 2017 they rose to 3.26%. Although in absolute terms this increase was not that large, GISs began to be applied more frequently in decision-making at the institutional level and in the development of real-time monitoring systems for educational practices. The use of GISs for the visualization of educational data and its application in administrative and pedagogical decision-making began to be an area of growing interest.
In 2019, publications increased to 5.40%, marking a shift towards a deeper interest in the implementation of GISs, driven by improved technological capabilities, such as access to large volumes of data and the use of real-time analysis technologies. This trend was consolidated in 2020, when publications reached 7.09%, reflecting the significant impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in accelerating the adoption of digital technologies in education. The urgent need to manage distance education and improve efficiency in the use of educational resources in a health crisis context likely drove this growth. During this period, GISs were used to map gaps in access to education, manage resource availability, and provide predictive analytics on academic performance (Mitchell et al., 2018; Thatcher & Imaoka, 2018).
- Consolidation (2021–2024)
The last part of the data shows a consolidation and exponential growth in academic production related to GISs. In 2021, publications accounted for 5.96%, and in 2022 they increased to 7.54%. This growth reflects a maturity in the integration of GISs in education, as they have consolidated themselves as key tools in data-driven decision-making. In 2023, publications reached 6.41%, and in 2024 they reached 8.44%, which constitutes a notable peak in research on the use of GISs in education. This continuous increase demonstrates that research in this field is diversifying, with an emphasis on real-time data analysis and the creation of predictive models that can improve the educational process in a variety of contexts.
The sustained growth in recent years can be attributed to several factors. First, the consolidation of real-time data technologies and their accessibility in educational platforms, allowing for greater integration of GISs. Second, the growing interest in data analytics in education, driven by the need to personalize learning and improve student outcomes. Finally, the maturation of GISs and their ability to be used in diverse educational contexts, across geographic areas and in the management of educational infrastructures, the design of curricula, and the enhancement of the learning experience through real-time data analysis.
The analysis of these data reveals a clear trend towards increasing scientific production related to fostering educational practices through GISs and RTD. From the early years of the 21st century, with limited interest, to recent years, where publications have increased significantly, this field has experienced sustained growth, driven by the digitalization of education, the adoption of emerging technologies, and the interest in improving decision-making in the educational field using big data. As technology continues to advance, the use of intelligent GISs will become established as a fundamental tool for improving educational processes and optimizing resources, and its application will continue to be a relevant area for educational research in the coming years (Kerski et al., 2013; Mamun et al., 2024).
4.2. Keyword Trend Analysis (2000–2024)
The co-occurrence analysis allowed us to identify the main areas of research between 2000 and 2024, highlighted by the most influential actors in this field. Using the VOSviewer software, five clusters were established, each representing a particular thematic focus. Table 1 presents the 30 most relevant keywords of each cluster.

Table 1.
Top 30 keywords (2000–2024).
The analysis on the integration of GISs in education highlights the evolution of various areas of knowledge in relation to teaching and the management of spatial data in real time. In this context, key terms such as “spatial analysis” and “spatial data” are essential, as they allow us to understand how geospatial information is processed and represented in different educational applications (Anunti et al., 2020). Geography education has undergone significant transformations with the incorporation of GISs, facilitating the teaching of spatial phenomena and promoting learning based on geographic evidence.
Teaching in this field benefits from the use of advanced technologies, including remote sensing and mapping, which give students access to satellite imagery and digital terrain models. In higher education, GISs have improved the understanding of complex spatial data by integrating interactive tools that support hands-on learning. The inclusion of learning within the study of GISs highlights the importance of pedagogical strategies that incorporate data set and satellite data analysis at different educational levels.
In urban environments, the use of GISs is key to urban area analysis and urban planning, allowing for the visualization and evaluation of infrastructure, population distribution, and sustainable planning. The incorporation of the Internet as a means of accessing and sharing geospatial data in real time has transformed teaching and research in this field, providing new opportunities for collaboration and innovation. The impact of GIS in the field of socioeconomics is also notable, as it facilitates the analysis of development patterns, resource distribution and spatial inequalities (Kamruzzaman, 2014).
In secondary education, GISs have improved access to spatial analysis tools, promoting learning based on exploration and experimentation. In methodological terms, spatial–temporal analysis plays a key role in the interpretation of dynamic phenomena and environmental changes, which in turn affects information management in different educational contexts.
The use of satellite imagery expands teaching possibilities in areas such as environmental education, facilitating the analysis of changes in the landscape, deforestation and the impact of climate change. In relation to sustainable development, the use of GISs in education allows environmental and social issues to be addressed from a comprehensive perspective, providing key data for informed decision-making (Mulaku & Nyadimo, 2011).
From a demographic point of view, GISs are essential tools for the study of demographics, allowing the analysis of migration patterns, population distribution and urbanization trends. In the field of engineering education, the use of intelligent GISs optimizes the teaching of infrastructures and spatial models, improving the training of future professionals in disciplines related to territorial management and urban design.
The process of real-time data acquisition allows for greater precision in the collection and analysis of spatial information, which has an impact on improving educational quality (Tepavčević et al., 2012). In this sense, risk assessment and vulnerability evaluation using GIS in the educational field facilitate the identification of areas prone to natural disasters, promoting education in resilience and prevention.
The concept of “knowledge” in the use of GISs in education highlights the importance of geospatial literacy and the ability to interpret spatial data in different academic and professional contexts. Cartography continues to play a central role in the visualization of geospatial information, allowing for a clearer and more understandable representation of spatial data (Duever & McGinn, 2020).
The analysis of the “spatial distribution” of natural and social phenomena through GISs has allowed for a better understanding of geography and its interrelation with different disciplines. In this sense, the teaching of “geography” through GISs improves the perception of geographic space and its representation through interactive tools (Kim et al., 2013).
Finally, the use of “computer simulation” in GIS-based education has opened new possibilities for experimentation and modeling of spatial scenarios in real time, optimizing learning in disciplines related to territorial management and geospatial analysis. Together, these keywords reflect the evolution and impact of the use of GISs in education, highlighting its potential to transform teaching and learning at multiple academic and professional levels (Ferrandino, 2015).
Subsequently, a co-occurrence analysis of the keywords present in the selected articles was carried out. Figure 2 shows the network representation of these terms. As a result, it was identified that the keywords were organized into five groups with homogeneous characteristics.
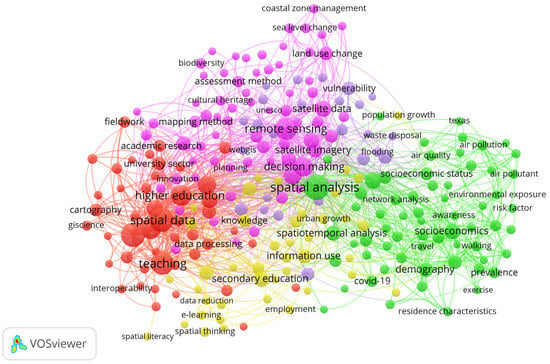
Figure 2.
Keyword Co-occurrence Dynamics (2000–2024).
- Cluster 1: Education and Geospatial Technologies for Sustainable Development
This line of research (pink) addresses the role of education in the application of geospatial technologies, such as remote sensing and GISs, for environmental management and territorial planning (Golumbeanu & Avdimiotis, 2009). The use of satellite images, geospatial data and computer simulation has allowed us to improve training in disciplines related to sustainability, environmental conservation and territorial planning.
One of the main contributions of this cluster is the development of innovative educational approaches that integrate remote sensing and geospatial analysis in the teaching of urban planning, forest management and environmental assessment. The incorporation of technologies such as GPS, AI, and data modeling has facilitated project-based learning and informed decision-making on phenomena such as sea level change, watershed management and protected area planning (Kurniawan et al., 2024).
This line of research highlights the importance of citizen science and public participation in the collection and analysis of geospatial data, promoting more collaborative and contextualized learning. The inclusion of crowdsourcing methodologies and environmental simulation has allowed students and professionals to develop skills in the evaluation of anthropogenic impacts, ecosystem management and the design of conservation strategies (Golumbeanu & Avdimiotis, 2009).
This cluster highlights how education, supported by geospatial technologies, can contribute to the training of citizens and professionals with an interdisciplinary approach, capable of addressing the challenges of sustainable development and territorial planning with advanced scientific tools.
- Cluster 2: Education and Urban Society
This line of research (green) examines the intersection between spatial analysis, education, and socioeconomic factors, highlighting how geospatial analysis tools can improve understanding of educational challenges in urban and rural environments. Through techniques such as spatiotemporal analysis, AI, and machine learning, urbanization patterns, population distribution, and environmental factors that impact educational equity are studied (Calvo-Sotelo, 2009; Magzoub et al., 2024).
One of the main contributions of this cluster is the identification of educational disparities based on geographic location, socioeconomic status, and exposure to environmental factors such as air pollution and access to public transportation. The integration of tools such as Landsat Thematic Mapper and network analysis has made it possible to model how variables such as poverty, population density, and residential characteristics affect primary education and educational attainment in different regions (Xia et al., 2017).
This approach allows us to understand the impact of emerging factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic on education, analyzing the relationship between urban mobility, access to technology, and population dynamics on academic performance. The combination of census data, predictive modeling, and environmental justice assessment has been key to designing more inclusive and sustainable educational policies. This cluster underlines the importance of spatial analysis as an educational and planning tool, providing key information to improve educational quality, reduce access gaps, and promote equity in global educational development (van Leusen et al., 2016).
- Cluster 3: Geospatial Education and Emerging Technologies
This strand (red) focuses on the integration of spatial data and emerging technologies such as GISs in the educational field. It addresses how geospatial tools, data collection and visualization, and the adoption of technologies such as virtual reality and cyberinfrastructure can transform pedagogical approaches and improve education at various levels, especially in higher education (Zhang, 2020).
A key aspect of this cluster is “GIS education”, which examines how to teach and apply GIS principles, as well as the processing and management of geospatial data in educational contexts. Research in this field highlights the importance of preparing students to use tools such as “big data” and “data visualization” in spatial decision-making and complex problem-solving. “Educational technology” and “interoperability” are recurring themes, as they allow educational systems and technological tools to connect efficiently, promoting collaborative and accessible learning.
The cluster highlights the impact of “information science education” and the use of “open data” to boost academic research and innovation in the field of geospatial sciences. “Cybergis” and “spatial data in-frastructure” applications also play a fundamental role by providing platforms that enable the acquisition, processing and analysis of geospatial data in real time, enriching both teaching and academic research (Jażdżewska et al., 2022). This line of research stands out for its ability to link theory with practice in interdisciplinary contexts, contributing to the evolution of higher education in geospatial sciences.
- Cluster 4: Education and Urban Development with Space Technologies
This cluster (yellow) focuses on how spatial technologies, combined with data analytics and education, can address challenges associated with urban growth, economic development, and the improvement of educational systems, especially in secondary education and vocational training. This cluster highlights the intersection between “secondary education” and “environmental education”, examining how learning and teaching can integrate the principles of “spatial thinking” and “spatial literacy” to address urban and environmental issues (Hogrebe et al., 2008).
One of the most relevant contributions in this field is the application of tools such as GISs, “arcgis”, and “digital mapping”, which allow the visualization and analysis of spatial phenomena. These tools are fundamental for teaching students to understand spatial variability and how urban development patterns, such as “urban growth” or “urban transportation”, affect both public policies and the social and economic environment.
Likewise, the use of data mining is essential to extract valuable insights from large volumes of data, enabling educators and students to make informed decisions about the use of urban infrastructure and sustainable development (Bédard et al., 2007; López-Meneses et al., 2025). The cluster also highlights the importance of integrating innovative learning environments and technologies such as e-learning to enhance the teaching of complex subjects in engineering and other technical disciplines, supporting both vocational training and the continuing development of educators in professional development contexts.
- Cluster 5: Education and Management of Environmental Risks
This line of research (cyan) focuses on how education can play a key role in capacity building for risk and disaster management, using geospatial technologies and environmental impact assessment models. This axis connects spatial analysis with the development of educational policies aimed at disaster prevention and land use planning in contexts of vulnerability, especially in regions of the “developing world” (Eddy, 2024).
One of the main contributions of this cluster is the use of “risk assessment models” and tools such as “WebGIS” to assess the spatial distribution of hazards such as floods, natural disasters or the environmental impact of human activities. These technologies allow for more effective management of resources and risk mitigation, while training students and professionals in making informed decisions through a “data” and “geology” based approach.
The research also highlights the importance of “distance education” and the integration of GIS into vocational training programs for “disaster management” and “territorial planning” (Duever & McGinn, 2020). The analysis of the “socio-economic” and “environmental impacts” of natural disasters, together with the training of “key stakeholders”, facilitates the creation of educational policies that promote community resilience, and the development of skills to mitigate the negative effects of natural phenomena.
4.3. Future Directions of Research
This section aims to study new areas of research in the field of intelligent GISs applied to education, RTD with human participation and advanced spatial analysis. Based on a thorough review of the literature and analysis of keywords, the main emerging lines of research in this field have been identified. Global research in this topic continues to advance, incorporating innovative approaches that offer new opportunities for study. Based on the analysis of the most recent terms associated with this topic, the research directions that are emerging can be clearly outlined.
Cluster analysis is a valuable tool for identifying emerging trends and problems in any scientific discipline. This process consists of grouping the units of analysis into clusters with similar characteristics, identifying the most relevant terms using their importance score, and linking those terms to growing research areas. Table 2 shows the future research directions detected through the relevance score, which are described in detail below.

Table 2.
Future research directions based on relevance score.
- Collaborative Spatial Data Analysis for Educational Innovation
This line of research marks a significant evolution in the application of geospatial technologies to education by reinforcing data-driven decision-making within collaborative environments. It broadens the scope of GISs through the integration of participatory methodologies for real-time spatial data analysis. The rationale lies in the increasing need to address complex educational challenges through the collective interpretation of spatial data. By employing collaborative models, both students and educators can dynamically analyze and visualize spatial information, fostering problem-based learning and encouraging interdisciplinary perspectives. The synergy between spatial analysis and collaborative learning enhances essential competencies in higher education, including digital literacy, critical thinking, and data fluency (González-Zamar et al., 2020b; Kurniawan et al., 2024; Testi & Giorgetti, 2021).
It should examine the creation of interactive platforms that allow students to work together on projects based on spatial data, the development of algorithms that optimize geospatial analysis in educational environments, and the generation of predictive models in academic planning (Kurniawan et al., 2024).
- Enhancing Spatial Thinking Skills through Intelligent GIS Tools
This line stands as a fundamental pillar in the advancement of educational practices grounded in geospatial technologies. Its significance lies in the imperative to enhance students’ ability to understand, analyze, and interpret spatial data, thereby improving decision-making processes in dynamic and evolving learning environments (Berendsen et al., 2023).
The justification for this line lies in the increasing demand for spatial competencies across disciplines such as geography, data science, architecture, and urban planning. Integrating Intelligent GISs into educational contexts facilitates the visual representation of complex information, enabling students to develop more accurate and context-sensitive analytical thinking. The use of real-time data (RTD) promotes interaction with virtual environments and simulations, fostering experiential learning and enhancing students’ engagement with real-world spatial challenges (Lulu et al., 2022).
The contributions to be examined will include the design of teaching methodologies that incorporate the use of key intelligent GISs in teaching, the identification of pedagogical strategies to improve the visualization of spatial patterns and the development of adaptive learning platforms based on spatial data (Perugini & Bodzin, 2020).
- Understanding Societal Dynamics to Foster Critical Thinking via GIS Education
Exploring the intersection of social dynamics and geospatial technologies, this line of research examines how the use of GISs and RTD contributes to the development of critical thinking in educational settings. By engaging with spatial data and analyzing real-world social phenomena, students are encouraged to question, interpret, and evaluate information critically. This approach strengthens their analytical capacity and promotes informed, evidence-based reasoning (skills that are increasingly essential in complex, data-driven societies) (Sanabria-Z & Olivo, 2024; Wang et al., 2025).
In an increasingly interconnected and data-rich world, there is a pressing need to educate citizens who can critically interpret complex information and make informed decisions. This research line addresses that need by leveraging intelligent GISs to enable students to analyze spatial patterns, assess socio-economic impacts, and explore the links between geographic factors and social issues. Through this approach, students engage in evidence-based learning, fostering the development of critical thinking, data literacy, and a more reflective and socially responsible citizenship.
The contributions to be examined will include the identification of pedagogical methodologies that integrate geospatial analysis and critical thinking, the design of strategies to improve the interpretation of spatial data in the resolution of social problems, and the evaluation of the impact of geospatial literacy in decision-making (Sanabria-Z & Olivo, 2024).
- Spatiotemporal GIS-Based Learning Environments for Real-Time Data Interpretation
Advancing the integration of spatiotemporal perspectives in education, this research line explores the potential of GIS-based learning enhanced with real-time data to transform teaching and decision-making across diverse educational contexts. By incorporating dynamic models, it enables a more effective understanding of geospatial phenomena and strengthens students’ analytical skills in identifying patterns, trends, and temporal relationships within spatial data (Haedrich et al., 2023; Smith & Shirowzhan, 2022).
As geospatial literacy becomes increasingly vital in higher education, this line of research emphasizes its role in cultivating essential cognitive skills such as spatial reasoning, problem-solving, and systems thinking. By embedding spatiotemporal data into the learning process, students engage with dynamic, real-world information, fostering a more immersive and applied educational experience that bridges theoretical knowledge with practical challenges.
The contributions to be examined will include the development of pedagogical methodologies that integrate real-time data in GIS environments, the identification of strategies to improve the interpretation of spatial and temporal relationships, and the evaluation of the impact of spatiotemporal learning on decision-making (G. Almatar et al., 2020). We will analyze how the use of intelligent GISs with dynamic data models can facilitate interdisciplinary teaching, allowing a better understanding of socio-environmental phenomena and their evolution over time.
5. Discussion
The integration of GISs in education has been a growing topic in recent decades, especially with the incorporation of RTD that provides a dynamic and practical approach to learning. The results obtained from the bibliometric analysis of the reviewed literature confirm that GISs are transforming educational practices, opening new possibilities for active, project-based and student-centered learning. The adoption of these technologies in higher education and other training levels is aligned with the broader trends observed in the digitalization of teaching and the implementation of innovative pedagogical approaches.
Firstly, the findings of the study indicate that GISs are increasingly being used in a variety of disciplines, particularly in areas that require spatial and geographical understanding, such as geography, urban planning, environmental sciences and social sciences (Park, 2022). This type of integration has great potential to improve the teaching of complex concepts, as it offers a visual and dynamic representation of spatial phenomena and patterns, which in turn facilitates the understanding of relationships and processes in the real world. This aspect is consistent with the research stream that suggests that the use of advanced technologies, such as GISs, can enrich traditional teaching and allow for more immersive learning experiences, in which students interact with data in real time and actively participate in its analysis (Shi, 2003).
RTD emerge as one of the most significant innovations in the use of GISs in education, as they allow for the continuous and accurate visualization of real-world situations. The possibility of working with real-time data provides students with a deeper and more contextualized understanding of the phenomena studied, which favors more dynamic and situated learning. In relation to this idea, previous studies have shown that GISs not only allow for the analysis of spatial data but also offer the possibility of interacting with it, which promotes an active and participatory approach to learning. In fact, the use of real-time GISs has been associated with an increase in students’ motivation and an improvement in their analytical and problem-solving skills, two key aspects for the development of 21st century competencies (Theo, 2011).
Furthermore, the analysis of the literature indicates that one of the most relevant applications of GISs in education is its capacity to transform traditional pedagogical practices, especially regarding project-based teaching. GISs allow students to work with real data and solve complex problems through spatial analysis. This approach is closely linked to constructivist learning theories, which promote the idea that students learn more effectively when they interact with content in an active and contextualized way. By facilitating this type of interaction, GISs provide an ideal platform for project-based learning, where students can apply their knowledge in real-life situations, improving both the understanding of concepts and the development of practical skills.
A key finding of the study is the identification of several challenges in the implementation of GISs in classrooms, which is in line with some research streams that warn about barriers to their widespread adoption. The lack of specialized training for teachers, the limited technological infrastructure in some educational institutions, and the complexity of GISs have been cited as major obstacles hindering a broader implementation of these tools in the educational field (Curl et al., 2015). These problems are not new and have been addressed by several previous studies, which have highlighted the need to offer continuous training and adequate support to teachers so that they can effectively integrate technologies into their pedagogical practices. Likewise, the development of more accessible platforms adapted to the needs of educators and students could contribute to overcoming these barriers, as suggested by several studies in the field of technological education.
However, despite these difficulties, the benefits of integrating GISs in education seem to far outweigh the obstacles. The results obtained from the reviewed studies indicate that, when implemented correctly, GISs can significantly improve students’ spatial understanding, facilitate autonomous learning, and encourage a more interactive and collaborative approach to learning (Kerski, 2003; Walther et al., 2019). This point reinforces the ideas of researchers who argue that the key to successful adoption of advanced technologies in education lies in the personalization of learning, that is, in creating adaptive educational environments that allow students to develop at their own pace and according to their needs. GISs can play a fundamental role in this process, as they offer a flexible environment where students can examine data, perform analysis, and apply their knowledge in real-life situations.
The literature also reveals that applications of GISs in the classroom are not limited to specific knowledge areas but extend to other fields such as disaster management, urban planning, environmental management, and urban mobility analysis (Wilhelmi & Betancourt, 2005). This finding highlights the interdisciplinary potential of GISs, which allows students to address complex problems from a global and multidisciplinary perspective. The ability of GISs to integrate data from diverse sources and analyze it in real time facilitates informed decision-making and enhances students’ ability to understand the interconnections between the phenomena being studied. For example, in the context of disaster management, students can use GISs to analyze the risks associated with various natural phenomena, such as floods or earthquakes, and develop solutions to mitigate their effects on communities. These types of applications demonstrate how GISs can be used as educational tools in real-world and relevant contexts, increasing student motivation and engagement (Jakab et al., 2017; Summerby-Murray, 2001).
In terms of future research directions, the results of this study suggest that as the adoption of GISs in education continues to advance, there is a need to further analyze the different pedagogical models that can fully leverage the potential of these technologies. Future research should focus on developing specific pedagogical approaches that effectively integrate GISs and RTD in classrooms. This involves investigating new ways of teaching and learning that align with the characteristics of these tools, such as collaborative learning, project-based learning, and gamification. Furthermore, it would be relevant to examine how GISs can contribute to educational inclusion by providing students with disabilities or from marginalized backgrounds with accessible and adaptive tools for their learning (Benhart, 2000; Summerby-Murray, 2001). Another aspect that should be the subject of future research is the evaluation of the long-term impact of the integration of GISs on student learning. While current studies show immediate benefits, such as developing analytical skills and improving spatial understanding, there is a need to assess how these technologies influence students’ academic performance over time and their readiness for the job market. This will require longitudinal studies that follow students throughout their academic and professional career paths, as well as research that assesses the impact of GISs on interdisciplinary learning and the formation of transferable skills (Perugini & Bodzin, 2020).
Although this paper relies primarily on bibliometric analysis and a literature review, future studies could benefit from the inclusion of case studies or empirical data derived from real-world applications of GISs in educational settings. Incorporating case studies would provide concrete examples of how GISs are implemented in classrooms, offering valuable insights into the practical challenges and benefits of its integration. By analyzing real-world use cases, future research could further strengthen the arguments presented here and offer a more comprehensive understanding of the impact of GIS technology in education. Such empirical evidence would complement the trends identified in this study, providing a more holistic view of GISs’ role in transforming educational practices.
Finally, future collaboration between educational institutions, technology companies, and governments should be considered to develop intelligent GIS platforms that are accessible, affordable, and easy to implement in diverse educational contexts (Benhart, 2000; Summerby-Murray, 2001). Creating these collaborative learning environments and incorporating real-time data could be instrumental in overcoming current technological barriers and ensuring that all students, regardless of their socioeconomic background, have access to these powerful learning tools.
The results of this study thus confirm the growing potential of GISs in education, especially regarding RTD. Although there are challenges that need to be overcome for their widespread adoption, the benefits that these systems offer in terms of active, interactive and project-based learning justify their wider integration in classrooms. The future of GISs in education will depend on further research into their pedagogical applications, ongoing teacher training and the development of more accessible technologies that support inclusive and personalized learning.
6. Conclusions
This study analyses the impact and potential of GISs in educational practices, especially through the implementation of RTD, to transform teaching and learning in various educational contexts. The analysis reveals a landscape in which GISs are gaining ground as key tools for improving pedagogical methodologies, offering new forms of interaction, understanding, and data analysis. This research contributes to the understanding of how the integration of these technologies can revolutionize education, providing students with more dynamic, interactive, and contextualized learning experiences.
The main contribution of GISs is their ability to make learning more immersive and active, allowing students to work with real-time data and visualize complex phenomena in a clear and accessible way. This feature highlights the potential of GISs to facilitate project-based learning, one of the most effective methodologies for developing student competencies. GISs enable students to directly interact with data, analyze real-world situations, and make informed decisions based on their observations, which fosters a better understanding of concepts and promotes critical skills such as analysis, problem-solving, and informed decision-making. Furthermore, the use of GISs aligns with current trends in education, which promote more student-centered pedagogical approaches. The results of the study suggest that GISs can be used as tools that complement traditional teaching and offer a new learning paradigm that emphasizes the active participation of students in their own learning process. RTD allow for continuous and accurate visualization of phenomena, which promotes a more situated and contextualized approach, key to effective learning. This feature also highlights the ability of GISs to adapt to different disciplines and educational levels, since the applications of these systems are not limited to geography or environmental sciences, but cover a wide spectrum of areas, from urban planning to disaster management and mobility analysis.
Despite the obvious benefits of GISs, the study also highlights several challenges and barriers that limit their widespread adoption in classrooms. Key obstacles include a lack of specialized training among teachers, insufficient technological infrastructure in many educational institutions, and the complexity of GISs, which require technical skills to operate. These challenges are consistent with other research in the field of integrating advanced technologies in education, which underlines the need to provide teachers with the appropriate tools and training to enable them to effectively incorporate these technologies into their teaching practices. Moreover, the implementation of GISs must be accompanied by adequate development of technological infrastructures and reflection on best pedagogical practices to ensure that students can fully benefit from these tools.
Furthermore, the study highlights the enormous potential of GISs to foster interdisciplinary learning. By enabling the integration of data from diverse sources and the analysis of phenomena from different perspectives, intelligent GISs promote a holistic view of the problems that students address. This ability of GISs to cross disciplinary boundaries reflects a growing trend in higher education toward more integrated approaches, which prepare students to tackle complex problems in a collaborative and multidimensional manner. GISs enable students to acquire technical and analytical knowledge, and develop teamwork, communication, and collective decision-making skills—competences that are increasingly valued in the professional field.
In response to the research questions formulated, the study provides an integrative overview of the scientific production on GISs applied to education. Regarding RQ1, the bibliometric analysis reveals a sustained growth in publications from 2000 to 2024, with a significant acceleration in the last five years. In relation to RQ2, keyword co-occurrence analysis identifies real-time data integration, spatial analysis, and interactive learning environments as dominant trends, reflecting the progressive alignment between GIS technologies and data-driven educational practices. Finally, RQ3 is addressed through the identification of future research directions, notably the convergence of GIS with AI and the potential for personalized and interdisciplinary learning environments. These findings reinforce the role of Intelligent GISs as a transformative tool in the educational landscape.
The findings of this study also suggest that GISs can be a key resource for improving educational management. Real-time data collection and analysis allows teachers and administrators to gain a clearer view of student progress, identify areas for improvement, and make more informed decisions about pedagogical strategies and necessary resources. In this sense, GISs can play a fundamental role in personalizing learning, as they provide detailed information about students’ needs and performance, facilitating the adaptation of educational methodologies and content to their individual characteristics. This student-centered approach allows for more effective learning while optimizing the use of available educational resources.
The analysis also highlights the importance of an ethical and responsible implementation of GISs in education. As these are technologies that involve the collection and analysis of large volumes of data, it is key to ensure the privacy and security of information. The adoption of these tools must be accompanied by clear policies on the use of data, ensuring transparency in the processes and avoiding possible biases in the analysis models. This aspect is especially relevant in the educational context, where equality and inclusion must be a priority. The responsible implementation of GISs must be accompanied by an ethical reflection on its use, ensuring that all students have access to the same opportunities and resources, regardless of their social or economic context.
As for future research directions, the results of this study point to the need to continue examining the pedagogical possibilities offered by GISs. As technologies advance, it is essential to investigate new educational methodologies that take full advantage of the potential of GISs, such as project-based learning and gamification. Research should focus on the development of more accessible and user-friendly systems, which allow teachers without technical experience to integrate these tools into their educational practices. There is also a need to carry out more in-depth studies on the long-term impact of GISs on student learning, evaluating how these tools affect their academic performance, the development of transversal competences, and their preparation for the world of work.
Hence, this study demonstrates that GISs have enormous potential to transform educational practices, offering new forms of active, interactive, and personalized learning. Through their integration into educational environments, GISs can improve the understanding of complex concepts, foster collaborative and interdisciplinary learning, and contribute to more efficient educational management. However, for their implementation to be effective, obstacles related to teacher training, technological infrastructure, and system complexity need to be overcome. As technology continues to evolve, GISs could play a pivotal role in the evolution of education, provided they are implemented ethically and responsibly, ensuring that all students can benefit from their advantages and opportunities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, software, formal analysis, resources, data curation and writing—original draft preparation, E.L.-M. and I.-M.P.-I.; investigation, validation, writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision, project administration, E.L.-M., I.-M.P.-I., M.-B.M.-C. and N.P.-P.; funding acquisition, E.L.-M. and I.-M.P.-I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study are openly available in Elsevier’s Scopus database at (https://www.scopus.com/, accessed 5 June 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Agrawal, S., De Beer, D. J., & Modi, Y. K. (2014). Conversion of a GIS surface data directly to a 3D STL part for terrain modeling. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 20(5), 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladaǧ, E. (2010). The effects of GIS on students’ academic achievement and motivation in seventh-grade social studies lessons in Turkey. International Research in Geographical and Environmental Education, 19(1), 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anunti, H., Vuopala, E., & Rusanen, J. (2020). A portfolio model for the teaching and learning of gis competencies in an upper secondary school: A case study from a finnish geomedia course. Review of International Geographical Education Online, 10(3), 262–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusiak, A., Kutt, F., Musznicki, P., & Nieznański, J. (2024). Engineering education for smart grid systems in the quasi-industrial environment of the LINTE^2 laboratory. Global Journal of Engineering Education, 26(2), 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Barcus, H. R., & Smith, L. J. (2016). Facilitating native land reacquisition in the rural USA through collaborative research and Geographic Information Systems. Geographical Research, 54(2), 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearman, N., Jones, N., André, I., Cachinho, H. A., & DeMers, M. (2016). The future role of GIS education in creating critical spatial thinkers. Journal of Geography in Higher Education, 40(3), 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhart, J. (2000). An approach to leaching applied gis: Implementation for local organizations. Journal of Geography, 99(6), 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, M. E., Hodza, P., & Hamerlinck, J. D. (2023). Researching student interaction with GIS software while learning spatial concepts: Toward a standard measure of GIS interaction. Journal of Geography, 122(4), 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bédard, Y., Bernier, E., Badard, T., Chrisman, N., Roche, S., Edwards, G., Mostafavi, M. A., Pouliot, J., Gervais, M., Hubert, F., Brodeur, J., & Devillers, R. (2007). Research in geographic information systems, data management and dissemination, and new geospatial technologies|La recherche en systèmes d’information géographique, en gestion et diffusion des données, et en nouvelles technologies géospatiales. Geomatica, 61(3), 299–314. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S., Küçük, Z. D., Rickard, A., Lonergan, J., Abernethy, R., McNerney, L., McNerney, E., Foley, R., Behan, A., Byrne, A., Faull, J., & Cahalane, C. (2024). The role of teacher agency in using GIS to teach sustainability: An evaluation of a lower secondary school story mapping GIS initiative in Ireland. International Research in Geographical and Environmental Education, 33(1), 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Sotelo, P. C. (2009). La Educación, un hecho espacial: El “Campus Didáctico” como arquitectura para el Espacio Europeo de Educación Superior. La Cuestión Universitaria, 5, 98–120. [Google Scholar]
- Carrión Montalván, B. K., Pillajo Angos, C. G., Castellanos Fonseca, J. A., & Vega Aguaiza, R. (2024). The influence of artificial intelligence in higher education based on four thematic axes: A bibliometric study. Sapienza: International Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies, 5(2), e24035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X., Chang-Richards, A. Y., Pelosi, A., Jia, Y., Shen, X., Siddiqui, M. K., & Yang, N. (2022). Implementation of technologies in the construction industry: A systematic review. Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management, 29(8), 3181–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curl, A., Nelson, J. D., & Anable, J. (2015). Same question, different answer: A comparison of GIS-based journey time accessibility with self-reported measures from the National Travel Survey in England. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 49, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duever, M., & McGinn, E. (2020). Teaching GIS in a digital humanities environment. Journal of Map and Geography Libraries, 16(3), 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, M. J., Winkler, E., Sugiyama, T., Cerin, E., Dutoit, L., Leslie, E., & Owen, N. (2010). Relationships of land use mix with walking for transport: Do land uses and geographical scale matter? Journal of Urban Health, 87(5), 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, B. (2024). A GIS methodology for mapping regional and community vitality for Canada using the CanEcumene 3.0 Geodatabase with census data. One Ecosystem, 9, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandino, J. (2015). Using GIS to apply learning across the undergraduate criminal justice curriculum. Journal of Criminal Justice Education, 26(1), 74–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G. Almatar, M., Alazmi, H. S., Li, L., & Fox, E. A. (2020). Applying GIS and text mining methods to Twitter data to explore the spatiotemporal patterns of topics of interest in Kuwait. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 9(12), 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giski, Z. E., & Ebrahimzadeh, A. (2019). Unifying entropies of quantum logic based on Rényi entropies. Reports on Mathematical Physics, 83(3), 305–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golumbeanu, M., & Avdimiotis, S. (2009). Destination management, coastal spatial analysis and GIS. The case of Chalkidiki Greece. Journal of Environmental Protection and Ecology, 10(4), 1100–1112. [Google Scholar]
- González-Zamar, M. D., & Abad-Segura, E. (2024). Analysing the teaching-learning process in the university virtual classroom at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. Culture and Education, 36(1), 190–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Zamar, M. D., Abad-Segura, E., & Belmonte-Ureña, L. J. (2020a). Meaningful learning in the development of digital skills. Trend analysis|Aprendizaje significativo en el desarrollo de competencias digitales. Análisis de tendencias. International Journal of Educational Research and Innovation, 2020(14), 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Zamar, M.-D., Abad-Segura, E., Luque de la Rosa, A., & López-Meneses, E. (2020b). Digital education and artistic-visual learning in flexible university environments: Research analysis. Education Sciences, 10(11), 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haedrich, C., Petras, V., Petrasova, A., Blumentrath, S., & Mitasova, H. (2023). Integrating GRASS GIS and Jupyter notebooks to facilitate advanced geospatial modeling education. Transactions in GIS, 27(3), 686–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallak, J., & Polat, E. G. (2021). A MCDM based on goal programming and GIS-based risk assessment for the evaluation of educational locations in conflict areas. Foundations of Computing and Decision Sciences, 46(4), 361–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawthorne, T. L., & Kwan, M.-P. (2012). Using GIS and perceived distance to understand the unequal geographies of healthcare in lower-income urban neighbourhoods. Geographical Journal, 178(1), 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogrebe, M. C., Kyei-Blankson, L., & Zou, L. (2008). Examining regional science attainment and school-teacher resources using GIS. Education and Urban Society, 40(5), 570–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakab, I., Ševčík, M., & Grežo, H. (2017). Model of higher GIS education. Electronic Journal of E-Learning, 15(3), 220–234. [Google Scholar]
- Jażdżewska, I. A., Lechowski, Ł., & Babuca, D. (2022). GIS-based approach for the analysis of geographical education paths. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 11(1), 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, R. H. G. d., Barros, M. V., Salvador, R., Souza, J. T. d., Piekarski, C. M., & Francisco, A. C. d. (2021). Forming clusters based on strategic partnerships and circular economy for biogas production: A GIS analysis for optimal location. Biomass and Bioenergy, 150, 106097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Espada, M., Cuartero, A., & Breton, M. L. (2022). Sustainability assessment through urban accessibility indicators and GIS in a middle-sized world heritage city: The case of Cáceres, Spain. Buildings, 12(6), 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamruzzaman, M. (2014). Development of an integrated GIS and land use planning course: Impacts of hybrid instructional methods. Journal of Geography in Higher Education, 38(3), 323–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, J. W., Herrick, J. E., & Browning, D. M. (2012). A strategy for rangeland management based on best available knowledge and information. Rangeland Ecology and Management, 65(6), 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerski, J. J. (2003). The implementation and effectiveness of geographic information systems technology and methods in secondary education. Journal of Geography, 102(3), 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerski, J. J., Demirci, A., & Milson, A. J. (2013). The Global Landscape of GIS in Secondary Education. Journal of Geography, 112(6), 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M., Kim, K., & Lee, S.-I. (2013). Pedagogical potential of a web-based GIS application for migration data: A preliminary investigation in the context of South Korea. Journal of Geography, 112(3), 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klooster, D., Strout, N., & Smith, D. (2022). GIS in the jungle: Experiential Environmental Education (EEE) in Panama. Journal of Environmental Studies and Sciences, 12(1), 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, E., Syifauddin, M., Sholeh, M., Sriyanto, & Sari, S. N. (2024). Environmental problem-solving learning model with geographic information system-based learning media. International Journal of Environmental Impacts, 7(3), 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z., Zhou, H., Hu, W., & Liu, G.-P. (2023). Flipping laboratories toward future experimentation systems: The blended use of hands-on, pocket, and online laboratories. IEEE Industrial Electronics Magazine, 17(2), 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Q. (2003). Fuzzy cognitive maps in GIS data analysis. Soft Computing, 7(6), 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Q., & Satur, R. (1999). Contextual fuzzy cognitive map for decision support in geographic information systems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 7(5), 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Meneses, E., López-Catalán, L., Pelícano-Piris, N., & Mellado-Moreno, P. C. (2025). Artificial intelligence in educational data mining and human-in-the-loop machine learning and machine teaching: Analysis of scientific knowledge. Applied Sciences, 15(2), 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lulu, J., Xiuhua, L., & Wei, F. (2022). Analysis of animation peripheral design ability based on artificial intelligence. Scientific Programming, 2022, 3245441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magzoub, M. E., Taha, M. H., Waller, S., Al Eissa, A. M., Hamdy, H., Norcini, J., Al Marzooqi, S., Shaban, S., Elhassan Abdalla, M., & Schmidt, H. (2024). Going beyond competencies: Building blocks for a patient- and population-centered medical curriculum. Medical Teacher, 46(12), 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M. A., Roy, N., Gozal, D., Almerab, M. M., Hossain, M. S., & Al Mamun, F. (2024). Prevalence and associated factors of cigarette smoking and substance use among university entrance test-taking students: A GIS-based study. PLoS ONE, 19(8), e0308697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- March, G., & Scarletto, E. (2017). The evolution of GIS services within North American academic libraries: Documenting change through the decades (1995–2016). Journal of Map and Geography Libraries, 13(2), 222–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merry, K., Bettinger, P., Grebner, D., Boston, K., & Siry, J. (2016). Assessment of geographic information system (GIS) skills employed by graduates from three forestry programs in the United States. Forests, 7(12), 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milson, A. J., & Earle, B. D. (2007). Internet-based GIS in an inductive learning environment: A case study of ninth-grade geography students. Journal of Geography, 106(6), 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J. T., Roy, G., Fritch, S., & Wood, B. (2018). GIS professional development for teachers: Lessons learned from high-needs schools. Cartography and Geographic Information Science, 45(4), 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D., Altman, D. G., Liberati, A., & Tetzlaff, J. (2011). PRISMA statement. Epidemiology, 22(1), 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, J. D., Eddy, B., & Coffey, J. W. (2022). Activating student engagement with concept mapping: A Web GIS case study. Journal of Geography in Higher Education, 46(1), 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulaku, G. C., & Nyadimo, E. (2011). GIS in education planning: The Kenyan school mapping project. Survey Review, 43(323), 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y. M. (2022). A GPS-enabled portable air pollution sensor and web-mapping technologies for field-based learning in health geography. Journal of Geography in Higher Education, 46(2), 241–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perugini, S., & Bodzin, A. M. (2020). Using web-based GIS to assess students’ geospatial knowledge of hurricanes and spatial habits of mind. Journal of Geography, 119(2), 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, B. G., Messina, J. P., Lin, Z., & Snapp, S. S. (2020). Crop climate suitability mapping on the cloud: A geovisualization application for sustainable agriculture. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 15487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezan, C. A., Maxwell, A. E., & Meadows, J. T. (2024). An analysis of qualifications and requirements for geographic information systems (GIS) positions in the United States. Transactions in GIS, 28(5), 1090–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkofske, J. E., Pavlis, T. L., & Ramirez, S. (2022). Applications of modern digital mapping systems to Assist inclusion of persons with disabilities in geoscience education and research. Journal of Structural Geology, 161, 104655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanabria-Z, J., & Olivo, P. G. (2024). AI platform model on 4IR megatrend challenges: Complex thinking by active and transformational learning. Interactive Technology and Smart Education, 21(4), 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W. (2003). State-of-the-art and future of geographic information systems in Hong Kong. Geographic Information Sciences, 9(1–2), 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K. I., & Shirowzhan, S. (2022). A GIS-based spatiotemporal analysis of the relationship between the outbreak of COVID-19, delta variant and construction in Sydney and Melbourne. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 11(12), 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofias, T. A., & Pierrakeas, C. J. (2023). Student engagement and educational benefits of web GIS-based projects. International Journal of Web-Based Learning and Teaching Technologies, 18(1), 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerby-Murray, R. (2001). Analysing heritage landscape with historical GIS: Contributions form problem-based inquiry and constructivist pedalogy. Journal of Geography in Higher Education, 25(1), 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedyyana, A., Ahmad, A. A., Idrus, M. R., Shabli, A. H. M., Seman, M. A. A., Ghazali, O., Jaroji, & Razak, A. H. A. (2024). Enhance telecommunication security through the integration of support vector machines. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 15(3), 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepavčević, B., Sijakov, M., & Signanin, P. (2012). Gis technologies in urban planning and education. Pollack Periodica, 7(Suppl. S1), 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testi, E., & Giorgetti, A. (2021). Blind wireless network topology inference. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 69(2), 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, J. E., & Imaoka, L. B. (2018). The poverty of GIS theory: Continuing the debates around the political economy of GISystems. Canadian Geographer, 62(1), 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theo, L. (2011). Simplifying central place theory using GIS and GPS. Journal of Geography, 110(1), 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinker, R. F. (1992). Mapware: Educational applications of geographic information systems. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 1(1), 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N. J., & Waltman, L. (2007). VOS: A new method for visualizing similarities between objects. In Advances in data analysis (pp. 299–306). Studies in classification, data analysis, and knowledge organization. Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N. J., & Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics, 84(2), 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N. J., Waltman, L., Noyons, E. C. M., & Buter, R. K. (2010). Automatic term identification for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics, 82(3), 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leusen, P., Ottenbreit-Lefwich, A. T., & Brush, T. (2016). Interpersonal consulting skills for instructional technology consultants: A multiple case study. TechTrends, 60(3), 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, S. C., Dengenis, E. M., & Gurung, K. (2019). Using GIS and remote sensing to map grassroots sustainable development for a small NGO in Nepal. International Journal of Geospatial and Environmental Research, 6(1), 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Waltman, L., van Eck, N. J., & Noyons, E. C. M. (2010). A unified approach to mapping and clustering of bibliometric networks. Journal of Informetrics, 4(4), 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D., Liu, Y., Jing, X., Liu, Q., & Lu, Q. (2025). Catalyst for future education: An empirical study on the impact of artificial intelligence generated content on college students’ innovation ability and autonomous learning. Education and Information Technologies, 30, 9949–9968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmi, O. V., & Betancourt, T. L. (2005). Evolution of NCAR’s GIS initiative. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 86(2), 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J., Zhang, Y. Y., Xiong, L. H., He, S., Wang, L. F., & Yu, Z. B. (2017). Opportunities and challenges of the Sponge City construction related to urban water issues in China. Science China Earth Sciences, 60(4), 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. (2020). Expanding library GIS instruction to web mapping in the age of neogeography. Journal of Map and Geography Libraries, 16(3), 264–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).