A Systematic Review of the Recent Empirical Literature on Math and Science Teacher Recruitment and Retention
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- What are the characteristics of math and science teachers who enter and remain in the teaching profession?
- (2)
- What strategies and mechanisms are used to recruit and retain math and science teachers?
- (3)
- What factors influence individuals to enter and remain in math and science teaching roles?
2. Literature Overview
3. Supply and Demand Framework
4. Methods
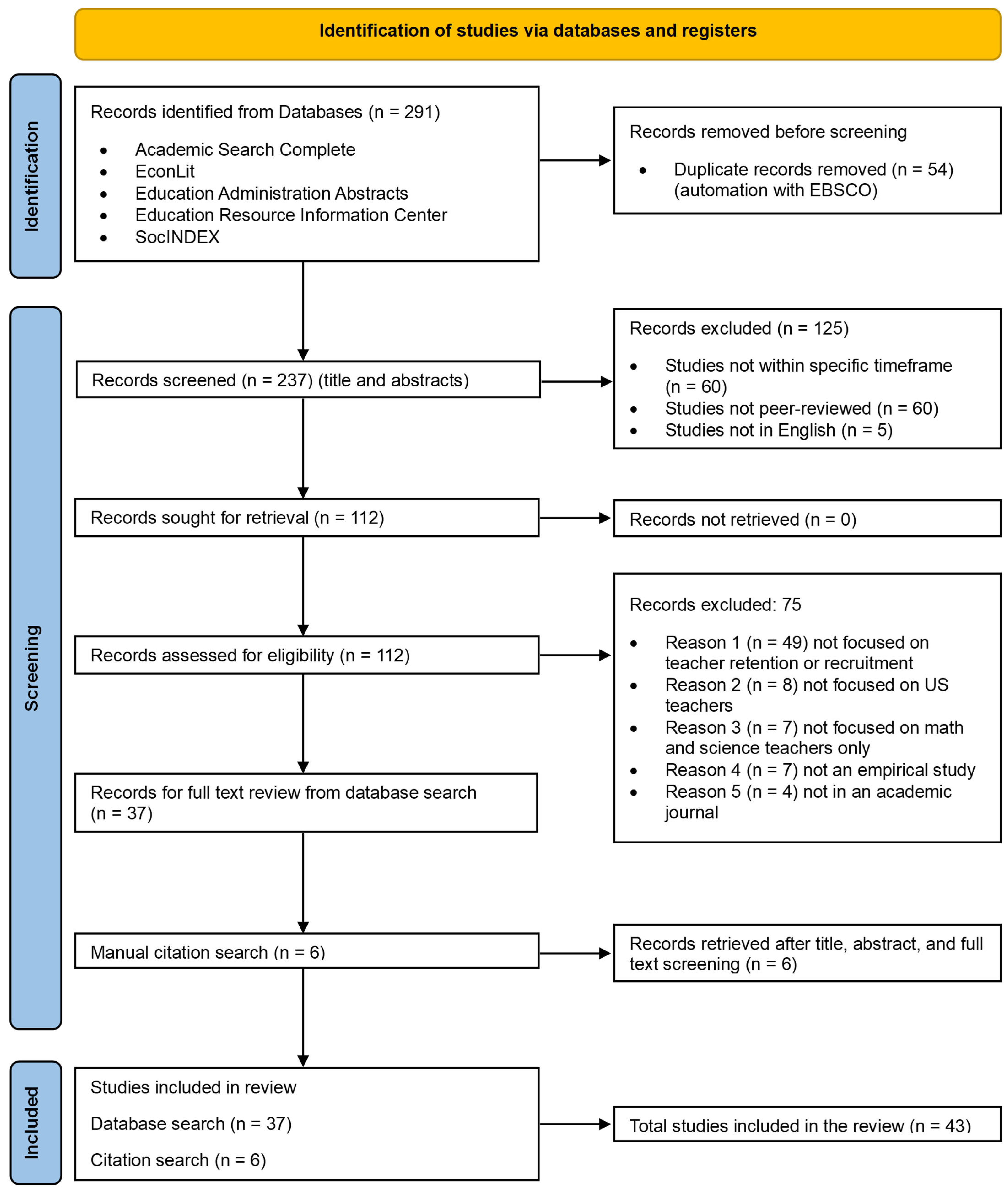
4.1. Search Strategy
4.2. Screening and Review Criteria
4.3. Data Extraction and Analysis
4.4. Limitations
5. Results
5.1. Characteristics of Math and Science Teachers Who Enter and Remain in Teaching
5.1.1. Demographics and Qualifications
5.1.2. Certification Pathways
5.1.3. Pedagogical and Content Training
5.1.4. Supply and Demand
5.1.5. Retention Patterns
5.2. Strategies and Mechanisms Used to Recruit and Retain Math and Science Teachers
5.2.1. Monetary Incentives
5.2.2. Experiential Learning
5.2.3. Mentorship and Professional Development
5.3. Factors That Influence Individuals to Enter the Teaching Profession and Remain in Math and Science Classrooms
5.3.1. Psychological and Sociocultural
5.3.2. Working Conditions
6. Discussion
6.1. Characteristics of Math and Science Teachers
6.2. Strategies and Mechanisms to Recruit and Retain Math and Science Teachers
6.3. Factors That Influence Individuals to Become Math and Science Teachers and Stay in Teaching
6.4. Implications
7. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abell, S., Boone, W., Arbaugh, F., Lannin, J., Beilfuss, M., Volkmann, M., & White, S. (2006). Recruiting future science and mathematics teachers into alternative certification programs: Strategies tried and lessons learned. Journal of Science Teacher Education, 17(3), 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Association for the Advancement of Science. (n.d.). Robert noyce teacher scholarship program. Available online: https://www.nsfnoyce.org (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Armitage, L., Bourne, M., Simone, J. D., Jones, A., & Neave, S. (2020). Engineering UK 2020 educational pathways into engineering. Engineering UK. Available online: https://www.engineeringuk.com/media/196594/engineering-uk-report-2020.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Artzt, A. F., & Curcio, F. R. (2008). Recruiting and retaining secondary mathematics teachers: Lessons learned from an innovative four-year undergraduate program. Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, 11(3), 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, V., & Murray, K. (2015). Uncovering the need for diversity among PK-12 STEM educators. Teacher Education & Practice, 28(2–3), 255–268. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, A. M., Bostedt, G., Michel-Schertges, D., & Wüllner, S. (2023). Studying teacher shortages: Theoretical perspectives and methodological approaches. Journal of Pedagogical Research, 7(1), 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J. A., Wojcikiewicz, S. K., Darling-Hammond, L., & Wei, W. (2023). Strengthening pathways into the teaching profession in Texas: Challenges and opportunities. Learning Policy Institute. [Google Scholar]
- Borgerding, L. A. (2015). Recruitment of early STEM majors into possible secondary science teaching careers: The role of science education summer internships. International Journal of Environmental & Science Education, 10(2), 247–270. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, D., Grossman, P., Hammerness, K., Lankford, H., Loeb, S., Ronfeldt, M., & Wyckoff, J. (2012). Recruiting effective math teachers: Evidence from new york city. American Educational Research Journal, 49(6), 1008–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozeman, T. D., Scogin, S., & Stuessy, C. L. (2013). Job satisfaction of high school science teachers: Prevalence and association with teacher retention. Electronic Journal of Science Education, 17(4), 1–19. Available online: http://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1188384.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Brantlinger, A. (2021). Entering, staying, shifting, leaving, and sometimes returning: A descriptive analysis of the career trajectories of two cohorts of alternatively certified mathematics teachers. Teachers College Record, 123(9), 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantlinger, A., & Grant, A. A. (2022). The first-school retention of black and latinx community-insiders and elite college graduates: Implications for the recruitment, selection, and training of urban mathematics teachers. Education Policy Analysis Archives, 30(111), 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantlinger, A., & Grant, A. A. (2024). Capital flight: Examining teachers’ socioeconomic status and early career retention. Sociology of Education, 97(4), 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantlinger, A., Grant, A. A., & Cooley, L. (2023). How long do community insiders and outsiders stay? Mathematics teacher preparation and retention in an urban school district. American Journal of Education, 129(4), 481–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, P. C., & Brantlinger, A. (2023). Altruism, jobs, and alternative certification: Mathematics teachers’ reasons for entry and their retention. Education and Urban Society, 55(9), 1089–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter Andrews, D. J., Castro, E., Cho, C. L., Petchauer, E., Richmond, G., & Floden, R. (2019). Changing the narrative on diversifying the teaching workforce: A look at historical and contemporary factors that inform recruitment and retention of teachers of color. Journal of Teacher Education, 70(1), 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver-Thomas, D. (2022). Teacher shortages take center stage. Learning Policy Institute. Available online: https://learningpolicyinstitute.org/blog/teacher-shortages-take-center-stage (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Carver-Thomas, D., & Darling-Hammond, L. (2019). The trouble with teacher turnover: How teacher attrition affects students and schools. Education Policy Analysis Archives, 27(36), 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A., Siegel-Hawley, G., Bridges, K., & Williams, S. E. (2024). Drawn into policy: A systematic review of school rezoning rationales, processes, and outcomes. Review of Educational Research, 94(4), 539–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, D., Pawlewicz, R. J., Earley, P. M., & McGeehan, A. P. (2017). Where are all the black teachers? Discrimination in the teacher labor market. Harvard Educational Review, 87(1), 26–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling-Hammond, L. (2010). Recruiting and retaining teachers: Turning around the race to the bottom in high-needs schools. Journal of Curriculum and Instruction, 4(1), 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, T. S. (2004). Teachers, race, and student achievement in a randomized experiment. Review of Economics and Statistics, 86, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cruz, J. A., & Goldman, S. (2023). Impact of a mathematics early teaching experience for undergraduates: A teacher preparation recruitment strategy. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education, 18(4), em0759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, W. (2024). Persistence despite structural barriers: Investigating work environments for black and latinx teachers in urban and suburban schools. Urban Education, 59(4), 1159–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L., & Sass, T. R. (2017). The impact of incentives to recruit and retain teachers in “hard-to-staff” subjects. Journal of Policy Analysis and Management, 37(1), 112–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M. H., & Royster, D. (2016). Mathematics teachers’ support and retention: Using Maslow’s hierarchy to understand teachers’ needs. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology, 47(7), 993–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser-Abder, P. (2010). Reflections on success and retention in urban science education: Voices of five african-american science teachers who stayed. School Science and Mathematics, 110(5), 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershenson, S., Hart, C. M. D., Hyman, J., Lindsay, C. A., & Papageorge, N. W. (2022). The long-run impacts of same-race teachers. American Economic Journal. Economic Policy, 14(4), 300–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gist, C. D., & Bristol, T. J. (Eds.). (2022). Handbook of research on teachers of color and indigenous teachers (1st ed.). American Educational Research Association. [Google Scholar]
- Gjefsen, H. M. (2020). Wages, teacher recruitment, and student achievement. Labour Economics, 65, 101848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhaber, D., Krieg, J., Theobald, R., & Goggins, M. (2022a). Front end to back end: Teacher preparation, workforce entry, and attrition. Journal of Teacher Education, 73(3), 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhaber, D., Ronfeldt, M., Cowan, J., Gratz, T., Bardelli, E., & Truwit, M. (2022b). Room for improvement? Mentor teachers and the evolution of teacher preservice clinical evaluations. American Educational Research Journal, 59(5), 1011–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodpaster, K. P. S., Adedokun, O. A., & Weaver, G. C. (2012). Teachers’ perceptions of rural STEM teaching: Implications for rural teacher retention. The Rural Educator, 33(3), 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, A. A., & Brantlinger, A. (2023). It’s tough to make predictions, especially about the future: The difference between teachers’ intended and actual retention. Teaching and Teacher Education, 130, 104156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, A. A., & Brantlinger, A. M. (2022). Demography as destiny: Explaining the turnover of alternatively certified mathematics teachers in hard-to-staff schools. Teachers College Record, 124(4), 35–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, C. M., Santibañez, L., & Daley, G. A. (2006). Teacher recruitment and retention: A review of the recent empirical literature. Review of Educational Research, 76(2), 173–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthery, S., & Bailes, L. P. (2022). Patterns of teacher attrition by preparation pathway and initial school type. Educational Policy, 36(2), 223–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D., & Hur, H. (2022). Managing turnover of STEM teacher workforce. Education and Urban Society, 54(2), 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, P. E., Thompson, R., & Brooks, K. (2019). Leaving schools behind: The impact of school student body and working conditions on teacher retention and migration. Journal of Science Teacher Education, 30(2), 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, C., & Brantlinger, A. (2022). Patterns in critical incidents: Understanding teacher retention through career decision making. Teaching and Teacher Education, 109, 103557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, L. F. (2012). Addressing the STEM teacher shortage in american schools: Ways to recruit and retain effective STEM teachers. Action in Teacher Education, 34(5–6), 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingersoll, I. (2001). Teacher turnover and teacher shortages: An organizational analysis. American Educational Research Journal, 38(3), 499–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingersoll, R., & May, H. (2012). The magnitude, destinations, and determinants of mathematics and science teacher turnover. Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 34(4), 435–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingersoll, R., & Perda, D. (2010). Is the supply of mathematics and science teachers sufficient? American Educational Research Journal, 47(3), 563–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingersoll, R. M. (2011). Do we produce enough mathematics and science teachers? Phi Delta Kappan, 92(6), 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingersoll, R. M., & Strong, M. (2011). The impact of induction and mentoring programs for beginning teachers: A critical review of the research. Review of Educational Research, 81(2), 201–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, S. L. (1990). Change in entry-level salary and the recruitment of novice teachers. Journal of Education Finance, 15(3), 408–413. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D., Koedel, C., Kong, W., Ni, S., Podgursky, M., & Wu, W. (2021). Pensions and late-career teacher retention. Education Finance and Policy, 16(1), 42–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, M. A., Marinell, W. H., & Yee, D. S.-W. (2016). School organizational contexts, teacher turnover, and student achievement: Evidence from panel data. American Educational Research Journal, 53(5), 1411–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, D. B., Patzelt, S. P., Ahmed, K. M., Carletta, L., & Gaynor, C. R. (2022). Portraying secondary science teacher retention with the person-position framework: An analysis of a state cohort of first-year science teachers. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 59(7), 1235–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, S., Johnson, T., & Small, C. (2020). Watering our own lawn: Exploring the impact of a collaborative approach to recruiting African Caribbean STEM majors into teaching. Journal of Negro Education, 88(3), 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, S., & Myung, J. (2010). Economic approaches to teacher recruitment and retention. Available online: https://cepa.stanford.edu/sites/default/files/loeb,myung_Economic%20Approaches%20to%20Teacher%20Recruitment%20and%20Retention.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Marco-Bujosa, L. M., Galczyk, A., Stannard, R., Koetting, P., & Friedman, A. A. (2024). “Connecting the dots” for recruiting secondary science teachers in urban schools: An exploration of career choice for undergraduate science majors. The Urban Review, 56(5), 648–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marder, M., Bernard, D., & Hamrock, C. (2020). Math and science outcomes for students of teachers from standard and alternative pathways in Texas. Education Policy Analysis Archives, 28, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marder, M., Horn, C., Stephens, S., & Rhodes, A. (2022). Student learning and teacher retention for graduates of Texas Noyce programs. Education Policy Analysis Archives, 30(147), 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinie, S., Nguyen, T., Nusser, T., Spencer, C., & Natarajan. (2023). Recruitment and retention of mathematics teachers in high-need schools. Mathematics Teacher Education and Development, 25(2), 1. [Google Scholar]
- Morettini, B. W. (2014). Going back to school: Why STEM professionals decide to teach through alternative certification programs. Journal of the National Association for Alternative Certification, 2(9), 3–23. Available online: http://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1053330.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- National Center for Education Statistics [NCES]. (2020). Projection of education statistics. Available online: https://nces.ed.gov/programs/pes/ (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- National Center for Education Statistics [NCES]. (2022). U.S. schools report increased teacher vacancies due to COVID-19 pandemic, new NCES data show. Available online: https://nces.ed.gov/whatsnew/press_releases/3_3_2022.asp (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- National Center for Education Statistics [NCES]. (2023). Characteristics of public school teachers. The Condition of Education. U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences. Available online: https://nces.ed.gov/programs/coe/indicator/clr/public-school-teachers (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- National Commission on Excellence in Education. (1983). A nation at risk: The imperative for educational reform. The Elementary School Journal, 84(2), 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, K. J., Fornaro, E., & Pecore, J. (2020). Program completion and retention of career changers pursuing alternative teacher certification: Who drops, who commits, and why? Journal of the National Association for Alternative Certification, 15(1), 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T. D., & Redding, C. (2018). Changes in the demographics, qualifications, and turnover of American STEM teachers, 1988–2012. AERA Open, 4(3), 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odell, S. J., & Ferraro, D. P. (1992). Teacher mentoring and teacher retention. Journal of Teacher Education, 43(3), 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olitsky, S. (2020). Teaching as emotional practice or exercise in measurement? School structures, identity conflict, and the retention of black women science teachers. Education and Urban Society, 52(4), 590–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olitsky, S., Perfetti, A., & Coughlin, A. (2019). Filling positions or forging new pathways? Scholarship incentives, commitment, and retention of STEM teachers in high-need schools. Science Education, 104(2), 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J. M., Akl, E. A., Brennan, S. E., Chou, R., Glanville, J., Grimshaw, J. M., Hróbjartsson, A., Lalu, M. M., Li, T., Loder, E. W., Mayo-Wilson, E., McDonald, S., … Moher, D. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 134, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, M., Kelly, A. M., & Krakehl, R. (2022). Physics teacher retention, migration, and attrition. Journal of Science Teacher Education, 33(4), 368–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrachione, B. A., Rosser, V. J., & Peterson, G. J. (2008). Why do they stay? Elementary teachers’ perceptions of job satisfaction and retention. Professional Educator, 32(2), 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Podolsky, A., Tara, K., Bishop, J., & Darling-Hammond, L. (2016). Solving the teacher shortage how to attract and retain excellent educators. Learning Policy Institute. Available online: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED606767.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology. (2010). Available online: https://www.nitrd.gov/pubs/PCAST-NITRD-report-2010.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Redding, C., Booker, L. N., Smith, T. M., & Desimone, L. M. (2019). School administrators’ direct and indirect influences on middle school math teachers’ turnover. Journal of Educational Administration, 57(6), 708–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redding, C., & Smith, T. M. (2016). Easy in, easy out: Are alternatively certified teachers turning over at increased rates? American Educational Research Journal, 53(4), 1086–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronfeldt, M., Loeb, S., & Wyckoff, J. (2013). How teacher turnover harms student achievement. American Educational Research Journal, 50(1), 4–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S. (2025, May 19). National science foundation cancels more than 400 STEM grants; DOGE called the awards, meant to improve STEM teaching, “wasteful DEI grants”. Education Week. [Google Scholar]
- See, B. H., Gorard, S., Gao, Y., Hitt, L., Siddiqui, N., Demie, F., Tereshchenko, A., & El Soufi, N. (2024). Factors related to the recruitment and retention of ethnic minority teachers: What are the barriers and facilitators? Review of Education, 12(3), e70005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K. N. (2021). The North Carolina teaching fellows program: A case study of the use of forgivable loans in recruiting future STEM teachers. The Journal of Student Financial Aid, 50(3), 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcher, L., Darling-Hammond, L., & Carver-Thomas, D. (2016). A coming crisis in teaching? Teacher supply, demand, and shortages in the US. Available online: https://learningpolicyinstitute.org/product/coming-crisis-teaching (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Sutcher, L., Darling-Hammond, L., & Carver-Thomas, D. (2019). Understanding teacher shortages: An analysis of teacher supply and demand in the United States. Education Policy Analysis Archives, 27(35), 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, R. H., Liu, C. Q., & Fan, X. (2006). Alternative certification and retention of secondary math and science teachers: A study based on “SASS/TFS”. Journal of the National Association for Alternative Certification, 1(2), 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, R. H., Liu, C. Q., & Fan, X. (2007). factors influencing retention of mathematics and science teachers in secondary schools—A study based on SASS/TFS. Science Educator, 16(2), 27. [Google Scholar]
- The National Academies. (2007). Rising above the gathering storm: Energizing and employing America for a brighter economic future. The National Academies Press. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, M. M., Turner, J. E., & Nietfeld, J. L. (2012). A typological approach to investigate the teaching career decision: Motivations and beliefs about teaching of prospective teacher candidates. Teaching and Teacher Education, 28(3), 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of Education. (n.d.). Teacher loan forgiveness. Available online: https://studentaid.gov/manage-loans/forgiveness-cancellation/teacher (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Viviani, W., Brantlinger, A., & Grant, A. A. (2023). Teacher preparedness and retention. Teacher Education Quarterly, 50(3), 54–77. [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield, J., Banerjee, M., Waxman, H. C., Scott, T. P., & Capraro, M. M. (2021). Recruitment and retention of STEM teachers through the Noyce Scholarship: A longitudinal mixed methods study. Teaching and Teacher Education, 103, 103361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S. S., & Luft, J. A. (2015). Secondary science teachers’ beliefs and persistence: A longitudinal mixed-methods study. Journal of Science Teacher Education, 26(7), 619–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worsham, H. M., Friedrichsen, P., Soucie, M., Barnett, E., & Akiba, M. (2014). Recruiting science majors into secondary science teaching: Paid internships in informal science settings. Journal of Science Teacher Education, 25(1), 53–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahner, W., Chapin, S., Levine, R., He, L. A., & Afonso, R. (2019). Examining the recruitment, placement, and career trajectories of secondary mathematics teachers prepared for high-need schools. Teachers College Record, 121(2), 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G., & Zeller, N. (2016). A longitudinal investigation of the relationship between teacher preparation and teacher retention. Teacher Education Quarterly, 43(2), 73–92. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solis Rodriguez, J. A Systematic Review of the Recent Empirical Literature on Math and Science Teacher Recruitment and Retention. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15081073
Solis Rodriguez J. A Systematic Review of the Recent Empirical Literature on Math and Science Teacher Recruitment and Retention. Education Sciences. 2025; 15(8):1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15081073
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolis Rodriguez, Janet. 2025. "A Systematic Review of the Recent Empirical Literature on Math and Science Teacher Recruitment and Retention" Education Sciences 15, no. 8: 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15081073
APA StyleSolis Rodriguez, J. (2025). A Systematic Review of the Recent Empirical Literature on Math and Science Teacher Recruitment and Retention. Education Sciences, 15(8), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15081073





