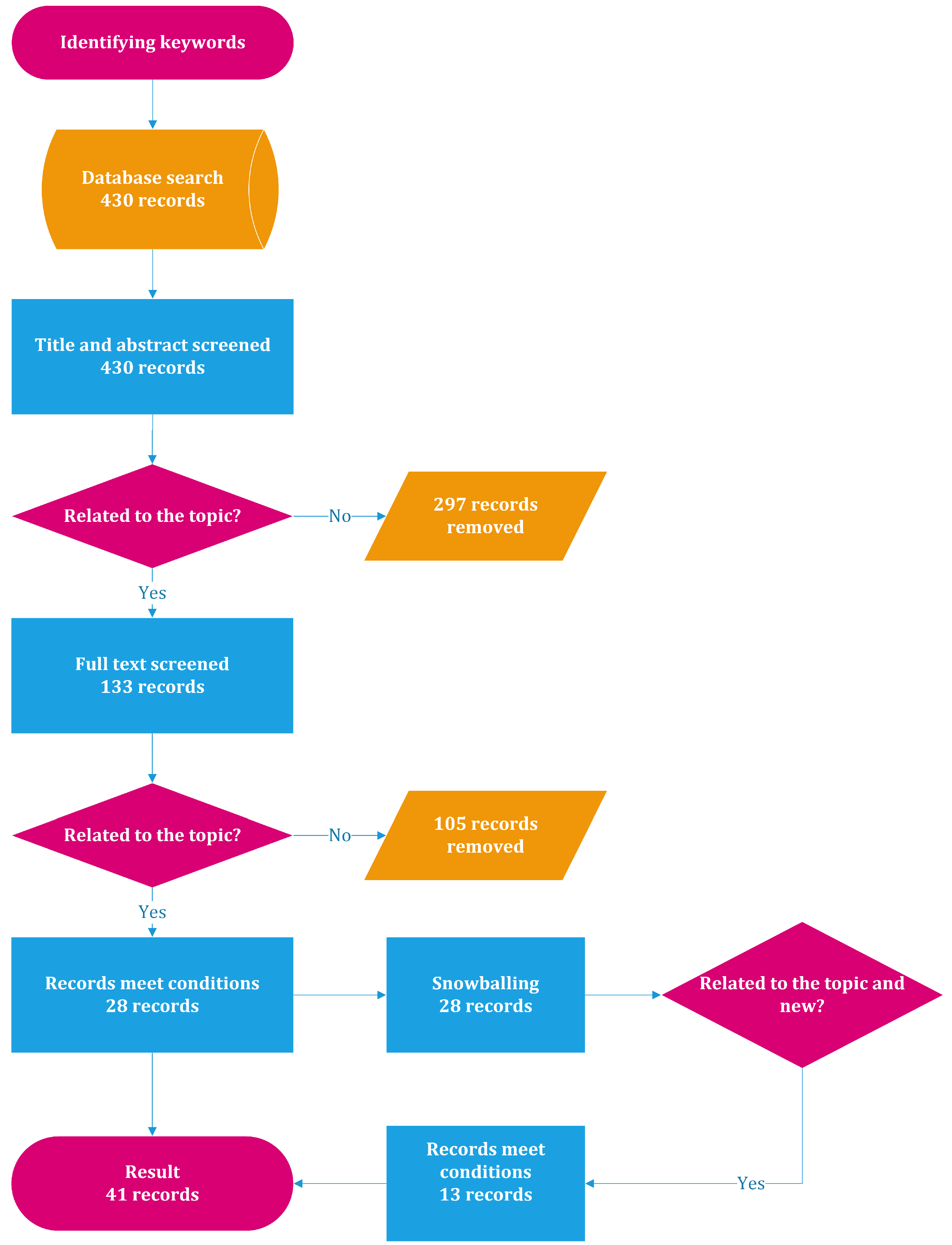
5.3. Answer to Research Question RQ3
As we have seen, UNO® and UNO-type games are becoming increasingly integrated into mathematics education. We also sought to answer the question of what role these games play in mathematics education. First, we review the information found in the records regarding the educational role of the game used.
The article of
Campbell (
1989) describes a collection of card games designed to help primary students practise basic maths facts. This early paper suggests that card games used in maths education can help students practise and reinforce basic maths facts in a fun and interactive way. The article emphasises that the games can involve elementary students of varying ability levels. The rules can be modified to align with the curriculum, and teachers can change the size and composition of the groups. The article concludes that card games with regular mathematics instruction can help teach and reinforce basic skills. Two years later,
McBride and Lamb (
1991) discusses the adaptation of existing popular games, such as UNO
®, for mathematical practise at the primary level. The authors suggested modifying the rules of UNO
® so that players throw out cards by forming equations or combinations instead of matching numbers or colours. It was mentioned that, in order to practise combinations involving two-digit numbers, adaptations of UNO
® allow two or more numbers to be used in sequence to create a larger number or operation. The article highlights that teacher-made maths games can be an effective way to practise specific maths skills. Fourteen articles cited the work of
McBride and Lamb (
1991) according to Google Scholar, but only one is relevant to the research topic:
Leonard and Tracy (
1993) collected and organised games to support mathematics learning for middle school students. Their paper includes a detailed table of maths-related games that meet the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) standards. According to the table, UNO
® meets the standards for problem-solving, mathematics as communication, mathematics as reasoning, and the topics of patterns and functions. The table suggests that UNO
® was a potential tool for teachers to reinforce maths skills in accordance with learning standards in the 1990s.
Baturo et al. (
2004) wrote about mathematics education for indigenous children in Australia and examined how games familiar to them could be incorporated into teaching. The authors observed that many indigenous children perform poorly on maths tests and recommend linking maths to children’s home and community experiences. The article presents several card games played by indigenous children. One of these is UNO
®. The original UNO
® cards were used during the game, but they were not played according to the original rules; instead, the deck was used as a teaching tool with new rules. According to the authors, UNO
® enables players to develop number recognition, counting, and strategic thinking; however, no test data are included in the article. The article highlights that incorporating such games can help children understand mathematical concepts and provide teachers with opportunities to assess children’s knowledge and improve teaching effectiveness.
Woodruff (
2009) conducted six UNO
®-based intervention sessions with second-grade students experiencing difficulties in mathematics, using both control and treatment groups. However, the results showed no statistically significant differences between the groups regarding addition and subtraction accuracy, cognitive strategy use, spatial ability, or place value knowledge. According to
Jumaroh et al. (
2022), the UNO
® game media plays a multifaceted role in education, primarily focused on enhancing the learning experience for students. Its introduction aims to improve students’ understanding of integer operations by making the learning process more enjoyable and engaging. By reducing boredom and promoting active participation, the UNO
® game medium positively impacts student learning outcomes and encourages them to become more independent learners. This practical and accessible tool also helps sharpen students’ counting skills, making it a valuable asset in mathematics education.
Numbered Heads Together (NHT) is an alternative questioning strategy which can be used to improve student performance in general education classrooms. During the NHT teaching method, students work in groups to solve a problem within a given time frame (
Revilla-Cuesta et al., 2020). The study of
Fitri et al. (
2020) examines the use of UNO
® cards in conjunction with the NHT cooperative learning model to improve students’ maths performance. UNO
® cards, with their numerical values, help students practise arithmetic operations. The authors used standard UNO
® decks for the maths problems, with the numbers on the cards serving as a basis for practising arithmetic operations. Only numbered cards were used during the experiment; action cards were not used. Research indicates that using UNO
® cards in the classroom increases student motivation and improves maths learning outcomes. In this context, the use of UNO
® cards within the NHT cooperative learning model contributes to active student participation and collaboration.
Special education programmes are common in primary schools to support students with learning disabilities or other needs. Using a quantitative approach, the study of
Syafitri (
2023) found that the UNO
® card game positively affected the ability of children with mild intellectual disabilities to recognise number symbols 1-10, effectively increasing this ability through engaging gameplay. UNO
® is not just a game but a tool that can serve as a practical, versatile alternative or complementary learning method to improve students’ learning abilities. The research study of
Grünke et al. (
2025) assesses the effectiveness of the pegword method in enhancing multiplication skills among students with maths difficulties. The pegword method is a mnemonic strategy that pairs numbers with rhyming words, creating both visual and verbal associations to aid memory. This method is designed for sixth-grade students who experience persistent learning challenges in mathematics. Before the intervention, the students played the UNO
® card game for 30 min during the baseline phase. Our interpretation is that this activity was included to allow students to start with a familiar task, potentially easing them into the session before tackling multiplication problems. Moreover, because UNO
® involves working with numbers, it may have provided a helpful warm-up for students struggling with maths, activating their number recognition and numerical skills before the multiplication test.
The original UNO
® game also offers a promising avenue in secondary and university mathematics education, in areas such as basic probability theory, algebra, and game theory, where students often face comprehension challenges. Its appeal lies in the ability to capture student interest and foster active participation, transforming learning from a passive reception of facts into an engaging exploration of mathematical concepts. Research indicates that integrating UNO
® cards as a learning medium can significantly increase mathematical thinking skills, paving the way for a more intuitive grasp of probability (
Meyrath et al., 2024;
Ziliwu et al., 2024).
Wulandari and Ambara (
2021) used the digital version of the UNO
® card game to develop number recognition and counting skills in preschoolers during the pandemic. According to the study, UNO
® cards can provide a solution to the challenges of online teaching because they are interactive and engaging, which helps to maintain children’s attention. The authors’ measurements suggest that interactive UNO
® cards can support the development of children’s cognitive abilities beyond number recognition and counting.
The U-Kids card game is a graphic-based educational tool designed to stimulate logical–mathematical intelligence in children aged 5–6 years, created by
Kholida et al. (
2020). The game incorporates colours, shapes, and numbers. It functions as a type of active learning game that encourages children to use strategic thinking. The game is designed to stimulate a child’s awareness of numbers, with an understanding of the concepts of less and more, arranging things in serial, categorical, and hierarchical ways, analysing objects quickly, understanding numeric symbols, and counting. Instead of numbers, geometric shapes (circle, triangle, square, and rectangle) are depicted on the base cards to represent different quantities, as shown in
Figure 7.
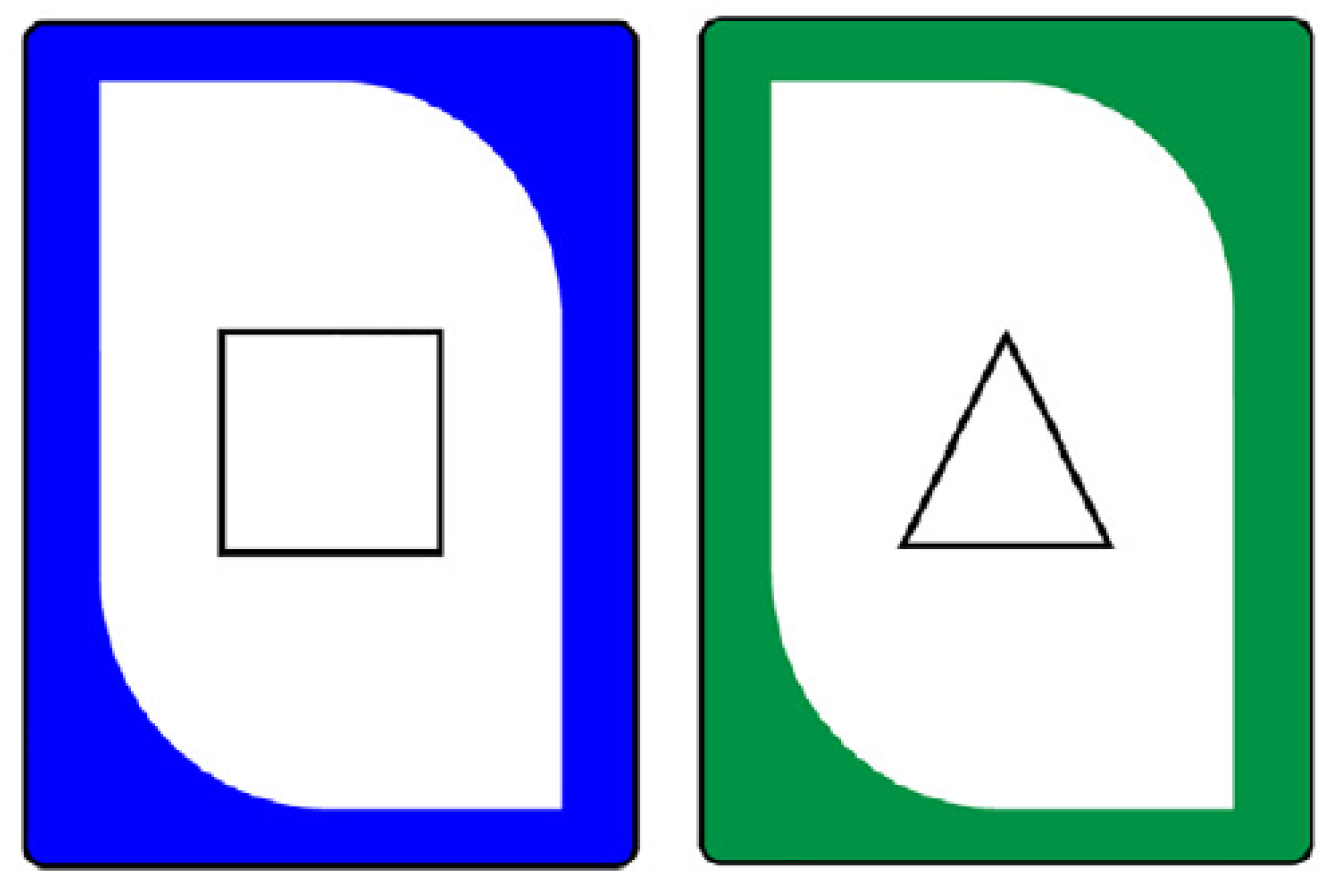
The Match It game is a shape and colour matching game at the preschool level (
Ramani & Scalise, 2020). It allowed researchers to tease apart the improvements in children’s numerical skills that could be attributed to practice with the numerical game, as opposed to other maths-related experiences. Additionally, because the game involved labelling shapes, it was hypothesised that playing it would improve children’s shape knowledge. According to
Scalise et al. (
2022), children who played the Match It matching game had significantly higher post-test scores on both shape naming and shape matching measures. In
Figure 8, two cards can be seen from the Match It deck.
The article by
Rahmatin and Khabibah (
2016) discusses the development of the UNO-type card game, called U-Math (UNO Mathematics), as a learning medium for integer operations at the primary school level. The card game was designed to provide students with a more engaging and enjoyable way to practise integer operations, addressing the students’ lack of ability in this area. The study involves testing the card game on 31 students and evaluating its effectiveness through observation, tests, and questionnaires. Research results indicated that the U-Math card game is a good learning medium that meets the goals. The game developed by
Chong et al. (
2022) (Intego, a combination of UNO
® and integers) is a tool to teach and learn integer operations. Their study suggests that using this non-digital card game can effectively improve students’ performance in integer operations and promote concrete mathematics instruction, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills, aligning with student-centred learning approaches. The Intego game allows students to think critically and discover how to treat the sign roles in integer operations. According to
Murtiana and Yulianto (
2025), the NumeriUNO game is a valuable tool to improve mathematics learning among primary school students. By integrating game-based elements, such as the familiar concept of UNO
® cards, NumeriUNO transforms traditional learning into an engaging and interactive experience. This approach not only captures students’ interest but also fosters a deeper understanding of the mathematical concept of multiplication. Through hands-on participation, teamwork, and healthy competition, NumeriUNO promotes a constructivist learning environment where students actively build their knowledge. Its effectiveness has been demonstrated through improved learning outcomes, increased student motivation, and positive feedback from both educators and learners, highlighting its potential to make mathematics more accessible and enjoyable for young students. The UN-MATH card game, developed by
Aprilia and Nugraheni (
2025), was designed to improve problem-solving skills, specifically in addition and subtraction, for elementary school students. This game-based learning approach promotes active participation and engagement, making the learning process more enjoyable and motivating. By focusing on mathematical story problems, the UN-MATH card game aids in the development of conceptual understanding.
The findings of
Suciati and Wahyuni (
2018) highlighted the challenges students face with fractions. They found that students had a concept error of 80.70%, a principle error of 13.16%, and a calculation error of 6.15% when adding fractions. These errors suggested that students struggle with understanding and applying fraction concepts and operations. To address the problem, one of the authors developed a UNO-type game. The article by
Suciati (
2020) details the UNO Matematika game which is an engaging method to teach fractions. The game aims to strengthen students’ understanding of fraction concepts.
Ulfah et al. (
2016) described the development of another UNO-type educational game. The primary goal of this new game was to help fourth-grade students understand and practise concepts related to units of length. The authors provided data supporting the effectiveness and feasibility of the developed UNO-type learning game. Expert evaluations and student evaluations indicated strong effectiveness, through ratings of student engagement and a high level of interest. Similarly,
Harlin and Arini (
2023) concluded that their UNO-type card game is an appropriate and effective tool for teaching weight units to fourth-grade students because it offers an engaging and interactive approach that improves learning outcomes.
The U-Math game has a multifaceted role in elementary mathematics (
Utami & Leonard, 2023). It fosters motivation, transforming mathematics into an enjoyable subject rather than an intimidating one. Through gameplay, students better understand mathematical principles, with the game serving as an engaging evaluation tool. U-Math also develops critical cognitive skills such as memory and problem-solving, all while contributing to a positive and stress-free learning environment. Its versatility extends to various mathematical topics, including integer arithmetic, measurement, geometry, fractions, and spatial reasoning, making it a comprehensive educational tool.
The thesis of
Anggraini (
2018) dealt with the development process and methodology of the U-Math (quadratic functions) game as an engaging and effective teaching tool for learning quadratic functions. The study highlighted the game’s effect on fostering participation, enhancing understanding, and positively influencing education. Students’ responses showed that the most important factors were learning motivation, positive character, language use, and design. The study by
Mayangsari and Mahardhika (
2019) explores using an UNO-type card game with mathematical questions to motivate secondary school students in learning maths. The game is an interactive tool, with the teacher supervising and facilitating the activity to encourage active problem-solving and engagement. Qualitative feedback indicates that students found this approach motivating and enjoyable, offering a fresh learning experience.
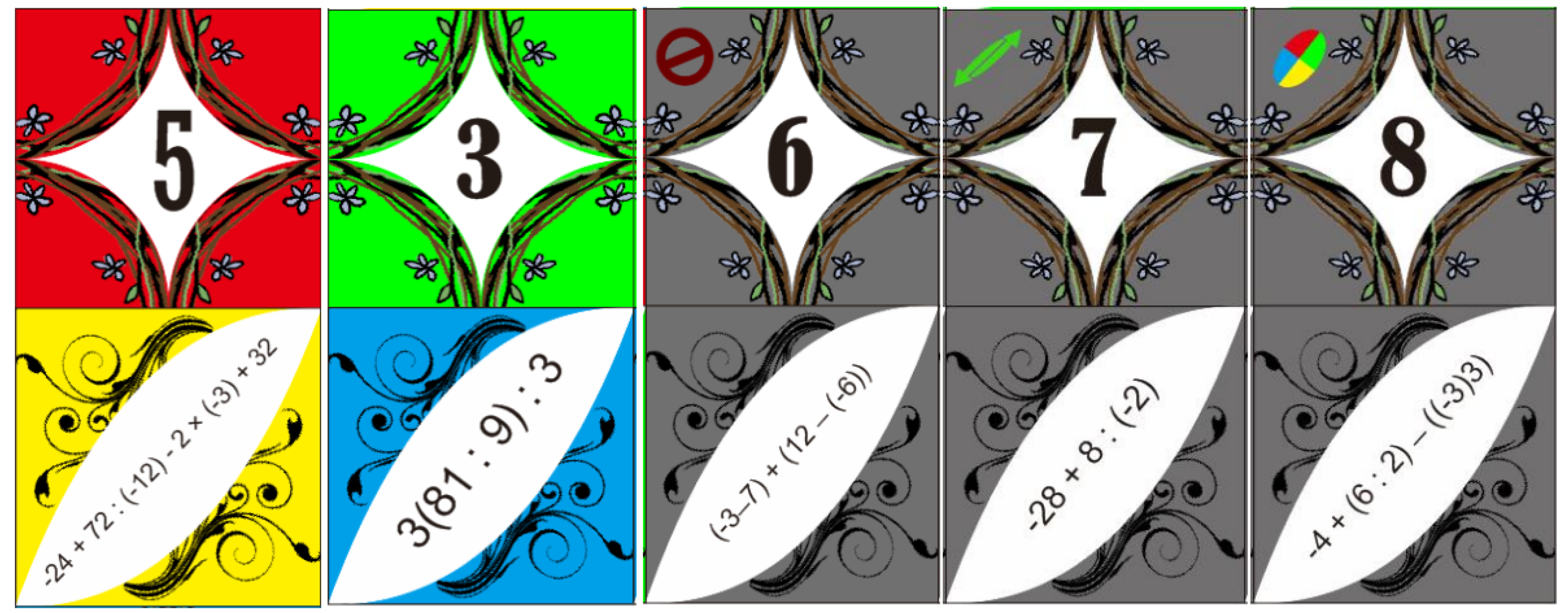
The great advantage of UNO-type games is that almost everyone knows the rules, so minimal time is needed to explain how to play. The research paper of
Srintin et al. (
2019) details the development and evaluation of the Umino game, a card game designed to teach integer operations (
Figure 9). Umino aims to provide an engaging and effective learning experience by leveraging the familiar mechanics of popular card games. A key aspect of Umino’s design is its deliberate connection to UNO
®. The gameplay structure of Umino mirrors that of UNO
®, with players taking turns matching cards based on specific characteristics. This familiar structure allows students to quickly grasp the rules and focus on the mathematical content.
Robiana and Handoko (
2020) developed the UnoMath card media designed to enhance mathematical communication skills and self-regulated learning. The authors employed a quantitative experimental approach, using a pre- and post-test design with a control group. Data collection involved tests to measure mathematical communication skills and questionnaires to assess self-regulated learning. The study found that applying UnoMath led to a statistically significant improvement in mathematical communication skills. Furthermore, the use of UnoMath also significantly enhanced self-regulated learning.
UNO
® Spin is a variation of the classic UNO
® card game that includes a spinning wheel. The wheel introduces a random element to the game, altering the rules or affecting players in various ways. The purpose of UNO
® Spin is to make the game more exciting and unpredictable, but the core gameplay remains similar to that of the original UNO
® (
Peña Pérez Negrón et al., 2023). The game typically includes action cards that force players to spin the wheel. The wheel might make players discard cards, draw more cards, skip their turn, or even swap hands with another player. The UNO
® Spin game also provides a directed learning experience, offering students the opportunity to discuss with each other (
Ridwan et al., 2024).
Najiah and Panggabean (
2021) created the UNO Spin Maths game because they identified a need for more engaging and varied mathematics learning tools in the topic of algebra. While maintaining core UNO
® Spin gameplay elements, such as matching cards and using a spinning wheel to introduce dynamic changes, the authors differentiated their version by integrating algebraic equations on the cards. This key difference transforms the game from purely recreational to an educational tool specifically designed for junior high school students. By blending entertainment with learning, the UNO Spin Maths game offers several advantages, including increased student engagement, active participation, improved understanding of algebraic concepts, collaborative learning opportunities, and a multi-sensory learning experience.
The UNO-type game by
Sulisawati and Murtinasari (
2018), the GEO cards, is a learning medium for the topic of quadrilateral flat shapes. It is intended to make learning more engaging, practical, and effective. The validation process was detailed in the article, which showed the establishment of the credibility and reliability of the GEO cards as a valuable educational resource. The educational game U-Math, developed by
Ficky (
2021), aims to reinforce mathematical concepts related to the volume and surface area of three-dimensional shapes. U-Math helps to consolidate understanding of geometric formulas and concepts while developing problem-solving skills and strategic thinking. Teachers have found the game to be extremely effective, and students have found it very practical. Another UNO-type game with a geometry topic is the Uno Math game. It is a practical and effective tool for mathematics education, particularly for understanding the concept of the area of flat shapes (
Harahap et al., 2022). It aims to improve student engagement, offering a more interactive and enjoyable way to learn mathematics. By implementing the Uno Maths game, educators can overcome negative perceptions of mathematics, fostering a more active and interesting learning environment. Ultimately, the game functions as a medium to facilitate deeper understanding and improve student performance in mathematics. Similarly, the role of the UNO Matematika game in education is to improve the understanding of mathematical concepts among junior high school students on the topic of financial mathematics. This learning medium was designed to make learning more engaging and effective (
Anita et al., 2022). The study of
Lutfi et al. (
2024) identified several key benefits of Uno Math. It increases student motivation, makes learning more enjoyable, aids in understanding mathematical formulas, and generally has a positive impact on the learning process. The use of Uno Math helps to sharpen students’ learning while reducing boredom and attracting their attention. The research indicates that Uno Math can be a valuable tool for teachers to facilitate student learning and generate motivation in mathematics. The results also suggest that female students tend to exhibit higher levels of math learning motivation when using Uno Math compared to male students.
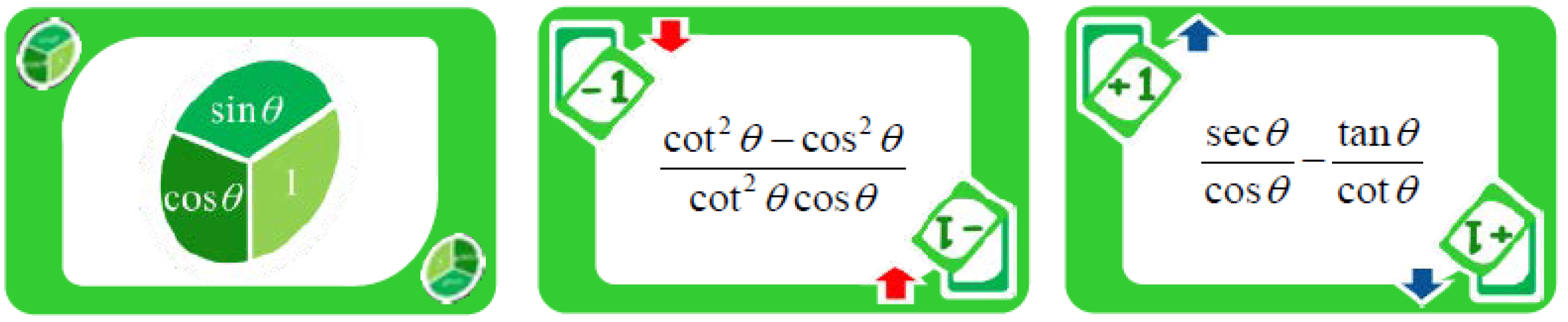
The TrigOno card game is a valuable tool in education by fostering mastery learning, particularly in trigonometry (
Fuentes, 2024). It addresses the common issue of limited practice opportunities that hinder students’ progress in mathematics. In
Figure 10, three cards can be seen from the TrigOno deck.
The game’s design promotes engagement, motivation, and repeated practise of essential skills, leading to better retention and conceptual understanding. As a non-digital, game-based learning intervention, TrigOno offers a remedial approach that enhances social interaction and encourages students to develop problem-solving strategies. By improving computational reasoning, mathematical thinking, and self-efficacy, TrigOno aims to minimise negative perceptions of mathematics and create a more enjoyable and effective learning experience.
Kurniati et al. (
2025) focused on enhancing mathematics education through contextual learning. Their study aimed to make maths more relatable and engaging for local students by developing UNO-type cards linked to a traditional Indonesian game. Instead of abstract concepts, the card game provides a practical, real-world connection to mathematical operations. The integration of a familiar cultural element into the learning process was expected to boost student motivation and facilitate better understanding, thus bridging the gap between theoretical maths and its practical application within the students’ environment. The developed UNO-type game was designed to help children practise maths operations in a familiar and enjoyable setting, showcasing the benefits of contextual learning. The study of
Ahsan et al. (
2024) indicates that incorporating the Smart Cards game, which is a UNO-type learning medium, into the learning process leads to increased student engagement and enthusiasm, making the maths subject more approachable. The Smart Card game helps visualise abstract mathematical concepts, making them easier to understand and remember, as students can observe the cards, hold them in their hands, and analyse their content. By offering interactive activities and immediate feedback, they allow students to actively participate in their learning and develop a deeper conceptual grasp. So, using the Smart Card game contributes to a more effective and enjoyable learning environment, improving student mathematics performance.
Genius Up! is an educational project designed to promote scientific and technological literacy among students, particularly those who are potentially entering university. It uses gamification, specifically serious video games and adapted card games, to make science learning more engaging and accessible. The project aims to expand knowledge transfer in areas such as mathematics, physics, chemistry, and biology through these engaging and interactive methods (
Perales et al., 2019). The Maze Cards non-digital game was developed at the Universitat de les Illes Balears (UIB) in Spain, as part of the Genius Up! project. The Maze Cards game combines UNO
® with questions related to mathematics, physics, chemistry, and biology, reinforcing knowledge entertainingly. Maze Cards retains the basic game mechanics of UNO
®, but the theme, educational purpose, questions, and special codes differ significantly from traditional UNO
®.
LimStorm integrates learning into the gameplay by requiring players to calculate the limit of a sequence on the card before discarding it, reinforcing understanding of limits and providing immediate feedback (
Szilágyi & Körei, 2021). LimStorm aims to address the challenge of keeping students engaged in mathematics by introducing a fun, interactive approach to learning, which complements traditional teaching methods in university and can be used in practical classes, consultation sessions, workshops, or even at home (
Szilágyi & Körei, 2022). Through gameplay, students not only practise calculating limits but also develop logical thinking, memory, problem-solving, and teamwork skills. LimStorm seeks to improve motivation and create a more successful learning experience for higher education students.
Figure 11 shows the red cards from the LimStorm deck.
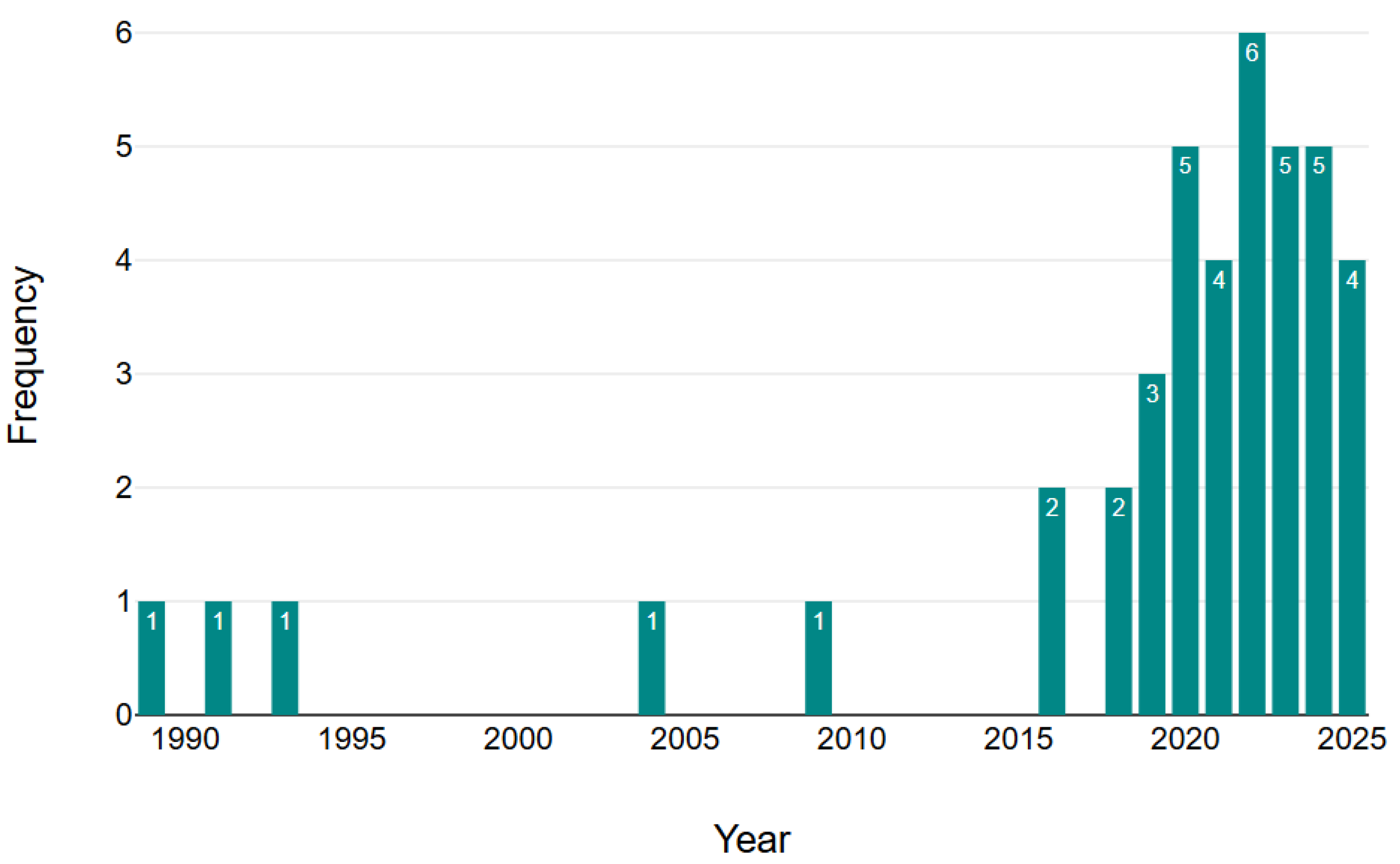
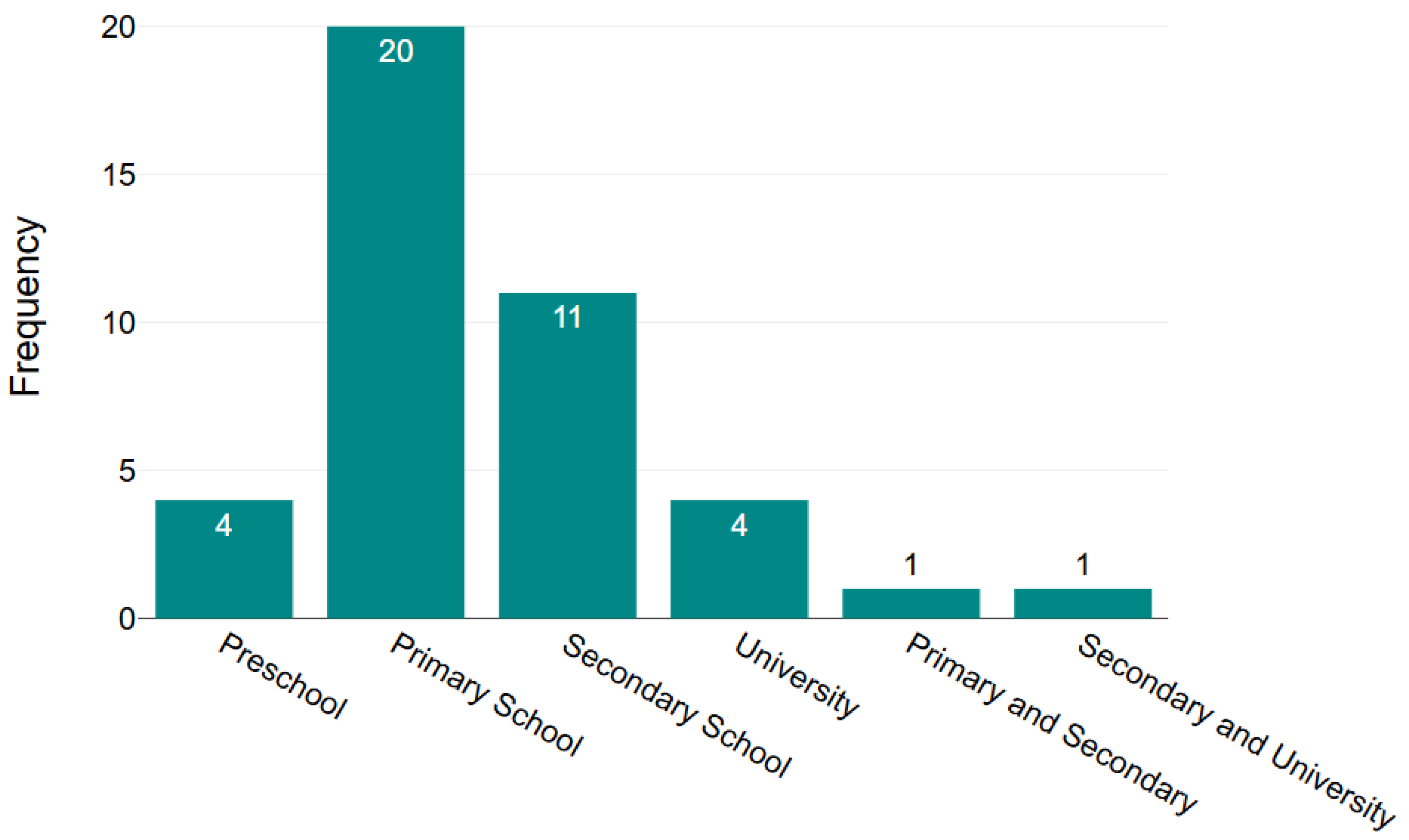
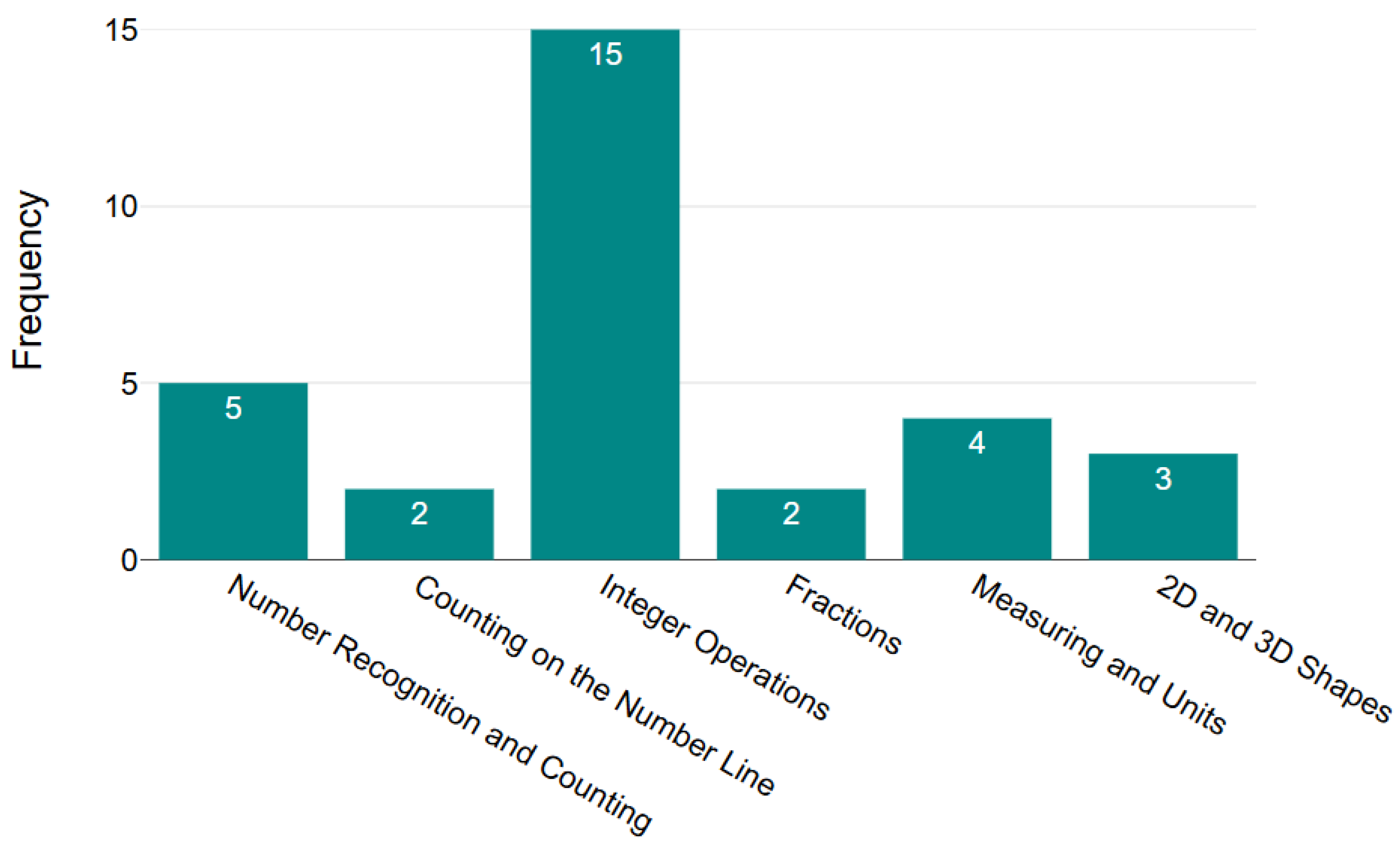
Based on the analysed 41 records, we answer research question RQ3. The primary role of UNO® and UNO-type games in mathematics education is to make learning more attractive and effective for students. These games transform learning into engaging, fun, and interactive experiences that help students understand and reinforce mathematical concepts at various levels. They use the familiar mechanics of UNO® cards, but with mathematical content on the cards, providing both entertainment and educational value. During gameplay, students can strengthen their understanding of concepts such as number recognition, arithmetic, algebra, geometry, fractions, and probability, while simultaneously developing critical skills such as problem solving, independent learning, collaboration, and reasoning. These games promote inquiry-based learning environments that focus on students and bridge the gap between abstract theoretical ideas and tangible applications in the real world. Their versatility allows for adaptation to diverse topics and educational contexts, including special education, community-based learning, and digital platforms. In general, UNO® and UNO-type games serve as effective tools to foster deeper mathematical understanding, increase motivation, and improve active participation, making mathematics education more engaging and meaningful for learners.