Mixed Reality Laboratory for Teaching Control Concepts: Design, Validation, and Implementation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design of MR Laboratories
2.1. Platform Design
- As in simulation software, the platform must be able to emulate the behavior of different electromechanical systems. The input and output variables should be available for measurement and control. Plant emulation allows students to control different systems on their own computers (unlike physical labs).
- As in hands-on laboratories, the platform must allow to control and monitor the system variables through external electronic devices so that interaction between the virtual system and the real world is possible. This feature helps the student to practice the implementation of controllers in real hardware (unlike virtual labs).
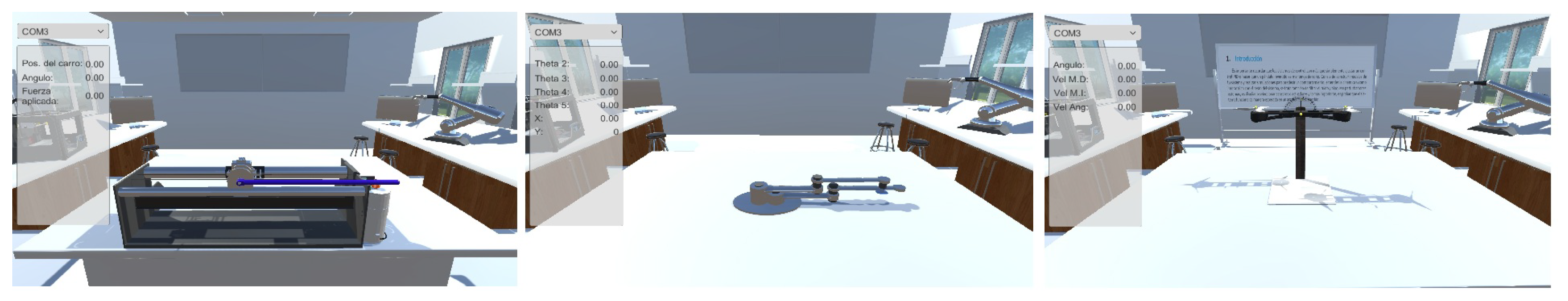
- The platform enables virtual electromechanical systems to be visualized with different technologies, such as virtual laptops and virtual-reality MR headsets (which may increase student motivation).
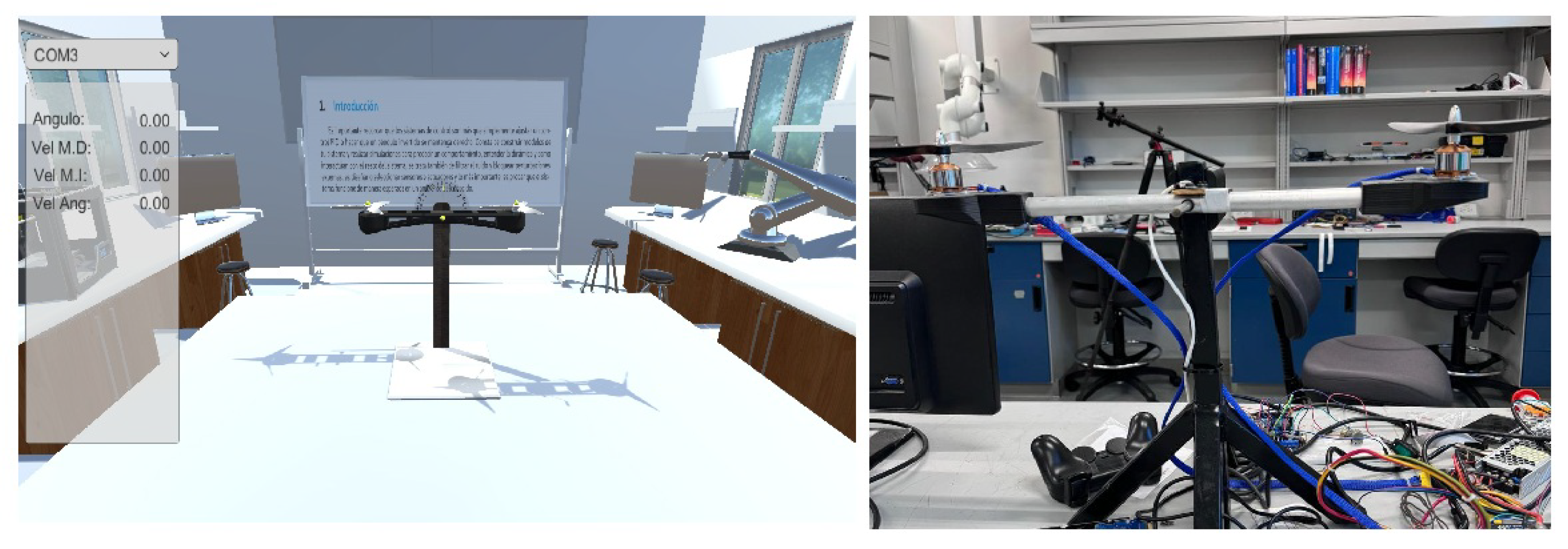
2.2. Virtual Propeller-Based Seesaw System
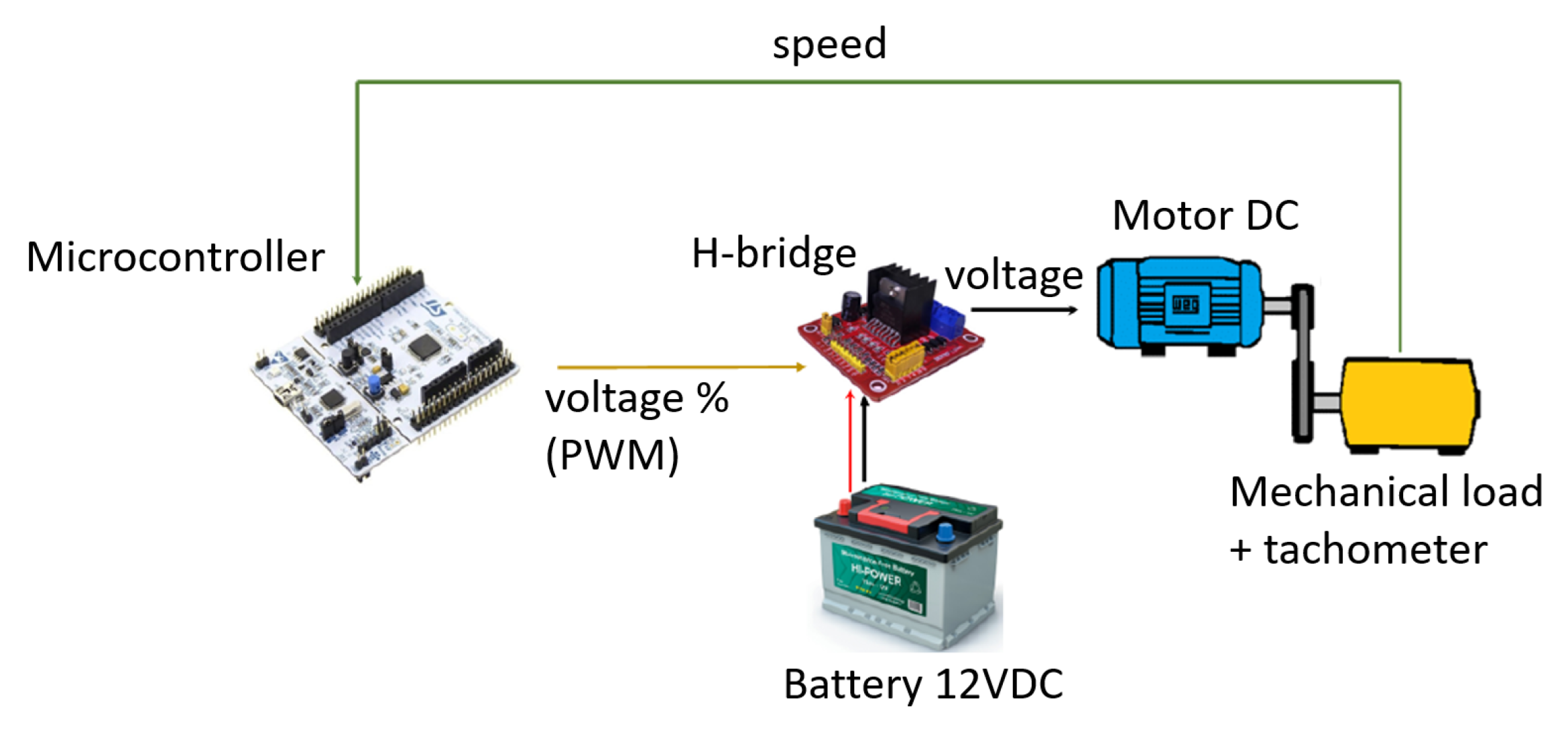
2.3. Real Propeller-Based Seesaw System
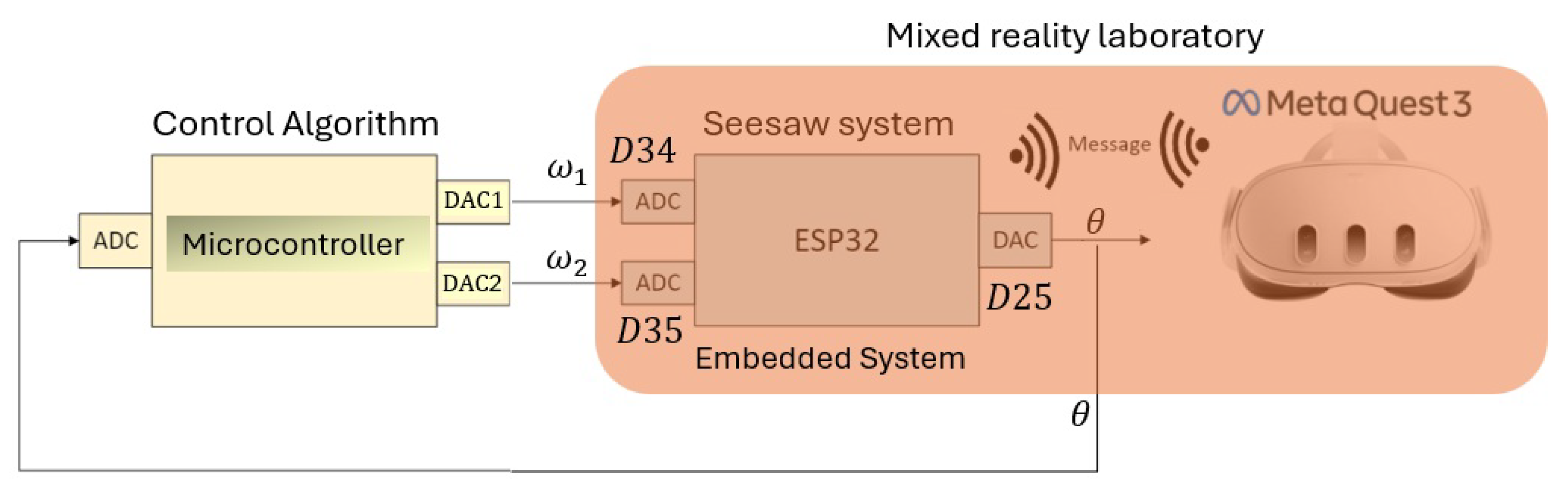
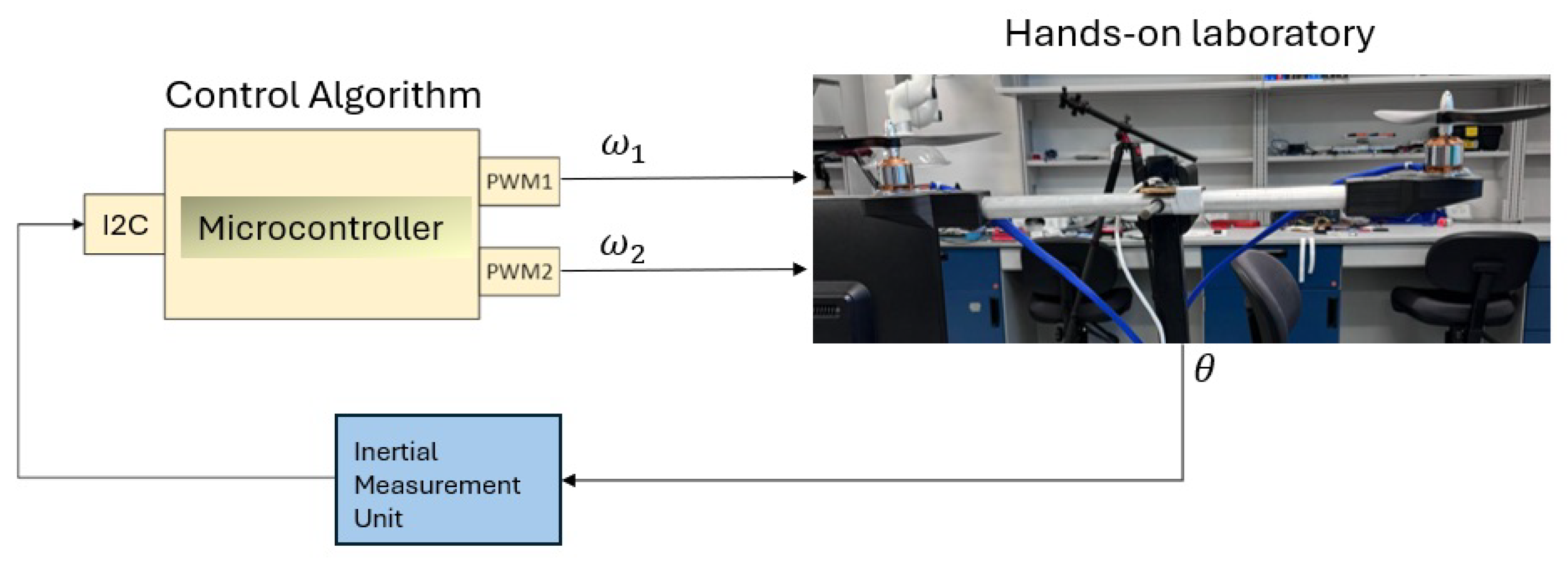
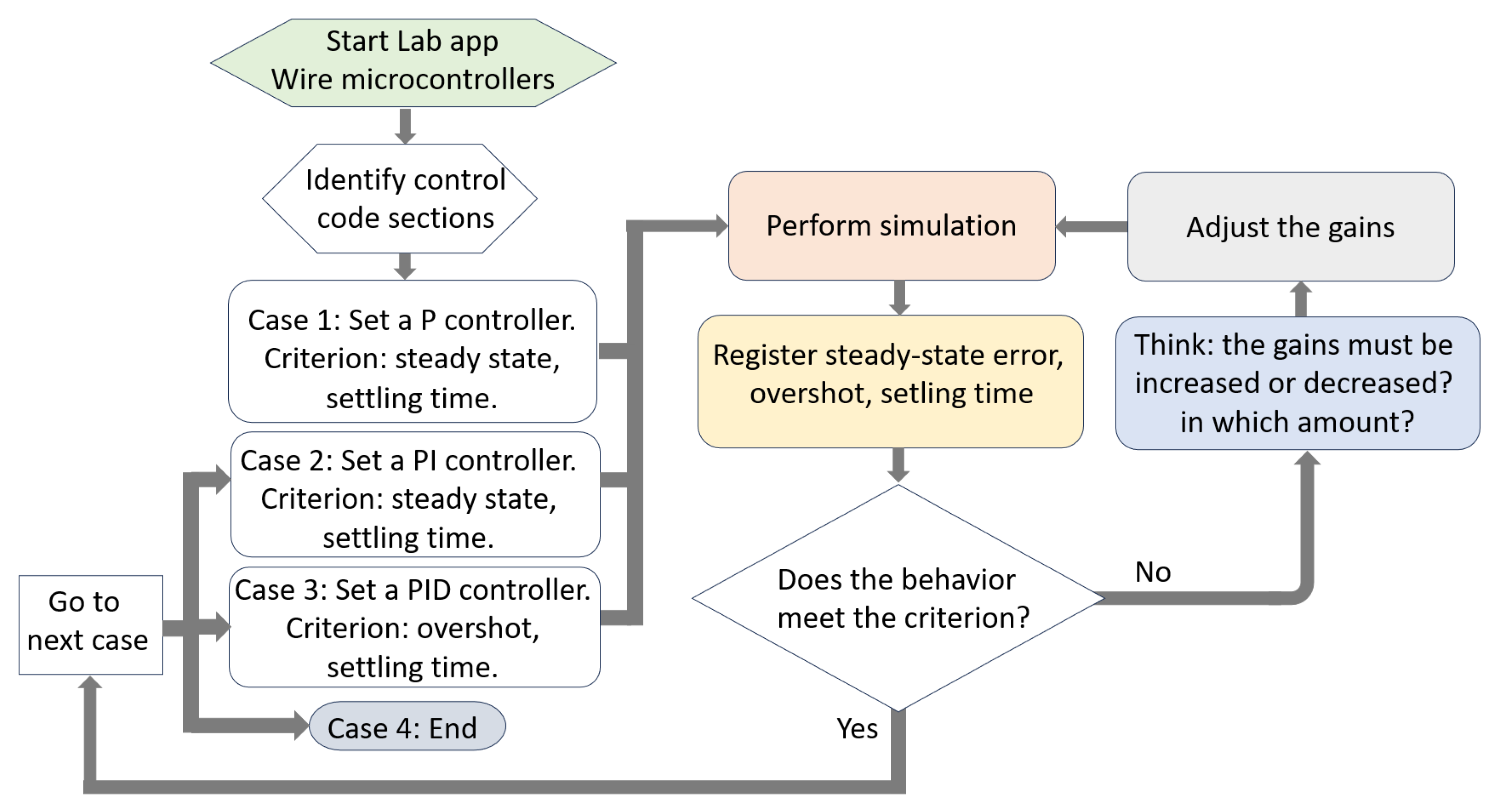
3. Validation for Control Implementation: MR Lab vs. Hands-On Lab
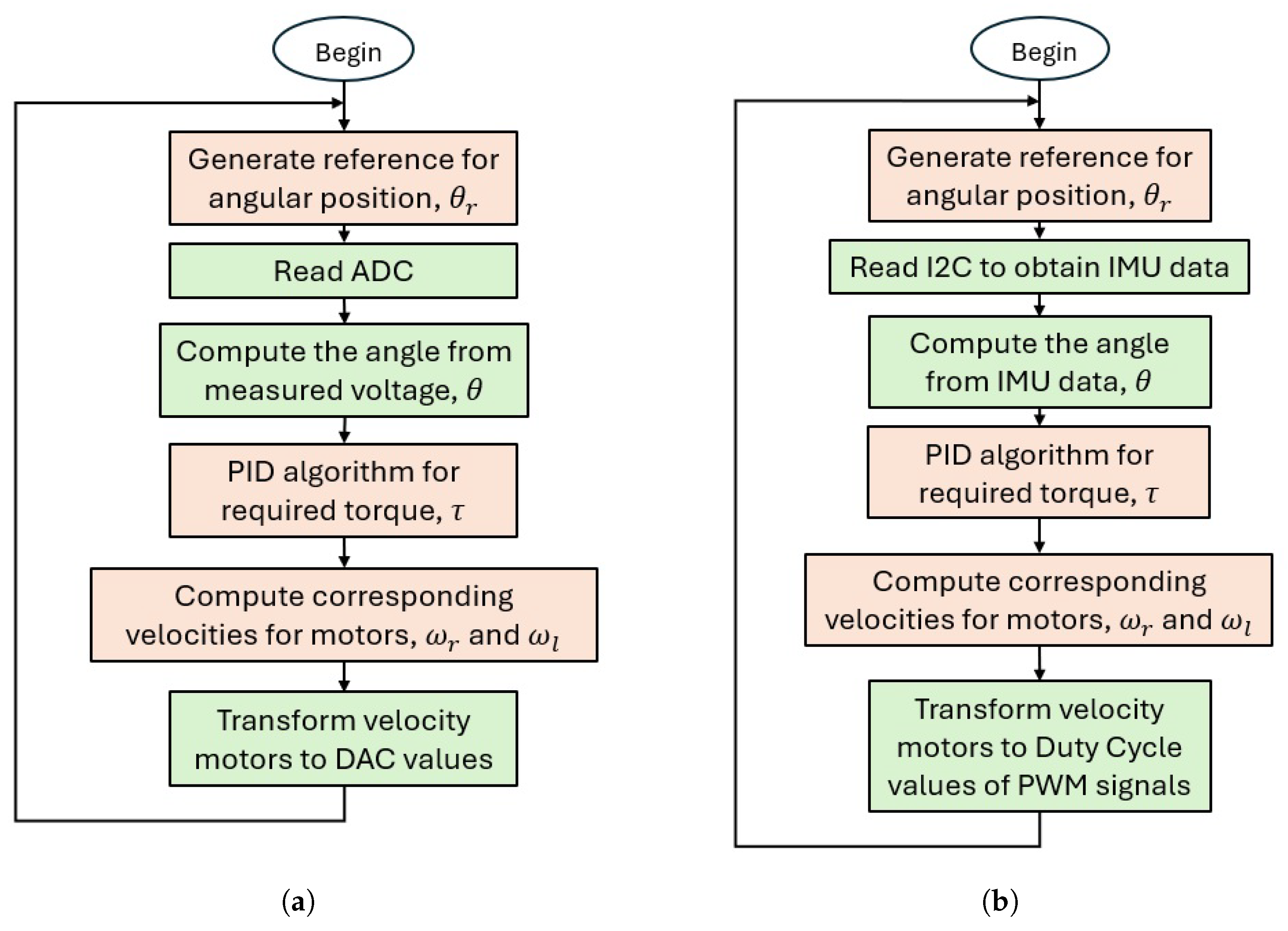
3.1. Control Algorithm for the MR Laboratory
| Listing 1. Arduino code fragment for PID control. |
| time = time + dt; // Angular position reference if (time < 15) { thetaref = -20 / 57.2956; } else if (time >= 15 && time < 25) { thetaref = -10 / 57.2956; } else if (time >= 25 && time < 35) { thetaref = 0; } else if (time >= 35 && time < 45) { thetaref = 10 / 57.2956; } else { thetaref = 20 / 57.2956; } // Read sensors :(0 V, 5 V)->(-pi/2, pi/2) theta=1.5708∗((float(analogRead(A0))-512))/511 + 0.0349; // PID Controller error = thetaref - theta; der_e = (error - error1) / dt; error1 = error; int_e = int_e + error ∗ dt; m = Kp ∗ error + Ki ∗ int_e + Kd ∗ der_e; Torque = m; // Decoupling (Thrust, Torque) -> (w1, w2) radical1 = (Thrust ∗ 0.5 + Torque / (2 ∗ L)) / alpha; radical2 = (Thrust ∗ 0.5 - Torque / (2 ∗ L)) / alpha; if (radical1 < 0) { radical1 = 0; } if (radical2 < 0) { radical2 = 0; } w1 = sqrt(radical1); w2 = sqrt(radical2); // PWM signals Output1 = int(w1 ∗ 255 / 5); Output2 = int(w2 ∗ 255 / 5); if (Output1 > 255) { Output1 = 255; } if (Output2 > 255) { Output2 = 255; } analogWrite(9, Output1); analogWrite(10, Output2); |
3.2. MR Lab Validation: Implementing the Control Algorithm in the Real Seesaw System
4. Implementation on a Learning Experience: Measuring Motivation and Learning Outcomes
- A pre-test for evaluating the previous knowledge of the students and using it to form groups of students to avoid biased results of the learning outcome measure after using the MR labs.
- The laboratory practice for the MR labs was implemented following a guide specially designed for this purpose, which implements Kolb’s cycle.
- A post-test designed by a collegiate group of subject matter experts was administered to measure the students’ ability to implement a PID control.
- An Intrinsic Motivation Inventory (a well-established test for assessing motivation in educational interventions) was administered to students after they used the MR laboratory.
4.1. Contextualization
- Industrial Automation.
- Modeling and Automation.
- Design of Control Systems.
- Analysis of Control Systems.
4.2. Practice Design Based on Kolb’s Experiential Learning Cycle
4.3. Student Experience Using the MR Laboratories
| Listing 2. STM32 code fragment for PID control. |
| // Reference signal if (t < 6000) { thetaref = -20 / 57.2956; } else if (t < 12000) { thetaref = 0 / 57.2956; } else if (t < 18000) { thetaref = 20 / 57.2956; } else { t = 0; } // Read angle value with ADC // Start ADC conversion ADC (pag. 266) ADC1->CR |= ADC_CR_ADSTART; // Wait for finish conversion (pag. 247) while ((ADC1->ISR & ADC_ISR_EOC) == 0); // Read channel 3 (pag. 273) analogRead3 = ADC1->DR; // Scaling from (0 V, 3.3 V) -> (-pi/4, pi/4) radians theta = 0.7854 * (analogRead3 - 2048) / 2048; // PID Controller error = thetaref - theta; derror = (error - error_1) / dt; integral = integral + error * dt; Torque = Kp * error + Kd * derror + Ki * integral; error_1 = error; // Decoupling (Thrust, Torque) -> (w1, w2) radical1 = (Thrust * 0.5 + Torque / (2 * L)) / alpha; radical2 = (Thrust * 0.5 - Torque / (2 * L)) / alpha; if (radical1 < 0) { radical1 = 0; } if (radical2 < 0) { radical2 = 0; } w1 = sqrt(radical1); w2 = sqrt(radical2); Output1 = (w1 * 255 / 3.3); Output2 = (w2 * 255 / 3.3); if (Output1 > 255) { Output1 = 255; } if (Output2 > 255) { Output2 = 255; } TIM3->CCR4 = Output1; TIM3->CCR3 = Output2; |
4.4. Results on Motivation
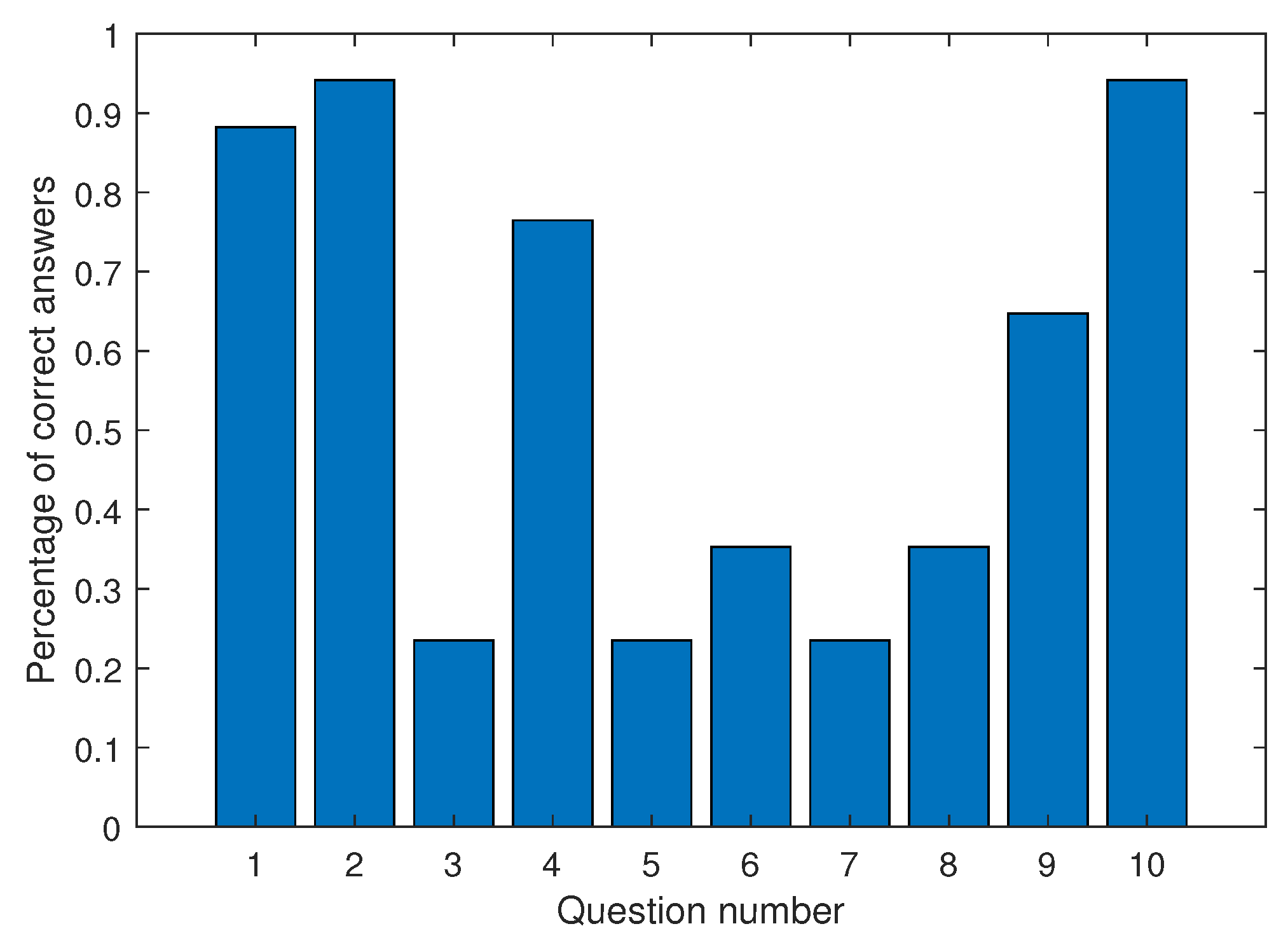
4.5. Results on Learning Control Concepts
- PID control: Q1 and Q6 ask to identify the type of controller implemented by the pseudo-code and the most relevant term in the implemented controller.
- Sampling time: Q2, Q3, and Q10 ask to identify the sampling time, determine the consequences of modifying the sampling time, and determine the number of control cycles per second.
- Noise effects: Q4 and Q8 ask about the influence of measurement noise and the effect of high-frequency noise on the PID control terms.
- Control modifications: Q5 and Q7 ask about the pseudo-code lines to be replaced if a different control law is required (the control law is given in the question in continuous time) and the consequences of replacing the control law by a proportional controller with positive gain.
- Control constraints: Q9 asks about how to implement control action bounds.
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MR | Mixed Reality |
| PID | Proportional–Integral–Derivative |
| ARCS | Attention, Relevance, Confidence, and Satisfaction |
| IMI | Intrinsic Motivation Inventory |
| CAD | Computer-Aided Design |
| PLC | Programmable Logic Controller |
| ADC | Analog-to-Digital Converter |
| DAC | Digital-to-Analog Converter |
| PWM | Pulse Width Modulation |
| ESC | Electronic Speed Controller |
| IMU | Inertial Measurement Unit |
References
- Abdulwahed, M., & Nagy, Z. K. (2009). Applying kolb’s experiential learning cycle for laboratory education. Journal of Engineering Education, 98(3), 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebersold, M., Voepel-Lewis, T., Cherara, L., Weber, M., Khouri, C., Levine, R., & Tait, A. R. (2018). Interactive anatomy-augmented virtual simulation training. Clinical Simulation in Nursing, 15, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaleh, S., Tepljakov, A., Köse, A., Belikov, J., & Petlenkov, E. (2022). ReImagine lab: Bridging the gap between hands-on, virtual and remote control engineering laboratories using digital twins and extended reality. IEEE Access, 10, 89924–89943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés-Cruz, C., & Villegas-Cortez, J. (2019). A smartphone-based augmented reality system for university students for learning digital electronics. Computer Applications in Engineering Education, 27(3), 615–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, E., Winkler, A., Tucker, E., Qian, L., Doswell, J., Navab, N., & Kazanzides, P. (2018, July 18–21). Can mixed-reality improve the training of medical procedures? 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC) (pp. 4065–4068), Honolulu, HI, USA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, F. A., Alsaeed, A. S., Sulaiman, S., Ariffin, M. K. A. M., & Al-Hakim, M. F. (2020). Mixed reality improves education and training in assembly processes. Journal of Engineering & Technological Sciences, 52(4), 598–607. [Google Scholar]
- Barsom, E. Z., Graafland, M., & Schijven, M. P. (2016). Systematic review on the effectiveness of augmented reality applications in medical training. Surgical Endoscopy, 30(10), 4174–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrakceken, M. K., & Arisoy, A. (2013). An educational setup for nonlinear control systems: Enhancing the motivation and learning in a targeted curriculum by experimental practices [Focus on Education]. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 33(2), 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondin, A., & Zammit, J. P. (2025). Education 4.0 for industry 4.0: A mixed reality framework for workforce readiness in manufacturing. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction, 9(5), 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsci, S., Lawson, G., & Broome, S. (2015). Empirical evidence, evaluation criteria and challenges for the effectiveness of virtual and mixed reality tools for training operators of car service maintenance. Computers in Industry, 67, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, R. R., & Arbesú, R. S. (2015). Augmented reality in automation. Procedia Computer Science, 75, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-M., Li, M.-C., & Tu, C.-C. (2024). A mixed reality-based chemistry experiment learning system to facilitate chemical laboratory safety education. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 33(4), 505–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Belen, R. A. J., Nguyen, H., Filonik, D., Favero, D. D., & Bednarz, T. (2019). A systematic review of the current state of collaborative mixed reality technologies: 2013–2018. AIMS Electronics and Electrical Engineering, 3(2), 181–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edward McAuley, T. D., & Tammen, V. V. (1989). Psychometric properties of the intrinsic motivation inventory in a competitive sport setting: A confirmatory factor analysis. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport, 60(1), 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, J. A., & Kapila, V. (2017). Mixed-reality learning environments: Integrating mobile interfaces with laboratory test-beds. Computers & Education, 110, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavish, N., Gutiérrez, T., Webel, S., Rodríguez, J., Peveri, M., Bockholt, U., & Tecchia, F. (2015). Evaluating virtual reality and augmented reality training for industrial maintenance and assembly tasks. Interactive Learning Environments, 23(6), 778–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Franco, M., Pizarro, R., Cermeron, J., Li, K., Thorn, J., Hutabarat, W., Tiwari, A., & Bermell-Garcia, P. (2017). Immersive mixed reality for manufacturing training. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grévisse, C. (2022, October 17–21). Flash, who? On the obsolescence of digital technology and its impact on e-learning applications: A case study. 2022 XVII Latin American Conference on Learning Technologies (LACLO) (pp. 1–7), Armenia, Colombia. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-de Menéndez, M., Vallejo Guevara, A., & Morales-Menendez, R. (2019). Virtual reality laboratories: A review of experiences. International Journal on Interactive Design and Manufacturing, 13(3), 947–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jailly, B., Gravier, C., Preda, M., & Fayolle, J. (2011). Interactive mixed reality for collaborative remote laboratories. In Proceedings of the third international acm workshop on multimedia technologies for distance learning (pp. 1–6). Association for Computing Machinery. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, D. P., Mantri, A., & Horan, B. (2021). A framework utilizing augmented reality to enhance the teaching–Learning experience of linear control systems. IETE Journal of Research, 67(2), 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, D. A. (2014). Experiential learning: Experience as the source of learning and development. FT Press. [Google Scholar]
- Kucera, E., Haffner, O., & Leskovský, R. (2018, January 31–February 3). Interactive and virtual/mixed reality applications for mechatronics education developed in unity engine. 2018 Cybernetics & Informatics (K & I) (pp. 1–5), Lazy pod Makytou, Slovakia. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J., & Bohuslava, J. (2018, January 31–February 3). Augmented reality as an instrument for teaching industrial automation. 2018 Cybernetics & Informatics (K&I) (pp. 1–5), Lazy pod Makytou, Slovakia. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, D., Terkowsky, C., Varney, V., & Boehringer, D. (2023). Between hands-on experiments and Cross Reality learning environments—Contemporary educational approaches in instructional laboratories. European Journal of Engineering Education, 48(5), 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejías Borrero, A., & Andújar Márquez, J. (2012). A pilot study of the effectiveness of augmented reality to enhance the use of remote labs in electrical engineering education. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 21, 540–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, J. A., & Gonzalez, E. J. (2011). Implementing motivational features in reactive blended learning: Application to an introductory control engineering course. IEEE Transactions on Education, 54(4), 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz de la Peña, D., Domínguez, M., Gomez-Estern, F., Reinoso, O., Torres, F., & Dormido, S. (2022). Overview and future trends of control education. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 55(17), 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D., Bruns, F. W., Erbe, H.-H., Robben, B., & Yoo, Y.-H. (2007). Mixed reality learning spaces for collaborative experimentation: A challenge for engineering education and training. International Journal of Online Engineering, 3(4). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeh, S., Shanab, S. A., Anabtawi, M., & Hodrob, R. (2013). A remote engineering lab based on augmented reality for teaching electronics. International Journal of Online Engineering (iJOE), 9(S5), 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, S., Wi, Y., Invernizzi, D., Cescon, M., & Lovera, M. (2024). Experiential learning in automatic control using quadrotor UAVs. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 58(16), 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, E., Heijligers, B., de Kievith, J., Razafindrakoto, X., van Oosterhout, R., Santos, C., Mayer, I., & Louwerse, M. (2016, September 7–9). Design for collaboration in mixed reality: Technical challenges and solutions. 2016 8th International Conference on Games and Virtual Worlds for Serious Applications (VS-GAMES) (pp. 1–7), Barcelona, Spain. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahok, S. A., Oneda, H., Osawa, S., & Ozaki, K. (2019). Motivation system for students to learn control engineering and image processing. Journal of Robotics and Mechatronics, 31(3), 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, R. M. (2016). Experiential learning in control systems laboratories and engineering project management [Doctoral dissertation, University of Illinois—Urbana-Champaign]. Available online: https://dissertation.com/abstract/2071125 (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Rodriguez, J., Esparragoza, I. E., & Ocampo, J. R. (2017, June 25–28). Comparison of intrinsic motivation of freshmen engineering students as they participate in a multinational design project. 2017 ASEE Annual Conference & Exposition, Columbus, OH, USA. Available online: https://peer.asee.org/28055 (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Rossiter, J., Zakova, K., Huba, M., Serbezov, A., & Visioli, A. (2020). A first course in feedback, dynamics and control: Findings from 2019 online survey of the international control community. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 53(2), 17264–17275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval Pérez, S., Gonzalez Lopez, J. M., Villa Barba, M. A., Jimenez Betancourt, R. O., Molinar Solís, J. E., Rosas Ornelas, J. L., Riberth García, G. I., & Rodriguez Haro, F. (2022). On the use of augmented reality to reinforce the learning of power electronics for beginners. Electronics, 11(3), 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaf, F. M., Paladini, S., & Pereira, C. E. (2012a, April 17–20). 3D AutoSysLab prototype. 2012 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON) (pp. 1–9), Marrakech, Morocco. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaf, F. M., Paladini, S., & Pereira, C. E. (2012b). 3D AutoSysLab prototype—A social, immersive and mixed reality approach for collaborative learning environments. International Journal of Engineering Pedagogy (iJEP), 2(2), 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selek, M., & Kıymaz, Y. E. (2020). Implementation of the augmented reality to electronic practice. Computer Applications in Engineering Education, 28(2), 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G., Mantri, A., Sharma, O., Dutta, R., & Kaur, R. (2019). Evaluating the impact of the augmented reality learning environment on electronics laboratory skills of engineering students. Computer Applications in Engineering Education, 27(6), 1361–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S., Wang, R., Zhou, R., Chen, Z., & Zhou, F. (2023). The effectiveness of virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality training in total hip arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research, 18(1), 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghian, A., Abo-Zahhad, M., Sayed, M. S., & Abd El-Malek, A. H. (2023). Virtual and augmented reality in biomedical engineering. Biomedical Engineering Online, 22(1), 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuli, N., Singh, G., Mantri, A., & Sharma, S. (2022). Augmented reality learning environment to aid engineering students in performing practical laboratory experiments in electronics engineering. Smart Learning Environments, 9(1), 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, H., Heradio, R., Donoso, M., & Farias, G. (2023). Teaching automation with Factory I/O under a competency-based curriculum. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 82(13), 19221–19246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, D., Extremera, J., Rubio, M. P., & Dávila, L. P. (2019). Meaningful learning through virtual reality learning environments: A case study in materials engineering. Applied Sciences, 9(21), 4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, D., Extremera, J., Rubio, M. P., & Dávila, L. P. (2020). The technological obsolescence of virtual reality learning environments. Applied Sciences, 10(3), 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanasin, W., Chatwattana, P., & Piriyasurawong, P. (2021). Engineering project-based learning using a virtual laboratory and mixed reality to enhance engineering and innovation skills. World Transactions on Engineering and Technology Education, 19(2), 232–237. [Google Scholar]
- Webel, S., Bockholt, U., Engelke, T., Gavish, N., Olbrich, M., & Preusche, C. (2013). An augmented reality training platform for assembly and maintenance skills. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 61(4), 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerfield, G., Mitrovic, A., & Billinghurst, M. (2015). Intelligent augmented reality training for motherboard assembly. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 25, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zata, N. M., van Niekerk, T. I., & Fernandes, J. M. (2016, November 30–December 2). A process control learning factory with a plant simulation integrated to industry standard control hardware. 2016 Pattern Recognition Association of South Africa and Robotics and Mechatronics International Conference (PRASA-RobMech) (pp. 1–8), Stellenbosch, South Africa. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guajardo-Cuéllar, A.; Corona-Echauri, R.; Meza-Flores, R.A.; Vázquez, C.R.; Rodríguez-Arreola, A.; Navarro-Gutiérrez, M. Mixed Reality Laboratory for Teaching Control Concepts: Design, Validation, and Implementation. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070883
Guajardo-Cuéllar A, Corona-Echauri R, Meza-Flores RA, Vázquez CR, Rodríguez-Arreola A, Navarro-Gutiérrez M. Mixed Reality Laboratory for Teaching Control Concepts: Design, Validation, and Implementation. Education Sciences. 2025; 15(7):883. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070883
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuajardo-Cuéllar, Alejandro, Ricardo Corona-Echauri, Ramón A. Meza-Flores, Carlos R. Vázquez, Alberto Rodríguez-Arreola, and Manuel Navarro-Gutiérrez. 2025. "Mixed Reality Laboratory for Teaching Control Concepts: Design, Validation, and Implementation" Education Sciences 15, no. 7: 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070883
APA StyleGuajardo-Cuéllar, A., Corona-Echauri, R., Meza-Flores, R. A., Vázquez, C. R., Rodríguez-Arreola, A., & Navarro-Gutiérrez, M. (2025). Mixed Reality Laboratory for Teaching Control Concepts: Design, Validation, and Implementation. Education Sciences, 15(7), 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070883





