Graduate Teaching Assistants (GTAs): Roles, Perspectives, and Prioritizing GTA Workforce Development Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Graduate Student Teaching Assistants and Their Roles in Higher Education
1.2. The Value of GTA Positions
1.3. Challenges to GTA Professional Development and Success
1.4. Purpose and Scope of Study
- What is the nature of the GTA workload at an R2 institution as it pertains to class type, class size, and course responsibilities?
- Is there a correlation between GTA tenure and perception of value?
- What training programs and opportunities exist at departmental and institutional levels to support GTA professional development?
- What do GTAs at an R2 institution recommend as beneficial and impactful training in support of teaching?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection Survey
2.2. Statistical Tools and Methods
3. Results
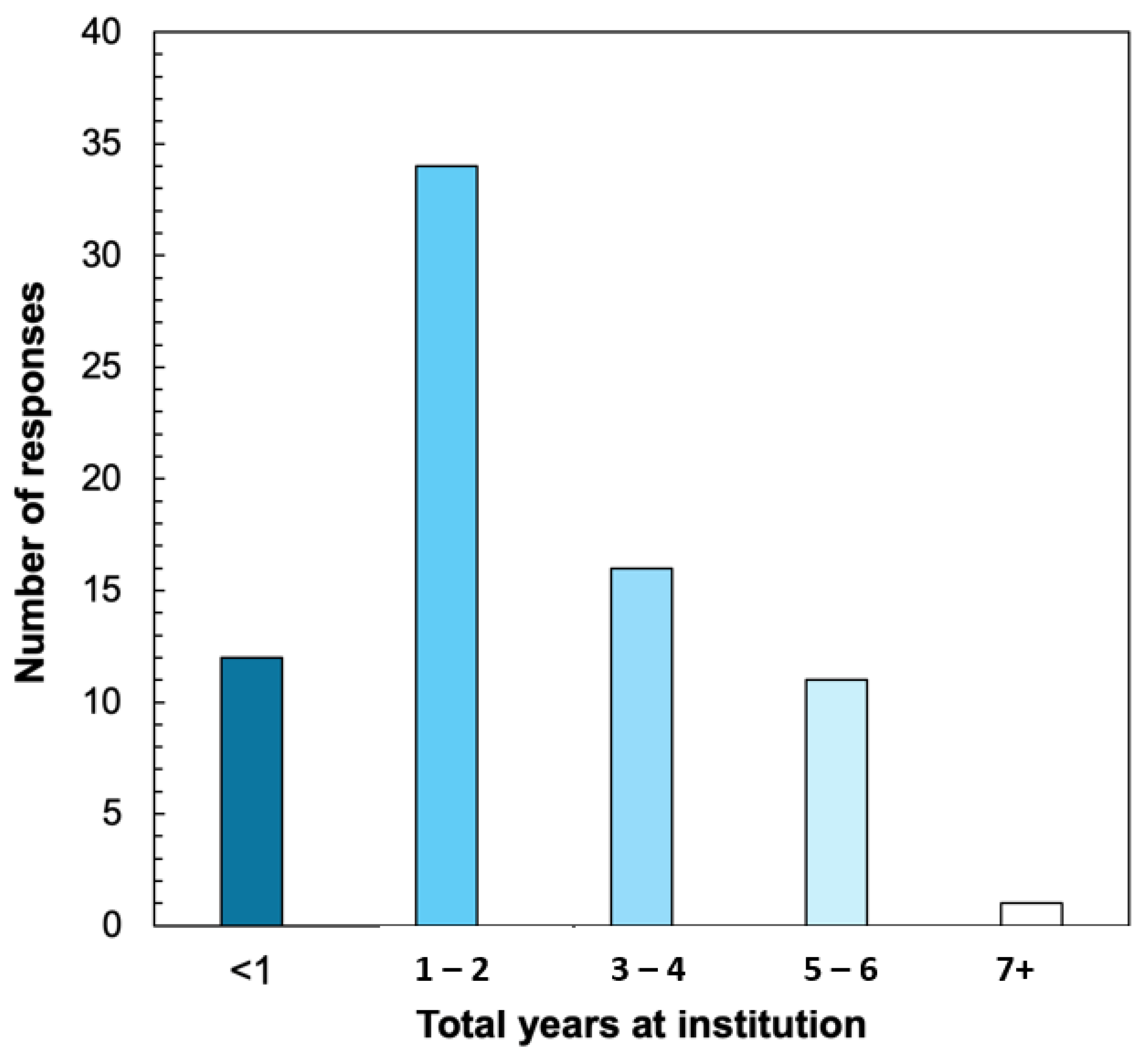
3.1. Survey Respondents
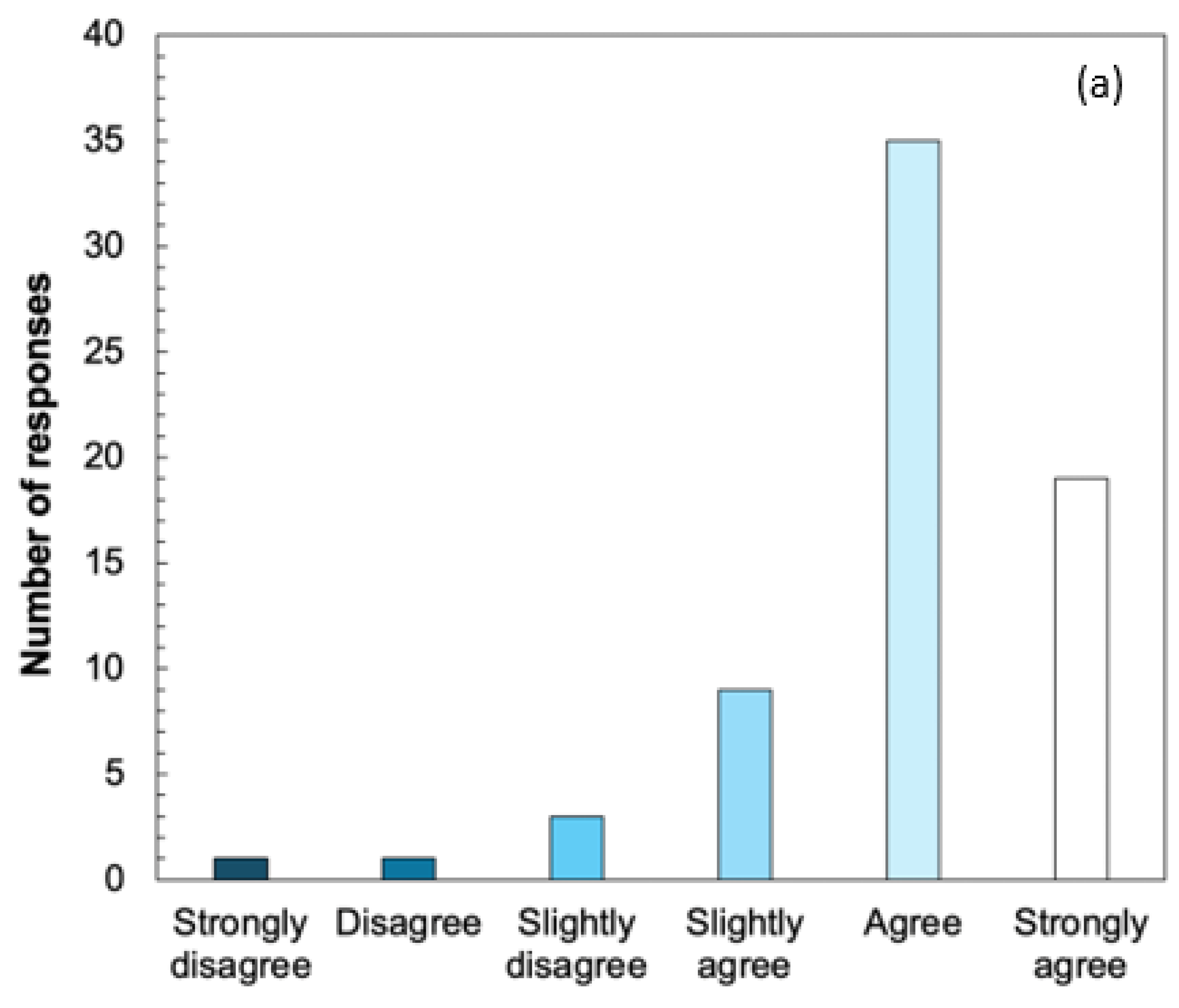
3.2. GTAs Perception of Value
3.3. Teaching-Related Support for GTAs
4. Discussion
4.1. GTAs in U.S. Higher Education and Current Training Gaps
4.2. Onboarding and Training GTAs: Potential Opportunities
| Theme | Supporting Context and Example Responses |
|---|---|
| Lack of coordinated and sustained GTA training/lack of awareness and relevance | Little or no knowledge of existing GTA training and professional development opportunities and/or their relevance to GTA-specific needs: “none I am aware of” “I cannot name any” “I am not familiar with what is here” “teacher development training–is not geared towards TA positions and is intended for those going into academia” “There are workshops at the center for teaching excellence but they don’t seem to be geared for graduate students” |
| Existing initiatives that support GTA development | Peer mentoring within departments, departmental seminars focused on GTA needs, seminars and workshops offered by the CTE: “peer mentoring” “peer and teacher observations” “Graduate Onboarding” “Pedagogy Seminar at the start of my first year” “The Certificate of College Teaching” “webinars and workshops on specific aspects of teaching” |
| Requested program-level support for GTA preparation | Increased offering of pre-semester orientations with sustained professional development throughout the semester which is tailored to need: “would be very helpful to receive teaching feedback from students in a more timely manner” “A more concrete orientation for graduate students” “More workshops on teaching software like TopHat and Canvas functionality hosted by CTE or departmental entities.” “education seminars or workshops for those who teach upper-level courses” |
| Resources to aid in course logistics | Teaching support tools (and training) to aid in the classroom (or lab): “More training on canvas and other software related to teaching” “being provided a clicker and adapters to connect personal laptops to teaching computers” “Templates for organization of emails” “(e.g., federal attendance requirement, building Canvas, how to add/drop students, how to put in midterm or final grades, etc.) would be helpful.” |
| Strategies to support GTA investment and role ownership | Including GTAs in TA-related decisions and offering incentives, and rewards, to support GTA professional development: “Allowing GAs to have more input in which class they are assigned to” “more incentives for participating in teaching effectiveness initiatives/programs at Miami–ideally monetary (especially for us graduate students).” “Trainings for graduate assistants and reward for them” |
4.3. GTA Training Through Cognitive Apprenticeship: Career-Readiness and Workforce Development
4.4. Study Limitations and Next Steps
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
| Question/Statement for Evaluation | Response Options/Comments |
|---|---|
| 1. Which college/division are you primarily affiliated with? | College of Arts and Science; College of Creative Arts; College of Education, Health and Society; College of Engineering and Computing; College of Liberal Arts and Applied Science; Farmer School of Business; Prefer not to respond; Not applicable |
| 2. Do you teach primarily in a STEM field? | Yes; No; Prefer not to respond |
| 3. Total years at Miami University: (enter a number) | Numeric response |
| 4. What course modalities do you teach in a typical academic year? Select all that apply. | Online, asynchronous; Online synchronous; Hybrid; Face-to-face; Sprint; Prefer not to respond |
| 5. In a typical academic year, I teach: (include separate course sections, do not include independent study) | 1–2 courses; 3–4 courses; 5–6 courses; 7–8 courses; 8+ courses; Prefer not to respond |
| 6. In a typical academic year, I teach courses that serve individual class sizes of: (select all that apply) | <12; 12–30; 31–50; 51–120; 121–200; 200+; Prefer not to respond |
| 7. I estimate the time put towards my teaching in a typical week to be: (include class preparation, assignment/lecture development, course delivery, grading, course-related emails, student “office” hours). Do not include hours advising. | <5 h; 5–10 h; 11–20 h; 21–30 h; 31–40 h; 41–50 h; 51–60 h; 61 h+; Prefer not to respond |
| 8. What type of courses do you teach in a typical academic year? Select all that apply. | Introductory-level lab; Intermediate-level class; Intermediate-level lab; Upper-level class; Upper-level lab; Graduate-level; Prefer not to respond |
| 9. My teaching efforts are recognized and valued by my students | Strongly agree; Agree; Slightly agree; Slightly disagree; Disagree; Strongly disagree; Prefer not to respond |
| 10. The efforts I put towards my teaching are valued in my department. | Strongly agree; Agree; Slightly agree; Slightly disagree; Disagree; Strongly disagree; Prefer not to respond |
| 11. Are course materials shared within your department? | Yes, often and highly encouraged. Materials are freely shared, for example, through a shared drive; Yes, frequently if requested, for example, by new faculty members; Yes, to some extent although it is rare and materials are shared with hesitation; No; Do not know; Prefer not to respond; Other |
| 12. How often do you consult peer-reviewed literature associated with discipline-based education research (DBER) to inform and enhance your teaching? | Very often (weekly); Often (every couple of weeks); Sometimes (at least once a month); Seldom (at least once a semester); Never; Prefer not to respond |
| 13. What departmental informal or formal initiatives/programs exist to promote teaching effectiveness? (e.g., peer mentoring, DBER seminars). | [open response] |
| 14. What divisional and institutional informal or formal initiatives/programs exist to promote teaching effectiveness? | [open response] |
| 15. Do you have any ideas for initiatives/programs at Miami you would like to see in support of teaching effectiveness? | [open response] |
| 16. What teaching support would be helpful? (e.g., software, equipment) | [open response] |
Appendix A.2
- agree—respondent’s consent to participate in the survey
- college—respondent’s college/division affiliation
- stem—whether respondent teaches a STEM field
- years—respondent’s year at Miami University
- valued.by.department—whether respondent feels their teaching efforts are valued by the department
- course.type—type of course respondent teaches in an academic year
- course.mode—course modalities respondent teaches in an academic year
- class.size—different class sizes of courses that respondent teaches in an academic year
- course.load—number of courses respondent teaches in an academic year
- hours.teaching—time per week that respondent puts towards teaching duties
- valued.by.students—whether respondent feels their teaching efforts are valued by the students
- materials.shared.freq—how respondent feels about the frequency of sharing materials in the department
- materials.shared.other—text answer for how respondent feels about the frequency of sharing materials in the department
- dber.freq—how often the respondent consults peer-reviewed literature associated with discipline-based education research (DBER) to inform and enhance their teaching
References
- Ahmed, S., & Rosen, L. (2018). Graduate students: Present instructors and future faculty. Faculty Focus. Available online: https://www.facultyfocus.com/articles/teaching-and-learning/graduate-students-present-instructors-and-future-faculty/ (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Ahn, B. (2016). Applying the cognitive apprenticeship theory to examine graduate and postdoctoral researchers’ mentoring practices in undergraduate research settings. International Journal of Engineering Education, 32(4), 1691–1703. [Google Scholar]
- American Association of University Professors (AAUP). (2023). Data snapshot: Tenure and contingency in US higher education. Available online: https://www.aaup.org/file/AAUP%20Data%20Snapshot.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- American Association of University Professors (AAUP). (2024). Academic workforce—IPEDS academic workforce. Available online: https://public.tableau.com/app/profile/american.association.of.university.professors/viz/IPEDSWF/TREND (accessed on 3 June 2024).
- Anderson, M. K., Anderson, R. J., Tenenbaum, L. S., Kuehn, E. D., Brown, H. K. M., Ramadorai, S. B., & Yourick, D. L. (2018). The Benefits of a Near-Peer Mentoring Experience on STEM Persistence in Education and Careers: A 2004–2015 Study. Journal of STEM Outreach, 2, 1−11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthropic. (2025). Claude [Large language model]. Available online: https://www.anthropic.com (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Arsenault, A. C., Heffernan, A., & Murphy, M. P. A. (2021). What is the role of graduate student journals in the publish-or-perish academy? Three lessons from three editors-in-chief. International Studies, 58(1), 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, A. E. (2002). Preparing the next generation of faculty: Graduate school as socialization to the academic career. The Journal of Higher Education, 73(1), 94–122. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/1558449 (accessed on 1 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Austin, A. E. (2009). Cognitive apprenticeship theory and its implications for doctoral education: A case example from a doctoral program in higher and adult education. International Journal for Academic Development, 14(3), 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, A. E., & McDaniels, M. (2006). Preparing the professoriate of the future: Graduate student socialization for faculty roles. In J. C. Smart (Ed.), Higher education: Handbook of theory and research (Vol. 21). Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowski, J. P., Deem, C. S., & Ellison, C. G. (2015). Publishing in academic journals: Strategic advice for doctoral students and academic mentors. The American Sociologist, 46, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterton, B. E., Neill, C. M., Biggs, C. R., & Rempel, H. S. (2024). A framework for training graduate students and campus communities in inclusive teaching. Journal of Microbiology & Biology Education, 25(3), e00125-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beath, J. A., Poyago-Theotoky, J., & Ulph, D. (2012). University funding systems: Impact on research and teaching. Economics. Available online: https://www.econstor.eu/bitstream/10419/44431/1/64478752X.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Becker, E. A., Easlon, E. J., Potter, S. C., Guzman-Alvarez, A., Spear, J. M., Facciotti, M. T., Igo, M. M., Singer, M., & Pagliarulo, C. (2017). The effects of practice-based training on graduate teaching assistants’ classroom practices. CBE Life Sciences Education, 16(4), 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, M. D., Plumb, S., & Beck, S. B. M. (2022). Effective use of peer teaching and self-reflection for the pedagogical training of graduate teaching assistants in engineering. European Journal of Engineering Education, 48(1), 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettinger, E. P., Long, B. T., & Taylor, E. S. (2016). When inputs are outputs: The case of graduate student instructors. Economics of Education Review, 52, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, J. P., & Worley, L. K. (2006). Conceptualizing the academic life: Graduate students’ perspectives. The Journal of Higher Education, 77(6), 1009–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop-Williams, K. E., Roke, K., Aspenlieder, E., & Troop, M. (2017). Graduate student perspectives of interdisciplinary and disciplinary programming for teaching development. The Canadian Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 8(3), n3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blanchard, C., & Haccoun, R. R. (2019). Investigating the impact of advisor support on the perceptions of graduate students. Teaching in Higher Education, 25(8), 1010–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouin, D. D., & Moss, A. R. (2015). Graduate student teacher training: Still relevant (and missing?) 20 years later. Teaching Sociology, 43(2), 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond-Robinson, J., & Rodriquez, R. A. B. (2006). Catalyzing graduate teaching assistants’ laboratory teaching through designed research. Chemical Education Research, 83, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, E. (1990). Scholarship reconsidered. In Priorities of the professoriate (160p). A Special Report. The Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching. [Google Scholar]
- Bragg, A. K. (1976). The socialization process in higher education (55p). The American Association of Higher Education. [Google Scholar]
- Breen, S. M., McCain, J., & Roksa, J. (2024). Breaking points: Exploring how negative doctoral advisor relationships develop over time. Higher Education, 88, 2319–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, S. J., Miller, B. C., Hollet, N., Grimes, J. R., & Moore, M. (2023). Providing support to first-year graduate teaching assistants: What do they really need? Journal of Teaching in Physical Education, 43(2), 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownell, S. E., & Tanner, K. D. (2012). Barriers to faculty pedagogical change: Lack of training, time, incentives and… tensions with professional identity. Life Sciences Education, 11(4), 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calarco, J. M. (2020). A field guide to grad school: Uncovering the hidden curriculum (480p). Princeton University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Chall, J. S. (1986). The Teacher as Scholar. The Reading Teacher, 39(8), 792–797. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, P. H. P., & Corrigan, P. (2019). A study of graduate teaching assistants’ self-efficacy in teaching: Fits and starts in the first triennium of teaching. Cogent Education, 6(1), 1579964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y., Kim, M., Svinicki, M. D., & Decker, M. L. (2011). Exploring teaching concerns and characteristics of graduate teaching assistants. Teaching in Higher Education, 16(3), 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicchino, A. (2020). A broader view: How doctoral programs in rhetoric and composition prepare their graduate students to teach composition. Writing Program Administration—Journal of the Council of Writing Program Administrators, 44(1), 86–107. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, L., Hansen, J., Hastie, A., Kunz, S., Standen, A., & Thorogood, J. (2021). Introduction to postgraduate pedagogies: Centering graduate teaching assistants in higher education. Postgraduate Pedagogies, 1(1), 7–26. [Google Scholar]
- Collier, K. M., & Blanchard, M. R. (2023). Toward a holistic understanding of factors that support or inhibit graduate student success. Trends in Higher Education, 2(3), 389–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A., & Kapur, M. (2014). Cognitive apprenticeship. In R. K. Sawyer (Ed.), The Cambridge handbook of the learning sciences (800p). Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Connolly, M. R., Lee, Y.-G., & Savoy, J. N. (2018). The effects of doctoral teaching development on early-career stem scholars’ college teaching self-efficacy. CBE-Life Sciences Education, 17(1), 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, A., & Komperda, R. (2018). Characterizing graduate student identity development in the context of an integrated research and teaching graduate student training course. Journal of Chemical Education, 99, 1747–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council of Graduate Schools (CGS). (2011). Preparing future faculty to assess student learning. A report on a CGS project supported by a grant from the Teagle Foundation. Available online: https://legacy.cgsnet.org/publication-pdf/2515/PFF_Assess.pdf.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Coy, M. W. (1989). Apprenticeship: From theory to method and back again (310p). State University of New York Press. [Google Scholar]
- Crowe, J., Ceresola, R., & Silva, T. (2013). Enhancing student learning of research methods through the use of undergraduate teaching assistants. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 39(6), 759–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, N., Stewart, A. J., & Ostrove, J. M. (2013). Fostering academic self-concept: Advisor support and sense of belonging among international and domestic graduate students. American Educational Research Journal, 50(1), 108–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeChenne, S. E., Lesseig, K., Anderson, S. M., Li, S. L., Status, N. K., & Barthel, C. (2012). Toward a measure of professional development for graduate student teaching assistants. The Journal of Effective Teaching, 12(1), 4–19. [Google Scholar]
- Dennen, V. P., & Burner, K. J. (2007). The cognitive apprenticeship model in educational practice. In D. Jonassen, M. J. Spector, M. Driscoll, M. D. Merrill, J. van Merrienboer, & M. P. Driscoll (Eds.), Handbook of research on educational communications and technology (1296p). Routledge. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, S. (2023). Preparing future faculty: Developing inclusive, future-focused educators and an adaptive program. In O. J. Neisler (Ed.), The Palgrave handbook of academic professional development centers. Palgrave Studies on Leadership and Learning in Teacher Education. Palgrave Macmillan. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diggs, A. B., Mondisa, J., & Scott, R. D. (2017, June 25–28). Toward a systematic review of the preparing future faculty program initiatives. 2017 ASEE Annual Conference & Exposition, Columbus, OH, USA. Available online: https://peer.asee.org/toward-a-systematic-review-of-the-preparing-future-faculty-program-initiatives (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Dillard, J. B., Sadek, K., & Muenks, K. (2024). Undergraduate perceptions of graduate teaching assistants: Competence, relatedness, and autonomy in practice. Higher Education Research & Development, 43(1), 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, E., & Johnson, D. (2009). Toward a holistic view of undergraduate research experiences: An exploratory study of impact on graduate/postdoctoral mentors. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 18, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadel, A. (2023). Tenured faculty in steady decline while part-time and graduate workers rise, per report. University Business. Available online: https://universitybusiness.com/tenured-faculty-in-steady-decline-while-part-time-and-graduate-workers-rise-per-report/ (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Doucette, D., Clark, R., & Singh, C. (2020). Professional development combining cognitive apprenticeship and expectancy-value theories improves lab teaching assistants’ instructional views and practices. Physical Review Physics Education Research, 16, 020102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, J., Powell, D. N., & Rouamba, N. H. (2016). Assessing graduate teaching assistants’ beliefs and practices. Journal on Excellence in College Teaching, 27(3), 35–61. [Google Scholar]
- Douin, T. A., DeCaro, M. S., Hieb, J. L., Chastain, R. J., & Fuselier, L. (2024). Participation in a discipline-based education research project mitigates barriers and enhances drivers to teaching reform differently across faculty positions and departments. Cogent Education, 12(1), 2437884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragisich, V., Keller, V., & Zhao, M. (2016). An intensive training program for effective teaching assistants in chemistry. Journal of Chemical Education, 93(7), 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drezner, N. D., & Pizmony-Levy, O. (2021). I belong, therefore, I give? The impact of sense of belonging on graduate student alumni engagement. Nonprofit and Voluntary Sector Quarterly, 50(4), 753–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, D. L., Bengtsen, S. S. E., Guccione, K., & Kobayashi, S. (2021). The hidden curriculum in doctoral education (166p). Springer Nature Switzerland. [Google Scholar]
- Emmioğlu, E., McAlpine, L., & Amundsen, C. (2017). Doctoral students experiences of feeling (or not) like an academic. International Journal of Doctoral Studies, 12, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethington, C. A., & Pisani, A. (1993). The RA and TA experience: Impediments and benefits to graduate study. Research in Higher Education, 34(3), 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, T. M., Bira, L., Gastelum, J. B., Weiss, L. T., & Vanderford, N. L. (2018). Evidence for a mental health crisis in graduate education. Nature Biotechnology, 36, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exter, M. E., & Ashby, I. (2019). Using cognitive apprenticeship to enculturate new students into qualitative research. Qualitative Report, 24(4), 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldon, D. F., Peugh, J., Timmerman, B. E., Maher, M. A., Hurst, M., Strickland, D., Gilmore, J. A., & Stiegelmeyer, C. (2011). Graduate students’ teaching experiences improve their methodological research skills. Science, 333, 1037–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finch, J. K., & Fernández, C. (2014). Mentoring graduate students in teaching: The FCCIC model. Teaching Sociology, 42(1), 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, A., O’Dwyer, A., Mannix-McNamara, P., & Leahy, J. J. (2017). Evaluating the impact of the “teaching as a chemistry laboratory graduate teaching assistant” program on cognitive and psychomotor verbal interactions in the laboratory. Journal of Chemical Education, 94(12), 1831–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, M. A., & Millen, D. R. (2004). Understanding the benefits and impact of communities of practice. In P. M. Hildreth, & C. Kimble (Eds.), Knowledge networks: Innovation through communities of practice (300p). Igi Global. [Google Scholar]
- French, D., & Russel, C. (2002). Do graduate teaching assistants benefit from teaching inquiry-based laboratories? BioScience, 52(11), 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedensen, R. E., Bettencourt, G. M., & Bartlett, M. L. (2024). Power-conscious ecosystems: Understanding how power dynamics in US doctoral advising shape students’ experiences. Higher Education, 87, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaff, J. G. (2002). Preparing future faculty and doctoral education. Change: The Magazine of Higher Learning, 34(6), 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, G. E., & Jones, M. G. (2011). Pedagogical preparation of the science graduate teaching assistant: Challenges and implications. Science Educator, 20(2), 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Geragosian, E. K., Zhu, D., Skriloff, M., & Shultz, G. V. (2024). Chemistry graduate teaching assistants’ teacher noticing. Chemistry Education Research and Practice, 25, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, J., Maher, M. A., Feldon, D. F., & Timmerman, B. (2014). Exploration of factors related to the development of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics graduate teaching assistants’ teaching orientations. Studies in Higher Education, 39(10), 1910–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, J., Wofford, A. M., & Maher, M. A. (2016). The flip side of the attrition coin: Faculty perceptions of factors supporting graduate student success. International Journal of Doctoral Studies, 11, 419–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glorieux, A., Spruyt, B., te Braak, P., Minnen, J., & van Tienoven, T. P. (2024). When the student becomes the teacher: Determinants of self-estimated successful PhD completion among graduate teaching assistants. Sage Open, 14(2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, E. C., Cary, J. R., Phan, V. D., Therrie, H., & Shortlidge, E. E. (2023). Graduate teaching assistants impact student motivation and engagement in course-based undergraduate research experiences. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 60(9), 1967–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, R. K., La Touche, R., Oslawski-Lopez, J., Powers, A., & Simacek, K. (2014). Betwixt and between: The social position and stress experiences of graduate students. Teaching Sociology, 42(1), 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, D. A., Cathcart, A., & Neale, L. (2016). Helping doctoral students teach: Transitioning to early career academia through cognitive apprenticeship. Higher Education Research & Development, 35(4), 712–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, N., & Schwen, T. M. (2008). Communities of practice in workplaces. Performance Improvement Quarterly, 19(2), 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardré, P. L., & Burris, A. O. (2012). What contributes to teaching assistant development: Differential responses to key design features. Instructional Science, 40, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, L., Sunderman, H., & Knopik, N. (2024). Maximizing the role of undergraduate teaching assistants (UTAs) to match signature pedagogies in leadership education. Journal of Leadership Education, 23(1), 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatt, B., Quach, L., Brown, S., & Anderson, A. (2009). Coffee talk: Negotiating/disrupting the hidden curriculum of graduate school. Journal of Curriculum Theorizing, 25(1), 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershock, C., Groscurth, C. R., & Milkova, S. (2011). Approaches to preparing future faculty for teaching, in advancing the culture of teaching on campus (C. R. Cook, & M. Kaplan, Eds.; 270p). Routledge. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoessler, C., & Godden, L. (2015). The visioning of policy and the hope of implementation: Support for graduate students’ teaching at a Canadian institution. Canadian Journal of Higher Education, 45(1), 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, M. J., Moore, B. N., Jeffrey, J. L., & Young, A. S. (2024). Equity, Diversity and inclusion: Demystifying the ‘hidden curriculum’ for minoritized graduate students. eLife, 13, e94422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, J., & Christopher, K. B. (2013). The research mentoring program: Serving the needs of graduate and undergraduate researchers. Innovative Higher Education, 38, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffmyer, A. S., & Lemus, J. D. (2019). Graduate TA teaching behaviors impact student achievement in a research-based undergraduate science course. Journal of College Science Teaching, 48(3), 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G., Yang, T., Tsai, C., & Yang, S. J. H. (2009). A context-aware ubiquitous learning environment for conducting complex science experiments. Computers & Education, 53(2), 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocente, N., & Baker, J. (2018). The sociology teaching fellowship: A mentorship model for graduate student teacher training. Teaching Sociology, 46(4), 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D. L. (2013). Making the connection: The impact of support systems on female transfer students in science, technology, Engineering, and mathematics (STEM). Community College Enterprise, 19(1), 19–33. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A. L., Davis, S. N., & Price, J. (2004). Preparing future faculty: A new approach at North Carolina state university. Teaching Sociology, 32(3), 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, K., & Howe, C. (2017). The perceived benefits and problems associated with teaching activities undertaken by doctoral students. Teaching in Higher Education, 23(4), 504–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, A., & Hassenfeldt, T. A. (2019). Utility of a peer teaching mentor to graduate teaching assistants. College Teaching, 68(1), 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajfez, R. L., & Matusovich, H. M. (2017). Competence, autonomy, and relatedness as motivators of graduate teaching assistants. Journal of Engineering Education, 106(2), 245–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefer, J. M. (2015). Experiencing doctoral liminality as a conceptual threshold and how supervisors can use it. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 52(1), 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, S. (2021). How to build teaching experiences and skills as a graduate student. the entomology profession, the entomological society of America. Available online: https://entomologytoday.org/2021/09/28/how-build-teaching-experiences-skills-entomology-graduate-student/ (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Kleinschmit, A. J., Rosenwald, A., Ryder, E. F., Donovan, S., Murdoch, B., Grandgenett, N. F., Pauley, M., Triplett, E., Tapprich, W., & Morgan, W. (2023). Accelerating STEM education reform: Linked communities of practice promote creation of open educational resources and sustainable professional development. International Journal of STEM Education, 10(1), 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezz, S., Berns, V., Schwabacher, J., & Coleman, A. (2024). Graduate student leadership in a TA training program. Journal of Chemical Education, 101(6), 2364–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, L. (2020). Podcasts in higher education: Teacher enthusiasm increases students’ excitement, interest, enjoyment, and learning motivation. Educational Studies, 47(5), 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpan, C. J. (2014). The apprenticeship of teaching assistants: Time to change? Transformative Dialogues: Teaching & Learning Journal, 7(3), 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Kost, C. R. (2008). Innovations in teaching assistant development: An apprenticeship model. Foreign Language Annals, 41(1), 29–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krsmanovic, M. (2024). Lessons learned from implementing preparing future faculty program and measuring its impact on graduate student self-efficacy. The Journal of Faculty Development, 38(2), 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kuh, G. D., Ikenberry, S. O., Jankowski, N. A., Cain, T. R., Ewell, P. T., Hutchings, P., & Kinzie, J. (2015). Using evidence of student learning to improve higher education (304p). National Institute for Learning Outcomes Assessment, Jossey-Bass. [Google Scholar]
- Kurdziel, J. P., & Libarkin, J. C. (2003). Research methodologies in science education: Training graduate teaching assistants to teach. Journal of Geoscience Education, 51(3), 347−351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, L. M., & Tice, S. L. (1993). Preparing graduate students to teach: A guide to programs that improve undergraduate education and develop tomorrow’s faculty (184p). American Association for Higher Education, Stylus Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, F. K., Randles, C. A., & Jeffrey, K. A. (2020). Developing and evaluating a graduate student teaching assistant training course in the chemistry department of a large American university. Journal of Chemical Education, 97(6), 1515–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechuga, V. M. (2011). Faculty-graduate student mentoring relationships: Mentors’ perceived roles and responsibilities. Higher Education, 62, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T., Chen, Y., Hamilton, M., & Harris, K. (2022). Peer mentoring to enhance graduate students’ sense of belonging and academic success. Human Kinetics Journal, 11(4), 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzetti, D. L., Shipton, L., Nowell, L., Jacobsen, M., Lorenzetti, L., Clancy, T., & Paolucci, E. O. (2019). A systematic review of graduate student peer mentorship in academia. Mentoring & Tutoring: Partnership in Learning, 27(5), 549–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckie, D. B., Mancini, B. A., Abdallah, N., Kadouh, A. K., Ungkuldee, A. C. P., & Hare, A. A. (2019). Undergraduate teaching assistants can provide support for reformed practices to raise student learning. Advances in Physiology Education, 44(1), 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luft, J. A., Kurdziel, J. P., Roehrig, G. H., & Turner, J. (2004). Growing a garden without water: Graduate teaching assistants in introductory science laboratories at a doctoral/research university. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 41(3), 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukes, L. A., Ibrahim, L. M., & Bray, L. (2023). Designing programs to prepare future faculty for academic careers: Insights from a longitudinal case study of a multidisciplinary cohort-based program model for doctoral students. To Improve the Academy: A Journal of Educational Development, 42(2), 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, L., Campbell, D., & Carrell, S. (2018). TAs like me: Racial interactions between graduate teaching assistants and undergraduates. Journal of Public Economics, 159, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyles, C. H., Huggins, N., & Robbins, C. K. (2022). Unveiling the hidden curriculum within graduate education (264p). Routledge. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantai, L. (2019). A source of sanity: The role of social support for doctoral candidates belonging and becoming. International Journal of Doctoral Studies, 14, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, E. (2001). The hidden curriculum in higher education (256p). Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Marx, R. D., Garcia, J. E., Butterfield, D. A., Kappen, J. A., & Baldwin, T. T. (2015). Isn’t it time we did something about the lack of teaching preparation in business doctoral programs? Journal of Management Education, 40(5), 489–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavri, A., Ioannou, A., & Loizides, F. (2021). Cross-organisational communities of practice: Enhancing creativity and epistemic cognition in higher education. The Internet and Higher Education, 49, 100792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, S. G. (2025). How do your teaching skills translate to other jobs? Available online: https://www.executivefunctioncoachingacademy.com/post/teaching-skills (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- McLaughlin, J. E., Morbitzer, K., Meilhac, M., Poupart, N., Layton, R. K., & Jarstfer, M. B. (2024). Standards needed? An exploration of qualifying exams from a literature review and website analysis of university-wide policies. Studies in Graduate and Postdoctoral Education, 15(1), 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan-Capehart, A., & Adeyemi-Bello, T. (2008). Prerequisite coursework as a predictor of performance in a graduate management course. Journal of College Teaching & Learning, 5(7), 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Meanwell, E., & Kleiner, S. (2014). The emotional experience of first-time teaching: Reflections from graduate instructors, 1997–2006. Teaching Sociology, 42(1), 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minshew, L. M., Olsen, A. A., & McLaughlin, J. E. (2021). Cognitive apprenticeship in STEM graduate education: A qualitative review of the literature. AERA Open, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, A., Jung, H., Marbouti, F., Rodgers, K., & Diefes-Dux, H. (2013, October 23–26). Undergraduate and graduate teaching assistants’ perceptions of their responsibilities—Factors that help or hinder. IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE) (pp. 1576–1578), Oklahoma City, OK, USA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M. (2002). The GTA experience: Grounding, practicing, evaluating, and reflecting. In S. C. Brown, & T. Enos (Eds.), The writing program administrator’s resource (558p). Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Musgrove, M. M. C., Cooley, A., Feiten, O., Petrie, K., & Schussler, E. E. (2021). To cope or not to cope? Characterizing biology graduate teaching assistant (GTA) coping with teaching and research anxieties. CBE-Life Sciences Education, 20(4), 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser-Abu Alhija, F., & Fresko, B. (2019). Graduate teaching assistants: Motives, difficulties and professional interactions and their relationship to perceived benefits. Higher Education Research & Development, 39(3), 546–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyquist, J. D., Abbott, R., Wulff, D. H., & Sprague, J. (1991). Preparing the professoriate of tomorrow to teach: Selected readings in TA training (457p). Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, A. A., Minshew, L. M., Jarstfer, M. B., & McLaughlin, J. E. (2020). Exploring the future of graduate education in pharmaceutical fields. Medical Science Educator, 30(1), 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neal, C., Wright, M., Cook, C., Perorazio, T., & Purkiss, J. (2007). The impact of teaching assistants on student retention in the sciences: Lessons for TA training. Journal of College Science Teaching, 36(5), 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- OpenAI. (2025). ChatGPT [Large language model]. Available online: https://chat.openai.com (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Oswalt, S. B., & Riddock, C. C. (2007). What to do about being overwhelmed: Graduate students, stress and university services. The College Student Affairs Journal, 21(1), 24–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ozdemir, E., & Papi, M. (2021). Mindsets as sources of L2 speaking anxiety and self-confidence: The case of international teaching assistants in the U.S. Innovation in Language Learning and Teaching, 16(3), 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özturgut, O., & Murphy, C. (2010). Literature vs. practice: Challenges for international students in the U.S. International Journal of Teaching and Learning in Higher Education, 22(3), 374–385. [Google Scholar]
- Paolucci, E. O., Jacobsen, M., Nowell, L., Freeman, G., Lorenzetti, L., Clancy, T., Paolucci, A., Pethrick, H., & Lorenzetti, D. L. (2021). An exploration of graduate student peer mentorship, social connectedness and well-being across four disciplines of study. Studies in Graduate and Postdoctoral Education, 12(1), 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C. (2004). The graduate teaching assistant (GTA): Lessons from north America experience. Teaching in Higher Education, 9, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C., & Ramos, M. (2002). The donkey in the department? Insights into the graduate teaching assistant (GTA) experience in the UK. Journal of Graduate Education, 3, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, M. A., Ashe, D., Boersma, J., Hicks, R., & Bennett, V. (2015). Good teaching starts here: Applied learning at the graduate teaching assistant institute. Canadian Journal of Higher Education, 45(3), 84–110. Available online: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1085405.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Peck, D. (2025). 15 Transferable skills from teaching (2025 guide). Available online: https://www.devlinpeck.com/content/transferable-skills-from-teaching (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Peng, H., Wu, Y., Zhou, R., Jiang, J., Chen, X., Wang, M., Ren, T., Yu, C., & Wu, T. (2024). Comparison of self-efficacy among graduate teaching assistants before and after training. BMC Medical Education, 24, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp, S. B., Tretter, T. R., & Rich, C. V. (2016). Undergraduate teaching assistant impact on student academic achievement. The Electronic Journal for Research in Science & Mathematics Education, 20(2), 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Pittaway, L., Brush, C., Corbett, A. C., & Tantawy, M. M. (2023). Doctoral programs in entrepreneurship: Building cognitive apprenticeships. Entrepreneurship Education and Pedagogy, 6(4), 608–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portelli, J. P. (1993). Exposing the hidden curriculum. Journal of Curriculum Studies, 25(4), 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prenger, R., Poortman, C. L., & Handelzalts, A. (2019). The effects of networked professional learning communities. Journal of Teacher Education, 70(5), 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyke, S. W., & Sheridan, P. M. (1993). Logistic regression analysis of graduate student retention. The Canadian Journal of Higher Education, 23(2), 44–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrko, I., Dörfler, V., & Eden, C. (2016). Thinking together: What makes communities of practice work? Human Relations, 70(4), 389–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainey, K., Dancy, M., Mickelson, R., Stearns, E., & Moller, S. (2018). Race and gender differences in how sense of belonging influences decisions to major in STEM. International Journal of STEM Education, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, N., Hosein, A., & Raaper, R. (2021). Doctoral students navigating the borderlands of academic teaching in an era of precarity. Teaching in Higher Education, 26(3), 454–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankar, S., Spencer-Drakes, T. C. J., Fernandes, I. H., Hayes, M. I., Coopwood, S., Spencer, I., & Neal, S. E. (2024). Empowering STEM students: A university-wide mentorship program fostering retention and belonging. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 239(7), e31348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. (2021). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Reeves, A. G., Bischoff, A. J., Yates, B., Brauer, D. D., & Baranger, A. M. (2022). A pilot graduate student-led near-peer mentorship program for transfer students provides a supportive network at an R1 institution. Journal of Chemistry Education, 100(1), 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchey, K. A., & Smith, S. (2019). Developing a training course for undergraduate teaching assistants. College Teaching, 67(1), 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, K. D. (2003). Teaching assistant anxiety and coping strategies in the classroom. Communication Research Reports, 20(1), 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushin, J. W., DeSaix, J., Lumsden, A., Streubel, D. P., Summers, G., & Bernson, C. (1997). Graduate teaching assistant training—A basis for improvement of college biology teaching and faculty development? The American Biology Teacher, 59, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadera, E., Suonio, E. E. K., Chen, J. C.-C., Herbert, R., Hsu, D., Bogdan, B., & Kool, B. (2024). Strategies and approaches for delivering sustainable training and professional development of graduate teaching assistants, teaching assistants, and tutors: A scoping review. Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education, 16(5), 2199–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Cardona, I., Sánchez-Lugo, J., & Vélez-González, J. (2012). Exploring the potential of communities of practice for learning and collaboration in a higher education context. Procedia—Social and Behavioral Sciences, 46, 1820–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, L., Allen, B., Frahm, J., & Morris, G. (2009). Enhancing the experience of student teams in large classes: Training teaching assistants to be coaches. Journal of Management Education, 33(5), 526–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvary, M. A., Asgari, M., Castelli, F. R., & Ruesch, J. M. (2025). Applying the mentor mindset to undergraduate and graduate student teaching assistant professional development in a laboratory course. Journal of Microbiology & Biology Education, e00049-25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosser, L. Z., Lyons, H. Z., Talleyrand, R. M., Kim, B. S. K., & Johnson, W. B. (2011). Advisor-advisee relationships in graduate training programs. Journal of Career Development, 38(1), 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schussler, E. E., Read, Q., Marbach-Ad, G., Miller, K., & Ferzli, M. (2015). Preparing biology graduate teaching assistants for their roles as instructors: An assessment of institutional approaches. CBE-Life Sciences Education, 14(3), 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A. M., Saltzman, E. S., Whiteman, R. C., & Brooks, P. J. (2022). Do graduate students’ teaching values align with their approaches to teaching and teaching practices? Scholarship of Teaching and Learning in Psychology, 8(3), 206–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semper, J. V. O., & Blasco, M. (2018). Revealing the hidden curriculum in higher education. Studies in Philosophy and Education, 37, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seron, C. (2002). The teacher-scholar. Law & Society Review, 36(1), 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyranian, V., Madva, A., Duong, N., Abramzon, N., Tibbetts, Y., & Harackiewicz, J. M. (2018). The longitudinal effects of STEM identity and gender on flourishing and achievement in college physics. International Journal of STEM Education, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A., & Raj, A. G. S. (2024, March 20–23). A review of cognitive apprenticeship methods in computing education research. 55th ACM Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education (Vol. 1, pp. 1202–1208), Portland, OR, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Shortlidge, E. E., & Eddy, S. L. (2018). The trade-off between graduate student research and teaching: A myth? PLoS ONE, 13(6), e0199576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shum, A., Lau, P., & Fryer, L. (2020). From learner to teacher: (re)training graduate teaching assistants’ teaching approaches and developing self-efficacy for and interest in teaching. Higher Education Research & Development, 40(7), 1546–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, T. M. (2009). The preparing future faculty (PFF) program: Examining relationships and regressions among professional identity, career expectations, and teaching efficacy [Ph.D. Dissertation, Howard University]. [Google Scholar]
- Simonton, T. (2019). Tenure and other variations. The chronicle of higher education, 65. Available online: https://www.chronicle.com/article/tenure-and-other-variations/?sra=true (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Sinche, M., Layton, R. L., Brandt, P. D., O’Connell, A. B., Hall, J. D., Freeman, A. M., Harrell, J. R., Cook, J. G., & Brennwald, P. J. (2017). An evidence-based evaluation of transferrable skills and job satisfaction for science PhDs. PLoS ONE, 12(9), e0185023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smallwood, Z. M., Spencer-Briggs, J. L., San, X. X., Ward, M. D., & Hyde, J. (2022). Design and delivery of a graduate teaching assistant (GTA) program in a UK university: Experiences and perspectives. Journal of Chemical Education, 99(2), 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, M. D., Armstrong, J. E., & Wischusen, E. W. (2005). A reappraisal of the status of introductory biology laboratory education in U.S. colleges and universities. American Biology Teacher, 67, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, J. E., Vahed, Z., & Zannella, L. (2022). Reflections from graduate student instructors on their first-time teaching reveal structural and individual challenges. Open Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 2(1), 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, K. A. (2009). Nurturing undergraduate tutors’ role in the university teaching community. Mentoring & Tutoring: Partnership in Learning, 17(2), 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, A. C. F. (2014). The role of a professional learning community in teacher change: A perspective from beliefs and practices. Teachers and Teaching, 21(1), 22–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasdale, R., Ryker, K., & Bitting, K. (2019). Training graduate teaching assistants in the geosciences: Our practices vs. perceived needs. Journal of Geoscience Education, 67(1), 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torvi, D. A. (1994). Engineering graduate teaching assistant instructional programs: Training tomorrow’s faculty members. Journal of Engineering Education, 83(4), 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townley, A. L. (2020). Leveraging communities of practice as professional learning communities in science, technology, engineering, math (STEM) education. Education Sciences, 10(8), 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L. T., Bui, H., Tan, G., & Rahimi, M. (2022). Post-graduation work visas and loopholes: Insights into support provision for international graduates from the perspectives of migration agents, universities, and international graduates. Evaluation Review, 46(4), 438–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. (2023). Occupational employment and wage statistics. Available online: https://www.bls.gov/oes/2023/may/oes259044.htm (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- U.S. News and World Report. (2017). 10 universities where TAS teach the most classes. Available online: https://www.usnews.com/education/best-colleges/the-short-list-college/articles/2017-02-21/10-universities-where-tas-teach-the-most-classes (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Wald, N., & Harland, T. (2018). Rethinking the teaching roles and assessment responsibilities of student teaching assistants. Journal of Further and Higher Education, 44(1), 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G. E., Golde, C. M., Jones, L., Conklin Bueschel, A., & Hutchings, P. (2008). The formation of scholars: Rethinking doctoral education for the twenty-first century. In The carnegie foundation for the advancement of teaching (256p). Jossey-Bass. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, T., Geraets, A. A., Doty, C. M., Saitta, E. K. H., & Chini, J. J. (2020). Characterizing science graduate teaching assistants’ instructional practices in reformed laboratories and tutorials. International Journal of STEM Education, 7(30). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner-Garcia, S. (2018). Translating PhD skills for non-academic employers. University of Santa Barbara Graduate Division. Available online: https://beyondacademia.ucsb.edu/sites/default/files/2020-09/Transferable-Skills_March-2018.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Weber, R. J., Gabbert, A., Kropp, J., & Pynes, P. (2007). Creating the teaching professor: Guiding graduate students to become effective teachers. The Journal of Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 7(1), 45−63. [Google Scholar]
- Weidert, J. M., Wendorf, A. R., Gurung, R. A. R., & Filz, T. (2012). A survey of graduate and undergraduate teaching assistants. College Teaching, 60(3), 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidman, J. C., Twale, D. J., & Stein, E. L. (2001). Socialization of graduate and professional students in higher education: A perilous passage? In ASHE-ERIC higher education report (Jossey-Bass Higher and Adult Education Series). Vol. 28. Available online: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED457710.pdf (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Wenger, E. (1998). Communities of practice: Learning, meaning, and identity (336p). Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, L. B., Maeng, J. L., & Whitworth, B. A. (2015). Teaching assistants’ perceptions of a training to support an inquiry-based general chemistry laboratory course. Chemistry Education Research and Practice, 16, 824–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins-Yel, K. G., Delaney, T., Gamio Cuervo, Á., Zounlome, N. O. O., & Sparks, P. D. (2024). Examining how graduate advisors mitigate or exacerbate the structural barriers women of color navigate in STEM doctoral programs. Journal of Diversity in Higher Education, 17(5), 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winstone, N., & Moore, D. (2016). Sometimes fish, sometimes fowl? Liminality, identify work and identity malleability in graduate teaching assistants. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 54(5), 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y., Lei, Y., & Sezaki, H. (2024). Impact of educational development programs on teaching self-efficacy in graduate students: A systematic literature review. Procedia Computer Science, 246, 4084–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerushalmi, E., Sayer, R., Marshman, E., Henderson, C., & Singh, C. (2017, July 26–27). Physics graduate teaching assistants’ beliefs about a grading rubric: Lessons learning. Physics Education Research Conference (pp. 408–411), Sacramento, CA, USA. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1701.01412 (accessed on 9 February 2025).
- Yoo, H. J., & Marshall, D. T. (2025). Exploring graduate students’ perceived helplessness, self-efficacy, social support and satisfaction. Studies in Graduate and Postdoctoral Education, 16(1), 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S. L., & Bippus, A. M. (2008). Assessment of graduate teaching assistant (GTA) Training: A case study of a training program and its impact on GTAs. Communication Teacher, 22(4), 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamiri, M., & Esmaeili, A. (2024). Strategies, methods, and supports for developing skills within learning communities: A systematic review of the literature. Administrative Sciences, 14(9), 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J., Cox, M. F., London, J., Hahn, J., & Ahn, B. (2013). Validation of a survey for graduate teaching assistants: Translating theory to practice. Journal of Engineering Education, 102(3), 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zippia. (2025). Graduate teaching assistant demographics and statistics in the US. Available online: https://www.zippia.com/graduate-teaching-assistant-jobs/demographics/ (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Zotos, E. K., Moon, A. C., & Shultz, G. V. (2020). Investigation of chemistry graduate teaching assistants’ teacher knowledge and teacher identity. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 57(6), 943–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Type of Program | University |
|---|---|
| Workshops and seminars on teacher training | Johns Hopkins University, Michigan State University, Tufts University, University of Texas at Austin, University of Rochester |
| co-teaching programs | Princeton University, Stanford University, Yale University |
| pedagogically focused courses | Case Western Reserve University, Clarkson University, University of California Berkeley |
| teaching certificate programs | Brown University, Duke University, Ohio State University, Miami University, University of Michigan |
| preparing future faculty programs | Georgia Institute of Technology, Iowa State University, Howard University, University of Cincinnati, University of Florida, University of Southern Carolina, Virginia Commonwealth University |
| discipline-specific trainings via professional societies | American Association of Physics Teachers, National Association of Geoscience Teachers |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McLeod, C.L.; Almquist, C.B.; Ess, M.P.; Zhang, J.; Schultz, H.; Nguyen, T.; Tran, K.; Hughes, M. Graduate Teaching Assistants (GTAs): Roles, Perspectives, and Prioritizing GTA Workforce Development Pathways. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070838
McLeod CL, Almquist CB, Ess MP, Zhang J, Schultz H, Nguyen T, Tran K, Hughes M. Graduate Teaching Assistants (GTAs): Roles, Perspectives, and Prioritizing GTA Workforce Development Pathways. Education Sciences. 2025; 15(7):838. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070838
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcLeod, Claire L., Catherine B. Almquist, Madeline P. Ess, Jing Zhang, Hannah Schultz, Thao Nguyen, Khue Tran, and Michael Hughes. 2025. "Graduate Teaching Assistants (GTAs): Roles, Perspectives, and Prioritizing GTA Workforce Development Pathways" Education Sciences 15, no. 7: 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070838
APA StyleMcLeod, C. L., Almquist, C. B., Ess, M. P., Zhang, J., Schultz, H., Nguyen, T., Tran, K., & Hughes, M. (2025). Graduate Teaching Assistants (GTAs): Roles, Perspectives, and Prioritizing GTA Workforce Development Pathways. Education Sciences, 15(7), 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070838








