Abstract
Smart classrooms leverage intelligent and mobile technologies to create highly interactive, student-centered environments conducive to personalized learning. However, measuring students’ personalized learning experiences in these technologically advanced spaces remains a challenge. This study addresses the gap by developing and validating a Smart Classroom Environment–Personalized Learning Scale (SCE-PL). Drawing on a comprehensive literature review, content-expert feedback, and iterative item refinement, an initial pool of 48 items was reduced to 39 and subsequently to 34 following item-level analyses. Two datasets were collected from Chinese middle-school students across three provinces, capturing diverse socio-economic contexts and grade levels (7th, 8th, and 9th). EFA on the first dataset (n = 424) revealed a nine-factor structure collectively explaining 78.12% of the total variance. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) on the second dataset (n = 584) verified an excellent model fit. Internal consistency indices (Cronbach’s α > 0.87, composite reliability > 0.75) and strong convergent and discriminant validity evidence (based on AVE and inter-factor correlations) further support the scale’s psychometric soundness. The SCE-PL thus offers researchers, policymakers, and practitioners a robust, theory-driven instrument for assessing personalized learning experiences in smart classroom environments, paving the way for data-informed pedagogy, optimized learning spaces, and enhanced technological integration.
1. Introduction
Advances in intelligent and mobile technologies have given rise to smart classrooms (SCs)—technology-driven learning environments that enhance teaching quality, student engagement, and personalized learning (Gambo & Shakir, 2023; Zhan et al., 2021). SCs integrate information technology, the internet, and digital tools to create intelligent, personalized, and digitized educational spaces (Lycurgus et al., 2024; Ma et al., 2024; Mugruza-Vassallo, 2023; Shaw & Patra, 2022). However, fully harnessing digital technologies requires a shift toward a student-centered, personalized learning culture (C.-M. Chen et al., 2005; S. Y. Chen et al., 2016; Walkington & Bernacki, 2020). Here, defined as a technology-assisted closed environment, SCs support personalized learning and innovative pedagogy (Major et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2020a, 2020b). In this study, we define personalized learning in smart classrooms as an approach that tailors learning experiences based on individual differences—including prior knowledge, cognitive and non-cognitive traits, interests, needs, and goals—through intelligent technologies and systematic instructional design (Hu et al., 2022; Z. Liu et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2023). Our aim is to develop a personalized learning measurement scale for smart classrooms, enabling the assessment of students’ experiences, optimization of teaching strategies, and advancement of personalized learning research.
1.1. Personalized Learning in Smart Classrooms
Personalized learning (PL), rooted in a learner-centered philosophy, respects individual differences by offering flexible methods that help students master knowledge and develop key skills at their own pace (C.-M. Chen et al., 2005; S. Y. Chen et al., 2016; Walkington & Bernacki, 2020). Historically, PL’s roots trace back to John Dewey’s early 20th-century learner-centered philosophy (Keefe & Jenkins, 2008; Redding, 2016). Characteristically, PL challenges the standardized, large-scale education model of the Industrial Revolution, driving modern educational reform (Basham et al., 2016). It acknowledges differences in students’ cognitive and non-cognitive characteristics (Sampson & Karagiannidis, 2002), where cognitive skills involve problem-solving and critical thinking, while non-cognitive traits influence personal growth, social engagement, and achievement (Farkas, 2003; Kell, 2018). S. Y. Chen and Macredie (2010) further identified factors like prior knowledge, cognitive styles, gender, and learning approaches that shape PL. To put it briefly, given its emphasis on individual differences, PL is central to student-centered instructional design.
Like many key concepts in the humanities and social sciences, PL lacks a unified definition. Principally, researchers viewed it through the lens of learner individuality, emphasizing a learner-centered philosophy that promotes active participation and choice in what, how, when, and where students learn (C.-M. Chen et al., 2005; S. Y. Chen et al., 2016; Walkington & Bernacki, 2020). Some define PL from a teaching perspective, considering individual differences (Patrick et al., 2013; U.S. Department of Education, 2010). Others emphasize the role of technology in PL, defining technology-enhanced personalized learning (TEL) as adaptive learning experiences based on real-time assessments (e.g., Bulger, 2016; Major et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2022). All in all, PL is designed based on respecting students’ individual differences, focusing on their cognitive, thinking, emotional aspects, and maximizing the autonomy and subjectivity of their learning (Bulger, 2016; Major et al., 2021; Patrick et al., 2013; U.S. Department of Education, 2010; Zhang et al., 2022).
While teachers can address personalized needs through direct guidance (Bulger, 2016; Holmes et al., 2018), TEL provides scalable solutions for overburdened educators and overcrowded classrooms (Fake & Dabbagh, 2020). As a result, PL approaches and techniques have gained widespread attention in education (Major et al., 2021; Pane et al., 2015; Van Schoors et al., 2021; Xie et al., 2019). Researchers increasingly integrate intelligent technologies into SCs to develop PL systems that deliver tailored recommendations and individualized experiences (Niknam & Thulasiraman, 2020; Ouf et al., 2017; Sungkur & Maharaj, 2021; Troussas et al., 2020). Nevertheless, while technology has shown promise in enhancing PL, its impact in SC environments remains underexplored.
A key challenge is the lack of effective tools to measure PL support, limiting both theoretical research and practical implementation. Although some researchers have developed personalized learning support instruments (PLSIs) based on the universal design for learning (UDL) framework (Zhang et al., 2022), these tools are designed for traditional classrooms and are unsuitable for smart learning environments (Chatti et al., 2010; Cheung et al., 2021; Kloos et al., 2020; Price, 2015; Sharma et al., 2018; Toivonen et al., 2018). Additionally, from our comprehensive literature review, we found that many researchers have explored technology-driven solutions to enhance PL. Wang et al. (2023) describe SCs as an advanced form of online and multimedia-based learning, emphasizing that technology is the key differentiator between smart and traditional classrooms. Hu et al. (2022) introduced a learning analytics dashboard (LAD) in an AI-supported smart learning environment (SLE), allowing students to track and optimize their learning behaviors, leading to significant academic improvement. Kaur and Bhatia (2022) further highlight the role of information and communication technology (ICT) components such as the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and edge computing in realizing this vision. Niknam and Thulasiraman (2020) created a learning path recommendation system using an ant colony optimization algorithm, significantly improving knowledge retention. Yu et al. (2024) developed an intelligent Q&A system for entrepreneurship education, utilizing natural language processing (NLP) to enhance knowledge retrieval and comprehension. Overall, most current research results often center on the application of specific systems or algorithms, and their effectiveness and universality in different environments and broader populations remain unclear (Hu et al., 2022; Kaur & Bhatia, 2022; Niknam & Thulasiraman, 2020; Wang et al., 2023; Yu et al., 2024). Thus, understanding students’ experiences with these innovative solutions becomes essential. Therefore, we adopted a constructivist theoretical perspective for understanding student experiences (Radcliffe, 2009).
1.2. Constructivism
Constructivism suggests that individuals actively construct their own understanding of the world through their experiences and interactions with the environment, and that this process of construction is ongoing throughout the lifespan (Charmaz, 2021; Glaser & Strauss, 1964). Social constructionism/constructivism is, “a theoretical perspective that assumes that people create social reality(ies) through individual and collective actions” (Charmaz, 2006, p. 189). This perspective focuses on how people in a particular time and place create their own perceptions of reality. Instead of assuming that reality exists independently of us, social constructionists “view that social properties are constructed through interactions between people, rather than having a separate existence” (Robson & McCartan, 2016, p. 24). Hence, Radcliffe (2009) proposed the pedagogy–space–technology theoretical framework to foster an understanding of student-centered constructivist pedagogies in education.
1.3. Pedagogy–Space–Technology Framework
David Radcliffe, after launching the “next generation learning spaces” project, proposed a framework for designing and evaluating learning spaces (Radcliffe, 2009). This framework suggests that the composition of a learning space includes three elements: pedagogy, learning space, and technology. It classifies stimuli based on their constituent elements, considering natural objective objects (technology), artificial objective objects (learning space), subjective objects (pedagogy), and other factors. According to the three-dimensional model for learning environment design and evaluation, students engaging in PL connect with teaching methods, the effective integration of technology, and the design of learning spaces (Reushle, 2012). We will examine the rationale for developing this scale in terms of PST dimensions.
1.3.1. Pedagogy
What kind of teaching and learning do we aim to promote, and for what reasons? (Radcliffe, 2009). This question forms the basis of the “pedagogy” dimension. The constantly evolving nature of education and the (so-called) new generation of students places considerable emphasis on the adaptive teaching and characteristics of teachers (Göncz, 2017). According to Huber and Seidel (2018), our understanding of the interplay between teachers and students has recently begun to improve. Compared to teacher-centered pedagogies, which overly emphasize the teacher’s dominant role and neglect students’ individual differences and active learning needs, student-centered pedagogies foster creativity and critical thinking by promoting student autonomy (Bulger, 2016; Major et al., 2021; Patrick et al., 2013; U.S. Department of Education, 2010; Zhang et al., 2022). Furthermore, Basham et al. (2016) found that designing PL experiences requires a restructured educational model that emphasizes individual growth in various areas. Currently, Cheng and Carolyn Yang (2023) summarize three types of student-centered pedagogies—team-based learning, problem-based learning, and project-based learning—and further clarify the differences among them. In addition, precision teaching (Lindsley, 1992) and flipped classrooms are also considered effective student-centered teaching methods (Fan, 2024; C. Liu & Wang, 2018). Since SCs and student-centered pedagogies are interdependent (Koh et al., 2020; Malekigorji & Hatahet, 2020), we recognized the pedagogy dimension as the first rationale.
1.3.2. Learning Spaces
The key question for this dimension is “Which elements of space design and the arrangement of furniture and fixtures influence pedagogical approaches?” (Radcliffe, 2009). A learning space naturally influences how people interact within it, shaped by interactions between students and their environments (Blumer, 1966; Bryant & Charmaz, 2007; Charmaz, 2021; Dai & Chen, 2013; Dai et al., 2011; Lemert, 1974; Mead, 1934/1972; Morse et al., 2021; Robson & McCartan, 2016; Sternberg, 2022; Wirthwein et al., 2019; Ziegler & Bicakci, 2023; Ziegler & Stoeger, 2012; Ziegler et al., 2012). A smart learning space is essentially an intelligent physical space equipped with interactive whiteboards, projectors, automatic assessment/feedback tools, cameras for recording and storing lectures, and sensors that control temperature, humidity, air quality, and acoustics (Saini & Goel, 2019). This is distinct from the commonly discussed “learning environment”, which solely refers to the social, psychological, or conceptual environment (Reushle, 2012; Zhan et al., 2021).
The intelligent systems of smart classrooms are considered as another element in the learning environment with the following interaction types (a) teacher–student, (b) student–student, (c) teacher–media, and (d) student–media (Zhan et al., 2021). Hence, compared to traditional multimedia classroom (TMC) environments, the infrastructural resources of SCs have the potential to significantly influence individuals’ educational pathways and experiences (c.f., Ziegler, 2005; Ziegler & Stoeger, 2017; Ziegler et al., 2012). Bringing it all together, students’ experiences are shaped by their individual perceptions of the learning space (Ketscher et al., 2025; Merton, 1995; Thomas & Thomas, 1928). Eventually, we noted learning spaces as the second rationale.
1.3.3. Technology
In what ways can technology be incorporated into space design to reinforce and improve the desired teaching and learning approaches? (Radcliffe, 2009). Technology supports learning, particularly in promoting PL for students, with a positive and beneficial impact. Some researchers have found that artificial intelligence (AI) technology can not only provide personalized feedback and expert guidance to learners (Yu et al., 2024), but also enhance engagement, offer PL experiences, and ultimately increase motivation and foster autonomous learning (Santhosh et al., 2023). That is to say, the technological infrastructure of SCs can lead to distinct pedagogical improvements compared to traditional and/or technology-integrated classrooms (Chatti et al., 2010; Cheung et al., 2021; Kloos et al., 2020; Price, 2015; Sharma et al., 2018; Toivonen et al., 2018). How learners use smart devices (such as smart tablets, smartphones, etc.) flexibly and effectively in a smart classroom is a key factor in promoting their PL. Thus, we have concluded the third rationale.
1.4. Summary of Research Rationale
The (so-called) new generation of students perceives technology as an integral part of learning and may struggle in technology-limited environments (Tapscott, 2009). Nevertheless, while Basham et al. (2016) find that PL environments demand more than technology, smart classrooms offer this “more” (Yang & Huang, 2015). SCs enhance adaptability and interactivity through advanced technology and AI, offering a more dynamic learning environment than TMCs, which rely on fixed resources and conventional software (Zhan et al., 2021). “Smart classroom is one direction in smart learning environment research”(Yang & Huang, 2015, p. 157). Hence, in this research body, our aim is to develop a scale to measure PL experiences in SC environments.
2. Method
2.1. Development Process of Smart Classroom Personalized Learning Scale (SCE-PL)
This study adopted a deductive approach to scale development, beginning with a comprehensive literature review to define the target construct of PL for middle-school students in SC settings (Hinkin, 1995). Existing scales and questionnaires were evaluated to identify gaps and areas for refinement, focusing particularly on five key instruments: Fraser (1998)’s What is happening in this class? (WIHIC), Zhang et al. (2022)’s personalized learning experience support instrument (PLSI), EDUCASE Learning Initiative (2021)’s learning space rating system, Timothy et al. (2010)’s self-directed learning with technology scale (SDLTS), and Yang and Huang (2015)’s classroom environment evaluation scale (CEES). From these sources, an initial pool of 48 items was generated, covering topics such as teaching methods and learning spaces. Subsequently, two Chinese information technology experts conducted three rounds of discussions to ensure clarity, exclusivity, and alignment with the scale’s objectives (DeVellis, 1991; Hambleton, 2005; Hinkin, 1995). Through this process, four items were removed for failing to meet relevance or clarity requirements (e.g., The view outside the classroom window relaxes me and enhances my learning atmosphere). This phase concluded with 44 initial items.
Content validity—how effectively an instrument’s items capture the intended construct (Polit & Beck, 2006)—was assessed by 11 experts (8 university professors and 3 secondary school teachers) in information technology (IT). After two rounds of expert feedback, 5 additional items were eliminated due to issues of redundancy or ambiguity (DeVellis, 1991; Hambleton, 2005), leaving 39 items in the initial scale (Appendix A, Table A1). The questionnaire comprised two sections: (1) demographic information about the respondents, and (2) the 39-item SCE-PL, rated on a 5-point Likert scale (1 = “strongly disagree”, 5 = “strongly agree”).
2.2. Sampling Frame and Participants
A combination of stratified and convenience sampling was employed to capture diverse educational contexts. Three provinces in China (Guangdong, Shaanxi, and Inner Mongolia) were selected to reflect variations in economic development and educational practices. Within each province, one representative school was purposively chosen, and students from multiple grade levels (7th, 8th, 9th) were included to enhance generalizability. All participating schools had adopted technology-enhanced PL strategies, providing a suitable environment for investigating the proposed scale.
The research targeted Chinese middle-school students who had experience in SC settings. A SC was defined as a learning space equipped with interactive whiteboards, recording systems, VR/AR devices, and student terminal devices, e.g., tablets and laptops (Lycurgus et al., 2024; Ma et al., 2024; Mugruza-Vassallo, 2023; Shaw & Patra, 2022). Prior to data collection, data collection approval was obtained from local school administrators, superintendents or principals, and class teachers. Furthermore, in order to avoid an ethical dilemma, we prepared our research under the guidance of people like Kropotkin (1922/1924) or Resnik (1998), and ethical codes such as the American Educational Research Association (AERA, 2011), American Psychological Association (APA, 2017), “The Nuremberg Code (1947)” (The Nuremberg Code (1947), 1996), and Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute’s research and publication ethics (MDPI, n.d.).
2.3. Data Collection
The questionnaire was distributed online through Wenjuanxing (https://www.wjx.cn/), with the assistance of IT teachers. Data were collected in two waves. The first dataset (n = 440 initially, 424 valid after screening) was designated for exploratory factor analysis (EFA), while the second dataset (n = 598 initially, 584 valid after screening) was reserved for confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) to verify the structural validity of the SCE-PL. The demographic composition of the participants is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The demographic composition of the samples.
2.4. Data Preparation
Two researchers jointly managed the statistical analyses to ensure consistency and accuracy. SPSS 26.0 was employed to conduct item analysis using the critical ratio (CR) method and reliability tests (Hair et al., 2010). The decision rules were (a) retain items with significant CR values (p < 0.05) and t > 3; and (b) ensure Cronbach’s α remains above 0.70, item-total correlation (CITC) exceeds 0.35, and that deleting an item does not elevate the dimension’s α (Yuan et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2023). Based on these criteria, five items (CG3, FMM4, SLV3, LD2, and DA3) were eliminated, leaving 34 items. Further reliability checks confirmed that all remaining items had α coefficients above 0.70, that removing them would lower the dimension’s reliability, and that item-total correlations exceeded 0.40 (Tabachnick & Fidell, 2007).
2.5. Data Analysis
EFA is routinely employed to assess the construct validity of an instrument. Prior to factor extraction, the data’s suitability was evaluated using the Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin (KMO) test and Bartlett’s test of sphericity (Huck et al., 1974; Zhao et al., 2023). The KMO value was 0.889 (>0.70), indicating strong inter-item correlations, and Bartlett’s test was highly significant (χ2 = 10,258.843, df = 561, p < 0.001), confirming that common factors were present (Table 2). Principal component analysis (PCA) with varimax rotation then extracted nine factors with eigenvalues greater than 1 (DeVellis, 1991).

Table 2.
KMO test and Bartlett’s test of sphericity.
CFA was conducted using AMOS 23.0 on the second dataset (n = 584) to verify whether the model derived from EFA aligned with theoretical expectations. Model fit was assessed via multiple indices: χ2, RMSEA, CFI, TLI, RMR, GFI, AGFI, NFI, and IFI. Common acceptance criteria include χ2/df < 5, RMR ≤ 0.05, RMSEA < 0.08, GFI and AGFI > 0.80, and CFI, NFI, IFI, and TLI > 0.90. After confirming model fit, reliability and validity tests (including convergent and discriminant validity) were performed to finalize the scale structure.
3. Results
EFA was conducted on the first dataset (n = 424) to identify the latent structure of the initial scale. The KMO value (0.889) and Bartlett’s test of sphericity (χ2 = 10,258.843, df = 561, p < 0.001) confirmed the adequacy of the data for factor analysis. PCA with varimax rotation extracted nine factors with eigenvalues exceeding 1. Together, these factors accounted for 78.12% of the total variance, surpassing typical benchmarks in educational and psychological research (Gruijters, 2019; Härdle & Simar, 2015; Tabachnick & Fidell, 2007). The scree plot (Figure 1) shows a sharp drop in eigenvalues over the first nine factors, followed by a distinct “elbow”, after which the remaining factors level out with eigenvalues below 1. Factor loadings exceeded 0.60 for all retained items, and no additional deletions were necessary, thus yielding a robust nine-factor structure for subsequent validation.
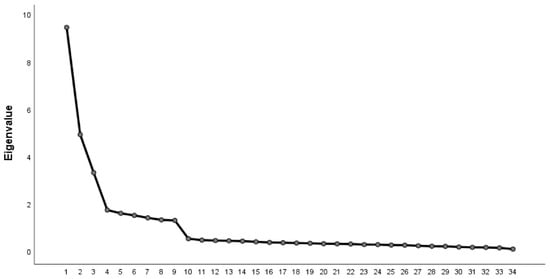
Figure 1.
Scree plot.
The second dataset (n = 584), with a ratio of approximately 17:1 respondents per item, was used to verify the nine-factor structure. AMOS 24.0 estimated a model comprising nine first-order factors—Timely Progress Monitoring (TPM), Intelligent Diagnosis and Services (IDS), Layout and Display (LD), Flexible Instructional Methods and Materials (FMM), Clear and Relevant Goals (CRG), Environmental Quality (EQ), Access to Resources (AR), Supporting Learner Variability (SLV), and Device Access (DA)—organized under three broader dimensions (pedagogy, space, and technology). Model fit was excellent (χ2/df = 1.515, RMSEA = 0.030, GFI = 0.929, AGFI = 0.918, NFI = 0.946, TLI = 0.979, and CFI = 0.981), and all factor loadings were significant (p < 0.001). No item showed cross-loadings, verifying that the 34 retained items accurately measured their intended constructs (Huck et al., 1974). Figure 2 illustrates the final model, while further analyses confirmed that variables were correctly assigned to the nine factors, each aligning with the theoretical dimensions established through expert review.
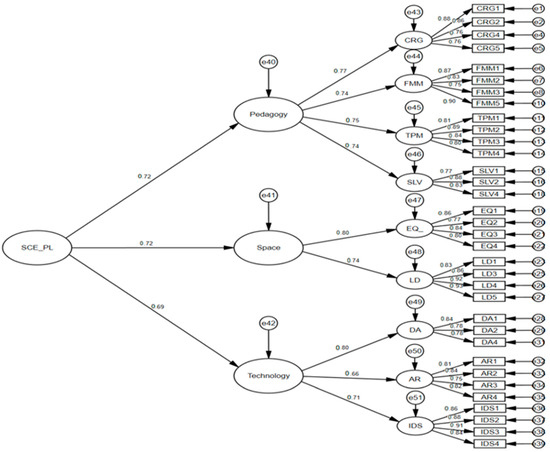
Figure 2.
Model of confirmatory factor analysis.
The rotated component matrix (Table 3) shows how each survey item clusters onto nine distinct factors, with each column (Components 1–9) corresponding to one factor. For example, items TPM1–TPM4 load strongly on Component 1 (all above 0.80), indicating they measure a single underlying construct (Timely Progress Monitoring). Similarly, items IDS1–IDS4 load on Component 2 (Intelligent Diagnosis and Services), LD1–LD5 on Component 3 (Layout and Display), etc. Consequently, this table supports the conclusion that the final 34-item questionnaire reliably measures nine distinct constructs, each capturing a unique aspect of PL in a SC environment.

Table 3.
Rotated component matrix.
Cronbach’s alpha was used to assess internal consistency. The overall alpha coefficient for the scale was 0.938, while the subscales ranged from 0.887 to 0.924, all well as being above the commonly accepted threshold of 0.70. Table 3 presents the means, standard deviations, and correlation coefficients among the nine latent constructs (CRG, FMM, TPM, SLV, EQ, LD, DA, AR, and IDS). The bold-faced diagonal entries (e.g., 0.820, 0.839) are the square roots of the AVE for each factor.
The Fornell–Larcker criterion supported discriminant validity: the square roots of the AVE for each factor surpassed the correlations with other factors, indicating that the nine constructs are empirically distinct. As shown in Table 4, the EFA and CFA findings, alongside favorable reliability and validity metrics, affirm that the nine-factor, 34-item SCE-PL is both psychometrically sound and theoretically coherent.

Table 4.
Discriminant validity.
Table 5 offers a detailed overview of the convergent validity indices for the SCE-PL. Convergent validity was established by factor loadings (>0.50), composite reliability (>0.70), and average variance extracted (>0.50) for each factor, confirming that items within each subscale converge on a single underlying dimension.

Table 5.
Convergent validity.
4. Discussion
This study developed and validated the smart classroom environment–personalized learning scale (SCE-PL), a measurement instrument designed to capture middle-school students’ PL experiences in SC environments. Drawing on literature reviews, expert consultations, and iterative item refinement, we generated a final instrument comprising 34 items and nine factors aligned with three overarching dimensions: pedagogy, learning space, and technology (Radcliffe, 2009). EFA indicated that these nine factors accounted for a substantial portion of the total variance, while confirmatory factor analysis confirmed strong model fit and factor loadings. Reliability tests (Cronbach’s alpha and composite reliability) met or exceeded standard criteria, and convergent and discriminant validity were supported through factor loadings, AVE, and the Fornell–Larcker criterion. These findings underscore that the nine-factor structure and strong psychometric properties of the SCE-PL scale corroborate the claim that PL in SCs emerges from a dynamic interplay of student-centered pedagogy, thoughtfully designed learning spaces, and well-integrated technology (Basham et al., 2016; Bulger, 2016; Chatti et al., 2010; S. Y. Chen et al., 2016; Fraser, 1998; Gambo & Shakir, 2023; Z. Liu et al., 2022; Mead, 1934/1972; Radcliffe, 2009; Yang & Huang, 2015; Zhan et al., 2021; Ziegler, 2005; Ziegler & Stoeger, 2017).
The results enrich the theoretical dialogue surrounding PL and SC research by systematically bridging pedagogy, space, and technology factors under a single measurement framework (Ouf et al., 2017; Pane et al., 2015; Price, 2015; Radcliffe, 2009; Reushle, 2012; Saini & Goel, 2019; Van Schoors et al., 2021; Walkington & Bernacki, 2020; Xie et al., 2019; Yang & Huang, 2015; Zhan et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2020a). Earlier research often centered on specific technologies (e.g., learning analytics dashboards and algorithm-based recommendation systems) or conceptual models lacking robust validation in varied contexts (e.g., Hu et al., 2022; Kaur & Bhatia, 2022; Niknam & Thulasiraman, 2020; Wang et al., 2023; Yu et al., 2024). By integrating Radcliffe’s (2009) PST framework with the conceptual underpinnings of PL, this study contributes a nuanced perspective that acknowledges both the instructional design (teacher strategies, student autonomy, and flexible methods) and environmental design (physical layout and device access) critical for personalizing students’ learning processes. Consequently, the SCE-PL may serve as a foundational tool for future empirical inquiries into how these dimensions interact to shape adaptive learning experiences.
From a constructivist perspective, learning is a process in which students actively construct meaning based on their experiences, interactions, and reflections. This study emphasizes the situated nature of PL by confirming that each of the nine subfactors is distinct yet correlated. Students are not merely passive recipients of knowledge; they engage with instructional materials, classroom technologies, peers, and teachers in ways profoundly shaped by individual differences and contextual factors. Such a view aligns with social constructionism, wherein reality—and, by extension, learning experiences (Charmaz, 2021; Glaser & Strauss, 1964; Robson & McCartan, 2016)—are co-constructed in specific social and technological contexts. The robust loadings of subfactors related to pedagogy further highlight that PL is not only about customizing content or pacing; it also depends on the interactive, learner-centered strategies that spark motivation and autonomy (Fraser, 1998; Tapscott, 2009; Yang & Huang, 2015; Zhan et al., 2021). The consistent internal consistency of these constructs suggests that educators who adopt learner-oriented pedagogies guided by constructivist principles significantly influence students’ PL experiences.
The findings validate prior arguments that student-centered instructional methods (e.g., team-based learning and flipped classrooms) are essential for personalizing the learning experience (Basham et al., 2016; Bulger, 2016; Cheng & Carolyn Yang, 2023). That Timely Progress Monitoring (TPM) loaded strongly under pedagogy underscores the importance of continuous, data-driven feedback loops, aligning with constructivist theories that posit real-time interaction as a core facilitator of deeper learning. A smart learning space includes elements like interactive whiteboards, flexible seating, and environmental controls (Saini & Goel, 2019). Hence, the significant loadings for Environmental Quality (EQ) and Layout and Display (LD) confirm the critical role of physical and infrastructural design in creating learning spaces (Blumer, 1966; Reushle, 2012). The data suggests that these factors are not merely aesthetic or comfort-related; they tangibly shape students’ perceptions of autonomy, engagement, and collaboration.
Strong factor loadings for Access to Resources (AR), Device Access (DA), and Intelligent Diagnosis and Services (IDS) reinforce the claim that smart technology is integral to PL, notably when it offers adaptive feedback, varied resources, and real-time assessments (Hu et al., 2022; Niknam & Thulasiraman, 2020; Yu et al., 2024). Such findings echo emerging stances on how technology mediates learning by providing interactive experiences that allow students to co-construct knowledge rather than passively receive it. Moreover, the evidence that these technological subfactors are empirically distinct yet interrelated with pedagogy and space underscores Radcliffe’s (2009) assertion that technology must be purposefully embedded within pedagogical strategies and physical infrastructure to maximize its educational impact. Furthermore, rather than seeing technology as a standalone enabler, the data illustrate that technology’s efficacy in personalizing education is contingent upon compatible pedagogical methods (such as immediate feedback and flexible pacing) and well-designed spaces (supportive seating, adjustable lighting, and interactive displays). Consequently, this study provides a more granular, empirically grounded articulation of how the synergy among pedagogy, space, and technology contributes to student-centered, adaptive learning cultures.
Finally, the validated structure of the SCE-PL enriches ongoing scholarly discourse on PL by merging classic learner-centered theories (John Dewey, Piaget, Vygotsky) with modern, technology-integrated approaches (Bulger, 2016; Major et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2022). The high internal consistency of subscales like Flexible Instructional Methods and Materials (FMM) or Supporting Learner Variability (SLV) highlights that personalizing education is not a single-pronged strategy but a holistic endeavor. Each dimension—be it real-time progress monitoring, physical layout, or AI-driven diagnostics—contributes uniquely to the learner’s constructivist process of active knowledge building (S. Y. Chen & Macredie, 2010). Moreover, mapping these subscales onto the pedagogy–space–technology matrix illustrates that personalization extends beyond simply providing digital resources or customizing tasks; it requires cohesive pedagogical design, flexible spatial arrangements, and sophisticated technological infrastructure. This integrated view resonates with the broader notion of “smart learning environments”, wherein learning transcends mere digitization to become an adaptive, interactive, and profoundly learner-centered experience (Ma et al., 2024; Mugruza-Vassallo, 2023; Yuan et al., 2021; Zhan et al., 2021).
Practitioners and policymakers can leverage the SCE-PL to diagnose and optimize PL initiatives within SCs. By pinpointing strengths and weaknesses across nine distinct factors—such as Timely Progress Monitoring (TPM), Device Access (DA), or Layout and Display (LD)—teachers and administrators gain actionable insights for targeted improvements. For instance, if students rate “Layout and Display” lower, schools might invest in rearranging seating or upgrading interactive displays to boost engagement. Likewise, higher scores in “Intelligent Diagnosis and Services” (IDS) but moderate scores in “Flexible Instructional Methods and Materials” (FMM) could imply that while real-time data analytics are robust, the range of pedagogical materials needs expansion. Overall, these diagnostic applications can foster continuous quality enhancement in SCs, aligning with broader global shifts toward data-informed educational practice (Kaur & Bhatia, 2022; C. Liu & Wang, 2018; Radcliffe, 2009; Reushle, 2012; Sharma et al., 2018; Zhan et al., 2021).
Despite its rigorous methodology, this study has several limitations. First, generalizability may be constrained by the sampling strategy, which, although stratified across three Chinese provinces, remains situated in specific cultural and educational contexts. Future validations in diverse regions—especially outside East Asia—are encouraged to ascertain the scale’s broader applicability. Second, self-reported data can be susceptible to social desirability bias, as students may overstate or understate their experiences (Diefes-Dux, 2019; Zhang et al., 2022). Incorporating observational or performance-based measures could yield a more holistic evaluation of PL (Sampson & Karagiannidis, 2002). Third, while the SCE-PL captures key dimensions aligned with the PST framework, other latent variables—such as motivation, self-efficacy, or teacher autonomy support—may also influence PL experiences (Fraser, 1998; Yang & Huang, 2015). Integrating these constructs could offer richer insights.
Building on the SCE-PL, researchers might explore longitudinal designs to assess how students’ PL experiences evolve over time, particularly as SC infrastructure and pedagogical innovations mature. Cross-cultural replication could illuminate whether the nine-factor structure holds under varying educational policies, socio-economic conditions, or technological advancements. Additionally, experimental or quasi-experimental designs could investigate causal relationships between improved scores on specific subscales and measurable outcomes such as academic performance, engagement, or self-regulated learning skills. Finally, further integration with learning analytics—for instance, correlating SCE-PL scores with real-time data from learning management systems—could refine our understanding of how different aspects of the scale map onto students’ actual learning behaviors.
To conclude, by uniting pedagogy, space, and technology elements into a validated nine-factor instrument, this study addresses a critical gap in measuring PL experiences within SCs. The SCE-PL offers a theoretically grounded and empirically substantiated tool for both researchers and practitioners, enabling more precise identification of strengths and challenges in technology-enriched instructional settings. Doing so lays the groundwork for data-driven refinements to PL strategies, ultimately advancing the broader goal of placing learner individuality at the heart of educational innovation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.Z., B.Z., P.T. and M.B.; methodology, P.T., A.Z. and M.B.; software, P.T.; validation, P.T.; formal analysis, P.T.; investigation, P.T. and M.B.; resources, P.T. and M.B.; data curation, P.T.; writing—original draft preparation, P.T. and M.B.; writing—review and editing, M.B., P.T. and A.Z.; visualization, P.T. and M.B.; supervision, A.Z. and B.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the China Scholarship Council’s 2023 Program for Study Abroad for Graduate Students from Key Universities (Grant No. 202306870075). No Article Processing Charge (APC) was incurred for this publication.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Faculty of Education, Shaanxi Normal University (date of 20 February 2025).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors up-on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AERA | American Educational Research Association |
| APA | American Psychological Association |
| AR | Access to Resources |
| AVE | Average Variance Extracted |
| CFA | Confirmatory Factor Analysis |
| CR | Composite Reliability |
| CRG | Clear and Relevant Goals |
| DA | Device Access |
| EFA | Exploratory Factor Analysis |
| EQ | Environmental Quality |
| FMM | Flexible Instructional Methods and Materials |
| IDS | Intelligent Diagnosis and Services |
| KMO | Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin |
| LD | Layout and Display |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| PST | Pedagogy–Space–Technology |
| SC | Smart Classroom |
| SCE_PL | Smart Classroom Environment–Personalized Learning |
| SLV | Supporting Learner Variability |
| TEL | Technology-Enhanced Personalized Learning |
| TMC | Traditional Multimedia Classrooms |
| TPM | Timely Progress Monitoring |
Appendix A

Table A1.
The 39 items on SCE-PLE developed in the first stage.
Table A1.
The 39 items on SCE-PLE developed in the first stage.
| Items | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. The teacher sets personalized learning goals for me based on my learning data. | |||||
| 2. I clearly understand the learning objectives of each smart classroom lesson. | |||||
| 3. The smart platform or smart devices (such as tablets, laptops, etc.) recommend suitable learning tasks to help me achieve the learning goals. | |||||
| 4. The teacher provides feedback on my progress toward achieving learning goals through the smart platform. | |||||
| 5. The smart classroom offers learning content and resources that I am interested in. | |||||
| 6. The teacher provides multiple learning content options through the smart platform, and I can choose the most suitable content based on my interests and needs. | |||||
| 7. The teacher uses smart tools (such as online resource libraries and learning path recommendation systems) to recommend diverse learning materials (such as videos, articles, exercises, etc.) for me. | |||||
| 8. I can participate in the course in different ways (such as online discussions, virtual experiments, group collaboration, etc.) through the smart platform or smart devices. | |||||
| 9. The teacher offers various ways to showcase learning outcomes (such as text, charts, videos, etc.) via the smart platform, allowing me to choose the most appropriate method. | |||||
| 10. The smart platform or smart devices provide abundant learning resources and materials, allowing me to flexibly choose the most suitable learning approach. | |||||
| 11. The teacher monitors my learning progress in real time through the smart platform and adjusts the teaching content and methods accordingly. | |||||
| 12. When I make mistakes in class, the teacher provides more accurate guidance based on the diagnostic feedback from the smart platform. | |||||
| 13. The teacher checks my learning progress in real time through the smart platform and provides timely feedback. | |||||
| 14. The teacher regularly checks my progress on completing learning tasks through the smart platform. | |||||
| 15. The teacher designs personalized learning tasks based on my learning data to help me better understand the course topics. | |||||
| 16. The teacher provides me with challenging tasks suited to my learning level through the smart platform. | |||||
| 17. The teacher uses smart tools (such as group functions) to help me collaborate with classmates to meet my personalized learning needs. | |||||
| 18. The teacher adjusts teaching strategies based on learning analysis reports from the smart platform to ensure that each student learns in the most suitable way. | |||||
| 19. The classroom has sufficient natural light, allowing me to see the blackboard and textbooks more clearly, which enhances my learning experience. | |||||
| 20. I can adjust the temperature of the smart classroom according to my needs, ensuring comfort without distractions. | |||||
| 21. I can adjust the brightness of the classroom lighting as needed, making the learning environment more comfortable. | |||||
| 22. The classroom’s sound system ensures that I can clearly hear the teacher’s explanations. | |||||
| 23. I find the seating in the classroom very comfortable, which helps me focus on learning. | |||||
| 24. The seating arrangement in the classroom is flexible, allowing me to move in and out easily and interact with others. | |||||
| 25. I can easily adjust the position of smart devices to participate in different types of learning activities. | |||||
| 26. The desk size is just right, providing enough space for textbooks, smart devices, and other materials. | |||||
| 27. The layout of the classroom’s central control system, interactive whiteboard, and smart projectors is well-organized, suitable for both teaching and learning. | |||||
| 28. I can easily use the smart devices provided by the school for learning. | |||||
| 29. The smart devices provided by the school are high-quality and capable of supporting a variety of learning tasks. | |||||
| 30. I can continue learning at home using the smart devices or smart platform provided by the school. | |||||
| 31. The school regularly updates and maintains the smart devices to ensure they are functioning properly. | |||||
| 32. I can easily access the learning resources recommended by the teacher (such as videos, articles, exercises, etc.) through the smart platform or smart devices. | |||||
| 33. I can access supplementary learning resources related to the course content through the smart platform or smart devices. | |||||
| 34. I can share learning resources with other classmates through the smart platform or smart devices. | |||||
| 35. The smart platform generates a personalized list of learning resources to help me complete learning tasks more effectively. | |||||
| 36. The smart platform or smart devices automatically analyze my learning weaknesses based on my learning data (such as quiz results, study time, etc.). | |||||
| 37. When I encounter learning difficulties, the smart platform or smart devices recommend suitable learning resources or solutions to assist me. | |||||
| 38. The smart platform or smart devices generate a personalized learning report to help me track my learning progress. | |||||
| 39. After completing learning tasks, the smart platform or smart devices provide detailed error analysis and improvement suggestions. |
References
- AERA. (2011). AERA code of ethics: American educational research association approved by the AERA council February 2011. Educational Researcher, 40(3), 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APA. (2017). Ethical principles of psychologists and code of conduct. American Psychological Association. Available online: https://www.apa.org/ethics/code/ethics-code-2017.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Basham, J. D., Hall, T. E., Carter, R. A., & Stahl, W. M. (2016). An operationalized understanding of personalized learning. Journal of Special Education Technology, 31(3), 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumer, H. (1966). Sociological implications of the thought of George Herbert mead. American Journal of Sociology, 71, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, A., & Charmaz, K. (2007). Grounded theory research: Methods and practices. In A. Bryant, & K. Charmaz (Eds.), The SAGE handbook of grouded theory (pp. 1–28). Sage. [Google Scholar]
- Bulger, M. (2016). Personalized learning: The conversations we’re not having. Data and Society, 22(1), 1–29. Available online: https://www.datasociety.net/pubs/ecl/PersonalizedLearning_primer_2016.pdf (accessed on 18 February 2025).
- Charmaz, K. (2006). Constructing grounded theory: A practical guide through qualitative analysis. Sage. [Google Scholar]
- Charmaz, K. (2021). The genesis, grounds, and growth of constructivist grounded theory. In J. M. Morse, B. J. Bowers, K. Charmaz, A. E. Clarke, J. Corbin, C. J. Porr, & P. N. Stern (Eds.), Developing grounded theory: The second generation revisited (2nd ed., pp. 153–187). Routledge. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatti, M. A., Agustiawan, M. R., Jarke, M., & Specht, M. (2010). Toward a personal learning environment framework. International Journal of Virtual and Personal Learning Environments (IJVPLE), 1(4), 66–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-M., Lee, H.-M., & Chen, Y.-H. (2005). Personalized e-learning system using item response theory. Computers & Education, 44(3), 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Y., Huang, P.-R., Shih, Y.-C., & Chang, L.-P. (2016). Investigation of multiple human factors in personalized learning. Interactive Learning Environments, 24(1), 119–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Y., & Macredie, R. (2010). Web-based interaction: A review of three important human factors. International Journal of Information Management, 30(5), 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C. C., & Carolyn Yang, Y. T. (2023). Impact of smart classrooms combined with student-centered pedagogies on rural students’ learning outcomes: Pedagogy and duration as moderator variables. Computers and Education, 207, 104911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, S. K. S., Kwok, L. F., Phusavat, K., & Yang, H. H. (2021). Shaping the future learning environments with smart elements: Challenges and opportunities. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 18(1), 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D. Y., & Chen, F. (2013). Three paradigms of gifted education: In search of conceptual clarity in research and practice. Gifted Child Quarterly, 57(3), 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D. Y., Swanson, J. A., & Cheng, H. (2011). State of research on giftedness and gifted education: A survey of empirical studies published during 1998–2010 (April). Gifted Child Quarterly, 55(2), 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVellis, R. F. (1991). Scale development: Theory and applications. Sage Publications, Inc. [Google Scholar]
- Diefes-Dux, H. A. (2019). Student self-reported use of standards-based grading resources and feedback. European Journal of Engineering Education, 44(6), 838–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EDUCASE Learning Initiative. (2021). Learning space rating system. Available online: https://www.educause.edu/focus-areas-and-initiatives/teaching-and-learning-program/initiatives/learning-space-rating-system (accessed on 21 February 2025).
- Fake, H., & Dabbagh, N. (2020). Personalized learning within online workforce learning environments: Exploring implementations, obstacles, opportunities, and perspectives of workforce leaders. Technology, Knowledge and Learning, 25(4), 789–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J. (2024). Construction and application of English smart classroom teaching model integrating MOOC and flipped classroom. Applied Mathematics and Nonlinear Sciences, 9(1), 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, G. (2003). Cognitive skills and noncognitive traits and behaviors in stratification processes. Annual Review of Sociology, 29, 541–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, B. J. (1998). Classroom environment instruments: Development, validity and applications. Learning Environments Research, 1, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambo, Y., & Shakir, M. Z. (2023). Evaluating students’ experiences in self-regulated smart learning environment. Education and Information Technologies, 28(1), 547–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, B. G., & Strauss, A. L. (1964). Awareness contexts and social interaction. American Sociological Review, 29(5), 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göncz, L. (2017). Teacher personality: A review of psychological research and guidelines for a more comprehensive theory in educational psychology. Open Review of Educational Research, 4(1), 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruijters, S. L. K. (2019). Using principal component analysis to validate psychological scales: Bad statistical habits we should have broken yesterday II. The European Health Psychologist, 20(5), 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., Anderson, R. E., & Tatham, R. L. (2010). Multivariate data analysis (Vol. 5). Prentice-Hall. [Google Scholar]
- Hambleton, R. K. (2005). Issues, designs, and techinical guidelenes for adapting tests into multiple languages and cultures. In R. K. Hambleton, P. F. Merand, & C. D. Spielberger (Eds.), Adapting educational and psychological tests for cross-cultural assessment. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc. Publishers. [Google Scholar]
- Härdle, W. K., & Simar, L. (2015). Applied multivariate statistical anaylsis (4th ed.). Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkin, T. R. (1995). A review of scale development practices in the study of organizations. Journal of Management, 21(5), 967–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, W., Anastopoulou, S., Schaumburg, H., & Mavrikis, E. (2018). Technology-enhanced personalised learning: Untangling the evidence. Robert Bosch Stiftung. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y., Huang, J., & Kong, F. (2022). College students’ learning perceptions and outcomes in different classroom environments: A community of inquiry perspective. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 1047027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S. A., & Seidel, T. (2018). Comparing teacher and student perspectives on the interplay of cognitive and motivational-affective student characteristics. PLoS ONE, 13(8), e0200609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huck, S. W., Cormier, W. H., & Bounds, W. G. (1974). Reading statistics and research. Harper & Row. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, A., & Bhatia, M. (2022). Smart classroom: A review and research agenda. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 71, 2430–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefe, J. W., & Jenkins, J. M. (2008). Personalized instruction: The key to student achievement (2nd ed.). Rowman & Littlefield Education. [Google Scholar]
- Kell, H. J. (2018). Noncognitive proponents’ conflation of “cognitive skills” and “cognition” and its implications. Personality and Individual Differences, 134(2018), 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketscher, L., Stoeger, H., Vialle, W., & Ziegler, A. (2025). Same classroom, different reality: Secondary school students’ perceptions of STEM lessons—A pioneering study. Education Sciences, 15(4), 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloos, C. D., Alario-Hoyos, C., Muñoz-Merino, P. J., Ibáñez, M. B., Estévez-Ayres, I., & Fernández-Panadero, C. (2020). Educational technology in the age of natural interfaces and deep learning. IEEE Revista Iberoamericana de Tecnologias del Aprendizaje, 15(1), 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y. Y. J., Schmidt, H. G., Low-Beer, N., & Rotgans, J. I. (2020). Team-based learning analytics: An empirical case study. Academic Medicine, 95(6), 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropotkin, P. (1924). Ethics: Origins and development (L. S. Friedland, & J. R. Piroshnikoff, Trans.). George G. Harrap and Co., Ltd. (Original work published 1922). Available online: https://theanarchistlibrary.org/library/petr-kropotkin-ethics-origin-and-development (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Lemert, E. M. (1974). Beyond Mead: The societal reaction to deviance. Social Problems, 21(4), 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsley, O. R. (1992). Precision teaching: Discoveries and effects. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 25(1), 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C., & Wang, X. (2018, March 2–4). Application of smart education in college English flipped classroom. 8th International Conference on Social Network, Communication and Education (SNCE 2018), Shenyang, China. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z., Zhang, N., Peng, X., Liu, S., Yang, Z., Peng, J., Su, Z., & Chen, J. (2022). Exploring the relationship between social interaction, cognitive processing and learning achievements in a MOOC discussion forum. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 60(1), 132–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lycurgus, T., Kilbourne, A., & Almirall, D. (2024). Approaches to statistical efficiency when comparing the embedded adaptive interventions in a SMART. Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics, 10769986241251419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X., Xie, Y., Yang, X., Wang, H., Li, Z., & Lu, J. (2024). Teacher-student interaction modes in smart classroom based on lag sequential analysis. Education and Information Technologies, 29(12), 15087–15111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, L., Francis, G. A., & Tsapali, M. (2021). The effectiveness of technology-supported personalised learning in low- and middle-income countries: A meta-analysis. British Journal of Educational Technology, 52(5), 1935–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekigorji, M., & Hatahet, T. (2020). Classroom response system in a super-blended learning and teaching model: Individual or team-based learning? Pharmacy, 8(4), 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MDPI. (n.d.). Research and publication ethics. MDPI. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/ethics (accessed on 22 February 2025).
- Mead, G. H. (1972). Mind, self, and society: From the standpoint of a social behaviorist. University of Chicago Press. (Original work published 1934). [Google Scholar]
- Merton, R. K. (1995). The Thomas theorem and the Matthew effect. Social Forces, 74(2), 379–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, J. M., Bowers, B. J., Clarke, A. E., Charmaz, K., Corbin, J., & Porr, C. J. (2021). The challenges to and future(s) of grounded theory. In J. M. Morse, B. J. Bowers, K. Charmaz, A. E. Clarke, J. Corbin, C. J. Porr, & P. N. Stern (Eds.), Developing grounded theory: The second generation revisited (2nd ed., pp. 289–319). Routledge. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugruza-Vassallo, C. A. (2023). A “fractal” expander-compressor-supplier formative research method on array processing. Education and Information Technologies, 28(12), 16349–16372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, M., & Thulasiraman, P. (2020). LPR: A bio-inspired intelligent learning path recommendation system based on meaningful learning theory. Education and Information Technologies, 25(5), 3797–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouf, S., Abd Ellatif, M., Salama, S. E., & Helmy, Y. (2017). A proposed paradigm for smart learning environment based on semantic web. Computers in Human Behavior, 72, 796–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pane, J. F., Steiner, E. D., Baird, M. D., & Hamilton, L. S. (2015). Promising evidence on personalized learning; RAND Corporation. Available online: https://eric.ed.gov/ED571009 (accessed on 22 February 2025).
- Patrick, S., Kennedy, K., & Powell, A. K. (2013). Mean what you say: Defining and integrating personalized, blended and competency education; International Association for K-12 Online Learning. Available online: http://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED561301.pdf (accessed on 22 February 2025).
- Polit, D. F., & Beck, C. T. (2006). The content validity index: Are you sure you know what’s being reported? Critique and recommendations. Research in Nursing & Health, 29(5), 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J. K. (2015). Transforming learning for the smart learning environment: Lessons learned from the Intel education initiatives. Smart Learning Environments, 2(1), 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radcliffe, D. (2009). A pedagogy-space-technology (PST) framework for designing and evaluating learning spaces. In D. Radcliffe, H. Wilson, D. Powell, & B. Tibbets (Eds.), Learning spaces in higher education—Positive outcomes by design. Proceedings of the Next Generation Learning Spaces 2008 Colloquium. University of Queensland. [Google Scholar]
- Redding, S. (2016). Competencies and personalized learning. In M. Murphy, S. Redding, & J. Twyman (Eds.), Handbook on personalized learning for states, districts, and schools (pp. 3–18). Centeril. [Google Scholar]
- Resnik, D. B. (1998). The ethics of science: An introduction. Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Reushle, S. (2012). Designing and evaluating learning spaces: PaSsPorT and design-based research. In M. Keppell, K. Souter, & M. Riddle (Eds.), Physical and virtual learning spaces in higher education: Concepts for the modern learning environment (pp. 87–101). IGI Global. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, C., & McCartan, K. (2016). Real world research: A resource for users of social research methods in applied setting (4th ed.). Wiley. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, M. K., & Goel, N. (2019). How smart are smart classrooms? A review of smart classroom technologies. ACM Computing Surveys, 52(6), 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, D. G., & Karagiannidis, C. (2002). Personalised learning: Educational, technological and standardisation perspective. Digital Education Review, 24–39. [Google Scholar]
- Santhosh, J., Dzsotjan, D., & Ishimaru, S. (2023). Multimodal assessment of interest levels in reading: Integrating eye-tracking and physiological sensing. IEEE Access, 11, 93994–94008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B. N., Nand, R., Naseem, M., Reddy, E., Narayan, S. S., & Reddy, K. (2018, December 4–7). Smart learning in the pacific: Design of new pedagogical tools. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Teaching, Assessment, and Learning for Engineering (TALE), Wollongong, NSW, Australia. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, R., & Patra, B. K. (2022). Classifying students based on cognitive state in flipped learning pedagogy. Future Generation Computer Systems, 126(C), 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, R. J. (2022). Giftedness as trait vs. state. Roeper Review, 44(3), 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungkur, R. K., & Maharaj, M. S. (2021). Design and implementation of a SMART learning environment for the upskilling of cybersecurity professionals in Mauritius. Education and Information Technologies, 26(3), 3175–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (2007). Using multivariate statistics (5th ed.). Allyn & Bacon/Pearson Education. [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott, D. (2009). Grown up digital: How the net generation is changing the world. McGraw Hill. [Google Scholar]
- (1996). The Nuremberg Code (1947). BMJ, 313(7070), 1448. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W. I., & Thomas, D. S. (1928). The child in America: Behavior problems and programs. Knopf. [Google Scholar]
- Timothy, T., Seng Chee, T., Chwee Beng, L., Ching Sing, C., Joyce Hwee Ling, K., Wen Li, C., & Horn Mun, C. (2010). The self-directed learning with technology scale (SDLTS) for young students: An initial development and validation. Computers & Education, 55(4), 1764–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, T., Jormanainen, I., Montero, C. S., & Alessandrini, A. (2018). Innovative maker movement platform for K-12 education as a smart learning environment. In M. Chang, E. Popescu Kinshuk, N.-S. Chen, M. Jemni, R. Huang, & J. M. Spector (Eds.), Challenges and solutions in smart learning. Singapore. [Google Scholar]
- Troussas, C., Krouska, A., & Sgouropoulou, C. (2020). Collaboration and fuzzy-modeled personalization for mobile game-based learning in higher education. Computers & Education, 144, 103698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Education. (2010). Transforming American education: Learning powered by technology; Office of Educational Technology. Available online: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED512681.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- Van Schoors, R., Elen, J., Raes, A., & Depaepe, F. (2021). An overview of 25 years of research on digital personalised learning in primary and secondary education: A systematic review of conceptual and methodological trends. British Journal of Educational Technology, 52(5), 1798–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkington, C., & Bernacki, M. L. (2020). Appraising research on personalized learning: Definitions, theoretical alignment, advancements, and future directions. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 52(3), 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., Xie, K., Liu, Q., Long, T., & Lu, G. (2023). Examining the effect of seat location on students’ real-time social interactions in a smart classroom using experience sampling method. Journal of Computers in Education, 10(2), 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirthwein, L., Bergold, S., Preckel, F., & Steinmayr, R. (2019). Personality and school functioning of intellectually gifted and nongifted adolescents: Self-perceptions and parents’ assessments. Learning and Individual Differences, 73, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H., Chu, H.-C., Hwang, G.-J., & Wang, C.-C. (2019). Trends and development in technology-enhanced adaptive/personalized learning: A systematic review of journal publications from 2007 to 2017. Computers & Education, 140, 103599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J., & Huang, R. (2015). Development and validation of a scale for evaluating technology-rich classroom environment. Journal of Computers in Education, 2(2), 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H., Wang, E., Lang, Q., & Wang, J. (2024). Intelligent retrieval and comprehension of entrepreneurship education resources based on semantic summarization of knowledge graphs. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies, 17, 1210–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X., Yu, L., & Wu, H. (2021). Awareness of sustainable development goals among students from a Chinese senior high school. Education Sciences, 11(9), 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z., Wu, Q., Lin, Z., & Cai, J. (2021). Smart classroom environments affect teacher-student interaction: Evidence from a behavioural sequence analysis. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 37(2), 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L., Basham, J. D., & Carter, R. A. (2022). Measuring personalized learning through the Lens of UDL: Development and content validation of a student self-report instrument. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 72, 101121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L., Basham, J. D., & Yang, S. (2020a). Understanding the implementation of personalized learning: A research synthesis. Educational Research Review, 31, 100339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L., Yang, S., & Carter, R. A. (2020b). Personalized learning and ESSA: What we know and where we go. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 52(3), 253–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J., Zhang, L., & Yao, X. (2023). Developing and validating a scale for university teacher’s caring behavior in online teaching. Education Sciences, 13(3), 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A. (2005). The actiotope model of giftedness. In Conceptions of giftedness (2nd ed., pp. 411–436). Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A., & Bicakci, M. (2023). Labeling the gifted: An overview of four core challenges [Keynote address]. Gifted Students: Nomen est Omen [Nadaný žák: Nomen est Omen], Zlin, Czechia. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, A., & Stoeger, H. (2012). Shortcomings of the IQ-based construct of underachievement. Roeper Review, 34(2), 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A., & Stoeger, H. (2017). Systemic gifted education: A theoretical introduction. Gifted Child Quarterly, 61(3), 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A., Stoeger, H., & Vialle, W. (2012). Giftedness and gifted education: The need for a paradigm change. Gifted Child Quarterly, 56(4), 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).