The Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Academic Learning Practices: A Comprehensive Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Objective
2.2. Participants
2.3. Instrument
2.4. Procedure
3. Results
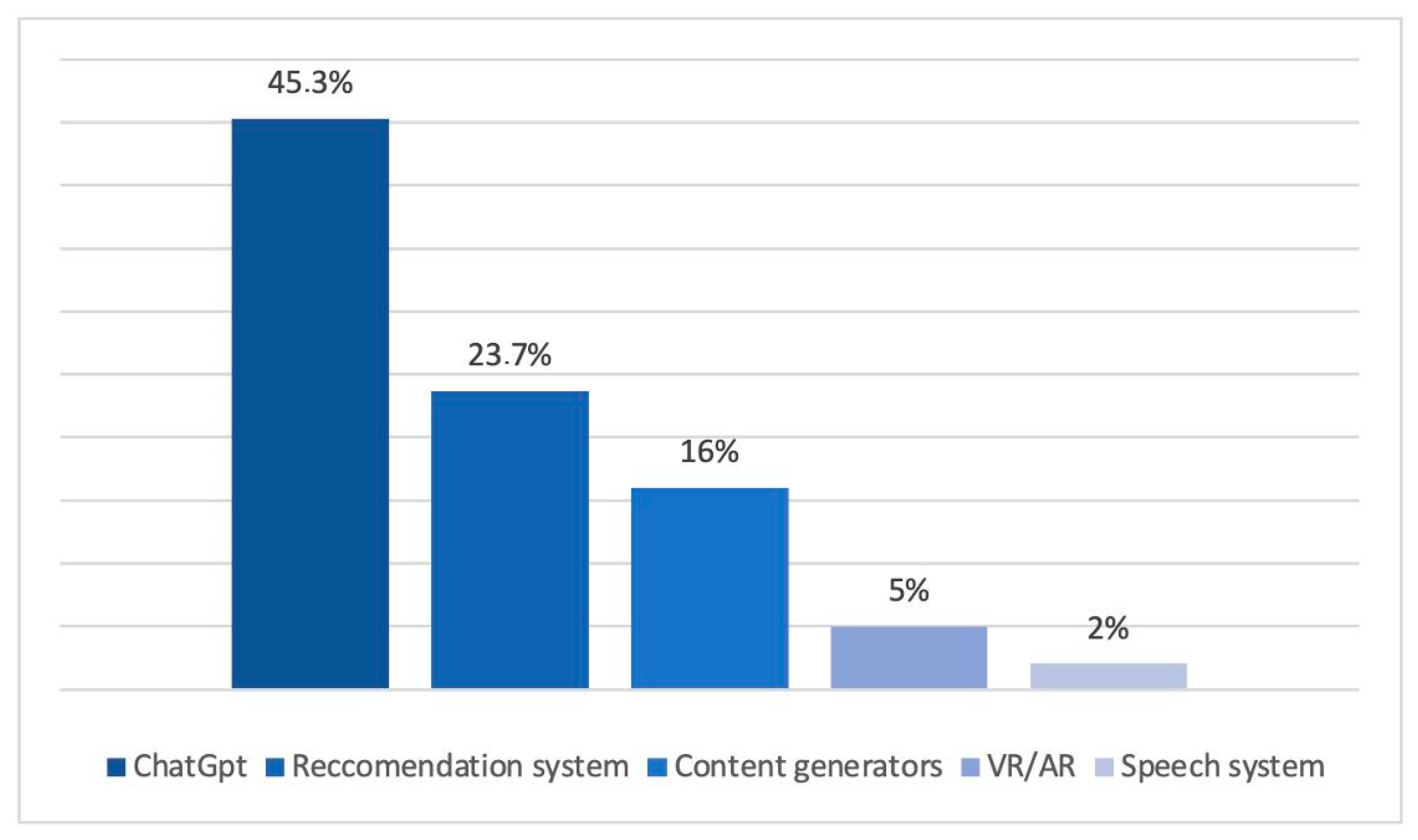
3.1. Students’ Attitudes and Types of AI Tools Used
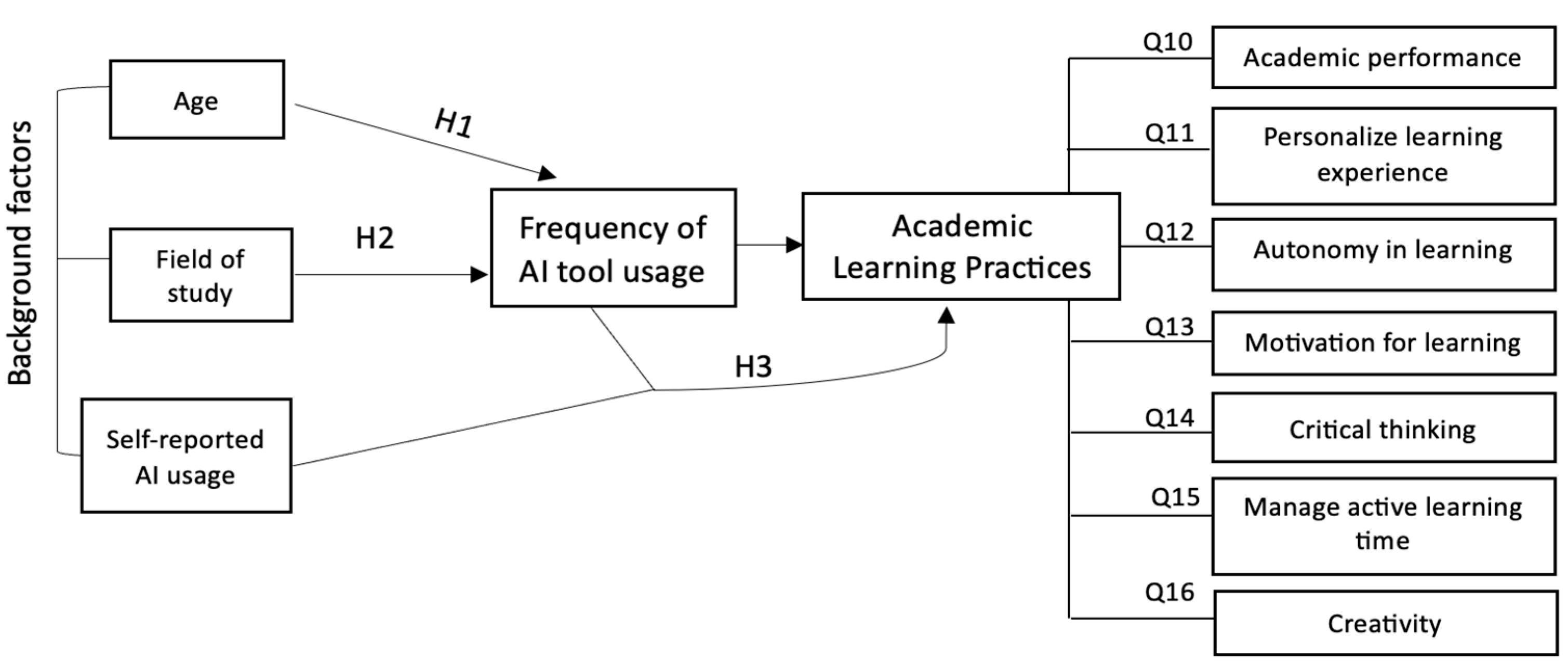
3.2. Frequency of AI Usage Based on Age and Field of Study
3.3. The Impact of AI on Academic Learning Practices
3.4. Correlation Between Self-Reported Competence and the Impact of AI on Academic Learning Practices
3.5. Study Limits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahadzadeh, A. S., Wu, S. L., & Xu, S. (2024). Exploring academic intentions for ChatGPT: A perspective from the theory of planned behavior. CMU Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities, 11(2), e2024016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S. F., Alam, M. M., Rahmat, M. K., Mubarik, M. S., & Hyder, S. I. (2022). Academic and administrative role of artificial intelligence in education. Sustainability, 14(3), 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S. F., Rahmat, M. C., Mubarik, M. S., Alam, M. M., & Hyder, S. I. (2021). Artificial intelligence and its role in education. Sustainability, 13, 12902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaiah, M. A., Alfaisal, R., Salloum, S. A., Hajjej, F., Thabit, S., El-Qirem, F. A., Lutfi, A., Alrawad, M., Al Mulhem, A., Alkhdour, T., Awad, A. B., & Al-Maroof, R. S. (2022). Examining the impact of artificial intelligence and social and computer anxiety in e-learning settings: Students’ perceptions at the university level. Electronics, 11(22), 3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artyukhov, A., Wołowiec, T., Artyukhova, N., Bogacki, S., & Vasylieva, T. (2024). SDG 4, academic integrity, and artificial intelligence: Clash or win-win cooperation? Sustainability, 16, 8483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, A., Prasad, A., & Śliwa, M. (2023). Generative artificial intelligence and academia: Implication for research, teaching and service. Management Learning, 54(5), 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, N. (2010). The shallows: How the internet is changing the way we think, read and remember. Atlantic Books Ltd. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, C. K. Y., & Hu, W. (2023). Students’ voices on generative AI: Perceptions, benefits, and challenges in higher education. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 20(1), 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L., Chen, P., & Lin, Z. (2020). Artificial intelligence in education: A review. IEEE Access, 8, 75264–75278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X., Li, Y., Zhang, Z., & Wang, J. (2022). Two decades of artificial intelligence in education. Educational Technology & Society, 25(1), 28–47. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y., Jensen, S., Albert, L. J., Gupta, S., & Lee, T. (2023). Artificial intelligence (AI) student assistants in the classroom: Designing chatbots to support student success. Information Systems Frontiers, 25(1), 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Code, J. (2020). Agency for learning: Intention, motivation, self-efficacy, and self-regulation. Frontiers in Education, 5, 00019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C. J., Aparicio, M., Aparicio, S., & Aparicio, J. T. (2024). The democratization of artificial intelligence: Theoretical framework. Applied Sciences, 14, 8236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, A., Khosravi, H., Sadiq, S., Gašević, D., & Siemens, G. (2024). Impact of AI assistance on student agency. Computers & Education, 210, 104967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demartini, C. G., Sciascia, L., Bosso, A., & Manuri, F. (2024). Artificial intelligence bringing improvements to adaptive learning in education: A case study. Sustainability, 16(3), 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S. V., & Roy, A. (2021). An empirical exploration of artificial intelligence in medical domain for prediction and analysis of diabetic retinopathy: Review. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1831, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrev, D. (2005). Formal definition of artificial intelligence. International Journal of Information Theories & Applications, 12(3), 277–285. [Google Scholar]
- Elaiess, R. (2023). The impact of artificial intelligence on academics: A concise overview. International Journal of Academic Multidisciplinary Research (IJAMR), 7(4), 218–220. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ramadan-Elaiess/publication/370944811_The_Impact_of_Artificial_Intelligence_on_Academics_A_Concise_Overview/links/64d95dae66f0e0067d931373/The-Impact-of-Artificial-Intelligence-on-Academics-A-Concise-Overview.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Fošner, A. (2024). University students’ attitudes and perceptions towards AI tools: Implications for sustainable educational practices. Sustainability, 16, 8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, B., & Wooden, O. (2023). Managing the strategic transformation of higher education through artificial intelligence. Administrative Sciences, 13(9), 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligorea, I., Cioca, M., Oancea, R., Gorski, A.-T., Gorski, H., & Tudorache, P. (2023). Adaptive learning using artificial intelligence in e-learning: A literature review. Education Sciences, 13(12), 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubareva, R., & Lopes, R. P. (2020). Virtual assistants for learning: A systematic literature review. CSEDU 1, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S., Vogel, T., Anli, X., & Thorne, E. (2024). How does generative artificial intelligence impact student creativity? Journal of Creativity, 34(1), 00072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojo-Lucena, F.-J., Aznar-Díaz, I., Cáceres-Reche, M.-P., & Romero-Rodríguez, J.-M. (2019). Artificial intelligence in higher education: A bibliometric study on its impact in the scientific literature. Education Sciences, 9(1), 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshyar, D., Tammets, K., Ley, T., Aus, K., & Kollom, K. (2023). Learning analytics in supporting student agency: A systematic review. Sustainability, 15(18), 13662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J., Saleh, S., & Liu, Y. (2021). A review on artificial intelligence in education. Academic Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies, 10(3), 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istenic, S. A. (2019). Human learning and learning analytics in the age of artificial intelligence. British Journal of Educational Technology, 50(6), 2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jwo, J. S., Lin, C. S., & Lee, C. H. (2021). Smart technology-driven aspects for human-in-the-loop smart manufacturing. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 114, 1741–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokina, J., & Davenport, T. H. (2017). The emergence of artificial intelligence: How automation is changing auditing. Journal of Emerging Technologies in Accounting, 14(1), 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzeretti, L., Lattarulo, A., & Ramaciotti, L. (2023). The emergence of artificial intelligence in the regional sciences: A literature review. European Planning Studies, 31(7), 1304–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M. H., Chen, H. C., & Liu, K. S. (2017). A study of the effects of digital learning on learning motivation and learning outcome. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 13(7), 3553–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C. K., Hew, K. F., & Jong, M. S. (2024). Influence of ChatGPT on student engagement: A systematic review and future research agenda. Computers & Education, 219, 105100. [Google Scholar]
- López-Chila, R., Llerena-Izquierdo, J., Sumba-Nacipucha, N., & Cueva-Estrada, J. (2024). Artificial intelligence in higher education: An analysis of existing bibliometrics. Education Sciences, 14(1), 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallillin, L. L. D. (2024). Artificial intelligence (AI) towards students’ academic performance. Innovare Journal of Education, 12(4), 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrone, R., Taddeo, V., & Hill, G. (2022). Creativity and artificial intelligence—A student perspective. Journal of Intelligence, 10(3), 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munir, H., Vogel, B., & Jacobsson, A. (2022). Artificial intelligence and machine learning approaches in digital education: A systematic revision. Information, 13(4), 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odegaard, N. B., Myrhaug, H. T., Dahl-Michelsen, T., & Røe, Y. (2021). Digital learning designs in physiotherapy education: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Medical Education, 21, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, W., & Davis, J. L. (2020). Attributions of ethical responsibility by artificial intelligence practitioners. Information, Communication & Society, 23(5), 719–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, F., & Jiao, P. (2021). Artificial intelligence in education: The three paradigms. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 2, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Mendoza, S., Guevara, C., Mayorga-Albán, A., & Fernández-Escobar, J. (2023). Artificial intelligence in higher education: A predictive model for academic performance. Education Sciences, 13(10), 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R., Silva, J., Oliveira, M., & Costa, P. (2022). Virtual assistants applications in education. In Technology and innovation in learning, teaching and education (pp. 468–480). Springer Nature. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisica, A. I., Edu, T., Zaharia, R. M., & Zaharia, R. (2023). Implementing artificial intelligence in higher education: Pros and cons from the perspectives of academics. Societies, 13(5), 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prensky, M. (2001). Digital natives, digital immigrants part 2: Do they really think differently? On the Horizon, 9(6), 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prensky, M. (2010). Teaching digital natives: Partnering for real learning. Corwin Press. [Google Scholar]
- Roll, I., & Wylie, R. (2016). Evolution and revolution in artificial intelligence in education. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 26, 582–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, L. D. (2010). Rewired: Understanding the iGeneration and the way they learn. St. Martin’s Press. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Rojas, L. I., Salvador-Ullauri, L., & Acosta-Vargas, P. (2024). Collaborative working and critical thinking: Adoption of generative artificial intelligence tools in higher education. Sustainability, 16(13), 5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M., & Shaalan, K. (2023). ChatGPT: Advancing education with virtual assistants. In Business intelligence and information technology (pp. 283–293). Springer Nature. [Google Scholar]
- Shchitova, A. A. (2020). Definition of artificial intelligence for legal regulation. In Proceedings of the 2nd international scientific and practical conference on digital economy (ISCDE 2020) (pp. 616–620). Atlantis Press. [Google Scholar]
- Sova, R., Tudor, C., Tartavulea, C. V., & Dieaconescu, R. I. (2024). Artificial intelligence tool adoption in higher education: A structural equation modeling approach to understanding impact factors among economics students. Electronics, 13(18), 3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenalt, M. H., & Hachmann, R. (2024). Is AI good for agency? Tidsskriftet Læring og Medier (LOM), 29, 1–7. Available online: https://tidsskrift.dk/lom/article/view/146773/190299 (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Sun, L., & Zhou, L. (2024). Does generative artificial intelligence improve the academic achievement of college students? A meta-analysis. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 62(7), 1896–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, W., Basil, M., & Al-Rawi, A. (2023). Assessment of awareness, perceptions, and opinions towards artificial intelligence among healthcare students in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Medicina, 59(5), 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanveer, M., Hassan, S., & Bhaumik, A. (2020). Academic policy regarding sustainability and artificial intelligence (AI). Sustainability, 12(22), 9435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapscott, D. (2009). Grown up digital: How the net generation is changing your world. McGraw-Hill. [Google Scholar]
- Vieriu, A. M., & Petrea, G. (2025). The impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on students’ academic development. Education Sciences, 15(3), 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Parra, J. C., Henao-Rodriguez, C., Lis-Gutierrez, J. P., & Palomino-Gamez, S. (2024). Importance of university students’ perception of adoption and training in artificial intelligence tools. Artificial Intelligence in Participatory Environments: Technologies, Ethics, and Literacy Aspects, 14(8), 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, Y. (2024). Embracing the future of artificial intelligence in the classroom: The relevance of AI literacy, prompt engineering, and critical thinking in modern education. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 21(1), 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L., & Li, W. (2024). The impact of AI usage on university students’ willingness for autonomous learning. Behavioral Sciences, 14, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P. (2019). On defining artificial intelligence. Journal of Artificial General Intelligence, 10(2), 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S., Sun, Z., & Chen, Y. (2023). Effects of higher education institutes’ artificial intelligence capability on students’ self-efficacy, creativity, and learning performance. Education and Information Technologies, 28, 4919–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T., Lund, B. D., Marengo, A., Pagano, A., Mannuru, N. R., Teel, Z. A., & Pange, J. (2023). Exploring the potential impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on international students in higher education: Generative AI, chatbots, analytics, and international student success. Applied Sciences, 13(11), 6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkel, M. (2024). Controlling the uncontrollable: The public discourse on artificial intelligence between the positions of social and technological determinism. AI & Society. Knowledge, Culture and Communication, 40, 1947–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winne, P. H. (2006). How software technologies can improve research on learning and bolster school reform. Educational Psychologist, 41(1), 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W., Burdina, G., & Gura, A. (2023). Use of artificial intelligence in teacher training. International Journal of Web-Based Learning and Teaching Technologies, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X., & Sankar, R. (2024). Classification and recognition of lung sounds using artificial intelligence and machine learning: A literature review. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 8(10), 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y., Luo, J., Yang, M., Yang, R., & Chen, J. (2023). From surface to deep learning approaches with generative AI in higher education: An analytical framework of student agency. Studies in Higher Education, 20(37), 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, R., & Karaoglan Yilmaz, F. G. (2023). The effect of generative artificial intelligence (AI)-based tool use on students’ computational thinking skills, programming self-efficacy, and motivation. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 4, 100147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yufei, L., Saleh, S., Jiahui, H., & Syed Abdullah, S. M. (2020). Review of the application of artificial intelligence in education. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 12(8), 548–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P., & Tur, G. (2024). A systematic review of ChatGPT use in K-12. European Journal of Education, 59(2), 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingoni, A., Taborri, J., Panetti, V., Bonechi, S., Aparicio-Martínez, P., Pinzi, S., & Calabrò, G. (2021). Investigating issues and needs of dyslexic students at university: Proof of concept of an artificial intelligence and virtual reality-based supporting platform and preliminary results. Applied Sciences, 11(10), 4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Frequency | Percent |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Female | 158 | 63.2% |
| Male | 92 | 36.8% |
| Total | 250 | 100% |
| Academic year | ||
| First year (1) | 95 | 38% |
| Second year (2) | 55 | 22% |
| Third year (3) | 57 | 22.8% |
| Master | 42 | 17.2% |
| Total | 250 | 100% |
| Age | ||
| 18–21 ani | 38 | 15.2% |
| 21–23 ani | 88 | 35.2% |
| 23–26 ani | 45 | 18% |
| 26–28 ani | 29 | 11.6% |
| >28 ani | 50 | 20% |
| Total | 250 | 100% |
| Age Group | Never | Rare | Often | Once a Week | Daily | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18–21 | 2 | 5 | 17 | 7 | 7 | 38 |
| 21–23 | 0 | 0 | 22 | 31 | 35 | 88 |
| 23–26 | 3 | 8 | 25 | 9 | 0 | 45 |
| 26–28 | 7 | 12 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 29 |
| >28 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 3 | 18 | 50 |
| Total | 20 | 35 | 85 | 50 | 60 | 250 |
| Field of Study | Never | Rare | Often | Once a Week | Daily | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Humanities | 16 | 31 | 76 | 36 | 64 | 223 |
| Exact Sciences | 4 | 4 | 10 | 7 | 2 | 27 |
| Total | 20 | 35 | 86 | 43 | 66 | 250 |
| Question | Statement (Do You Think AI Can…) | Mean (M) | Standard Deviation (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q10 | Contribute to the improvement of academic performance | 3.73 | 1.08 |
| Q11 | Personalize your learning experience | 3.73 | 1.08 |
| Q12 | Positively influence autonomy in learning | 3.45 | 1.05 |
| Q13 | Positively influence your motivation for learning | 3.39 | 1.16 |
| Q14 | Positively influence the development of critical thinking | 3.99 | 0.92 |
| Q15 | Help you manage your active learning time | 4.01 | 0.98 |
| Q16 | Negatively influence creativity | 3.33 | 1.18 |
| Variable | Self-Assessed Competence in Technology Use |
|---|---|
| Academic performance | 0.261 *** <0.001 |
| Personalization of learning | 0.196 ** <0.002 |
| Motivation for learning | 0.234 *** <0.001 |
| Critical Thinking | 0.273 *** <0.001 |
| Managing time in active learning | 0.254 *** <0.001 |
| Autonomy in learning | −0.091 |
| Negatively influencing creativity | −0.440 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anghel, G.A.; Zanfir, C.M.; Matei, F.L.; Voicu, C.D.; Neacșa, R.A. The Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Academic Learning Practices: A Comprehensive Approach. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15050616
Anghel GA, Zanfir CM, Matei FL, Voicu CD, Neacșa RA. The Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Academic Learning Practices: A Comprehensive Approach. Education Sciences. 2025; 15(5):616. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15050616
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnghel, Gabriela Alina, Cristina Mihaela Zanfir, Florentina Lavinia Matei, Camelia Delia Voicu, and Ramona Adina Neacșa. 2025. "The Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Academic Learning Practices: A Comprehensive Approach" Education Sciences 15, no. 5: 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15050616
APA StyleAnghel, G. A., Zanfir, C. M., Matei, F. L., Voicu, C. D., & Neacșa, R. A. (2025). The Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Academic Learning Practices: A Comprehensive Approach. Education Sciences, 15(5), 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15050616







