Participatory and Inclusive Design Models from the Perspective of Universal Design for Children with Autism: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methodology
2.1. Research Questions
2.2. Search Key
2.3. Databases
2.4. Inclusion Criteria
2.5. Exclusion Criteria
2.6. Selection Strategy
3. Results and Discussion
- The participation of children with autism at a young age (4–10 years old) and directly;
- The participation of primary stakeholders in the process of developing new technologies for children with autism;
- Uses methods for children with autism through adaptability and universal design.
4. Analysis of Research Questions through Working Groups
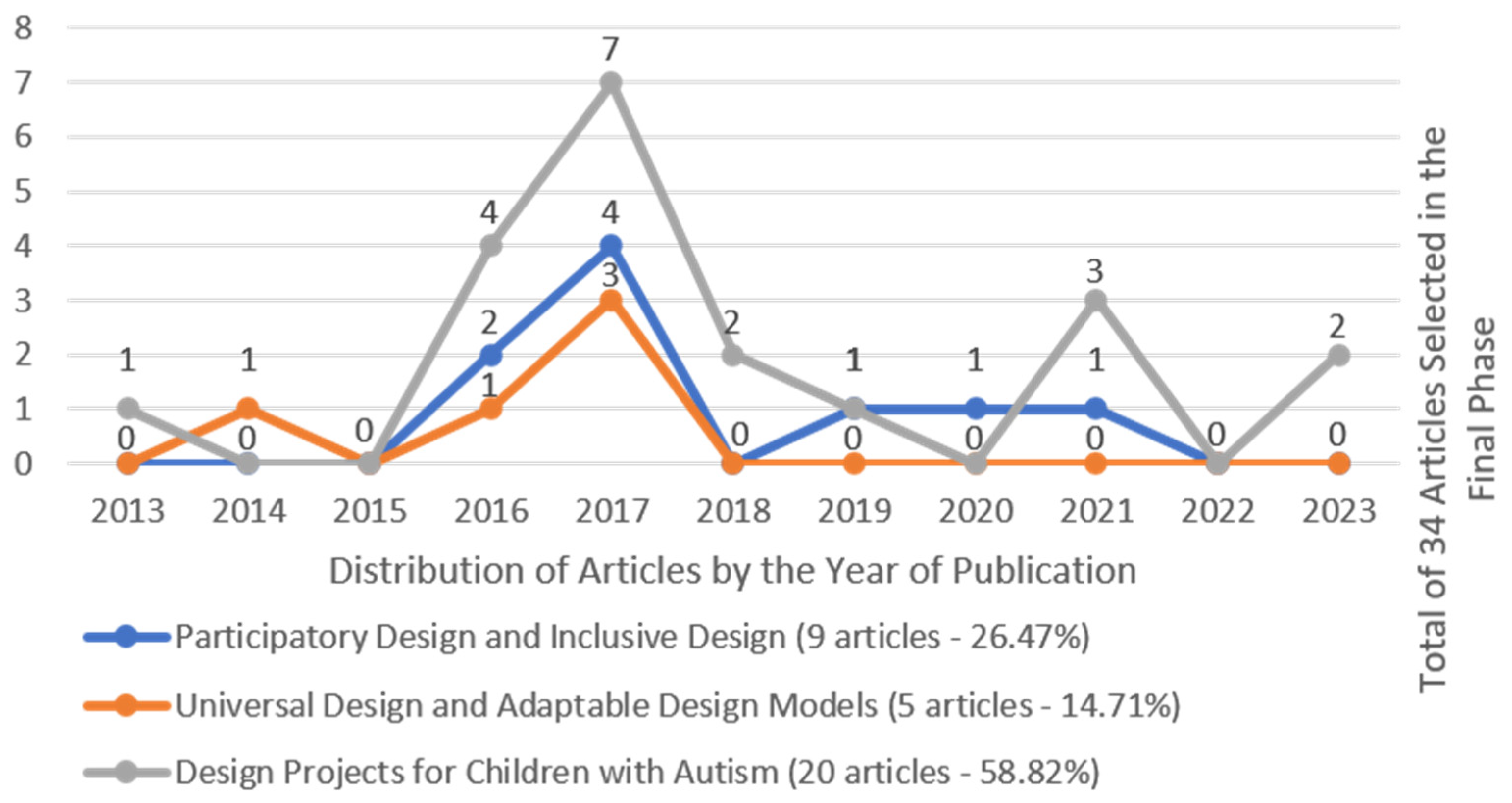
4.1. Participatory Design and Inclusive Design (RQ1)
4.2. Universal Design (RQ1) and Adaptable Design Models (RQ2)
4.3. Design Projects for Children with Autism (RQ3)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benton, L.; Vasalou, A.; Khaled, R.; Johnson, H.; Gooch, D. Diversity for design: A framework for involving neurodiverse children in the technology design process. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Toronto, ON, Canada, 26 April–1 May 2014; pp. 3747–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucke, U.; Castro, T. The Process of Inclusive Design. In Proceedings of the IEEE 16th International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT), Austin, TX, USA, 25–28 July 2016; pp. 446–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, G.C.; Collazos, C.; Bautista, S.; Moreira, F. FRIDA, a Framework for Software Design, Applied in the Treatment of Children with Autistic Disorder. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braz, L.M. Design Para Todos e Educação Inclusiva: Envolvendo Professores na Criação de Tecnologias. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, São Paulo, Brazil, 2017; 120p. Available online: https://www.unicamp.br/unicamp/teses/2017/11/22/design-para-todos-e-educacao-inclusiva-envolvendo-professores-na-criacao-de (accessed on 15 May 2021).
- Marins, S.C.F. Design Universal, Acessibilidade e Tecnologia Assistiva: A Formação Profissional do Terapeuta Ocupacional na Perspectiva da Equidade. Ph.D Thesis, Universidade Federal de São Carlos, São Paulo, Brazil, 2011. Available online: https://repositorio.ufscar.br/handle/ufscar/2875?show=full (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Lowy, R.; Gao, L.; Hall, K.; Kim, J.G. Toward Inclusive Mindsets: Design Opportunities to Represent Neurodivergent Work Experiences to Neurotypical Co-Workers in Virtual Reality. In Proceedings of the 2023 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI ‘23), Hamburg, Germany, 23–28 April 2023; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023. Article 783. pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, K. Interactive Technology for Inclusive Play. In Proceedings of the 2016 CHI Conference Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI EA ‘16), San Jose, CA, USA, 7–12 May 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umanski, D.; Avni, Y.; Rinott, M. Sonora: Inclusive voice play for children with various abilities. In Extended Abstracts Publication of the Annual Symposium on Computer-Human Interaction in Play; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo-Alcázar, A.; Arias, J.; Albornoz, I.; Alvarado, A.; Luján-Mora, S. Method for the Development of Accessible Mobile Serious Games for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Center for Universal Design. State University NC. 1995. Available online: https://projects.ncsu.edu/ncsu/design/cud/about_ud/about_ud.htm (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- Alzahrani, M.; Uitdenbogerd, A.L.; Spichkova, M. Impact of animated objects on autistic and non-autistic users. In Proceedings of the 2022 ACM/IEEE 44th International Conference on Software Engineering: Software Engineering in Society (ICSE-SEIS ‘22), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 21–29 May 2022; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britto, T.C.P.; Pizzolato, E.B. Gaia: Uma proposta de um guia de recomendações de acessibilidade de interfaces web com foco em aspectos do autismo. In V Congresso Brasileiro de Informática na Educação (CBIE 2016); Sociedade Brasileira de Computação (Realizadora): Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2016; p. 816. ISSN 2316-6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.L.R.; Mcmeekin, D.A.; Falkmer, M.; Tan, T. Holistic Approach for Sustainable Adaptable User Interfaces for People with Autism Spectrum Disorder. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on World Wide Web Companion (WWW ‘17 Companion), Perth, Australia, 3–7 April 2017; International World Wide Web Conferences Steering Committee, Republic and Canton of Geneva, Switzerland: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1553–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, K.; Rector, K.; Evans, S.; Kientz, J.A. Incloodle: Evaluating an Interactive Application for Young Children with Mixed Abilities. In Proceedings of the 2016 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI ‘16), San Jose, CA, USA, 7–12 May 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijab, M.H.F.; Al-Thani, D. En Route to Co-designing Inclusive Play with and For Autistic Children. In Proceedings of the 2022 9th International Conference on Behavioural and Social Computing (BESC), Matsuyama, Japan, 29–31 October 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterfield, D.; Fabri, M. User Participatory Methods for Inclusive Design and Research in Autism: A Case Study in Teaching UX Design. In International Conference of Design, User Experience, and Usability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firsanova, V. Towards Building a Mobile App for People on the Spectrum. In Proceedings of the Companion Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023 (WWW ‘23 Companion), Austin, TX, USA, 30 April–4 May 2023; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchenham, B.; Charters, S. Guidelines for Performing Systematic Literature Reviews in Software Engineering. 2007. Available online: https://www.cs.auckland.ac.nz/~norsaremah/2007%20Guidelines%20for%20performing%20SLR%20in%20SE%20v2.3.pdf (accessed on 11 August 2023).
- Peters, M.; Godfrey, C.; Mcinerney, P.; Khalil, H.; Larsen, P.; Marnie, C.; Pollock, D.; Tricco, A.; Munn, Z. Best practice guidance and reporting items for the development of scoping review protocols. JBI Evid. Synth. 2022, 20, 953–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Weighted kappa: Nominal scale agreement with provision for scaled disagreement or partial credit. Psychol. Bull. 1968, 70, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, C.; Lizarondo, L.; Carrier, J.; Godfrey, C.; Reiger, K.; Salmond, S.; Apostolo, J.; Kirkpatrick, P.; Loveday, H. Methodological guidance for the conduct of mixed methods systematic reviews. JBI Evid. Synth. 2020, 18, 2108–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoli, C. A guide to conducting a standalone systematic literature review. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2015, 37, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aromataris, E.; Munn, Z. (Eds.) JBI Reviewer’s Manual. JBI. 2020. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342595638_Chapter_1_JBI_Systematic_Reviews (accessed on 10 October 2023). [CrossRef]
- Sofian, N.M.; Sobri; Hashim, A.; Sarlan, A. Multimedia Elements in Designing Mobile App Interface for Autistic Children: Proxy User Perspective. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer & Information Sciences (ICCOINS), Kuching, Malaysia, 13–15 July 2021; pp. 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubin, S.A.; Poh, M.W.A.; Rohizan, R.; Abidin, A.Z.Z.; Wei, W.C. A Gamification Design Framework for Supporting ASD Children Social Skills. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Developments in eSystems Engineering (DeSE), Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 7–10 December 2021; pp. 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesário, V.; Rodrigues, J.; Li, H.; Wu, I.; Nisi, V. Crescendo: Routine Learning App for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Interaction Design and Children (IDC ‘16), Manchester, UK, 21–24 June 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.Y. Helping Neuro-typical Individuals to “Read” the Emotion of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: An Internet-of-Things Approach. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Interaction Design and Children (IDC ‘16), Manchester, UK, 21–24 June 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, A.; Teixeira, A.; Silva, S. On the Creation of a Persona to Support the Development of Technologies for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 9739, pp. 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Yao, C.; Zhao, Y.; Ying, F. An EEG-based Adaptive Training System for ASD Children. In Proceedings of the Adjunct Publication of the 30th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology (UIST ‘17), Québec City, QC, Canada, 22–25 October 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frauenberger, C.; Makhaeva, J.; Spiel, K. Blending Methods: Developing Participatory Design Sessions for Autistic Children. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Interaction Design and Children (IDC ‘17), Stanford, CA, USA, 27–30 June 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.; Brereton, M.; Ploderer, B.; Sitbon, L.; Saggers, B. Digital Strategies for Supporting Strengths- and Interests-based Learning with Children with Autism. In Proceedings of the 19th International ACM SIGACCESS Conference on Computers and Accessibility (ASSETS ‘17), Baltimore, MD, USA, 20 October–1 November 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolakowska, A.; Landowska, A.; Karpienko, K. Gyroscope-Based Game Revealing Progress of Children with Autism. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Machine Learning and Soft Computing (ICMLSC ‘17), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 13–16 January 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickstein-Fischer, L.A.; Pereira, R.H.; Gandomi, K.Y.; Fathima, A.T.; Fischer, G.S. Interactive Tracking for Robot-Assisted Autism Therapy. In Proceedings of the Companion of the 2017 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction (HRI ‘17), Vienna, Austria, 6–9 March 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.H.L.; Brereton, M. Mycalendar: Supporting children on the autism spectrum to learn language and appropriate behaviour. In Proceedings of the 29th Australian Conference on Computer-Human Interaction (OZCHI ‘17), Brisbane, Australia, 28 November–1 December 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiel, K.; Malinverni, L.; Good, J.; Frauenberger, C. Participatory Evaluation with Autistic Children. In Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI ‘17), Denver, CO, USA, 6–11 May 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 5755–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, Á.; Santos, J.; Rivero, L.; Barreto, R. Searching for Preferences of Autistic Children to Support the Design of User Interfaces. In Proceedings of the XVI Brazilian Symposium on Human Factors in Computing Systems (IHC 2017), Joinville, Brazil, 23–27 October 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017. Article 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.T.; Picard, R.W. SPRING: Customizable, Motivation-Driven Technology for Children with Autism or Neurodevelopmental Differences. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Interaction Design and Children (IDC ‘17), Stanford, CA, USA, 27–30 June 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.H.; Wang, C.P.; Su, C.C. The effectiveness of using auto organizational menu to communicate with classmates: A case study of autism spectrum disorders. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Software and Computer Applications (ICSCA ‘17), Bangkok, Thailand, 26–28 February 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibrian, F.L.; Mercado, J.; Escobedo, L.; Tentori, M. A Step towards Identifying the Sound Preferences of Children with Autism. In Proceedings of the 12th EAI International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare (Pervasive Health ‘18), New York, NY, USA, 21–24 May 2018; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Hardy, D.; Myers, T. Co-designing with Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder: From Ideation to Implementation. In Proceedings of the 31st Australian Conference on Human-Computer-Interaction (Ozchi’19), Fremantle, WA, Australia, 2–5 December 2019; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2019. 10p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhonson, K.; Narain, J.; Ferguson, C.; Picard, R.; Maes, P. The ECHOS Platform to Enhance Communication for Nonverbal Children with Autism: A Case Study. In Proceedings of the CHI ‘20: CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 April 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, V.; Marques, A.B. Accessibility-oriented design with a focus on autism aspects: Designing a mobile application for autistic children’s daily routine. In Proceedings of the XIX Brazilian Symposium on Software Quality (SBQS ‘20), Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 April 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2021. Article 27. pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruzaman, M.F.; Rani, N.M.; Nor, H.M.; Azahari, M.H.H. Developing User Interface Design Application for Children with Autism. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 217, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braz, P.; David, V.; Raposo, A.; Barbosa, S.; de Souza, C. An Alternative Design Perspective for Technology Supporting Youngsters with Autism; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, V.I.; Silva, R.P.; Aymone, J.L.F. Design inclusivo: Processo de desenvolvimento de prancha de comunicação alternativa e aumentativa para crianças com transtorno do espectro do autismo utilizando realidade aumentada. Des. E Tecnol. 2018, 8, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magkafa, D.; Newbutt, N. Implementing Co-Design Practices for the Development of a Museum Interface for Autistic Children. In Recent Advances in Technologies for Inclusive Well-Being; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 421–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.E.; Oliveira, A.; Damian, A.; Vasconcelos, P.; Marques, A.B. Um Processo de Design de Interface com foco em Usuários com Transtorno do Espectro Autista: Uma Experiência Prática. Comput. Beach 2023, 14, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.; Rodrigues, M.E.; Vasconcelos, P.; Marques, A.B. Utilizando Design Thinking no design de aplicativos educacionais para crianças autistas. Comput. Beach 2023, 37, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, T.; Castro, A.; Lima, D. A Playground Model to Stimulate Social Interaction in Autistic Children. In Proceedings of the 15th Brazilian Symposium on Human Factors in Computing Systems (IHC ‘16), São Paulo, Brazil, 4–7 October 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016. Article 57. 4p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinverni, L.; Mora-Guiard, J.; Padillo, V.; Valero, L.; Hervás, A.; Pares, N. An inclusive design approach for developing video games for children with autism spectrum disorder. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 71, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.I.; Breda, A.; Almeida, A.M. Learning Environment for Autism Spectrum Disorders: A universal approach to the promotion of mathematical reasoning. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Software Development and Technologies for Enhancing Accessibility and Fighting Info-exclusion (DSAI 2016), Vila Real, Portugal, 1–3 December 2016; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, T.; Lima, D. Designing for Children Using the RtD and HCD Approaches. In Universal Access in Human–Computer Interaction (UAHCI). Design and Development Approaches and Methods, Proceedings of the 11th International Conference, UAHCI 2017, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 9–14 July 2017; Antona, M., Stephanidis, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; ISSN 0302-9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, J.; Maia, I.; Ferreirada, A.; Rosa, L. Graphic Design of Interactive Tools for People with Autistic Spectrum Disorders. In Advances in Design for Inclusion. Proceedings of the AHFE 2018—Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, Orlando, FL, USA, 21–25 July 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passerino, L.; Rosangela Bez, M.; Carlos Gluz, J.; García, E.; Miguel Ramirez, J.; Lozano, C.D.C. SCALA e Siesta Cloud: Uma Integração Para Aplicações Homeschooling Visando a Inclusão. In Anais do II Congresso Brasileiro de Informática na Educação (CBIE 2013), Proceedings of the XXIV Simpósio Brasileiro de Informática na Educação (SBIE 2013); 2013; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/299667036_SCALA_e_Siesta_Cloud_uma_integracao_para_aplicacoes_homeschooling_visando_a_inclusao (accessed on 2 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Neto, A.F.O.; Rufino, H.L.P.; Nakamoto, P.T.; Palis, R.B.; Beira, D.G. Cotidiano: Um Software Para Auxiliar Crianças Autistas em Suas Atividades Diárias. In Anais do VI Congresso Brasileiro de Informática na Educação (CBIE 2017), Proceedings of the XXVIII Simpósio Brasileiro de Informática na Educação (SBIE 2017); 2017; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320993676_Cotidiano_um_software_para_auxiliar_criancas_autistas_em_suas_atividades_diarias (accessed on 22 July 2023). [CrossRef]
- Moita, F.M.G.S.C.; Viana, L.H.; Medeiros, F.M.; Candido, V.M.A. Design e Desenvolvimento de um Game Assistivo Para Autistas. In Anais do VI Congresso Brasileiro de Informática na Educação (CBIE 2017), Proceedings of the XXVIII Simpósio Brasileiro de Informática na Educação (SBIE 2017); 2017; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320994636_Design_e_desenvolvimento_de_um_game_assistivo_para_autistas (accessed on 2 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Raja, K.S.S.; Balaji, V.; Kiruthika, S.U.; Raman, C.J. An IoT-Based System for Supporting Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. In Proceedings of the Innovations in Power and Advanced Computing Technologies (i-PACT), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 27–29 November 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunathilake, Y.A.G.U.T.R.F.; Fasliya, R.D.A.R.; Premarathne, D.; Pasan Kalhara, A.; Karunasena; Bandara, P.S. A technological intervention for improving cognitive abilities based on the preferences of Autistic children. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering and Emerging Technologies (ICEET), Istanbul, Turkey, 27–28 October 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.J.; Ghinea, G. Towards developing digital interventions supporting empathic ability for children with autism spectrum disorder. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2022, 21, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.S.; Castro, T.H.C. Uma Abordagem Participativa para Identificação de Preferências de Design de Crianças Autistas. In Proceedings of the Simpósio Brasileiro de Informática na Educação (SBIE), Brazil, 2019; pp. 1311–1320. Available online: http://milanesa.ime.usp.br/rbie/index.php/sbie/article/view/8863 (accessed on 22 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Böckle, M.; Micheel, I.; Bick, M. A design framework for adaptive gamification applications. In Proceedings of the 51st Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS), Hilton Waikoloa Village, HI, USA, 3–6 January 2018; pp. 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, Á.; Cabrejos, L.; Santos, J.; Barreto, R. PersonAut: A Personas Model for People with Autism Spectrum Disorder. In Proceedings of the Anais do XIX Simpósio Brasileiro sobre Fatores Humanos em Sistemas Computacionais, Evento Online, 26–30 October 2020; pp. 466–471. Available online: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3424953.3426651 (accessed on 13 August 2023). [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Meng, J.; Wu, X.; Chen, J. Avatarizing Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder into Serious Games for Social Communication Skill Intervention. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference of Educational Innovation through Technology (EITT), Chongqing, China, 16–20 December 2021; pp. 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribu, K.; Patel, T. Developing a User-Centred Planning Tool for Young Adults with Development Disorders: A Research-Based Teaching Project. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2016, 229, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, S.; Kaur, S.; Sharma, A.; Chandna, S. An e-Learning Application for Children Suffering from Autism. In Learning and Collaboration Technologies(HCII 2023), Proceedings of the 10th International Conference, LCT 2023, Held as Part of the 25th HCI International Conference, HCII 2023, Copenhagen, Denmark, 23–28 July 2023; Zaphiris, P., Ioannou, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 14040, Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-34411-4_3 (accessed on 8 December 2023). [CrossRef]
- Chien, M.E.; Jheng, C.M.; Lin, N.M.; Tang, H.H.; Taele, P.; Tseng, W.S.; Chen, M.Y. iCAN: A tablet based pedagogical system for improving communication skills of children with autism. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2014, 73, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragone, G. Designing Embodied Musical Interaction for Children with Autism. In Proceedings of the 22nd International ACM SIGACCESS Conference on Computers and Accessibility (ASSETS ‘20), Virtual Event/Greece, 26–28 October 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020. Article 104. pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, S.A.; Rahman, K.M.N.; Swaron, M.R.; Saha, S.R.N.; Islam, M.M.; Razzak, M.A. Improvement of Verbal and Non-Verbal Communication Skills of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder using Human Robot Interaction. In Proceedings of the IEEE World AI IoT Congress (AIIoT), Seattle, WA, USA, 10–13 May 2021; pp. 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, W.; Cordeiro, R.; Aguiar, Y.; Saraiva, J.; Tardif, C.; Galy, E. Panorama das Publicações Nacionais sobre Autismo, Educação e Tecnologia. In Simpósio Brasileiro de Informática na Educação (SBIE); Fortaleza, Brazil, 2018; pp. 913–922. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328735888_Panorama_das_Publicacoes_Nacionais_sobre_Autismo_Educacao_e_Tecnologia (accessed on 15 October 2023). [CrossRef]
- Iltchenco, A.; Ribas, L. Características interacionais do brincar em crianças com suspeita do Transtorno do Espectro Autista. Distúrbios Comun. 2022, 34, e52065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.; Barker, T.; Aromataris, E.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Sears, K.; Klugar, M.; Leonardi-Be, J.; Munn, Z. From critical appraisal to risk of bias assessment: Clarifying the terminology for study evaluation in JBI systematic reviews. JBI Evid. Synth. 2023, 21, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
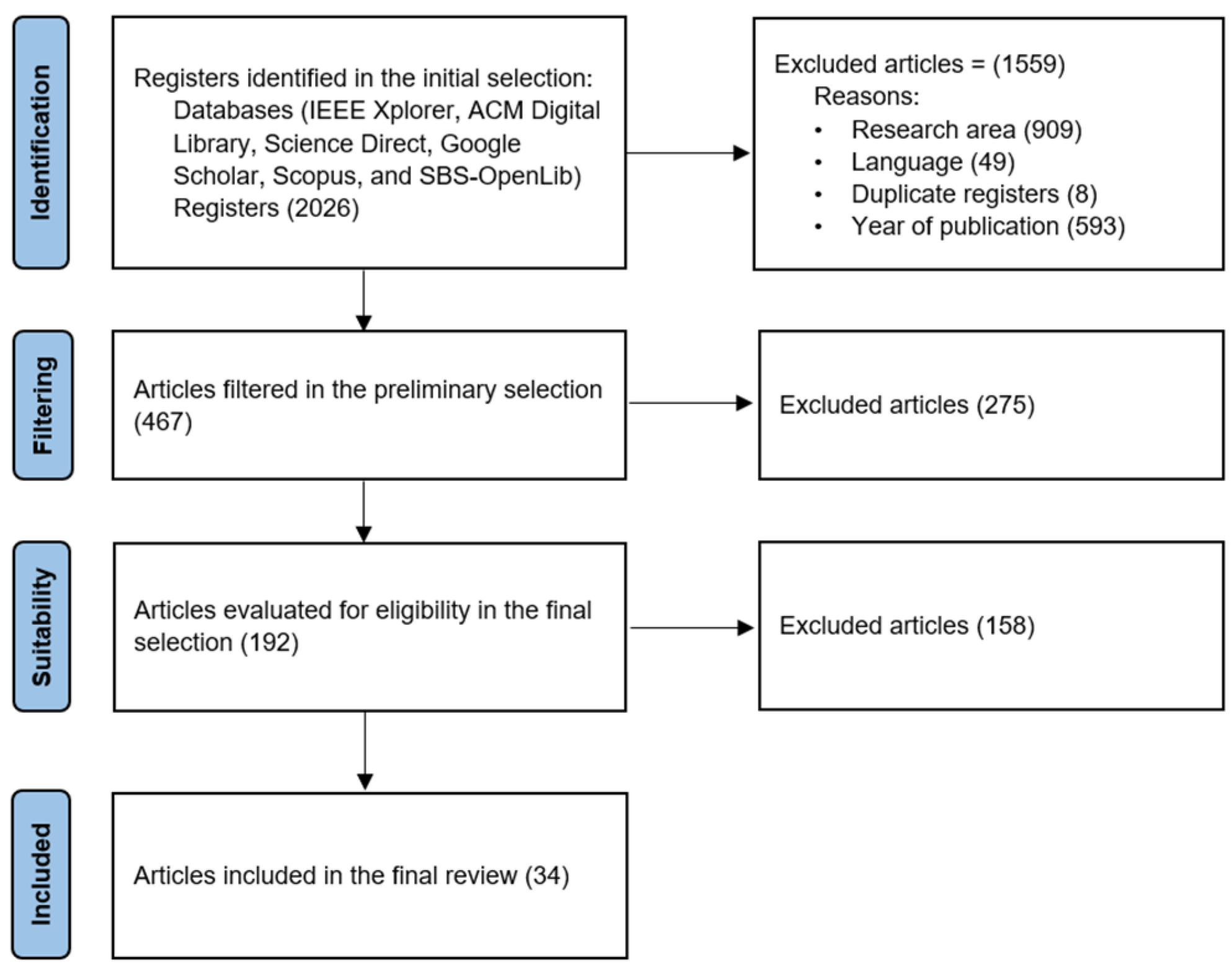
| Data Base | English | Portuguese | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| IEEE Xplore | 898 | 19 | 917 |
| ACM Digital Library | 632 | 20 | 652 |
| Science Direct | 176 | 5 | 181 |
| Google Scholar | 73 | 36 | 109 |
| Scopus | 96 | 7 | 103 |
| SBS-OpenLib | 59 | 5 | 64 |
| Total | 1934 | 92 | 2026 |
| Database | Exclusion Criteria | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Search Area | Language | Duplicate Records | Year of Publication | ||
| IEEE Xplore | 389 | 24 | 2 | 296 | 711 |
| ACM Digital Library | 304 | 16 | 4 | 223 | 547 |
| Science Direct | 88 | 3 | 0 | 32 | 123 |
| Google Scholar | 59 | 4 | 0 | 13 | 76 |
| Scopus | 57 | 2 | 2 | 8 | 69 |
| SBS-OpenLib | 12 | 0 | 0 | 21 | 33 |
| Total | 909 | 49 | 8 | 593 | 1559 |
| Database | Database Query | Initial Selection | Preliminary Selection | Final Selection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IEEE Xplore | 917 | 206 | 54 | 2 |
| ACM Digital Library | 652 | 105 | 65 | 17 |
| Science Direct | 181 | 58 | 14 | 1 |
| Google Scholar | 109 | 33 | 19 | 5 |
| Scopus | 103 | 34 | 21 | 6 |
| SBS-OpenLib | 64 | 31 | 19 | 3 |
| Total | 2026 | 467 | 192 | 34 |
| IEEE Xplorer | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Authors | Objectives | Evaluation Instrument | Children’s Participation | Participation of Professionals | Principles of Adaptability |
| 01 | Sofian, Hashim, and Sarlan (2021) [25] | Identifying the design preferences of children with autism through the perspective of proxy users. | Questionnaire | No | Yes | No |
| 02 | Mubin et al. (2021) [26] | Using gamification to improve social skills in children with autism. | Interview | No | No | Yes |
| ACM Digital Library | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Authors | Objectives | Evaluation Instrument | Children’s Participation | Participation of Professionals | Principles of Adaptability |
| 01 | Cesário et al. (2016) [27] | Assist children with autism in teaching and communicating through a virtual environment to become autonomous in atomized routines. | Observation and questionnaire | Yes | Yes | No |
| 02 | Tang (2016) [28] | Recognizing and reading the emotions of children with autism through an Internet of Things approach. | Observation and questionnaire | Yes | No | Yes |
| 03 | Leal, Teixeira, and Silva (2016) [29] | Design personas to improve communication and develop technologies for children with autism. | Questionnaire | Yes | Yes | No |
| 04 | Zheng et al. (2017) [30] | Design an adaptive training system to monitor the attention levels of children with autism. | Observation and interviews | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 05 | Frauenberger, Makhaeva, and Spiel (2017) [31] | Combining methods for participatory design with children with autism. | Case study | Yes | Yes | No |
| 06 | Wilson et al. (2017) [32] | Help children with autism record and express their interests in support, home, and classroom settings. | Study design | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 07 | Kolakowska, Landowska, and Karpienko (2017) [33] | Introduce a game designed to automate the measurement of therapy progress for children with autism. | Observation | Yes | No | No |
| 08 | Dickstein-Fische, Pereria, and Fischer (2017) [34] | Improve the collection of relevant data, such as gestures and expressions, in therapy sessions with children with autism. | Observation | Yes | No | No |
| 09 | Abdullah and Brereton (2017) [35] | Support the communication and interaction of children with autism in classroom activities to better express their real interests. | Observation | Yes | Yes | No |
| 10 | Spiel et al. (2017) [36] | Develop an approach for participatory assessment with children with autism. | Case study | Yes | No | Yes |
| 11 | Melo et al. (2017) [37] | Identify the preference patterns of children with autism regarding interface components. | Interview and case study | Yes | Yes | No |
| 12 | Johnson and Picard (2017) [38] | Accelerate learning and skill acquisition in children with different neurological developments. | Case study | Yes | No | Yes |
| 13 | Chen, Wang, and Su (2017) [39] | Develop operational communication skills and facilitate asking for help in children with autism. | Observation | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 14 | Cibrian et al. (2018) [40] | Understanding the attention and emotions of children with autism when listening to different sounds. | Observation | Yes | Yes | No |
| 15 | Zhu, Hardy, and Myers (2019) [41] | Involve children with autism in co-design workshops through a participatory and iterative process. | Co-design workshops | Yes | Yes | No |
| 16 | Johnson et al. (2020) [42] | Improving communicative and affective exchanges between non-verbal children with autism. | Interview and observation | Yes | No | No |
| 17 | Pinheiro and Marques (2021) [43] | Design an accessible app to automate daily routines for children with autism. | Inspection methods | No | Yes | No |
| Science Direct | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Authors | Objectives | Evaluation Instrument | Children’s Participation | Participation of Professionals | Principles of Adaptability |
| 01 | Kamaruzaman et al. (2016) [44] | The development of a numerical learning app for children with autism. | Task-centered design | Yes | Yes | No |
| Google Scholar | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Authors | Objectives | Evaluation Instrument | Children’s Participation | Participation of Professionals | Principles of Adaptability |
| 01 | Braz et al. (2014) [45] | Create alternative designs to personalize apps for children with autism. | Paper prototyping | Yes | No | Yes |
| 02 | Rosa, Silva, and Aymone (2018) [46] | Propose an approach to help children with autism communicate through design and augmented reality. | Case study and experiments | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 03 | Magkafa and Newbutt (2021) [47] | Implement co-design practices in creating accessible interfaces for children with autism. | Observation and feedback | Yes | Yes | No |
| 04 | Rodrigues et al. (2023) [48] | The creation of guidelines for designing accessible interfaces for individuals with autism. | Practical experience and questionnaires | No | Yes | No |
| 05 | Pereira et al. (2023) [49] | Facilitate the design of interfaces for individuals with autism through design thinking practices. | Interviews | Yes | Yes | No |
| Scopus | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Authors | Objectives | Evaluation Instrument | Children’s Participation | Participation of Professionals | Principles of Adaptability |
| 01 | Castro, Castro, and Lima (2016) [50] | Incorporate the social rules of peer interaction in children with autism through physical models. | Structured interview | Yes | No | Yes |
| 02 | Malinverni et al. (2016) [51] | Promote social initiation in children with autism using inclusive approaches in therapeutic games. | Participatory design workshops | Yes | Yes | No |
| 03 | Santos, Breda, and Almeida (2016) [52] | Evaluate a universal learning environment to support the development of mathematical reasoning in children with autism. | Case study | Yes | No | Yes |
| 04 | Castro and Lima (2017) [53] | Report a design method for designing intelligent and adaptive computational artifacts for children with autism. | Workshops and co-design sessions | No | Yes | Yes |
| 05 | Satterfield and Fabri (2017) [16] | Emphasize the importance of participatory design to understand the real needs of children with autism. | Case study | Yes | No | Yes |
| 06 | Leite et al. (2019) [54] | Present an ergonomic study to identify facial expressions in children with autism in order to assist them in teaching and social interaction. | Questionnaire | Yes | No | No |
| SBC-OpenLib | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Authors | Objectives | Evaluation Instrument | Children’s Participation | Participation of Professionals | Principles of Adaptability |
| 01 | Passerino et al. (2013) [55] | Integrate an alternative communication platform with another for developing activities to help children with autism with an emphasis on homecare and homeschooling. | Design centered on the context of use | No | No | Yes |
| 02 | Neto et al. (2017) [56] | Provide more autonomy and social inclusion through an app for children with autism. | Questionnaire and interview | Yes | Yes | No |
| 03 | Moita et al. (2017) [57] | Present the design, development, and validation of an assistive game, with a focus on building narratives for individuals with autism. | Observation and questionnaire | Yes | Yes | No |
| No. | Authors | Title | Methods/Techniques/Models | Journal/Conference/Book |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Kamaruzaman et al. (2016) [44] | Developing user interface design application for children with autism | Participatory design method with children with autism to develop a learning app. | Procedia—Social and Behavioral Sciences |
| 02 | Leal, Teixeira, and Silva (2016) [29] | On the Creation of a Persona to Support the Development of Technologies for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder | Persona technique to assist in the communication of children with autism and their proxies. | International Conference on Universal Access in Human–Computer Interaction |
| 03 | Frauenberger, Makhaeva, and Spiel (2017) [31] | Blending Methods: Developing Participatory Design Sessions for Autistic Children | Blending methods for participatory design sessions with children with autism | Research Concepts & Participatory Design |
| 04 | Spiel et al. (2017) [36] | Participatory Evaluation with Autistic Children | Approach to participatory assessment with children with autism | Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems |
| 05 | Wilson et al. (2017) [32] | Digital Strategies for Supporting Strengths- and Interests-based Learning with Children with Autism | Using self-expression technologies to improve communication with children with autism | Conference on Computers and Accessibility |
| 06 | Satterfield and Fabri (2017) [16] | User participatory methods for inclusive design and research in autism: A case study in teaching UX design | Participatory design methods for case studies with children with autism | International Conference of Design, User Experience, and Usability |
| 07 | Zhu, Hardy, and Myers (2019) [41] | Co-designing with Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder: From Ideation to Implementation | Co-designer technique for involving children with autism in the software design process | Australian Conference on Human–Computer Interaction |
| 08 | Jhonson et al. (2020) [42] | The ECHOS Platform to Enhance Communication for Nonverbal Children with Autism: A Case Study | Participatory case study to improve communication for children with autism | Interaction Design and Children |
| 09 | Magkafa and Newbutt (2021) [47] | Implementing co-design practices for the development of a museum interface for autistic children | Co-design in the context of participatory design to design accessible interfaces with children with autism | In book: Recent Advances in Technologies for Inclusive Well-Being |
| No. | Authors | Title | Methods/Techniques/Models | Journal/Conference/Book |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Braz et al. (2014) [45] | An Alternative Design Perspective for Technology Supporting Youngsters with Autism | Design using alternative metadesign and semiotic engineering to support communication for children with autism. | International Conference on Augmented Cognition |
| 02 | Santos, Breda, and Almeida (2016) [52] | Learning environment for Autism Spectrum Disorders: A universal approach to the promotion of mathematical reasoning | A universal design approach for evaluating a learning app for children with autism. | Conference on Software Development and Technologies for Enhancing Accessibility and Fighting Info-exclusion |
| 03 | Jhonson and Picard (2017) [38] | SPRING: Customizable, Motivation-Driven Technology for Children with Autism or Neurodevelopmental Differences | Heterogeneous case study to stimulate learning skills in children with autism. | Interaction Design and Children |
| 04 | Zheng et al. (2017) [30] | An EEG-based Adaptive Training System for ASD Children | Adaptive design for iterative learning for children with autism. | ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology |
| 05 | Castro and Lima (2017) [53] | Designing for children using the RtD and HCD approaches | Human-centered design and co-design to design computational artifacts for children with autism. | International Conference on Universal Access in Human–Computer Interaction |
| No. | Authors | Title | Methods/Techniques/Models | Journal/Conference/Book |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Passerino et al. (2013) [55] | SCALA e Siesta Cloud: uma integração para aplicações homeschooling visando a inclusão | Context-centered design for alternative communication with children with autism. | Simpósio Brasileiro de Informática na Educação |
| 02 | Malinverni et al. (2016) [51] | An inclusive design approach for developing video games for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder | Inclusive design and the fusion of methods to create therapeutic games for children with autism. | Computers in Human Behavior |
| 03 | Cesário et al. (2016) [27] | Crescendo: Routine Learning App for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders | Object-oriented tasks for automating routines with children with autism. | Interaction Design and Children |
| 04 | Tang (2016) [28] | Helping Neuro-typical Individuals to “Read” the Emotion of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: An Internet-of-Things Approach | An Internet of Things approach for emotion recognition in children with autism. | Interaction Design and Children |
| 05 | Castro, Castro, and Lima (2016) [50] | A playground model to stimulate social interaction in autistic children | Inclusive design process to support psychotherapy sessions for children with autism. | Simpósio Brasileiro sobre Fatores Humanos em Sistemas Computacionais |
| 06 | Abdullah and Bereton (2017) [35] | Mycalendar: Supporting Children on the Autism Spectrum to Learn Language and Appropriate Behaviour | Self-directed approach to supporting communication in non-verbal children with autism. | International Conference on Universal Access in Human–Computer Interaction |
| 07 | Chen, Wang, and Su (2017) [39] | The Effectiveness of Using Auto Organizational Menu to Communicate with Classmates: A Case Study of Autism Spectrum Disorders | Intervention method for the communication of children with autism through a case study. | International Conference on Software and Computer Applications |
| 08 | Dickstein-Fischer, Pereria, and Fischer (2017) [34] | Interactive Tracking for Robot-Assisted Autism Therapy | Applied behavior analysis therapy to collect relevant data from children with autism. | ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human–Robot Interaction |
| 09 | Kolakowska, Landowska, and Karpienko (2017) [33] | Gyroscope-Based Game Revealing Progress of Children with Autism | A combination of methods for measuring therapy progress with autistic children. | International Conference on Machine Learning and Soft Computing |
| 10 | Melo et al. (2017) [37] | Searching for Preferences of Autistic Children to Support the Design of User Interfaces | Case study and observation to identify interface patterns for children with autism. | Simpósio Brasileiro sobre Fatores Humanos em Sistemas Computacionais |
| 11 | Neto et al. (2017) [56] | Cotidiano: um software para auxiliar crianças autistas em suas atividades diárias | Educational intervention model for developing an app for children with autism. | Simpósio Brasileiro de Informática na Educação |
| 12 | Moita et al. (2017) [57] | Design e desenvolvimento de um game assistivo para autistas | Qualitative approach to developing an assistive game for children with autism. | Simpósio Brasileiro de Informática na Educação |
| 13 | Cibrian et al. (2018) [40] | A Step Towards Identifying the Sound Preferences of Children with Autism | Direct observation with the help of health professionals to identify sound preferences in children with autism. | International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare |
| 14 | Rosa, Silva, and Aymone (2018) [46] | Design inclusivo: processo de desenvolvimento de prancha de comunicação alternativa e aumentativa para crianças com transtorno do espectro do autismo utilizando realidade aumentada | Case study, experiments, and direct observation through design and augmented reality to aid communication in children with autism. | Biblioteca Digital Brasileira de Teses e Sissertações |
| 15 | Leite et al. (2019) [54] | Graphic design of interactive tools for people with autistic spectrum disorders | The systematic analysis of an ergonomic and inclusive study to create a graphic environment for children with autism. | In book: Advances in Design for Inclusion |
| 16 | Sofian, Hashin, and Sarlan (2021) [25] | Multimedia Elements in Designing Mobile App Interface for Autistic Children: Proxy User Perspective | Interface design from the perspective of proxies in app development for children with autism. | International Conference on Computer & Information Sciences |
| 17 | Mubin et al. (2021) [26] | A Gamification Design Framework for Supporting ASD Children Social Skills | Design techniques applied in the development of a gamification framework for children with autism. | International Conference on Developments in eSystems Engineering |
| 18 | Pinheiro and Marques (2021) [43] | Accessibility-oriented design with a focus on autism aspects: designing a mobile application for autistic children’s daily routine | UserX stories, proto-personas, and prototyping applied to the design of an application for children with autism. | Simpósio Brasileiro de Qualidade de Software |
| 19 | Pereira et al. (2023) [49] | Utilizando Design Thinking no design de aplicativos educacionais para crianças autistas | Collaborative design thinking approach applied to interface design for children with autism. | Computer on the Beach |
| 20 | Rodrigues et al. (2023) [48] | Um Processo de Design de Interface com foco em Usuários com Transtorno do Espectro Autista: Uma Experiência Prática | Practical experience designing interfaces for children with autism. | Computer on the Beach |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira, R.d.S.; Castro, T.H.C.d. Participatory and Inclusive Design Models from the Perspective of Universal Design for Children with Autism: A Systematic Review. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14060613
Ferreira RdS, Castro THCd. Participatory and Inclusive Design Models from the Perspective of Universal Design for Children with Autism: A Systematic Review. Education Sciences. 2024; 14(6):613. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14060613
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Rallyson dos Santos, and Thaís Helena Chaves de Castro. 2024. "Participatory and Inclusive Design Models from the Perspective of Universal Design for Children with Autism: A Systematic Review" Education Sciences 14, no. 6: 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14060613
APA StyleFerreira, R. d. S., & Castro, T. H. C. d. (2024). Participatory and Inclusive Design Models from the Perspective of Universal Design for Children with Autism: A Systematic Review. Education Sciences, 14(6), 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14060613








