Identity Trajectories of Faculty Members through Interdisciplinary STEAM Collaboration Paired with Public Communication
Abstract
1. Introduction and Background
1.1. Project Background
1.2. Identity
1.3. Conceptual Framework
2. Methods
2.1. Recruitment and Participants
2.2. Communication Training
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Limitations
3. Results
3.1. Intellectual Strand: Expanding Means of Intellectual Communication and Dominant Identities
“We didn’t overdo it with a PowerPoint, but we still need some visual other than just your face in most of these cases… But I think that the way that we set it up as almost like a live interview session where we interviewed each other instead of just talking at the crowd, I thought that was a nice twist and a different way of thinking about how to present who we are, what we do.”—Amy (Movement Cohort)
“I realized that it [adjusting your content] is also for those [community] audiences, tailoring the type and topic of content that you are putting out there. And then I felt like a lot of attracting those audiences was as much looking at the fairly broad umbrella and applications of the work I do and asking, ‘which part of this is possibly going to be interesting to my audience?’ And then creating some things around that.”—Kacey (Energy Cohort)
“I see the same behavior in college classes where students are far more engaged when they can relate their learnings to their day-to-day experiences. I realized that this is also a way of making them more interactive in class. I keep enhancing my slides with pictures of real-world examples.”—Alena (Energy Cohort)
“I like the research part where the teaching was involved in outreach. I mean, I like to be a mentor. So, I also take mentorship courses. I have a postdoc. I have graduate students. Over the summer I have five undergrads on an undergrad research project because that’s in the end what’s important to me.”—Jakob (Elements Cohort)
“I remember after that [Science Museum Exhibit] presentation, talking to my mom and I was like, ‘Mom, I’ve got some new ways to help you think about my research. And what it is that I do and to explain it’… So yeah, I think that it has definitely taught me how to better communicate and just get in a completely different way, maybe not even using some of the words that I would usually use. It made me very much think creatively out-of-the-box at the [Science Museum Exhibit]. So, I think that is very useful in my communication, especially with people like my family that just are interested, but only because it’s me, not because they’re interested in my work.”—Maria (Space)
“I think that it was mostly about how to communicate with others which I guess is relevant to me also as a researcher. I think the perspective that I gained is about how to make sure that people understand the connections, not just jumping into maybe the result, but explaining how it came to be.”—Lesley (Elements Cohort)
3.2. Institutional Strand: Engagement with Institutional Resources
“Learning how to communicate better, and I definitely feel like that was one of the major valuable aspects of this program for me, both in a very specific sense thinking back to [Science Museum Trainer] trainings at [Science Museum] and these kinds of formal trainings that we received. And there’s elements of those trainings that I continue to use in both my teaching and just interacting with people, little tricks and things like that.”—Mark (Space Cohort)
3.3. Networking Strand: Expanding Opportunities and Possibilities
“I do think that one thing I’ve learned is that in order to reach for collaborations far outside my discipline, I have to be willing to be more flexible with what I consider my “research interests.” While the project strayed rather far from my specific interests at the midpoint, it helped build connections that we ultimately harnessed in the final presentation, which I was able to bring back much closer to my own research areas and interests while still incorporating our common theme.”—Kacey (Energy Cohort)
“This is one of the very rare opportunities for me to reach out to other people who are doing entirely different things in their daily research and to attack the problem that has a common interest among all participants. That is very new and very refreshing and very rewarding.”—Jerry (Space Cohort)
“I think that this project set us up for success to collaborate because there was so much interaction and there was so much push for learning about each other, learn about each other and watch each other teach other things and get engaged this way. It’s taught me some things that I wish that I could do and so I’m thinking in the future about how I’m going to go about establishing collaborations for work.”—Maria (Space Cohort)
“I think, not only is it interesting, but it’s just extremely sort of strategic and mutually beneficial for us to be looking for these ways in which creative disciplines and scientific ones can combine. Because I just feel like art can be the megaphone for research. And these kinds of cross disciplinary projects allow, yes, they allow us as artists to get a wider audience. I feel like they allow scientists to reach a wider audience and to be louder and more interesting in their messaging, perhaps.”—Doug (Elements Cohort)
4. Discussion and Implications
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ross-Hellauer, T.; Tennant, J.P.; Banelytė, V.; Gorogh, E.; Luzi, D.; Kraker, P.; Pisacane, L.; Ruggieri, R.; Sifacaki, E.; Vignoli, M. Ten Simple Rules for Innovative Dissemination of Research. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1007704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Children’s Museum Indianapolis Children’s Museum Indianapolis. Available online: https://www.childrensmuseum.org/ (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- COSI COSI’s History. Available online: https://cosi.org/about-cosi/history-of-cosi (accessed on 13 June 2022).
- Smithsonian Institute Smithsonian. Available online: https://www.si.edu (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Franklinton Arts District Franklinton Fridays. Available online: http://www.franklintonartsdistrict.com/franklintonfridays.html (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Illinois Science Council Chicago Science Fest. Available online: https://www.illinoisscience.org/chicago-science-festival/ (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- OHI/O OHI/O Ohio State’s Hackathon Program. Available online: https://hack.osu.edu/ (accessed on 13 June 2022).
- Ohio Wesleyan University OWjL. Available online: https://www.owu.edu/about/offices-services-directory/owjl-camp/ (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- U.S. Space & Rocket Center Space Camp. Available online: https://www.spacecamp.com (accessed on 11 July 2022).
- Elsevier 10 Major Engineering Challenges of the next Decade. Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/rd-solutions/industry-insights/other/10-major-engineering-challenges-of-the-next-decade (accessed on 13 September 2022).
- NAE Grand Challenges for Engineering 14 Grand Challenges for Engineering in the 21st Century. Available online: http://www.engineeringchallenges.org/challenges.aspx (accessed on 13 September 2022).
- Falk, J.H.; Dierking, L.D. The 95 Percent Solution. Am. Sci. 2010, 98, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant, J.R.; Evans, G.A.; Thomas, G.P. The Public Understanding of Science. Nature 1989, 340, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee on Science Engineering and Public Policy. Rising Above the Gathering Storm Executive Summary; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine. Rising above the Gathering Storm, Revisited: Rapidly Approaching Category 5; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology. Engage to Excel: Producing One Million Additional College Graduates with Degrees in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics; President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology. Prepare and Inspire: K-12 Education in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (STEM) for America’s Future; President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, R.; Sherwood, O.L.; Clune, S.; Carroll, R.; McCabe, P.F.; Kane, A.; Kacprzyk, J. Botanical Boom: A New Opportunity to Promote the Public Appreciation of Botany. Plants People Planet 2022, 4, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.D. Public Understanding of Science and Technology in the Internet Era. Public Underst. Sci. 2022, 31, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myzeqari, I. The Increasing Need for Science Communication!-A Theoretical Approach. UET Press 2021, 20, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheufele, D.A. Thirty Years of Science–Society Interfaces: What’s next? Public Underst. Sci. 2022, 31, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, H.; Powell, P. Public Understanding of Science versus Public Understanding of Research. Public Underst. Sci. 2001, 10, 421–426. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.; Fahy, D. The ESConet Team Can Science Communication Workshops Train Scientists for Reflexive Public Engagement?: The ESConet Experience. Sci. Commun. 2009, 31, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhbanova, K.S. How the Arts Standards Support STEM Concepts: A Journey from STEM to STEAM. J. STEM Arts Crafts Constr. 2017, 2, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Erikson, E.H. The Problem of Ego Identity. J. Am. Psychoanal. Assoc. 1956, 4, 56–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markus, H.; Nurius, P. Possible Selves. Am. Psychol. 1986, 41, 954–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, J.P. Chapter 3: Identity as an Analytic Lens for Research in Education. Rev. Res. Educ. 2000, 25, 99–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignoles, V.L.; Schwartz, S.J.; Luyckx, K. Introduction: Toward an Integrative View of Identity. In Handbook of Identity Theory and Research; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ashforth, B.E.; Mael, F. Social Identity Theory and the Organization. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1989, 14, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schildkraut, D.J. Defining American Identity in the Twenty-First Century: How Much “There” Is There? J. Politics 2007, 69, 597–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, M.S. My Family, My Self: Reflections on Family Interactions of Malaysian Gay Men within the Asian Cultural Context. Asia-Pac. Soc. Sci. Rev. 2018, 17, 98–108. [Google Scholar]
- Kettler, N.; Frenzel Baudisch, N.; Micheelis, W.; Klingenberger, D.; Jordan, A.R. Professional Identity, Career Choices, and Working Conditions of Future and Young Dentists in Germany–Study Design and Methods of a Nationwide Comprehensive Survey. BMC Oral Health 2017, 17, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jue, J.; Ha, J.H. The Professional Identity, Career Commitment and Subjective Well-Being of Art Therapy Students. Arts Psychother. 2018, 57, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatmaker, D.M. Practicing Engineers: Professional Identity Construction through Role Configuration. Eng. Stud. 2012, 4, 121–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlpine, L.; Amundsen, C. Identity and Agency: Pleasures and Collegiality among the Challenges of the Doctoral Journey. Stud. Contin. Educ. 2009, 31, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlpine, L.; Amundsen, C. Identity-Trajectories of Early Career Researchers: Unpacking the Post-PhD Experience; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- McAlpine, L.; Amundsen, C.; Turner, G. Identity-Trajectory: Reframing Early Career Academic Experience. Br. Educ. Res. J. 2014, 40, 952–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlpine, L.; Amundsen, C. Chapter 10: Making Meaning of Diverse Experiences: Constructing an Identity Through Time. In Doctoral Education: Research-Based Strategies for Doctoral Students, Supervisors and Administrators; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 173–183. [Google Scholar]
- Benedict, B.; Verdín, D.; Rohde, J.A.; Brown, H.; Baker, R.; Thielmeyer, A.; Godwin, A. An Early Adaptation of Identity Trajectory to Understand the Identities of Undergraduate Engineering Students. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), Covington, KY, USA, 16–19 October 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, J.M.; Benedict, B.; Clements, R.; Perkins, H.; Godwin, A. See Me as an Engineer: Understanding the Role of Language and Multiple Role Identities on Engineering Students’ Identity Trajectory. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), Uppsala, Sweden, 21–24 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, L. Identity-Trajectory as a Theoretical Framework in Engineering Education Research. In Proceedings of the 2014 ASEE Annual Conference & Exposition, Indianapolis, Indiana, 15–18 June 2014; ASEE Conferences. pp. 24.688.1–24.688.11. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, A.; Willey, K. Academic Identity Reconstruction: The Transition of Engineering Academics to Engineering Education Researchers. Stud. High. Educ. 2018, 43, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, A.; Willey, K. Engineering Academics’ Identity Transitions in Becoming Established Engineering Education Researchers. In Proceedings of the 6th Research in Engineering Education Symposium: Translating Research into Practice, Dublin, Ireland, 13–15 July 2015; pp. 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, A.; Willey, K. Framing the Academic Identity of Emerging Researchers in Engineering Education. Int. J. Eng. Educ. 2016, 32, 2332–2351. [Google Scholar]
- McAlpine, L.; Amundsen, C. (Eds.) Doctoral Education: Research-Based Strategies for Doctoral Students, Supervisors and Administrators; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; ISBN 978-94-007-0506-7. [Google Scholar]
- McAlpine, L. Doctoral Journeys from Past to Present to Future. Aust. Univ. Rev. 2012, 54, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Walther, J.; Sochacka, N.W.; Kellam, N.N. Quality in Interpretive Engineering Education Research: Reflections on an Example Study. J. Eng. Educ. 2013, 102, 626–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, J.; Sochacka, N. Qualifying Qualitative Research Quality (the Q3 Project): An Interactive Discourse around Research Quality in Interpretive Approaches to Engineering Education Research. In Proceedings of the Frontiers in Engineering Education Conference, Madrid, Spain, 22–25 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pelan, R.R.; Desing, R.; Kajfez, R.L.; Dyche, A. Mapping Trajectories of Researcher Development with Qualitative Longitudinal Analysis: An Executive Summary. In Proceedings of the American Society for Engineering Education (ASEE) Annual Conference & Exposition, Virtual, 26–29 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Saldaña, J. The Coding Manual for Qualitative Researchers, 3rd ed.; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, R. Self-Selection Bias. In Encyclopedia of Survey Research Methods; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2011; p. 809. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, I.; Baptista, M. Teacher Professional Development in Integrated STEAM Education: A Study on Its Contribution to the Development of the PCK of Physics Teachers. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnis, D.R.; McNamara, K.T.; Kuczek, T.; Salvendy, G. The Instructional Benefits from Faculty Participation in Industrial Outreach. J. Eng. Educ. 2001, 90, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, M.J.; Koedinger, K.R.; Alibali, M.W. Expert Blind Spot: When Content Knowledge Eclipses Pedagogical Content Knowledge. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Cognitive Science, Beijing China, August 2001; Volume 644648, pp. 644–648. [Google Scholar]
- Selvakumar, M. Portal to the Public. In The Reflective Museum Practicioner; Routledge: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-0-429-02524-2. [Google Scholar]
- Selvakumar, M.; Storksdieck, M. Portal to the Public: Museum Educators Collaborating with Scientists to Engage Museum Visitors with Current Science. Curator Mus. J. 2013, 56, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brew, A. Teaching and Research: New Relationships and Their Implications for Inquiry-Based Teaching and Learning in Higher Education. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2003, 22, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinidad, J.E.; Ngo, G.R.; Nevada, A.M.; Morales, J.A. Engaging and/or Effective? Students’ Evaluation of Pedagogical Practices in Higher Education. Coll. Teach. 2020, 68, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C. Creating a STEAM Map: A Content Analysis of Visual Art Practices in STEAM Education. STEAM Educ. Theory Pract. 2019, 37–55. [Google Scholar]
- Perignat, E.; Katz-Buonincontro, J. STEAM in Practice and Research: An Integrative Literature Review. Think. Ski. Creat. 2019, 31, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.A.; Rule, A.C. Middle Level Preservice Teachers Experience a Natural History Arts-Integrated Interdisciplinary Thematic Unit. J. STEM Arts Crafts Constr. 2017, 2, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Kangas, T.C.; Cook, M.; Rule, A.C. Cinematherapy in Gifted Education Identity Development: Integrating the Arts through STEM-Themed Movies. J. STEM Arts Crafts Constr. 2017, 2, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Pittman, P.J.; Teske, J.K. Examining Natural Selection by Sketching and Making Models of the Finches of the Galapagos Islands. J. STEM Arts Crafts Constr. 2017, 2, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, C. From Interdisciplinary to Transdisciplinary: An Arts-Integrated Approach to STEAM Education. Art Educ. 2016, 69, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyropoulou, N.; Kameas, A. Augmenting the Impact of STEAM Education by Developing a Competence Framework for STEAM Educators for Effective Teaching and Learning. Educ. Sci. 2023, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
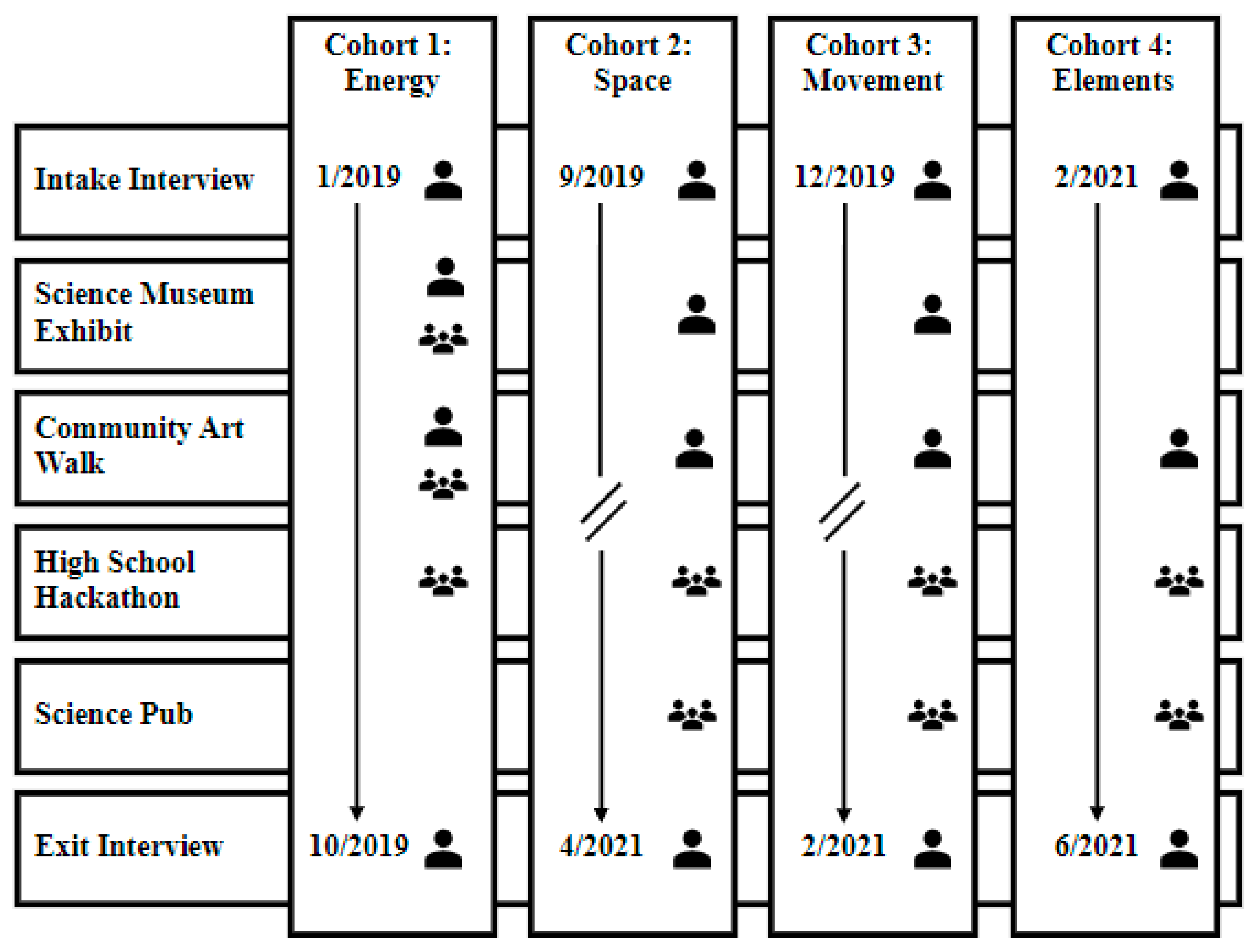
| Event | Event Description | Participant Engagement |
|---|---|---|
| Science Museum Exhibit | An adult 21 + event in which attendees explore the museum and stop by exhibit tables at their leisure | At tables, cohort members would engage with the attendees by providing an activity to teach the public about an application of their research. |
| High School Hackathon | A high school hackathon that gives students an opportunity to learn about computer science | Cohort participants created an integrated, interdisciplinary challenge for hackathon attendees, served as mentors to student teams throughout the day, and judged the final products. |
| Community Art Walk | A community event in the form of a gallery walk that showcases art, theater, food, science, and other exhibits | Cohort participants gave an informal talk about their research. |
| Science Pub | A monthly event that invites scientists to present their research to the public to improve science literacy | Cohort participants gave an online presentation to a community audience about their research topics. |
| Cohort Theme | # Members | Pseudonyms | Timeframe | # Events (Type) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | 3 | Alena Jack Kacey | January 2019–October 2019 | 5 (All in-person) |
| Space | 5 | Andrew Jerry Maria Mark Mitchell | September 2019–April 2021 (Interrupted by COVID) | 4 (2 in-person; 2 virtual) |
| Movement | 4 | Amy David James Todd | December 2019–February 2021 (Interrupted by COVID) | 4 (2 in-person; 2 virtual) |
| Elements | 4 | Doug Jakob Lesley Sean | February 2021–June 2021 | 3 (All virtual) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Desing, R.M.; Pelan, R.; Kajfez, R.L.; Wallwey, C.; Clark, A.M.; Gopalakrishnan, S. Identity Trajectories of Faculty Members through Interdisciplinary STEAM Collaboration Paired with Public Communication. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14050454
Desing RM, Pelan R, Kajfez RL, Wallwey C, Clark AM, Gopalakrishnan S. Identity Trajectories of Faculty Members through Interdisciplinary STEAM Collaboration Paired with Public Communication. Education Sciences. 2024; 14(5):454. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14050454
Chicago/Turabian StyleDesing, Renee M., Renee Pelan, Rachel L. Kajfez, Cassie Wallwey, Abigail M. Clark, and Sathya Gopalakrishnan. 2024. "Identity Trajectories of Faculty Members through Interdisciplinary STEAM Collaboration Paired with Public Communication" Education Sciences 14, no. 5: 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14050454
APA StyleDesing, R. M., Pelan, R., Kajfez, R. L., Wallwey, C., Clark, A. M., & Gopalakrishnan, S. (2024). Identity Trajectories of Faculty Members through Interdisciplinary STEAM Collaboration Paired with Public Communication. Education Sciences, 14(5), 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14050454






