An Investigation of the Cross-Language Transfer of Reading Skills: Evidence from a Study in Nigerian Government Primary Schools
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Cross Linguistic Transfer: L1–L2 and L2–L1
“To the extent that instruction in Lx is effective in promoting proficiency in Lx, transfer of this proficiency to Ly will occur provided there is adequate exposure to Ly (either in school or environment) and adequate motivation to learn Ly”. [1](p. 29)
1.2. Decoding and Phonological Awareness
1.3. School Policy in Nigeria
1.4. The Present Study
- Are there associations between phoneme and decoding scores between and within L1 and L2?
- Is there a bidirectional association between L1 and L2 word/decoding scores as per the interdependence hypothesis?
- How much of the variation in test scores is due to the pupil, school, and state level, and how does this affect predicted associations?
2. Method
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Instruments
3. Results
3.1. Bivariate Correlations
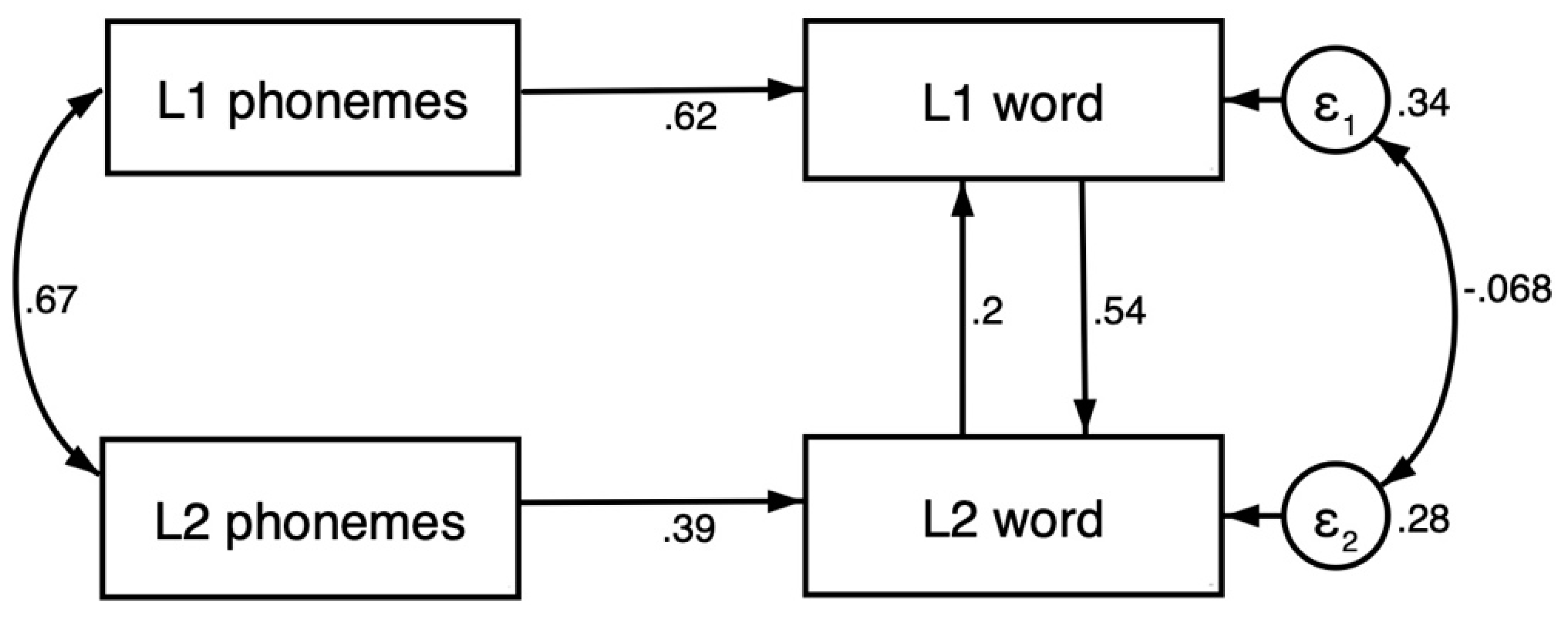
3.2. Feedback Path Model
3.3. Multilevel Modelling
4. Discussion and Implications for Practice and Policy
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cummins, J. The role of primary language development in promoting educational success for language minority students. In Schooling and Language Minority Students: A Theoretical Framework; California State Department of Education, Ed.; California State University: Los Angeles, CA, USA; Evaluation, Dissemination and Assessment Center: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Cummins, J. Teaching for Transfer in Multilingual School Contexts. In Bilingual and Multilingual Education; Garcia, O., Lin, A.M.Y., May, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 103–117. [Google Scholar]
- Cummins, J. Immersion Education for the Millennium: What Have We Learned from 30 Years of Research on Second Language Immersion? In Proceedings of the Second Katoh Gakuen International Symposium on Immersion and Bilingual Education, Katoh Gakuen, Japan; 1998; pp. 34–47. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/255638397_Immersion_Education_for_the_Millennium_What_We_Have_Learned_from_30_Years_of_Research_on_Second_Language_Immersion (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Cummins, J. Rethinking the Education of Multilingual Learners. A Critical Analysis of Theoretical Concepts; Multilingual Matters: Bristol, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- de Galbert, P.G. Language transfer theory and its policy implications: Exploring interdependence between Luganda, Runyankole-Rukiga, and English in Uganda. J. Multiling. Multicult. Dev. 2023, 44, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, J.; Swain, M. Bilingualism in Education: Aspects of Theory, Research and Practice; Longman: London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Appel, R.; Muysken, P. Language Contact and Bilingualism; Edward Arnold: London, UK; Baltimore, MD, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Krashen, S.; Biber, D. On Course: Bilingual Education’s Success in California; California Association for Bilingual Education: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Genesee, F. What do we know about bilingual education for majority language students? In Handbook of Bilingualism and Multiculturalism; Bhatia, T.K., Ritchie, W., Eds.; Blackwell: Malden, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 547–576. [Google Scholar]
- Jared, D.; Cormier, P.; Levy, B.A.; Wade-Woolley, L. Early predictors of biliteracy development in children in French immersion: A 4-year longitudinal study. J. Educ. Psychol. 2011, 103, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, L. Acquisition of biliteracy. AILA Rev. 1991, 8, 61–74. [Google Scholar]
- Gebauer, S.K.; Zaunbauer, A.C.M.; Moller, J. Cross-language transfer in English immersion programs in Germany: Reading comprehension and reading fluency. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 2013, 38, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usborne, E.; Caouteet, J.; Qumaaluk, Q.; Taylor, D.M. Bilingual education in an Aboriginal context: Examining the transfer of language skills from Inuktitut to English or French. Int. J. Biling. Educ. 2009, 12, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudell, B. Language and Education in Nigeria: A Review of Policy and Practice; British Council and UNICEF: Abuja, Nigeria, 2018; Available online: https://www.britishcouncil.org.ng/sites/default/files/j149_language_and_education_nigeria_final_web.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Adebayo, T.A. An evaluation of code-mixing and switching strategies on the efficacy of primary 1 pupils in numeracy in Kwara State. In The Abuja Regional Hornby School: Language Lessons from Africa; McIlwraith, H., Ed.; British Council: London, UK, 2016; pp. 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.G.; Piper, B. Cross-language transfer of reading skills: An empirical investigation of bidirectionality and the influence of instructional environments. Read. Writ. 2019, 32, 839–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawire, B.A.; Kim, Y.S.G. Cross-language transfer of phonological awareness and letter knowledge: Causal evidence and nature of transfer. Sci. Stud. Read. 2018, 22, 443–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veii, K.; Everatt, J. Predictors of reading among Herero–English bilingual Namibian school children. Biling. Lang. Cogn. 2005, 8, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.J. Beginning to Read: Thinking and Learning about Print; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD). Report of the National Reading Panel. Teaching Children to Read: An Evidence-Based Assessment of the Scientific Research Literature on Reading and Is Implications for Reading Instruction; Reports of the Subgroups; U.S. National Institutes of Health Publication No. 00-4769; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gottardo, A. The relationship between language and reading skills in bilingual Spanish-English speakers. Top. Lang. Disord. 2002, 22, 46–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, S.H.; Wade-Woolley, L.; Kirby, J. Crossover: The role of morphological awareness in French immersion children’s reading. Dev. Psychol. 2007, 43, 723–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottardo, A.; Mueller, J. Are First- and Second-Language Factors Related in Predicting Second-Language Reading Comprehension? A Study of Spanish-Speaking Children Acquiring English as a Second Language from First to Second Grade. J. Educ. Pshchol. 2009, 101, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgunoğlu, A.Y. Cross-linguistic transfer in literacy development and implications for language learners. Ann. Dyslexia 2002, 52, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melby-Lervåg, M.; Lervåg, A. Reading comprehension and its underlying components in second-language learners: A meta-analysis of studies comparing first- and second-language learners. Psychol. Bull. 2014, 140, 409–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, L.S.; Fuchs, D.; Hosp, M.K.; Jenkins, J.R. Reading competence: A theoretical, empirical, and historical analysis. Sci. Stud. Read. 2001, 5, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.G. Developmental, component-based model of reading fluency: An investigation of predictors of word-reading fluency, text-reading fluency, and reading comprehension. Read. Res. Q. 2015, 50, 459–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, J.F.; Katz, L.A. Effects of word and morpheme familiarity on reading of derived words. Read. Writ. 2006, 19, 669–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNICEF. Language in Education in Nigeria: Phase 2. 2022. Available online: https://www.unicef.org/nigeria/media/7861/file/Language%20in%20Education%20Report.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- UNICEF. Education in Nigeria: Evaluation of the Effectiveness and Impact of SDG4. 2022. Available online: https://nationalplanning.gov.ng/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/SDG-4-Education-in-Nigeria.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Oyetunde, T.; Ojo, G.; Korb, K.; Babudoh, G. Improving literacy instructional practices in primary schools in Nigeria: Strategies that work. LICEJ 2016, 6, 2323–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunode, N.J.; Mbata, F.O.; Ayoko, V.O. School Administrators in Basic Education in Nigeria. CAJMTCS 2023, 4, 9–17. Available online: https://cajmtcs.centralasianstudies.org/index.php/CAJMTCS/article/view/464 (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Ibrahim, J.; Gwandu, S.A. Language Policy on Education in Nigeria: Challenges of Multilingual Education and Future of English Language. Am. Res. J. Engl. Lit. 2016, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opanuga, A.A.; Okagbue, H.I.; Oguntunde, P.E.; Bishop, S.A.; Ogundile, O.P. Learning Analytics: Issues on the Pupil-Teacher Ratio in Public Primary Schools in Nigeria. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2019, 14, 180–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, A.; Tsiga, A.U.; Zuilkowski, S.S. Teaching reading in Northern Nigeria: The challenges of large class size. Pedagog. Cult. Soc. 2022, 30, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniran, A.; Ishaku, J.; Akanni, L.O. Is Nigeria experiencing a learning crisis: Evidence from curriculum-matched learning assessment. Int. J. Educ. Dev. 2020, 77, 102199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NERDC. National Policy on Education: Federal Republic of Nigeria; NERDC: Lagos, Nigeria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- NERDC. National Language Policy; NERDC: Lagos, Nigeria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- NERDC. National Reading Framework; NERDC: Lagos, Nigeria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Laitin, D.D.; Ramachandran, R.; Walter, S.L. The Legacy of Colonial Language Policies and Their Impact on Student Learning: Evidence from an Experimental Program in Cameroon. Econ. Dev. Cult. Chang. 2019, 68, 239–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerwin, J.T.; Thornton, R.L. Making the Grade: The Sensitivity of Education Program Effectiveness to Input Choices and Outcome Measures. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2021, 103, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, B.; King, S.; Mugenda, A. USAID/Kenya Primary Math and Reading (PRIMR) Initiative: Endline Impact Evaluation—Revised Edition; Prepared under the USAID EdData II Project, Task Order No. AID-623-M-11-00001 (RTI Task 13); RTI International: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Counihan, C.; Humble, S.; Gittins, L.; Dixon, P. The effect of different teacher literacy training programmes on student’s word reading abilities in government primary schools in Northern Nigeria. Sch. Eff. Sch. Improv. 2021, 33, 198–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNICEF. Girls’ Education Project Phase 3 (GEP3) in Northern Nigeria Final Evaluation Report; United Nations Children’s Fund: Abuja, Nigeria, 2022; Available online: https://www.unicef.org/nigeria/media/7846/file/GEP3%20Final%20Evaluation%20Brief.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Barnes, A.E.; Boyle, H. Baseline Assessment of Pre-Service Teacher Education Programs and Teacher Education Institutions in Bauchi and Sokoto States, Nigeria; Report No. AID-620-C-15-00002; USAID: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, A.E.; Boyle, H.; Zuilkowski, S.S.; Bello, Z.N. Reforming teacher education in Nigeria: Laying a foundation for the future. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2019, 79, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigerian Partnership for Education Project (NIPEP). Final Report on Conduct of Early Grade Reading and Learning Assessment of the NIPEP in Five States; Federal Ministry of Education, Department of Basic and Secondary Education World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bulat, J.; Brombacher, A.; Slade, T.; Iriondo-Perez, J.; Kelly, M.; Edwards, S. Projet d’Amélioration de la Qualité de l’Education (PAQUED): 2014. Endline Report of Early Grade Reading Assessment (EGRA) and Early Grade Mathematics Assessment (EGMA); Prepared for USAID under Contract No. AID-623-A-09-00010; Education Development Center and RTI International: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- USAID. Early Grade Reading Assessment Toolkit: Nigeria Northern Education Initiative, Nigeria; USAID: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Burdenski, T. Evaluating univariate, bivariate, and multivariate Normality using graphical and statistical procedures. MLRV 2000, 26, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gravetter, F.; Wallnau, L. Essentials of Statistics for the Behavioural Sciences, 8th ed.; Wadsworth: Belmont, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Humble, S. Quantitative Analysis of Questionnaires: Techniques to Explore Structures and Relationships; Routledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kenny, D.A. Correlation and Causality; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structured Equation Modelling, 4th ed.; Methodology in the Social Sciences; Guildford Press: Guilford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Loehlin, J.C.; Beaujen, A.A. Latent Variable Models; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bollen, K.A. Structural Equations with Latent Variables; Wiley Series in Probability and Mathematical Statistics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, H. Multilevel Statistical Models, 3rd ed.; Edward Arnold: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Schagen, I. Presenting the results of complex models—Normalised coefficients, star wars plots and other ideas. In But What Does It Mean? The Use of Effect Sizes in Educational Research; Schagen, I., Elliot, K., Eds.; National Foundation for Educational Research: Slough, UK, 2004; pp. 25–41. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, P.; Schagen, I.; Seedhouse, P. The impact of an intervention on children’s reading and spelling ability in low-income schools in India. Sch. Eff. Sch. Improv. 2011, 22, 461–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total Test Scores | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hausa Letter Sound Knowledge | Hausa Word Reading Decoding | English Letter Sound Knowledge | English Word Reading Decoding | |
| Total mean score (SD) | 22.086 (8.190) | 18.796 (12.744) | 27.961 (10.003) | 19.218 (12.299) |
| Skewness | −0.265 | 0.231 | −0.431 | 0.124 |
| Kurtosis | −0.589 | −1.319 | −0.628 | −1.244 |
| Hausa Scores (L1) | English Scores (L2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sounds | Words Decoding | Sounds | Words Decoding | |
| Hausa Sounds (L1) | 1 | |||
| Hausa Words Decoding (L1) | 0.751 ** | 1 | ||
| English Sounds (L2) | 0.674 ** | 0.553 ** | 1 | |
| English Words Decoding (L2) | 0.671 ** | 0.798 ** | 0.691 ** | 1 |
| Endogenous Variables | ||
|---|---|---|
| Exogenous Variables | L1 Word | L2 Word |
| L1 phonemes | 0.617 *** (0.031) | |
| L1 word | 0.545 *** (0.028) | |
| L2 phonemes | 0.390 *** (0.021) | |
| L2 word | 0.200 *** (0.043) | |
| Dependant Variable | Hausa Word Score | English Word Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | Standard Error | Estimate | Standard Error | |
| Base Case | ||||
| Intercept | 17.778 *** | 0.694 | 18.176 *** | 0.791 |
| Pupil variance | 67.344 | 2.219 | 61.314 | 2.023 |
| School variance | 93.238 | 7.365 | 89.493 | 7.047 |
| State variance | 1.757 | 2.565 | 3.080 | 3.448 |
| Final Model | ||||
| Pupil variance | 29.212 | 0.981 | 28.260 | 0.934 |
| Hausa sound score | 0.565 *** | 0.023 | ||
| Hausa word score | 0.555 *** | 0.014 | ||
| English word score | 0.540 *** | 0.016 | ||
| English sound score | 0.407 *** | 0.017 | ||
| School variance | 17.056 | 1.677 | 13.537 | 1.418 |
| State variance | 0.063 | 0.334 | 0.241 | 0.557 |
| Hausa Word Score | English Word Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hausa sound score | 51.1 | English sound score | 46.7 |
| English word score | 73.5 | Hausa word score | 81.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Humble, S.; Dixon, P.; Gittins, L.; Counihan, C. An Investigation of the Cross-Language Transfer of Reading Skills: Evidence from a Study in Nigerian Government Primary Schools. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14030274
Humble S, Dixon P, Gittins L, Counihan C. An Investigation of the Cross-Language Transfer of Reading Skills: Evidence from a Study in Nigerian Government Primary Schools. Education Sciences. 2024; 14(3):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14030274
Chicago/Turabian StyleHumble, Steve, Pauline Dixon, Louise Gittins, and Chris Counihan. 2024. "An Investigation of the Cross-Language Transfer of Reading Skills: Evidence from a Study in Nigerian Government Primary Schools" Education Sciences 14, no. 3: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14030274
APA StyleHumble, S., Dixon, P., Gittins, L., & Counihan, C. (2024). An Investigation of the Cross-Language Transfer of Reading Skills: Evidence from a Study in Nigerian Government Primary Schools. Education Sciences, 14(3), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14030274







