Abstract
Despite the widespread adoption of project-based learning in higher education, few empirical studies have explored its impact on situating learners within real-world contexts and enhancing student engagement. This study situates undergraduates in a technology integration course in an authentic context to increase the levels of engagement of the students. The project, requested by real-world clients from an elementary school, enabled students to develop learning resources around topics in need that aligned with state standards. We expected students engaged with real-world clients to demonstrate higher levels of behavioral, cognitive, and emotional engagement compared to those involved in non-real-world context projects. The results of our mixed-methods research revealed increased student engagement with an authentic, real-world context compared to a non-real-world context. The integration of real-world context not only heightened student involvement in the project and strengthened group dynamics but also facilitated a deeper understanding of technology integration and service learning. Implications for future research are also discussed.
1. Introduction
Higher education advocates for including learner-centered instruction as it provides opportunities for students to practice critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving skills [1,2]. Project-based learning (PjBL) is one commonly used learner-centered pedagogical approach, as it provides students with opportunities to integrate knowledge, make decisions, and develop new ideas via collaboration [3,4]. When designing and implementing PjBL in instruction, it has generally been assumed that a crucial aspect involves the provision of authentic contexts. Yet, for the last 40 years, less effort has been made to empirically study the impact of authentic contexts when implementing PjBL, despite a few research reporting a lack of authentic context as one of the potential barriers to disengaging learners in PjBL. Furthermore, earlier studies on PjBL are conducted in K-12 education settings rather than in higher education settings. There are only a limited number of empirical studies investigating the positive impacts of PjBL in higher education environments, which mostly focus only on examining its impact on the improvement in academic performance, such as the enhancement of content knowledge acquisition [5,6]. Assuming PjBL is implemented via an authentic context, instructors in higher education environments are recommended to implement PjBL as a core instructional strategy to prepare learners in higher education settings who will become professionals when they graduate. However, instructors question the effectiveness of PjBL due to the disengagement of the students, which yields social loafing issues and unsuccessful collaboration [5,7]. Considering that authentic context is one of the key components of PjBL, this study examines the impact of the authentic context in PjBL to promote the learning engagement of students in higher education.
1.1. Project-Based Learning in Higher Education
The PjBL approach is rooted in Dewey’s insight that students develop a deeper understanding of learning materials by solving problems in authentic tasks that emulate what experts do in the real world. This insight has evolved from the constructivist perspectives emphasizing students’ active participation and construction of their understandings via engaging in learning [8]. While previous research on PjBL reports its positive impact on students’ academic achievement in K-12 education [9,10], there are limited studies exploring the impact PjBL has on students in higher education. One study used PjBL to enhance undergraduate students’ understanding of various astronomical phenomena in a college course and found an improvement in learning performance but did not focus on its impact on student engagement [11]. Another study conducted an experimental study to measure the effectiveness of PjBL in undergraduate chemistry courses but only focused on measuring learning performance [12].
PjBL has also been implemented in teacher professional development programs [13,14] to expose pre- and in-service teachers to authentic classroom settings, but only a few empirical research has investigated its effectiveness. One study measured how PjBL affects in-service teachers’ self-efficacy [15], while another study measured how pre-service teachers perceive the value of PjBL and reported increased motivation and involvement in the course [16]. However, previous studies did not analyze which components of PjBL enhanced expected outcomes (e.g., learning performance, self-efficacy, or motivation) to empirically suggest how to improve the effectiveness of PjBL in college classroom settings.
Meanwhile, several researchers have voiced concerns about the lack of undergraduate student engagement in inquiry-based activities such as PjBL. One study found that first-year undergraduates in the social sciences failed to describe the values of inquiry-based learning experiences due to disengagement [17]. Other studies reported inequitable learning benefits of PjBL for higher- and lower-performing students (i.e., students who performed higher or lower than other students in test scores) [18]. Regardless of increased concerns, however, a limited number of studies empirically examined how to promote student engagement in PjBL in higher education. Given the fast-changing demands of society to have creative-minded students to work with complex problems and provide multifaceted solutions [19], it is critical to explore ways to promote learning engagement in PjBL.
1.2. Enhancing Real-World Contexts to Promote Student Engagement in PjBL
In describing key elements of project-based learning, providing authentic contexts has been primarily assumed in PjBL [3,6,20]. For example, the key elements of project-based learning environments are as follows: include driving questions within authentic context; learning goals; elicit student participation during problem-solving to respond to the driving question; apply scaffolded usages on technologies, peer, or instructional feedback; and develop tangible products that address the driving question. Nonetheless, detailed guidelines on the extent to which authenticity is required are missing.
Real-world problems allow college students to reflect on their experiences, help enhance the development of problem-solving skills [21], and allow them to engage in the communities and further develop academic knowledge and skills [21,22]. Explicit connections between PjBL and the real-world context are featured in the design of PjBL environments [23,24], with the lack of authentic context in PjBL found to have mixed levels of engagement and motivation of the students in engineering courses [22,25]. Regardless of these findings, the extent to which authenticity engaged students in learning via project-based learning has not been examined [26,27].
1.3. Framework of Engagement
There are various constructs of student engagement (e.g., two-dimensional or three-dimensional models of engagement). The three-dimensional model includes definitions of behavioral, emotional, and cognitive engagement [28]. Behavioral engagement represents students’ active participation in learning by measuring the time students invested in the learning task or whether students follow rules or use class time. Emotional engagement is the extent of positive or negative reactions to learning activities, teachers, peers, or the course. Cognitive engagement focuses on the student’s level of investment in learning, and its indicators include generating complex ideas and mastery of skills based on the comprehension of the subject matter.
1.4. The Study
In this study, a class project was re-designed to incorporate an authentic context to increase levels of engagement for college students in a PjBL-integrated technology course. Two research questions were addressed:
- How does a real-world context project promote students’ engagement in project-based learning?
- How do students perceive a real-world context project compared to a non-real-world context project?
This study adopted the three-dimensional model [28] and measured the behavioral, emotional, and cognitive engagement of college students in the course with a PjBL activity. Students’ behavioral engagement in the project was measured via the indications of developing an exploratory approach to technology with a willingness to try new applications; emotional engagement was measured via the perceptions towards self-belief and the value of using technology; cognitive engagement was measured via capturing how they apply the acquired knowledge in the course into the project.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Context
The study was conducted for four semesters with the participation of undergraduate students from 12 sections of a technology integration course at a large public university in the United States. The learning objectives of the course include introducing and exploring different ways in which teachers can integrate technology into their classrooms via various projects following the International Society of Educational Technology (ISTE) standards. Although the course was designed for pre-service teachers, enrollment was open to students from all majors. The courses were taught by six different instructors (three instructors for treatment groups and three for control groups), but all sections followed a unified course design, including the course objectives, types and instructions of projects, and evaluation criteria.
2.1.1. Stop Animation Project
Among five different ISTE standards-based projects in the course, this study was implemented as a project within the Creativity and Innovation unit, particularly in re-designing Stop Animation videos. Stop Animation videos, which consist of numerous images integrated into a video clip to show a continuous near-life movement [29], were selected as the implementation for the study. Researchers selected Stop Animation videos as the PjBL to implement in this project as developing these videos engaged pre-service teachers with the concept [30] and offered meaningful learning [30] in the past.
2.1.2. The Re-Designed Stop Animation Project
Refer to Figure 1 for a comparison between the original Stop Animation project (for control groups) and the re-designed Stop Animation project (for treatment groups). Classroom teachers in 1st, 2nd, and 4th grades in charter elementary schools in Southern California requested Stop Animation videos centered on specific content areas that teachers can use as learning resources in their lessons. The elementary school students, who are the real-world clients for this project, sent a greeting video to the college students, which provided authenticity to learning. The students then created the Stop Animation videos around the requested topic, which were published on YouTube. These videos were used by elementary teachers as learning resources. In creating the Stop Animation videos, the students formed groups of 3–4 to work together collaboratively and used strategic guidelines and rubrics created by the course instructors. Following the institution’s Ethics procedure, participants gave their informed consent.
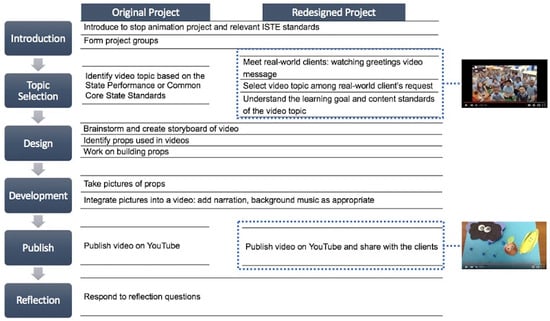
Figure 1.
Comparison of context between real-world context and non-real-world context projects.
2.2. Measures
This study employed a sequential explanatory mixed-methods design to examine both the process and learning outcomes of PjBL [31]. We used qualitative data as complementary and explanatory information to further understand the impact of authentic context on students’ learning experiences during PjBL. Additionally, we triangulated the quantitative data with multiple qualitative sources (e.g., reflection journals and interviews) to examine the complex phenomenon of students’ engagement in PjBL with an authentic context from multiple angles.
2.2.1. Quantitative Measures
To measure student engagement between the control and treatment groups, two validated instruments were adapted: the National Survey of Student Engagement (NSSE) [32] instrument and the Engagement vs. Disaffection with Learning (EvsD) scale [33]. To measure cognitive engagement in the project, we adapted four NSSE items that measure academic challenges (higher-order learning, reflective and integrative learning, and learning strategies) and learning with peers (collaborative learning and discussion with diverse others) (Cronbach alpha = 0.78–0.91). EvsD was adapted to measure behavioral (two items) and emotional engagement (two items) in learning activities (Cronbach alpha = 0.53–0.68). In total, we asked eight multiple-choice questions and an open-ended question in addition to background information on each student, including major and grade level, as these might affect students’ prior knowledge and experiences.
2.2.2. Qualitative Measures
To explore students’ perceptions about the project and how it affected their engagement, a semi-structured open-ended question, students’ online reflection journals, and interviews were collected. Responses from the open-ended question and reflection journals were collected from both control and treatment groups. The open-ended question was designed to measure students’ emotional engagement or disaffection by providing a reflective question related to the project. The reflection journal was semi-structured, and students wrote their reflections on the project in their individual blogs with guiding prompts asking about the PjBL experiences (Appendix A). Interviews were conducted with students from the treatment group, as we particularly sought to gain additional insights into how the real-world PjBL influences their engagement.
2.3. Data Analyses
2.3.1. Quantitative Data
The survey analysis involved a random effects model and t-tests. To measure the differences in student engagement (e.g., behavioral, cognitive, and emotional) levels in the real-world context and non-real-world context project, we used the random effects model [34] to control the influence of different student-instructor interactions associated with different sections. Independent t-tests were used to measure engagement differences based on the types of engagement (e.g., behavioral, cognitive, and emotional). A total of 121 students were invited to complete the survey, and 103 students from 12 sections of the course agreed to be involved in the study and completed the survey: 51 students from six sections of treatment groups and 52 students from six sections of control groups. In the treatment group, 35% of the students were education majors, while 42% of the students in the control group were education majors. The homogeneity of covariance assumption was checked using Box’s M test, and the homogeneity of variances was checked using Levene’s test.
2.3.2. Qualitative Data
Based on the participants’ consent, a total of 121 reflection journals were analyzed, including 46 journals in the control groups and 75 journals in the treatment groups. From the treatment group, seven students voluntarily participated in the 20 min long interview. Interviews were recorded, transcribed verbatim, and coded via multiple transcript readings by the three authors. The first author created a codebook based on the literature review, and the second and third authors coded the reflection journals and interviews. The interrater reliability score was 95%. The codebook and emerging themes with quotes from the treatment group are summarized in Appendix B.
2.3.3. Triangulation
Results from quantitative data analyses were triangulated with multiple qualitative data to corroborate and validate how the re-designed PjBL influenced student engagement. Trustworthiness is ensured via researcher triangulation by having multiple investigators with different perspectives code and discuss the data to create the final set of themes [35].
3. Results
3.1. Quantitative Results
Random effects model results revealed that students with real-world context projects reported higher engagement in the course than students in the non-real-world context, F (1, 101) = 15.66, p < 0.005. Estimating mean scores of student engagement in the treatment group were 0.63 higher than that of the control group, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Estimates of fixed effects of engagement mean score gap between control and treatment groups.
t-test results also showed statistically higher overall engagement from students with real-world context than non-real-world context, t (101) = 3.95, p = 0.00, as shown in Table 2. Among the three different domains of engagement we measured, only cognitive and emotional engagement showed significant differences between the treatment and control groups. t-test results showed significantly higher cognitive engagement scores of students with real-world context than non-real-world context, t (101) = 3.95, p = 0.00. Students with real-world context showed higher emotional engagement than those with non-real-world context; t (101) = 2.10, p = 0.03. (See Appendix C for details).

Table 2.
t-test results to measure engagement differences per item between treatment and control group per engagement type.
3.2. Triangulated Results
To further understand factors that may affect student engagement in the re-designed project, we triangulated the data by comparing quantitative results with qualitative data. During the triangulation, we particularly focused on examining the impact of authentic context on students’ learning experiences. We describe our findings below with some of the highlighted quotes, but more quotes per code and theme are available in Appendix B.
3.2.1. Cognitive Engagement
We measured two aspects of students’ cognitive engagement: integrative learning and higher-order learning. As reported in the quantitative results, compared to students with non-real-world contexts, students with real-world contexts reported higher engagement in three survey items: in learning something that changed their understanding of using technology in education; in learning ways to use technology for practical problems or new situations; analyzing an idea; and in the learning experience, or line of reasoning in depth by examining its parts.
Among multiple themes that emerged from qualitative analysis, the majority of themes indicated an increase in students’ cognitive engagement in a real-world context project. As students recognized real audiences, they tried to apply their prior and acquired knowledge. When designing storyboards and writing scenarios for the videos, students willfully considered elementary students’ (i.e., real-world clients) linguistic abilities and prior knowledge levels, with one student sharing, “you basically have to find the most basic way to explain the topic to the students, while still providing them with all of the information they need to know. Although this was one of the most challenging aspects of the project, it was also one of the most rewarding”. The student then went on to describe how this experience will help in working with elementary students in the future by stating, “it also gave me the opportunity to learn how to simplify information for young minds. The experiences I had breaking down this material into an elementary level will really come in handy as I go on to pursue a career in the field of education”.
Moreover, students tried to apply what they learned about educational theories to create meaningful learning resources while reflecting on their prior learning experiences with multimedia resources. One group decided to use iMovie to make the Stop Animation videos and explained how it was “a lot easier to maneuver” compared to another tool they had used in the past, and further shared seeing the possibility of teachers using these videos as an introduction to the bigger unit, by explaining “I definitely think this video could be used by teachers in the future to show their students a simplified idea of what they are learning before they go into the lesson”. Students’ consideration of real-world audiences also influenced their perceptions of multimedia-based learning resources and their potential benefits. One student described the value of stop animation-type learning resource as a “great (format) for getting kids to learn about concepts that involve processes” as “the video keeps kids focused and helps them remember the topics”. Students perceived their videos as open educational resources that can be used anywhere at any time by anyone in need, including themselves in the future. Students expressed their hopes during the interview that “this project will not only help teach a specific fourth-grade class but will also help other students learning about this topic” and eventually “can have an impact on fellow students around the globe”.
3.2.2. Emotional Engagement
As the quantitative data indicated, we observed statistically meaningful emotional engagement of the students in the treatment group compared to the control group. Qualitative evidence also documented students’ emotional engagement in the re-designed project. As a semi-structured question, we provided options to choose the adjective (i.e., interested, bored, or nervous) of their perceptions about the project and their rationale for the selection. Students in both the treatment and control groups demonstrated positive emotional engagement, albeit for different rationales. For the treatment group, the result showed that 64% of students were interested, excited, happy, and motivated to create a video for the kids in the real world. One of the students shared, “I was excited because our hard work would actually be used in a classroom. The children will actually be able to learn a little bit from the video we created”. Meanwhile, 32% of students in the treatment group reported that they were nervous because they knew their videos would actually be used as learning resources in the real-world classroom. For instance, one student shared the impact of their work on the real world by stating, “I was excited but also a little nervous. We have never created anything that had a true purpose or audience before. It made the stakes a little higher”. Only 4% of the students in the treatment group chose negative perception (i.e., bored or indifferent) when they were introduced to the real-world context project. For the control group, on the other hand, 85% of the students reported they were excited, happy, and relieved. But the main reason for the positive feelings was related to finally being able to complete the time-consuming project. The rest of the students in the control group reported negative feelings (e.g., frustration, annoyance, and nervousness) in the project due to the amount of time and effort they needed to put in to complete the project. Reflection journal analysis also showed that students in the treatment group enjoyed the project because they knew that they were “doing it (the project) for real children” and “making an informational video for students who live on the other side of the country”. In the interview, students also shared that the project inspired them to “try harder with this project because students in another school would be watching our animation videos and actually learning from it”.
3.2.3. Behavioral Engagement
Survey results showed no statistically significant differences in behavioral engagement between students in the treatment group and the control group. Qualitative findings from students’ reflection journals showed that having real audiences and virtually meeting them via video made students put more time and effort into creating better quality products as they wished to positively influence younger audiences’ learning experiences. The interview data showed students’ behavioral engagement in communication and collaboration via the real-world context project. Having real-world audiences motivated students “to try harder with this project and spend more time creating the animations for the movie”. One student mentioned that this project helped to further develop “communication and collaboration skills working in my group”. Group members also tried to “come up with good ideas and combine all of our ideas into one to make the best video possible”.
4. Discussion
This study aimed to further improve students’ engagement in a technology integration course designed with project-based learning by providing a real-world context. Triangulated survey results indicated that real-world context projects enhanced students’ engagement in a technology integration course and, eventually, enhanced students’ understanding of the course objectives, technology integration in learning, and potential possibilities to contribute to society. This study is meaningful because it provides empirical evidence around the value of real-world audiences in PjBL and the impact of PjBL in a technology integration course on college students’ engagement.
4.1. Real-World Audiences in Project-Based Learning
Situating learners in the real world within an authentic context that engages a client for the project has been indicated and suggested as one of the core components of PjBL [36]. However, scenarios [37] have been dominantly provided in practice and research instead of specific and lived audiences or situations. Yet, the impact of providing real-world audiences compared to plausible scenarios would be different. Past studies showed that providing projects with real-world audiences enhanced the skill development of the students in marketing when with real-world audiences [23,38]. From our study, we found students invested more time and effort in PjBL and had a higher engagement in the project in comparison to the projects without real-world audiences. Compared to producing educational resources for unspecified audiences (i.e., anyone who might be interested in the animation topic), having real audiences helped students put more endeavors into creating quality learning resources to satisfy the real audiences whom they met virtually via video. All in all, the non-traditional approach of engaging with real audiences in learning enabled students to experience firsthand the effects their work has in the real world and enabled them to interact with others beyond the classroom context.
In addition, the real-world context project provided students with opportunities to think about the possibilities to contribute to society. As reviewed in the literature, past studies investigating the effects of PjBL on learning focused on students’ competence, such as their problem-solving abilities, collaboration or teamwork skills, and critical thinking skills [11,18,19]. In this project, students expanded their real-world problem-solving abilities from a simple class activity into a service opportunity. They interpreted their projects as an opportunity to contribute globally as they created open educational resources. The real-world context contributed towards students expanding on their work from simply providing solutions to the given problems but went beyond to contribute their solutions to society, thus providing authentic and concrete solutions and impact. As a result, students directly experienced the impact of service learning on communities [39] and reflected on the challenges that our societies face [37]. The study found the ways in which the context of this project supported students’ learning experiences in developing their competence in PjBL, as well as in understanding how their projects are being used in the real world and therefore contributing to society. In summary, engaging in the real-world context via PjBL enabled students to realize the direct benefit of their work, which is necessary as it provides meaningful implications for their learning [17].
4.2. Project-Based Learning Experiences in a Technology Integration Course
The findings from this study also revealed that real-world context-based PjBL promotes student understanding of technology integration. In previous studies, PjBL has been used in technology integration courses to promote learning gains, self-efficacy, or self-confidence of pre-service teachers [39,40]. However, students’ level of engagement has been indicated as one of the critical factors that affect teachers’ efforts in integrating technology in the classroom [41]. Our study found that PjBL offered opportunities for students to personalize and apply their knowledge and further utilize it for the benefit of others using technology while creating videos for real audiences.
Furthermore, via the enhanced engagement of the carefully planned and designed PjBL experiences offered, students developed the necessary communication and collaboration skills, which are the core skills to be developed in higher education [2]. The study affirms that carefully designed projects support the development of students’ communication, collaboration, critical thinking skills [42,43], and creativity [44]. The participants reported that they engaged in critical thinking processes to find a solution to the given authentic problem, which aligns with the quantitative analysis findings measuring cognitive engagement. Moreover, qualitative analysis suggested that students appreciated PjBL as they perceived the learning activities as helpful in further developing their communication and collaboration skills and combining ideas from previous knowledge and experiences.
The study results further suggest future research on the impact of real-world context problems on pre-service teacher education regarding technology integration and service learning. Previous research indicates that teachers’ pedagogical beliefs affected the actual use of technology and instruction in classes [45]. The study had 24 pre-service teachers in the treatment group as this class was open to all majors, and they were prominently engaged in the project and tried to connect their learning experiences with their future careers. Longitudinal studies measuring the effects of real-world context projects on their career paths or community service activities may also be meaningful to measure in the future.
5. Limitations
Despite the significance of the study, readers should be cautious when interpreting our results and applying our approaches in their own contexts. First, researcher bias may influence our findings during qualitative analysis. Although we triangulated the multiple qualitative data with quantitative data sources to minimize the potential influence of researcher bias, our roles as researchers may have influenced the analysis. Second, our study was conducted in a large research-intensive university in the US. Different results may be reported when tested in a smaller size university or non-US setting where students’ autonomy and motivation may be different. Lastly, our analysis heavily relied on self-reported data. In the future, incorporating peer evaluation data may complement the limitation of self-reported data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.C. and J.C.; Methodology, Y.C., J.C. and M.Ş.-A.; Software, Y.C.; Validation, J.C. and M.Ş.-A.; Formal Analysis, Y.C., J.C. and M.Ş.-A.; Investigation, Y.C., J.C. and M.Ş.-A.; Resources, J.C. and Y.C.; Data Curation, Y.C.; Writing—original draft preparation, Y.C. and J.C.; Writing—review and editing, Y.C., J.C. and M.Ş.-A.; Visualization, Y.C.; Supervision, Y.C.; Project Administration, Y.C. and J.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of the University of Georgia (protocol code 00002031 approval date 16 April 2015).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used for this manuscript are not publicly available. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the elementary classrooms that worked in collaboration to provide a real-world context for the project. We would also like to extend our appreciation to Gretchen Thomas for the support of this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. Reflection Journal Prompt
Think about when the project and its ideas were first introduced, and during video development. What were your initial thoughts when the project was introduced? Has your expectation and/or perception towards a class project changed? What did you find to be the most important aspect in the project? How do you see the roles of this project being used by others in the future? Jot down your thoughts, and further explain what you’ve written in a paragraph (18–20 sentences).
Appendix B. Excerpted Quotes and Emerged Codes

Table A1.
Excerpted quotes and emerged codes per theme.
Table A1.
Excerpted quotes and emerged codes per theme.
| Engagement | Themes | Emerged Codes | Quotes from Interviews and Short Responses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emotional | Expressing emotional reaction to the project |
|
|
| Cognitive | Combining ideas from prior knowledge and experiences |
|
|
| Applying facts, theories, or methods |
|
| |
| Analyzing ideas, experiences, or reasoning |
|
| |
| Connecting learning to societal problems or issues |
|
| |
| Forming new ideas from various pieces of information |
|
| |
| Behavioral | Behavioral changes in individual or group learning process |
|
|
Appendix C. t-Test Results across Treatment and Control Group

Table A2.
t-test results to measure engagement differences per item between the treatment and control groups per item.
Table A2.
t-test results to measure engagement differences per item between the treatment and control groups per item.
| Engagement Survey | Treatment (n = 51) | Control (n = 52) | t-Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | t | p | ||
| E1 | 1. Among EDIT2000 projects, I enjoyed Stop Animation the most. | 5.370 | 1.428 | 4.850 | 1.513 | 1.815 | 0.072 |
| C1 | 2. I learned something that changed my understanding of using technology in education. | 6.120 | 0.840 | 5.210 | 1.348 | 4.085 | 0.000 * |
| C2 | 3. I connected ideas from Stop Animation to my prior experiences and knowledge. | 5.570 | 1.153 | 4.850 | 1.377 | 2.883 | 0.005 * |
| B1 | 4. I have put more time and effort towards Stop Animation than other projects. | 5.710 | 1.346 | 5.600 | 1.390 | 0.407 | 0.685 |
| E2 | 5. Stop Animation was more interesting than other projects. | 5.710 | 1.254 | 5.100 | 1.718 | 2.054 | 0.043 * |
| C3 | 6. How much has Stop Animation emphasized, “Ways to use technology to practical problems or new situations”? | 5.920 | 0.956 | 5.190 | 1.358 | 3.146 | 0.002 * |
| C4 | 7. How much has Stop Animation emphasized, “Analyzing an idea, experience, or line of reasoning in depth by examining its parts”? | 5.820 | 1.090 | 5.100 | 1.361 | 2.990 | 0.004 * |
| C5 | 8. How much has Stop Animation emphasized, “Forming a new idea or understanding from various pieces of information”? | 6.080 | 0.845 | 5.370 | 1.237 | 3.409 | 0.001 * |
* p < 0.05.
References
- Hoidn, S.; Reusser, K. Foundations of Student-Centered Learning and Teaching. In The Routledge International Handbook of Student-Centered Learning and Teaching in Higher Education; Routledge: London, UK, 2020; pp. 17–46. ISBN 978-0-429-25937-1. [Google Scholar]
- Fairweather, J. Linking Evidence and Promising Practices in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) Undergraduate Education; The National Academies National Research Council Board of Science Education: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Krajcik, J.; Shin, N. Project-Based Learning. In The Cambridge Handbook of The Learning Science; Keith, D.S., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 275–297. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Hill, J.; Hannafin, M. Emerging Trends to Foster Student-Centered Learning in the Disciplines: Science, Engineering, Computing and Medicine. In The Routledge International Handbook of Student-Centered Learning and Teaching in Higher Education; Routledge: London, UK, 2020; ISBN 978-0-429-25937-1. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, P.; Saab, N.; Post, L.S.; Admiraal, W. A Review of Project-Based Learning in Higher Education: Student Outcomes and Measures. Int. J. Educ. Res. 2020, 102, 101586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helle, L.; Tynjälä, P.; Olkinuora, E. Project-Based Learning in Post-Secondary Education: Theory, Practice and Rubber Sling Shots. High. Educ. 2006, 51, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Lee, E. Addressing the Challenges of Online and Blended STEM Learning with Grounded Design. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 2022, 38, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.S.; Delawsky, S. Project-Based Learning and Student Engagement. Acad. Res. Int. 2013, 4, 560. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-H.; Yang, Y.-C. Revisiting the Effects of Project-Based Learning on Students’ Academic Achievement: A Meta-Analysis Investigating Moderators. Educ. Res. Rev. 2019, 26, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaçalli, S.; Korur, F. The Effects of Project-Based Learning on Students’ Academic Achievement, Attitude, and Retention of Knowledge: The Subject of “Electricity in Our Lives”. Sch. Sci. Math. 2014, 114, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ridgway, A.J.; Sachs, D. Cultivating Preservice Secondary Teachers for Project-Based Learning: A Four-Step Model. AILACTE J. 2015, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Barak, M.; Dori, Y.J. Enhancing Undergraduate Students’ Chemistry Understanding through Project-Based Learning in an IT Environment. Sci. Educ. 2005, 89, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan, M.E.; Coronado, J.M. Problem-Based and Project-Based Learning: Promoting Differentiated Instruction. Natl. Teach. Educ. J. 2014, 7, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Tsybulsky, D.; Muchnik-Rozanov, Y. The Development of Student-Teachers’ Professional Identity While Team-Teaching Science Classes Using a Project-Based Learning Approach: A Multi-Level Analysis. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2019, 79, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, B. How Does Learner-Centered Education Affect Teacher Self-Efficacy? The Case of Project-Based Learning in Korea. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2019, 85, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, O. A Project-Based Learning Approach to Teaching Physics for Pre-Service Elementary School Teacher Education Students. Cogent Educ. 2016, 3, 1200833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, P.; Petrulis, R. How Do First-Year University Students Experience Inquiry and Research, and What Are the Implications for the Practice of Inquiry-Based Learning? Stud. High. Educ. 2012, 37, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Kim, H.; Byun, H. Are High Achievers Successful in Collaborative Learning? An Explorative Study of College Students’ Learning Approaches in Team Project-Based Learning. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2017, 54, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditomo, A.; Goodyear, P.; Bliuc, A.-M.; Ellis, R.A. Inquiry-Based Learning in Higher Education: Principal Forms, Educational Objectives, and Disciplinary Variations. Stud. High. Educ. 2013, 38, 1239–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenfeld, P.C.; Soloway, E.; Marx, R.W.; Krajcik, J.S.; Guzdial, M.; Palincsar, A. Motivating Project-Based Learning: Sustaining the Doing, Supporting the Learning. Educ. Psychol. 1991, 26, 369–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundiers, K.; Wiek, A.; Redman, C.L. Real-world Learning Opportunities in Sustainability: From Classroom into the Real World. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2010, 11, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badir, A.; O’Neill, R.; Kinzli, K.-D.; Komisar, S.; Kim, J.-Y. Fostering Project-Based Learning through Industry Engagement in Capstone Design Projects. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohm, A.J.; Stefl, M.; Ward, N. Future Proof and Real-World Ready: The Role of Live Project-Based Learning in Students’ Skill Development. J. Mark. Educ. 2021, 43, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajkov, O.; Mitrevski, B. Project-Based Learning: Dilemmas and Questions! Maced. Phys. Teach. 2012, 48, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Foley, R.W. Motivational Factors of Undergraduate Engineering Students in Introductory Non-Technical Courses. In Proceedings of the 2018 ASEE Annual Conference & Exposition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 24–27 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.; Blackwell, S.; Drake, J.; Moran, K.A. Taking a Leap of Faith: Redefining Teaching and Learning in Higher Education through Project-Based Learning. Interdiscip. J. Probl.-Based Learn. 2014, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, M.M. Learning, Beliefs, and Products: Students’ Perspectives with Project-Based Learning. Interdiscip. J. Probl.-Based Learn. 2011, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredricks, J.A.; Blumenfeld, P.C.; Paris, A.H. School Engagement: Potential of the Concept, State of the Evidence. Rev. Educ. Res. 2004, 74, 59–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keast, S.; Cooper, R.; Berry, A.; Loughran, J.; Hoban, G. Slowmation as a Pedagogical Scaffold for Improving Science Teaching and Learning. Brunei Int. J. Sci. Math. Educ. 2010, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hoban, G.; Nielsen, W. Creating a Narrated Stop-Motion Animation to Explain Science: The Affordances of “Slowmation” for Generating Discussion. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2014, 42, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, J.W. A Concise Introduction to Mixed Methods Research; SAGE: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-4833-5904-5. [Google Scholar]
- Chickering, A.W.; Gamson, Z.F. Seven Principles for Good Practice in Undergraduate Education. AAHE Bull. 1987, 3, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, E.A. Perceived Control, Motivation, & Coping; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1995; Volume 8, ISBN 0-8039-5561-8. [Google Scholar]
- Raudenbush, S.W.; Bryk, A.S. Hierarchical Linear Models: Applications and Data Analysis Methods; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2002; Volume 1, ISBN 0-7619-1904-X. [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln, Y.S.; Guba, E.G. Naturalistic Inquiry; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1985; ISBN 0-8039-2431-3. [Google Scholar]
- DeFillippi, R.; Milter, R.G. Problem-Based and Project-Based Learning Approaches: Applying Knowledge to Authentic Situations. In The Sage Handbook of Management Learning, Education and Development; SAGE Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 2009; pp. 344–363. [Google Scholar]
- Aránguiz, P.; Palau-Salvador, G.; Belda, A.; Peris, J. Critical Thinking Using Project-Based Learning: The Case of The Agroecological Market at the “Universitat Politècnica de València”. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassone, V.C.; O’Mahony, C.; McKenna, E.; Eppink, H.J.; Wals, A.E. (Re-) Designing Higher Education Curricula in Times of Systemic Dysfunction: A Responsible Research and Innovation Perspective. High. Educ. 2018, 76, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdamli, F. The Experiences of Teacher Candidates in Developing Instructional Multimedia Materials in Project Based Learning. Procedia—Soc. Behav. Sci. 2011, 15, 3810–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastergiou, M. Learning to Design and Implement Educational Web Sites within Pre-service Training: A Project-based Learning Environment and Its Impact on Student Teachers. Learn. Media Technol. 2005, 30, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.L.; Maeng, J.L.; Binns, I.C. Learning in Context: Technology Integration in a Teacher Preparation Program Informed by Situated Learning Theory. J. Res. Sci. Teach. 2013, 50, 348–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen-Akbulut, M.; Diler, Ö. Developing Pre-Service Teachers’ Technology Competencies: A Project-Based Learning Experience. Cukurova Univ. Fac. Educ. J. 2021, 50, 247–275. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-S.; Ma, J.-T.; Kuo, K.Y.-C.; Chou, C.-T.C. Examining the Efficacy of Project-Based Learning on Cultivating the 21st Century Skills among High School Students in a Global Context. J. Sch. Educ. Technol. 2015, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- You, J.W. Enhancing Creativity in Team Project-Based Learning amongst Science College Students: The Moderating Role of Psychological Safety. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2021, 58, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Koehler, M.J. Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge: A Framework for Teacher Knowledge. Teach. Coll. Rec. 2006, 108, 1017–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).