Science and Mathematics Teachers’ Integration of TPACK in STEM Subjects in Qatar: A Structural Equation Modeling Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. What Is the TPACK
2.2. TPACK in the Context STEM Teachers
2.3. SEM in TPACK Modeling Studies
2.4. Research Question
- 1.
- How do TPACK and its components affect each other?
- 1.1.
- What is the effect, if any, of TK, PK and CK on STEM teachers’ TPACK?
- 1.2.
- What is the effect, if any, of TK on STEM teachers’ TPK and PCK?
- 1.3.
- What is the effect, if any, of PK on STEM teachers’ TCK, TPK, and PCK?
- 1.4.
- What is the effect, if any, of CK on STEM teachers’ TPK and PCK?
- 1.5.
- What is the effect, if any, of TPK, TCK, and PCK on STEM teachers’ TPACK?
- 2.
- How do the demographic variables of gender, minor degree, and major degree in STEM disciplines effect TPACK and its sub-dimensions?
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Participants
3.2. Data Tools
3.3. Data Analysis
4. Results
Structural Equation Model
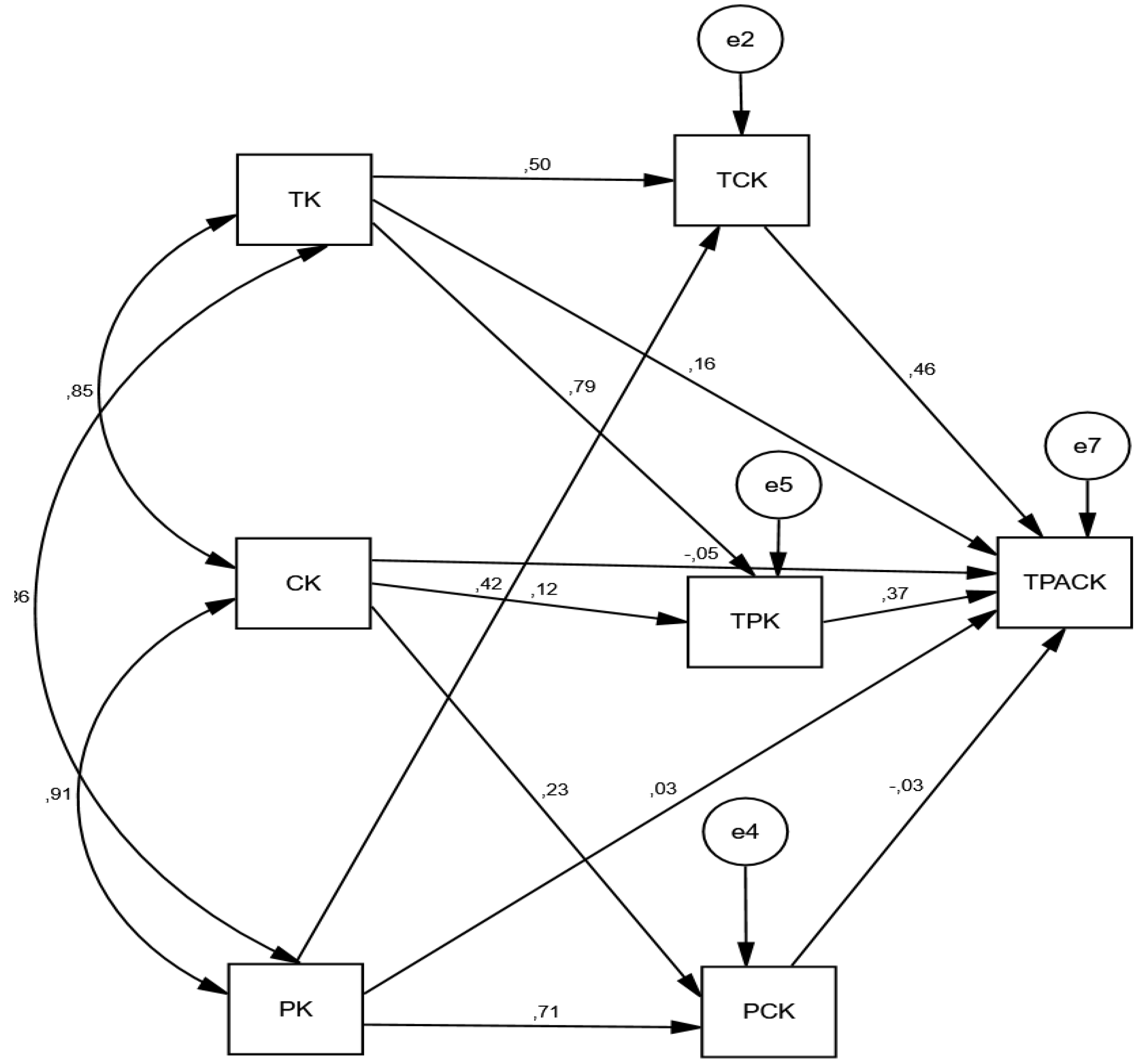
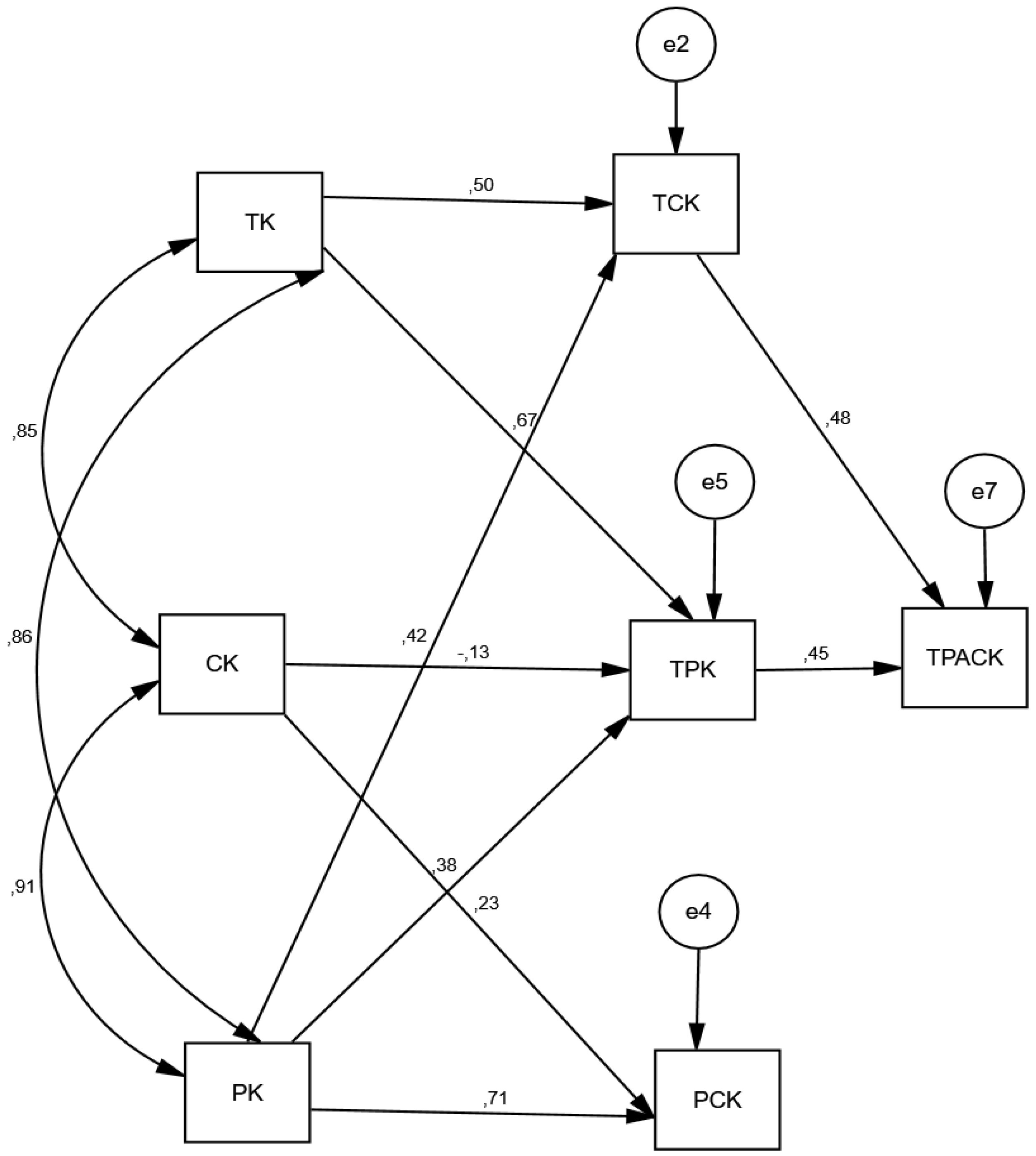
- For the sub-question 1.1,TK, PK, and CK do not significantly affect STEM teachers’ TPACK. TK positively affects TPK (β = 0.50) and PCK (β = 0.67), both directly and significantly (p < 0.001).
- Regarding the sub-question 1.2,PK has a positive, direct, and significant effect on TCK (β = 0.16), TPK (β = 0.39), and PCK (β = 0.71) (p < 0.001).
- For sub-question 1.3,CK has a significant, direct effect on TCK (β = 0.14) and PCK (β = 0.23) (p < 0.001).
- For the sub-question 1.4,TCK (β = 0.47) and PCK (β = 0.44) have a significant, direct, and positive effect on TPACK (p < 0.001), with TCK being the most significant external variable influencing TPACK, followed by PCK. However, TPK did not have a significant effect on TPACK.
5. Discussion
5.1. What Is the Effect, If Any, of TK, PK, and CK on STEM Teachers’ TPACK?
5.2. What Is the Effect, If Any, of TK on STEM Teachers’ TPK and PCK?
5.3. What Is the Effect, If Any, of PK on STEM Teachers’ TCK, TPK, and PCK?
5.4. What Is the Effect, If Any, of CK on STEM Teachers’ TPK and PCK?
5.5. What Is the Effect, If Any, of TPK, TCK, and PCK on STEM Teachers’ TPACK?
5.6. How Do the Demographic Variables of Gender, Minor Degree, and Major Degree in STEM Disciplines Effect on TPACK and Its Sub-Dimensions?
6. Conclusions and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Society for Technology in Education [ISTE]. ISTE Standards. 2020. Available online: https://www.iste.org/standards (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Mansour, N. Students’ and facilitators’ experiences with synchronous and asynchronous online dialogic discussions and e-facilitation in understanding the nature of science. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024, 29, 15965–15997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, L.S. Those who understand: Knowledge growth in teaching. Educ. Res. 1986, 15, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Koehler, M.J. Technological pedagogical content knowledge: A framework for teacher knowledge. Teach. Coll. Rec. 2006, 108, 1017–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, N.; Wegerif, R.; Postlethwaite, K.; Skinner, N.; Hetherington, L. Investigating and promoting trainee science teachers’ conceptual change of the nature of science with digital dialogue games “InterLoc”. Res. Sci. Educ. 2016, 46, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, N.; EL-Deghaidy, H. STEM in Science Education and S in STEM: From Pedagogy to Learning; Brill-Sense Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kafyulilo, A.; Fisser, P.; Voogt, J. Factors affecting teachers’ continuation of technology use in teaching. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2016, 21, 1535–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.S.; Jong, M.; Yin, H.B.; Chen, M.; Zhou, W. Validating and modelling teachers’ technological pedagogical content knowledge for integrative science, technology, engineering and mathematics education. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2019, 22, 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- John, P.D.; La Velle, L.B. Devices and desires: Subject subcultures, pedagogical identity and the challenge of information and communications technology. Pedagog. Educ. 2004, 13, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, M.J.; Mishra, P. What is technological pedagogical content knowledge? Contemp. Issues Technol. Teach. Educ. 2009, 9, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, R.M.; Sumarmi, S.; Astina, I.K.; Utomo, D.H.; Ridhwan, R. Increasing students critical thinking skills and learning motivation using inquiry mind map. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. (iJET) 2021, 16, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.H.L.; Chai, C.S.; Tsai, C.C. Examining practicing teachers’ perceptions of technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK) pathways: A structural equation modeling approach. Instr. Sci. 2013, 41, 793–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.S.; Koh, J.H.L.; Tsai, C.C. Exploring the factor structure of the constructs of technological, pedagogical, content knowledge (TPACK). Asia Pac. Educ. Res. 2011, 20, 595–603. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, C.S. Teacher professional development for science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) education: A review from the perspectives of technological pedagogical content (TPACK). Asia Pac. Educ. Res. 2019, 28, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahan, E.; Canbazoğlu Bilici, S. STEM eğitiminde teknoloji entegresyonu [technology integration in STEM education]. In Fen Bilimleri Öğretimi ve STEM Etkinlikleri [Science Teaching and STEM Activities], 1st ed.; Tekbıyık, A., Cakmakcı, G., Eds.; Nobel Publishing: Çankaya, Türkiye, 2018; pp. 265–280. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, C.; Abel, Y.; Denisova, E. Urban elementary STEM initiative. Sch. Sci. Math. 2015, 115, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.P.E.; Avilla, R.; Sarmiento, C.; Elipane, L.; Palisoc, C.; Palomar, B.; Ayuste, T.O.; Butron, B. Experiences and practices of STEM teachers through the lens of TPACK. J. Turk. Sci. Educ. 2022, 19, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Warr, M. Contextualizing TPACK within systems and cultures of practice. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2021, 117, 106673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porras-Hernandez, L.H.; Salinas-Amescua, B. Strengthening TPACK: A broader notion of context and the use of teacher’s narratives to reveal knowledge construction. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 2013, 48, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.J.; Voithofer, R.; Cheng, S.-L. Mediating factors that influence the technology integration practices of teacher educators. Comput. Educ. 2019, 128, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozudogru, M.; Ozudogru, F. Technological pedagogical content knowledge of mathematics teachers and the effect of demographic variables. Contemp. Educ. Technol. 2019, 10, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Brianza, E.; Petko, D. Developing a short assessment instrument for technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK.xs) and comparing the factor structure of an integrative and a transformative model. Comput. Educ. 2020, 157, 103967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamuk, S.; Ergun, M.; Cakir, R.; Yilmaz, H.B.; Ayas, C. Exploring relationships among TPACK components and development of the TPACK instrument. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2015, 20, 241–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dina, L.N.A.B.; Faizah, S.N.; Anggraini, E.A. Structural equation model: Analysis of pre-service elementary teachers on technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK). In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Multidisciplinary Sciences for Humanity in Society 5.0 Era, Malang, Indonesia, 17 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Li, B. Unravelling the dynamics of technology integration in mathematics education: A structural equation modelling analysis of TPACK components. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowfan, M.; Yaakob, M.F.M.; Habibi, A. Technological, pedagogical, and content knowledge for technology integration: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Eval. Res. Educ. 2024, 13, 212–222. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, H.H.; Weng, C.Y.; Huang, F.C. A structure equation model among factors of teachers’ technology integration practice and their TPCK. Comput. Educ. 2015, 86, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanti, N.; Hadiyanto; Mukminin, A. The Effects of TPACK instrument variables on teacher candidates in higher education. J. High. Educ. Theory Pract. 2022, 22, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Huang, M.; Ma, Y. A study of K-12 teachers’ TPACK on the technology acceptance of E-Schoolbag. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2021, 29, 1062–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz-Durak, H.; Atman Uslu, N.; Canbazoğlu Bilici, S.; Güler, B. Examining the predictors of TPACK for integrated STEM: Science teaching self-efficacy, computational thinking, and design thinking. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 28, 7927–7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, J.W. Educational Research: Planning, Conducting, and Evaluating Quantitative and Qualitative Research, 4th ed.; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rahi, S. Research design and methods: A systematic review of research paradigms, sampling issues and instruments development. Int. J. Econ. Manag. Sci. 2017, 6, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.A.; Baran, E.; Thompson, A.D.; Mishra, P.; Koehler, M.J.; Shin, T.S. Technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK). J. Res. Technol. Educ. 2009, 42, 123–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, N.; Said, Z.; Abu-Tineh, A. Factors impacting science and mathematics teachers’ competencies and self-efficacy in TPACK for PBL and STEM. EURASIA J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2024, 20, em2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schermelleh-Engel, K.; Moosbrugger, H. Evaluating the fit of structural equation models: Tests of significance and descriptive goodness-of-fit measures. Methods Psychol. Res. Online 2003, 8, 23–74. [Google Scholar]
- Bentler, P.M.; Bonett, D.G. Significance tests and goodness of fit in the analysis of covariance structures. Psychol. Bull. 1980, 88, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.W.; Cudeck, R. Alternative ways of assessing model fit. In Testing Structural Equation Models; Bollen, K.A., Long, J.S., Eds.; Sage: Beverly Hills, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 136–162. [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel, J.R.; Wallen, N.E. How to Design and Evaluate Research in Education; McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Archambault, L.; Crippen, K. Examining TPACK among K-12 online distance educators in the United States. Contemp. Issues Technol. Teach. Educ. 2009, 9, 71–88. [Google Scholar]
- Muthén, B. A general structural equation model with dichotomous, ordered categorical, and continuous latent variable indicators. Psychometrika 1984, 49, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, G.; Paul, J. CB-SEM vs PLS-SEM methods for research in social sciences and technology forecasting. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 173, 121092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Howard, M.C.; Nitzl, C. Assessing measurement model quality in PLSSEM using confirmatory composite analysis. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 109, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, F.H.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM); Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, T.J.B. Psychological Testing: A Practical Approach to Design and Evaluation; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Aydın Günbatar, S.; Yerdelen Damar, S.; Boz, Y. A Closer examination of TPACK-self-efficacy construct: Modeling elementary pre-service science teachers’ TPACK-Self efficacy. İlköğr. Online 2017, 16, 917–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiray, S.A. Development of a TPACK self-efficacy scale for preservice science teachers. Int. J. Res. Educ. Sci. 2016, 2, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, M.E. Technology integration practice as a function of pedagogical expertise. J. Res. Comput. Educ. 2001, 33, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santika, V.; Indriayu, M.; Snagka, B.M. Investigating of the relations among tpack components of economic teacher candidates in sebelas maret university (UNS) in 2020: A structural equation Modeling. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. (AEVEC) 2020, 1808, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskeva, F.; Bouta, H.; Papagianni, A. Individual characteristics and computer self-efficacy in secondary education teachers to integrate technology in educational practice. Comput. Educ. 2008, 50, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niess, M.L. Investigating TPACK: Knowledge growth in teaching with technology. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 2011, 44, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulaksız, T.; Karaca, F. A path model of contextual factors influencing science teachers’ technological pedagogical content knowledge. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 28, 3001–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Koehler, M.J. Exploring the intention behaviour gap in the technology acceptance model: A mixed methods study in the context of foreign-language teaching in China. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2019, 50, 2536–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Oliver, J.S. Revisiting the conceptualization of pedagogical content knowledge (PCK): PCK as a conceptual tool to understand teachers as professionals. Res. Sci. Educ. 2008, 38, 261–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, Z.; Mansour, N.; Abu-Tineh, A. Integrating technology pedagogy and content knowledge in Qatar’s preparatory and secondary schools: The perceptions and practices of STEM teachers. EURASIA J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2023, 19, em2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, C.S.; Ng, E.M.W.; Li, W.; Hong, H.Y.; Koh, J.H.L. Validating and modelling technological pedagogical content knowledge framework among Asian preservice teachers. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 2013, 29, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Cha, C.S.; Sang, G.Y.; Koh, J.H.L.; Tsai, C.C. Exploring the profiles and interplays of pre-service and in-service teachers’ technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK) in China. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2015, 18, 158–169. [Google Scholar]
- Koehler, M.J.; Mishra, P.; Yahya, K. Tracing the development of teacher knowledge in a design seminar: Integrating content, pedagogy and technology. Comput. Educ. 2007, 49, 740–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, C.; Valanides, N. Epistemological and methodological issues for the conceptualization, development, and assessment of ICT-TPCK: Advances in technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPCK). Comput. Educ. 2009, 52, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.H.L.; Divaharan, S. Developing pre-service teachers’ technology integration expertise through the TPACK-Developing Instructional Model. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 2011, 44, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T. Towards a theory of online learning. In Theory and Practice of Online Learning, 2nd ed.; Anderson, T., Ed.; Athabasca University, AUPress: Athabasca, AB, Canada, 2008; pp. 24–74. [Google Scholar]
- Sojanah, J.; Suwatno, S.; Kodri, K.; Machmud, A. Factors affecting teachers’ technological pedagogical and content knowledge (a survey on economics teacher knowledge). J. Ilm. Pendidik. 2021, 40, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuşkaya Mumcu, F.; Haşlaman, T.; Usluel, Y.K. Indicators of Effective Technology Integration within the Framework of Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge Model; International Educational Technology; Oral Presentation; Anadolu University: Tepebaşı, Türkiye, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Habibi, A.; Yusop, F.D.; Razak, R.A. The role of TPACK in affecting pre-service language teachers’ ICT integration during teaching practices: Indonesian context. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2020, 25, 1929–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrang, M.S.; Mehdi, V.D. Examining efl teachers’ perceptions of technological pedagogical content knowledge and web 2.0 technologies using a structural equation modeling technique. J. Mod. Res. Engl. Lang. Stud. 2022, 9, 51–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khine, M.S.; Ali, N.; Afari, E. Exploring relationships among TPACK constructs and ICT achievement among trainee teachers. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2017, 22, 605–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khine, M.S.; Afari, E.; Ali, N. Investigating technological pedagogical content knowledge competencies among trainee teachers in the context of ICT course. Alta. J. Educ. Res. 2019, 65, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Lee, K.S. Inquiry of pre-service teachers’ concern about integrating Web 2.0 into instruction. Eur. J. Teach. Educ. 2017, 40, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, J.K.; Cavlazoglu, B.; Scogin, S.C.; Stuessy, C.L. The art of teacher talk: Examining intersections of the strands of scientific proficiencies and inquiry. Int. J. Educ. Math. Sci. Technol. (IJEMST) 2017, 5, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, D. Descriptive and prescriptive aspects of ICT in education-FATİH project example. In Proceedings of the XVIII Internet in Turkey Conference, İstanbul, Türkiye, 18 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, J.; Hofer, M. Technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK) in 834 action: A descriptive study of secondary teachers’ curriculum-based, technology-related 835 instructional planning. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 2011, 43, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, S.D. From TPACK-in-action workshops to classrooms: Call competency developed and integrated. Lang. Learn. Technol. 2015, 19, 139–164. [Google Scholar]
- Akyıldız, S.; Altun, T. Investigation of technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK) of prospective classroom teachers according to some variables. Trak. Univ. J. Fac. Educ. 2018, 8, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, M.; Archambault, L.M.; Shelton, C.C. Professional Development for International Teachers: Examining TPACK and Technology Integration Decision Making. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 2017, 49, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamuk, S. Understanding preservice teachers’ technology use through TPACK framework. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2012, 28, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Awidi, H.M.; Alghazo, I. The effect of student teaching experience on preservice elementary teachers’ self-efficacy beliefs for technology integration in the UAE. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2012, 60, 923–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J. Tenured Teachers & Technology Integration In The Classroom. Contemporary Issues in Education Research 2013, 6, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thinzarkyaw, W. The practice of technological pedagogical content knowledge of teacher educators in education colleges in Myanmar. Contemp. Educ. Technol. 2020, 11, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jang, S.J.; Tsai, M.F. Exploring the TPACK of Taiwanese secondary school science teachers using a new contextualized TPACK model. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 2013, 29, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmares, M.P.; Batisla-Ong, S.N. Technological, pedagogical, content knowledge (tpack) of science teachers: Basis of in-service training design development. Cosm. J. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilici, S.; Guler, C. Ortaogretim ogretmenlerinin TPAB duzeylerinin ogretim teknolojilerini kullanma durumlarina gore incelenmesi [Investigation of teachers’ TPACK levels with respect to use of instructional technologies]. Ilkogr. Online 2016, 15, 898–921. [Google Scholar]
- Bal, M.S.; Karademir, N. Social studies teachers’ technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK) determination of self-evaluation levels on the subject. J. Pamukkale Univ. Fac. Educ. 2013, 34, 15–32. [Google Scholar]
- Valtonen, T.; Sointu, E.; Kukkonen, J.; Mäkitalo, K.; Hoang, N.; Häkkinen, P.; Järvelä, S.; Näykki, P.; Virtanen, A.; Pöntinen, S.; et al. Examining preservice teachers’ technological pedagogical content knowledge as evolving knowledge domains: A longitudinal approach. J. Comput. Assist. Learn 2019, 35, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleickmann, T.; Richter, D.; Kunter, M.; Elsner, J.; Besser, M.; Krauss, S.; Baumert, J. Teachers’ content knowledge and pedagogical content knowledge. J. Teach. Educ. 2013, 64, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voogt, J.; Fisser, P.; Roblin, N.P.; Tondeur, J.; Braak, J. Technological pedagogical content knowledge: A review of the literature. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2013, 29, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, H.; Kim, B. Learning about problem-based learning: Student teachers integrating technology, pedagogy, and content knowledge. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 2009, 25, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromik, N.; Litz, D.; Liu, B. Technology, Pedagogy, and Content Knowledge: An Australian Case Study. Educ. Sci. 2023, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, M.; Cerovac, M.; Bellis, N.; Lancaster, G. Collaborative Inquiry: Building Pre-Service Teachers’ Capacity for ICT Pedagogical Integration. Aust. Educ. Comput. 2013, 27, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.-H. Exploring the Instructional Strategies of Elementary School Teachers When Developing Technological, Pedagogical, and Content Knowledge via a Collaborative Professional Development Program. Int. Educ. Stud. 2013, 6, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozden, S.Y.; Yang, H.; Wen, H.; Shinas, V.H. Reflections from a teacher education course built on the TPACK framework: Examining the impact of the technology integration planning cycle on teacher candidates’ TPACK development and practice. Soc. Sci. Humanit. Open 2024, 9, 100869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidlich, J.; Kalz, M. How well does teacher education prepare for teaching with technology? A TPACK-based investigation at a university of education. Eur. J. Teach. Educ. 2023, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
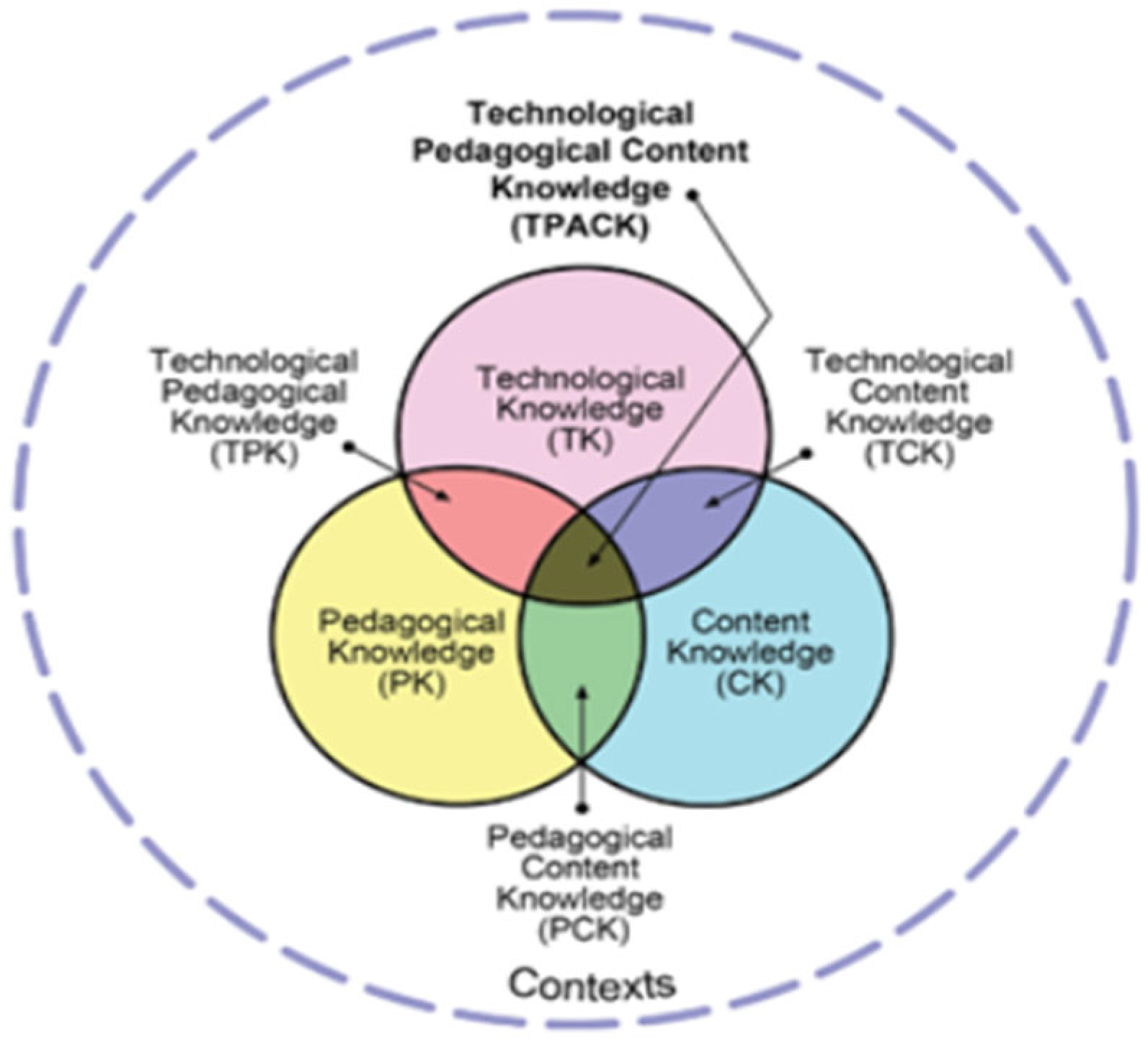


| Dimensions | Definitions |
|---|---|
| Content Knowledge (CK) | Information related to the subject area |
| Technology Knowledge (TK) | Technological knowledge of everything that makes life easier |
| Pedagogical Knowledge (PK) | General information about learning and teaching methods |
| Technological Pedagogical Knowledge (TPK) | Knowledge about how the use of technology affects teaching and learning strategies |
| Technological Content Knowledge (TCK) | Knowledge of presenting the subject with technology |
| Pedagogical Content Knowledge (PCK) | The pedagogical knowledge required for the teaching of a particular subject area |
| Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPCK) | Presenting a specific subject area by integrating knowledge of technology and pedagogy |
| Variables | Category | N | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 121 | 49.4 |
| Male | 124 | 50.6 | |
| Minor Degree in STEM (Minor D) | Yes | 108 | 44.1 |
| No | 137 | 55.9 | |
| Certificate in Education (CE) | Yes | 110 | 44.9 |
| No | 135 | 55.1 | |
| Years of Experience in Qatari School (YEQS) | <5 years | 53 | 21.6 |
| 5–10 | 88 | 35.9 | |
| >10 years | 104 | 42.4 | |
| Majors Degree in STEM (MD) | Biology | 48 | 19.6 |
| Chemistry | 59 | 24.1 | |
| Computer Science | 3 | 1.2 | |
| Earth science | 2 | 0.8 | |
| Mathematics | 96 | 39.2 | |
| Engineering | 5 | 2.0 | |
| Physics | 30 | 12.2 | |
| others | 2 | 0.8 | |
| Highest Academic Degree (HAD) | Vocational certification | 4 | 1.6 |
| Bachelor’s degree | 173 | 70.6 | |
| High Diploma degree | 32 | 13.1 | |
| Master’s degree | 32 | 13.1 | |
| Doctorate | 4 | 1.6 |
| Fit Indices | TPACK Fit Variables | Excellent Fit | Acceptable Fit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 χ2/sd | 2.79 | 0 ≤ χ2/sd ≤ 2 | 2 ≤ χ2 /sd ≤ 3 |
| 2 GFI | 0.97 | 0.95 ≤ GFI ≤ 1.00 | 0.90 ≤ GFI ≤ 0.95 |
| 3 AGFI | 0.91 | 0.90 ≤ AGFI ≤ 1.00 | 0.85 ≤ AGFI ≤ 0.90 |
| 3 CFI | 0.99 | 0.95 ≤ CFI ≤ 1.00 | 0.90 ≤ CFI ≤ 0.95 |
| 3 NFI | 0.99 | 0.95 ≤ NFI ≤ 1.00 | 0.90 ≤ NFI ≤ 0.95 |
| 3 NNFI (TLI) | 0.98 | 0.95 ≤ NNFI (TLI) ≤ 1.00 | 0.90 ≤ NNFI (TLI) ≤ 0.95 |
| 3 IFI | 0.99 | 0.95 ≤ IFI ≤ 1.00 | 0.90 ≤ IFI ≤ 0.95 |
| 4 RMSEA | 0.08 | 00 ≤ RMSEA ≤ 0.05 | 0.05 ≤ RMSEA ≤ 0.08 |
| CK | PK | PCK | TK | TPK | TCK | TPACK | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1 | ||||||
| PK | 0.91 ** | 1 | |||||
| PCK | 0.88 ** | 0.92 ** | 1 | ||||
| TK | 0.84 ** | 0.86 ** | 0.84 ** | 1 | |||
| TPK | 0.79 ** | 0.84 ** | 0.81 ** | 0.89 ** | 1 | ||
| TCK | 0.81 ** | 0.85 ** | 0.84 ** | 0.86 ** | 0.88 ** | 1 | |
| TPACK | 0.73 ** | 0.78 ** | 0.75 ** | 0.82 ** | 0.86 ** | 0.86 ** | 1 |
| Research Questions | Path | Path Coefficient | Standard Error | Critical Ratio | Effect Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub-question 1.1 | TK → TPACK | N.S. | No | ||
| CK → TPACK | N.S. | No | |||
| PK → TPACK | N.S. | No | |||
| Sub-question 1.2 | TK → TCK | 0.50 *** | 0.02 | 8.74 | Yes |
| TK → TPK | 0.67 *** | 0.04 | 12.47 | Yes | |
| Sub-question 1.3 | PK → PCK | 0.71 *** | 0.05 | 12.14 | Yes |
| PK → TPK | 0.39 *** | 0.04 | 5.70 | Yes | |
| PK → TCK | 0.16 *** | 0.02 | 7.41 | Yes | |
| Sub-question 1.4 | CK → TPK | 0.14 ** | 0.07 | 2.29 | Yes |
| CK → PCK | 0.23 *** | 0.09 | 3.99 | Yes | |
| Question 2 | TCK → TPACK | 0.47 *** | 0.10 | 7.36 | Yes |
| TPK → TPACK | 0.44 *** | 0.06 | 6.93 | Yes | |
| PCK → TPACK | N.S. | No |
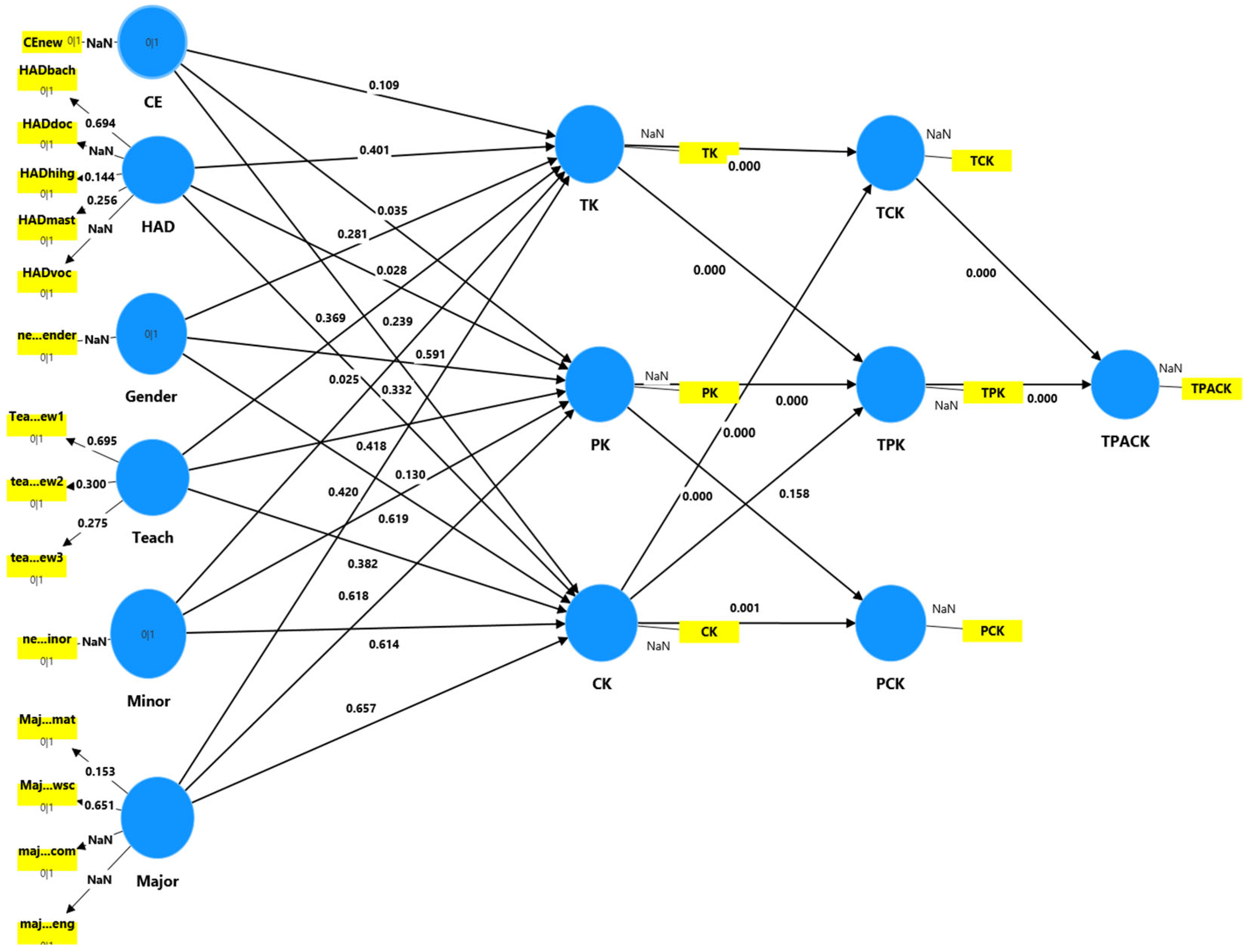
| Original Sample (O) | Standard Deviation (STDEV) | t Statistics (O/STDEV) | p Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE → CK | −0.16 | 0.14 | 1.97 | 0.04 * |
| CE → PK | −0.29 | 0.14 | 2.11 | 0.03 * |
| CE → TK | −0.22 | 0.14 | 1.95 | 0.04 * |
| CK → PCK | 0.23 | 0.07 | 3.11 | 0.00 * |
| CK → TPK | −0.12 | 0.08 | 2.94 | 0.00 * |
| Gender → CK | 0.23 | 0.15 | 1.55 | 0.12 |
| Gender → PK | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.52 | 0.60 |
| Gender → TK | 0.16 | 0.15 | 1.07 | 0.28 |
| HAD → CK | 0.45 | 0.20 | 2.20 | 0.02 * |
| HAD → PK | 0.44 | 0.20 | 2.16 | 0.03 * |
| HAD → TK | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.84 | 0.39 |
| Major → CK | −0.25 | 0.57 | 0.45 | 0.65 |
| Major → PK | −0.41 | 0.80 | 0.51 | 0.61 |
| Major → TK | −0.54 | 0.66 | 0.81 | 0.41 |
| Minor → CK | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.30 | 0.75 |
| Minor → PK | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.37 | 0.71 |
| Minor → TK | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.38 | 0.69 |
| PK → PCK | 0.71 | 0.07 | 9.37 | 0.00 * |
| PK → TCK | 0.42 | 0.08 | 5.21 | 0.00 * |
| PK → TPK | 0.38 | 0.09 | 4.25 | 0.00 * |
| TCK → TPACK | 0.47 | 0.07 | 6.25 | 0.00 * |
| TK → TCK | 0.50 | 0.08 | 6.26 | 0.00 * |
| TK → TPK | 0.67 | 0.06 | 10.65 | 0.00 * |
| TPK → TPACK | 0.44 | 0.07 | 5.88 | 0.00 * |
| ** Teach → CK | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.87 | 0.38 |
| ** Teach → PK | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.81 | 0.41 |
| ** Teach → TK | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.90 | 0.36 |
| Path Coefficient | Standard Deviation (STDEV) | t Statistics (O/STDEV) | p Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE → CK | −0.21 | 0.12 | 1.93 | 0.04 * |
| CE → PK | −0.28 | 0.12 | 2.30 | 0.02 * |
| CE → TK | −0.22 | 0.12 | 1.95 | 0.04 * |
| CK → PCK | 0.23 | 0.07 | 3.11 | 0.00 * |
| CK → TPK | −0.12 | 0.08 | 1.94 | 0.05 * |
| HAD → CK | 0.33 | 0.18 | 2.25 | 0.03 * |
| HAD → PK | 0.32 | 0.18 | 1.97 | 0.04 * |
| PK → PCK | 0.71 | 0.07 | 9.37 | 0.00 * |
| PK → TCK | 0.42 | 0.08 | 5.21 | 0.00 * |
| PK → TPK | 0.38 | 0.09 | 4.25 | 0.00 * |
| TCK → TPACK | 0.47 | 0.07 | 6.25 | 0.00 * |
| TK → TCK | 0.50 | 0.08 | 6.26 | 0.00 * |
| TK → TPK | 0.67 | 0.06 | 10.65 | 0.00 * |
| TPK → TPACK | 0.44 | 0.07 | 5.88 | 0.00 * |
| CEnew → CE | 1.0 | 0.00 | n/a | n/a |
| ** HADbach → HAD | −0.38 | 0.61 | 1.85 | 0.06 |
| ** HADdoc → HAD | 0.31 | 0.55 | 3.11 | 0.00 * |
| ** HADhigh → HAD | 0.82 | 0.44 | 1.44 | 0.15 |
| ** HADmast → HAD | 0.50 | 0.51 | 1.95 | 0.04 * |
| ** HADvoc → HAD | 0.21 | n/a | 1.77 | 0.07 |
| Path Coefficient | Standard Deviation (STDEV) | t Statistics (|O/STDEV|) | p Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE → PCK | −0.25 | 0.11 | 2.15 | 0.03 * |
| CE → TCK | −0.23 | 0.10 | 2.18 | 0.02 * |
| CE → TPACK | −0.21 | 0.09 | 2.15 | 0.03 * |
| CE → TPK | −0.23 | 0.10 | 2.15 | 0.03 * |
| CK → TPACK | −0.05 | 0.03 | 1.45 | 0.14 |
| HAD → PCK | 0.30 | 0.16 | 1.92 | 0.04 * |
| HAD → TCK | 0.13 | 0.08 | 1.60 | 0.10 |
| HAD → TPACK | 0.10 | 0.06 | 1.54 | 0.12 |
| HAD → TPK | 0.08 | 0.06 | 1.34 | 0.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mansour, N.; Said, Z.; Çevik, M.; Abu-Tineh, A. Science and Mathematics Teachers’ Integration of TPACK in STEM Subjects in Qatar: A Structural Equation Modeling Study. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14101138
Mansour N, Said Z, Çevik M, Abu-Tineh A. Science and Mathematics Teachers’ Integration of TPACK in STEM Subjects in Qatar: A Structural Equation Modeling Study. Education Sciences. 2024; 14(10):1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14101138
Chicago/Turabian StyleMansour, Nasser, Ziad Said, Mustafa Çevik, and Abdullah Abu-Tineh. 2024. "Science and Mathematics Teachers’ Integration of TPACK in STEM Subjects in Qatar: A Structural Equation Modeling Study" Education Sciences 14, no. 10: 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14101138
APA StyleMansour, N., Said, Z., Çevik, M., & Abu-Tineh, A. (2024). Science and Mathematics Teachers’ Integration of TPACK in STEM Subjects in Qatar: A Structural Equation Modeling Study. Education Sciences, 14(10), 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14101138






