Abstract
Digitalization has been a widely discussed topic in recent years, and it has entered various areas, including education. The issue of identifying and applying pedagogical aspects in digitalization has not been sufficiently discussed in the literature. This deficiency is particularly obvious in terms of assessment, an integral part of the education. Assessment is one of the most important aspects in managing education environments. The research data were obtained by combining two methods: ten pedagogical practices were examined that utilized various technologies in assessment already in use before the pandemic; data from the previous focus group discussions were reviewed regarding to pedagogical principles. A concept map was used in formulating the principles. Finally, the Delphi method with five experts from four counties was applied to obtain an expert view. As a result, five pedagogical principles of digital assessment were developed: (1) the clear purpose of the assessment and explicit criteria; (2) choice of adequate technology; (3) sufficient digital competence and technological equipment; (4) use of technological opportunities; (5) consistent analysis and use of assessment data. This is especially important given the need to demonstrate the appropriate and full use of technology. Those pedagogical principles contribute to a shared understanding between stakeholders in education.
1. Introduction
The importance and role of assessment in effective learning cannot be overestimated. This is related to the two theoretical underpinnings of this paper: constructivism [1] and a student-centered approach [2]. These approaches will not be discussed in detail in the assumption that they are familiar concepts to educational researchers or practitioners.
Assessment is one of the components of the educational process that has undergone changes in recent years because of digitalization. First, it is necessary to clarify which type of assessment is being discussed in this publication, as the term is widely used and interpreted differently in various aspects of education. The pedagogical principles proposed in the heading are thus formulated for so-called small-scale assessment (as opposed to large-scale assessment [3]), which refers to the assessment of the performance of the learner during the learning process and beyond carried out by an educator or other staff involved in the learning and teaching process. It also includes concepts such as classroom assessment and examinations. Of course, there is a possibility that these principles can be applied, at least partly, during a large-scale assessment, but this is not currently the subject of this discussion.
The use of the term digital assessment should also be clarified, as the literature also refers to e-assessment and online assessment, online exams, computer-aided assessments, and technology-enhanced assessment, which are very often considered synonymous. This publication basically uses the term digital assessment to refer to an assessment that uses technology in at least some or all the components of the assessment process.
Undoubtedly, digitalization has been a topical issue in educational research for many years [4,5,6,7,8], as the gradual entry of technology was replaced by the forced rapid use of technology [9,10,11]. Because of this, there was no time to evaluate the pedagogical aspects of this use of technology. Recent studies draw attention to digital assessment practices in education [12]. The post-pandemic situation led to changes, during which many different technologies have entered the education process, some of them permanently. Currently, educational institutions are, by and large, provided with technology. In any case, the issue of the purposeful and meaningful use of technology in every component of the learning process, including assessment, is relevant. This provides an opportunity to formulate the problem discussed in this paper, i.e., that the choice of technology to assess performance is not always sufficiently considered to achieve the assessment objectives and that the consideration of pedagogical conditions is lacking. Therefore, within the framework of a larger research project, one of the tasks was to formulate pedagogical principles for digital assessment based on theoretical and empirical research.
The aim of this study is to formulate pedagogical principles for digital assessment, summarizing and analyzing the findings in the scientific literature and in the practice of various educators and discussing possible formulations with representatives of the education sector. The research question is as follows: What pedagogical aspects are essential for appropriate digital assessment? This paper seeks to critically evaluate the ways in which emerging technologies can support assessment.
What follows is a literature review of the theoretical basis of the concepts related to assessment and digitalization in learning and assessment, including insights into learning analytics.
2. Literature Review
2.1. An Insight into the Basic Concepts of Assessment
Assessment is not just a sequential step in the learning process; it is a necessary component of learning. A set of assessment purposes that complement each other has been outlined in the related literature: to demonstrate learning achievements in a certain period of time; to obtain and give feedback that is timely and useful for improving student learning and for staff teaching; to empower self-regulation by students and enable them to critically evaluate their own performance [13,14,15,16,17]. The importance of self-assessment has increased in this context [18]. However, the researchers conclude that assessment is still more focused on reporting achievements and qualifications than the main purpose of supporting learning [17]. One of the possibilities offered by technology could be to direct assessment to this purpose.
It is useful to provide an overview of the different concepts used in educational research related to the assessment of learners’ performance. The nature of these concepts does not change whether they are in the traditional or digital format, but it is important to understand what is meant by each concept.
Formative assessment (also known as assessment for learning) influences and promotes learning through direct feedback. This type of assessment refers to the collection of data to improve student learning [19,20]. It is essential to create feedback that encourages students to respond to it with the goal of deciding what further learning is needed [21,22,23]. Some researchers refer to formative assessment as a learning process in which evidence is gathered with the goal of improving student performance [24]. It is true that there are researchers who consider assessment for learning as an assessment approach that includes both formative and summative assessment, directing them towards the one goal of supporting learning [25]. In any case, all these different viewpoints emphasize the mission of formative assessment to promote learning.
Summative assessment refers to the collection of data to determine the extent of student knowledge after a learning phase [20]. Unfortunately, summative assessment has thus far created unnecessary tension in grade-centered societies, as it is most often associated with negative emotions among students, thereby reducing motivation and learning, especially for low-performing students [26]. Not only the teacher’s assessment, but also self-assessment and peer-assessment are important in summative assessment, which is a contribution in the context of self-directed learning, evaluating the achievement of set goals [27]. In any case, there is clearly a need for objective summative assessment in formal education.
Cumulative assessment is a type of summative assessment where summative assessments are accumulated throughout the learning process and a summative assessment is calculated at the end. This approach aims to guide student learning behavior by ensuring that students learn throughout the course; however, how this affects knowledge growth has not been sufficiently explored [28]. In parallel, there is also the concept of continuous assessment, meaning a combination of formative assessment and summative assessment, but it is pointed out that in practice, this usually only means repeated summative assessments with assigned grades and minimal feedback to students [29]. Few researchers divide cumulative assessment into formative and summative, where the formative information excludes the obtained grades in the calculation of the final assessment [30]. However, a cumulative assessment should include and not replace a formative assessment.
Diagnostic assessment is used to determine the learner’s level of knowledge and skills before learning [31]. On the other hand, interim assessment [32] measures student performance during the learning process, which is more of an administrative necessity if formative assessment is not fully applied or more information needs to be acquired for program assessment purposes.
2.2. Digitalization in Education and Pedagogical Principles in Digital Learning
Initially, the application of technology in education was discussed as a vehicle for future progress and change, concerning their effect on learning and learners [6,33,34]. Both optimism and some pessimisms are necessary when analyzing this phenomenon [35]. In recent years, the term d-learning (digital learning) has increasingly replaced e-learning. The term refers to the use of information and communication technology (ICT) in open and distance learning [4]. Learning opportunities have become more diverse with the entry of various types of online tools, such as apps, blogs, videos, and podcasts, including wikis, which create the opportunity to form digital communities, including learning communities [36]. It can make education and learning more accessible and productive.
The term ‘smart’ has recently emerged in the literature about technologies in education. As an illustration, a smart classroom is defined by characteristics that include intelligent technologies, collaborative spaces, convenient access to learning resources, and interactivity of teaching and learning [37]. Consequently, smart pedagogy is related to pedagogical aspects in education, such as attitude, motivation, knowledge, diversity, and assessment obtained in a technology-enriched pedagogical environment [38]. Smart learning environments (SLEs) are also mentioned in various studies, including technological solutions that provide individualized learning to incorporate the individual perspective [8]. It is expected that this approach will continue to develop.
It is essential to consider the didactic principles defined in the context of technology-enhanced learning [27] and to include the following aspects: didactically based knowledge acquisition and development of new knowledge for training digital teachers; learner centered, research-based, and technology-enhanced didactic systems; teacher–learner cooperation using extensive information resources that are discussed with colleagues and learners; self-assessment, peer assessment, and teacher assessment using the full-fledged technological support of the e-learning system; and the iterative planning of educational development according to rapid technical development. These principles create prerequisites for providing adequate education for modern society.
2.3. Digital Assessment and Assessment Literacy
Assessment opportunities are currently expanding as technology facilitates the extraction of various data. Either web-based websites or downloadable applications can be used for digital assessment [39]. Computer-aided assessment is useful to promote learning if the questions are created pedagogically correctly [40]. The benefits of automating feedback and thus creating effective formative assessment are widely reported in the literature [36,41]. However, it has also been concluded in studies that teacher feedback has a greater impact on improvements in student texts than automated feedback [42]. While the possibilities of digital technology are rapidly developing and expanding, it is not the purpose of this publication to list all the possibilities for digital assessment.
Diversity in digital assessment methods is essential because it is not possible to effectively and objectively assess all learning outcomes expressed in knowledge, skills, and competence with either one or even a few methods [43,44]. A classic example of digital assessment is computer-based tests that require a large initial investment, especially if they are intended for either large-scale or high-stake assessments [45,46]. Online discussion forums are not only a tool for collaboration, but also allow students to demonstrate understanding; thus, they can be used even in summative assessment if the questions are linked to learning outcomes [47]. Automated feedback is one of the features offered by technology [48] that provides support and scaffolding to learners. Technology allows the customization and personalization of feedback but requires an extensive database and appropriate intelligent solutions [34]. Of course, more accurate, automated scoring is recognized as a benefit of such tests [49], but requires the careful development of wide and precise question banks to reduce the “luck factor”. Admittedly, while there is no consensus among researchers on the automated scoring of essay texts, there is both optimism about the objectivity and the speed of assessment [33] and doubts about the inability to evaluate the originality and special quality of the text [50]. Of course, for now, we can only talk about written material in the most widely spoken languages. As for many other national languages, this method will not be applicable for a long time.
In this paper, it is worth mentioning some other methods that provide authentic assessment of knowledge and skills. One of them is simulation, which is used in the assessment of professional knowledge and skills in a situation closer to reality. In the last decade, it has been utilized for educating members of the transport sector (maritime, aviation, and elsewhere) and in medical education [51,52], as well as in business education [53]. Simulations are included in Medical Student Skills Monitoring [54], a digitized tool for collecting and analyzing evidence of knowledge and skills.
In recent years, when learning has been forced to take place remotely for long periods of time, it has also been a great testing ground for digital assessment, with educators trying out and testing different digital assessment methods and approaches [55,56]. Technology makes many processes more convenient and faster in assessment, but unfortunately, risks related to technology use have also been identified, particularly in summative assessment. A variety of cheating practices and deceptive techniques have been identified, while various technological and social solutions to reduce cheating have been developed [57]. The most important aspect of assessment relates to the choice of the most appropriate technologies for each assessment task. It is not acceptable to first choose a technology and then try to understand what task can be adapted to it, what can be measured, and what can be assessed. It is good to start by determining the skills to be assessed, then preparing the task, and only then choosing the technology, being aware that some tasks cannot be carried out with technology at all [58]. These are insights that should be considered in teacher education and professional development.
Since the beginning of the century, research has highlighted the need for a framework for teacher assessment literacy, describing a set of knowledge and skills [59,60,61]. The assessment competence needed today must be adapted to the digital environment and pedagogic approaches of the 21st century when learning and assessment take place in a technology-enriched environment [19]. Along with the big data mining opportunities provided by technology [62], not only digital skills, but also data analysis skills are essential. However, assessment literacy should be viewed and developed in the context of other pedagogical competencies. Students’ self-assessment situations are more complex, as teachers still rely more on their own assessment competence when deciding on further instructions that would improve learning. When teaching students about assessment skills, teachers’ assessment competence becomes content knowledge [60]; here, both competences significantly interact. Thus, it is important to develop both content and assessment competence in teacher education and professional development. Assessment literacy is an important competence for educators. Only educators with assessment competence understand the importance of aligning achievement targets with the relevant assessment for further student lifelong learning.
However, educators’ digital assessment literacy alone is not enough if students are to be involved in their own assessment. In this case, it is useful to develop the student’s assessment literacy to ensure the student’s full potential to engage in assessment [63]. In summary, the skills to manage technology and assessment strategies are essential for both educators and learners.
2.4. Interrelations between Assessment and Learning Analytics
The digitization of the educational process has enabled the development of learning analytics, which is the acquisition, accumulation, and analysis of various learning data to predict and guide further learning. However, it is important to distinguish between learning data and assessment data.
Learning analytics include methods and metrics that help to understand the current situation and evaluate the effectiveness of teaching and learning, as well as utilizing technologies for data visualization, interpretation, and immediate analysis [64]. Various technology-based methods, such as intelligent tutors, games, simulations, and rubric-based peer review, provide the ability to obtain structured data that conform to developed data models [62]. The most significant potential for the use of learning analytics is specifically for the individualization and customization of learning [33], as well as for the possibility of predicting failure [65], but the most important thing is to make a connection between computer-based assessment data and classroom instruction [66]. Therefore, these data make significant contributions to learning.
Among other things, learning analytics also includes various assessment data that can be obtained from formative and summative assignments. Pedagogical practices and epistemic assumptions define assessment regimes, which must be further aligned with learning analytics [67]. The use of different technologies makes it possible to diversify evidence of learning [43] by providing different types of assessment data. Assessment data are part of learning data and not vice versa. They describe the learning outcome and should not be affected by learning process data, which is a separate issue.
3. Method
Two sources of data were used to obtain the data for formulating pedagogical principles. The first was the investigation of pedagogical practices (n = 10) at different levels of the educational system in Latvia (in-depth, semi-structured interviews). Data collection through interviews was stopped when the new data no longer provided an addition to the already discovered categories, i.e., the data were saturated [68,69]. The second source was previous focus group discussions (n = 11, with 37 participants; 11 educational institutions at different levels of the educational system). A data set of those focus groups was also reviewed, and data related to preliminary pedagogical principles were selected.
The selection of research participants for the investigation of pedagogical practices was based on information related to what is currently happening in educational institutions. More than three years of experience in using technology in the learning process and especially in assessment was a basic criterion. Invitations were sent to 10 general education institutions and 10 universities, but a better result was obtained from those respondents who were approached personally. It was observed that some respondents avoided online communication, preferring a face-to-face conversation. As a result, four participants represented higher education (from the fields of natural sciences, social sciences, and medicine), and six represented general education (three from primary schools, three from secondary schools; from the fields of social sciences, engineering sciences, and natural sciences). The age range of the study participants was from 28 to 62 years. Three case studies took place face-to-face. During those sessions, the respondents reported on their digital assessment practice, and the narrative was guided by semi-structured interview questions. Various related examples were also used in the form of documents or real screen views to gain more information. Interview protocols were created with informed consent and a confidentiality clause.
Questions in semi-structured interviews were related to digital assessment practices already in use before the pandemic (characterizing assessment and feedback), to recent useful additions, to various risks, to limitations and challenges, as well as questions about the most valuable lessons from this experience.
The research conversations were recorded and transcribed, and finally, a thematic analysis was conducted, while data reduction was performed at the same time. When conducting the thematic analysis [70], opinions related to the initial (pre-pandemic) experience were not separated from those related to the most recent period, as the aim of the study was to identify pedagogical insights, not their historical development. Codes (keywords and word combinations) were marked in the transcripts, which significantly characterize the researched concepts of digital assessment. After defining the basic categories, the data were enriched with findings from previously conducted focus group interviews. While the main topic of these interviews was different, these discussions did highlight the lessons learned in the practice of digital assessment.
Key concepts were identified in each of the categories and then summarized in the concept map, and finally, the pedagogical principles of digital assessment were formulated. Concept mapping was used as a form of data display for the whole set of interviews. The key features of digital assessment were structured as a network type [71], because this more accurately reflects the interrelationship between the concepts. The created concept map and the initial eight principles formulations, created on the basis of interview data analysis, were offered for discussion to educators at schools and universities. Seven discussions took place; as a result, five pedagogical principles were formulated.
The last step of the methodology for developing pedagogical principles was the Delphi method, when five experts from Finland, England, United States of America, and Latvia were invited to analyze and evaluate the formulated principles. Only two rounds were needed for the experts to reach a consensus, probably because the previous formulations of pedagogical principles were honed with the help of educators at schools and universities.
The experience of the study’s author must be considered as an influencing factor affecting the interpretation of the data in the formulation of the pedagogical principles, as she has studied digital assessment since May 2020, and this may have gradually formed the position she has taken. Thus, the objectivity of the research results was strengthened by the Delphi method [72], where independent experts from different countries came to a consensus.
4. Results and Discussion
The description of the study’s results is emphasized by illustrating each of the categories with the most vivid examples. The concept mapping is described next, closing with the formulated pedagogical principles, each including its theoretical and practical basis. Examples of the findings were not directly translated and included in this publication as quotations but were instead paraphrased, indicating the study participant code.
4.1. Analysis of Categories
There is no doubt that a clear purpose of assessment is very important, so this category will be the starting point. Respondents indicated that it was first necessary to understand whether the assignments were for measurement or for learning (6LLP). If for measurement, then next came understanding this measurement—will the chosen assignment truly measure what needs to be measured (8RKR)? It is also necessary to understand what will be achieved with the results and how they will be analyzed after each test (V6B). It is important to understand exactly what knowledge or skills you want to measure; only then will one be able to find the most suitable format and technology for an assignment (2DLR; 10ALV). For example, the simulations are considered a suitable tool for assessing complex skills (9NMR).
The next set of findings is related to the category criteria, which should also be clearly established. Practitioners recommend building assignment criteria based on what has been taught, rather than using tasks found on the Internet, which are usually simplified and do not test complex skills (4EBSC). The criteria must be defined from the beginning, they must derive from the learning outcomes, and they must also be clear for learners (7LVV; 10ALV). The criteria set at the beginning of learning must not be changed, and the learner must also know all about (or be familiar with) the assignments (V6B; 10ALB).
The category technologies includes codes of a wide variety of aspects, and as a result, subcategories are formed: automation, safety, and reliability. Automated scoring is considered effective (2DLR; 1AZL), but not all assignment types can provide this (1AZL). Several practitioners have pointed to assessing the technology’s (both devices and applications) suitability for the assignment. For instance, tablets have uses, but are not convenient for writing essays (V4A) and Paint is not suitable for writing texts at all (2DLR). In addition, it should be noted that not all websites or applications work equally well on all devices (6LLP). Sometimes it must be accepted that some aspect of competence cannot be measured with technology, as the appropriate one has not yet been invented (10ALV). When choosing technologies, it is important to be aware of their usefulness in the long term so that there is no need to constantly spend much time learning newer technologies (6LLP; 2DLR). Technology can create a breeding ground for dishonest behavior, even though at the same time creating some restrictions on it. Therefore, comprehension-oriented questions, time and video control, and the use of combined assignments when discussing about what has been achieved are important parts of the assessment (V6B; J1C; 1AZL; 2DABA).
The category digital competence is very important, and it has been coupled with the category technological equipment, emphasizing the exact equipment, because both categories indicate the necessary, vital support components in digital assessment. Both educators and learners must have good digital skills (5ISV), and everyone must first master the technologies that will be used in the assessment. These skills are most effectively used first in the formative assessment, and only then in the summative assessment (4EBSC; 5ISV; J1D). In addition, mastering and practicing the technology is very important so that time is not wasted thinking about the correct use (V6C). Measures to remedy issues such as a broken phone, unavailable technology, or weak internet strength should be taken proactively, as they can affect the assessment result (V1A; V1C; V2A). The important thing is to understand which is the best tool, learn to use it effectively, and provide access, for example, in a classroom, so that everyone has the same conditions (8RKR).
Separately, the category representing the broader opportunities created by technology was distributed. Students generally respond well to technology because they can see their results and their mistakes, sometimes compare them to a previous result, and are therefore able to correct mistakes (V5A; V6A; 9NMR; V1C). Moreover, fast and prompt feedback is available to the educator from different aspects, both about the learner and about the task (2DLR; V9A). Technologies open the possibility for widespread use of self-assessment and peer assessment. A few examples of this are as follows: online discussion recordings and evaluation, writing and commenting blogs, self-assessment tests with the opportunity to make mistakes without penalty, and posting different types of assignments on websites where other students can evaluate them (2DLR; 10ALV; V2A; V9B). Discussions about what has been achieved are necessary in addition to the automated feedback, and comments are also good feedback for the educator (5ISV; 7LVV). Technology helps create a motivating learning environment (V6A).
The list is rounded off by the category assessment data, which may in some way be considered to be an assessment product. Practitioners appreciate being able to see statistics about the assessment process (work completion time, sequence, and so on). It is important not only to accumulate assessment data but also to analyze and draw conclusions to identify weak points (V6B; V2A; 8RKR; 9NMR). To achieve learning results, both formative assessment data and diagnostic data are important as well, and participation data can be used to encourage less motivated students (3DABA; 7LVV).
Concept mapping was conducted to understand the interrelationships between the concepts included in these categories. Information in different formats can be structured and displayed in concept maps, showing links and relations [72,73]. Of course, concept maps are widely used in education, including assessment [74,75], but they also have their place in the research process [71]. The purpose of creating the concept map was to present the most important features of digital assessment in a structured way. Later, the model of digital assessment principles is created based on the concept map developed in this paper (see Figure 1).
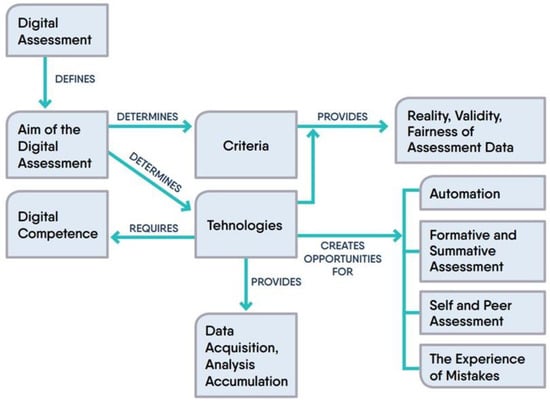
Figure 1.
The concept map of digital assessment.
The next subsection will finally name and describe the five pedagogical principles of digital assessment, and as already promised in the title of the publication, practice and theory will be linked.
4.2. Pedagogical Principles for Digital Assessment
4.2.1. The Clear Purpose of the Assessment and Explicit Criteria—What? Why? and How?
The defining aspects related to the selection of the assessment tool (assignment criteria and technology) according to the purpose of the study are as follows: linking with learning outcomes and the purpose of assessment being clear to both the educator and the learner. Research also highlights the application possibilities of digital assessment for various assessment purposes [31,76] and the creation of an appropriate assignment [44,47,49,53,77]. Therefore, it is important to ensure clarity and understanding of the purpose of the assessment.
4.2.2. Choice of Adequate Technology
Dishonest behavior, such as cheating and the use of unauthorized assistance, can be mitigated by various technological solutions for control (authorization, authentication, video control, and control of computer activity), and technologies suitable for the assessment of specific learning outcomes can also be used. Additionally, there are studies examining the choice of appropriate technologies [36,39,43,78,79], designed to ensure integrity in examinations, control construct-irrelevant factors [46,57], and provide diagnostic assessment with automated feedback [48,80,81]. When choosing technologies, it is essential to create an authentic assessment [82]. In the pedagogical aspect, it is important to think about the choice of appropriate technologies to ensure the validity of assessment [83]. The purpose of assessment can only be achieved with appropriate technologies.
4.2.3. Sufficient Digital Competence and Technological Equipment
It is important not only to find the most appropriate technologies but also to ensure that there are equivalent conditions in digital assessment, which includes digital skills, technology, and the Internet. The research literature addresses aspects such as digital competence for assessment [17,84,85] as well as the availability of equivalent technologies [86,87,88,89]. Therefore, it is important to provide suitable conditions for digital assessment.
4.2.4. Use of Technological Opportunities
A characteristic aspect of these technologies is fast, operative feedback, which is very useful in assessments by educators or for self-assessment, as well as peer assessments. These strategies can foster the ability to see mistakes and learn from them, improving performance and creating a desire to understand and accurately carry out an assignment and reduce guessing, all of which can boost motivation. Studies have emphasized the presence of students and agency in assessment [17,90], the importance of feedback [17,21,34,41,91], and active learning during authentic assessment [51,54]. Technology also supports learning in assessment.
4.2.5. Consistent Analysis and Use of Assessment Data
Various types of data are included here: data related to actions and results; formative assessment data for performance improvement; data acquisition to visualize knowledge and skills; and participation data for motivating engagement. Similar conclusions are also drawn from other studies on assessment data and the application of these data [17,53,62,66,92]. In addition, [17,93,94] support the necessity of the motivational aspect in assessment.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, it should be reiterated that the aim of this study was to formulate pedagogical principles for digital assessment by summarizing and analyzing the findings in the scientific literature and in the practice of various educators. The author believes that this aim has been achieved, as the five pedagogical principles have been formulated through the analysis of both the experience of practitioners and the findings of research. In addition, educators in schools and universities were involved in the development of formulations.
The present study makes several noteworthy contributions for different target groups. For researchers, by the further conceptualization of theory on digital assessment and for practitioners, by refining the evaluation of their digital assessment practice. A checklist from these principles can be created before developing an assessment design. It should be emphasized once again that some of these principles are essential, not only for digital assessment, but also for assessment in general. The alignment of pedagogical and technological aspects in these principles marks the way to sustainable education.
Limitations should also be mentioned. While diverse literature from different countries was combined with the experience of practitioners from only one country, the researcher believes this approach was appropriate and adequate to formulate the pedagogical principles she has outlined. In addition, the expertise of these principles with the use of the Delphi method involving experts from different countries was realized. This significantly reduced the impact of various research biases, for example, the predominance of the author’s past experience.
Funding
This research was funded by a grant from the European Regional Development Fund project “Models of Assessment in the Digital Learning Environment (MADLE)” No. 1.1.1.2/VIAA/3/19/561 within the Activity 1.1.1.2 “Post-doctoral Research Aid”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by Academic Ethics Commission (with invited experts) with Approval Code No. 2022/2.; approved on 4 August 2022) for studies involving humans.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available (in Latvian) by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Burhanuddin, N.A.N.; Ahmad, N.A.; Said, R.R.; Asimiran, S. Learning Theories: Views from Behaviourism Theory and Constructivism Theory. Int. J. Acad. Res. Progress. Educ. Dev. 2021, 10, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, T. Helping Students Learn in a Learner-Centered Environment: A Guide to Facilitating Learning in Higher Education; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suurtamm, C.; Thompson, D.R.; Kim, R.Y.; Moreno, L.D.; Sayac, N.; Schukajlow, S.; Silver, E.; Ufer, S.; Vos, P. Assessment in Mathematics Education: Large-Scale Assessment and Classroom Assessment; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.K.; Wotto, M.; Bélanger, P. E-learning, M-learning and D-learning: Conceptual definition and comparative analysis. E-Learn. Digit. Media 2018, 15, 191–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumol, U.; Bockshecker, A. Evolutionary change of higher education driven by digitalization. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Information Technology Based Higher Education and Training (ITHET), Ohrid, Macedonia, 10–12 July 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, P. School as a learning organization: The specific contribution of the information and communication technologies (ICT). In Proceedings of the EDULEARN12 Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 2–4 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, N. Digital Technologies and Change in Education: The Arena Framework, 1st ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freigang, S.; Schlenker, L.; Köhler, T. A conceptual framework for designing smart learning environments. Smart Learn. Environ. 2018, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, A.; Sharma, R.C. Emergency remote teaching in a time of global crisis due to Corona Virus pandemic. Asian J. Dis. Educ. 2020, 15, i–vi. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, C.; Moore, S.; Lockee, B.; Trust, T.; Bond, A. The Difference between Emergency Remote Teaching and Online Learning. Educause. 2020. Available online: https://er.educause.edu/articles/2020/3/the-difference-between-emergency-remote-teaching-and-online-learning#fn17 (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- Williamson, B.; Eynon, R.; Potter, J. Pandemic politics, pedagogies and practices: Digital technologies and distance education during the coronavirus emergency. Learn. Media Technol. 2020, 45, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viberg, O.; Mutimukwe, C.; Hrastinski, S.; Cerratto-Pargman, T.; Lilliesköld, J. Exploring teachers’ (future) digital assessment practices in higher education: Instrument and model development. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ada, M.B. Evaluation of a Mobile Web Application for Assessment Feedback. Technol. Knowl. Learn. 2021, 28, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, P.; Wiliam, D. Classroom assessment and pedagogy. Assess. Educ. Princ. Policy Pract. 2018, 25, 551–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C. Making Sense of Assessment Feedback in Higher Education. Rev. Educ. Res. 2013, 83, 70–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, P.E. Clarifying the purposes of educational assessment. Assess. Educ. 2007, 14, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmis, S.; Broadfoot, P.; Sutherland, R.; Oldfield, A. Rethinking assessment in a digital age: Opportunities, challenges and risks. Br. Educ. Res. J. 2016, 42, 454–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Chiu, M.M.; Ko, P.Y. Effects of self-assessment diaries on academic achievement, self-regulation, and motivation. Assess. Educ. Princ. Policy Pract. 2020, 27, 562–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elay, L. Digital Assessment Literacy—The core role of the teacher in a digital environment. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2012, 15, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Dixson, D.D.; Worrell, F.C. Formative and Summative Assessment in the Classroom. Theory Into Pract. 2016, 55, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, L.X.; Bearman, M.; Boud, D. Understanding feedback in online learning—A critical review and metaphor analysis. Comput. Educ. 2021, 173, 104271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, A.M.; Andrade, H.L. The Next Black Box of Formative Assessment: A Model of the Internal Mechanisms of Feedback Processing. Front. Educ. 2022, 7, 751548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, S.; Humphrey, S.; Steele, J. Using Technology Tools for Formative Assessments. J. Educ. Online 2019, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, C.M.; Brookhart, S.M. Advancing Formative Assessment in Every Classroom; ASCD: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Carless, D. Scaling up assessment for learning: Progress and prospects. In Scaling Up Assessment for Learning in Higher Education; Carless, D., Bridges, S.M., Chan, C.K.Y., Glofcheski, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, H.L.; Heritage, M. Using Formative Assessment to Enhance Learning, Achievement, and Academic Self-Regulation, 1st ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Žogla, I. Principles of learner learning-centred didactic in the context of technology-enhanced learning. In Didactics of Smart Pedagogy: Smart Pedagogy for Technology Enhanced Learning; Daniela, L., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 71–94. [Google Scholar]
- Cecilio-Fernandes, D.; Nagtegaal, M.; Noordzij, G.; Tio, R.A. Cumulative assessment: Does it improve students’ knowledge acquisition and retention? Sci. Medica 2018, 28, 31880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.; Hyland, A.; Ryan, N. Writing and Using Learning Outcomes: A Practical Guide; Cork, University College: Cork, Ireland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Boer, A.W.D.; Verkoeijen, P.P.; Heijltjes, A.E. Comparing Formative and Summative Cumulative Assessment: Two Field Experiments in an Applied University Engineering Course. Psychol. Learn. Teach. 2020, 20, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaikh, A.A. The Degree of Utilizing E-Assessment Techniques at Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University: Faculty Perspectives. J. Educ. Soc. Res. 2020, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, L.A. Commentary: Evaluating the Validity of Formative and Interim Assessment. Educ. Meas. Issues Pract. 2009, 28, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milakovich, M.; Wise, J.-M. Digital Learning: The Challenges of Borderless Education; Edward Elgar Publishing: Northampton, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, J.M.; Ifenthaler, D.; Samspon, D.; Yang, L.; Mukama, E.; Warusavitarana, A.; Lokuge Dona, K.; Eichhorn, K.; Fluck, A.; Huang, R.; et al. Technology enhanced formative assessment for 21st century learning. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2016, 19, 58–71. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, C.; Hammond, M.; Younie, S. Theorising technology in education: An introduction. Technol. Pedagog. Educ. 2019, 28, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, B.; Turnquist, A.; Zaver, F.; Hall, A.K.; Chan, T.M. Communication, learning and assessment: Exploring the dimensions of the digital learning environment. Med. Teach. 2019, 41, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfoudari, A.M.; Durugbo, C.M.; Aldhmour, F.M. Understanding socio-technological challenges of smart classrooms using a systematic review. Comput. Educ. 2021, 173, 104282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniela, L.; Lytras, M.D. SMART Pedagogy: (Re) defining pedagogy. In Learning Strategies and Constructionism in Modern Education Settings; Daniela, L., Lytras, M.D., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Appiah, M.; van Tonder, F. E-assessment in higher education: A review. Int. J. Bus. Man. Econ. Res. 2018, 9, 1454–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Greenhow, M. Effective computer-aided assessment of mathematics; principles, practice and results. Teach. Math. Its Appl. Int. J. IMA 2015, 34, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, M.E.; Prasse, D.; Phillips, M.; Kadijevich, D.M.; Angeli, C.; Strijker, A.; Carvalho, A.A.; Andresen, B.B.; Dobozy, E.; Laugesen, H. Challenges for IT-Enabled Formative Assessment of Complex 21st Century Skills. Technol. Knowl. Learn. 2018, 23, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Han, F. The Effects of Teacher Feedback and Automated Feedback on Cognitive and Psychological Aspects of Foreign Language Writing: A Mixed-Methods Research. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 909802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundell, C.N. Teacher use of digital technologies for school-based assessment: A scoping review. Assess. Educ. Princ. Policy Pract. 2021, 28, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaheim, A.; Mathiassen, K.; Moen, V.; Lona, I.; Gynnild, V.; Bunæs, B.R.; Hasle, E.T. Digital assessment–How does it challenge local practices and national law? A Norwegian case study. Eur. J. High. Educ. 2019, 9, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhammer, F.; Scherer, R.; Greiff, S. Editorial: Advancements in Technology-Based Assessment: Emerging Item Formats, Test Designs, and Data Sources. Front. Psychol. 2020, 10, 3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, S.L. Controlling construct-irrelevant factors through computer-based testing: Disengagement, anxiety, & cheating. Educ. Inq. 2019, 10, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallatly, R.; Carciofo, R. Using an online discussion forum in a summative coursework assignment. J. Educ. Online 2020, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, M.; Gibson, D. Technology enhanced assessment in complex collaborative settings. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2015, 20, 675–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babo, R.; Babo, L.V.; Suhonen, J.T.; Tukiainen, M. E-assessment with multiple-choice questions: A 5 year study of students’ opinions and experieNCE. J. Inf. Technol. Educ. Innov. Pract. 2020, 19, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, M.R. Writing Assessment and the Revolution in Digital Texts and Technologies; Teachers College Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sellberg, C.; Lundin, M.; Säljö, R. Assessment in the zone of proximal development: Simulator-based competence tests and the dynamic evaluation of knowledge-in-action. Classr. Discourse 2021, 13, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, H.Y.; Chen, P.P.; Wong, G.K.C.; Chan, T.T.N. Simulation in medical education. J. R. Coll. Physicians Edinb. 2019, 49, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifried, J.; Brandt, S.; Kögler, K.; Rausch, A. The computer-based assessment of domain-specific problem-solving competence—A three-step scoring procedure. Cogent Educ. 2020, 7, 1719571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavinska, A.; Grigorovica, E.; Palkova, K.; Jansone-Ratinika, N.; Silis, M.; Sabeļņikovs, O.; Pētersons, A. Skills Monitoring in healthcare studies—For patient safety and healthcare quality. Soc. Integr. Educ. Proc. Int. Sci. Conf. 2021, 1, 611–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurāne-Brēmane, A.J. Changes of assessment in remote learning: Educators’ perceptions and findings. Int. J. Learn. Chang. 2022, 1, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trust, T.; Whalen, J. Should teachers be trained in emergency remote teaching? Lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Technol. Teach. Educ. 2020, 28, 189–199. [Google Scholar]
- Butler-Henderson, K.; Crawford, J. A systematic review of online examinations: A pedagogical innovation for scalable authentication and integrity. Comput. Educ. 2020, 159, 104024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marek, M.W.; Wu, P.N. Digital learning curriculum design: Outcomes and affordances. In Pedagogies of Digital Learning in Higher Education; Daniela, L., Ed.; Routledge: Abingdon, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, W.S. Teachers’ assessment literacies and practices: Developing a professional competency and learning framework. Adv. Scholarsh Teach. Learn. 2015, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Herppich, S.; Praetorius, A.-K.; Förster, N.; Glogger-Frey, I.; Karst, K.; Leutner, D.; Behrmann, L.; Böhmer, M.; Ufer, S.; Klug, J.; et al. Teachers’ assessment competence: Integrating knowledge-, process-, and product-oriented approaches into a competence-oriented conceptual model. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2018, 76, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, S.; Andrade, H.L. Teacher assessment literacy: A three-dimensional model. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2019, 84, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, B.; Kalantzis, M. Big Data Comes to School: Implications for Learning, Assessment, and Research. AERA Open 2016, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannigan, C.; Alonzo, D.; Oo, C.Z. Student assessment literacy: Indicators and domains from the literature. Assess. Educ. Princ. Policy Pract. 2022, 29, 482–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.-K.; Cheung, S.K.S.; Kwok, L.-F. Learning analytics: Current trends and innovative practices. J. Comput. Educ. 2020, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sclater, N. Learning Analytics Explained; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Admiraal, W.; Vermeulen, J.; Bulterman-Bos, J. Teaching with learning analytics:how to connect computer-based assessment data with classroom instruction? Technol. Pedagog. Educ. 2020, 29, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, S.; Shum, S.B. Theory and learning analytics. In Handbook of Learning Analytics; Lang, C., Siemens, G., Wise, A., Gaševič, D., Eds.; Society for Learning Analytics Research: Edinburgh, UK, 2017; pp. 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, J.W.; Poth, C.N. Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing among Five Approaches; Sage Publications: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hennink, M.; Kaiser, B.N. Sample sizes for saturation in qualitative research: A systematic review of empirical tests. Soc. Sci. Med. 2021, 292, 114523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, G.; Hayfield, N.; Clarke, V. Thematic analysis. In The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Research in Psychology, 2nd ed.; Willig, C., Stainton-Rogers, W., Eds.; SAGE: London, UK; San Jose, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 17–37. [Google Scholar]
- Kinchin, I.M.; Streatfield, D.; Hay, D.B. Using Concept Mapping to Enhance the Research Interview. Int. J. Qual. Methods 2010, 9, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink-Hafner, D.; Dagen, T.; Doušak, M.; Novak, M.; Hafner-Fink, M. Delphi Method: Strengths and Weaknesses. Adv. Methodol. Stat. 2019, 16, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, J.D.; Cañas, A.J. Theoretical origins of Concept Maps, how you construct them, and used in education. Reflect. Educ. 2007, 3, 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Schwendimann, B.A. Multi-level analysis strategy to make sense of concept maps. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Concept Mapping, Santos, Brazil, 22–25 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Anohina-Naumeca, A. Determining the Set of Concept Map Based Tasks for Computerized Knowledge Self-Assessment. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 69, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hartmeyer, R.; Stevenson, M.P.; Bentsen, P. A systematic review of concept mapping-based formative assessment processes in primary and secondary science education. Assess. Educ. Princ. Policy Pract. 2017, 25, 598–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Smadi, M.; Gutl, C. Past, present and future of e-assessment: Towards a flexible e-assessment system. In Proceedings of the Conference ICL2008, Villach, Austria, 24–26 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Amante, L.; Oliveira, I.R.; Gomes, M.J. E-Assessment in Portuguese higher education: Framework and perceptions of teachers and students. In Handbook of Research on E-Assessment in Higher Education; Azevedo, A., Azevedo, J., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 312–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- El Asame, M.; Wakrim, M.; Battou, A. Designing e-assessment activities appropriate to learner’s competency levels: Hybrid pedagogical framework and authoring tool. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2021, 27, 2543–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Koong, C.-S.; Liao, C. Influences of integrating dynamic assessment into a speech recognition learning design to support students’ English speaking skills, learning anxiety and cognitive load. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2022, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csapó, B.; Molnár, G. Online Diagnostic Assessment in Support of Personalized Teaching and Learning: The eDia System. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieminen, J.H.; Bearman, M.; Ajjawi, R. Designing the digital in authentic assessment: Is it fit for purpose? Assess. Eval. High. Educ. 2022, 48, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, P.; Bearman, M.; Dollinger, M.; Boud, D. Validity matters more than cheating. Assess. Eval. High. Educ. 2024, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltovskaia, S. Student engagement with automated written corrective feedback (AWCF) provided by Grammarly: A multiple case study. Assess. Writ. 2020, 44, 100450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alruwais, N.; Wills, G.; Wald, M. Advantages and Challenges of Using e-Assessment. Int. J. Inf. Educ. Technol. 2018, 8, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilvinskis, J.; Borden, V.M.H. Concluding Thoughts. New Dir. High. Educ. 2017, 2017, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cereci, S. Modern communication education: Technological equipments. Int. J. New Trends Educ. Implic. 2018, 9, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hynes, P.; Younie, S. Bring your own device? In Debates in Computing and ICT Education; Younie, S., Bradshaw, P., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 153–166. [Google Scholar]
- Kazimirov, A.N. Monitoring the State of Technological Equipment in the Application to the Educational Process. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering, Applications and Manufacturing (ICIEAM), Sochi, Russia, 17–21 May 2021; pp. 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adie, L.E.; Willis, J.; Van der Kleij, F.M. Diverse perspectives on student agency in classroom assessment. Aust. Educ. Res. 2018, 45, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, O.; Cutumisu, M.; Singh, D.; Aquilina, A.M. Guidelines for Generating Effective Feedback from E-Assessments. Hacet. Univ. J. Educ. 2020, 35, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, T.; Rushby, N. Assessment and learning technologies: An overview. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2015, 47, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.; Liu, Y.; Enderson, M. Student understanding of a system of equations and inequalities: A comparison between online and face-to-face learning. J. Educ. Online 2020, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kiryakova, G. E-assessment-beyond the traditional assessment in digital environment. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1031, 012063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).