Abstract
Due to the rapidly increasing number of students at universities in recent years, universities may arrange students from different majors in the same class, which may bring several challenges in teaching and learning for students and teachers, such as poor class experience, less class discussion and more workload for teachers. In this paper, we investigate the learning achievements of students with different major backgrounds based on a large-size course of Introduction to Java Programming. Approaches of difficulty index, incrimination index, failure rate, median average mark, average mark and standard deviation are used to evaluate students’ learning achievements based on students’ coursework assignments, continuous assessment and the final exam. Results show that major backgrounds could significantly affect learning achievements even in the same teaching and learning environment. To achieve a better learning experience and performance, we finally divided the original module into two separate modules for students with different major backgrounds.
1. Introduction
Due to the rapidly increasing number of students at universities, tighter budgets and shortage of qualified teachers [1] in recent years, some introductory courses at the undergraduate level are usually taught in large-size classes with large numbers of students from different majors. However, actively involving students in the learning process is crucial for improving students’ understanding [2]. A high student–teacher ratio will increase teachers’ workload and decrease the communication between students and teachers. As a result, many students feel discouraged from actively joining class discussions and have a poor overall learning experience in large-size classes. On the one hand, many studies have shown that smaller classes are beneficial to students’ learning experience, efficiency and achievements [3,4,5]. On the other hand, other studies have shown little, if any, improvement in student learning efficiency in small classes [6,7,8]. To reduce teachers’ workload in large-size classes, online learning platforms are being widely used as an additional interaction platform between teachers and students [9]. With the rapid development of information technology and the Internet, online learning resources have been rapidly developed, and we can obtain learning resources we are interested in anytime and anywhere via the Internet. Many assessment models have been proposed to evaluate the impact of online learning on students’ learning achievements [10,11]. The difficulty index [12,13], discrimination index [14], distractor efficiency [15] and meta-analysis [16] were widely used to evaluate students’ examination performance and learning achievements. The Open University in the UK indicated that compared to traditional on-site courses, online courses could save an average of 90% less energy and 85% fewer CO2 emissions for each student [17]. Online learning is becoming more popular around the world for its advantages in overcoming the time and spatial barriers of traditional on-site learning [18]. Many E-learning tools with rich features have been developed for online teaching, learning and meeting, such as Zoom, Microsoft Teams, Tencent Meeting and Google Meet [19]. Compared to traditional on-site teaching and learning activities, these online teaching and learning tools, technologies and platforms help instructors manage students in a large class more efficiently. Though online teaching and learning platforms can support large-size classes much better and help instructors have large-size classes with large numbers of students from different schools and majors, little research has been carried out to confirm whether the difference in major backgrounds can affect student learning achievements when they are in the same teaching and learning environment.
During the COVID-19 global pandemic, there was a significant change in education as schools and universities shut down on-site instruction and moved to online teaching and learning [20]. Xi’an Jiaotong-Liverpool University (XJTLU) also suffered from the outbreak of COVID-19. Thus, XJTLU officially launched Learning Mall (LM), an online education platform, on 22 May 2020 to support online teaching and learning. Integrated with other online teaching and meeting tools, such as Zhumu, BigBlueButton virtual classroom, Mediasite, etc., it provides a powerful online platform both for teachers and students to support teaching and learning activities. The online space of Learning Mall is an online community platform gathering educational products and resources created by XJTLU and other top global partners. It also provides online and on-site space for top global partners to share their learning resources with their users. The Learning Mall can promote the concept of lifelong learning by integrating on-site and online programmes and courses developed by the University, industry, and external partners and offering them as learning resources to a wide net of different education consumers.
CPT105 (Introduction to Programming in Java) is a Java programming course for Y2 students that opened in Semester 1. With the rapid development of computer programming in various industries, programming courses are widely welcomed not only by computer science students but also by students from other majors. As an introductory computer programming course, the module is open to students from five schools at XJTLU: the School of Advanced Technology (SAT), School of Film and Television Arts (FTA), International Business School (IBSS), School of Science (SCI) and School of Humanities and Social Science (HSS). Because it is the first computer programming course both for computer-science-related students in SAT and non-SAT schools, we arranged all students from the five schools together and formed a large-size class for CPT105. With the rapid development of XJTLU in recent years, the number of students in CPT105 also increased rapidly, resulting in one of the largest modules at XJTLU. It had 1012 students in 2021 with three academic staff and 16 teaching assistants (master and PhD students) to take lectures, labs, coursework assignments and the final exam. Due to the effects of COVID-19 in 2021, some students, especially international students, could not return to campus. Thus, we conducted mixed teaching based on Learning Mall both for on-site and online students. Students on campus were required to participate in on-site lectures and labs, and they could have face-to-face interaction with teachers. At the same time, the teaching process was broadcast to the online students in real-time using BigBlueButton, Zoom and other online teaching and learning tools, and the online students can communicate with the teachers and on-site students in real time via the Internet. In addition, all the coursework assignments and the final exam were changed from on-site to online to provide the same assessment environment for both on-site and off-site students. On the one hand, the change from traditional on-site teaching and learning activities to mixed teaching and learning brought teachers more extra workload to prepare for the online teaching and assessment materials. On the other hand, it also provided an opportunity to analyze and assess the students’ learning performance based on the detailed results of students’ coursework assignments and exams saved in the online teaching and learning platform.
In this paper, we analyze the learning achievements of all students in CPT105 with different major backgrounds based on massive teaching and learning data collected from the Learning Mall. We introduce the assessment methods in Section 2. Section 3 analyzes the learning performance of students from five different schools. Finally, we make a conclusion in Section 4 and point out the future research direction.
2. Assessment Methods
Exams are always preferred to assess whether students have obtained the necessary learning outcomes that are expected after the completion of a course and to fairly distinguish their performance and achievements. To evaluate student learning performance at all stages and in all of the fields of education, multiple question categories are widely used in CPT105, such as true–false tests, multiple-choice questions, fill-in-the-blank questions, short-answer tests and written examinations [21]. There are three coursework assignments and one final exam for the assessment of CPT105. The mark distribution and assessment methods are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Assessment of CPT105.
Coursework 1 is a continuous online assessment and contributes towards 15% of the final mark. Each week, after the lecture and lab session, students were required to complete some online programming tasks on the Learning Mall. These tasks were automatically graded by Learning Mall when students submitted their source programming codes. Instant feedback and grades were sent to students to help them confirm whether they have mastered the knowledge taught in the lectures and lab sessions. Coursework 2 also contributes towards 15% of the final mark and includes two in-class tests in Weeks 5 and 9, respectively. These two tests were arranged in lab sessions. Though these two tests were online using the Learning Mall platform, all of the on-site students were required to complete online tests in the laboratory under on-site invigilation. Off-campus students were required to participate in the online test remotely at the same time and log into BigBlueButton for remote invigilation via live videos. Coursework 3 is an individual programming task including four programming questions and contributes towards 30% of the final mark. Students were asked to complete them after class and submit all of the source codes to the Learning Mall before the deadline for teachers to grade manually. The final exam includes twenty-five MCQ questions and seven written questions (one fill-in-the-blank question and six programming questions) contributing towards 40% of the final mark. Similarly to Coursework 1 and 2, all of the on-site students were required to complete the final exam online but in the laboratory under on-site invigilation, while off-campus students attended the online exam remotely at the same time under live video invigilation.
3. Results, Analysis and Discussion
3.1. Overall Learning Achievement
Besides eight students who withdrew from the module due to individual issues, 1004 students completed the study of CPT105 in Semester 1, 2020–2021. Table 2 shows the overall learning achievements of all students in CPT105.

Table 2.
Overall learning achievements of CPT105.
From Table 2, we find that the final average mark is 72.6 and the final failure rate is 8.6% for all students in CPT105, both in a reasonable range. However, we find that the average mark is decreased from 77.2 for Coursework 1 to 68.2 for the final exam, while the failure rate of these assessments is also decreased from 14.2% for Coursework 1 to 6.1% for the final exam. This is because Coursework 1 takes place each week in the early stages of the semester, aiming to examine fundamental concepts in each lecture and allow students to become familiar with the assessment format. However, Coursework 2, 3 and the final exam required students to use the knowledge they had learned and examined students’ comprehensive programming skills. Thus, the difficulty level from Coursework 1 to the final exam is increased gradually, the average marks of these assessments are also decreased and Coursework 1 has the highest average mark while the final exam has the lowest mark. However, considering that most students may have had no academic background in programming, Coursework 1 is still a challenging assignment for some students, resulting in the highest failure rate compared to other assessments. The standard deviation of Coursework 1 is also higher than other assessments, which means that the individual mark of Coursework 1 has a higher level of dispersion than other assessments. As the study continued and students mastered more programming knowledge, the failure rate was slightly reduced from 12% to 10.4% and 6.1% for Coursework 2, Coursework 3 and the final exam, respectively. In addition, the standard deviation is also decreased from 29.7 for Coursework 1 to 18.6 for the final exam.
3.2. Overall Difficulty Index Analysis
The difficulty index is a powerful analytical tool, which is widely used for statistical analysis, especially when evaluating the validity of exam questions in an educational setting. It has been identified as one of the approaches that can evaluate the difficulty level of examination questions and classify them into three levels, namely, easy, moderate and hard. A low value of the difficulty index means the question is difficult for students, and a too-high index value indicates that the question is too easy for most students. For objective questions, such as MCQ and fill-in-the-blank questions, the difficulty index is defined as the ratio of the number of students who could answer the questions correctly to the total number of students who participated in the exam [22]. The higher this ratio, the lower the difficulty. It is calculated by the following equation:
where is the difficulty index of question i; represents the number of students who answered question i correctly and N is the total number of students who participated in the exam.
However, for subjective questions, such as short-answer and programming questions, the difficulty index of a question can be defined as the ratio of the average mark of all students to the full mark of the question, which is defined as follows [23]:
where is the score of question i achieved by student j; represents the total score obtained for question i of all the students; N is the number of all students and is the full mark of question i.
Because most questions of Coursework 1, 2 and 3 were programming questions, we regarded the three coursework assignments as subjective questions and calculated their difficulty index using Equation (2). The difficulty index of the three coursework assignments is shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Difficulty index of three coursework assignments.
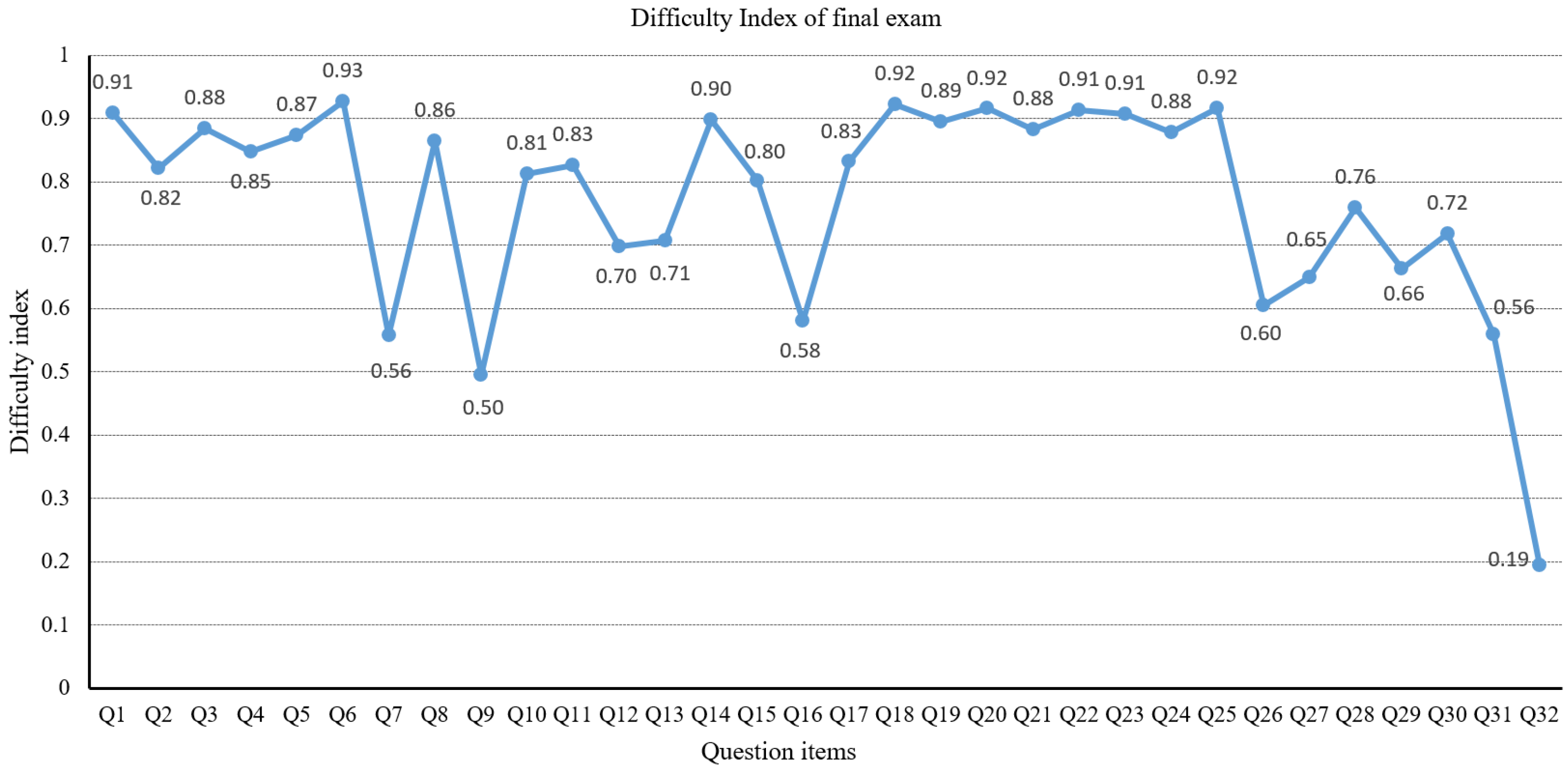
The final exam includes twenty-five MCQ questions and seven written questions. To evaluate the final exam in detail, we calculated the difficulty index for MCQ questions using Equation (1) and for the remaining seven written questions using Equation (2). Figure 1 shows the detailed difficulty index for all final exam questions.
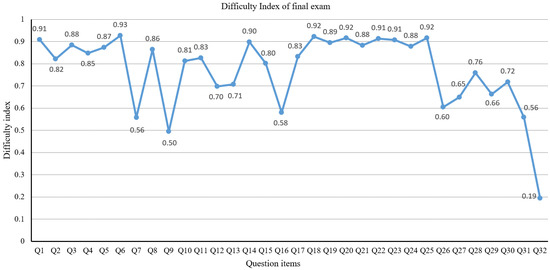
Figure 1.
Difficulty index of questions in the final exam.
According to the difficulty index classification [24], the optimal difficulty index range is between 0.2 and 0.80. Table 3 shows that all of these three coursework assignments are in the reasonable difficulty range. Figure 1 shows that Q32 is the most difficult question for students, and its difficulty index is 0.19. Considering that Q32 is the last question of the final exam, we think it is reasonable to set a relatively higher difficulty level to the last question to distinguish the learning performance of each student. The easiest question is Q6, with the highest difficulty index of 0.93. The average difficulty index of all twenty-five MCQ questions is 0.82, while for the seven written questions it is 0.54. This means that the written questions are a little bit more difficult than the MCQ questions. The overall difficulty index of the final exam is 0.68, which is also in the optimal range.
3.3. Overall Discrimination Index Analysis
The discrimination index estimates how discriminating questions in an exam are, i.e., how well a question can differentiate between students who scored highly on the total test and those whose scores were low. It is an effective measurement for each question in the exam based on the performance comparison between stronger and weaker candidates. Based on the analysis of the discrimination index, we can identify whether a question is too hard even for the group of students with high marks or whether the question is too easy meaning that even the group of students with lower marks could answer it correctly. A discrimination index of 0.40 and above is regarded as a very good question, 0.30–0.39 is reasonably good, 0.20–0.29 is a marginal question (i.e. subject to improvement) and 0.19 or lower is a poor question [25,26]. The discrimination index can be calculated using Equation (3):
where is the total score of 25% of students with the highest final mark, is the total score of 25% of students with the lowest final mark, N is 25% of the total number of students who participated in the exam, is the maximum mark for the question and is the minimum mark for the question.
There were 1004 students who completed the study of CPT105. We sorted the students in descending order according to their final marks and selected the first 251 students and the last 251 students, respectively, to calculate the discrimination index. The discrimination index of the three coursework assignments is shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Discrimination index of three coursework assignments.
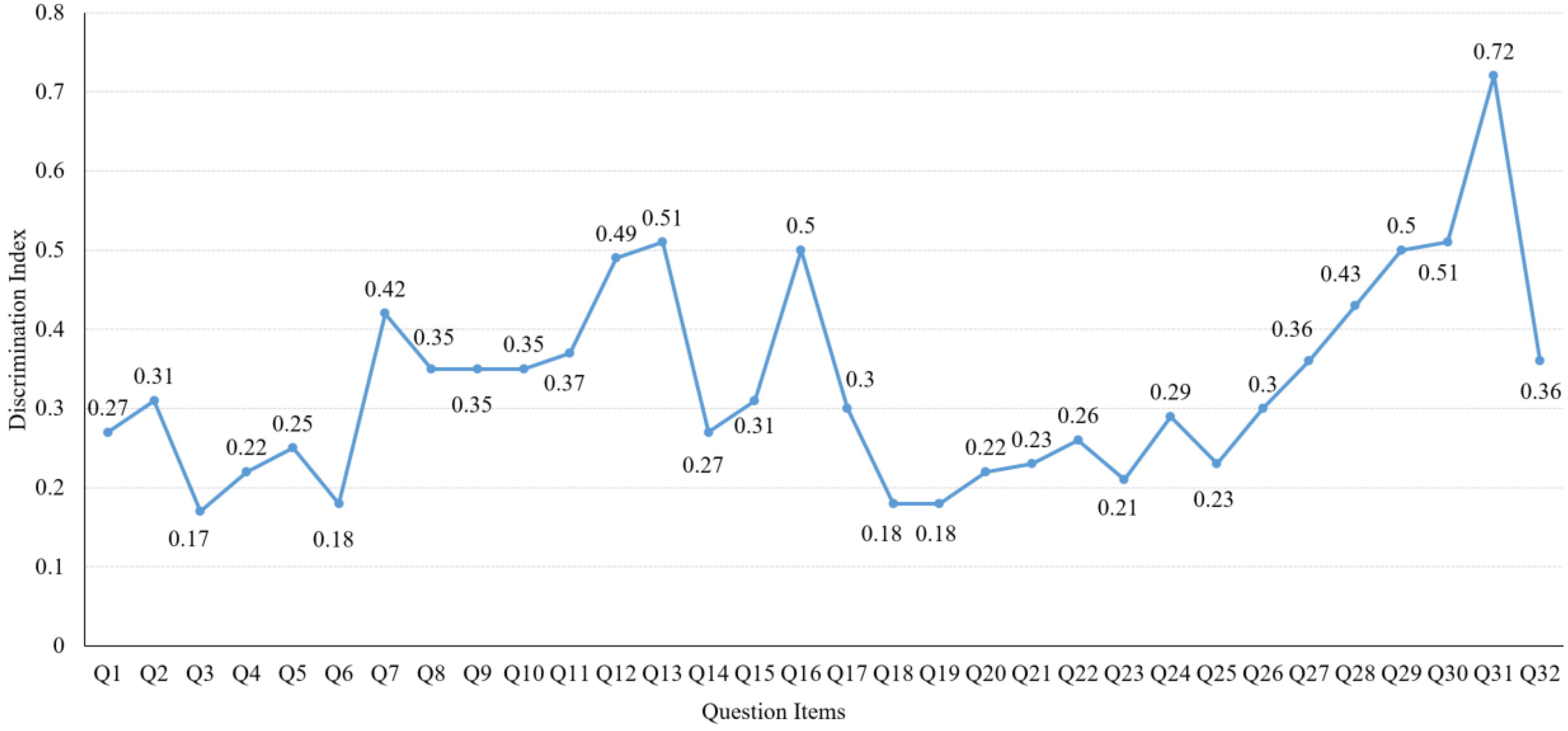
The discrimination indexes of all three of these coursework assignments are larger than 0.4 and less than 0.6, which means that all of these three coursework assignments have good positive discrimination. Figure 2 shows the discrimination index of each question for the final exam.
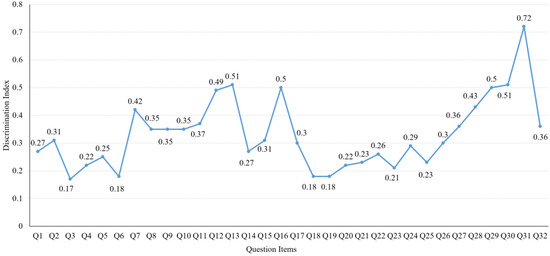
Figure 2.
Discrimination index of questions in the final exam.
Figure 2 shows that the discrimination indexes of Q3, Q6, Q18 and Q19 are 0.17, 0.18, 0.18 and 0.18, respectively, and are considered to be a little bit lower discrimination indexes than usual. Compared to the difficulty index in Figure 1, we find that these four questions also have very high difficulty indexes of 0.88, 0.96, 0.92 and 0.89, separately. From Figure 1 and Figure 2, we find that, in general, difficult questions (low difficulty indexes) usually have high discrimination indexes. It is because, compared to students with high marks, difficult questions are much harder for students with low marks, and they get fewer marks, resulting in high discrimination indexes. Besides the four questions with low discrimination index, the discrimination indexes of the remaining 23 questions are all in the normal range. The average discrimination index of the final exam (all questions) is 0.36, which is also in the reasonable range.
3.4. Learning Achievement Analysis for Students in Different Schools
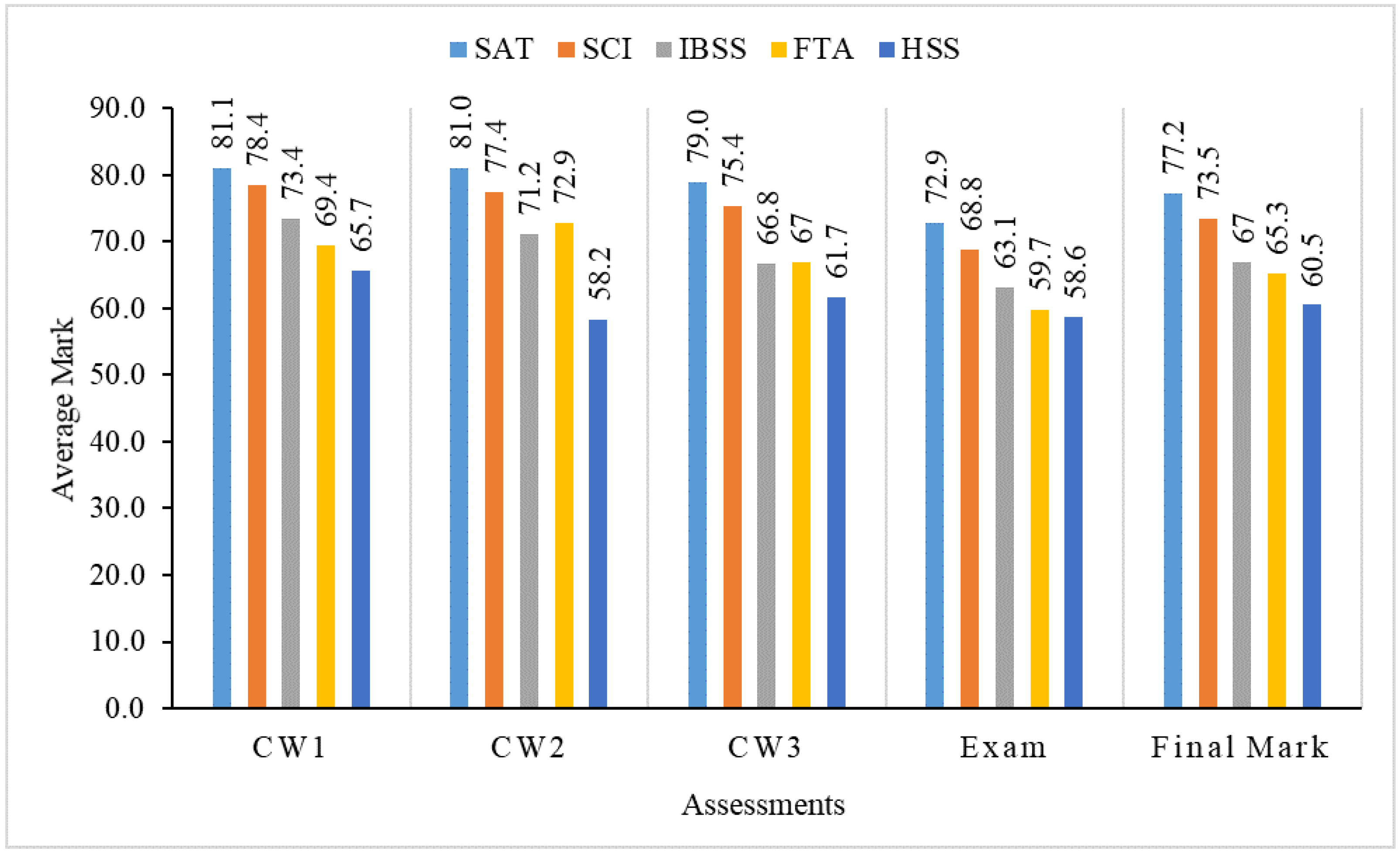
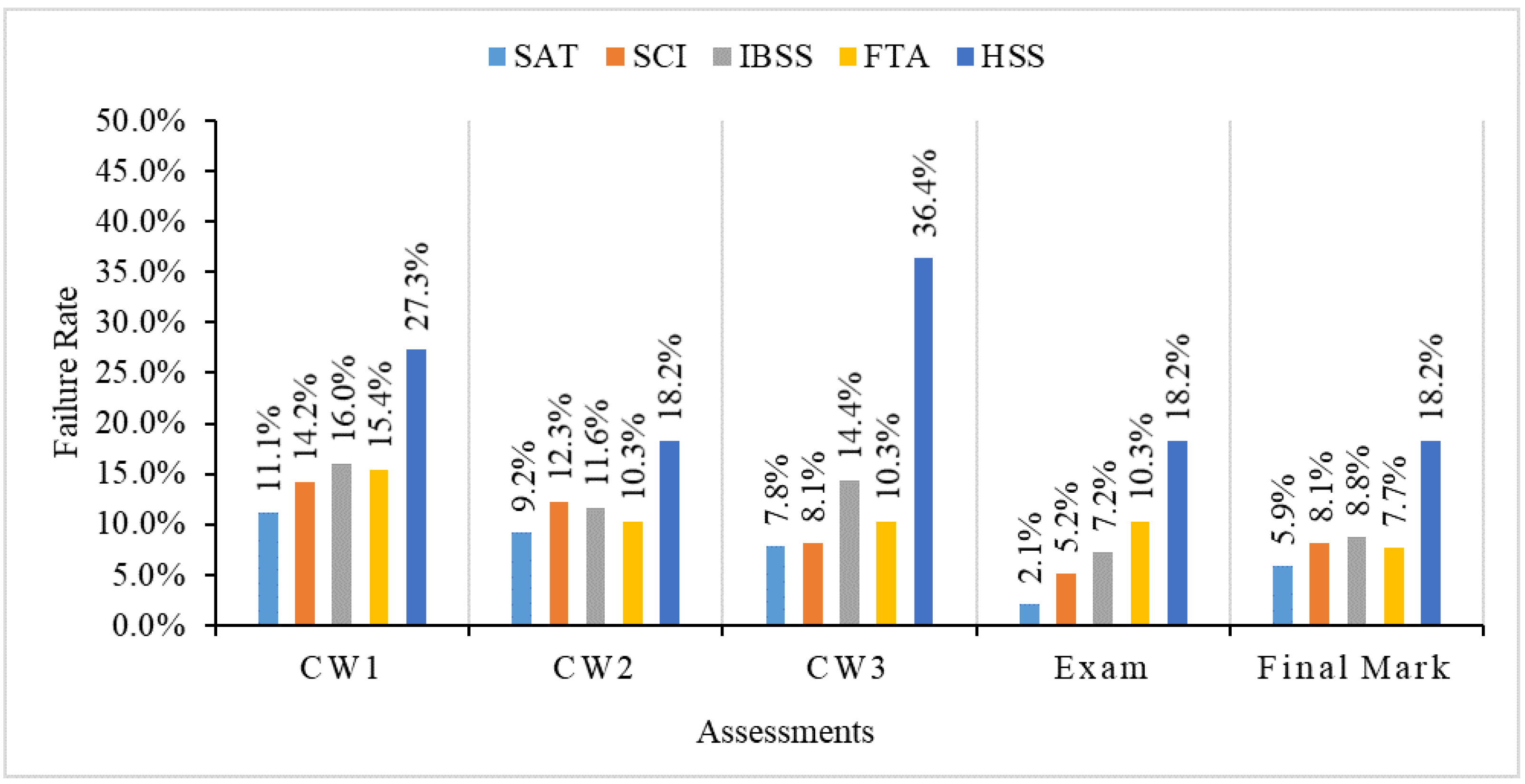
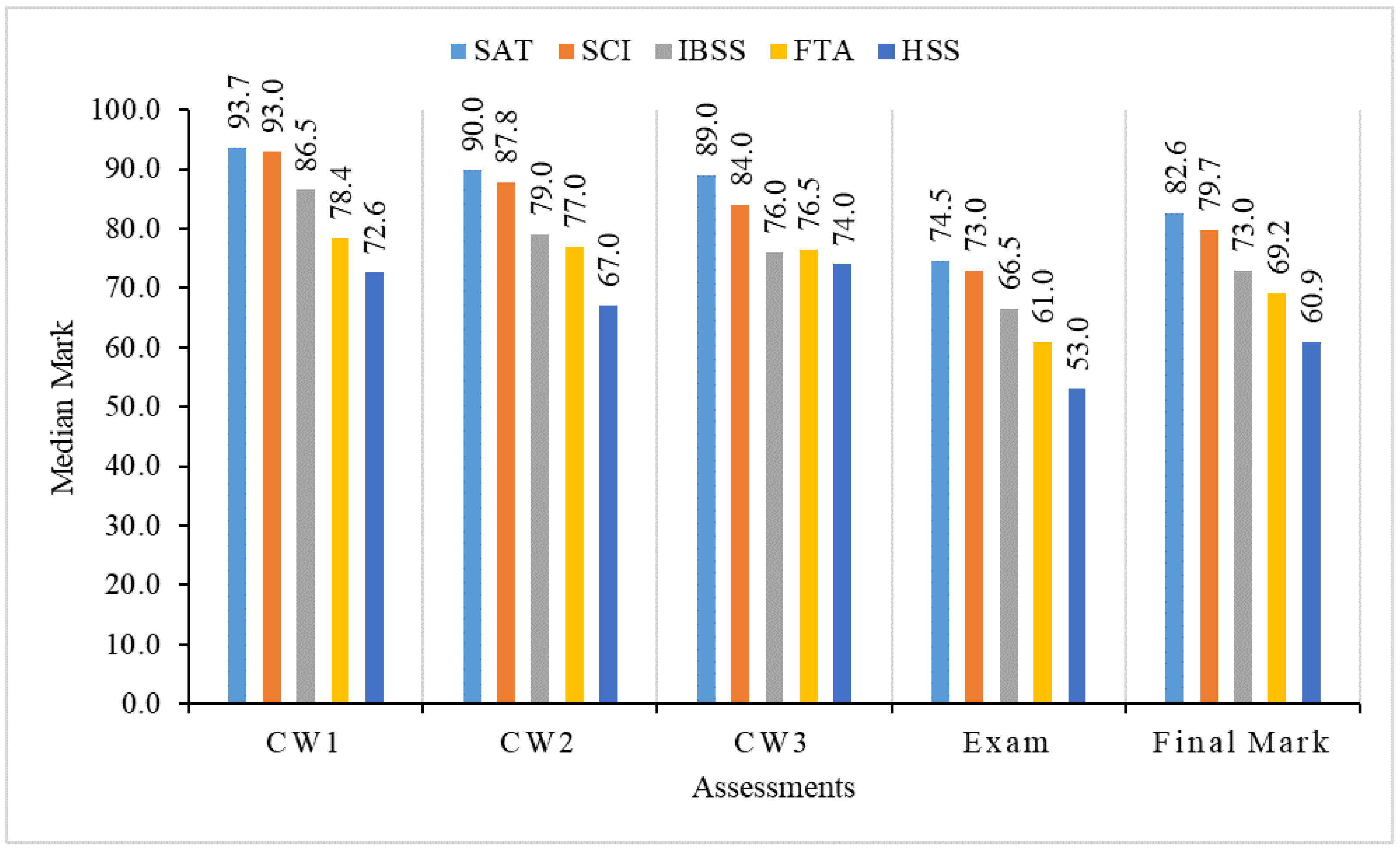
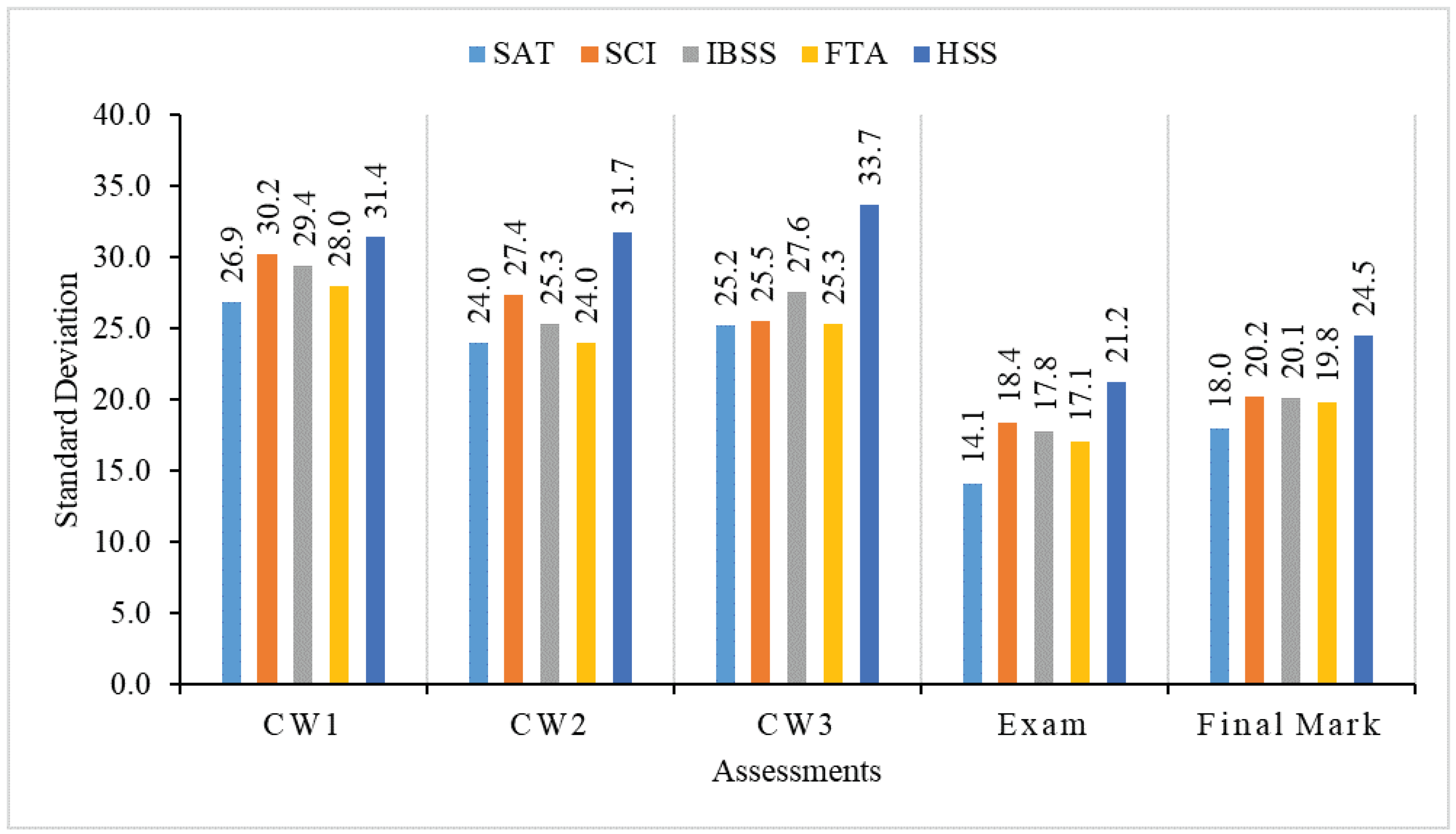
From the analysis in Section 3.2 and Section 3.3, we find that the difficulty index and discrimination index of 3 coursework assignments and the final exam are all in reasonable ranges. It means that we can use the results of these coursework assignments and the final exam to assess the learning performance of all students in this module. To observe detailed learning achievements of students in different schools, we divided all of the students into five groups (SAT, SCI, IBSS, FTA and HSS) and analyzed their learning achievements for the three coursework assignments, the final exam and the final mark, respectively. Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 show the average mark, failure rate, median mark and standard deviation, respectively, for students in each school.
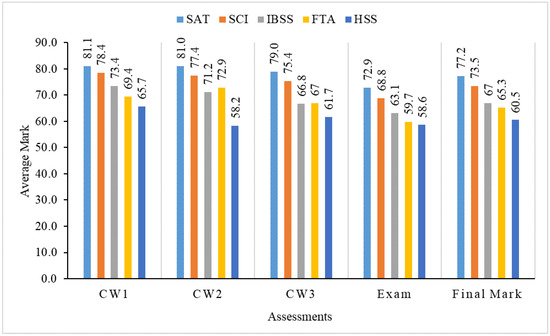
Figure 3.
Average mark of students in five schools.
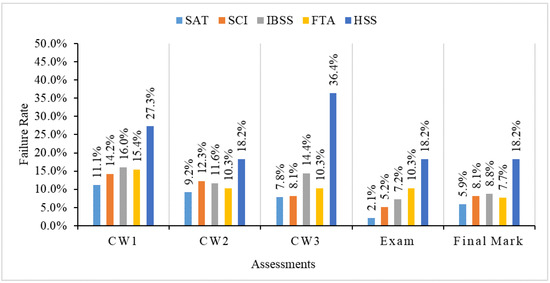
Figure 4.
Failure rate of students in five schools.
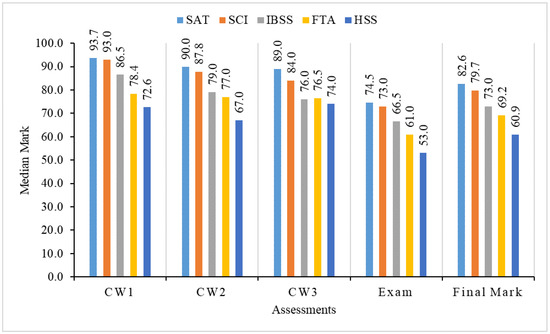
Figure 5.
Median mark of students in five schools.
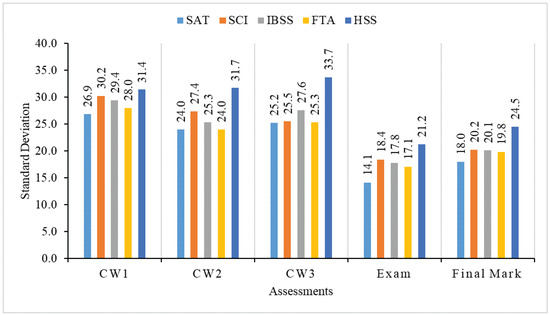
Figure 6.
Standard deviation of students in five schools.
Figure 3 indicates that SAT students have the highest average mark on all assessments and the final mark, while HSS students have the lowest average mark in all aspects. The average final mark of HSS students is 16.7 points less than that of SAT students, which shows a significant gap between SAT and HSS students. The final average mark for the schools in descending order for SAT, SCI, IBSS, FAT and HSS is 77.2, 73.5, 67, 65.3 and 60.5, respectively. We also find that SCI students have the second-highest average marks in all assessments and the final mark. The gap in marks between SAT and SCI students is slight, compared to the gap between SAT and other schools.
The failure rate in Figure 4 shows that the SAT students also have the lowest failure rate on all three coursework assignments and the final exam, while HSS students have the highest failure rate on all assessments. The final failure rate of SAT students is 5.9%, while that of HSS students is much higher at 18.2%, which is more than three times that of SAT students. The failure rate of SAT students is significantly decreased from 11.1% for CW1 to 2.1% for the final exam, which means that the failure rate of SAT students has dropped by 81% during the learning process. However, the failure rate of HSS students is 27.3% for CW1 and 18.2% for the final exam, which is only a drop by 33.7%. From the first coursework to the final exam, the failure rate of SCI, IBSS and FTA students dropped by 64.3%, 55% and 33%, respectively. We also find that the failure rate of SCI students is a little bit higher but very close to the failure of SAT students, which is similar to the average mark of SAT and SCI students in Figure 3.
The median mark in Figure 5 shows similar results as in Figure 3 and Figure 4. We find that SAT students have the highest median mark for each coursework and the final exam, while HSS students have the lowest mark. It also indicates that SAT students have the best learning performance compared to others, while HSS students have the worst learning performance.
We find from Figure 6 that the standard deviation mark of SAT students is also much lower than other students, which means that the learning performance of SAT students is higher even in CPT105 than other students in SCI, IBSS, FAT and HSS.
Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 indicate that though all students have the same lectures and teachers within the same class, SAT students have the best learning performance, while HSS students have the worst performance in all aspects. We reviewed all assignments and exam questions and found that there were many questions that required students to have some mathematical knowledge and logical reasoning skills, especially those with lower difficulty indexes and higher discrimination indexes (difficult questions for students). Thus, we think this is mainly because the programming module requires mathematical knowledge and logical reasoning skills. Good mathematics and logical reasoning ability helped SAT students to adapt to the teaching of computer programming quickly and achieve the highest academic performance in the end. In addition, SAT students also realise that as the first programming module for their major, CPT105 is essential for their further study in the next three years, which may encourage them to study harder than other students and spend more time on this module. SCI students also have strong mathematical backgrounds and achieve higher final marks than IBSS, FTA and HSS students. However, on the one hand, some FTA and HSS students may not have strong mathematics and logical reasoning skills. Thus, CPT105 is a little bit more difficult for them. On the other hand, computer programming may not be essential for their majors, and they may not spend much time on this module. Thus, they achieve the lowest final mark compared to the other students.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, we analyzed the learning achievements and performance of CPT105, the first introductory programming module, for 1012 students with different majors in different schools. Results showed that although all students had the same learning environment, SAT students showed the best learning performance, while HSS students got the worst performance in all aspects. The difference in learning achievements between SAT and HSS students is significant. Our research contributes to findings and confirms via massive data analysis that students’ major background can significantly affect their learning motivation and achievements, especially when a course needs some particular academic background knowledge that some students do not have or may not be good at. This finding is consistent with the conclusions proposed in [27] that the correlation between mathematics ability and achievement in basic programming is positive and significant. It is also similar to [28] in the sense that knowledge and organization can affect the final course grade. Therefore, we should consider the impact of majors when we make a large-size class for students from different majors.
Based on the learning achievements analyzed above and considering that it is a challenging task for teachers to manage on-site teaching and lab sessions with so many students, we decided to split CPT105 into two modules: CPT105 for non-SAT students and CPT112 for SAT students, to improve the teaching and learning experience both for teachers and students. In addition, we decided to slightly increase the teaching content for CPT112 and increase the assignments’ difficulty indexes to improve the learning outcomes for SAT students. For non-SAT students (IBSS, SCI, FTA and HSS), we will slightly enhance the teaching content to reduce the mathematical requirement while increasing the programming knowledge and skills.
The limitation of this paper is that we have not collected massive teaching and learning data to evaluate the effect of teaching SAT and non-SAT students in two different modules. In the future, we will continue to track and analyze students’ learning achievements in these two modules by collecting more data, and evaluate the improvement in learning performance by separating SAT and non-SAT students into two separate classes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.C. and Y.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, X.Z.; writing—review and editing, Y.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Suzhou Science and Technology Project (SYG202122), the Teaching Development Fund of XJTLU (TDF21/22-R25-185), the Key Program Special Fund of XJTLU (KSF-A-19) and the Research Development Fund of XJTLU (RDF-19-02-23).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Xi’an Jiaotong-Liverpool University (protocol code ER-SAT-0010000123520221224093411, on 26 Deceomber 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Shi, M. The effects of class size and instructional technology on student learning performance. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2019, 17, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S. Impact of Educational Technology-Based Learning Environment on Students’ Achievement Goals, Motivational Constructs, and Engagement. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM Conference on International Computing Education Research, Toronto, ON, Canada, 12–14 August 2019; pp. 321–322. [Google Scholar]
- Mosteller, F. The Tennessee study of class size in the early school grades. Future Child. 1995, 5, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, J.D.; Gerber, S.B.; Boyd-Zaharias, J. Small classes in the early grades, academic achievement, and graduating from high school. J. Educ. Psychol. 2005, 97, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, N.; Celik, B. The impact of number of students per teacher on student achievement. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 177, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chingos, M.M. The impact of a universal class-size reduction policy: Evidence from Florida’s statewide mandate. Econ. Educ. Rev. 2012, 31, 543–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Glewwe, P.; Whitler, M. Do reductions in class size raise students’ test scores? Evidence from population variation in Minnesota’s elementary schools. Econ. Educ. Rev. 2012, 31, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ake-Little, E.; von der Embse, N.; Dawson, D. Does class size matter in the university setting? Educ. Res. 2020, 49, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusnilita, N. The impact of online learning: Student’s views. ETERNAL (Engl. Teach. J.) 2020, 11, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.L.; Jin, Y.Q.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, S.W.; Su, Y.S. Factors influence students’ switching behavior to online learning under COVID-19 pandemic: A push–pull–mooring model perspective. Asia-Pac. Educ. Res. 2021, 30, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Arias, A.; Chalela-Naffah, S.; Bermúdez-Hernández, J. A proposed model of e-learning tools acceptance among university students in developing countries. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2019, 24, 1057–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taib, F.; Yusoff, M.S.B. Difficulty index, discrimination index, sensitivity and specificity of long case and multiple choice questions to predict medical students’ examination performance. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2014, 9, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadag, N.; Sahin, M.D. Analysis of the Difficulty and Discrimination Indices of Multiple-Choice Questions According to Cognitive Levels in an Open and Distance Learning Context. Turk. Online J. Educ. Te Chnology-TOJET 2016, 15, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ramzan, M.; Khan, K.W.; Bibi, S.; Shezadi, S.I. Difficulty and Discrimination Analysis of End of Term Multiple-Choice Questions at Community Medicine Department, Wah Medical College. Pakistan Armed Forces Med. J. 2021, 71, 1308–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacherjee, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Bhandari, K.; Rout, A.J. Evaluation of multiple-choice questions by item analysis, from an online internal assessment of 6th semester medical students in a rural medical college, West Bengal. Indian J. Community Med. Off. Publ. Indian Assoc. Prev. Soc. Med. 2022, 47, 92. [Google Scholar]
- Nazarianpirdosti, M.; Janatolmakan, M.; Andayeshgar, B.; Khatony, A. Evaluation of self-directed learning in nursing students: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Educ. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 2112108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korde, S.; Kale, G.; Dabade, T. Comparative Study of Online Learning and Classroom Learning. Anwesh 2021, 6, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Law, V.T.; Yee, H.H.; Ng, T.K.; Fong, B.Y. Transition from Traditional to Online Learning in Hong Kong Tertiary Educational Institutions During COVID-19 Pandemic. Technol. Knowl. Learn. 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, M.; Ramzan, M.J.; Khan, S.U.R.; Rehman, I.U.; Khan, T.A. A Pilot Study on Online-Education Supportive Tools in COVID-19 Context. It Prof. 2021, 23, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.L. Developing lifelong learning with heutagogy: Contexts, critiques, and challenges. Distance Educ. 2020, 41, 381–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, F.; Çelikler, D. Development of Achievement Test: Validity and Reliability Study for Achievement Test on Matter Changing. J. Educ. Pract. 2015, 6, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Dixit, C.; Joshi, G.; Ayachit, N.H.; Shettar, A. Difficulty index of a question paper: A new perspective. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Engineering Education: Innovative Practices and Future Trends (AICERA), Kottayam, India, 19–21 July 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Nitko, A.J. Educational Assessment of Students; ERIC: Cottesloe, WA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, I.A.M.; Moalwi, A.A. Correlation between difficulty and discrimination indices of MCQs type A in formative exam in anatomy. J. Res. Method Educ. 2017, 7, 28–43. [Google Scholar]
- Johari, J.; Sahari, J.; Abd Wahab, D.; Abdullah, S.; Abdullah, S.; Omar, M.Z.; Muhamad, N. Difficulty index of examinations and their relation to the achievement of programme outcomes. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2011, 18, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johari, J.; Abd Wahab, D.; Ramli, R.; Saibani, N.; Sahari, J.; Muhamad, N. Identifying student-focused intervention programmes through discrimination index. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 60, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owolabi, J.; Olanipekun, P.; Iwerima, J. Mathematics Ability and Anxiety, Computer and Programming Anxieties, Age and Gender as Determinants of Achievement in Basic Programming. GSTF J. Comput. (JoC) 2014, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenbeck, S. Factors affecting the success of non-majors in learning to program. In Proceedings of the International Computing Education Research Workshop, Seattle, WA, USA, 1–2 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).