Learning Mediated by Social Network for Education in K-12: Levels of Interaction, Strategies, and Difficulties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Reference
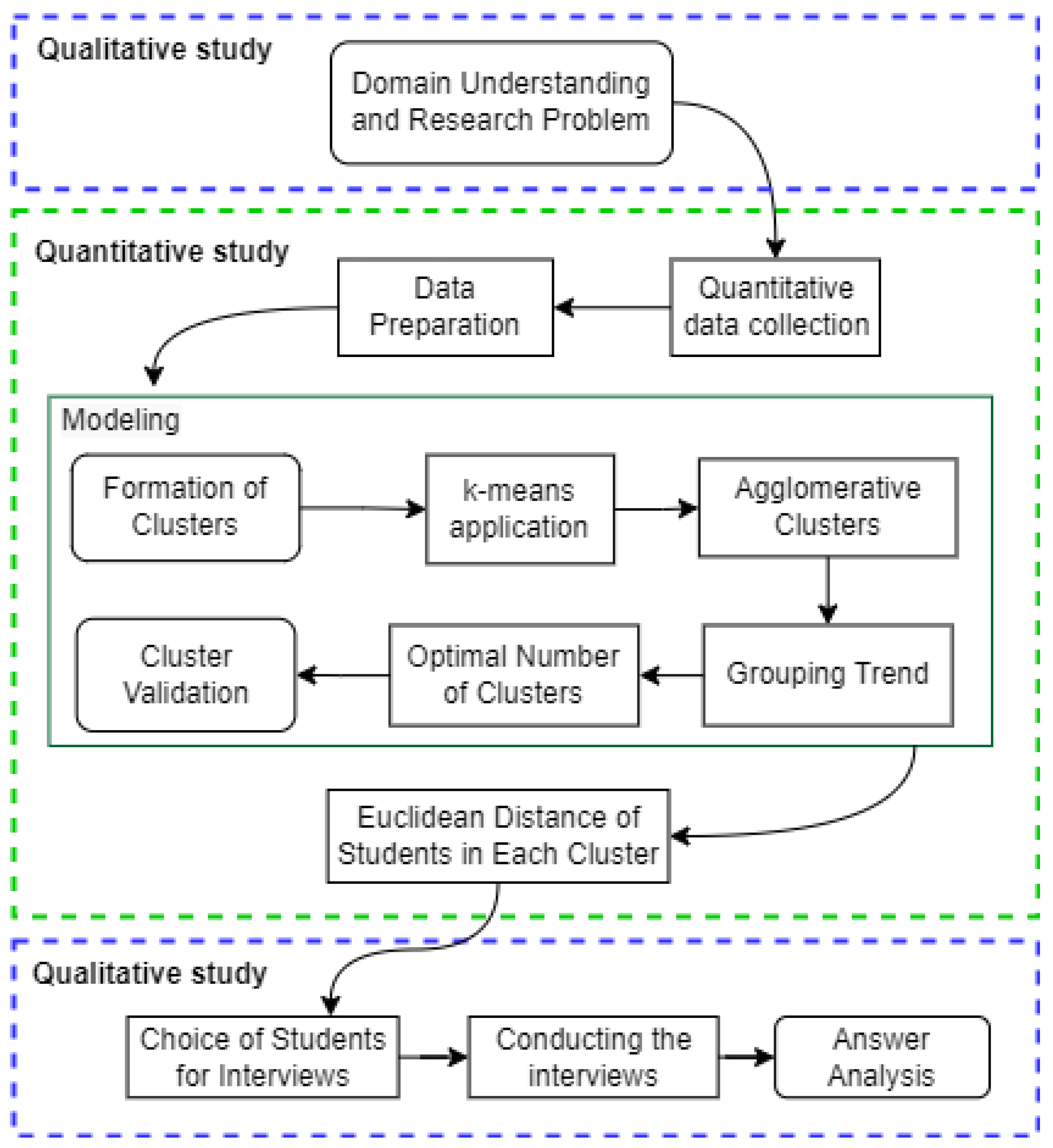
3. Methodology
3.1. Approach
3.2. Units of Analysis
3.3. Collection Techniques: Digital Data and Pre-Processing in the Virtual Environment
3.4. Analysis Processing: Digital Data Modeling and Clustering
- nearest to the centroid (NC): students who are at the level of interaction closest to the center point of the interaction levels;
- farthest from the centroid (FC): students who are at the level of interaction farthest from the center point of the interaction levels between students in each group;
- centroid middle distance (CMD): students who are at an average distance relating to the closest and the most distant in each group;
- centroid median distance (CMeC): students who are in the larger half (closer to the center point and average distance) and smaller half (closer to the farthest and average distance).
3.5. Collection Techniques: Qualitative Data on Interactions between Participants
3.6. Analysis Processing: Qualitative Data on Interactions between Participants
4. Results
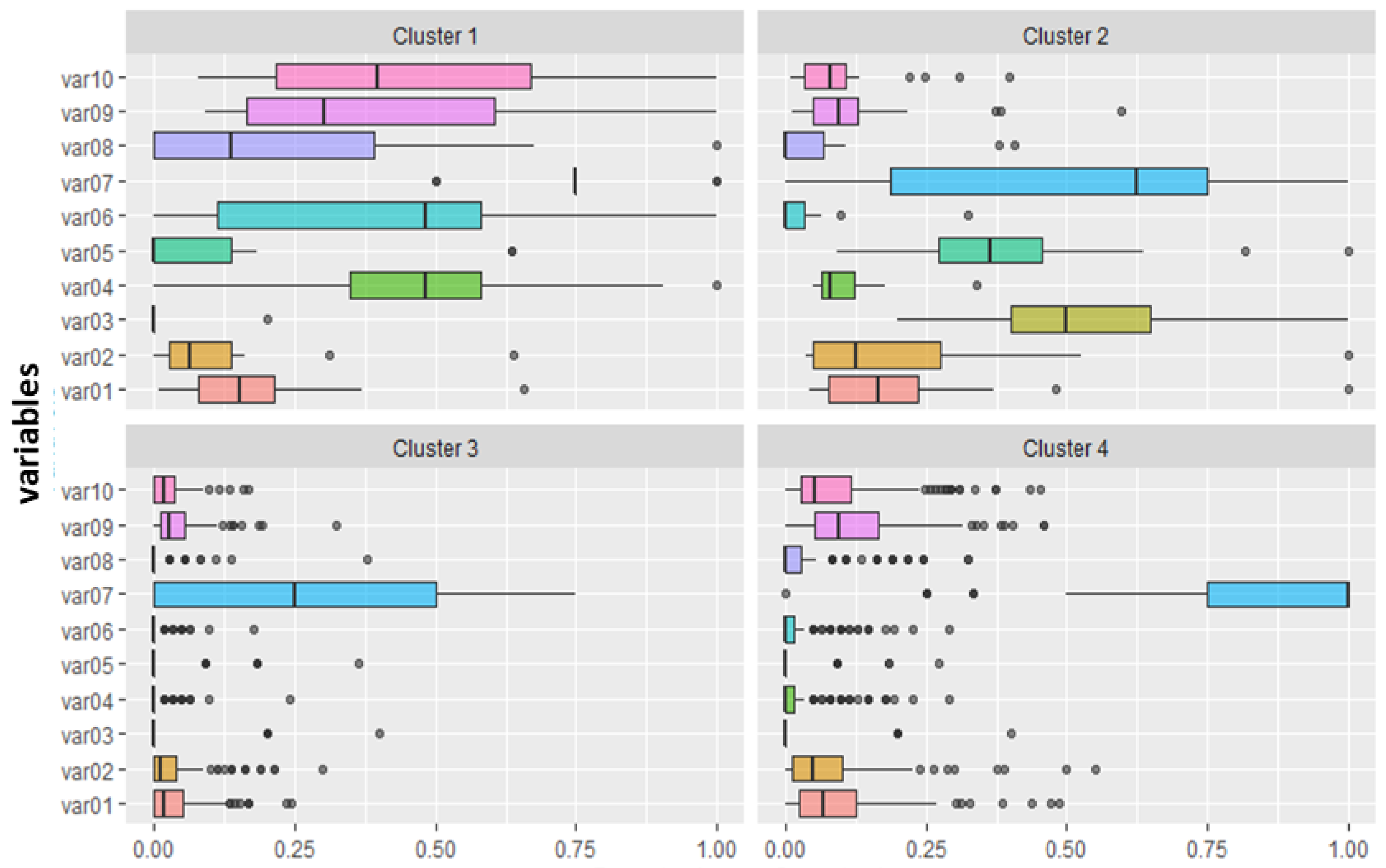
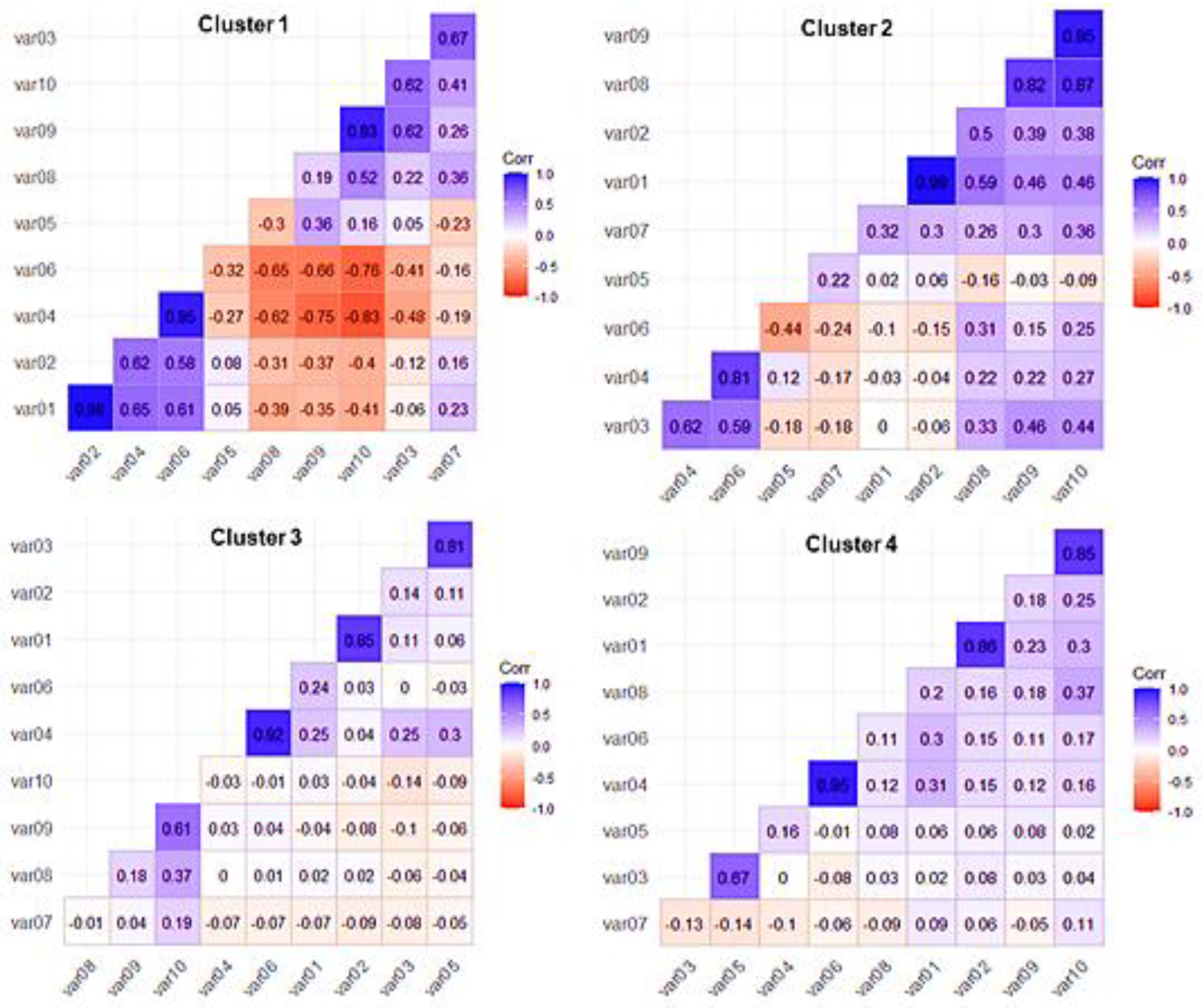
4.1. Grouping of Students by the Similarity of Interaction Patterns
4.1.1. Interaction Levels of K-9 Students
4.1.2. Interaction Levels of K-12 Students
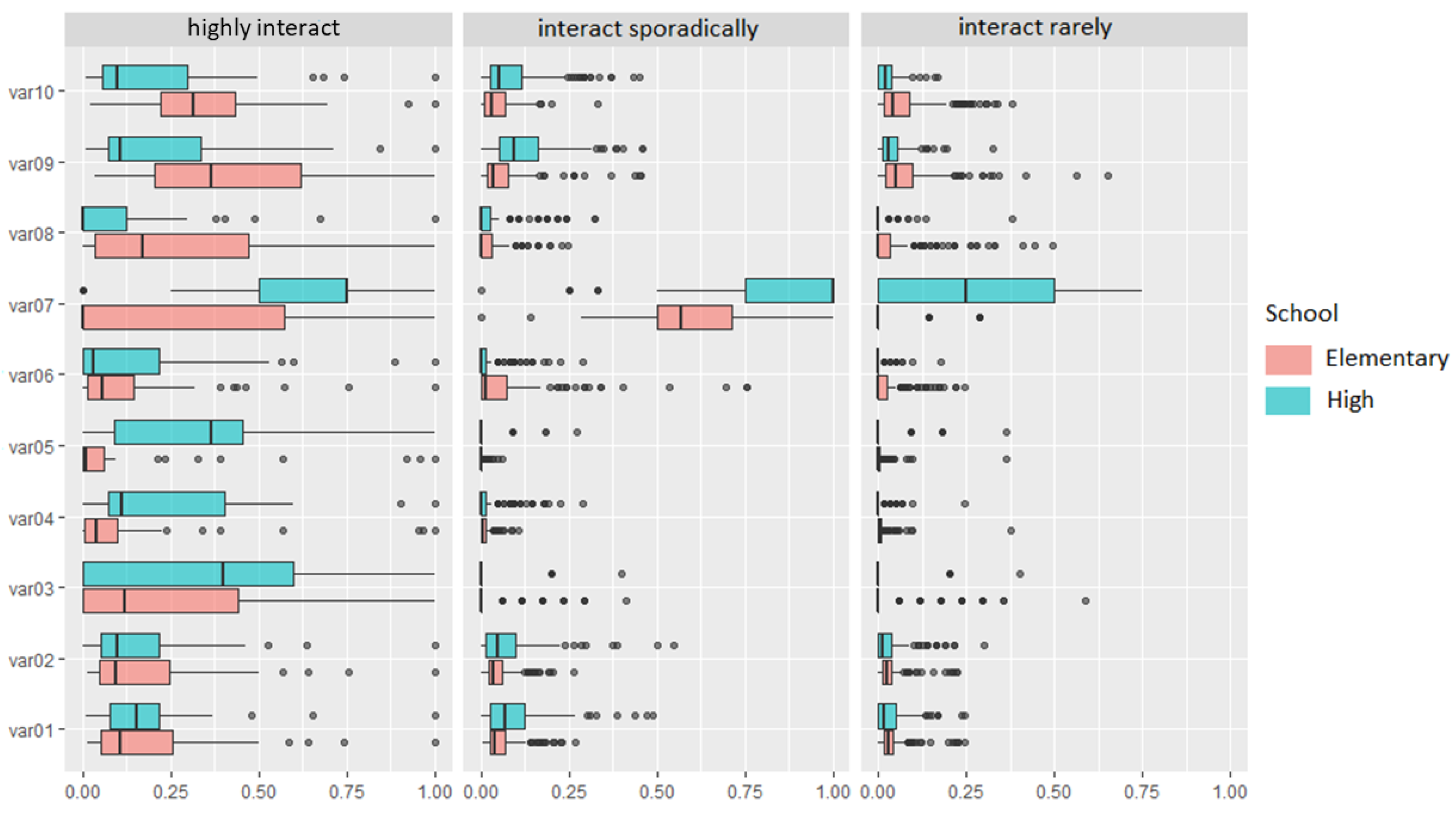
4.1.3. Characterization of Interactions of K-12 Elementary and High School Students
4.2. Qualification of Interactions and Identification of Difficulties
Interactions in the Virtual Environment
4.3. Interaction Alternatives beyond the Virtual Environment
4.4. Student Difficulties
5. Conclusions
Limitations and Future Research Opportunities
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bozkurt, A.; Jung, I.; Xiao, J.; Vladimirschi, V.; Schuwer, R.; Egorov, G.; Lambert, S.R.; Al-Freih, M.; Pete, J.; Olcott, J.D.; et al. A global outlook to the interruption of education due to COVID-19 pandemic: Navigating in a time of uncertainty and crisis. Asian J. Distance Educ. 2020, 1, 1–126. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Whitelock-Wainwright, A.; Guan, Q.; Wen, G.; Gašević, D.; Chen, G. Students’ experience of online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic: A province-wide survey study. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2021, 52, 2038–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harapan, H.; Itoh, N.; Yufika, A.; Winardi, W.; Keam, S.; Te, H.; Megawati, D.; Hayati, Z.; Wagner, A.L.; Mudatsir, M. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A literature review. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, S.P.; Breaux, R.; Cusick, C.N.; Dvorsky, M.R.; Marsh, N.P.; Sciberras, E.; Langberg, J.M. Remote learning during COVID-19: Examining school practices, service continuation, and difficulties for adolescents with and without attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J. Adolesc. Health 2020, 67, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardullo, V.; Wang, C.; Burton, M.; Dong, J. K-12 teachers’ remote teaching self-efficacy during the pandemic. J. Res. Innov. Teach. Learn. 2021, 14, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebebci, M.T.; Bertiz, Y.; Alan, S. Investigation of views of students and teachers on distance education practices during the Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic. Int. J. Technol. Educ. Sci. 2020, 4, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, P. Impact of COVID-19 emergency transition to on-line learning onto the international students’ perceptions of educational process at Russian university. J. Soc. Stud. Educ. Res. 2020, 11, 270–302. [Google Scholar]
- McFayden, T.C.; Breaux, R.; Bertollo, J.R.; Cummings, K.; Ollendick, T.H. COVID-19 remote learning experiences of youth with neurodevelopmental disorders in rural Appalachia. J. Rural Ment. Health 2021, 45, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotas, E.E.; Cahapay, M.B. Difficulties in remote learning: Voices of Philippine University students in the wake of COVID-19 crisis. Asian J. Distance Educ. 2020, 15, 147–158. [Google Scholar]
- Schleicher, A. The Impact of COVID-19 on Education Insights from Education at a Glance. Available online: http://hdl.voced.edu.au/10707/550385 (accessed on 13 July 2022).
- Subedi, S.; Nayaju, S.; Subedi, S.; Shah, S.K.; Shah, J.M. Impact of e-learning during COVID-19 pandemic among nurshing students and teachers of Nepal. Int. J. Sci. Healthc. Res. 2020, 5, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Arimi, A.M.A.-K. Distance learning. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 152, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affouneh, S.; Salha, S.; Khlaif, Z.N. Designing quality e-learning environments for emergency remote teaching in coronavirus crisis. Interdiscip. J. Virtual Learn. Med. Sci. 2020, 11, 135–137. [Google Scholar]
- Hodges, C.; Moore, S.; Lockee, B.; Trust, T.; Bond, A. The difference between emergency remote teaching and online learning. Educ. Rev. 2020, 27, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Govaerts, S.; Holzer, A.; Kocher, B.; Vozniuk, A.; Garbinato, B.; Gillet, D. Blending digital and face-to-face interaction using a co-located social media app in class. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 2018, 11, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isohätälä, J.; Näykki, P.; Järvelä, S.; Baker, M.J.; Lund, K. Social sensitivity: A manifesto for CSCL research. Int. J. Comput.-Support. Collab. Learn. 2021, 16, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.G. The theory of transactional distance. In Handbook of Distance Education; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 84–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumble, G. The Planning and Management of Distance Education. In Routledge. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/1188073 (accessed on 18 July 2022).
- Orben, A.; Tomova, L.; Blakemore, S.-J. The effects of social deprivation on adolescent development and mental health. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.B. Mediated interaction in the digital age. Theory Cult. Soc. 2018, 37, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenenbaum, H.R.; Winstone, N.E.; Leman, P.J.; Avery, R.E. How effective is peer interaction in facilitating learning? A meta-analysis. J. Educ. Psychol. 2020, 112, 1303–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.G. Editorial: Three types of interaction. Am. J. Distance Educ. 1989, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirumi, A. Three levels of planned elearning interaction: A framework for grounding research and the design of elearning programs. Q. Rev. Distance Educ. 2013, 1, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Chanel, G.; Lalanne, D.; Lavoué, E.; Lund, K.; Molinari, G.; Ringeval, F.; Weinberger, A. Grand challenge problem 2: Adaptive awareness for social regulation of emotions in online collaborative learning environments. In Grand Challenge Problems in Technology-Enhanced Learning II: MOOCs and Beyond; Eberle, J., Lund, K., Tchounikine, P., Eds.; Springer Briefs in Education; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauß, S.; Rummel, N. Promoting interaction in online distance education: Designing, implementing and supporting collaborative learning. Inf. Learn. Sci. 2020, 121, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, J.; Claudeivan, L.; Veloso, F.; Gomes, A.S. Análise das práticas de colaboração e comunicação: Estudo de caso utilizando a rede social educativa redu. An. Workshop Inf. Esc. 2011, 1, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Brinton, C.G.; Chiang, M. Social learning networks: A brief survey. In Proceedings of the 48th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems (CISS), Princeton, NJ, USA, 19–21 March 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinton, C.G.; Buccapatnam, S.; Zheng, L.; Cao, D.; Lan, A.S.; Wong, F.M.F.; Ha, S.; Chiang, M.; Poor, H.V. On the efficiency of online social learning networks. IEEE ACM Trans. Netw. 2018, 26, 2076–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overdijk, M.; van Diggelen, W.; Kirschner, P.A.; Baker, M. Connecting agents and artifacts in CSCL: Towards a rationale of mutual shaping. Int. J. Comput.-Support. Collab. Learn. 2012, 7, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounikine, P. Contribution to a theory of CSCL scripts: Taking into account the appropriation of scripts by learners. Int. J. Comput.-Support. Collab. Learn. 2016, 11, 349–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiyono, B.B.; Indreswari, H.; Prestiadi, D. The use of technology-based communication media in the teaching-learning interaction of educational study programs in the pandemic of covid 19. In Proceedings of the IEEE 11th International Conference on Electronics Information and Emergency Communication (ICEIEC), Beijing, China, 18–20 June 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehall, S. Purposeful interpersonal interaction: What is it and how is it measured? Online Learn. 2020, 24, 182–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreijns, K.; Kirschner, P.A.; Vermeulen, M. Social aspects of CSCL environments: A research framework. Educ. Psychol. 2013, 48, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, J.B. Interaction through technological lenses. J. Lang. Soc. Psychol. 2012, 31, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahunty, J.; Verenikina, I.; Jones, P. Socio-emotional connections: Identity, belonging and learning in online interactions. A literature review. Technol. Pedagog. Educ. 2014, 23, 243–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Rojas, J.; Sánchez, J. How prepared was the world for emergency distance learning in K-12 education? A literature review. In Learning and Collaboration Technologies. Designing the Learner and Teacher Experience; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, J.W.; Clark, V.L.P. Designing and Conducting Mixed Methods Research, 3rd ed.; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wirth, R.; Hipp, J. CRISP-DM: Towards a standard process model for data mining. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on the Practical Applications of Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Manchester, UK, 11–13 April 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bardin, L. Análise de conteúdo. Lisb. Edições 1977, 70, 200–225. [Google Scholar]
- Parecer CNE/CP No: 5/2020, Ministerio da Educação. Conselho Nacional de Educação. Available online: http://www.abrafi.org.br/js/ckeditor/foto_internas/pcp005_20.pdf (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Portaria no 343, de 17 de Março de 2020, 343, Ministério da Educação. Available online: http://www.in.gov.br/en/web/dou/-/portaria-n-343-de-17-de-marco-de-2020-248564376 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Medida Provisória no 934, de 1o de Abril de 2020. Available online: http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_ato2019-2022/2020/mpv/mpv934.htm (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Kassambara, A. Practical Guide to Cluster Analysis in R: Unsupervised Machine Learning (Sthda); CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform: North Charleston, SC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hartigan, J.A.; Wong, M.A. Algorithm AS 136: A K-means clustering algorithm. Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatriain, X.; Jaimes, A.; Oliver, N.; Pujol, J.M. Data mining methods for recommender systems. In Recommender Systems Handbook; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 39–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edhlund, B.; Mcdougall, A. NVivo 12 Essentials; Lulu.com: Morrisville, NC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, H. Alleviating the challenges with remote learning during a pandemic. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widjaja, G.; Aslan, A. Blended learning method in the view of learning and teaching strategy in geography study programs in higher education. Nazhruna J. Pendidik. Islam 2022, 5, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, A.M.; Natsuaki, M.N. Coping with the pandemic: Implementing social and emotional learning in the California K-12 school system. Policy Insights Behav. Brain Sci. 2021, 8, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.K. New interpretation of extracurricular activities via social networking sites: A case study of artificial intelligence learning at a secondary school in Hong Kong. J. Educ. Train. Stud. 2020, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javornik, K.; Kavkler, M.; Lychatz, S.; Košak Babuder, M. How the COVID-19 pandemic was experienced by Slovenian and German adolescents with specific learning difficulties. Cent. Educ. Policy Stud. J. 2021, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, J.; Finlay, J.; O’Connor Bones, U. “Education cannot cease”: The experiences of parents of primary age children (age 4–11) in Northern Ireland during school closures due to COVID-19. Educ. Rev. 2021, 29, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makki, A.; Bali, A.O. The use of social media as a platform in education: Ramifications of COVID-19 in Iraq. Acad. J. Interdiscip. Stud. 2021, 10, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daftary, A.-M.H.; Sugrue, E.P.; Gustman, B.D.; Lechuga-Peña, S. Pivoting during a pandemic: School social work practice with families during COVID-19. Child. Sch. 2021, 43, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, F.G.K.; Yılmaz, R. Exploring the role of sociability, sense of community and course satisfaction on students’ engagement in flipped classroom supported by Facebook groups. J. Comput. Educ. 2022, 30, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Ma, Q.; Santos, I.M. Inquiry into online learning communities: Potential for fostering collaborative writing. J. China Comput.-Assist. Lang. Learn. 2022, 2, 20–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiş Erümit, S. The distance education process in K–12 schools during the pandemic period: Evaluation of implementations in Turkey from the student perspective. Technol. Pedagog. Educ. 2021, 30, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCoito, I.; Estaiteyeh, M. Online teaching during the COVID-19 pandemic: Exploring science/STEM teachers’ curriculum and assessment practices in Canada. Discip. Interdiscip. Sci. Educ. Res. 2022, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, B. Educational entropy in the 21st century. In Complexity and Values in Nurse Education; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2022; pp. 138–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, W.; Lowenthal, P. Experiences and perceptions of exchange students learning online during the COVID-19 pandemic in the Republic of Korea: An exploratory descriptive study. Asian J. Distance Educ. 2021, 16, 119–140. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, F.; Xie, K.; Bolliger, D.U. Engaging learners in the emergency transition to online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 2022, 54, S1–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, T.K.F. Student engagement in K-12 online learning amid COVID-19: A qualitative approach from a self-determination theory perspective. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2021, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinderliter, H.; Xie, Y.; Ladendorf, K.; Muehsler, H. Path analysis of internal and external factors associated with parental satisfaction over K-12 online learning. Comput. Sch. 2021, 38, 354–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huck, C.; Zhang, J. Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on K-12 education: A systematic literature review. Educ. Res. Dev. J. 2021, 24, 53–84. [Google Scholar]
- Hafiza Hamzah, N.; Khalid, M.; Nasir, M.; Abdul Wahab, J. The effects of principals’ digital leadership on teachers’ digital teaching during the Covid-19 pandemic in Malaysia. J. Educ. E-Learn. Res. 2021, 8, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grooms, A.A.; Childs, J. We need to do better by kids: Changing routines in U.S. schools in response to COVID-19 school closures. J. Educ. Stud. Placed Risk 2021, 26, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trust, T.; Whalen, J. Emergency remote teaching with technology during the COVID-19 pandemic: Using the whole teacher lens to examine educator’s experiences and insights. Educ. Media Int. 2021, 58, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toto, G.A.; Limone, P. Motivation, stress and impact of online teaching on Italian teachers during COVID-19. Computers 2021, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domina, T.; Renzulli, L.; Murray, B.; Garza, A.N.; Perez, L. Remote or removed: Predicting successful engagement with online learning during COVID-19. Socius Sociol. Res. Dyn. World. 2021, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Sahoo, S.; Pandey, S. Research trends in online distance learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. Distance Educ. 2021, 42, 494–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Variables | Description |
|---|---|
| STUDENT_ID | Sequential unique identifier of the database for the student |
| CLASS_ID | Identifier of the class in which the student is enrolled |
| SERIES | Name of the class in which the student is enrolled |
| LEVEL_EDUCATION | Level of K-12 education that the student is at |
| LOGIN_COUNT | Number of accesses to the virtual environment performed by the student |
| REGISTRATION_YEAR_USER | Year in which the student was registered in the virtual environment |
| DAYS_LAST_LOGIN | Most recent access in the virtual environment |
| VAR01 | The overall number of friends |
| VAR02 | Number of friends who are students |
| VAR03 | Number of different colleagues that the student sent messages to |
| VAR04 | The overall number of messages sent by the student |
| VAR05 | Number of messages sent (student–student) |
| VAR06 | Number of messages sent (student–teacher) |
| VAR07 | Number of exercises completed by the student |
| VAR08 | Number of help requests |
| VAR09 | Number of comments made by the student |
| VAR10 | The overall number of responses to posts received by the student |
| VAR11 | The shift of the day that the student commented the most |
| # | Questions |
|---|---|
| 1 | What changes have you noticed from face-to-face to remote classes? |
| 2 | How was your experience as a student in remote classes? Could you give examples of situations? |
| 3 | What were your principal difficulties in interacting with colleagues and teachers? Could you tell me how it happened? |
| 4 | Have learning groups (study groups) been formed for interaction among students? How did it happen? Could you tell/report it? |
| 5 | What kind of interactions with other peers or teachers did you enjoy most during remote classes? Detail remarkable cases. |
| 6 | How and through what means did you raise questions and resolve your doubts in remote classes? Try to describe examples. |
| 7 | When you needed help with some content or activity, how did you proceed (what did you do)? Could you give examples? |
| 8 | How did you go about tracking remote classes? How was it organized? |
| 9 | Tell us episodes in which you were interacting with colleagues or teachers to solve a learning difficulty. Describe how it happened. |
| 10 | What were the practices/methods of the teachers’ performance that helped you in your studies? Mention it through examples and episodes. |
| 11 | What requirements do you consider essential for your studies and were unable to meet through the virtual environment Redu? |
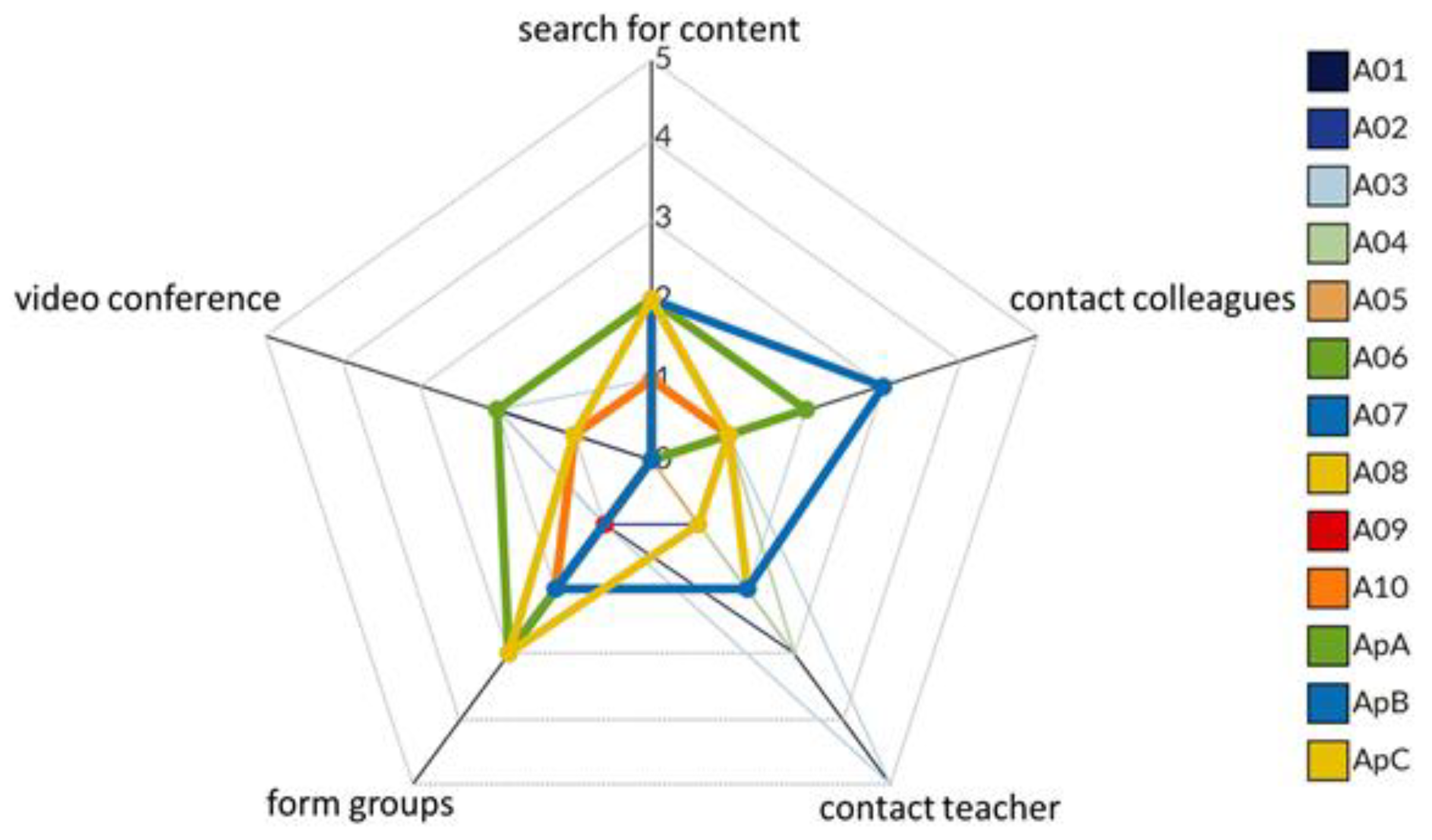
| Students | Class | Teaching | Cluster | Criterion | Length of Study at the Institution | Had Contact with Remote Learning | Interaction Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ApA | 2nd year | HS | Cluster 4 | CMD | 2 years | Previously | S. I. |
| ApB | 2nd year | HS | Cluster 4 | CMD | 4 years | Only in 2020 | S. I. |
| ApC | 2nd year | HS | Cluster 3 | CMD | 4 years | Only in 2020 | R. I. |
| A01 | 2nd year | HS | Cluster 4 | FC | 1 year | Only in 2020 | S. I. |
| A02 | 9th year | ES | Cluster 2 | NC | 4 years | Only in 2020 | S. I. |
| A03 | 8th year | ES | Cluster 2 | CMeD | 1 year | Previously | S. I. |
| A04 | 7th year | ES | Cluster 4 | CMeD | 2 years | Only in 2020 | H. I. |
| A05 | 6th year | ES | Cluster 4 | CMD | 7 years | Only in 2020 | H. I. |
| A06 | 9th year | ES | Cluster 2 | CMeD | 1 year | Only in 2020 | S. I. |
| A07 | 9th year | ES | Cluster 3 | FC | 3 years | Only in 2020 | R. I. |
| A08 | 8th year | ES | Cluster 2 | CMeD | 2 years | Only in 2020 | S. I. |
| Variables | Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | Cluster 3 | Cluster 4 | Average of Variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAR01 | 195.4 (53.2%) | 36.40 (9.9%) | 21.31 (5.8%) | 113.86 (31.0%) | 91.74 |
| VAR02 | 162.8 (54.7%) | 27.29 (9.2%) | 16.24 (5.5%) | 91.54 (30.7%) | 74.47 |
| VAR03 | 7.2 (60.2%) | 0.52 (4.3%) | 0.47 (3.9%) | 3.78 (31.6%) | 2.99 |
| VAR04 | 524 (91.4%) | 7.66 (1.3%) | 4.28 (0.7%) | 37.43 (6.5%) | 143.34 |
| VAR05 | 516.6 (94.8%) | 2.04 (0.4%) | 2.74 (0.5%) | 23.73 (4.4%) | 136.28 |
| VAR06 | 7.4 (27.2%) | 5.46 (20.1%) | 1.49 (5.5%) | 12.86 (47.3%) | 6.80 |
| VAR07 | 0.6 (11.3%) | 3.28 (61.9%) | 0.07 (1.3%) | 1.35 (25.5%) | 1.33 |
| VAR08 | 12 (37.0%) | 1.48 (4.6%) | 2.12 (6.5%) | 16.81 (51.9%) | 8.10 |
| VAR09 | 284.4 (48.9%) | 38.69 (6.6%) | 39.58 (6.8%) | 219.24 (37.7%) | 145.48 |
| VAR10 | 81.8 (45.2%) | 10.10 (5.6%) | 13.89 (7.7%) | 75.03 (41.5%) | 45.20 |
| Cluster Average | 179.22 (52.4%) | 13.29 (12.4%) | 10.22 (4.4%) | 59.56 (30.8%) | 65.57 |
| Variables | Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | Cluster 3 | Cluster 4 | Average of Variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAR01 | 23 (36.2%) | 25.4 (40.0%) | 4.43 (7.0%) | 10.63 (16.8%) | 15.87 |
| VAR02 | 10.45 (30.0%) | 16.4 (47.0%) | 2.39 (6.9%) | 5.62 (16.1%) | 8.72 |
| VAR03 | 0.09 (3.0%) | 2.8 (92.7%) | 0.08 (2.6%) | 0.05 (1.7%) | 0.76 |
| VAR04 | 29.73 (77.9%) | 6.7 (17.6%) | 0.43 (101%) | 1.28 (3.4%) | 9.54 |
| VAR05 | 1.55 (25.4%) | 4.35 (71.2%) | 0.12 (2.0%) | 0.09 (1.5%) | 1.52 |
| VAR06 | 26.18 (88.7%) | 2.0 (6.8%) | 0.27 (0.9%) | 1.08 (3.7%) | 7.38 |
| VAR07 | 2.91 (37.7%) | 1.7 (22.0%) | 0.74 (9.6%) | 2.36 (30.6%) | 1.93 |
| VAR08 | 9.73 (73.7%) | 2.2 (16.7%) | 0.25 (1.9%) | 1.02 (7.7%) | 3.30 |
| VAR09 | 77.55 (58.5%) | 25.65 (79.5%) | 7.14 (5.4%) | 22.18 (16.7%) | 33.13 |
| VAR10 | 50.09 (67.3%) | 11.85 (15.9%) | 2.64 (3.5%) | 9.81 (13.2%) | 18.60 |
| Cluster Average | 23.13 (49.8%) | 9.91 (34.9%) | 1.85 (4.1%) | 5.41 (11.1%) | 10.07 |
| Characterization of Interactions | Educational Clusters | Description of Student Profiles | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elementary School | High School | ||
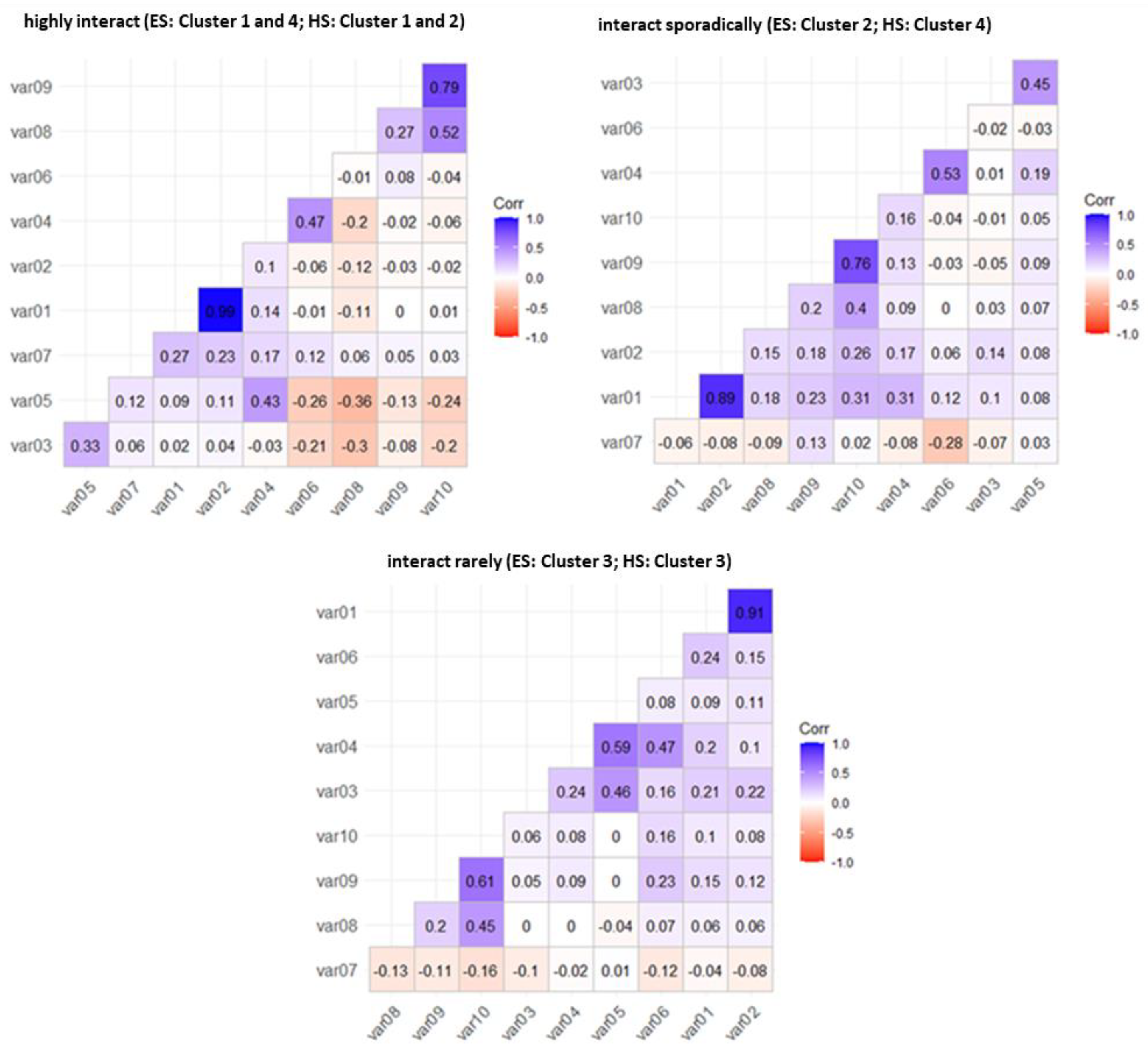
| Highly interact | Clusters 1 and 4 42 (8.3%) | Clusters 1 and 2 31 (6.8%) | The students present in this group were the ones who interacted the most among the others. They have a higher number of friends in the virtual environment, send more messages to colleagues and teachers, and sent few messages have more interactions via forums when asking for help and making comments. They receive more responses to posts made. This group has more interactive students in the virtual environment, representing a percentage of 83.2% of the interactions that took place among elementary school students and 84.7% in high school. However, the percentage of students represented in this group is low, 8.3% in elementary school and 6.8% in high school. |
| Sporadically interact | Cluster 2 113 (32.5%) | Cluster 4 234 (51.0%) | Students in this group have the characteristics of being in occasional interactions mediated by the virtual environment. From the correlations of the variables observed, few messages were sent to colleagues and teachers. However, they are reduced to carrying out exercises. However, performing the exercises. The group has percentages of interactions of 12.4% for elementary school students and 11.1% for high school students. The number of students in this group is quite representative, 32.5% in elementary school and 51% in high school. |
| Rarely interact | Cluster 3 298 (59.1%) | Cluster 3 194 (42.3%) | This group was considered to have the worst level of interaction among the others, given that the students present in this group have few friends, send few messages, and have low values for the variables observed. They have lower interaction levels: 4.4% in elementary school and 4.1% in high school. However, the group represents 59.1% of elementary school students and 42.3% of high school students, which is quite representative. |
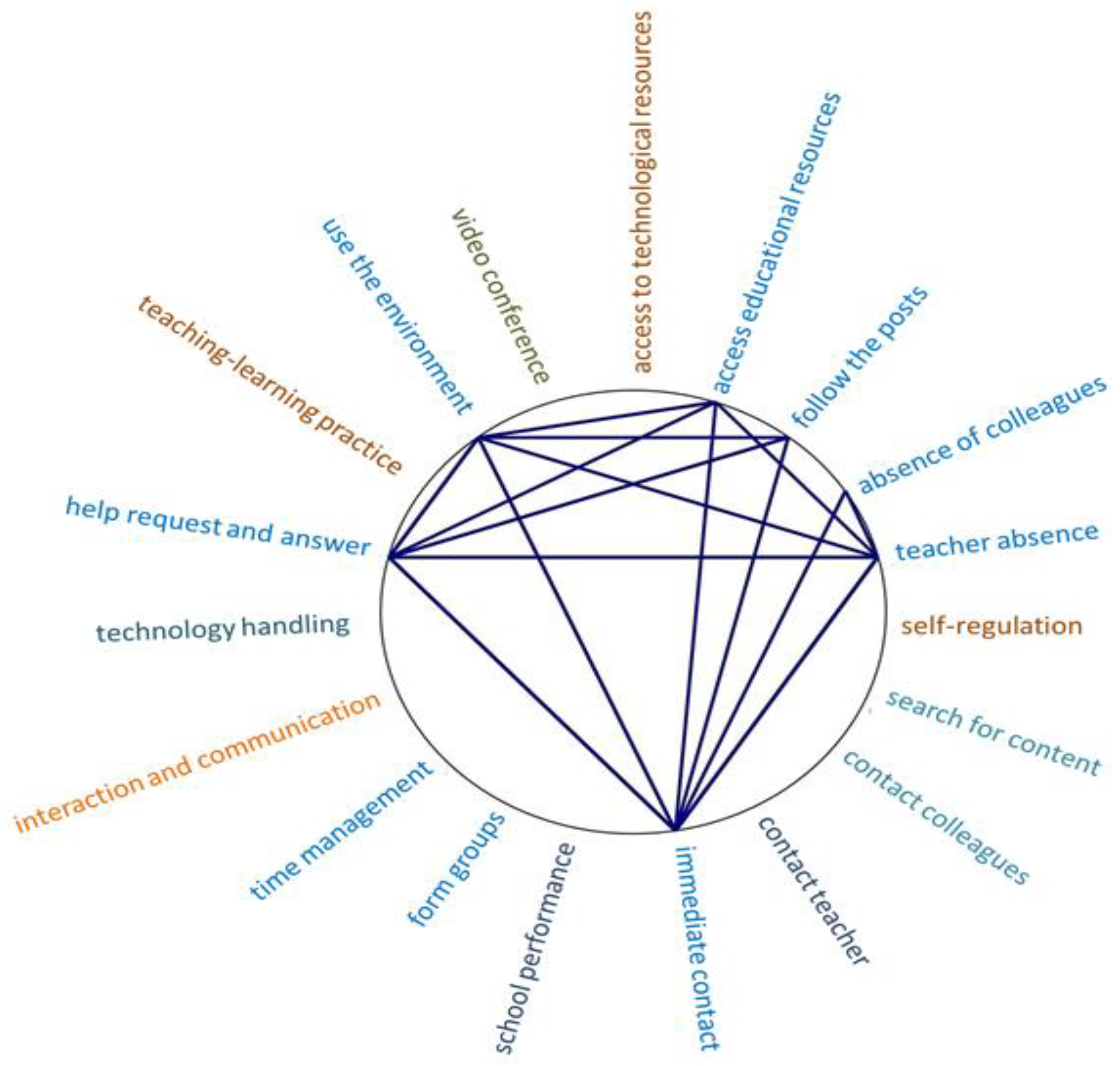
| Dimension | Strategies | Description of Data Collected in the Category |
|---|---|---|
| In the virtual environment Redu | Access to educational resources | Access to digital classroom materials posted in the virtual environment regarding the possibility of viewing, retaining, and sharing. |
| Following the posts | Descriptions of reciprocal interaction in which teachers post and students follow their posts, view comments, and ask for help. | |
| Absence of colleagues | Situations in which they want the presence of other students in the environment. | |
| Absence of teacher | Situations in which they want the presence of teachers in the environment. | |
| Immediate contact | Interactions or circumstantial interactional needs to receive urgent responses. | |
| Help request and response | Reciprocal interaction in case of doubts and questions. | |
| Use of environment | A result of mediation and use of resources made available in the virtual environment Redu. | |
| External to the virtual environment Redu | Search for content | Acts inherent to the need to complement studies with digital educational resources or not. |
| Contacting colleagues | Description of moments of reciprocal interaction between a student and one or more colleagues in a bidirectional way. | |
| Contacting teacher | Bidirectional reciprocal student–teacher interaction. | |
| Formation of groups | The reciprocal interaction between three or more members to communicate with each other. | |
| Video conference | Reciprocal interaction situations mediated by multimedia resources (video, audio, among others) in real time, which occurred through platforms other than the virtual environment of this study. | |
| Difficulties | Access to technological resources | Impossibility of access to computers, cell phones, internet. |
| Self-regulation | Strategic situations to manage resources in the teaching–learning process. | |
| School performance | Indicative of how the teaching–learning process is going. | |
| Time management | Procedures for organization, management, and planning of studies. | |
| Interaction and communication | Unmet needs regarding dynamism and proximity in interactional and communication needs. | |
| Technology handling | Evidence of problems in understanding and using technological resources and educational technology. | |
| Teaching–learning practice | Circumstances of adaptation to methods and methodologies adopted by teachers in the teaching–learning context, because, in some, teachers continue to use classroom teaching practices, and these are not appropriate for the teaching modality mediated by technologies. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pereira, A.J.; Gomes, A.S.; Primo, T.T.; Rodrigues, R.L.; Júnior, R.P.M.; Moreira, F. Learning Mediated by Social Network for Education in K-12: Levels of Interaction, Strategies, and Difficulties. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13020100
Pereira AJ, Gomes AS, Primo TT, Rodrigues RL, Júnior RPM, Moreira F. Learning Mediated by Social Network for Education in K-12: Levels of Interaction, Strategies, and Difficulties. Education Sciences. 2023; 13(2):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13020100
Chicago/Turabian StylePereira, Aluisio José, Alex Sandro Gomes, Tiago Thompsen Primo, Rodrigo Lins Rodrigues, Ronaldo Pereira Melo Júnior, and Fernando Moreira. 2023. "Learning Mediated by Social Network for Education in K-12: Levels of Interaction, Strategies, and Difficulties" Education Sciences 13, no. 2: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13020100
APA StylePereira, A. J., Gomes, A. S., Primo, T. T., Rodrigues, R. L., Júnior, R. P. M., & Moreira, F. (2023). Learning Mediated by Social Network for Education in K-12: Levels of Interaction, Strategies, and Difficulties. Education Sciences, 13(2), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13020100








