Use of a Gamified Platform to Improve Scientific Writing in Engineering Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Gamification and Writing
2.2. Scientific Writing in Engineering
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Design
3.2. Participants
3.3. Instrument to Assess Knowledge
3.4. Description of the Gamified Platform
3.5. Course Description and Course/Program Structure
3.6. Validation of the Gamified Platform through Expert Judgment
3.7. Participants in the Experimental Group for the Use of the Gamified Platform
3.8. Instrument for Satisfaction with the Use of the Gamified Platform
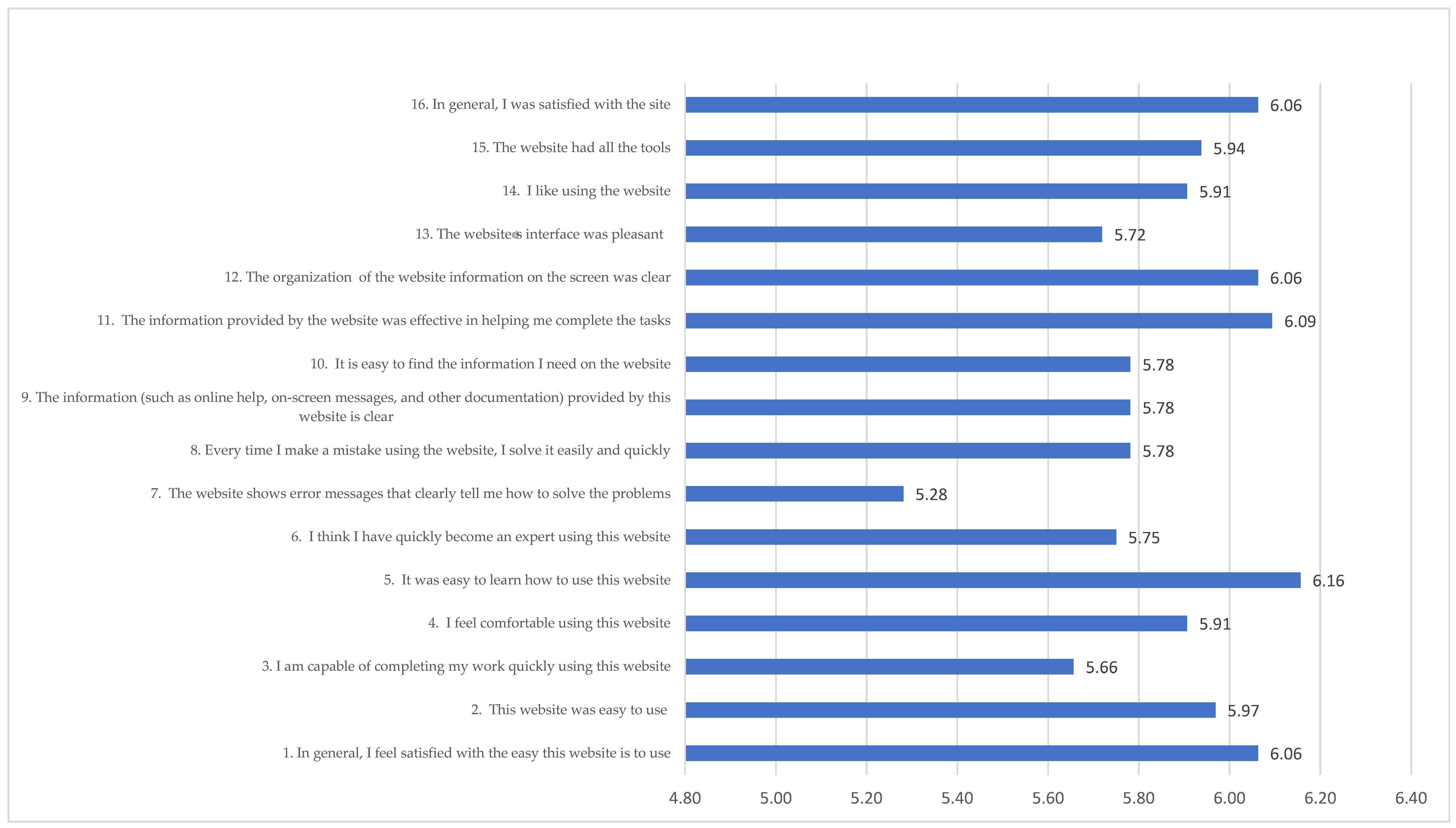
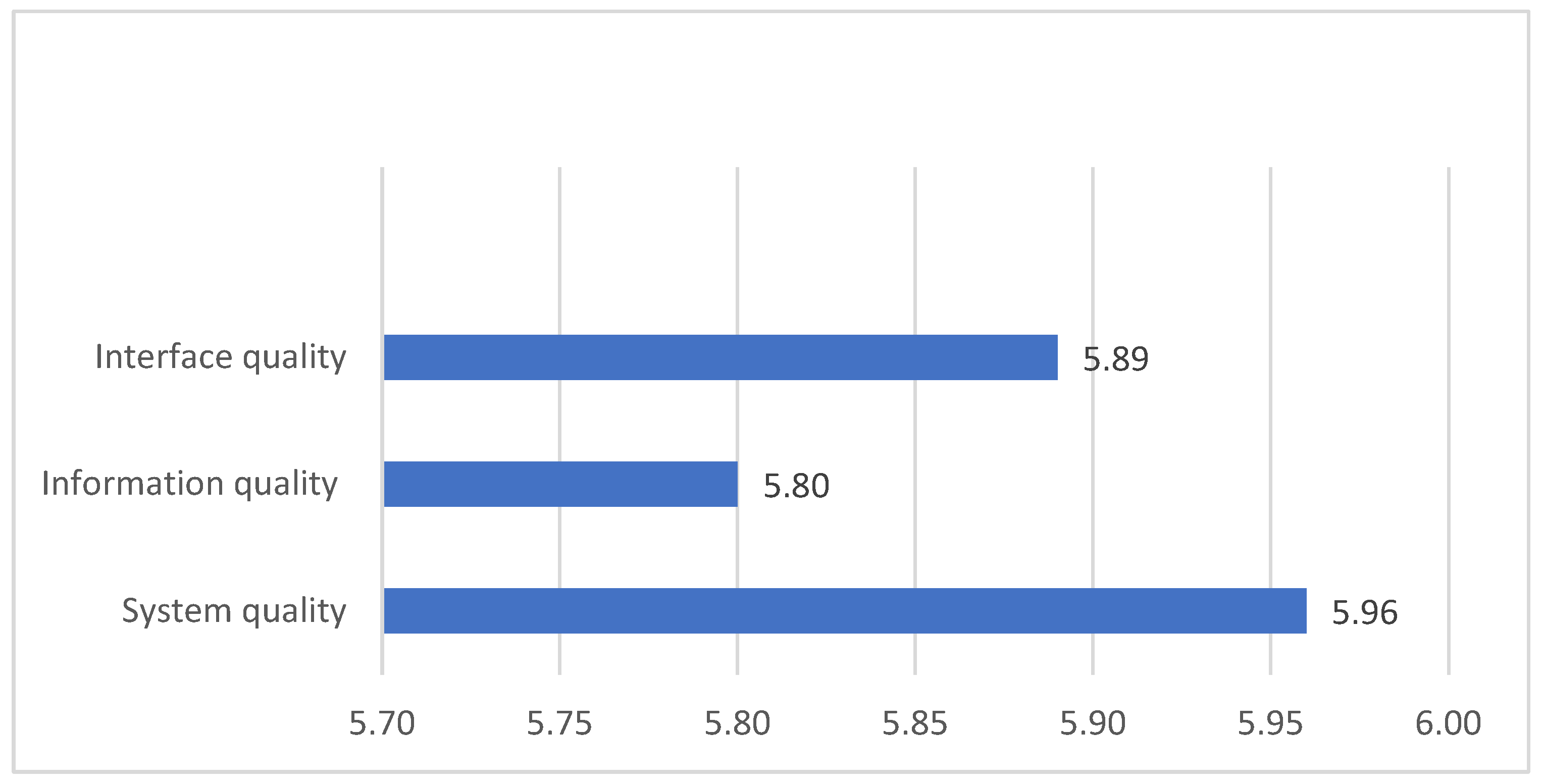
4. Results
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mandow, A.; Martínez, J.; García-Cerezo, A. Project-based learning of scientific writing and communication skills for postgraduate students. In Proceedings of the IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), Madrid, Spain, 22–25 October 2014; pp. 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Refaei, B. Problem-based learning pedagogy fosters students’ critical thinking about writing. Interdiscip. J. Probl.-Based Learn. 2017, 11, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Y.; Hew, K.; Chiu, K. Improving Hong Kong Secondary School Students’ Argumentative Writing: Effects of a Blended Learning Approach and Gamification. Lang. Learn. Technol. 2018, 22, 97–118. Available online: https://cutt.ly/IYz9VCt (accessed on 8 July 2023).
- Deterding, S.; Dixon, D.; Khaled, R.; Nacke, L. From game design elements to gamefulness. In Proceedings of the 15th International Academic MindTrek Conference on Envisioning Future Media Environments—MindTrek ’11, Tampere, Finland, 28–30 September 2011; pp. 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, C.; Walsh, C.; Swinger, N.; Auerbach, M.; Castro, D.; Dewan, M.; Khattab, M.; Rake, A.; Harwayne-Gidansky, I.; Raymond, T.; et al. Gamification in Action: Theoretical and Practical Considerations for Medical Educators. Acad. Med. 2018, 93, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huotari, K.; Hamari, J. Defining gamification. In Proceeding of the 16th International Academic MindTrek Conference on MindTrek ’12, Tampere, Finland, 3–5 October 2012; pp. 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Manzano, A.; Almela-Baeza, J. Gamification and transmedia for scientific promotion and for encouraging scientific careers in adolescents. Comunicar 2018, 55, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dichev, C.; Dicheva, D. Gamifying education: What is known, what is believed and what remains uncertain: A critical review. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2017, 14, 9. Available online: https://bit.ly/2tDUWoA (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Villalustre Martínez, L.; del Moral Pérez, M.E. Gamificación: Estrategia para optimizar el proceso de aprendizaje y la adquisición de competencias en contextos universitarios. Digit. Educ. Rev. 2015, 27, 13–31. Available online: https://raco.cat/index.php/DER/article/view/299734 (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- Prieto Andreu, J.M. Una revisión sistemática sobre gamificación, motivación y aprendizaje en universitarios. T. Educ. 2020, 32, 73–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicen, H.; Kocakoyun, S. Perceptions of students for gamification approach: Kahoot as a case study. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2018, 13, 72–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozada-Ávila, C.; Betancur-Gómez, S. La gamificación en la educación superior: Una revisión sistemática. Rev. Ing. Univ. De Medellín 2017, 16, 97–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, M.; Escudero-Nahón, A.; Canchola-Magdaleno, S. “Gamificación” de la enseñanza para ciencia, tecnología, ingeniería y matemáticas: Cartografía conceptual. Sinéctica 2020, 54, e1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, G.; Ríos, J. Gamificación como estrategia de aprendizaje en la formación de estudiantes de Ingeniería. Estud. Pedagógicos 2019, 45, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bybee, R. Advancing STEM Education: A 2020 Vision. Technol. Eng. Teach. 2010, 70, 30–35. Available online: https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ898909 (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Núñez-Pacheco, R.; Espinoza-Montoya, C.; Yucra-Quispe, L.M.; Turpo-Gebera, O.; Aguaded, I. Serious video games in engineering education: A scoping review. J. Technol. Sci. Educ. 2023, 13, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Polo, F.; Sánchez-Martín, J.; Hipólito-Ojalvo, F.; Luque-Sendra, A. Utilización de la gamificación para el desarrollo de competencias transversales en el grado de Ingeniería Mecánica. In Proceedings of the XXIII Congreso Internacional de Dirección e Ingeniería de Proyectos, Málaga, Spain, 10 July 2019; pp. 1957–1967. Available online: https://idus.us.es/handle/11441/137376 (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- El Tantawi, M.; Sadaf, S.; Al Humaid, J. Using gamification to develop academic writing skills in dental undergraduate students. Eur. J. Dent. Educ. 2018, 22, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, A.; Ágredo, A. Implementando una metodología de gamificación para motivar la lectura y escritura en jóvenes universitarios. Kepes 2016, 13, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira, J.; Serna, R.; Bernabé, C. Nuevas estrategias digitales para la Educación Literaria: Gamificación y narrativas transmedia en constelaciones literarias. In Tecnología, Innovación e Investigación en Los Procesos de Enseñanza-Aprendizaje; Roig-Vila, R., Ed.; Octaedro: Barcelona, Spain, 2016; pp. 2968–2976. [Google Scholar]
- González-Cabrera, J.; Castro-Villalobos, S. Gamificación y el desarrollo de la destreza de la escritura en estudiantes de inglés como lengua extranjera. INNOVA Res. J. 2022, 7, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S. Academic Writing: A Handbook for International Students, 2nd ed.; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chura-Quispe, G.; García-Castro, R.; Llapa-Medina, M.; Salamanca-Chura, E. Efecto del Flipped Classroom virtual en la escritura académica: Autopercepción de universitarios. Pixel-Bit Rev. Medios Educ. 2022, 65, 121–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee-Rad, H.; Namaziandost, E.; Razmi, M.H. Integrating STAD and flipped learning in expository writing skills: Impacts on students’ achievement and perceptions. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 2022, 55, 710–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelló, M.; Mateos, M.; Castells, N.; Iñesta, A.; Cuevas, I.; Solé, I. Prácticas de redacción académica en las universidades españolas. Electron. J. Res. Educ. Psychol. 2012, 10, 569–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlino, P. El proceso de escritura académica: Cuatro dificultades de la enseñanza universitaria. Educere Rev. Venez. Educ. 2004, 8, 321–327. Available online: https://cutt.ly/JYz2Upz (accessed on 21 June 2023).
- Boillos, M.M. La autopercepción de las habilidades escritoras en el inicio de la etapa universitaria. Ens. Rev. Esc. Univ. Form. Profr. Albacete 2018, 33, 149–158. Available online: http://www.revista.uclm.es/index.php/ensayos (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Pollington, M.F.; Wilcox, B.; Morrison, T.G. Self-perception in writing: The effects of writing workshop and traditional instruction on intermediate grade students. Read. Psychol. 2001, 22, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vine-Jara, A.E. La escritura académica: Percepciones de estudiantes de Ciencias Humanas y Ciencias de la Ingeniería de una universidad chilena. Íkala Rev. De Leng. Y Cult. 2020, 25, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Fernández, J.; Corcelles, M.; Bañales, G.; Castelló, M.; Gutiérrez-Braojos, C. Exploring conceptions about writing and learning: Undergraduates’ patterns of beliefs and the quality of academic writing. Electron. J. Res. Educ. Psychol. 2016, 14, 107130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology (ABET). Criteria for Accrediting Enginering Programs. 2023. Available online: https://bit.ly/48V1KT0 (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Steiner, D.G. The communication habits of engineers: A study of how compositional style and time affect the production of oral and written communication of engineers. J. Tech. Writ. Commun. 2011, 41, 33–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, V.O. Hints on writing technical papers and making presentations. IEEE Trans. Educ. 1999, 42, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pierson, M.M.; Pierson, B.L. Beginnings and endings: Keys to better engineering technical writing. IEEE Trans. Prof. Commun. 1997, 40, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shaw, M. Writing good software engineering research papers. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Software Engineering, IEEE Computer Society, Portland, OR, USA, 3 May 2003; pp. 726–736. [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn, R.; Renaud-Assemat, I. Developing technical report writing skills in first and second year engineering students: A case study using self-reflection. High. Educ. Pedagog. 2020, 5, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.L.; Sloan, J.A. Implementing technical communication instruction in a civil engineering course: The value of knowledge surveys and peer review. J. Civ. Eng. Educ. 2023, 149, 05023004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K.; Slaboch, P.E.; Jamshidi, R. Technical writing improvements through engineering lab courses. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Educ. 2022, 50, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, N.B.A.; Balakrishnan, S.; Hamdzah, N.A.; Mokhtar, S.A. Academic Writing Course Evaluation: Perspective of Engineering Students. Int. J. Nanoelectron. Mater. 2022, 15, 209–218. Available online: http://eprints.utem.edu.my/id/eprint/26561/ (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Zemliansky, P.; Berry, L. A writing-across-the-curriculum faculty development program: An experience report. IEEE Trans. Prof. Commun. 2017, 60, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, E. Programa de Redacción de Artículos Basado en los Estándares Internacionales IEEE para la Mejora de la Competencia de Comunicación Escrita de los Estudiantes de Ingeniería de la Universidad Nacional de San Agustín de Arequipa – Perú. Ph.D. Dissertation, Universidad Nacional de San Agustín de Arequipa, Arequipa, Perú, 2021. Available online: https://repositorio.unsa.edu.pe/items/7de29979-f04f-4fda-8d05-7e80de2986b6 (accessed on 29 May 2023).
- Jauregui-Velarde, R.; Conde-Arias, F.; Herrera-Salazar, J.L.; Cabanillas-Carbonell, M.; Andrade-Arenas, L. Mobile Application Design: Sale of Clothes Through Electronic Commerce. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2022, 13, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedlefs-Aguilar, M.; de la Garza-Gonzáles, A.; Sánchez-Miranda, M.; Garza-Villegas, A. Adaptación al español del Cuestionario de Usabilidad de Sistemas Informáticos CSUQ. RECI Rev. Iberoam. De Las Cienc. Comput. E Inform. 2015, 4, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera, D.; Arnedo-Moreno, J. κPAX: Experiences on designing a gamified platform for serious gamin. Form. Assess. Learn. Data Anal. Gamification 2016, 1, 271–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz Sanabria, L.; Vargas Ordoñez, L. EDUMAT: Herramienta web gamificada para la enseñanza de operaciones elementales. Campus Virtuales 2019, 8, 9–17. Available online: http://uajournals.com/ojs/index.php/campusvirtuales/article/view/489/343 (accessed on 25 July 2023).
- Smithsonian Science Education Center. The STEM Imperative. 2019. Available online: https://ssec.si.edu/stem-imperative (accessed on 27 July 2023).
- Longo, B. Writing like an engineering professional. In Proceedings of the IEEE Women in Engineering (WIE) Forum USA East, Baltimore, MD, USA, 30 November–2 December 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, R.; Willey, K. “It’s not my job to teach writing”: Activity theory analysis of [invisible] writing practices in the engineering curriculum practices in the engineering curriculum. J. Acad. Lang. Learn. 2016, 10, A118–A129. Available online: https://journal.aall.org.au/index.php/jall/article/view/383 (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Lombardo, S.J. Teaching technical writing in a lab course in chemical engineering. Chem. Eng. Educ. 2010, 44, 58–62. Available online: https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ877806 (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- Walton, G. Writing skills development in an engineering geology course through practice and feedback on report submissions using a rubric. J. Geosci. Educ. 2020, 68, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
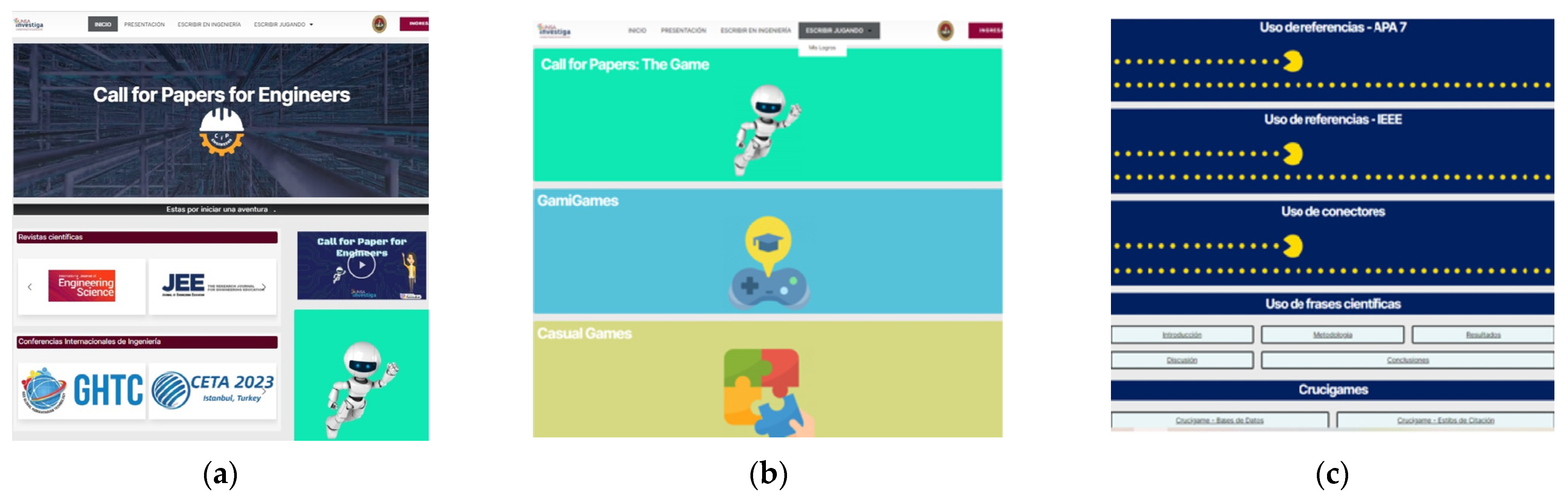
| Missions to Be Completed. | Resources Used |
|---|---|
| Quest 1: Selection and reading of the specialty thesis | Thesis repository |
| Quest 2: Adaptation of the thesis into a scientific article format | Gamified platform Call for Papers for Engineers |
| Quest 3: Searching for articles in databases | Google Scholar, Scielo Scopus, Web of Science |
| Quest 4: Article planning | Gamified platform Call for Papers for Engineers |
| Quest 5: Article writing | Gamified platform Call for Papers for Engineers |
| Quest 6: Revision of the article | Gamified platform Call for Papers for Engineers, virtual classroom |
| Quest 7: Dissemination of the article | YouTube and Facebook platforms |
| Gamified Activities | Description of Activity |
|---|---|
| GamiChallenge 1: Reading articles | Students read scientific articles related to the area of engineering. |
| GamiChallenge 2: Elements of the abstract | Students rearranged the elements of the abstract: background, methodology, results, and conclusion. |
| GamiChallenge 3: Relationship between abstract and keywords | Students should select keywords from the abstracts of the articles. |
| GamiChallenge 4: Using APA7 and IEEE references | Students should check for correctness of references in APA7 or IEEE styles. |
| GamiChallenge 5: Using connectors | Students should identify the different types of connectors. |
| GamiChallenge 6: Use of scientific phrases | Students should identify the most common scientific phrases for each part of the article. |
| GamiChallenge 7: CruciGame1 and CruciGame2 | Students should solve the proposed crossword puzzles. |
| GamiChallenge 8: Call for papers: The Game | Students should play the game Call for Papers: The Game. |
| Criteria | Design |
|---|---|
| P1 | Does the platform have a simple interface? |
| P2 | Does the platform present a pleasant visual environment? |
| P3 | Is the information on the platform well organized? |
| Criteria | Usability |
| P4 | Is the platform intuitive and easy to use? |
| P5 | Does the platform offer easy navigation? |
| P6 | Is the information on the platform user-friendly? |
| Criteria | Content |
| P7 | Is the content of the platform appropriate for teaching scientific writing in engineering? |
| P8 | Does the platform present valuable content for teaching engineering science writing? |
| P9 | Are the contents of the platform motivating for students? |
| Criteria | Instructional quality |
| P10 | Are the contents of the platform clear? |
| P11 | Do the exercises proposed on the platform facilitate the learning of scientific writing? |
| P12 | Does the use of the platform in general promote the learning of scientific writing in engineering? |
| Criteria | Question | Mean | DS | Nivel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Design | P1 | 2.33 | 0.577 | High |
| P2 | 2.67 | 0.577 | High | |
| P3 | 2.67 | 0.577 | High | |
| Usability | P4 | 2.33 | 0.577 | High |
| P5 | 2.67 | 0.577 | High | |
| P6 | 2.67 | 0.577 | High | |
| Contents | P7 | 3.00 | 0.000 | High |
| P8 | 3.00 | 0.000 | High | |
| P9 | 2.67 | 0.577 | High | |
| Instructional quality | P10 | 3.00 | 0.000 | High |
| P11 | 2.67 | 0.577 | High | |
| P12 | 2.67 | 0.577 | High |
| Knowledge | Experimental Group | Control Group | t (58) | p | Cohen’s d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | DS | M | DS | ||||
| Pre-test | 12 | 3.2 | 13.11 | 2.79 | −1.416 | 0.162 | |
| Post-test | 15.82 | 2.56 | 13.26 | 3.28 | 3.385 | 0.001 | 0.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Núñez-Pacheco, R.; Vidal, E.; Castro-Gutierrez, E.; Turpo-Gebera, O.; Barreda-Parra, A.; Aguaded, I. Use of a Gamified Platform to Improve Scientific Writing in Engineering Students. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13121164
Núñez-Pacheco R, Vidal E, Castro-Gutierrez E, Turpo-Gebera O, Barreda-Parra A, Aguaded I. Use of a Gamified Platform to Improve Scientific Writing in Engineering Students. Education Sciences. 2023; 13(12):1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13121164
Chicago/Turabian StyleNúñez-Pacheco, Rosa, Elizabeth Vidal, Eveling Castro-Gutierrez, Osbaldo Turpo-Gebera, Aymé Barreda-Parra, and Ignacio Aguaded. 2023. "Use of a Gamified Platform to Improve Scientific Writing in Engineering Students" Education Sciences 13, no. 12: 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13121164
APA StyleNúñez-Pacheco, R., Vidal, E., Castro-Gutierrez, E., Turpo-Gebera, O., Barreda-Parra, A., & Aguaded, I. (2023). Use of a Gamified Platform to Improve Scientific Writing in Engineering Students. Education Sciences, 13(12), 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13121164







