Abstract
In the last decade, the extensive use of new Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) in education in recent years has changed the nature of the teaching–learning environment. However, the adequate use of ICT is necessary for promoting educational practices that contribute to sustainable development. The systematization of the research in this area is presented as an opportunity to provide a contribution to the already existing theories and practices related to the use of ICT and the development of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The aim of this study is to conduct a systematic review of articles that address innovative approaches to sustainability in digital education. The PRISMA 2020 guidelines were used to review the literature of articles published in the last decade in the Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus databases. The results presented are based on the research questions that will guide the search and analysis of the information. They are divided into theoretical and practical research, giving relevance to the relationship between educational innovation with ICT and sustainability. The main variables that are taken into account in contributing to the SDGs through the use of ICT in educational practice are also presented. A critical discussion on this topic is elaborated, which will help to support a solid theoretical framework. Last, a conclusion on the effectiveness of digital education and its contribution to a sustainable development are provided.
1. Introduction
Education is undoubtedly the basis for a country’s sustainable development in any of its three dimensions: economic, social, and environmental. It is an important factor in eliminating inequalities and contributing to poverty reduction. One of the challenges in education today is training new generations in the fulfillment of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the 2030 agenda. Education is one of the most effective ways to contribute to the implementation of sustainability [1]. The global health crisis triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic revealed major shortcomings in the pedagogical integration of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT), raising awareness that digital competence is no longer an option, but a necessity [2].
From the educational practice itself, at any level of education, it is necessary to promote good academic results in students, forming responsible citizens capable of solving problems associated with any of the SDGs. In this sense, the use of ICTs is vital in the knowledge society, where technological tools mediate in different daily aspects, including education, health, and government management [3].
Several educators and researchers have contributed to the research of sustainability, not only in the theory, but also in the practice of it. In the last decade, some systematic reviews and mappings have been published which delve deeper into the trends of Educational Sustainability [4]. Some of these reviews focus only on one level of education, such as higher education [5], while others only base their analysis on environmental sustainability [6], and many do not consider innovation in digital education [7]. Recent research reaffirms that even though there is a lot of research on Sustainability in Education, it is still considered insufficient [8], as there is a lack of studies that systematise the innovative proposals that contribute to meeting the challenges of educational sustainability, especially “Sustainable Development Goal 4” (Ensure inclusive, equitable and quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all).
In this sense, with regard to digital education, it is necessary to answer, among others, the following questions: What are the main challenges of sustainability in digital education? In addition, in coherence with this question, how do we overcome these challenges from educational innovation? This motivated us to carry out this systematic review. These and other questions will be answered in the following systematic review.
Digital Education, Innovation, and Sustainability
Digital education is the innovative incorporation of modern technology and digital tools to support and strengthen teaching and learning activities [2]. Some authors state that digital education goes far beyond virtual or distance learning; it establishes the use of technological resources to contribute to higher quality education [4]. Not only does this involve the integration of digital devices and tools, but it also involves an educational transformation that improves learning in the classroom. This vision will help schools to advance and students to adapt to new jobs [9].
Digital education is not just a concept, but a set of facts that triggered a new way of imparting knowledge and using it as an instrument of technology to meet a goal [10]. In particular, digital education seeks to: enhance skills such as problem solving, critical thinking, creativity, team work, and communication, generating autonomous people who assume individual and collective responsibilities [11].
The aforementioned digital education requires constant innovation. Specifically, innovation in education implies a radical transformation of the educational model. It is necessary to unlearn the model focused on information, memorisation and verticality, and to build models based on active learning methodologies, learning to learn, self-regulation of learning, and collaborative and cooperative work [12].
Thus, when we talk about educational innovation, the notions of change and reform are strongly intermingled. We understand the concept of educational innovation based on the following characteristics [13]:
- ▪ It implies an idea perceived as novel by someone, and at the same time includes the acceptance of this novelty.
- ▪ It implies a change that seeks the improvement of an educational practice.
- ▪ It is a deliberate and planned effort aimed at the qualitative improvement of educational processes.
- ▪ It involves learning for those who are actively involved in the innovation process.
Education and digital innovation must contribute to sustainable development [2]. The sustainability of education is based on the three fundamental pillars of sustainable development: social, economic, and environmental sustainability [14]. The reconciliation and synchrony of these factors is a firm basis for the viability of a harmonious project with the terms and society. However, these projects are difficult to achieve. Sustainable development is a long-term approach to managing both the environment and the economy, without sacrificing one for the other. It seeks to meet human needs today without compromising the ability to meet those needs in the future [15]. Education for sustainable development is key to achieving these goals.
The fundamental purpose of sustainable education is to integrate the values inherent in sustainable development into all facets of learning with a view of fostering the behavioral changes needed to achieve a more sustainable and just society for all [5]. Last, it is important to note that the main features of education for sustainability are [1]:
- ▪ It develops critical thinking, confronts dilemmas, and allows the search for solutions to problems.
- ▪ It is action oriented. Awareness alone does not produce change. Beyond awareness, sustainability in education must promote commitment.
- ▪ It involves participation in decision making, including those related to the environment and how we learn.
2. Materials and Methods
A systematic review is based on the compilation of the results of scientific research published over a period according to previous selection criteria, with the aim of answering specific research questions [16]. The current review followed (PRISMA) guidelines for systematic reviews and meta-analyses [17], and its extension PRISMA-S PRISMA statement for reporting literature searches in systematic reviews [18]. The PRISMA protocol consists of a checklist that governs the correct design of systematic reviews.
Step 1: Purpose of the research. The objective of this research is to conduct a systematic review of articles that address innovative approaches to sustainability in digital education. To meet this objective, research questions were posed around two areas (Table 1): (a) documentary characteristics to identify the year of publication, subjects, geographical location (first author’s country of residence), rank of the journal in its database, and research methodologies used, and (b) pedagogical dimension to determine the SDGs developed, the educational levels, the sustainability challenges addressed, and the innovative practices developed.

Table 1.
Areas, questions, and criteria for special coding.
2.1. Validity Threat Criteria
Step 2: Review protocol
- Internal validity. Each investigation was analysed through a process that included: key words; summary; strategy used; type of investigation.
- External validity. All the investigations that did not validate their results or did not argue the innovation were discarded.
- Validity of the conclusion: The assessment criteria for systematic reviews proposed by the Joanna Briggs Institute [19] and the guidelines for analysing transparency, replicability, and quality were followed [20].
2.2. Selection Procedure, and Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- Selection procedure. The Keywording technique [21] and the Mendeley manager were used to eliminate duplicates.
- Inclusion criteria. (a) Articles published between 2013 and 2022; (b) articles indexed in WoS or Scopus; (c) experimental studies, case studies, innovation proposals; (b) studies that promote sustainability based on the use of technologies (see Supplementary).
- Exclusion criteria: Date of publication, type of research (reviews, tutorials, trials), and relation to the object of study (studies that do not contribute directly to one of the SDGs using ICTs or that do not make any innovative proposal).
2.3. Search Strategy
The WoS and Scopus databases were used for the selection of articles. In these databases the keywords “sustainability”, “education”, and “ICT” were used and the search was limited to within the last 10 years. The search syntaxes were as follows:
WoS: ((TI = (sustainab* AND ICT AND education*))) OR AK = ((sustainab* AND ICT AND education*))
- Scopus: TITLE-KEY (sustainability AND education AND (ICT OR technologies OR technology)) AND PUBYEAR > 2013
2.4. Coding and Quality Criteria
An in-depth analysis of the content of the studies was carried out. Relevant information and knowledge was stored in a data matrix based on what was established for the analysis, synthesis, and grouping of the information [17]. Among the information stored, the following stand out: authors; date of publication; study variables; type of research; and educational level. The Mendeley bibliographic manager was used for data collection.
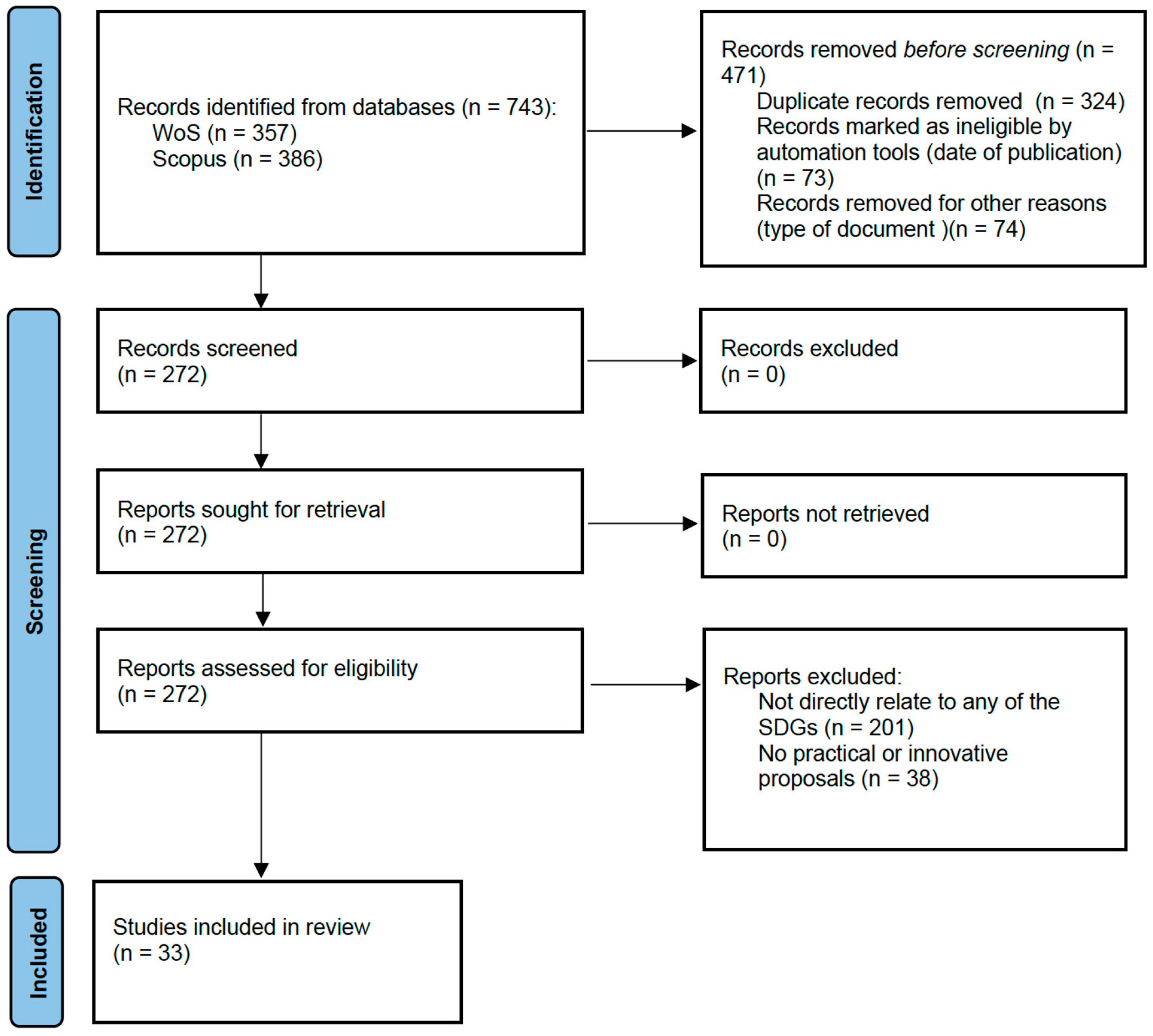
The four researchers, first independently and then by consensus, acted in the different phases of selection according to the criteria for prior inclusion and definitive inclusion in the review. To reduce bias, each study was coded with a rating of “1–5, where 5 is the maximum rating” according to the evaluation of each researcher. The criteria used were the following questions: Are the instruments and the research process described? Are the results argued? Are there references to any SDGs? Figure 1 (PRISMA flow diagram) summarises the procedure followed.
Figure 1.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) figure that demonstrates the study selection process.
3. Results
3.1. RQ1. What Is the Distribution of Articles by Journal and Their Position in the Database?
According to the Q level of the journals, the systematic review is distributed as follows: 21.2% are indexed in quartile 1 (Q1), 63.7% in Q2, 3.0% in Q3, and 12.1% in Q4 (Table 2).

Table 2.
Distribution of articles according to journals and their position in the database.
3.2. RQ2. What Is the Geographical Distribution of the Studies?
The number of countries represented is 18, with the most represented being Spain (42.4%), Romania (6.1%), and South Korea (6.1%). Other countries have only one study published.
3.3. RQ3. What Research Methodologies Are Developed in the Research and, If Any, What Is the Sample Size?
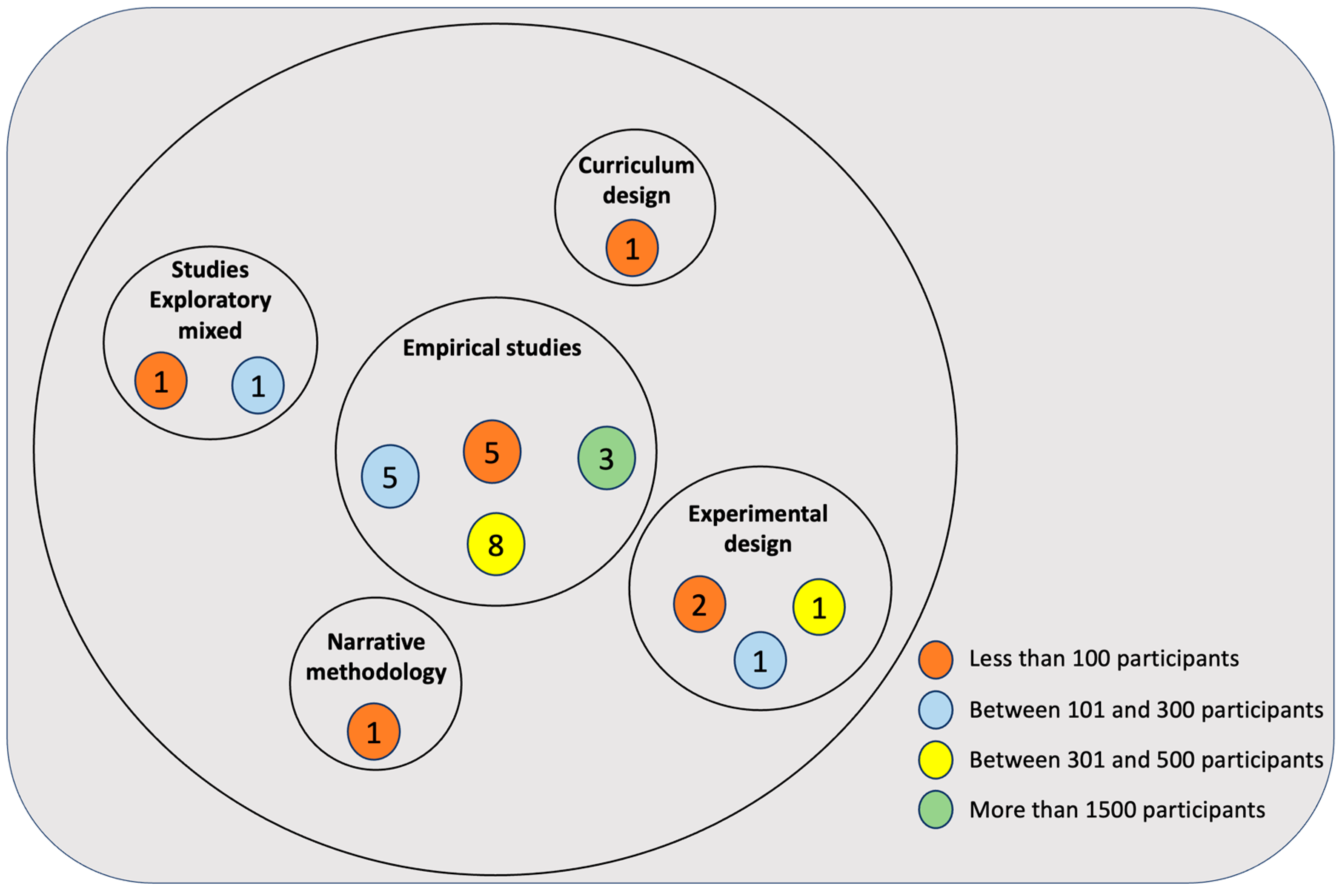
Empirical studies (72, 4.6%) are the most frequent. Experimental (12.1%) and Curricular (9.1%) designs follow, although they are less frequent. The least frequent are Mixed Exploratory (6.1%) and Narrative Methodology (3.0%).
Only 4 studies do not refer to the use of samples. In relation to the others, the most frequent are those using less than 100 participants (30.3%), followed by those studies with samples of between 300 and 1500 subjects (27.3%). In third place are those with a sample size between 101 and 300 participants (21.2%), and at the end are those using more than 1500 subjects (9.1%). Figure 2 summarises the methodologies used and the sample size.
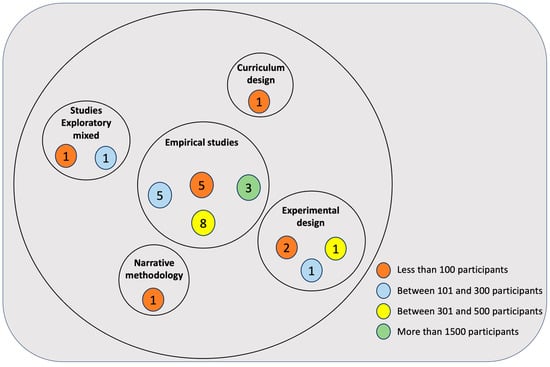
Figure 2.
Distribution and number of articles by research methodology and sample size.
3.4. RQ4. To Which Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Does the Research Refer?
Although all the studies, directly or indirectly, refer to SDG 4 (Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all), only 87.9% of the studies point out accurately and uniquely this SDG 4. On the other hand, 9.1% of the studies place greater emphasis on SDG 13 (Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts) and only 3.0% on SDG 9 (Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialisation and foster innovation).
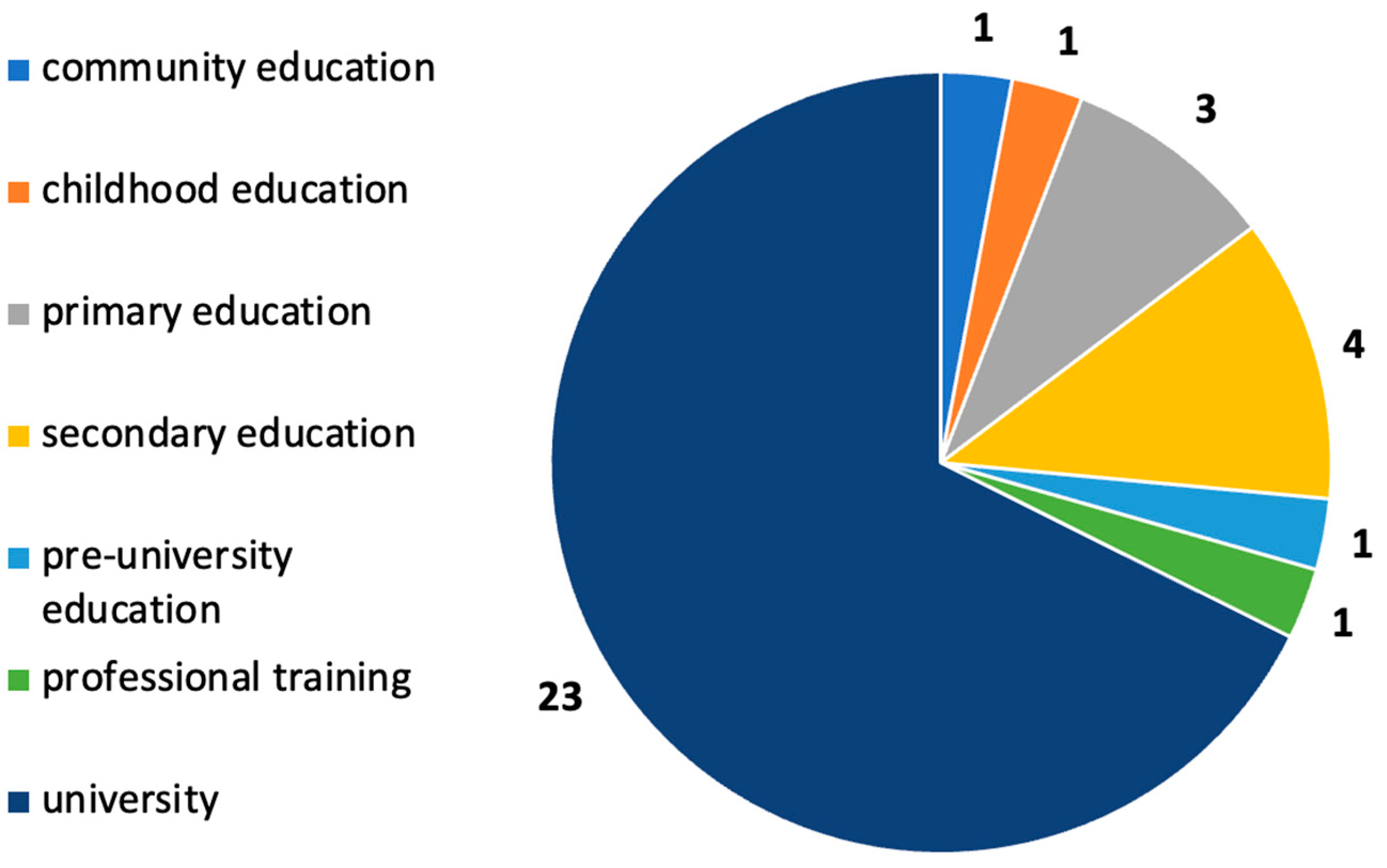
3.5. RQ5. At What Educational Levels Do the Selected Studies Take Place?
Most of the research is carried out at the university level (69.7%). This is followed by primary education (12.1%) and secondary education (9.1%). It is worth noting that one study includes these two levels, whereas only one study (3.0%) represents the levels of infant, high school, vocational training, and community education (Figure 3).
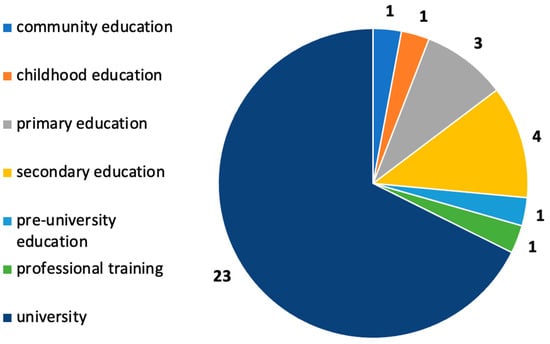
Figure 3.
Educational levels where the selected studies are carried out.
3.6. RQ6. What Sustainability Challenges Does the Selected Research Aim to Solve?
There are several challenges to be solved, all of them related to education through technologies. Among the challenges mostly included are:
- Challenges associated with environmental and ecological sustainability: Researchers seek to create environmental awareness in students through education [22], giving special relevance to the need to achieve ecological sustainability [23] and contribute to the fight against climate change [24].
- Curriculum redesign: It is necessary to rethink the curriculum, promote new training [25] and design educational programs that include topics associated with sustainability in digital education [26].
- Sustainable use of educational technology: This is one of the most common challenges. It is approached from various angles, ranging from the effectiveness of ICT in education [27], the technological savings that need to be made (10), the use of active learning methodologies [28], and the digital divide in the use of ICT [29], among others.
- Inclusive digital education: To ensure that ICT meet everybody’s needs, regardless of the characteristics of each student [30], also promoting as well the development of a variety of strategies, tools, and digital activities [2].
- Particularisation in the teaching of sciences: Encourage digital teaching to be particularised in several specific sciences, such as the teaching of mathematics [31], tourism [32], citizenship education [33], etc.
The challenges are described in detail for each of the 33 research studies that were finally included in the systematic review in Table 3.
3.7. RQ7. What Innovative Practices Are Developed in the Literature?
To respond to the challenges posed, several very interesting innovative practices were developed. Among them, the following are highlighted:
- Design of educational experiences in virtual environments: Creation of virtual courses designed ad hoc [34], e-learning in less favored environments [35], and the analysis of teachers’ competencies to develop online teaching [36].
- Design and validation of instruments: Several instruments were developed to contribute to sustainability in digital teaching from an empirical viewpoint. For example, scales to determine the self-perceived digital competence of teachers [32], as well as an instrument that seeks to assess the influence of the e-portfolio in the activation of sustainable awareness [37].
- Engagement: It is shown how the ethical use of ICTs favors student engagement [38] Similarly, proposals are made for the co-creation of content in digital learning [39].
- Experiments: A few experimental studies are conducted, some for the development of digital competence focused on vulnerable children [2], and others to see the effects of video games on education in sustainability [40].
- Curricular designs: These range from the inclusion of ICTs in the engineering curriculum [41] to the creation of master’s degree programs on sustainable education [25].
Table 3 shows all the innovative practices carried out to contribute to the challenges of sustainability in digital education.

Table 3.
Summary of included articles in the systematic review (n = 33).
Table 3.
Summary of included articles in the systematic review (n = 33).
| Authors/Year | Reference Number | Article Title | Sustainability Challenges | Innovative Proposals |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Colás-Bravo et al., 2018) | [37] | Identification of Levels of Sustainable Consciousness of Teachers in Training through an E-Portfolio | Awareness in the construction of sustainable development | Use of e-portfolio for activation of sustainable awareness |
| (Martínez-Villar et al., 2016) | [22] | Assessing virtual training in environmental awareness for professional groups | Contribution to environmental awareness | Virtual training for environmental awareness |
| (Romero Yesa et al., 2021) | [34] | A good practice for making training accessible to university faculty members through ICTs: syllabus planning support training | Development of sustainable technological tools | Creation of a virtual tool/course for quality education |
| (Shobande & Asongu, 2022) | [24] | The Critical Role of Education and ICT in Promoting Environmental | Fight against climate change | Strategy to reduce the impact of climate change through an empirical study |
| (Kebaetse et al., 2014) | [35] | Integrating eLearning to Support Medical Education at the New University of Botswana School of Medicine | Equitable and quality education | Strategies for implementing e-learning |
| (Kabadayi et al., 2022) | [42] | ICT Equipment in the Kindergartens for Sustainable Education from Kindergarten Principals’ Perspectives in the Czech Republic | Education in sustainability | Analysis of the ICT equipment required for sustainable education |
| (Jeong & González-Gómez, 2020) | [43] | Adapting to PSTs’ Pedagogical Changes in Sustainable Mathematics Education through Flipped E-Learning: Ranking Its Criteria with MCDA/F-DEMATEL | Quality mathematics education | Classification of the criteria for teaching mathematics in the context of the flipped classroom system |
| (Martínez-Borreguero et al., 2020) | [40] | Development of ICT-Based Didactic Interventions for Learning Sustainability Content: Cognitive and Affective Analysis | Education in sustainability | Design and validate ICT-based learning interventions for sustainability content |
| (Hilty & Huber, 2018) | [44] | Motivating students on ICT-related study programs to engage with the subject of sustainable development | Education in sustainability | Proposes specific topics from the field of sustainable development that have the greatest potential to motivate students in ICT-related programs of study |
| (Aguayo & Eames, 2017) | [23] | Promoting community socio-ecological sustainability through technology: A case study from Chile | Ecological sustainability | Design and effective use of technology for community-based learning in ecological awareness |
| (Pertegal-Felices et al., 2020) | [45] | Comparison of the Effects of the Kahoot Tool on Teacher Training and Computer Engineering Students for Sustainable Education | Quality education | Gamification proposal with ICT to increase the probability of success and sustainability of educational institutions |
| (Rodríguez-Loinaz et al., 2022) | [33] | ICT tools and citizen science: a pathway to promote science learning and Education for Sustainable Development in schools | Quality science and sustainability education | Development and implementation of innovative ICT tools that allow teachers to engage their students in activities based on citizen science and sustainability |
| (Deaconu et al., 2018) | [32] | The Use of Information and Communications Technology in Vocational Education and Training—Premise of Sustainability | Teaching tourism from a sustainable perspective | Development of an educational experiment based on the use of ICT to promote better academic performance |
| (Barragán-Sánchez et al., 2020) | [46] | Teaching Digital Competence and Eco-Responsible Use of Technologies: Development and Validation of a Scale | Redesigning education toward sustainable models | Design of a scale to measure the self-perceived digital competence of teachers in relation to the eco-responsible use of technologies |
| (Klimova et al., 2016) | [25] | An international Master’s program in green ICT as a contribution to sustainable development | Redesigning education curricula towards sustainable models | Development of an international master’s degree program entitled “Pervasive computing and communications for sustainable development”. |
| (Ahn, 2020) | [27] | Unequal Loneliness in the Digitalized Classroom: Two Loneliness Effects of School Computers and Lessons for Sustainable Education in the E-Learning Era | Effectiveness of ICT for sustainable education | Study of the relationship between the use of technology and several socio-emotional variables of students |
| (Körtesi et al., 2022) | [31] | Challenging Examples of theWise Use of Computer Tools for the Sustainability of Knowledge and Developing Active and Innovative Methods in STEAM and Mathematics Education | Quality mathematics education | Implementation of active teaching methodologies with software such as computer algebra systems and dynamic geometry systems |
| (Kerras et al., 2022) | [29] | Closing the Digital Gender Gap among Foreign University Students: The Challenges Ahead | Digital divide in the use of ICTs | Empirical study providing an econometric analysis on the existence of a correlation between the gender digital divide and the gender gap in university studies |
| (Song et al., 2022) | [47] | Research on Open Practice Teaching of Off-Campus Art Appreciation Based on ICT | Sustainable development of aesthetic education | Proposal for the appreciation of local art with the support of mobile positioning technology and information platforms |
| (Rangel-Pérez et al., 2021) | [48] | The Massive Implementation of ICT in Universities and Its Implications for Ensuring SDG 4: Challenges and Difficulties for Professors | Quality university education | Study of the relationship between the adaptation of university professors to the massive use of ICT and educational digitalization |
| (Batez, 2021) | [36] | ICT Skills of University Students from the Faculty of Sport and Physical Education during the COVID-19 Pandemic | Quality online education | A study of ICT competence levels for online teaching and learning |
| (Rodríguez-Abitia et al., 2020) | [49] | Digital Gap in Universities and Challenges for Quality Education: A Diagnostic Study in Mexico and Spain | Sustainable use of ICT for education | Quantitative study of the factors that favor the application of technologies to the educational process |
| (Mâță et al., 2020) | [38] | The development and validation of a scale to measure university teachers’ attitude towards ethical use of information technology for a sustainable education | Education in sustainability | Design of a self-administered measurement instrument to obtain data on the ethical attitude of university professors for sustainable education |
| (Al-Rahmi et al., 2020) | [50] | Digital communication: Information and communication technology (ICT) usage for education sustainability | Education in sustainability | Análisis de los factores que influyen en la intención de los estudiantes de utilizar las TIC en una educación sostenible, así como su satisfacción el uso de dichas tecnologías. |
| (Monavvarifard et al., 2019) | [39] | Increasing the sustainability level in agriculture and Natural Resources Universities of Iran through students’ engagement in the value Cocreation process | Engagement to promote sustainable education | Analysis of university and student engagement factors in the process of value co-creation in academic environments |
| (Lim et al., 2019) | [51] | The Digital Divide? Analyzing Regional Differences of Tablet PC Use in Korean Middle Schools for Sustainable Development | Sustainable use of ICT for education | Analysis of the effects of digital learning environments through the use of tablet PCs in Korean metropolitan and rural high schools |
| (Asongu et al., 2019) | [30] | Inequality, information technology and inclusive education in sub-Saharan Africa | Sustainable use of ICTs for inclusive education | Establishment of the thresholds of inequality that must not be exceeded for ICT to promote inclusive education |
| (Berzina, 2019) | [26] | Learning by doing. Case study: Education for sustainable development at the University of Latvia | Redesigning education curricula towards sustainable models | Design of a master’s degree program in education for sustainable development entitled “Natural sciences, global change and technologies for sustainable development” |
| (Kim, 2018) | [52] | ICT and the UN’s sustainable development goal for education: Using ICT to boost the math performance of immigrant youths in the US | Sustainable use of ICT for education | Empirical analysis of the potential of information and communication technologies (ICTs) as a means of providing quality education for all |
| (García et al., 2016) | [53] | La formación docente en la sociedad digital: propiciando la reflexión sobre el impacto medioambiental y social del consumo de tecnología | Contribution to environmental awareness | Characterisation of the consumption, use, and recycling habits of electronic devices of future primary education teachers |
| (Moreno et al., 2013) | [41] | Engineering education for sustainability: A multistakeholder case study on ICT and transportation | Awareness in the construction of sustainable development | Engineering education model in a more sustainable manner |
| (Zhou et al., 2013) | [28] | Facilitating sustainability of education by problem-based learning (PBL) and information and communication technology (ICT) | Use of ICT and active strategies for sustainable education | Use of Problem-Based Learning (as a strategy of the pedagogical approach and the application of ICT as a strategy of the techno-logical approach in quality education) |
| (Casillas-Martín et al., 2020) | [2] | DigiCraft: A Pedagogical Innovative Proposal for the Development of the Digital Competence in Vulnerable Children | Sustainable use of ICT for inclusive education | Development of a technological and pedagogical proposal for the development of digital competence focused on vulnerable children |
4. Discussion
The aim of this study was to conduct a systematic review of articles that address innovative approaches to sustainability in digital education. To this end, we have developed a systematic literature review which was conducted in order to answer the seven research questions considered: the documentary characteristics of the research in terms of database indexing, the pedagogical dimension of the studies, the identification of the related SDGs, the levels of education, the sustainability challenges targeted by the selected research, and the pedagogical and innovative practices developed.
Regarding the distribution of the articles according to their source, it is worth noting that most of them are published in the journal “Sustainability”, most probably because as its name indicates, its objective is to develop topics associated with the SDGs. With regard to the methodologies used, questionnaires prevail in much more descriptive research together with case studies. It would be interesting to observe a greater scientific production that gives relevance to experimental studies due to their high scientific value [31]. Mixed research and proposals for technological tools designed for use in digital education are scarce [34].
On the other hand, it is important to highlight that the vast majority of studies explicitly referred to SDGs 4 (Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all). The findings discovered in this research question make us think about the fact that digital education itself should seek mechanisms that enable the direct contribution to other SDGs on a more regular basis [42].
Most of the studies are developed at the university level. For example, we did not find curricular designs developed at other educational levels. Perhaps a large part of the educational community has not become aware of the relevance of dealing with this subject from an early age [2]. The treatment given to vocational training and non-formal education is almost nil [23].
The most relevant findings of this systematic review are to be found, on the one hand, in the identification of the challenges posed to promote sustainable development through digital education. This framework allows us to know not only the key concepts that articulate current innovative practice, but also the relationships they establish with the SDGs themselves. In this way, we have an indicative “guide” of the current state of knowledge and can contribute to it in future research. This research demonstrated the relevance of technologies to develop digital innovation, either through the creation of technological resources [33] or through their proactive use [37]. However, it would be interesting and perhaps essential to pose challenges that go beyond the mere use of ICT in education, an element that demonstrates the simplicity with which digital education is sometimes characterised [27].
Looking to the role of ICT in educational innovation processes related to sustainability, it is mostly related to the design of gamification and experimentation strategies through virtual simulations (even immersive). These can be very motivating and exciting for students, while facilitating the understanding of reality and abstract concepts that are difficult to understand for some students, especially those with learning difficulties. These strategies can avoid displacements to explore places or situations. Moreover, they provide safe scenarios for active experimentation, which means achieving a higher degree of sustainability in educational proposals. On the other hand, the use of the e-portfolio can be an element of awareness in stimulating more sustainable behaviors. At the same time, the use of paper in the delivery of reports and academic work is avoided, contributing to a professional culture that cares for the environment.
In relation to the impact on citizens, it is highlighted that social networks and fast and massive communication channels are raising public awareness, creating a global public opinion in favor of caring for the planet and the need to take actions to reduce the impact of climate change. This change has been influenced by educational innovation projects being developed at higher education in many countries.
On the other hand, considering that sustainability includes social justice and the fight against the digital breach, there are still significant problems for the entire population, especially for students to have access to the necessary devices, and to digital content and virtual education under equal conditions. In this sense, education policy must continue to address strategies that ensure equity in the context of lifelong education and e-learning.
However, this study has some limitations. First, the broad complexity of the SDGs was not fully considered, as well as their internal relationship and the impact of one on another. In addition, it would be interesting to analyse in greater depth the concentration of Spanish research on the subject under study, with the purpose of exploring possible biases in the searches that may lead to these results.
As a very positive element, it has been interesting to observe the response given by the scientific community to the challenges encountered. The variability of the different innovative proposals affirm that there is a niche of possibilities to contribute even more to the achievement of the SDGs through educational innovation, where ICTs play a fundamental role.
5. Conclusions
A systematic literature review has been carried out and the scientific literature on sustainability in digital education in the last decade has been evaluated. It is necessary to consider that the results of this study are based on a selection of articles extracted from two specific databases, not including other scientific and pedagogical documents, which would expand the knowledge on this topic. Despite the granularity of the bibliography, studies from European institutions (mainly Spanish) predominate, which may not reflect the reality of other educational centers in other regions. Authors’ biases may also have influenced the analysis of the articles.
The results of this systematic literature review allow us to conclude that an adequate educational approach to the phenomenon of sustainability in digital education requires: (a) a didactic approach with a broad vision of the use of ICT-based learning experiences; (b) initial and ongoing teacher training that promotes the development of sustainability with adequate knowledge of the SDGs and digital competence; and (c) the formation of interdisciplinary teams of education and digital competencies for research and teaching.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/educsci13010033/s1, Excel S1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.G.-H. and A.G.-V.M.-R.; methodology, A.G.-H., S.C.-M. and M.C.-G.; software A.G.-H.; validation, M.C.-G. and A.G.-V.M.-R.; formal analysis, A.G.-H., A.G.-V.M.-R. and M.C.-G.; investigation, A.G.-H. and M.C.-G.; resources, S.C.-M.; data curation, M.C.-G., A.G.-V.M.-R. and A.G.-H.; writing—original draft preparation, A.G.-H.; writing—review and editing, A.G.-V.M.-R., S.C.-M. and M.C.-G.; visualization, A.G.-H., A.G.-V.M.-R., S.C.-M. and M.C.-G.; supervision, A.G.-V.M.-R. and S.C.-M.; project administration, M.C.-G. and A.G.-H.; funding acquisition, A.G.-H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financed by the European Union (NextGenerationEU) and the Ministry of Universities of Spain, under Grant Margarita Salas.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data is available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7382351 (accessed on 10 October 2022).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Munoz-Rodriguez, J.M.; Sánchez-Carracedo, F.; Barron-Ruiz, A.; Serrate-Gonzalez, S. Are We Training in Sustainability in Higher Education? Case Study: Education Degrees at the University of Salamanca. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casillas-Martín, S.; Cabezas-González, M.; García-Valcárcel Muñoz-Repiso, A. DigiCraft: A Pedagogical Innovative Proposal for the Development of the Digital Competence in Vulnerable Children. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevado-Peña, D.; López-Ruiz, V.R.; Alfaro-Navarro, J.L. Improving quality of life perception with ICT use and technological capacity in Europe. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 148, 119734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-García, S.; Aznar-Díaz, I.; Cáceres-Reche, M.P.; Trujillo-Torres, J.M.; Romero-Rodríguez, J.M. Systematic Review of Good Teaching Practices with ICT in Spanish Higher Education. Trends and Challenges for Sustainability. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, C.R.M.; Soares, T.C.; de Lima, M.A.; Veras, M.O.; Guerra, J.B.S.O.D.A. Sustainability funding in higher education: A literature-based review. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2020, 21, 441–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGain, F.; Muret, J.; Lawson, C.; Sherman, J.D. Environmental sustainability in anaesthesia and critical care. Br. J. Anaesth. 2020, 125, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Olmedo, A.M.; Valor, C.; Carrero, I. Mindfulness in education for sustainable development to nurture socioemotional competencies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Educ. Res. 2020, 26, 1527–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabban, F.; Selamat, A.; Ibrahim, R.; Krejcar, O.; Maresova, P.; Herrera-Viedma, E. The Influence of Personal and Organizational Factors on Researchers’ Attitudes towards Sustainable Research Productivity in Saudi Universities. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veletsianos, G.; VanLeewuen, C.A.; Belikov, O.; Johnson, N. An Analysis of Digital Education in Canada in 2017–2019. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2021, 22, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minerva, T. Bridging researches in Digital Education. J. E-Learn. Knowl. Soc. 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashalova, N.N.; Vasiltsov, V.S. Digital Education: New Challenges and Opportunities. Sci. Tech. Inf. Process. 2020, 47, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Castillo, J.J. Digital innovation in education. EDMETIC 2020, 10, I. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedderer, K.; Townsend, K. Crafting progress through research education and digital innovation. Craft Res. 2020, 11, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, J.B. Leadership for Sustainability in Higher Education. Learn. Teach. Int. J. High. Educ. Soc. Sci. 2021, 14, 114–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumber, A. Transforming sustainability education through transdisciplinary practice. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 24, 7622–7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Serrano, S.; Pedraza-Navarro, I.; Donoso-González, M. ¿Cómo hacer una revisión sistemática siguiendo el protocolo PRISMA? Usos y estrategias fundamentales para su aplicación en el ámbito educativo a través de un caso práctico. Bordón. Rev. Pedagog. 2022, 74, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rethlefsen, M.L.; Kirtley, S.; Waffenschmidt, S.; Ayala, A.P.; Moher, D.; Page, M.J.; Koffel, J.B. PRISMA-S: An extension to the PRISMA Statement for Reporting Literature Searches in Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, C.; Munn, Z.; Porritt, K. Qualitative research synthesis. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Iso, A.; Eizaguirre, A.; García-Olalla, A.M. Una revisión sistemática del concepto de actividad extracurricular en Educación Superior. Educ. XX1 2020, 23, 307–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada Molina, O.; Fuentes-Cancell, D.; García-Hernández, A. Evaluating usability in educational technology: A systematic review from the teaching of mathematics. LUMAT Int. J. Math Sci. Technol. Educ. 2022, 10, 65–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Villar, A.; Gutiérrez-Pérez, J.; Perales-Palacios, F.J. Evaluando la formación virtual en sensibilización ambiental para sectores profesionales. Educ. Siglo XXI 2016, 34, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aguayo, C.; Eames, C. Promoting community socio-ecological sustainability through technology: A case study from Chile. Int. Rev. Educ. 2017, 63, 871–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobande, O.A.; Asongu, S.A. The Critical Role of Education and ICT in Promoting Environmental Sustainability in Eastern and Southern Africa: A Panel VAR Approach. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 176, 121480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimova, A.; Rondeau, E.; Andersson, K.; Porras, J.; Rybin, A.; Zaslavsky, A. An international Master’s program in green ICT as a contribution to sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzina, D. Learning by doing. Case study: Education for sustainable development at the University of Latvia. Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2019, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J. Unequal Loneliness in the Digitalized Classroom: Two Loneliness Effects of School Computers and Lessons for Sustainable Education in the E-Learning Era. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Purushothaman, A.; Rongbutsri, N. Facilitating Sustainability of Education by Problem-Based Learning (PBL) and Information and Communication Technology (ICT). Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2013, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerras, H.; Bautista, S.; Piñeros Perea, D.S.; de-Miguel Gómez, M.D. Closing the Digital Gender Gap among Foreign University Students: The Challenges Ahead. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asongu, S.A.; Orim, S.M.I.; Nting, R.T. Inequality, information technology and inclusive education in sub-Saharan Africa. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 146, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körtesi, P.; Simonka, Z.; Szabo, Z.K.; Guncaga, J.; Neag, R. Challenging Examples of the Wise Use of Computer Tools for the Sustainability of Knowledge and Developing Active and Innovative Methods in STEAM and Mathematics Education. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaconu, A.; Dedu, E.; Igreț, R.; Radu, C. The Use of Information and Communications Technology in Vocational Education and Training—Premise of Sustainability. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Loinaz, G.; Ametzaga-Arregi, I.; Palacios-Agundez, I. ICT tools and citizen science: A pathway to promote science learning and Education for Sustainable Development in schools. J. Biol. Educ. 2022, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero Yesa, S.; Aláez-Martínez, M.; Ferran Zubillaga, A.; García-Olalla, A. A good practice for making training accessible to university faculty members through ICTs: Syllabus planning support training. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2021, 20, 573–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebaetse, M.B.; Nkomazana, O.; Haverkamp, C. Integrating eLearning to Support Medical Education at the New University of Botswana School of Medicine. Electron. J. e-Learn. 2014, 12, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Batez, M. ICT Skills of University Students from the Faculty of Sport and Physical Education during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colás-Bravo, P.; Magnoler, P.; Conde-Jiménez, J. Identification of Levels of Sustainable Consciousness of Teachers in Training through an E-Portfolio. Sustainability 2018, 15, 3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mâță, L.; Clipa, O.; Tzafilkou, K. The Development and Validation of a Scale to Measure University Teachers’ Attitude towards Ethical Use of Information Technology for a Sustainable Education. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monavvarifard, F.; Baradaran, M.; Khosravipour, B. Increasing the sustainability level in agriculture and Natural Resources Universities of Iran through students’ engagement in the value Co-creation process. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Borreguero, G.; Perera-Villalba, J.J.; Mateos-Núñez, M.; Naranjo-Correa, F.L. Development of ICT-Based Didactic Interventions for Learning Sustainability Content: Cognitive and Affective Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, A.; Lumbreras, J.; Matáix, C.; Pérez, I.J. Engineering education for sustainability a multistakeholder case study on ICTand transportation. Int. J. Eng. Educ. 2013, 29, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Kabadayi, A.; Skutil, M.; Maněnová, M. ICT Equipment in the Kindergartens for Sustainable Education from Kindergarten Principals’ Perspectives in the Czech Republic. TEM J. 2022, 27, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.S.; González-Gómez, D. Adapting to PSTs’ Pedagogical Changes in Sustainable Mathematics Education through Flipped E-Learning: Ranking Its Criteria with MCDA/F-DEMATEL. Mathematics 2020, 8, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilty, L.M.; Huber, P. Motivating students on ICT-related study programs to engage with the subject of sustainable development. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2018, 19, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertegal-Felices, M.L.; Jimeno-Morenilla, A.; Sánchez-Romero, J.L.; Mora-Mora, H. Comparison of the Effects of the Kahoot Tool on Teacher Training and Computer Engineering Students for Sustainable Education. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragán-Sánchez, R.; Corujo-Vélez, M.C.; Palacios-Rodríguez, A.; Román-Graván, P. Teaching Digital Competence and Eco-Responsible Use of Technologies: Development and Validation of a Scale. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; He, B.; Wang, Z.; Lin, R.; Yang, J.; Zhou, R. Research on Open Practice Teaching of Off-Campus Art Appreciation Based on ICT. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Pérez, C.; Gato-Bermúdez, M.J.; Musicco-Nombela, D.; Ruiz-Alberdi, C. The Massive Implementation of ICT in Universities and Its Implications for Ensuring SDG 4: Challenges and Difficulties for Professors. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Abitia, G.; Martínez-Pérez, S.; Ramirez-Montoya, M.S.; Lopez-Caudana, E. Digital Gap in Universities and Challenges for Quality Education: A Diagnostic Study in Mexico and Spain. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rahmi, W.M.; Alzahrani, A.I.; Yahaya, N.; Alalwan, N.; Kamin, Y. Digital Communication: Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Usage for Education Sustainability. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.; Kim, Y.; Kim, M.; Jang, Y.; Joo, M.H. The Digital Divide? Analyzing Regional Differences of Tablet PC Use in Korean Middle Schools for Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. ICT and the UN’s Sustainable Development Goal for Education: Using ICT to Boost the Math Performance of Immigrant Youths in the US. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, B.; Muñoz, E.M.; Rodríguez, M.A. La formación docente en la sociedad digital: Propiciando la reflexión sobre el impacto medioambiental y social del consumo de tecnología. Opción 2016, 13, 104–132. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).