Context-Aware Ubiquitous Learning Based on Case Methods and Team-Based Projects: Design and Validation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Design
2.2. Procedure
2.2.1. Model Development
2.2.2. Product Validation
Validator
Trial Subject
Instrument
Data Analysis Technique
3. Results
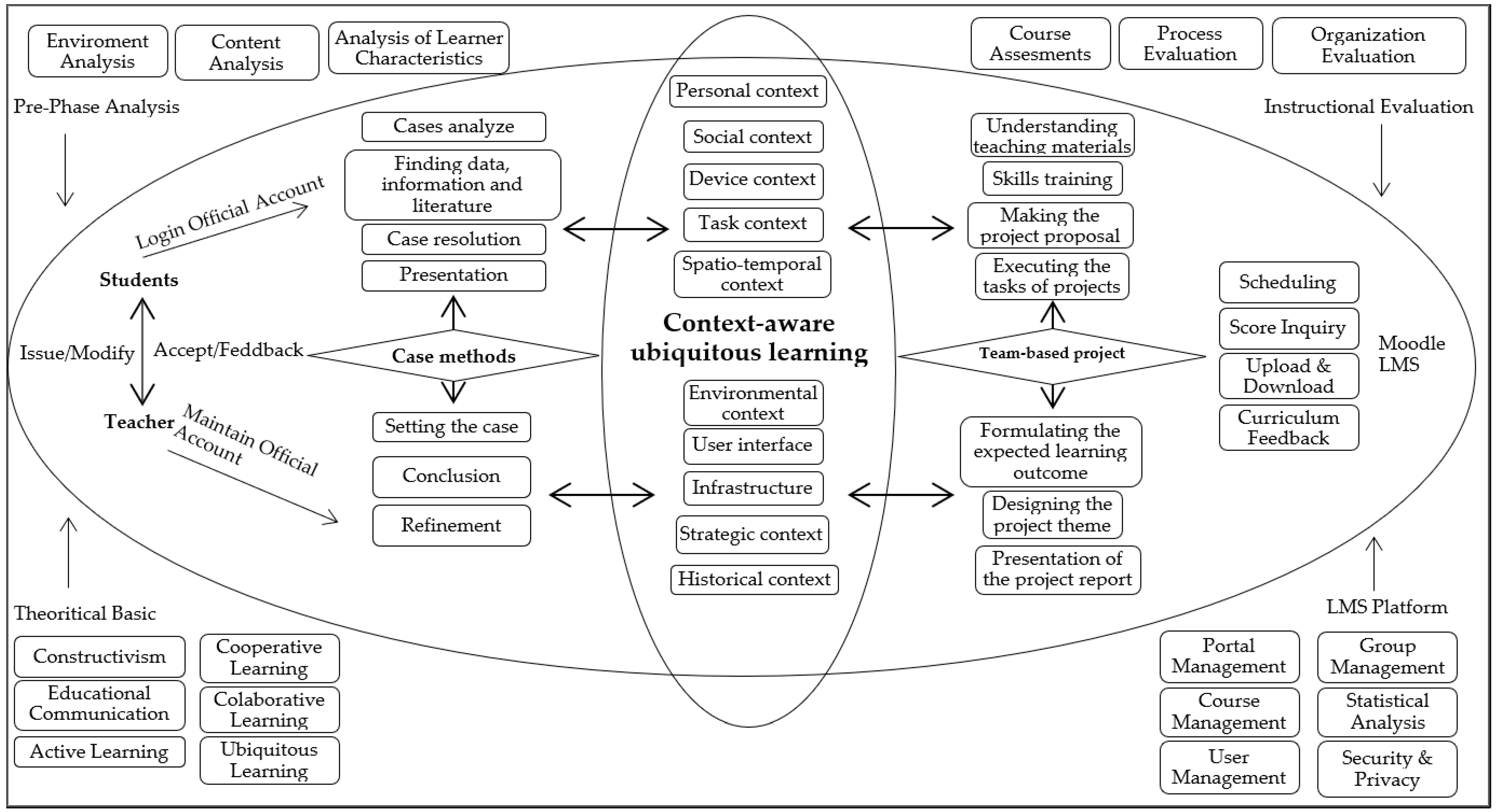
3.1. Context-Aware Ubiquitous Learning Model Design Based on Case Methods and Team-Based Projects for the ‘Learning Media’ Course
3.2. The Final Product
- (1)
- Introduction to courses
- (2)
- Learning activities 1: The position of ‘learning media’
- (3)
- Learning activities 2: Basic concepts of ‘learning media’
- (4)
- Learning activities 3: Classification of ‘learning media’
- (5)
- Learning activities 4: The characteristics of the types of ‘learning media’
- (6)
- Learning activities 5: ‘Learning media’ management
- (7)
- Learning activities 6: Selection of ‘learning media’
- (8)
- Mid-semester exam
- (9)
- Learning activities 7: Analysis of ‘learning media’ needs
- (10)
- Learning activity 8: Design and production of ‘learning media’
- (11)
- Learning activity 9: Evaluation of ‘learning media’
- (12)
- Learning activities 10: Use of ‘learning media’
- (13)
- Work practice 1: Production of simple ‘learning media’
- (14)
- Work practice 2: Digital ‘learning media’ production
- (15)
- Final exams
- (1)
- Determine cases based on the environmental context by selecting issues associated with using ‘learning media’ in schools close to the student environment
- (2)
- Analyze cases with the principle of social context by identifying or perceiving cases based on the closest social environment
- (3)
- Independently find information, data, and literature based on personal context by using the device brought individually in line with their interests, motivations, knowledge, and concerns
- (4)
- Determine the steps to solve the cases through spatio-temporal context by applying spatial-temporal reasoning to solve multi-step problems
- (5)
- Discuss and conclude the answers together using the historical context by paying attention to the social, political, cultural, economic, and environmental situations affecting the events or trends observed at a certain time.
- (6)
- Present the findings through the spatio-temporal, environmental, and historical contexts
- (7)
- Improve on the findings based on the personal and social contexts
- (1)
- Formulate the expected learning outcome based on the task context by having a set of special conditions characterizing the situation related to the task. This assists in adjusting the resource capabilities and directing efforts to better fit the situation in order to reduce inefficiencies and avoid several potential errors.
- (2)
- Understand the concept of the teaching materials based on personal context through the provision of subject matter by considering the preferences, interests, motivations, knowledge, and concerns of each individual.
- (3)
- Develop skills based on the device and infrastructure contexts by providing different alternative exercises based on the device owned by each individual
- (4)
- Design the project theme based on the task context
- (5)
- Produce the project proposal through the task, personal, device, and infrastructure contexts
- (6)
- Execute the tasks of the projects based on the strategic context by ensuring accuracy in the steps to achieve the stated goals
- (7)
- Present the project report based on the spatio-temporal, environmental, and historical contexts
3.3. Product Validity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Recommendations
- This research product needs to be implemented among groups of university students taking ‘learning media’ courses.
- The lecturers should provide directions for students using this learning model for the first time even though it is designed for independent learning.
- The model design can be disseminated through different activities such as academic seminars organized by universities, training activities for the development of ‘learning media’, collaboration with learning centers, educational and training institutions, and other forums. It is designed and developed for several people interested in studying ‘learning media’.
- The efforts to develop context-aware ubiquitous learning need to be implemented by the optimization of more varied presentation methods.
- It is necessary to pursue further research activities to identify the effectiveness of using this product through both classroom action research methods and experimental research in a wider target group.
7. Limitations
- It needs to be applied using a computer or mobile device.
- It requires adequate internet access.
- It is limited to ‘learning media’ materials.
- No effectiveness test was conducted.
- The evaluation conducted did not consider the long-term impact.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Indira, E.W.M.; Hermanto, A.; Pramono, S.E. Improvement of Teacher Competence in the Industrial Revolution Era 4.0. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Science and Education and Technology (ISET), Semarang, Indonesia, 29 June 2020; Volume 443, pp. 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuti, M.; Arifin, Z.; Mutohhari, F.; Nurtanto, M. Competency of Digital Technology: The Maturity Levels of Teachers and Students in Vocational Education in Indonesia. J. Educ. Technol. 2021, 5, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zein, S. Pre-service education for primary school English teachers in Indonesia: Policy implications. Asia Pac. J. Educ. 2014, 36, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarma, I.K.; Prabawa, D.G.A.P.; Suartama, I.K. The Application of Information Processing Theory to Design Digital Content in Learning Message Design Course. Int. J. Inf. Educ. Technol. 2022, 12, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemay, D.J.; Bazelais, P.; Doleck, T. Transition to online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. Comput. Hum. Behav. Rep. 2021, 4, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfan, M.; Kusumaningrum, B.; Yulia, Y.; Widodo, S.A. Challenges During The Pandemic: Use of E-learning in Mathematics Learning in Higher Education. Infin. J. 2020, 9, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusnilita, N. The Impact of Online Learning: Student’s Views. Eternal. Engl. Teach. J. 2020, 11, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, S. Online Learning: A Panacea in the Time of COVID-19 Crisis. J. Educ. Technol. Syst. 2020, 49, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Anwar, K. Online learning amid the COVID-19 pandemic: Students perspectives. J. Pedagog. Sociol. Psychol. 2020, 2, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deák, C.; Kumar, B.; Szabó, I.; Nagy, G.; Szentesi, S. Evolution of New Approaches in Pedagogy and STEM with Inquiry-Based Learning and Post-Pandemic Scenarios. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhlanga, D.; Moloi, T. COVID-19 and the Digital Transformation of Education: What Are We Learning on 4IR in South Africa? Educ. Sci. 2020, 10, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo-Correa, P.; Monsalve-Pulido, J.; Tabares-Betancur, M. A systematic mapping review of context-aware analysis and its approach to mobile learning and ubiquitous learning processes. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2020, 39, 100335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subiyakto, A.; Hidayah, N.A.; Gusti, G.; Hikami, M.A. Readiness and Success of Ubiquitous Learning in Indonesia: Perspectives from the Implementation of a Pilot Project. Information 2019, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.-J.; Tsai, C.-C.; Yang, S.J.H. Criteria, Strategies and Research Issues of Context-Aware Ubiquitous Learning. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2008, 11, 81–91. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Sun, S.; Kansen, M.; Huang, T.; He, A. A Personalized Ubiquitous Education Support Environment by Comparing Learning Instructional. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications (AINA’05) Volume 1 (AINA Papers), Taipei, Taiwan, 25–30 March 2005; Volume 2, pp. 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruo, N.; Koyoharu, P.H.; Yasufumi, K.; Shiho, M. Designing Ubiquitous and Universal Learning Situations: Integrating Textbooks and Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual Conference of Distance Teaching and Learning, Madison, WI, USA, 13–15 August 2003; pp. 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.Y.; Sheu, J.P. Design and implementation of ad hoc classroom and eSchoolbag systems for ubiquitous learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Wireless and Mobile Technologies in Education, WMTE 2002, Vaxjo, Sweden, 30 August 2002; pp. 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, M.A.; Haavisto, E.; Liikanen, E.; Kääriäinen, M. Ubiquitous learning environments in higher education: A scoping literature review. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2017, 23, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glahn, C.; Gruber, M.R. Designing for Context-Aware and Contextualized Learning., In Emerging Technologies and Pedagogies in the Curriculum. Bridging Human and Machine: Future Education with Intelligence; Yu, S., Ally, M., Tsinakos, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.-J.; Chu, H.-C.; Shih, J.-L.; Huang, S.-H.; Tsai, C.-C. A Decision-Tree-Oriented Guidance Mechanism for Conducting Nature Science Observation Activities in a Context-Aware Ubiquitous Learning Environment. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2010, 13, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, T.T. Multiplatform E-Learning Systems and Technologies: Mobile Devices for Ubiquitous ICT-Based Education; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongkoo, K.; Panjaburee, P.; Daungcharone, K. A development of ubiquitous learning support system based on an enhanced inquiry-based learning approach. Int. J. Mob. Learn. Organ. 2019, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; He, L.; Deng, W.; Zhu, J.; Su, A.; Zhang, Y. The effectiveness of the combined problem-based learning (PBL) and case-based learning (CBL) teaching method in the clinical practical teaching of thyroid disease. BMC Med. Educ. 2020, 20, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J. Pre-Service Teachers’ Project-Based Instruction with Mathematics Problem-Solving. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Han, S.C.; Bilal, H.S.M.; Lee, S.; Kang, M.J.Y.; Kang, B.H.; Razzaq, M.A.; Amin, M.B. iCBLS: An interactive case-based learning system for medical education. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2018, 109, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.E. The Promise of Educational Psychology Volume II: Teaching for Meaningful Learning; Pearson Education Inc: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Soboleva, E.V.; Karavaev, N.L. Characteristics of the project-based teamwork in the case of developing a smart application in a digital educational environment. Eur. J. Contemp. Educ. 2020, 9, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S. Project-Based Learning. In Encyclopedia of the Sciences of Learning; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 2707–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lim, C.; Kim, H. Development of an instructional design model for flipped learning in higher education. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2016, 65, 427–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suartama, I.K.; Setyosari, P.; Sulthoni, S.; Ulfa, S. Development of an Instructional Design Model for Mobile Blended Learning in Higher Education. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. (iJET) 2019, 14, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richey, R.C.; Klein, J.D. Design and Development Research; Lawrence Erlbaum: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Richey, R.C. Validating instruction design and development models. In Innovations in Instructional Technology: Essays in Honor of M. David Merrill; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 171–185. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.-K.; Hwang, G.-J. A context-aware ubiquitous learning approach for providing instant learning support in personal computer assembly activities. Interact. Learn Environ. 2012, 22, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalinus, N.; Nabawi, R.A.; Mardin, A. The Seven Steps of Project Based Learning Model to Enhance Productive Competences of Vocational Students. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Technology and Vocational Teachers (ICTVT), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 28 September 2017; Volume 102, pp. 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suartama, I.K.; Setyosari, P.; Sulthoni, S.; Ulfa, S. Development of Ubiquitous Learning Environment Based on Moodle Learning Management System. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol. (iJIM) 2020, 14, 182–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.F.; Hess, R.D. Instructional Software: Principles and Perspectives for Design and Use; Wadsworth Publishing Company: Belmont, OH, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Debattista, M. A comprehensive rubric for instructional design in e-learning. Int. J. Inf. Learn. Technol. 2018, 35, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukardjo, S. Evaluasi Pembelajaran. Buku Pegangan Kuliah; PPs Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta: Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.-H.; Hwang, G.-J.; Tsai, W.-H. An expert system-based context-aware ubiquitous learning approach for conducting science learning activities. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2013, 16, 217–230. [Google Scholar]
- Munawaroh, N. The Influence of Teaching Methods and Learning Environment to the Student’s Learning Achievement of Craft and Entrepreneurship Subjects at Vocational High School. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 2017, 12, 665–678. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnel, W. Improving feedback to students in online courses. Nurs. Educ. Perspect. 2008, 29, 290–294. [Google Scholar]
- Divayana, D.G.H.; Sudirtha, I.G.; Suartama, I.K. Digital Test Instruments Based on Wondershare-Superitem for Supporting Distance Learning Implementation of Assessment Course. Int. J. Instr. 2021, 14, 945–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Dennen, V.P.; Mei, L. Influential factors for mobile learning acceptance among Chinese users. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2016, 65, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjaya, D.B.; Suartama, I.K.; Suastika, I.N.; Sukadi, S. The Effect of the Conflict Resolution Learning Model and Portfolio Assessment on the Students’ Learning Outcomes of Civic Education. Int. J. Instr. 2022, 15, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertmer, P.A.; Koehler, A.A. Online case-based discussions: Examining coverage of the afforded problem space. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2014, 62, 617–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, A.A.; Cheng, Z.; Fiock, H.; Janakiraman, S.; Wang, H. Asynchronous Online Discussions During Case-Based Learning: A Problem-Solving Process. Online Learn. J. 2020, 24, 64–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Bozic, C.; Gretter, S.; Nauman, E. Benefits and challenges of implementing case-based instruction: A student perspective. Int. J. Eng. Educ. 2015, 31, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar]
- Bada, S.O.; Olusegun, S. Constructivism Learning Theory: A Paradigm for Teaching and Learning. J. Res. Method Educ. 2015, 5, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Tawfik, A.A.; Kolodner, J.L.; Tawfik, A.A.; Illinois, N.; Kolodner, J.L.; Concord, T. Systematizing Scaffolding for Problem-Based Learning: A View from Case-Based Reasoning. Interdiscip. J. Probl. Learn. 2016, 10, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, A.A.; Ertmer, P.A.; Newby, T.J. Developing Preservice Teachers’ Instructional Design Skills Through Case-Based Instruction: Examining the Impact of Discussion Format. J. Teach. Educ. 2018, 70, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Saab, N.; Post, L.S.; Admiraal, W. A review of project-based learning in higher education: Student outcomes and measures. Int. J. Educ. Res. 2020, 102, 101586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, H.B.; Khataibeh, A. The Effect of Using Project Based Learning on Improving the Critical Thinking among Upper Basic Students from Teachers’ Perspectives. Pegem. Egit. Ve. Ogr. Derg. 2021, 11, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, R.D.; Brant-Ribeiro, T.; Mendonça, I.E.S.; Mendes, M.M.; Dorça, F.A.; Cattelan, R.G. Social and collaborative interactions for educational content enrichment in ULEs. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2017, 20, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Suartama, I.K.; Setyosari, P.; Sulthoni, S.; Ulfa, S.; Yunus, M.; Sugiani, K.A. Ubiquitous Learning vs. Electronic Learning: A Comparative Study on Learning Activeness and Learning Achievement of Students with Different Self-Regulated Learning. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. (iJET) 2021, 16, 36–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.J.H. Context aware ubiquitous learning environments for peer-to-peer collaborative learning. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2006, 9, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Aspect | Indicator |
|---|---|
| Material | The suitability of the material with the competencies to be achieved Concept truth Material updates Order of material presentation The suitability of the given example |
| Learning | Learning objectives Motivation Summary Clarity of learning indicators Giving training Suitability of images, and videos provided to clarify the material |
| Language | The suitability of language with students’ thinking level Simple language Accuracy of terms Grammar and spelling accuracy Ability to arouse students’ curiosity |
| Main Standards | Specific Standards |
|---|---|
| Course opening | Behavior Role Accessibility Integrity Technical competences Ownership |
| Instructional resources for teaching and learning | Openness Provision Entitlement Application Variety Academic integrity |
| Interaction and community | Peer learning Fostering Management |
| Learner support | Academic Instructional Administrative Technical |
| Technology design | Interface Access Centricity Investment Authentication Management |
| Course closing | Conclusions Archiving Resolution |
| Assessment of learning | Measurement Grading Management Feedback |
| Instructional design cycle | Academic Administrative Technical |
| Value/Category | Score | |
|---|---|---|
| Formula | Calculation | |
| Very good | X > +1.80 Sbi | X > 4.21 |
| Good | + 0.60 Sdi < X ≤ + 1.80 Sdi | 3.40 < X ≤ 4.21 |
| Quite good | − 0.60 Sdi < X ≤ + 0.60 Sdi | 2.60 < X ≤ 3.40 |
| Not good | − 1.80 Sdi < X ≤ − 0.60 Sdi | 1.79 < X ≤ 2.60 |
| Bad | X ≤ − 1.80 Sdi | X ≤ 1.79 |
| Topics | Method | Type of Teaching Material | Moodle LMS Features | Implementation of Context-Aware Ubiquitous Learning | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resource | Activities | ||||
| Position of ‘learning media’ | Case methods | Document (pdf) | Page File URL | Forum Assignments Feedback | Personal context Social context Spatio-temporal context Environmental context Historical context |
| The basic concept of ‘learning media’ | Case methods | Presentation (ppt) | Page File URL | Forum Assignments Feedback | Personal context Social context Spatio-temporal context Environmental context Historical context |
| Classification of ‘learning media’ | Team-based projects | Videos (mp4) | Book File URL | Assignments Chatting Feedback | Task context Device context User interface Infrastructure Strategic context |
| Characteristics of various types of ‘learning media’ | Case methods | Document (pdf) | File URL | Lesson BigBlueButtonBN (web conference) Messages | Personal context Social context Spatio-temporal context Environmental context Historical context |
| Learning media management | Case methods | Presentation (ppt) | Label Page | Workshop Assignments | Personal context Social context Spatio-temporal context Environmental context Historical context |
| Selection of ‘learning media’ | Case methods | Videos (mp4) | Page File URL | Forum Assignments Feedback | Personal context Social context Spatio-temporal context Environmental context Historical context |
| Analysis of ‘learning media’ needs | Team-based projects | Documents (doc, pdf) | Page File URL | Forum Assignments Feedback | Task context Device context User interface Infrastructure Strategic context |
| ‘Learning media’ design and production | Team-based projects | Presentation (ppt) | Page File URL | Forum Assignments Feedback | Task context Device context User interface Infrastructure Strategic context |
| Evaluation of ‘learning media’ | Team-based projects | Images (jpg, png) | Page File URL | Forum Assignments Feedback | Task context Device context User interface Infrastructure Strategic context |
| Use of ‘learning media’ | Case methods | Videos (mp4) | Page File URL | Forum Assignments Feedback | Personal context Social context Spatio-temporal context Environmental context Historical context |
| Simple media production practice | Team-based projects | Document (pdf) | Page File URL | Forum Assignments Feedback | Task context Device context User interface Infrastructure Strategic context |
| Digital ‘learning media’ production work practice | Team-based projects | Presentation (ppt) | Page File URL | Forum Assignments Feedback | Task context Device context User interface Infrastructure Strategic context |
| Assessment Aspect | Average Score | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Material Aspect | 4.32 | Very good |
| Learning Aspect | 4.23 | Very good |
| Language Aspect | 4.24 | Very good |
| Average Overall Score | 4.26 | Very good |
| Assessment Aspect | Average Score | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Opening | 4.83 | Very good |
| Learning resources | 4.67 | Very good |
| Interaction and communication | 4.67 | Very good |
| Student/study support | 4.70 | Very good |
| Technology design | 4.73 | Very good |
| Closing/course closing | 4.73 | Very good |
| Evaluation | 4.80 | Very good |
| Learning cycle | 4.60 | Very good |
| Average Overall Score | 4.72 | Very good |
| Assessment Aspect | Average Score | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Material Aspect | 4.35 | Very good |
| Learning Aspect | 4.44 | Very good |
| Language Aspect | 4.38 | Very good |
| Opening | 4.40 | Very good |
| Learning resources | 4.39 | Very good |
| Interaction and communication | 4.38 | Very good |
| Student support | 4.32 | Very good |
| Technology design | 4.29 | Very good |
| Closing/course closing | 4.36 | Very good |
| Evaluation | 4.38 | Very good |
| Learning cycle | 4.34 | Very good |
| Average Overall Score | 4.37 | Very good |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suartama, I.K.; Triwahyuni, E.; Suranata, K. Context-Aware Ubiquitous Learning Based on Case Methods and Team-Based Projects: Design and Validation. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12110802
Suartama IK, Triwahyuni E, Suranata K. Context-Aware Ubiquitous Learning Based on Case Methods and Team-Based Projects: Design and Validation. Education Sciences. 2022; 12(11):802. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12110802
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuartama, I Kadek, Eges Triwahyuni, and Kadek Suranata. 2022. "Context-Aware Ubiquitous Learning Based on Case Methods and Team-Based Projects: Design and Validation" Education Sciences 12, no. 11: 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12110802
APA StyleSuartama, I. K., Triwahyuni, E., & Suranata, K. (2022). Context-Aware Ubiquitous Learning Based on Case Methods and Team-Based Projects: Design and Validation. Education Sciences, 12(11), 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12110802







