Abstract
Underperformance in mathematics has been an issue that plagues the education system in Jamaica. Studies in first world countries have shown that enrichment programs, including Mathematics Enhancement Programmes (MEPs,) have been positively impacting attainment in mathematics. This quasi-experimental research design study investigated the impact of an MEP on Jamaican students’ attainment in mathematics. A sample of seven grade one classes from two primary schools in representative areas in Jamaica were selected for the intervention group. The treatment involved teaching the Jamaican grade one mathematics standards using the MEP resources for nine months. A statistically significant improvement and large effect size of the intervention was found, indicating that the MEP had a substantial impact on students’ achievement and attitudes towards mathematics. This study has implications for designing enrichment programs geared at addressing mathematics underperformance in Jamaica and in similar countries.
1. Introduction
1.1. Overview of Jamaica and Its Education System
Jamaica is nested in the Greater Antilles, is the largest island in the Caribbean Sea and boasts a very rich and varied landscape [1]. The island is globally recognized through its reggae music and its participation in international sporting events [2,3]. The population of Jamaica emerged from a historical process that brought people from different continents together. Jamaica’s culture is heavily influenced by its African heritage, while formal behaviour is unmistakably British in style [1].
Jamaica’s education system is best explained and understood in the context of the island’s colonial history [4]. Prior to the slaves being emancipated in 1834, Jamaica had a minimal formal and cohesive education system for whites and no system for educating its indigenous people and slaves [4,5]. Only a few slave children were privy to schooling which focused on religion and virtues of submission at plantation schools established by foreign missionaries. Once slavery was abolished in 1834, education was viewed as an important way to integrate ex-slaves into the colonial economy and to ensure a peaceful lower class. After gaining independence in 1962 all children were allowed to attend infant and elementary schools [6] but only a few students had access to secondary education due to the need to pass a stringent primary exit examination and financial constraints for those who passed the exam [6]. In the years following independence, leading up to the late 1970s educational provisions in Jamaica were still limited, resulting in the nation having a high level of illiteracy. During the 1980s, educational provisions deteriorated and ‘the poorer strata in the society were generally more seriously affected by the deteriorating provision’ [7]. During this period, teachers had limited or no resources to work with, enrolment in primary schools declined and there were high levels of grade repetitions and school dropouts. Currently, Jamaica is transforming its education system and building the capacity of a network of institutions to improve the quality of its educational services [8].
1.2. Background to the Study
It is Jamaica’s vision to develop an education and training system that produces well-rounded and qualified individuals who will be empowered to learn for life and productively function in society and be competitive in a global context [9]. As Jamaica strives to take its place within a fiercely competitive and highly globalized marketplace, its school graduates must be equipped with the requisite mathematical knowledge needed to access the kinds of jobs that are emerging and to be able to compete internationally [10]. This vision is, however, hampered by the underachievement that still prevails in mathematics in Jamaica despite efforts to improve mathematical instructions. This view has been endorsed by Buddo [11], who opines that the school subject of mathematics in Jamaica has always presented challenges for learners at all levels of the educational system. Buddo [11] further lamented that, since the 1980s, the Jamaican Ministry of Education has embarked on various projects or initiatives to address the poor performance in mathematics by students who sit the national assessment tests or the Caribbean Examination Council’s Secondary Education Certificate Examination (CSEC). However, despite these interventions, the overall performance in mathematics continues to be below expectations. It is clearly evident from statistical data, which show that, for the ten-year period 2009–2018, students’ average attainment rate on: The Grade Four Numeracy Test fluctuated between a low of 41 percent and a high of 66 percent; The Grade Six Achievement Test (GSAT) scores in mathematics fluctuated between a low of 53 percent and a high of 62 percent; The Caribbean Secondary Examination Certificate (CSEC) examination fluctuated between a low of 31.7% and a high of 62% [12].
The unsatisfactory performance of students in mathematics and the low levels of numeracy exhibited by students and graduates of the Jamaican educational system have been a cause of much concern for stakeholders in education in the private and public sectors [10]. As stated in Jamaica’s mathematics and numeracy policy, the Ministry of Education, Youth and Culture (MOEYC) recognised that the nature of teaching and learning is a contributing factor to the poor performance and underachievement in mathematics [10]. Ministry policy has identified effective teacher pedagogy as an important tool that can be used to promote high levels of numeracy and facilitate the overall mathematical development and achievement of students. It was clearly outlined in the policy that experiences provided in the classroom should be geared towards the development of skills which enable not only meaningful use of the ideas learnt but also the development of problem solving and critical thinking skills. This is difficult to achieve, however, unless focus is placed on the quality of mathematics teaching. As suggested by the Ministry of Education [10], mathematics lessons should be focused on facilitating the development of problem-solving skills so that mathematics teaching at all levels of the educational system will enable the development of analytical, reasoning and critical thinking skills. One way to achieve this goal is to identify, adapt and implement the best practice observed in mathematically high-performing countries.
The Mathematics Enhancement Programme (MEP), which was pioneered by Professor David Burghes, is based on the premise of best practices observed in mathematically high-performing countries such as Hungary, Poland, Czech Republic, Japan, Singapore and Finland [13,14]. Therefore, the structure of the MEP may be able to help the Jamaican education system address some of the issues it faces in its mathematics classrooms. As suggested by Burghes [14], the MEP is geared at helping students develop their analytical and critical thinking skills, which are the skills that the Jamaican educational system identifies as being critical if performance in mathematics is to be improved [10]. Studies have shown that the MEP has been able to positively impact performance in mathematics in several first world countries [13,14]. The question then is that if the MEP is adapted, tailored and implemented in Jamaican mathematics Primary classrooms, would it have a similar impact. This study investigated the impact of the MEP has on Jamaican students’ attainment in mathematics.
Studies have shown that there is a significant correlation between students’ attitude towards mathematics and their performance in the discipline [14,15,16,17]. As defined by Eshun [18], attitude towards mathematics is ‘A disposition towards an aspect of mathematics that has been acquired by an individual through his or her beliefs and experiences, but which could be changed’. Zan and Martino [19] suggested that a positive attitude towards mathematics reflects a positive emotional disposition in relation to the subject and a negative attitude towards mathematics relates to a negative emotional disposition. Eshun [18] added that a student’s disposition towards a subject area affects the way he/she performs in the subject. It was also suggested by Eshun [18] that one is likely to achieve better in a subject that one enjoys, has confidence in or finds useful. Evidence of this was recorded in the work of Nicolaidou and Philippou [16] where is it was found that students who had a positive attitude towards mathematics performed better than those who displayed a negative attitude. Eshun [18] concluded that positive attitudes towards mathematics are desirable since they may influence one’s willingness to learn and the benefits one can derive from mathematics instruction. For a Mathematics Enhancement Programme to be effective, it must aid in helping students develop a positive attitude towards the subject. What impact will the MEP have on students’ attitude towards mathematics? To answer this question, this study also investigated the impact the MEP has on students’ attitudes towards mathematics.
1.3. Research Questions
This research was guided by the following questions:
- What effect does the implementation of MEP have on Jamaican primary school students’ performance in mathematics?
- How does students’ participation in the MEP impact their attitude towards mathematics?
2. Perspectives
2.1. The Impact of Enrichment Programmes on Mathematics Education
Studies have shown that the implementation of enrichment programs aid in nurturing social and behavioural skills, as well as academic skills [20,21]. Enrichment in mathematics helps to deepen students’ mathematical understanding [22]. Additionally, it has been found that the implementation of enrichment programs in mathematics positively impact performance in the discipline [23,24].
Enriched mathematics classrooms have aided in filling the instructional and learning gaps and have been impacting academic achievement [23,24,25]. The Mathematics Enhancement Programme (MEP) is an enriched mathematics program that is used in primary mathematics classrooms in England [14,26]. The MEP as an enriched Mathematical program has, ‘…proven to be a successful strategy because of pupils’ high attainment in the discipline with a very low standard deviation’ [13].
2.2. The Mathematics Enrichment Programme (MEP)
2.2.1. An overview of the MEP
The MEP was based on the observation of best practices in mathematically high-performing countries, such as Hungary, Poland, Czech Republic, Japan, Singapore, Russia and Finland (Burghes 2000; Burghes 2012). In these countries, great emphasis is placed on creating a strong mathematical foundation in the primary years [13,14] on the basis that students from countries which provide a strong mathematical foundation in the primary sector are more capable of being successful at the secondary level [14]. As set forward by McAleavy [26], countries that are strongest in the field of mathematics implement strong mathematical foundations in the primary years and they encourage and enable their pupils to think mathematically and be creative and confident using mathematics. The MEP is focused on enhancing primary mathematics based on the hypothesis that the best way to produce young people who are mathematically confident and capable is to start in the primary phase [14].
‘The MEP involves a friendly and non-confrontational style of learning that encourages classes to engage in pupil-led discussions and to find solutions to maths problems; In this context, the teacher orchestrates the activities but does not lead the class in the traditional way [26]’. The MEP is aimed at challenging all abilities with the expectations that attainment will be positively impacted [14]. The MEP provides ample opportunity for educators to develop good classroom practices [14]. As proposed by Burghes 2012, for the MEP to be effectively implemented, some key components need to be implemented, and these are outlined in Table 1.

Table 1.
The key components of the Mathematics Enhancement Programme (MEP).
The innovative structure of the MEP ensures that pre-prepared lesson plans and resources support varied, fast paced class work [26]. As stated by McAleavy [26], the spiral curriculum enforced by the MEP is a comprehensive programme that ensures continued revision through small and logical steps, but with key aims of mastering each year. That is, rather than simply reviewing the same material until all pupils have it memorized, the spiral process allows for continual development to challenge the most able learners, while also continuing to visit earlier areas of knowledge for those who struggle with mathematics [26].
2.2.2. Subject Knowledge Enhancement Programmes—How Important Is the SKE in Preparing Teachers for the MEP?
SKE Pogrammes aid in improving teachers’ subject knowledge, attitudes, understanding and confidence [27]. As put forward by French [28], subject knowledge, which embraces depth of understanding, an ability to think mathematically and subject-related pedagogical knowledge, as well as content knowledge at an appropriate level, is vitally important to all who teach mathematics. Ball, Thames and Phelps [29] endorsed this view when they posited that ‘Teaching requires knowledge beyond that being taught to students’ and teachers require what they call ‘unpacked’ mathematical knowledge, which they use to teach ‘decompressed mathematical knowledge’ to learners so that students eventually ‘develop fluency with compressed mathematical knowledge’. It is, therefore, implied that teachers of mathematics must have sound technical mathematical knowledge beyond the scope of the grade level that they are teaching before they can effectively help their students develop an understanding of mathematical concepts within the teaching and learning discourse [28,29].
In rationalizing the need for implementing the MEP, Burghes [14] identified that too few teachers having adequate mathematical knowledge and understanding as one of the reasons for the continued difficulties faced in developing an education system that supports all pupils to reach their mathematical potential. Teachers’ mathematical competency (mathematical subject knowledge) is a crucial aspect of success in improving mathematics in schools [14]. If the mathematical competence of teachers is an issue, then focus needs to be placed on mathematical concepts in a relevant and practical way [14]; one way to achieve this is through building teachers’ subject knowledge. It was implied by Burghes [14] that teachers’ mathematical competencies, (especially subject knowledge for teaching) is important for the effective implementation of the MEP.
2.2.3. The Impact of MEP on Mathematics Education
The MEP aims to equip children with the disposition to become good learners, inspiring them as mathematicians, questioning and challenging them to be logical thinkers and creating a safe environment where they can be confident enough to excel [30]. This view was endorsed by Burghes [14], who purports that the MEP supports children to raise their attainment and progress and provides them with opportunities to explore their own and each other’s thinking. The MEP helps students to develop and display a positive attitude towards mathematics [14]. After the implementation of the MEP, students viewed the subject as interesting and one which was worth persevering with when they were challenged by a task [14]. Additionally, the MEP aids in getting pupils to be more engaged and see themselves as being successful learners of mathematics [15].
Studies have shown that the implementation of the MEP into mathematics classrooms has positively impacted the teaching and learning of mathematics [14]. Burghes [14] added that children’s use of reasoning, thinking, and mathematical language is positively impacted by the MEP. Burghes [14] also indicated that the MEP positively impacted:
- The children’s development and use of mathematical language;
- The children’s analytical and logical thinking skills.
Based on the research done by Burghes [13], the MEP succeeded in raising students’ understanding of basic mathematical concepts, which subsequently positively impacted their attainment in the subject.
3. Methods
3.1. Research Design
The design of this research was a quasi-experimental study.
3.2. Participants and Sampling Procedures
The sample for the intervention group consisted of 150 first-grade students and seven teachers from two primary schools in representative areas in Jamaica. The comparison group consisted of 50 grade one students and two teachers from one primary school in Jamaica. The participating schools from both groups broadly represent a typical Jamaican primary school. The average age of the participants from both groups was 6.5 years with an SD of 3 months. The participants of the intervention and the comparison groups were randomly selected from the country’s first graders who were underperforming in mathematics and whose schools were not supported with coaching assistants. The schools that participated in both groups were all ranked as category 3 primary schools in Jamaica and served children from similar socioeconomic backgrounds. All the student participants were learning the grade standards in mathematics, established by the Ministry of Education, based on termly pacing guides. Additionally, the teaching experiences of the teachers of the intervention group ranged from 4 years to 16 years, while the teaching experiences of the teachers in the comparison group was 7 years and 13 years.
3.3. Procedures, Materials and Instruments
3.3.1. Procedure
Ethical approval was granted by University of Plymouth to carry out this research. The university’s research protocols and ethical standards regarding privacy, confidentiality, anonymity, informed consent and data preservation were followed.
Prior to the implementation of the MEP, the teachers in the intervention group were trained in subject knowledge enhancement to ensure that they were equipped with the requisite content knowledge needed to implement the MEP. Additionally, training was conducted in the components of the MEP aimed at helping teachers develop the skill sets needed to effectively incorporate the MEP resources in their teaching and learning discourse. Throughout the intervention, quarterly continued professional development sessions were provided for the teachers. Each session was held at the respective participating schools and lasted for an average of two and a half hours, totalling approximately 12 h of training across the intervention. The sessions focused on lesson studies related to the MEP, best MEP practices, conquering the challenges associated with implementing the MEP, video presentations that highlights the key components of the MEP and teachers’ reflections.
Prior to the intervention, the mathematics pre-test and pre-attitudinal survey were administered to both groups. Participants in the intervention group were then taught the Jamaican Grade One mathematics standards in lessons lasting 60 min, three times a week using the adapted and tailored MEP resources over the nine-month period (September 2017–June 2018). The students from the comparison group were taught mathematics using the traditional teaching methods employed across Jamaican primary mathematics classrooms. The teachers in this group used the Ministry of Education’s assigned textbooks and resources in their daily practice. Following the intervention, the mathematics post-test and post-attitudinal surveys were administered to both groups.
3.3.2. Materials
The materials used for this study are the adapted MEP resources that were tailored to fit the Jamaican mathematics classroom setting. Once these resources were adapted, modifications were made to ensure that the resources were fully aligned to the Jamaican primary mathematics curriculum in terms of content, sequence, and language. Teachers were provided with support plans for each suggested lesson. Students were furnished with the MEP support materials, which included:
- Mathematics Reasoning Practice Books
- Number lines
- Number cards
- Shape cards
3.3.3. Instruments
Attainment Measure
To measure the impact of the MEP on students’ attainment in mathematics, data were collected using the adapted MEP standardized tests. Test 0, which consisted of questions with a total of 10 marks, was administered as a pre-test and test 1 which consisted of the questions with a total of 20 marks (ten marks from test 0 and ten new marks) was administered as a post-test. Both tests were designed to test students’ understanding of number concepts and basic operations with numbers. Test 0 and Test 1 were analysed using SPSS software, version 25. Students’ attainment was compared using boxplots, mean difference and effect size. Chi- Squared tests were used to measure the association between progress scores and attainment.
Attitude Measure
To measure the impact of the MEP on students’ attitude towards mathematics, data were collected using an attitudinal survey. This survey consisted of 10 questions which evaluated how students’ viewed mathematics in terms of affection, difficulty, and relevance. The attitudinal survey is presented in Figure 1. The same attitudinal survey which applied a Likert three-point scale was given prior to and after the intervention. The pre- and post-test and the pre- and post-attitudinal surveys use comparative summary tables.

Figure 1.
Students’ mathematics attitudinal survey.
4. Results
4.1. The Impact of MEP on Students’ Attainment in Mathematics
The first research question was geared towards examining the effect that the implementation of the MEP in Jamaican mathematics classes would have on students’ attainment in mathematics. To answer this question, the results from the pre-test and the post-test were analysed. The results are shown in the figures and tables below:
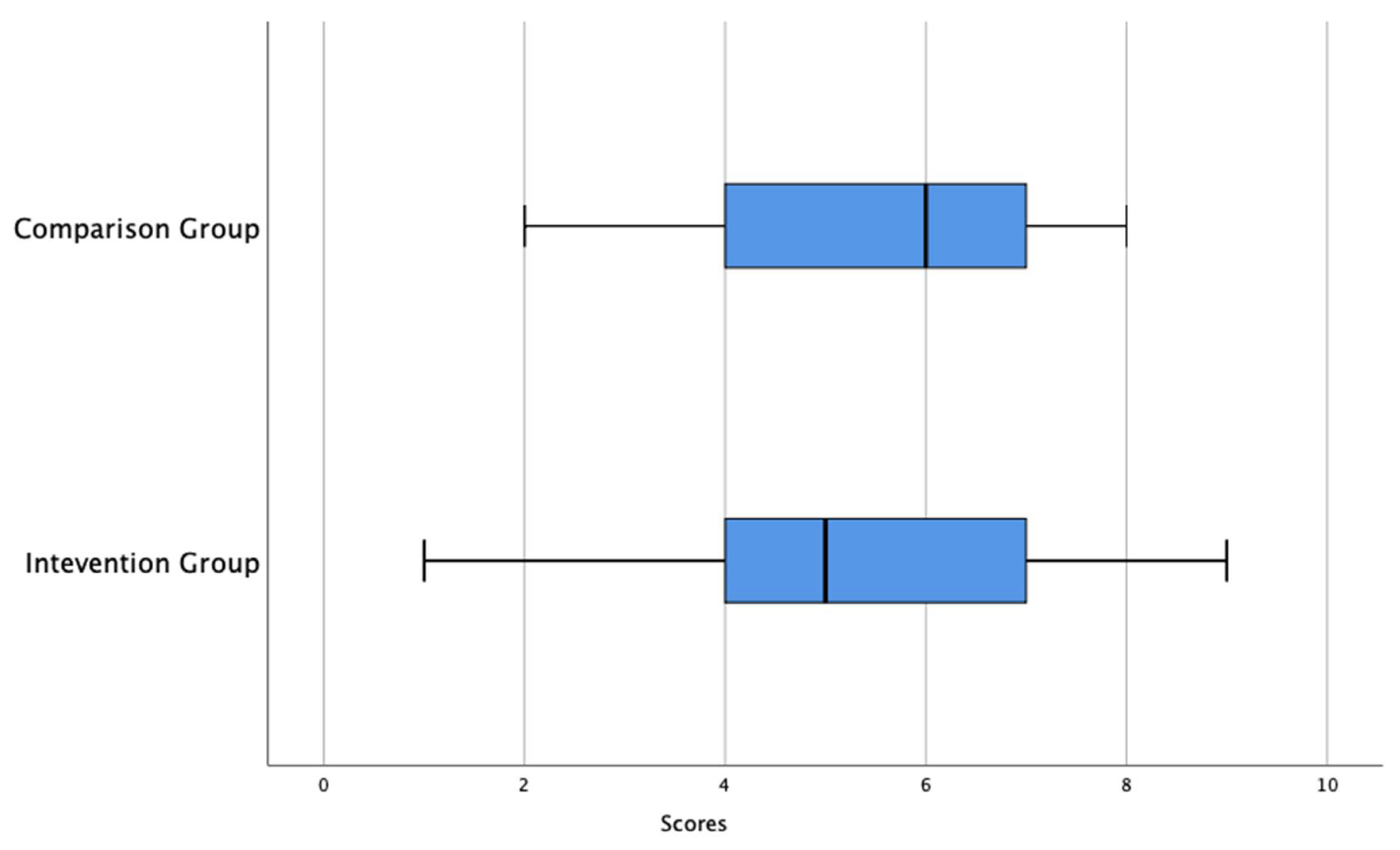
Figure 2 shows that, for the pre-test (test0), the intervention group has a median score of 5 and the comparison group has a median score of 6. This is an indicator that, for the pre-test, the median score of the intervention group is less than the median score of the comparison group. The range of score for the intervention group is 8 and the interquartile range is 3; while the range of scores for the comparison group is 6, the interquartile range is 3. That is, the pre-test score variability of the intervention group is greater than the comparison group. For the intervention group, the lower 25% of the scores lies between 1 and 4, the middle 50% of the test scores of the lies between 4 and 7 the upper 25% of scores lies between 7 to 9. For the comparison group, the lower 25% of the scores lies between 2 and 4; the middle 50% of the test scores lies between 4 and 7; the upper 25% of scores lies between 7 and 8.
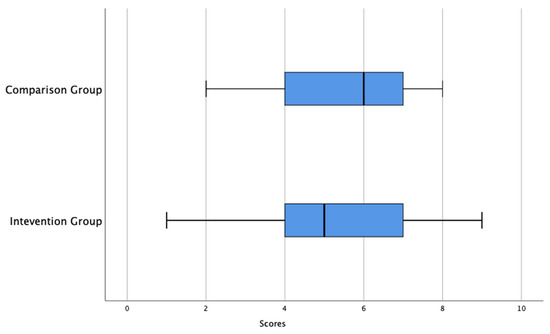
Figure 2.
Double boxplots of results of pre-test (test 0) for intervention and comparison groups.
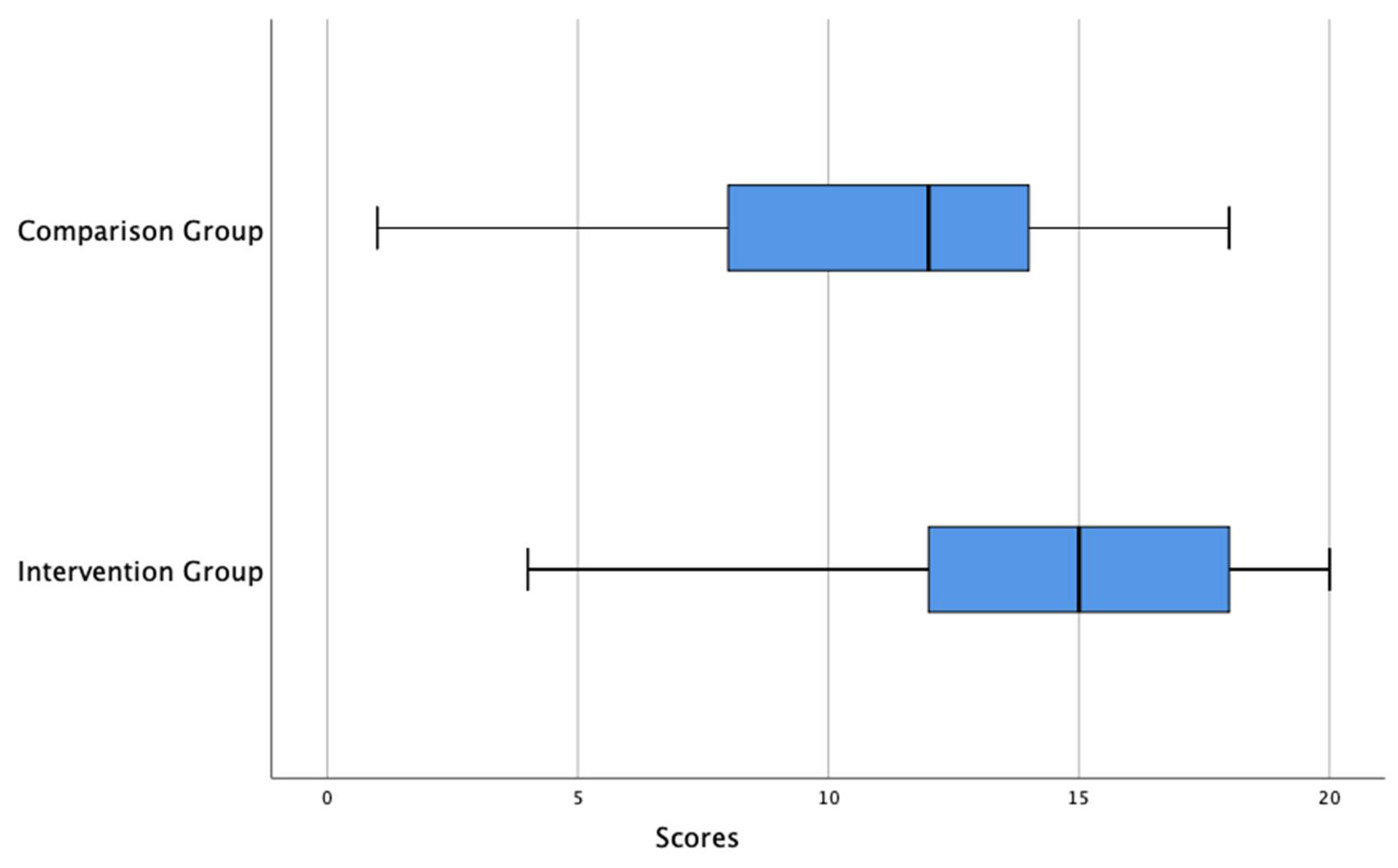
Figure 3 shows that, for the post-test (test1), the intervention group has a median score of 15 and the comparison group has a median score of 12. This is an indicator that, for the post-test, the median score of the intervention group is greater than the median score of the comparison group. The range of scores for the intervention group is 16 and the interquartile range is 6, while the range of scores for the comparison group is 17 and the interquartile range is 6. That is, the post-test variability score of the intervention group is less than the comparison group. For the intervention group, the lower 25% of the scores lies between 4 and 12, the middle 50% of the test scores of the lies between 12 and 18 the upper 25% of scores lies between 18 to 20. For the comparison group, the lower 25% of the scores lies between 1 and 8; the middle 50% of the test scores lies between 8 and 14; the upper 25% of scores lies between 14 to 18.
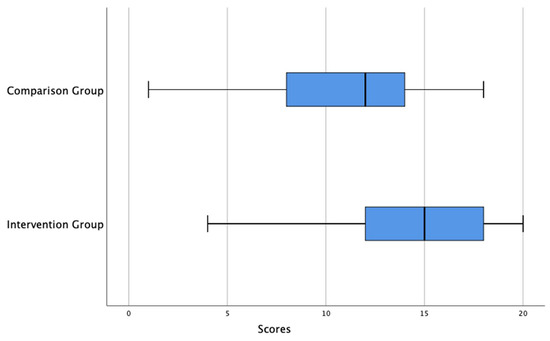
Figure 3.
Double boxplots of results of post-test (Test1) for intervention and comparison groups.
The results of the Pearson Chi-Squared Test scores for the association between progress scores and groups was 23.4 with 3 degrees of freedom, which is statistically significant at the 0.05 level. This is represented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Pearson Chi-Square tests showing the association between progress scores and the groups.
Table 3 reveals that the mean difference between the pre- and post-tests for the comparison group is 0.12 with a standard deviation of 2.64 and effect size of 0.045. As summarized in Table 3, the mean difference between the pre- and post-tests for the intervention group is 2.23, standard deviation is 1.84 and the effect size is 1.21. Based on Cohen’s d convention, the effect size for the comparison group is small, since 0.045 < 0.2 and, effectively, zero whereas the effect size for the intervention group is large, since 1.21 > 0.8. Hattie’s [31] synthesis of meta-analysis of interventions in the field of education found that the average overall effect size, using Cohen’s d statistic was 0.4. Therefore, an effect size of 1.21 is well above average and can be considered to indicate a very substantial impact of the MEP intervention.

Table 3.
Cohen’s d effect size of the pre- and post-tests for each group.
Based on the results presented in Figure 2 and Figure 3 it can be concluded that the implementation of the MEP has had a substantial positive impact on students’ attainment in mathematics. The findings presented in Table 2 and Table 3 revealed that there is a significant association between progress scores and groups, indicating that the implementation of the MEP significantly impacted students’ attainment in mathematics.
Additionally, the results of the ANCOVA (F (1, 197) = 53.9, p = 0.00] indicated a significant difference in post-test scores between the two groups after adjusting for the pre-test scores. The participants in the intervention group obtained higher scores on the post-test than those in the comparison group, with an effect size reported (η2 = 0.215). Since Montgomery [30] has stated that the eta squared effect size cut off points are small = 0.01, medium = 0.06 and large = 0.14, an effect size of η2 = 0.215 indicates a large effect size. The adjusted marginal mean post-test scores are displayed in Table 4.

Table 4.
Adjusted marginal mean post-test scores.
Covariates appearing in the model are evaluated at the following values: pre-test = 5.5200.
4.2. The Effect of the MEP on Students’ Attitude towards Mathematics
The second research question was geared at examining how the MEP impacted students’ attitude towards mathematics. To answer this question, the results from the pre and post student attitudinal surveys were analysed. The specific scale that applied to the attitudinal survey is: 1—no, 2—unsure and 3—yes.
Table 5 and Table 6 show that students’ attitude towards mathematics were positively impacted by the implementation of the MEP into Jamaican primary mathematics classroom. Higher percentage increases were observed in students’ responses on items from the survey that addressed positive feeling towards mathematics in the intervention group. Evidence of this was noted with item 1 of the survey, where it was revealed that 10% more of the students from the intervention group indicated that they liked mathematics more after being exposed to the MEP, while there were no changes in the number of students who indicated that they liked mathematics in the comparison group. Similarly, 8% more of the students of the intervention indicated that they liked going to mathematics classes on the post-attitudinal survey, while 6% more students of the comparison group indicated that they enjoyed going to mathematics classrooms on the post-attitudinal survey. It was also noted that 6% less of the students in the intervention group found mathematics hard on the post-attitudinal survey, while 2% more of the students in the comparison group found mathematics hard on the post attitudinal survey.

Table 5.
Pre- and post-students’ mathematics attitudinal survey for the intervention group.

Table 6.
Pre- and post-students’ mathematics attitudinal survey for the comparison group.
The results obtained indicated that the implementation of the MEP into Jamaican Primary classrooms positively impacted students’ attitudes towards mathematics. This was evident in the data collected, where it was observed that more students from the intervention group, when compared with the comparison group, responded ‘yes’ to questions that addressed positive attitudes towards mathematics after they were exposed to the MEP. For example, 10 percent more of the students from the intervention group indicated that they liked mathematics on the post attitudinal survey. Whereas, in the comparison group, there were no changes in the number of students who indicated that they liked mathematics on the post-attitudinal survey. Additionally, 6 percent less students in the intervention group indicated that mathematics was hard after they were exposed to the MEP, whereas in the comparison group, two percent more students indicated that mathematics was hard on the post attitudinal survey.
5. Conclusions
Study findings showed that the implementation of the MEP in Jamaican primary classes had a substantial positive impact on students’ attainment in mathematics, as indicated by an effect size of 1.21, based on Cohen D’s convention of effect size, whereas the comparison group was found to have a near-zero effect size of 0.045. This large effect size was confirmed by the analysis of covariance, which found the eta squared effect size to be large (η2 = 0.215). This finding is supported by prior research on the MEP, which indicated that performance in mathematics is positively impacted when the MEP is integrated into Mathematics classes [13,14]. Additionally, enrichment programs, such as the MEP, have been found to help deepen students’ mathematical understanding [22], which subsequently aids in improving performance in mathematics [23,24].
The findings also showed that the use of the MEP resources to teach mathematics positively impacted students’ attitude towards mathematics. The results of the post-attitudinal survey indicated that more students from the intervention group indicated that they liked mathematics, enjoyed going to mathematics class and thought mathematics was fun after they were exposed to the MEP. Additionally, after being exposed to the MEP, less students thought that mathematics was difficult. This is an indicator that students’ disposition and attitudes towards mathematics were positively impacted by the implementation of the MEP. The findings of this research are supported by previous research, which indicated that the MEP helped students to develop and display positive attitudes towards mathematics [14]. A previous study, conducted by Burghes [14], also indicated that, after the implementation of the MEP, students viewed mathematics as being an interesting subject and one which was worth persevering with when they were challenged by a task.
6. Limitations
This study examined the impact of the MEP on Jamaican students’ attainment in and attitude towards mathematics. Limitations to this study included having a small sample size, particularly for the comparison group, and the duration of the intervention. The comparison group only consisted of two classes, while the intervention group had seven classes. Comparisons were, however, made between the different intervention and comparison groups. Significant mean differences were obtained between the pre- and post-tests on mathematics performance in the sample group. The number of students in the intervention and comparison groups was not the same, which may have affected the validity of the differences obtained. The impact of the MEP on student attainment in mathematics would have been more valid if the study lasted beyond longer than nine months and if MEP resources were used for all mathematics lessons. Additionally, although teachers were observed weekly, there were no other measures in place to ensure that the teachers were implementing the MEP with fidelity when not being observed. Additionally, the impact of the MEP on Jamaican primary mathematics would have been more valid if its impact was compared to another intervention that was implemented for the same amount of time. Therefore, future research on the impact of the MEP and similar initiatives on Jamaican Primary mathematics is necessary.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.K.K.B.-T. and D.B.; Data Curation, S.K.K.B.-T.; Formal Analysis, S.K.K.B.-T.; Funding acquisition, D.B.; Methodology, S.K.K.B.-T.; Project administration S.K.K.B.-T.; Resources, D.B., Supervision, G.H., and D.B.; Validation, G.H. and D.B.; Writing—original draft S.K.K.B.-T.; Writing—review & editing, G.H. and D.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by The Centre of Innovation in Mathematics Teaching (CiMT, University of Plymouth, UK.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted according to the guidelines of the University Research Ethics Committee (UREC) and approved by University of Plymouth’s Education Research Ethics Sub-committee, with approval number 17/18-209.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data are not publicly available due to privacy restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Murphy, X. An Overview of Jamaica, the Island and People. Available online: https://jamaicans.com/fact/ (accessed on 5 December 2020).
- Dagnini, K.J. The importance of Reggae Music in the Worldwide Cultural Universe. Available online: https://journals.openedition.org/etudescaribeennes/4740?lang=en (accessed on 17 March 2021).
- Franklyn, D. Sports in Jamaica: A Local and International Perspective. Available online: http://gracekennedy.com/lecture/GRACE-Lecture-2010.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Education in Jamaica. Available online: https://www.studycountry.com/guide/JM-education.htm (accessed on 17 December 2020).
- Jamaica History & Background. Available online: https://education.stateuniversity.com/pages/725/Jamaica-HISTORY-BACKGROUND.html (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Tyson, E. Education Then and Now. Available online: http://jamaica-gleaner.com/gleaner/20120805/cleisure/cleisure4.html (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Kirton, C.; Ferguson, J. An Overview of the Economy of Jamaica. In Jamaica Debt and Poverty; Oxfam GB: Oxford, UK, 1992; Available online: https://oxfamilibrary.openrepository.com/bitstream/handle/10546/123007/bk-debt-poverty-jamaica-part-ii-010192-en.pdf;jsessionid=16B8CD7DE783850B1470F1445DD577AD?sequence=23 (accessed on 26 September 2020).
- Hastings, J. Jamaica Takes Big Steps Towards Improving its Educational System. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/results/2015/09/16/jamaica-big-steps-improving-educational-system (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Vision 2030 Jamaica. National Development Plan. Available online: http://www.vision2030.gov.jm/Portals/0/NDP/Vision%202030%20Jamaica%20NDP%20Full%20No%20Cover%20(web).pdf (accessed on 22 August 2020).
- Ministry of Education. National Mathematics Policy Guidelines. Available online: https://moey.gov.jm/sites/default/files/National%20Mathematics%20Policy%20Guidelines%20(2013).pdf (accessed on 7 July 2019).
- Buddo, C. Mathematics Education: A Case for Problem Solving. Education Matters. Available online: http://www.jamaicaobserver.com/columns/Mathematics-education--A-case-for-problem-solving_90150 (accessed on 15 March 2019).
- Government of Jamaica, Ministry of Education Youth and Information. Statistics—Varying Articles. Available online: https://www.moey.gov.jm/statistics (accessed on 17 June 2019).
- Burghes, D. Mathematics Enhancement Programme: The First 3 Years; University of Exeter, Centre for Innovation in Mathematics Teaching: Exeter, UK, 2000; Available online: https://www.cimt.org.uk/projects/mep/intrep00.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2018).
- Burghes, D. Enhancing Primary Mathematics Teaching and Learning; CfBT Education Trust: Reading, UK, 2012; pp. 33–35, 45–82, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, L.; Waheed, H. Secondary students’ attitude towards mathematics in a selected school of Maldives. Int. J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2011, 1, 77–281. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaidou, M.; Philippou, G. Attitudes towards mathematics, self-efficacy and achievement in problem solving. In European Research in Mathematics Education III; Mariotti, M.A., Ed.; University of Pisa: Pisa, Italy, 2003; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, K.; Zimmerman, L.; Ye, R. Secondary students’ attitudes toward mathematics. Acad. Exch. Q. 2004, 8, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Eshun, B. Sex-difference in attitude towards mathematics in secondary schools. Math. Connect. 2004, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, R.; Martino, P. Attitude toward mathematics: Overcoming the positive/negative dichotomy. In Beliefs and Mathematics; Sriraman, B., Ed.; The Montana Mathematics Enthusiast: Monograph Series in Mathematics Education; Age Publishing: Charlotte, NC, USA; The Montana Council of Teachers of Mathematics: Charlotte, NC, USA, 2008; pp. 197–214. [Google Scholar]
- Hynes, K.; O’Connor, S.; Chung, A.M. Literacy: Exploring Strategies to Enhance Learning in After-School Programs; Wellesley College Center for Research on Women: Boston, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Schacter, J. Reducing Social Inequality in Elementary School Reading Achievement: Establishing Summer Literacy Day Camps for Disadvantaged Children; Milken Family Foundation: Santa Monica, CA, USA, 2001; Available online: http://www.mff.org/pubs/reading_camp_study2001.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Johnson, D.T.; Sher, B.T. Recourse Guide to Mathematics Curriculum Materials for High-Ability Learners in Grades K-8; College of William and Mary, Center for Gifted Education: Williamsburg, VA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Alzoubi, S.M. Effects of Enrichment Programs on the Academic Achievement of Gifted and Talented Students. J. Educ. Young Sci. Gift. 2014, 2, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins, H.; Harding, A.; Engelbrecht, J. Student enrichment in mathematics: A case study with first year university students. Int. J. Math. Educ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 48 (Suppl. 1), S16–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M. A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Enrichment Programs on Gifted Students. Gift. Child Q. 2016, 60, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McAleavy, T. Exploring Approaches to Teaching Primary Maths. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/teacher-network/2012/jul/20/primary-maths-programme (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- Stevenson, M. ‘Profound understanding of fundamental mathematics’: A study into aspects of the development of a curriculum for content and pedagogical subject knowledge. Proc. Br. Soc. Res. Learn. Math. 2008, 28, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- French, D. Subject Knowledge and Pedagogical Knowledge. Available online: http://www.maths.manchester.ac.uk/~avb/pdf/DougFrenchSubjectKnowledge.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2019).
- Ball, D.; Thames, M.; Phelps, G. Content Knowledge for Teaching: What Makes It Special? J. Teach. Educ. 2008, 59, 389–407. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/28835113/Content_Knowledge_for_Teaching_What_Makes_It_Special (accessed on 1 January 2021). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 8th ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hattie, J. Visible Learning: A Synthesis of over 800 Meta-Analyses Relating to Achievement; Routledge: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).