Mapping of Scientific Production on Blended Learning in Higher Education
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Bibliometric Analysis
3.2. Content Analysis
3.2.1. Analysis of Models, Designs, and Development
3.2.2. Model Comparison
3.2.3. Implications for Participants
3.2.4. Agents’ Evaluation
3.2.5. Identifying Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonetti, O.C. Algunos retos a la educación superior universitaria: Enseñar a nuevas generaciones ¿‘millennials’ y ‘centennials’? Rev. Methodo Investig. Apl. A Las Cienc. Biol. 2020, 5, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, P.; Diago, M.L. Los estilos de aprendizaje: Su utilidad en las aulas y herramientas de detección adecuadas. In Investigación e Innovación en la Enseñanza Superior. Nuevos Contextos, Nuevas Ideas; Roig-Vila, R., Ed.; Octaedro: Barcelona, Spain, 2019; pp. 194–203. [Google Scholar]
- Briones, E.; Palomera, R.; Gómez-Linares, A. Motivaciones, ideas implícitas y competencias del alumnado de Magisterio. Rev. Interuniv. Form. Profr. 2021, 96, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robledo, P.; Fidalgo, R.; Arias, O.; Álvarez Fernández, L. Percepción de los estudiantes sobre el desarrollo de competencias a través de diferentes metodologías activas. Rev. Investig. Educ. 2015, 33, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-March, A. Metodologías activas para la formación de competencias. Educ. Siglo XXI 2006, 24, 35–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ballesta, J.; Izquierdo, T.; Romero, B.E. Percepción del alumnado de Pedagogía ante el uso de metodologías activas. Educ. Siglo XXI 2011, 29, 353–368. [Google Scholar]
- López-Belmonte, J.; Segura-Robles, A.; Fuentes-Cabrera, A.; Parra-González, M.E. Evaluating Activation and Absence of Negative Effect: Gamification and Escape Rooms for Learning. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2020, 17, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayor Paredes, D. El aprendizaje-servicio como eje articulador de procesos de desarrollo personal-estudiantil y social en el estudiantado universitario. Perf. Educ. 2019, 41, 124–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Sogorb, A.; Aparicio, P.; Granados, L. Percepción del alumnado universitario sobre las metodologías que desarrollan la competencia profesional coeducacional. In El Compromiso Académico y Social a Través de la Investigación e Innovación Educativas en la Enseñanza Superior; Roig-Vila, R., Ed.; Octaedro: Barcelona, Spain, 2018; pp. 175–184. [Google Scholar]
- Quitián, S.; González, J. Aspectos pedagógicos para ambientes Blended-Learning. HAMUT’AY 2020, 7, 48–59. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, H.; Gu, X. Determining the differences between online and face-to-face student–group interactions in a blended learning course. Internet High. Educ. 2018, 39, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, K.J.; Graham, C.R.; Hadlock, C. The current landscape of international blended learning. Int. J. Technol. Enhanc. Learn. 2016, 8, 84–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi-Steele, G.; Drew, S. The literature landscape of blended learning in higher education: The need for better understanding of academic blended practice. Int. J. Acad. Dev. 2013, 18, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pima, J.M.; Odetayo, M.; Iqbal, R.; Sedoyeka, E. A thematic review of blended learning in higher education. Int. J. Mob. Blended Learn. 2018, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R. Blended learning in higher education: Trends and capabilities. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2019, 24, 2523–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halverson, L.R.; Graham, C.R.; Spring, K.J.; Drysdale, J.S.; Henrie, C.R. A thematic analysis of the most highly cited scholarship in the first decade of blended learning research. Internet High. Educ. 2014, 20, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drysdale, J.S.; Graham, C.R.; Spring, K.J.; Halverson, L.R. An analysis of research trends in dissertations and theses studying blended learning. Internet High. Educ. 2013, 17, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikandi, J.W.; Morrow, D.; Davis, N.E. Online formative assessment in higher education: A review of the literature. Comput. Educ. 2011, 57, 2333–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthonysamy, L.; Koo, A.; Hew, S. Self-regulated learning strategies and non-academic outcomes in higher education blended learning environments: A one decade review. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2020, 25, 3677–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, B.G.; Rivera, L.A.; Delgadillo, R.S. Integration of learning management system technology and social networking sites in the e-learning mode: A review and discussion. Comput. Educ. J. 2019, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Nortvig, A.; Petersen, A.K.; Balle, S.H. A literature review of the factors influencing e-learning and blended learning in relation to learning outcome, student satisfaction and engagement. Electron. J. e-Learn. 2018, 16, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Sola-Martínez, T.; Cáceres-Reche, M.P.; Romero-Rodríguez, J.J.; Ramos-Navas, M. Estudio Bibliométrico de los documentos indexados en Scopus sobre la Formación del Profesorado en TIC que se relacionan con la Calidad Educativa. Rev. Electrónica Interuniv. Form. Profr. 2020, 23, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-González, V.; Sans-Rosell, N.; Jové-Deltell, M.C.; Reverter-Masia, J. Comparación entre Web of Science y Scopus, estudio bibliométrico de las revistas de anatomía y morfología. Int. J. Morphol. 2016, 34, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrútia, G.; Bonfill, X. Declaración PRISMA: Una propuesta para mejorar la publicación de revisiones sistemáticas y metaanálisis. Med. Clínica 2010, 135, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Raan, A. Measuring Science: Basic principles and application of advanced bibliometrics. In Springer Handbook of Science of Technology Indicators; Glänzel, W., Moed, H.F., Schmoch, U., Thelwall, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 237–280. [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln, Y.S.; Guba, E.G. Naturalistic Inquiry; SAGE: California, CA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Friberg, F.; Öhlen, J. Searching for knowledge and understanding while living with impending death-a phenomenological case study. Int. J. Qual. Stud. Health Well-Being 2007, 2, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Text mining and visualization using VOSviewer. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1109.2058v1. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, J. Blended learning environments: Using social networking sites to enhance the first year experience. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 2010, 26, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskal, P.; Dziuban, C.; Hartman, J. Blended learning: A dangerous idea? Internet High. Educ. 2013, 18, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, A.; Del Aguila-Obra, A.R.; Garrido-Moreno, A. Perceived playfulness, gender differences and technology acceptance model in a blended learning scenario. Comput. Educ. 2013, 63, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, W.W.; Graham, C.R.; Spring, K.A.; Welch, K.R. Blended learning in higher education: Institutional adoption and implementation. Comput. Educ. 2014, 75, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, C.R.; Woodfield, W.; Harrison, J.B. A framework for institutional adoption and implementation of blended learning in higher education. Internet High. Educ. 2013, 18, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pérez, M.V.; Pérez-López, M.C.; Rodríguez-Ariza, L. Blended learning in higher education: Students’ perceptions and their relation to outcomes. Comput. Educ. 2011, 56, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziuban, C.; Graham, C.R.; Moskal, P.D.; Norberg, A.; Sicilia, N. Blended learning: The new normal and emerging technologies. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2018, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokolo, A.; Kamaludin, A.; Romli, A.; Mat Raffei, A.F.; Eh Phon, D.N.; Abdullah, A.; Leong Ming, G.; Shukor, N.A.; Shukri Nordin, M.; Baba, S. A managerial perspective on institutions administration readiness to diffuse blended learning in higher education: Concept and evidence. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 2020, 52, 37–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokolo, A.; Kamaludin, A.; Romli, A.; Mat Raffei, A.F.; Eh Phon, D.N.; Abdullah, A.; Leong Ming, G.; Shukor, N.A.; Shukri Nordinm, M.; Baba, S. Exploring the role of blended learning for teaching and learning effectiveness in institutions of higher learning: An empirical investigation. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2019, 24, 3433–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canessa, E.; Logofatu, B. Pinvox method to enhance self-study in blended learning. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2013, 8, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirriahi, N.; Alonzo, D.; Fox, B. A blended learning framework for curriculum design and professional development. Res. Learn. Technol. 2015, 23, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidarra, J.; Rusman, E. Towards a pedagogical model for science education: Bridging educational contexts through a blended learning approach. Open Learn. 2017, 32, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciamani, S.; Perrucci, V.; Iannaccone, A. Peer feedback in a blended university course: Construction of a coding scheme. Qwerty 2018, 13, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyudi, W. The effectiveness of sharing blended project based learning (SBPBL) model implementation in operating system course. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2020, 15, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbertink, M.M.J.; Kelders, S.M.; Woudt-Mittendorff, K.M.; Westerhof, G.J. Participatory design of persuasive technology in a blended learning course: A qualitative study. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2020, 25, 4115–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, D.S.; Adha, M.M.; Pitoewas, B. The problems of implementing blended learning class in civic education students, university of lampung. Univers. J. Educ. Res. 2020, 8, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M.; Mehran, P.; Koguchi, I.; Takemura, H. Evaluating a blended course for japanese learners of english: Why quality matters. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2019, 16, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya-Muñoz, I.; Fonseca-Argüello, M.; Majano-Benavides, J.; Ugalde-Villalobos, M.E. Evaluación del diseño y desarrollo didáctico de tres asignaturas blended learning. Plan Piloto en la Facultad de Ciencias Sociales de la Universidad Nacional, Costa Rica. Rev. Electrónica Educ. 2019, 23, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlewska, A.; Beyer, W.; Whetstone, S.; Schaefli, L.; Rose, J.; Talan, B.; Kamin-Patterson, S.; Lamb, C.; Forcione, M. Converting a large lecture class to an active blended learning class: Why, how, and what we learned. J. Geogr. High. Educ. 2019, 43, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Liu, H. Effectiveness analysis of edmodo-based blended english learning mode. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2019, 14, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. An analysis on blended learning pattern based on blackboard network platform. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2016, 11, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Han, C. A case study of the application of a blended learning approach to web-based college english teaching platform in a medical university in eastern china. Theory Pract. Lang. Stud. 2012, 2, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucaromana, U. The effects of blended learning on the intrinsic motivation of thai EFL students. Engl. Lang. Teach. 2013, 6, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Du, X. Implementation of a blended learning model in content- based EFL curriculum. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2019, 14, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oweis, T.I. Effects of using a blended learning method on students’ achievement and motivation to learn english in Jordan: A pilot case study. Educ. Res. Int. 2018, 91, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isiguzel, B. The blended learning environment on the foreign language learning process: A balance for motivation and achievement. Turk. Online J. Distance Educ. 2014, 15, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alducin-Ochoa, J.M.; Vázquez-Martínez, A.I. Academic performance in blended-learning and face-to-face university teaching. Asian Soc. Sci. 2016, 12, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banyen, W.; Viriyavejakul, C.; Ratanaolarn, T. A blended learning model for learning achievement enhancement of thai undergraduate students. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2016, 11, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, V.; Morello, A.; Oster, C.; Redmond, C.; Vnuk, A.; Lennon, S.; Lawn, S. E-learning for self-management support: Introducing blended learning for graduate students—A cohort study. BMC Med Educ. 2018, 18, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, L.; Tuz, M.A.; Pacheco, L.V.; Pérez, G.; Estrada, S.; Cauich, J. Use of information and communication technologies as a motivational strategy in the blended learning classroom. Electron. J. Res. Educ. Psychol. 2019, 17, 683–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, M.; Awang, S.; Rahman, R.A. Are MOOCs in blended learning more effective than traditional classrooms for undergraduate learners? Univers. J. Educ. Res. 2019, 7, 2417–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owston, R.; York, D.N.; Malhotra, T. Blended learning in large enrolment courses: Student perceptions across four different instructional models. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 2019, 35, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukatiman, A.M.; Siswandari, R. Implementation of blended learning in vocational student’s to achieve hot skills (V-hots). Univers. J. Educ. Res. 2020, 8, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurkhin, A.; Kardoyo, P.H.; Setiyani, R.; Widhiastuti, R. Applying blended problem-based learning to accounting studies in higher education; Optimizing the utilization of social media for learning. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2020, 15, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galustyan, O.V.; Solyankin, A.V.; Skripkina, A.V.; Shchurov, E.A.; Semeshkina, T.V.; Ledeneva, A.V. Application of blended learning for formation of project competence of future engineers. Int. J. Eng. Pedagog. 2020, 10, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Huang, C.K.; Ko, C.J. The impact of perceived enjoyment on team effectiveness and individual learning in a blended learning business course: The mediating effect of knowledge sharing. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 2020, 36, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, N.; Hamzah, M.I. Impact of implementing blended learning on students’ interest and motivation. Univers. J. Educ. Res. 2020, 8, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, J.; Meyer, D.; Phillips, B. Using blended learning in postgraduate applied statistics programs. Turk. Online J. Distance Educ. 2019, 20, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obukhova, L.A.; Galustyan, O.V.; Baklanov, I.O.; Belyaev, R.V.; Kolosova, L.A.; Dubovitskaya, T.V. Formation of organizational competence of future engineers by means of blended learning. Int. J. Eng. Pedagog. 2020, 10, 19–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Rodríguez, Y.; Lara-Verástegui, R. Percepción del blended learning en el proceso enseñanza aprendizaje por estudiantes del posgrado de Odontología. Educ. Méd. 2018, 19, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo Maza, E.M.; Gómez Lozano, M.T.; Cardozo Alarcón, A.C.; Moreno Zuluaga, L.; Gamba Fadul, M. Blended learning supported by digital technology and competency-based medical education: A case study of the social medicine course at the universidad de los andes, colombia. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Awamleh, A. Students’ satisfaction with blended learning programmes in the Faculty of Physical Education. Sci. Educ. Today 2019, 9, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocak, M.A.; Topal, A.D. Blended learning in anatomy education: A study investigating medical students’ perceptions. Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2015, 11, 647–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmitadila, R.; Widyasari, W.; Humaira, M.A.; Tambunan, A.R.S.; Rachmadtullah, R.; Samsudin, A. Using blended learning approach (BLA) in inclusive education course: A study investigating teacher students’ perception. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2020, 15, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiedat, R.; Nasir Eddeen, L.; Harfoushi, O.; Koury, A.; Al-Hamarsheh, M.; AlAssaf, N. Effect of blended-learning on academic achievement of students in the university of Jordan. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2014, 9, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Yu, H. Effectiveness study of English learning in blended learning environment. Theory Pract. Lang. Stud. 2012, 2, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, C.; Fulton, C. Digital literacy in higher education: A case study of student engagement with e-tutorials using blended learning. J. Inf. Technol. Educ. Innov. Pract. 2019, 18, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Shi, X. On the effects of computer-assisted teaching on learning results based on blended learning method. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2019, 14, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, M.A. Student’s perception about quality of a blended learning environment with Moodle assistance. Pixel-Bit Rev. Medios Educ. 2018, 53, 193–205. [Google Scholar]
- Ridwan, H.H.; Aras, I. Blended learning in research statistics course at the english education department of Borneo Tarakan University. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2020, 15, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandakatla, R.; Berger, E.J.; Rhoads, J.F.; DeBoer, J. Student perspectives on the learning resources in an Active, Blended and Collaborative (ABC) pedagogical environment. Int. J. Eng. Pedagog. 2020, 10, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, D.; Orsi, H. Blended learning as a modality of active interaction and critical reflection: A teaching experience report in Brazil. Texto Livre 2017, 10, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zibin, A.; Altakhaineh, A.R.M. The effect of blended learning on the development of clause combining as an aspect of the acquisition of written discourse by jordanian learners of english as a foreign language. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2019, 35, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsuddin, N.; Kaur, J. Students’ learning style and its effect on blended learning, does it matter? Int. J. Eval. Res. Educ. 2020, 9, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnova, L.; Shurygin, V. Blended learning of physics in the context of the professional development of teachers. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2019, 14, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.Y.M. Blended learning dilemma: Teacher education in the confucian heritage culture. Aust. J. Teach. Educ. 2019, 44, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, D.; Núñez, M.C. Una experiencia flipped classroom en educación superior: La formación del profesorado de secundaria. In Investigar con y Para la Sociedad; ADIPE: Cádiz, Spain, 2015; pp. 1707–1720. Available online: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=5189994 (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Castañeda, L.; Selwyn, N. Reiniciando la Universidad: Buscando un Modelo de Universidad en Tiempos Digitales; Editorial UOC: Barcelona, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bati, T.B.; Gelderblom, H.; Van Biljon, J. A blended learning approach for teaching computer programming: Design for large classes in sub-saharan africa. Comput. Sci. Educ. 2014, 24, 71–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isayeva, O.; Shumylo, M.; Khmilyar, I.; Mylyk, O.; Myskiv, I. Blended Learning in Higher Medical Education: Principles and Strategies of Teaching Foreign Languages. Adv. Educ. 2020, 7, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, R.M.; Borokhovski, E.; Schmid, R.F.; Tamim, R.M.; Abrami, P.C. A meta-analysis of blended learning and technology use in higher education: From the general to the applied. J. Comput. High. Educ. 2014, 26, 87–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Means, B.; Toyama, Y.; Murphy, R.; Baki, M. The effectiveness of online and blended learning: A meta-analysis of the empirical literature. Teach. Coll. Rec. 2013, 115, 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Husban, N.; Shorman, S. Perceptions of syrian student refugees towards blended learning: Implications for higher education institutions. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2020, 15, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
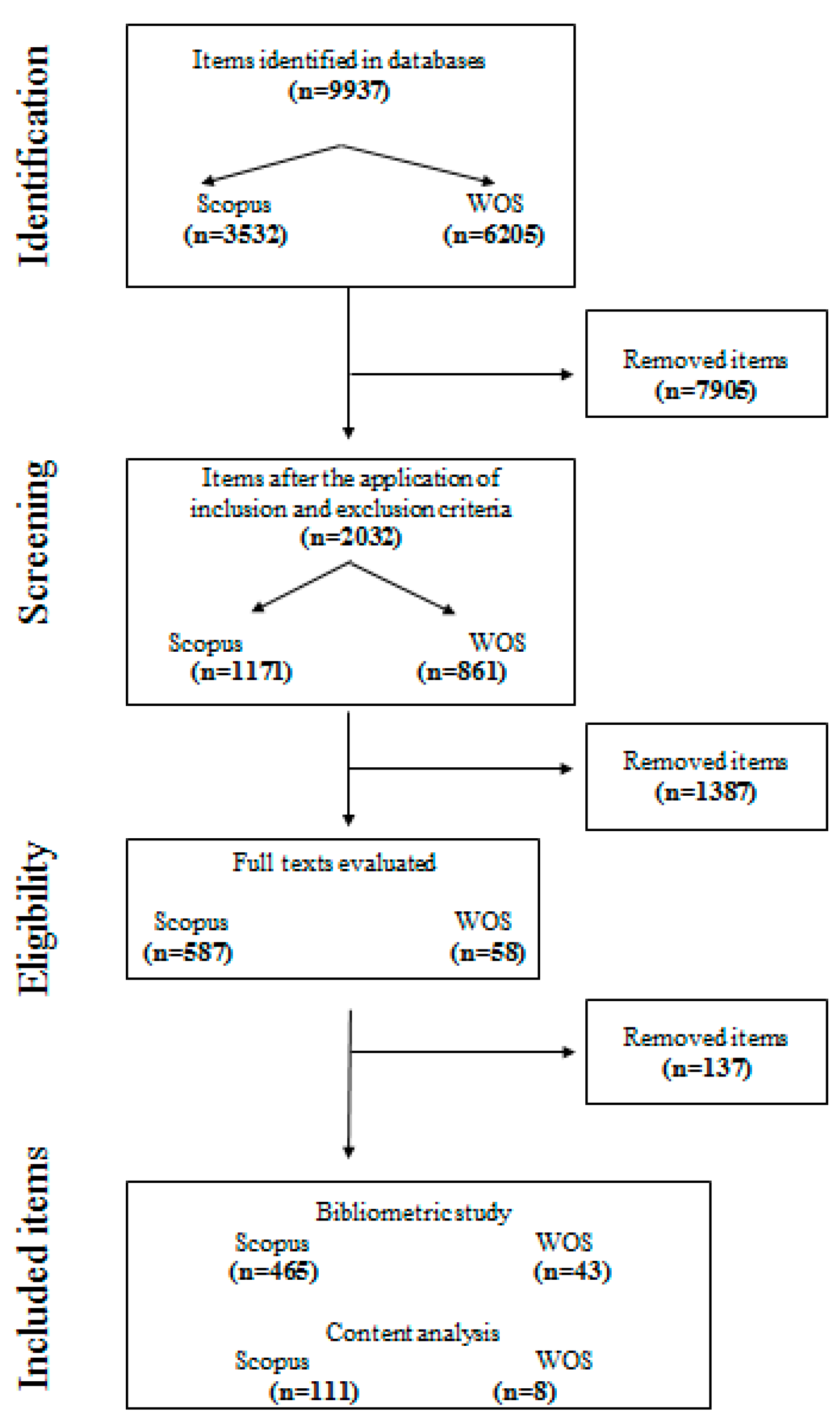
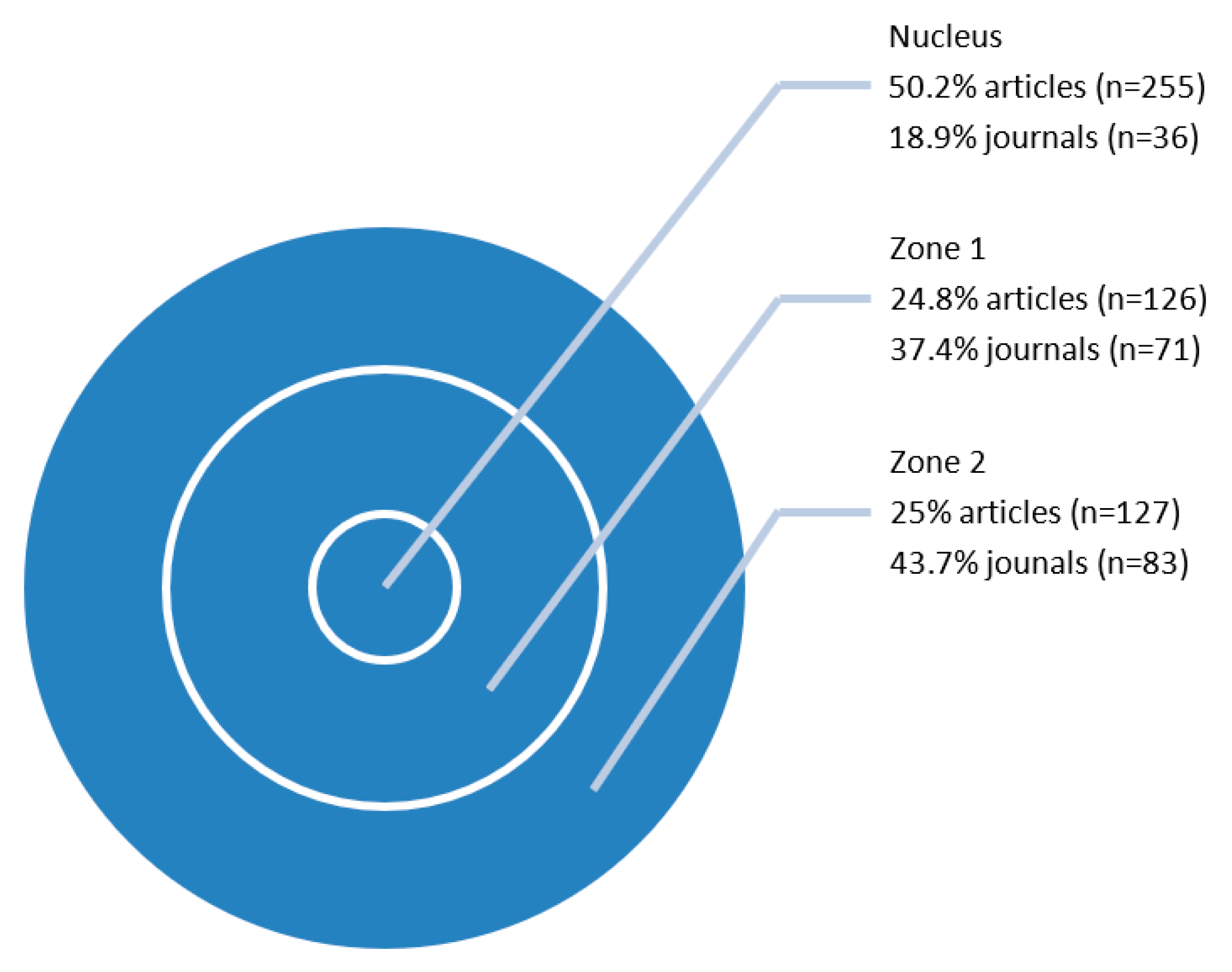
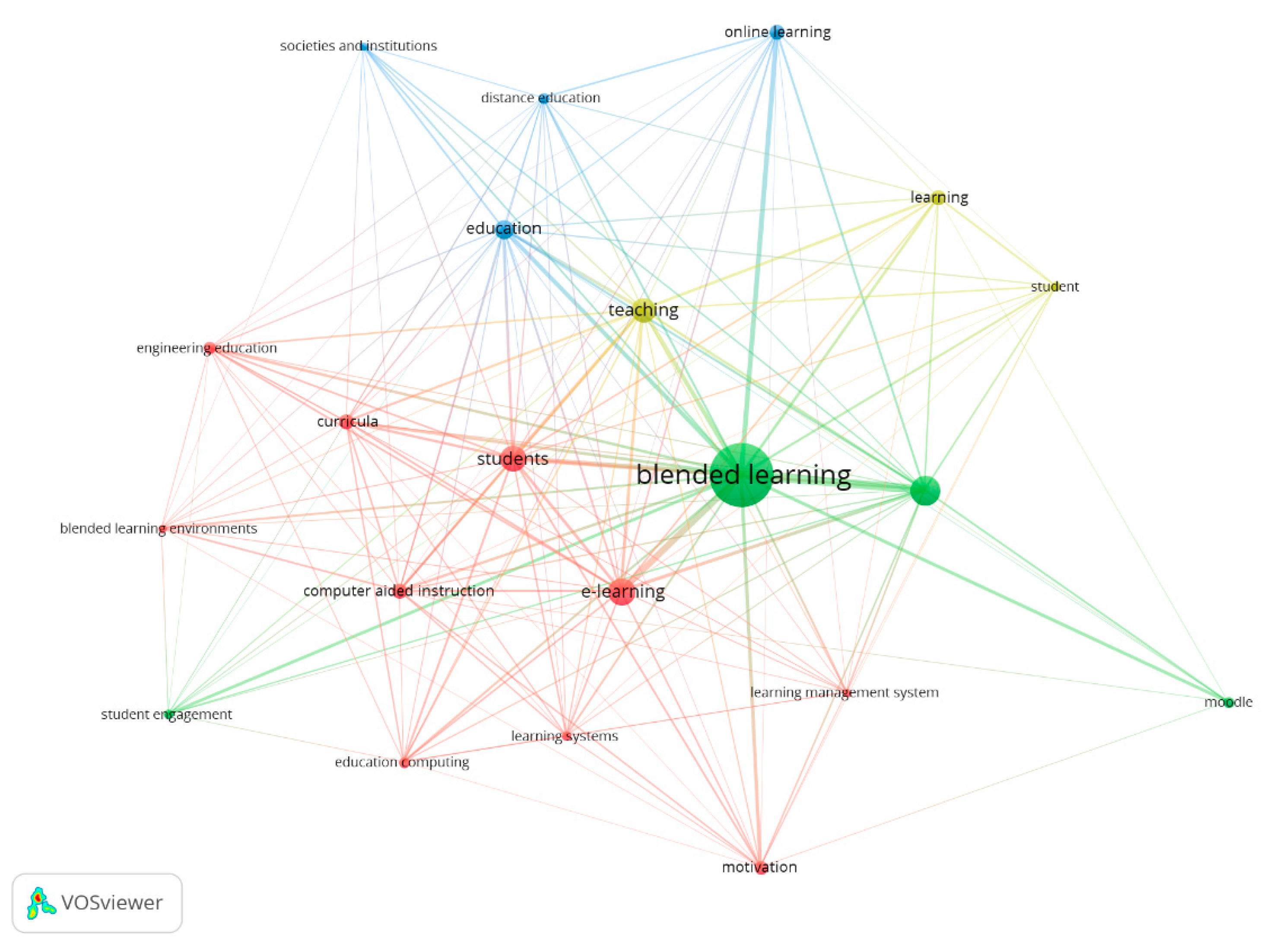
| Variables | Inclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Databases | Renowned international databases: Scopus and WOS. |
| Keywords | University OR higher education AND blended learning. |
| Year of publication | 2010–2020. |
| Document type | Scientific papers on Blended Learning implementation. |
| Area of research | Social sciences. |
| Country | No exclusion criteria was applied. The five top countries are identified. |
| Affiliation | Institutions with more than 5 papers were analysed. |
| Journals | Journals with more than 10 papers were analysed. |
| Languages | Keywords in English, Spanish, Portuguese, and French. |
| Citations | Papers with more than 150 citations were analysed. |
| Authors | Authors with more than 10 articles were identified. |
| Bibliometric map | Including keywords with more than 10 occurrences. |
| Journals | N | % | Citations | Impact Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning | 25 | 4.9% | 62 | 2.48 |
| Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology | 18 | 3.5% | 88 | 4.89 |
| Computers and Education | 14 | 2.8% | 1083 | 77.36 |
| Education and Information Technologies | 14 | 2.8% | 41 | 2.93 |
| Internet and Higher Education | 14 | 2.8% | 834 | 59.6 |
| International Journal of Mobile and Blended Learning | 12 | 2.4% | 30 | 0.25 |
| International Journal of Continuing Engineering Education and Life-Long Learning | 10 | 2% | 26 | 2.6 |
| Australasian Journal of Educational Technology | 10 | 2% | 247 | 26.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castro-Rodríguez, M.M.; Marín-Suelves, D.; López-Gómez, S.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, J. Mapping of Scientific Production on Blended Learning in Higher Education. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11090494
Castro-Rodríguez MM, Marín-Suelves D, López-Gómez S, Rodríguez-Rodríguez J. Mapping of Scientific Production on Blended Learning in Higher Education. Education Sciences. 2021; 11(9):494. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11090494
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastro-Rodríguez, Mª Montserrat, Diana Marín-Suelves, Silvia López-Gómez, and Jesús Rodríguez-Rodríguez. 2021. "Mapping of Scientific Production on Blended Learning in Higher Education" Education Sciences 11, no. 9: 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11090494
APA StyleCastro-Rodríguez, M. M., Marín-Suelves, D., López-Gómez, S., & Rodríguez-Rodríguez, J. (2021). Mapping of Scientific Production on Blended Learning in Higher Education. Education Sciences, 11(9), 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11090494







