The Use of Monologue Speaking Tasks to Improve First-Year Students’ English-Speaking Skills
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
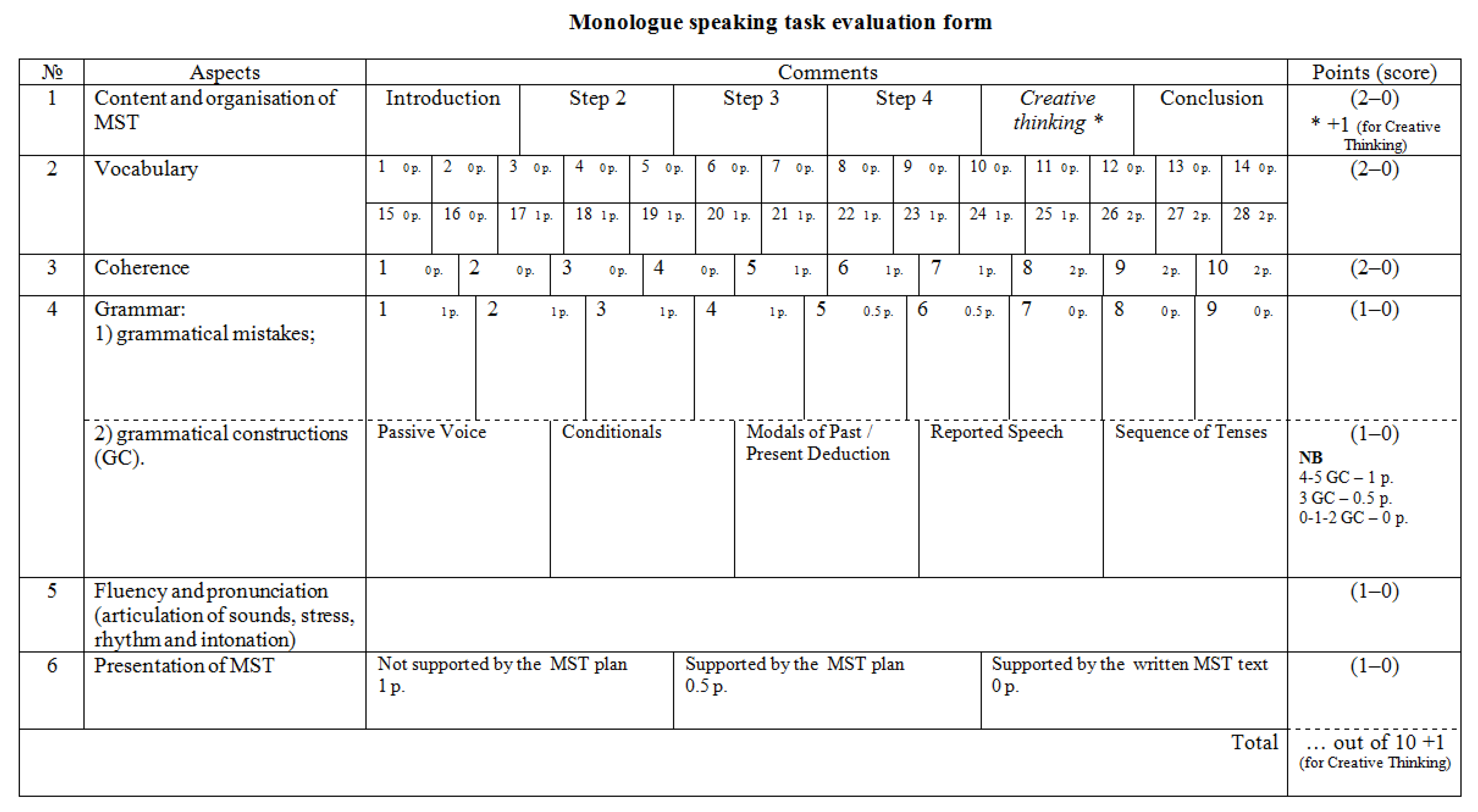
- the table with all parameters and criteria for MST evaluation (Table 1);
- the list of topic vocabulary that consisted of collocations and idioms to use in a monologue;
- the list of linkers to make logical connections of ideas;
- the detailed plan of a monologue, which included five steps (an introduction, three subtopics on the main topic, and a conclusion). See Appendix A, Table A1.
- (1)
- content and organisation of a monologue (the degree of topic elaboration and the relevance of all structural elements to the MST plan);
- (2)
- vocabulary (the usage of topic vocabulary);
- (3)
- coherence of MST structural elements and the use of linking words and phrases;
- (4)
- grammar (the use of grammatical constructions and the number of grammar mistakes made);
- (5)
- fluency and pronunciation (articulation of sounds, stress, rhythm, and intonation);
- (6)
- presentation of a monologue.
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Example of the MST Plan on the Topic “Personality”
| You Are Going to Give a Talk about PERSONALITY | Vocabulary | Linking Words and Phrases |
|---|---|---|
| REMEMBER! Your speech will be graded according to the following criteria: relevance, coherence, fluency, grammar & vocabulary (see ‘Parameters and criteria for MST evaluation’). | Fill in the columns with
| |
| Step 1. Introduction 1. Make up a hook sentence that will attract listener’s attention to your speech (a quote, proverb, tongue-twister, etc.) 2. Lead your speech steadily to the 2nd step. 3. Introduction consists of 4–6 sentences. | ||
| Step 2. Personality Types (PT) 1. Speak about PTs (extroverts and introverts). 2. Does your future profession correspond with your PT? Is it right to choose the profession relying on the PT? | ||
| Step 3. Exploring Personality 1. Speak about the problems that are connected with personality tests. 2. Do you trust them? Why? When can they be used? | ||
| Step 4. Charisma 1. Speak about what charisma is. Is it inborn? 2. …the person with charisma. Does he/she use it in the right/wrong way? | ||
| Step 5. CREATIVE THINKING Introduce your own extra idea(s) on personality that hasn’t/haven’t been mentioned before. Substantiate your choice. | ||
| Step 6. Conclusion 1. Repeat the main idea of the introduction in other words. 2. Summarise the ideas of steps 2, 3, 4, 5. | ||
References
- Fernández, M.; Araújo, A.; Vacas, C.; Almeida, L.; Rodríguez González, M. Predictors of students’ adjustment during transition to university in Spain. Psicothema 2017, 29, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlov, A.; Pazukhina, S.; Yakushin, A.; Ponomareva, T. Study of first-year students’ adaptation difficulties as the basis to promote their personal development in university education. Psychol. Russ. State Art 2018, 11, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneyers, E.; De Witte, K. Interventions in higher education and their effect on student success: A meta-analysis. Educ. Rev. 2018, 70, 208–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, P.; Burakova, D.; Tokareva, E. Effective Teaching Techniques for Engineering Students to Mitigate the Second Language Acquisition. In Proceedings of the Integrating Engineering Education and Humanities for Global Intercultural Perspectives, St. Petersburg, Russia, 25–27 March 2020; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2020; Volume 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroganova, O.; Bozhik, S.; Voronova, L.; Antoshkova, N. Investigation into the professional culture of a foreign language teacher in a multicultural classroom from faculty and international students’ perspectives. Educ. Sci. 2019, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjanggi, R.; Kusumaningsih, L. The correlation between social anxiety and academic adjustment among freshmen. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 219, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlashkina, O.; Naumova, E.; Tevlyukova, O. Social adaptation of the first-year university students (following the research data). Theory Pract. Soc. Dev. 2017, 11, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Clinciu, A. Adaptation and stress for the first year university students. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 78, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindina, T.A.; Knyazeva, N.V.; Usmanova, N.V.; Chuvashova, A.D. The basic department as the adaptation tool of students to the professional environment. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ata, A.W.; Tran, L.T.; Liyanage, I. Educational Reciprocity and Adaptivity; Routledge: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beech, S.E. Adapting to change in the higher education system: International student mobility as a migration industry. J. Ethn. Migr. Stud. 2017, 44, 610–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Noltemeyer, A.; Wang, A.; Zhang, J.; Shaw, K. Cross-cultural adaptation of international college students in the United States. J. Int. Stud. 2018, 8, 821–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odinokaya, M.A.; Barinova, D.O.; Sheredekina, O.A.; Kashulina, E.V.; Kaewunruen, S. The Use of e-Learning Technologies in the Russian University in the Training of Engineers of the XXI Century. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 940, 012131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odinokaya, M.A.; Karpovich, I.A.; Ju Mikhailova, O.; Piyatnitsky, A.N.; Klimova, B. Interactive technology of pedagogical assistance as a means of adaptation of foreign first-year students. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpovich, I.A.; Krepkaia, T.N.; Voronova, L.S.; Combarros-Fuertes, P. Novice university educators: Professional, psychological and motivational spheres of adaptation. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitasari, P.; Wahab, M.; Othman, A.; Herawan, T.; Sinnadurai, S. The relationship between study anxiety and academic performance among engineering students. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2010, 8, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A. EFL effective factors: Anxiety and motivation and their effect on Saudi College student’s achievement. Arab. World Engl. J. 2015, 6, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odinokaya, M.; Karpovich, I. Modern condition of problems of adaptation of Russian teachers at the initial stage of work in the university. Azimuth Sci. Res. Pedagog. Psychol. 2019, 8, 211–214. [Google Scholar]
- Van Rooij, E.; Jansen, E.; van de Grift, W. First-year university students’ academic success: The importance of academic adjustment. Eur. J. Psychol. Educ. 2018, 33, 749–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronova, L.; Karpovich, I.; Stroganova, O.; Khlystenko, V. The Adapters public institute as a means of first-year students’ pedagogical support during the period of adaptation to studying at a university. In Proceedings of the Conference Integrating Engineering Education and Humanities for Global Intercultural Perspectives, St. Petersburg, Russia, 25–27 March 2020; Volume 133, pp. 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasylkiw, L. Students’ perspectives on pathways to university readiness and adjustment. J. Educ. Train. Stud. 2016, 4, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemers, M.M.; Hu, L.T.; Garcia, B.F. Academic self-efficacy and first-year college student performance and adjustment. J. Educ. Psychol. 2001, 93, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumrei-Mancuso, E.J.; Newton, F.B.; Kim, E.; Wilcox, D. Psychosocial factors predicting first-year college student success. J. Coll. Stud. Dev. 2013, 54, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razinkina, E.; Pankova, L.; Trostinskaya, I.; Pozdeeva, E.; Evseeva, L.; Tanova, A. Influence of the educational environment on students’ managerial competence. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 110, 02097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonta, I.; Bulgak, A. The adaptation of students to the academic environment in university. Rev. Rom. Pentru Educ. Multidimens. 2019, 11, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinto, V. Taking retention seriously: Rethinking the first year of college. NACADA J. 1999, 19, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linton, D.L.; Farmer, J.K.; Peterson, E. Is peer interaction necessary for optimal active learning? CBE Life Sci. Educ. 2014, 13, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazova, N.; Rubtsova, A.; Eremin, Y.; Kats, N.; Baeva, I. Tandem Language Learning as a Tool for International Students Sociocultural Adaptation. In Proceedings of the Integrating Engineering Education and Humanities for Global Intercultural Perspectives, St. Petersburg, Russia, 25–27 March 2020; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2020; pp. 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarraju, M.; Musulkin, S.; Bhattacharya, G. Role of student–faculty interactions in developing college students’ academic self-concept, motivation, and achievement. J. Coll. Stud. Dev. 2010, 51, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, B.E.; Orehovec, B.E.E. Faculty-student interaction outside the classroom: A typology from a residential college. Rev. High. Educ. 2007, 30, 343–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borschenko, G. Streaming of EFL Students: Evaluation Of Effectiveness. In Proceedings of the Joint Conferences: Professional Culture of the Specialist of the Future & Communicative Strategies of Information Society, St. Petersburg, Russia, 26–27 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odinokaya, M.; Krepkaia, T.; Karpovich, I.; Ivanova, T. Self-regulation as a basic element of the professional culture of engineers. Educ. Sci. 2019, 9, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazara, S. Students’ Perception on EFL Speaking Skill Development. JET J. Engl. Teach. 2011, 1, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doe, T. Oral Fluency Development Activities: A One-Semester Study of EFL Students; ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, Temple University: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017; p. 276. [Google Scholar]
- Almazova, N.; Bernavskaya, M.; Barinova, D.; Odinokaya, M.; Rubtsova, A. Interactive learning technology for overcoming academic adaptation barriers. Lect. Notes Netw. Syst. 2020, 131, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedeva, O.D.; Andreeva, S.S.; Krepkaia, T.N. Teaching listening comprehension through online academic lectures. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, R.P.; Davies, B.L. Monologue as a turn in dialogue: Towards an integration of exchange structure and rhetorical structure theory. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. 1992, 587, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubtsova, A. Socio-linguistic innovations in education: Productive implementation of intercultural communication. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 497, 012059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhana, J. Psychological Factors That Hinder Students from Speaking in English Class (a Case Study in a Senior High School in South Tangerang, Banten, Indonesia). J. Educ. Pract. 2012, 3, 100–110. [Google Scholar]
- Marhamah, M. The Relationship between Shyness and Motivation to Speak English of the First Year Students of English Study Program of FKIP UIR Pekanbaru. J-SHMIC J. Engl. Acad. 2016, 3, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmansyah, F.; Sudarsono, S.; Eni, R. Teaching speaking narrative monologue by using shrinking story strategy. J. Pendidik. Dan Pembelajaran Untan 2014, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, H.D. Teaching by Principles: An Interactive Approach to Language Pedagogy, 2nd ed.; San Fransisco State University: San Fransisco, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Harmer, J. Essential Teacher Knowledge: Core Concepts in English Language Teaching, 1st ed.; Pearson Longman: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Council of Europe. Common European Framework of Reference for Languages: Learning, Teaching, Assessment—Companion Volume, Council of Europe Publishing, Strasbourg, 2020. Available online: www.coe.int/lang-cefr (accessed on 3 June 2021).
- Pavlikova, K. Use of Monologues, Games and Problem Solving Activities for Development of Speaking Skills; Boosting the Educational Experiencing of Language; International Association for the Educational Role of Language: Gdańsk, Poland, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Karatas, H.; Alci, B.; Bademcioglu, M.; Ergin, A. An investigation into university students. Foreign language speaking anxiety. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 232, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahiri, A.; Berlin, S.; Sumarsih. To What extent do anxiety and self-efficacy effect the EFL students’ English monologue speaking skill? Int. J. Educ. Res. 2017, 5, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Roysmanto, R. A Correlation between Self-Confidence and the Students’ Speaking Skill. Res. Innov. Lang. Learn. 2018, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürler, İ. Correlation between Self-confidence and Speaking Skill of English Language Teaching and English Language and Literature Preparatory Students. Curr. Res. Soc. Sci. 2015, 1, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Leong, L.M.; Ahmadi, S.M. An Analysis of Factors Influencing Learners’ English Speaking Skill. Int. J. Res. Engl. Educ. 2017, 2, 34–41. Available online: http://ijreeonline.com/files/site1/user_files_68bcd6/sma1357-A-10-26-1-fefa0eb.pdf (accessed on 3 June 2021). [CrossRef]
- Borisova, Y.V.; Maevskaya, A.Y.; Skornyakova, E.R. Specific Purposes Texts’ Translation Training for Mining and Civil Engineering Specialties Students. In Proceedings of the Joint Conferences: Professional Culture of the Specialist of the Future & Communicative Strategies of Information Society, St. Petersburg, Russia, 26–27 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gömleksiż, M.N. Effectiveness of cooperative learning (Jigsaw II) method in teaching English as a foreign language to engineering students (case of Firat University, Turkey). Eur. J. Eng. Educ. 2007, 32, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kırkgöz, Y. Students’ and lecturers’ perceptions of the effectiveness of foreign language instruction in an English-Medium University in Turkey. Teach. High. Educ. 2009, 14, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anosova, N.; Dashkina, A. The Teacher’s Role in Organizing Intercultural Communication between Russian and International Students. In Proceedings of the Integrating Engineering Education and Humanities for Global Intercultural Perspectives, St. Petersburg, Russia, 25–27 March 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 131, pp. 465–474. [Google Scholar]
- Adachi, C.; Hong-Meng Tai, J.; Dawson, P. Academics’ perceptions of the benefits and challenges of self and peer assessment in higher education. Assess. Eval. High. Educ. 2018, 43, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grez, L.; Valcke, M.; Roozen, I. How effective are self- and peer assessment of oral presentation skills compared with teachers’ assessments? Act. Learn. High. Educ. 2012, 13, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, L.R.; Brown, G.T.L. Opportunities and obstacles to consider when using peer- and self-assessment to improve student learning: Case studies into teachers’ implementation. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2013, 36, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrudula, P. The Influence of Peer Feedback on Self- and Peer-Assessment of Oral Skills. Lang. Test. 2002, 19, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, F.D.; Tjosvold, D. Effects of student participation in classroom decision making on attitudes, peer interaction, motivation, and learning. J. Appl. Psychol. 1980, 65, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A. Structuring peer interaction to promote high-level cognitive processing. Theory Pract. 2002, 41, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, J.W. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches, 4th ed.; SAGE Publications Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 80–83. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, H.; Shannon, S.E. Three approaches to qualitative content analysis. Qual. Health Res. 2005, 15, 1277–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assarroudi, A.; Nabavi, F.H.; Armat, M.R.; Ebadi, A.; Vaismoradi, M. Directed qualitative content analysis: The description and elaboration of its underpinning methods and data analysis process. J. Res. Nurs. 2018, 23, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramming, U. Calculating with Words: Perspectives from Philosophy of Media, Philosophy of Science, Linguistics and Cultural History. Technol. Lang. 2021, 2, 12–25. [Google Scholar]
- Da Re, L.; Zago, Z. Academic transition and peer tutoring: A case study at the University of Padova. In Education Applications & Developments Advances in Education and Educational Trends Series; Carmo, M., Ed.; InScience Press: Lisboa, Portugal, 2015; pp. 25–34. Available online: http://insciencepress.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/ISP_Education-Applications-Developments-Book.pdf (accessed on 18 May 2021).
- Poling, K. MySci advisors: Establishing a peer-mentoring program for first year science students’ support. Collect. Essays Learn. Teach. (CELT) 2015, 8, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Chang, Y.S. Assessing the effects of interactive blogging on student attitudes towards peer interaction, learning motivation, and academic achievements. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2012, 28, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollar, I.; Fischer, F. Peer assessment as collaborative learning: A cognitive perspective. Learn. Instr. 2010, 20, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk, D.H.; Ertmer, P.A. Self-Regulation and Academic Learning: Self-efficacy Enhancing Interventions. In Handbook of Self-Regulation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkworth, R.; McCann, B.; Matthews, C.; Nordström, K. First year expectations and experiences: Student and teacher perspectives. High. Educ. 2009, 58, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, D. The Skills of Argument; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, T.; Howe, C.; Soden, R.; Halliday, J.; Low, J. Peer interaction and the learning of critical thinking skills in further education students. Instr. Sci. 2001, 29, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odinokaya, M.; Krepkaia, T.; Sheredekina, O.; Bernavskaya, M. The culture of professional self-realization as a fundamental factor of students’ internet communication in the modern educational environment of higher education. Educ. Sci. 2019, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, M.; Oliver, R. Teaching metacognitive regulation of reading comprehension in an on-line environment. In Proceedings of the ED-MEDIA 2003—World Conference on Educational Multimedia, Hypermedia & Telecommunications, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–28 June 2003; pp. 2464–2471. [Google Scholar]
| No | Aspects | 2 Points | 1 Point | 0 Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Content and organisation of MST (the degree of the topic elaboration and relevance of all MST elements to its plan) | The topic is elaborate and MST structure fully corresponds to the MST plan. | Lack of one structural element or content discrepancy of one structural element. | Lack of two or more structural elements or content discrepancy of two or more structural elements. |
| Extra point is given for the section Creative Thinking | ||||
| 2. | Vocabulary (the usage of topic vocabulary from the list given to students) | The use of 75% of the vocabulary and more, i.e., 26 lexical units. NB. The lexical unit is accepted in case of its correct pronunciation and usage in the right context. | The use of 50–75% of the vocabulary, i.e., 17–25 lexical units. | The use of less than 50% of the vocabulary, i.e., 16 lexical units and less. |
| 1 point for each aspect | 0.5 point for each aspect | 0 point for each aspect | ||
| 3. | Coherence | All structural elements of MST are coherent. The use of 8 linkers and more. | The use of 5–7 linkers. | The use of fewer than 5 linkers. |
| 4. | Grammar: (1) grammatical mistakes. (2) grammatical constructions. | 1. No more than 4 grammatical mistakes (that do not affect understanding) are allowed. 2. The use of 4–5 unrepeated grammatical constructions: Passive Voice, Conditionals, Modals of Past/Present Deduction, Reported Speech, and Sequence of Tenses. | 1. 5–6 corrected grammatical mistakes are allowed. 2. The use of 3 unrepeated grammatical constructions. | 1. More than 6 grammatical mistakes are made that affect understanding. 2. The use of only 0–1–2 listed grammatical constructions. |
| 5. | Fluency and pronunciation (articulation of sounds, stress, rhythm, and intonation) | The speech is fluent (smooth with little or no pausing). Pronunciation corresponds to the norm. | The speech is rather fluent (fast enough, but disconnected and unclear). A few phonetic and prosodic mistakes are made. | The speech is slow with lots of pausing; the speech contains repetitions of the same words most of the time. A lot of phonetic and prosodic mistakes are made. |
| 6. | Presentation of MST (oral answer) | The speaker relies on the MST plan only while performing the utterance. | MST is supported by the plan together with the student’s notes (keywords, the first word of the sentence, etc.) | MST is supported by the text. |
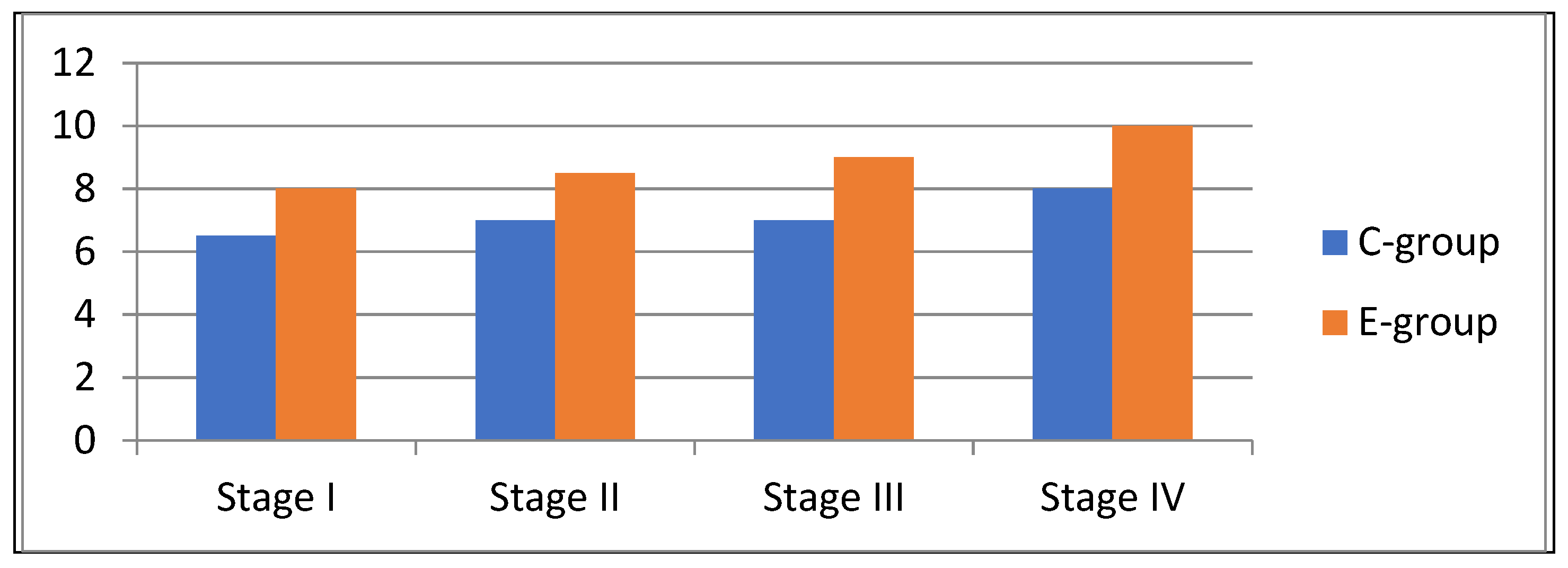
| Stages | Results (Means and Standard Deviations) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C Group | E Group | t-Test Sig. (2-Tailed) df—272 α = 0.05 | |
| Stage I | 6.5 SD—0.516 | 8 SD—0.271 | 0.000 |
| Stage II | 7 SD—0.437 | 8.5 SD—0.759 | 0.000 |
| Stage III | 7 SD—0.343 | 9 SD—0.364 | 0.000 |
| Stage IV | 8 SD—0.420 | 10 SD—0.364 | 0.000 |
| Progress in performing MST | 1.5 SD—0.373 | 2 SD—0.258 | 0.000 (df—136. α = 0.05) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karpovich, I.; Sheredekina, O.; Krepkaia, T.; Voronova, L. The Use of Monologue Speaking Tasks to Improve First-Year Students’ English-Speaking Skills. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11060298
Karpovich I, Sheredekina O, Krepkaia T, Voronova L. The Use of Monologue Speaking Tasks to Improve First-Year Students’ English-Speaking Skills. Education Sciences. 2021; 11(6):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11060298
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarpovich, Irina, Oksana Sheredekina, Tatyana Krepkaia, and Larisa Voronova. 2021. "The Use of Monologue Speaking Tasks to Improve First-Year Students’ English-Speaking Skills" Education Sciences 11, no. 6: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11060298
APA StyleKarpovich, I., Sheredekina, O., Krepkaia, T., & Voronova, L. (2021). The Use of Monologue Speaking Tasks to Improve First-Year Students’ English-Speaking Skills. Education Sciences, 11(6), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11060298






