Abstract
Virtual reality has shown to have great potential as an educational tool when it comes to new learning methods. With the growth and dissemination of this technology, there is a massive opportunity for teachers to add this technology to their methods of teaching a second/foreign language, since students keep showing a growing interest in new technologies. This systematic review of empirical research aims at understanding whether the use of gaming strategies in virtual reality is beneficial for the learning of a second/foreign language or not. Results show that more than half of the articles proved that virtual reality technologies with gaming strategies can be used to learn a foreign language. It was also found that “learning” was the most evaluated dependent variable among the chosen records, augmented reality was the leading technology used, primary education and lower secondary was the most researched school stages, and the most used language to evaluate the use of gamified technology was by far the English language. Given the lack of directed investigation, it is recommended to use these technologies to support second language learning and not entirely replace traditional approaches. A research agenda is also proposed by the authors.
1. Introduction
A tree is a great analogy for the area of education, being one of its important branches the learning of a foreign/second language. In fact, one’s interest to learn a second language started around the time of the Roman Empire, when Romans showed interest in studying the Greek language. Their way of studying a different language consisted of having Greek servants or having Greek tutors who taught them the language. From then on, people became interested in learning another language besides the native one, e.g., people from Europe started to think about Latin’s teaching methods [1].
It has been already found that some of the challenges related to learning a foreign language are related to teachers and their lack of proper training, lack of proper facilities, lack of oriented materials dependent on the students’ needs and reactions towards the errors made by the learners [2,3]. Thus, with the continuous evolution of technology, the student’s attention and interest in learning became even a bigger challenge for educators that are now faced with the inevitable challenge to innovate and develop new learning methods, which has therefore become a priority, helping students to better engage in the learning process [4].
E-learning has been growing over the years together with the digital learning resources, computers and mobile phones, which have all become part of our everyday life [5]. This is even more common in the digital native generation, also known as “Generation Z”, which consist of individuals born between 1990 and early 2010 [6]. It is noteworthy that this generation has grown up in a digital era where the use of technologies are appreciated and expected [7].
One of the technologies that this new generation is excited about is Virtual Reality (VR). This new medium transports the users to another dimension (the virtual world). Instead of being just an observer, the user becomes an actor in a digital world where they can interact [8] and receive feedback from those interactions. This medium can produce the perfect learning environment allowing students to learn by practising, acquiring new knowledge similarly to how they would in the real world. Gamification techniques can be introduced to improve user’s engagement further and achieve the best possible results.
Kim et al. [9] defined by gamification as a collection of steps to solve an obstacle adopting characteristics of games related elements. As an example, the main objective of the popular Space Invaders game is to save the world, but to reach it we must go through several steps such as killing aliens and dodging their attacks. There are also characteristics of the game, such as score points and rewards that the gamer receives by completing objectives, its remaining lives and the increasing difficulty of to consistently challenge the gamer abilities, that makes this game “gamified”.
VR and games, each in an individual way, have shown positive results in the most different areas [10,11,12,13,14,15], and were brought together through time with many purposes, e.g., entertainment [16], training [17], and education [18]. Education can benefit from VR technology, turning it into a powerful didactic and pedagogical instrument regarding the evolution of educational methodologies. Serious games, whose main objective is not entertainment, are examples where VR can bring added value to the education field since they can entertain users while they learn. There are some well-known games on other platforms, such as mobile phones and personal computers, but none of them can bring the learner a fully immersive experience like the one provided by VR. Instead, VR can provide mental and physical immersion, the sensation of being fully absorbed in the virtual environment. Therefore, this technology has been the object of much interest and application.
Some technologies can also be seen as VR solutions (VR based technologies) since they can also immerse the player into a virtual world, like the following examples: CAVE, cave automatic virtual environments, a system that can be defined as an immersive room whose walls, ceiling and floor surround the player with projected images [19]; Video-capture virtual reality, a system that provides a higher level of immersion with the use of video cameras together with computer technology [20,21]; Desktop or desktop VR, the use of an animated and interactive 3D virtual world resorting to a desktop display, without a head-mounted display [22,23]; Augmented Reality, where the user has the perception and interaction with the real world but can see virtual objects and information that could not otherwise get without recurring to this technology [24]; and head-mounted display (HMD) worn by the users allowing them to interact with the virtual environment, feeling as if they were a part of it.
In Alizadeh’s article [25] it is stated that VR can provide a great variety of representations of real-life by immersing students in a way that 2D multimedia cannot, representing the natural complexity of the real world in accurate tasks by displaying different contexts. With the delivery of case-based learning environments, students can bring personalized learning to their learning styles.
Regarding the evaluation of this technology towards learning, if a study has the objective of evaluating the learning of a foreign/language, it is expected that the authors have the variable “learning” as one of the dependent variables, i.e., reporting the participant’s knowledge after the lesson has been completed [26]. Another significant variable is the student “motivation” to learn. This attitudinal aspect is defined by Brophy [27] as being an “enduring disposition to value learning for its own sake”. Thus, the student can take joy in the process and be proud of the outcomes. The “attitude” perceived by the user towards the system is determined by its perception of the easiness of use and usefulness [28]. Along with these dependent variables, some studies also use variables such as fun, usability, flow and enjoyment.
The constant research and investigation on this area helps professionals to understand whether it is viable to invest in such a learning strategy or not. Some literature analyses have shown that several studies aimed at understanding the results of the use of VR as an instrument for learning of foreign/second language. For example, Lin and Lan [29], surveyed studies from 2004 to 2013 found that the use of VR to learn a language increased gradually during those nine years. According to their research, within that period, reviewed studies have frequently shown that virtual learning environments increase the learner’s autonomy, self-efficiency and reduces learning anxiety. The most common investigated research topics were interactive communication, behaviors, affections and beliefs. To complement their analysis, it was found that in that period, the most used multi-user virtual environment (MUVE) technologies were open-world social virtualities (Second Life, MOO, etc.,) and massive multiplayer online games (MMOGs) (World of Warcraft and Civilization).
Solak and Erdem [30] also analysed foreign language learning through VR technology in another systematic review. The authors gathered data from research papers published between 1995 and 2015. They came across with the fact that most of the papers used a qualitative methodology, stating that this was most preferred than quantitative ones in those years. Regarding the sample, it was found that undergraduate students were the most prevalent population. Furthermore, it was determined that studies were mostly centered on the effectiveness of VR and game-based learning. The authors concluded that when VR is appropriately used, it can enhance foreign language learning to a great extent. However, they also conclude that more studies should be made in learning second/foreign language and VR, since the sample was still not sufficient.
Parmaxi’s [31] systematic review limited the time frame of records from 2015 to 2018, to gather only recent VR development. The author found that most studies used Second Life and OpenSimulator (or customised virtual environments). Regarding the sample, most of the studies included university students, followed by primary school students. Most of the studies conducted had English as their target language. After this review, the author concluded that VR provides vast opportunities concerning language learning, besides the increase of skills and competences such as cultural awareness, autonomy and teamwork.
Although there is already some investigation regarding the use of VR to learn a foreign language, none of the identified studies included gamification. Given the positive influence that VR can have in our current world, it is a technology that generates interest in the focus of this study. This review of empirical research will allow to characterising the state of the art, develop guidelines through the analysis of the outputs of the surveyed studies, define an investigation agenda lines to be followed and, thus, contributing to updating this scientific area.
Using explicit and systematic accountable methods, this systematic review follows the very recommended research guidelines [32]. The following objectives are set to be accomplished at the end of the data collection and analysis of the selected records:
- An empirical review of Gamification using immersive technologies in learning a Second Language
- Identify the target audience of the already existent solutions;
- Identify the leading technology of the existent solutions;
- Identify the didactic impact of Gamification using virtual reality technology in learning a Second Language;
- Identify current research limitations
- Suggest a research agenda
To reach the previously mentioned objectives, this systematic review of empirical research will focus on the following research questions (RQ): RQ1. “Can virtual reality technologies, with gaming strategies, be used to learn a foreign language?”. In complement to this question, secondary questions are also proposed, such as RQ2. “What did the authors evaluate?”; RQ3. “What technologies were used?”; RQ4. “Which educational stages are covered?”; RQ5. “Which languages are covered?”.
2. Methodology
The foundations of a systematic review are identifying and analysing relevant studies to extract knowledge from, intending to answer particular research questions [33], being, in this case, the research questions before mentioned.PICOS was the base to create the research question and, consequently, the search query, inclusion and exclusion criteria, and the data collection table. The systematic review method followed was based on PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses) proposed by Moher et al. [34]. The PRISMA methodology establishes a series of procedures and guideline meant to help the research be clearer in presenting what was planned, what was done and what was found in the systematic review.
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
All the studies were selected based on the pre-defined inclusion criteria, which defined which articles were included or not. The criteria were:
- IC-1. The manuscript has in the abstract, title or keywords the following keywords: “Virtual Reality” or “Augmented Reality” or “VR” or “AR”, and “Second Language” or “Foreign Language” or “English” or “Language”, and “Gamification” or “Games”
- IC-2. The manuscript was written in English or Portuguese
- IC-3. The manuscript was published in a conference or journal
In terms of exclusion criteria, the following list was considered:
- EC-1. Not available
- EC-2. Not written in English or Portuguese
- EC-3. Do not use Virtual Reality or Augmented Reality
- EC-4. Not published in conference or journal
- EC-5. Do not have a study
- EC-6. Do not use games
- EC-7. Language learning is not being evaluated
2.2. Search Strategy
All the listed studies were collected after searching in electronic databases with the query of the inclusion criteria number one (IC-1): (“Virtual Reality” OR “Augmented Reality” OR “VR” OR “AR”) AND (“Second Language” OR “Foreign Language” OR “English” OR “Language”) AND (“Gamification” OR “Games”). Following it was applied, the filters referring to the written study’s language were applied, English or Portuguese, and its publication, journal or conference.No year restriction was applied to the search. This search query was performed in ACM, IEEE Xplore, Mary Ann Liebert, Scopus, Wiley and Web of Science as they are the most representative of the area of study considered in this article.
2.3. Study Selection
After listing the articles obtained following the above-specified search strategy, it began the first phase of study selection. This stage consisted of an eligibility assessment performed independently in a blinded standardised manner by two reviewers. The two reviewers analysed each paper and, if both of the analysts agreed to the acceptance or rejection, the decision would be automatically validated. If there were no consensus, that article would be automatically included for full reading to clarify any further doubt. Succeeding the article’s obtained in phase 1 of study selection came the second and final phase. This final step, made by one reviewer, made a full reading of the listed articles to go forward to the data collection if accepted by the reviewer (according to the previously defined criteria).
2.4. Data Extraction
A form was developed for the data extraction where all the data needed from each study for this systematic review was included. This information consisted of the following elements: title of the article; type of the article (if it was an article, short paper or conference); which mode of instruction (if mostly face-to-face, mostly online or blended); which languages were covered in the study; which educational stages were targetted; which factors were evaluated; whether if it was made a comparison with different VR conditions or not; if it was made a comparison with other forms of instruction or not; which immersive technology was used; how was learning investigated; if the measurement of learning was made quantitative or qualitative; how was “learning” addressed; and how were the outcomes of learning reported.
2.5. Quantitative Analysis
The present study aims at fulfilling a research gap by carrying out a systematic analysis of gamification in foreign language learning by using immersive technology. A bibliometric approach was used with word growth based on the abstracts of the listed articles. Using the bibliometrics helped find which ones are the most used variables and their appliance through time.
2.6. Quality Assessment
It was created a section for the quality assessment of each accepted article. In this phase, there was one part of the limitations of the article, where the reviewer could evaluate between one (no limitations), two (some limitations) and three (many limitations). On another part, the reviewer could provide an overall rating to the record, between one (poor article), two (acceptable article) and three (great article). Both evaluations made in the quality assessment were performed based on previous well-defined criteria. The assessment of the quality assessment was as objective and uniform as possible, without any statistical resource.
The authors carried out the quality assessment of the records. For the limitations, the sample size was taken into account in which “one (no limitations)” equals to the acceptable sample size, “two (some limitations)” referred to a reasonable sample size, and “three (many limitations” correspond to a very small sample size. However, in terms of overall rating it was taken into account the quality of the evaluation of the study and respective results report. When an article had a subjective evaluation (e.g., made by observations) and the results were not conclusive, or confusingly explained, it was given the evaluation of “one (poor article)”. If an article had an objective evaluation but the results were not conclusive or confusingly explained, it was given “two (acceptable article)”. Finally, when an article had an objective evaluation with outcomes very well explained, in was given “there (great article)”.
3. Results
The query (“Virtual Reality” or “Augmented Reality” or “VR” or “AR”, and “Second Language” or “Foreign Language” or “English” or “Language”, and “Gamification” or “Games”) was used to search on the previously chosen databases. It was found 29 articles in ACM (1998–2019), 212 in IEEE Xplore (1990–2020), 125 in Mary Ann Liebert (1997–2020), 531 in Scopus (1995–2020), 17 in Wiley (2018) and 100 in Web Of Science (2002–2020). In this way, as shown in Figure 1, the records identified through database searching were 1014. After comparing the records from all databases, the duplicated studies from the final list were removed, being 146 the duplicated ones and 868 records ready for the screening.
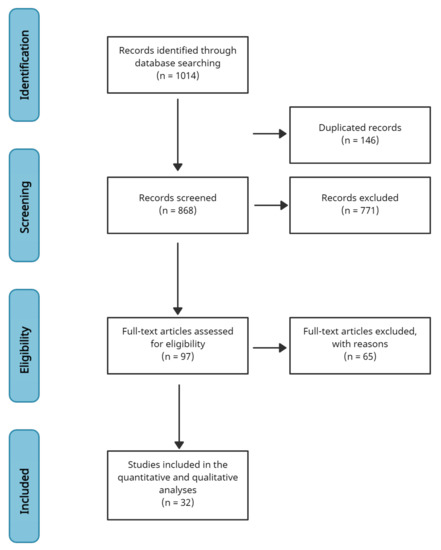
Figure 1.
Flow diagram that summarises all the steps of the study selection process.
Between the screened records, after reading the title and abstract of each one of them, 3 were not available to read (EC-1), 441 did not use VR technology (EC-3), 525 did not have any study (EC-5), 417 did not use games (EC-6), and 750 did not evaluate learning (EC-7), taking into account that a lot of them had more than one criteria of exclusion. In this way, 771 records were excluded.
Excluding the records not suitable for the review, 97 studies were applicable in the full-text articles for eligibility. Of the 97, 8 were not available for full-text reading (EC-1), 2 did not use games in the study (EC-5), 51 did not evaluate learning (EC-7), and 4 were duplicated. In this way, 65 full-text articles were excluded with reasons, being thirty-two (32) studies included in the quantitative and qualitative analyses. From this thirty-two (32) records, sixteen (16) (50%) are articles, and the other half are conference articles. Figure 1 summarises all the steps of the study selection process.
In order to obtain learning outcomes results, all the studies used some type of instruments to measure the learning, some of them used more than one instrument. Twenty-two (22) studies used “Objective Knowledge test”, six (6) used “Observation” as a method of measure, another 6 used “Interview”, 2 used “Group Discussion”, another 2 used “Questionnaires” and 3 used “Perception questionnaire”. Some instruments were used only once, such as: “Course performance (grade)”, “Logs analysis”, “Subjective knowledge test”, “Task performance”, “Survey”, “Learner journals”, “Questionnaire that contained both qualitative and quantitative questions” and “Field notes”.
Most of the records (75%) presented a positive answer to the main question, namely, “Can virtual reality be used as a gamification tool to learn a foreign language?”. The remaining articles (15%) had a different answer to this question, as seen in Figure 2. For more detailed information see Table 1.
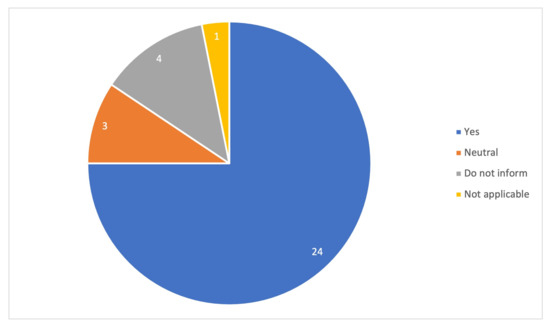
Figure 2.
Overall view of the impact of VR when used as a gamification tool to learn a foreign language.

Table 1.
Impact of VR when used as a gamification tool to learn a foreign language. Distribution of studies/sources for each learn result.
In 32 articles, “Learning” was a factor being evaluated in 31 and “Educational Performance” was evaluated in 1, meaning that all the records had learning outcomes in their studies. 7 articles, or conference articles, evaluated “Motivation”, 5 evaluated “Attitude”, 3 considered “Cognitive workload”, and “Enjoyment”, “Flow”, “Satisfaction” and “Usability”, each one evaluated by 2 studies. There were some factors that were only evaluated once, whose are presented in Figure 3. For more detailed information see Table 2.
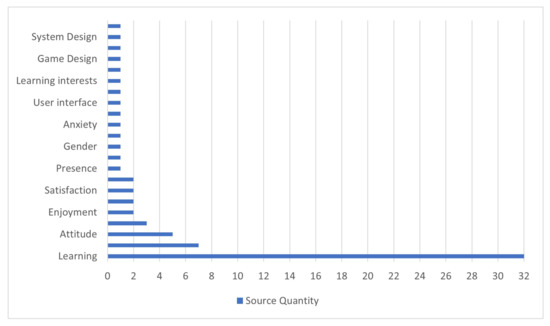
Figure 3.
Dependent variables that authors evaluated in the reviewed articles.

Table 2.
Dependent variables that authors evaluated in the reviewed articles and respective distribution of studies/sources for each variable.
The word “learning” was addressed in different ways in all of the records, being mentioned as “Learning” in 19 studies, “Performance” in 3 records, “Learning Effectiveness” and “Learning Achievement”, each one in other 3. “Learning Performance” was the term used in 2 articles or conference. “Achievement”, “Retention”, “Comprehension”, “Language Skills”, “Vocabulary acquisition” and “Foreign language acquisition” were the terms used in 1 article, each one of them.
Different technologies were used in each one of the studies. Half of the records (50%) used “Augmented Reality”, followed by “Desktop Games” (31.3%). The remaining (18.7%), used other technologies in their studies (see Figure 4 for more specification). For more detailed information, see Table 3.
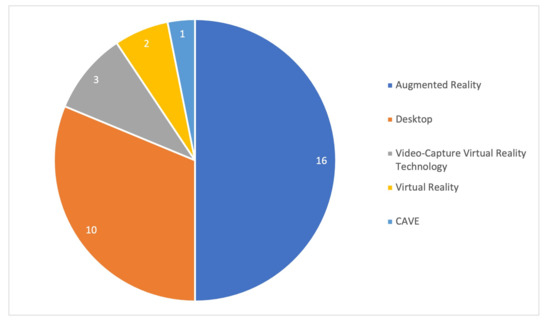
Figure 4.
Technologies that were used in the reviewed articles.

Table 3.
Technologies that were used in the reviewed articles and respective distribution of studies/sources for each technology.
Every study of the articles covered an educational stage. The primary education or first stage of basic education (28.1%) was the most covered, followed by the lower secondary or second basic education stage (15.6%). A considerable part of the records (28.1%) did not inform the stage. The remaining articles (28.8%) covered other stages, as described in Figure 5. For more detailed information, see Table 4.
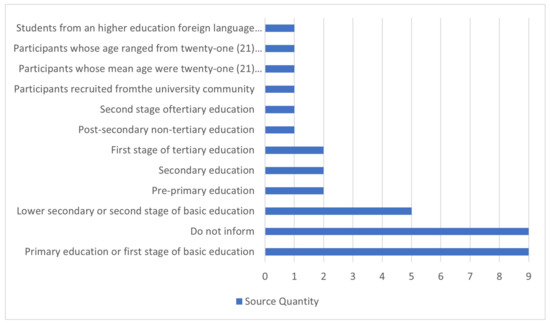
Figure 5.
Educational stages covered in the reviewed articles.

Table 4.
Educational stages covered in the reviewed articles and respective distribution of studies/sources for each stage.
In terms of languages, English was the most covered one as a foreign language (65.6%), followed by German (9.4%). The remaining articles (25%) used other languages shown in the pie chart of Figure 6. For more detailed information, see Table 5.
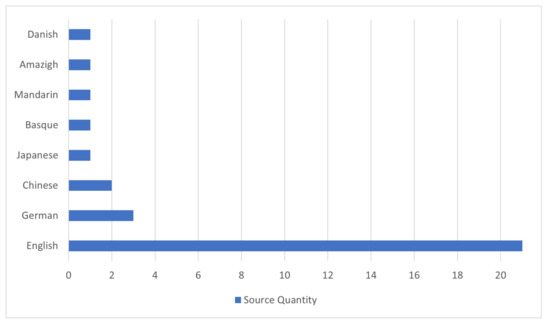
Figure 6.
Covered languages in the reviewed articles.

Table 5.
Covered languages in the reviewed articles and respective distribution of studies/sources for each language.
In each one of these studies, there were forms of instruction used with the users, being half of the studies (50%), 16, based in non-formal education (training), 12 based on formal education (system), 37.5% of the articles, 2 informal education (everyday life), 6.3% of the studies, and the last 2 studies did not inform which form of instruction were they covered (6.3%).
In terms of modes of instruction covered in the studies, 25 records (78.1%) made face-to-face learning (mostly presential), 4 studies (12.5%) made distance learning (mostly online), 2 studies (6.3%) made blended learning, both face-to-face and distance learning, and 1 record (3.1%) did not inform which mode of instruction used.
Half of the articles, or conference articles, made comparisons between the technology with other instruction forms; the other half (50%) of the studies did not make any comparison. The most made comparison was with “Face-to-face or real” (18.8%). The remaining studied comparisons are also specified in Figure 7.
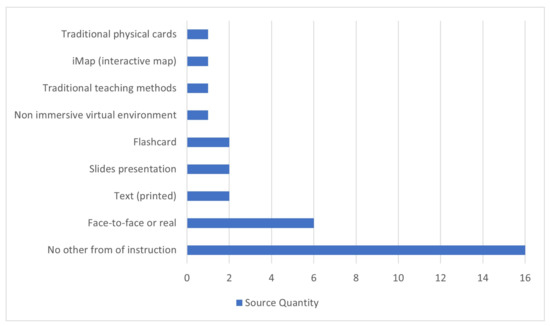
Figure 7.
Comparison with other form of instruction.
In these 32 studies, the learning measurement of learning was quantitative and qualitative, depending on the record. 14 records (43.8%) quantitatively performed the measurement, 13 studies (40.6%) performed quantitatively and qualitatively measurements, and 5 were performed in a qualitative way (15.6%).
As regards bibliometrics research, it is visually understandable that in word growth, Figure 8, the most frequent variables are “learning”, “language”, “game” and “english”. Since two thousand and thirteen (2013), growth has occurred in both “learning” and “english”.
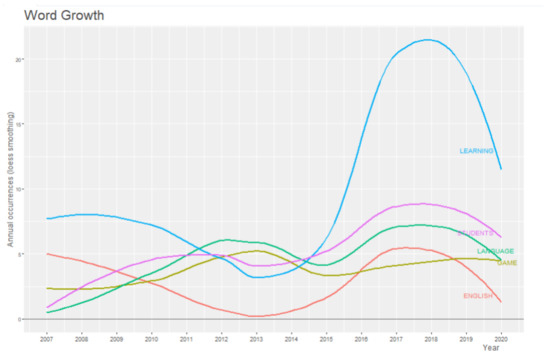
Figure 8.
Bibliometrics word Growth.
Figure 9 and Figure 10 reports a subjective evaluation concerning limitations and overall ratings about the collected articles. Even though most of the articles have no limitations, there is still a considerable quantity of records with a few and many limitations, such as preliminary evaluations. Consequently, the articles’ rating is not significant in the majority, thus being divided between great and reasonable.
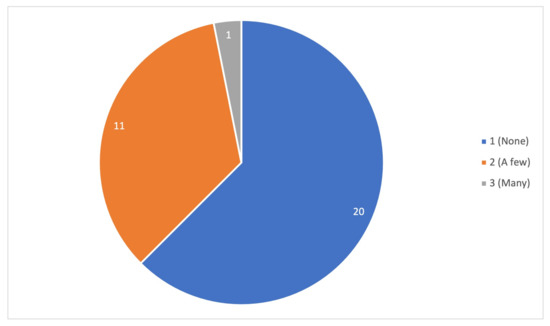
Figure 9.
Limitations of the records.
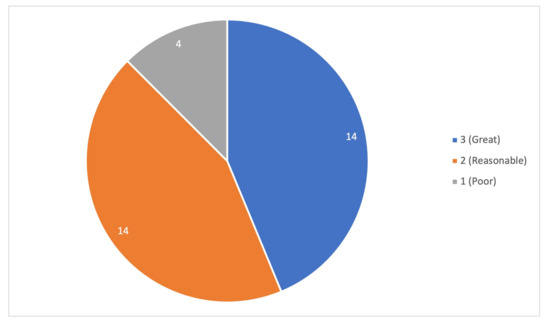
Figure 10.
Rating of the records.
4. Discussion
This study aimed to understanding whether the using of gaming strategies in VR is beneficial for the learning of a second/foreign language. Additionally, it was intended to identify what was evaluated, the main technologies, target audience, which languages were covered, and identify current research limitations. Subsequently, a research agenda is proposed. Findings are discussed below.
4.1. Findings
Most of the articles had a positive answer to the main question, as revealed in Figure 2. Each study made its way of research to understand whether virtual technology positively impacted learning. For example, Castañeda, Guerra and Ferro [35] and Barreira et al. [36] had a positive result because the virtual reality technology presented better results in the obtained learning progress than other examined method. This positive result corroborates Solak and Erdem [30] analysis, namely their research papers published between 1995 and 2015, where it was found to enhanced foreign language learning when VR is used properly. It also corroborates the systematic review of records between 2015 and 2018, made by Parmaxi [31]. The author concluded that VR provides a wide range of significant didactic opportunities for helping language learning.
Some studies are quite explicit on their positive outcomes. Some records found a positive impact and superior learning progress regarding educational performance and learning [35,36,47,52]. On the other hand, despite such refereed impact, other articles proved that gaming in VR technology provided similar learning achievements when compared to traditional ways, such as physical cards approach [42,56], PowerPoint presentation [21] and face-to-face learning (class) [37,46], improving students’ learning interest.
Furthermore, it was also found some proposed gaming applications that, when tested, had positive results towards learning. According to the research results, some of them improved students’ phonetics learning performance, and efficiency [40,54] and others proved that students had motivation, attitude and interest in using the systems and still have positive results towards learning a second language. [38,39,43,51,53,55] Some of these studies report that besides having positive results [49], participants highlighted the value of interacting with native speakers [43] since it places students in the context related to the target language and technology that contextualised learning is efficient in improving learning attitudes [41]. Also, this simulation of real-life scenarios can increase virtual reality experience and cultural knowledge [44].
Supplementary to this positive results previously mentioned, it is important to refer that some articles also indicate not so good elements about the use of this technology. One of these cases are referred by Anderson et al. [57] on their article where it was added that extended gaming exposure would likely lead to headache and eye strain. Another side that was taken into consideration is relative to technical elements. Chen [44] on his experience had to deal with unexpected computer freezing and connection interruptions, in other words, unstable technical difficulties. Likewise, Cheng et al. [58] had difficulties with the technology, but this time with the element of interaction, reporting that participants had problems with reading and interacting with the UI in the environment. Besides, participants also expressed negative feelings such as dizziness and sickness. Negative sides of gamified VR, specifically for the learning of a foreign/second language, are not usually reported so further investigation is needed to state major negative factors of its usage.
As it was said before, interactions between native and non-native speakers are helpful in second language learning, and games are a greater learning intermediary since some allow communication between communities. Therefore, cooperative game-play becomes a component that contributes to second language acquisition [46] since it provides real-time feedback and the learner is presented with vocabulary in context, making it easier to learn and understand the target language [48,57], and, also, improving their writing competence [45]. According to some students’ observations, this learning method is enjoyable, fun, motivating, improves their learning interest and decreases cognition load [50,56]. Regarding the articles that were neutral about the outcomes of learning: Cheng, Yang and Andersen [58] study result had no obvious evidence that the learning improved since the difference was not statistically significant; Yang et al. [59] article also presented no significant difference in their pretest and post-test of English achievement, between the experimental and control group; and Hansen and Petersen [60] study results showed that virtual reality could be used without decreasing the learner test scores. However, both teachers and students had trouble seeing it as a direct substitute for teacher based training.
Such a novel approach to second language learning corresponds to a sphere of didactic opportunities which may well enhance the learning process and its efficacy due to its many attractive elements as inspired by the world of Games. Indeed, the very process of engaging students, motivating actions, coming up with solutions to specific learning obstacles, the significant levels of interaction, the entertaining aspects of storytelling, the constant feedback, among others, are the very features of this new approach to a second language learning, which corresponds to the very reality as lived by today’s students [66].
Although some articles did not inform about learning outcomes [61,62,63,64], they were neutral, or did not have evidence, [58,59,60] or were not applicable [65], they too evaluated the learning of a second language in a game scenario but focused on others variables. For example, it was found that such technology is notable in bettering students’ motivation and effectiveness [61] and that the students positively receive this kind of approach and teachers [60] and promote their awareness of the environment [63].
In terms of covered educational stages, primary education (or first stage of basic education) was the most common, followed by lower secondary (or second stage of basic education), not corroborating Parmaxi [31] systematic review where it was found that the majority of the studies included university students, but corroborates Solak and Erdem [30] analysis where it is mentioned that undergraduate population were the most prevalent. This finding can be explained by the fact that students from primary education, or the first stage of basic education, usually have the same level of knowledge when it is about a secondary language. However, more investigation would be needed to understand if this idea/statement could be corroborated or not.
As proved in Parmaxi review [31], most of the studies conducted had English as their target language, corroborated with the developed research. Although Parmaxi’s study was made with records between two thousand and fifteen (2015) and two thousand and eighteen (2018), English still is the most used language for evaluating learning outcomes in a foreign language, followed by German and Chinese. In his article, Rao [67] said that there are several reasons that several reasons makes English the language that occupies the highest position among all the languages. This language is used by people worldwide and plays a massive role in many fields such as education, business, science, research, and much more areas. In this way, it is the language more frequently used for internet purposes and in business communication.
Nevertheless, these results could be biased by a possible limitation introduced by eligibility criteria: to consider only works written in English or Portuguese. This is mitigated by the fact that despite the language in which the article was written, we have not excluded the manuscripts by the language addressed in the learning process. Also, the core of the body of knowledge is written in English. For that reason, the most relevant works would follow this tendency even if they consider the teaching of other languages as a foreign language.
Related to the evaluation made by the authors of the included records, the focal point of every study was the Learning factor, followed by Motivation, Attitude, Cognitive Workload, Enjoyment, Flow, Satisfaction and Usability, which do not corroborate Lin and Lan [29] content analysis, of findings in literature from 2004 to 2013, where the most commonly investigated research topics were interactive communication, behaviours, affections and beliefs.
As seen, some statements could not be corroborated through previously seen reviews, and this can be justified by the lack of research on studies about gaming with VR technology to learn a second language/foreign language, and with the time difference between the screened records, meaning that studies and technology are evolving, together with the objectives of the studies are too.
A considerable majority of articles refer mainly to learning, education, and outcomes, but it is not explained why the authors have chosen some specific technology instead of another. For example, in some records based on evaluation with augmented reality, it is only informed that it improves the user’s knowledge since it requires more interaction and participation from him/her [35], a significant part of them promotes motivation and engagement [36], and that increases students interest [37], besides bringing an element of gamification to the learning task [38]. The found literature was not made any comparison between technologies and the objective of choosing the more indicated one. This can bring us to a conclusion/theory that most studies have used augmented reality because it is the most affordable one, both to the investigators and the students.
Figure 9 refers to the author’s quality assessment evaluation in terms of limitations on the articles, as described in Section 2.6. Most of the found limitations were the size of the sample, meaning that many articles only made preliminary studies, for example, the Chang, Sheldon and Hand’s article [43], where the project was in a preliminary stage, and it was made a study with 11 participants to have some initial observations; the study by Garcia et al. [55] was made with a focus group of 4 participants, and the results were based in observations; and Pu and Zhong’s [56] article were participants made the evaluation, 5 in the experimental group and 3 in the control group. This limitation was also indicated by the author: “the number of test samples may affect the speculation of the experimental results”. Besides the limitation of a small sample, some studies where made based on observations [44,46,50,55] being, in this way, exploratory, and the results are only suggestive and not confirmed. Therefore it is necessary to reinforce these studies to be corroborated.
The author made an overall subjective rating of the selected articles. Most of them were labelled as less than great (43.8% are reasonable, and 12.5% are poor), as can be seen in Figure 10. Most of the bad rating was due to the confusion in the studies’ evaluation and methodology. It was found a lack of well-explained results and reported procedures steps, missing in this way the heart of the investigation, leaving the reader with some questions about the study and the way that the authors obtained the reported results. Studies also stated that “x” solution is better than “x” traditional way. However, in some cases, it is never made a statistical and objective comparison and the “x” traditional way is not evaluated too.
Figure 8 shows a significant difference from 2015 onward, more pronounced in the word “learning”. This can be justified because, after 2015, the equipment of VR became affordable to the public in general [68].
Even though most of the articles did not identify limitations, there are still many records with some. There is still a lack of investigation addressing technology and tech-related devices to achieve a good learning outcome (second language learning). Although this systematic review of empirical research was directed to gaming in VR technologies, there are still limited number of records based on fully immersive technologies, although it was considered as VR games that used 3D worlds.
This empirical research recognise the potential of the use of VR technologies with gaming strategies to benefit and support the learning of a second language. In this way, the results of this research validate the adoption of this gamified technology to advance in the area of education and to enhance its outcomes. The complement with traditional learning methods are a must to advance in the area of knowledge in a way to facilitate the adaptation of learning in different methods of interaction and different contexts, specially in the area of learning a foreign language.
Therefore, this research grant a whole review in the area of the application of gamified VR technologies, to learn a second/foreign language, without limitations of year of publication and the target learned language, offering the reader a full experience in what has been done in this area and which outcomes have been found within its usage.
4.2. Research Agenda
After the conclusion of the systematic review, the authors concluded that virtual reality is getting much interest from researchers to understand if the gamification using this technology can help them in the learning process, in this case, of a foreign language. Although this interest, there is still a lack of sense in terms of investigating the area. With the gather information, the following research agenda is purposed by the authors.
First of all, it is crucial to have some agreement between investigators related to the used terms. When searching the terms that some article evaluated, sometimes the same factor has a different name in another article evaluating the same thing. In this way, it would be important to develop guideline research to guide the researchers to use universal terms, helping the general understanding between investigators and facilitating the search of research with the pretended factors by the searcher.
Second, since it has been already made several studies about the level of satisfaction and usability by the student towards virtual reality technology, or the application itself, it is time to move forward and make more extensive studies with larger samples in order to corroborate the results that the current state of the art indicates.
Third, to save some time and to avoid duplicated studies, it would be gratifying to carry research considering another already made. When developing some kind of study, it should be made some investigation previous the planning of experiences to know if the intended results were already statistically verified by another previously made study. In this way, this would help advance the area with an in-depth study, using a previously made investigation and reinforce the results with the results of a more focused area. Suppose the investigators follow this way of thinking. In that case, the area will grow in the most different branches of knowledge, facilitating the interested people’s decisions interested people in implementing this technology.
Fourth, it is needed to carry studies comparing technologies so the researchers can have a scientific foundation to determine what they should use on their experiences/investigation and why the chosen technology is the more indicated one.
Fifth and final, it is necessary to have more investigation to understand which educational stages are the most appropriate to have experiences and if it is within possibility their English level since it needs to be levelheaded between participants.
5. Conclusions
This article had as objective the development of an empirical review about gamification in foreign language learning using VR. To fulfil this objective, the authors considered five research questions, which were: RQ1. “Can virtual reality technologies, with gaming strategies, be used to learn a foreign language?”. Moreover, secondary questions are also proposed, namely: RQ2. “What did the authors evaluate?”; RQ3. “What technologies were used?”; RQ4. “Which educational stages are covered?”; RQ5. “Which languages are covered?”. With the obtained results of the investigation the authors were able to answer each one of them.
In this way, more than half of the articles proved that virtual reality technologies, with gaming strategies, can be used to learn a foreign language, answering the main research question (RQ1), with no articles proving otherwise. The records that did not answer affirmatively to this question did not answer negatively, but were neutral, not applicable or did not inform. The neutral articles had no obvious evidence that the the learning was improved, meaning that had no significant differences in the results, and showed that VR could be used without a decrease in the learner scores.
All of the authors of the articles evaluated (RQ2) “learning” as a dependent variable, followed by “motivation”, “attitude” and “cognitive workload”. Within the scope of VR, half of the authors resorted to the use (RQ3) of augmented reality followed by desktop, probably because they were the most affordable solutions. However, in fact, it was never specified why these technologies were chosen instead of others. Since the obtained records were all targeted to foreign language learning, it was important to understand which education stages were covered by the authors (RQ4). In this way, it was found that primary education (or first stage of basic education) and lower secondary (or second stage of basic education) were the most investigated stages. In this context, the most used language (RQ5), to evaluate the use of gamified technology was, by far, English.
It is clear from the results that the comparisons between newer technologies and traditional approaches are still lacking. Therefore, it is hard to affirm that this new learning method is better than the old one in terms of performance. Although most of the studies had a positive learning outcome when using VR, it is not enough to affirm that it would be positive to change traditional learning methods altogether. Given the lack of targeted investigation, it is only possible to recommend using technologies to support second language learning and not entirely replace traditional approaches. With the growing of e-learning and, with it, the growth of digital learning methods, it is easier to complement education with technologies that are so common in our everyday life, especially in the generation that was born in the digital era.
Based on our analysis, it is imperative to keep track of other experiences with the new tech-related devices. Aiming at a more efficient second language teaching/learning practice, the didactics of languages’ very efforts consist of testing and practising new and more efficient methods and strategies of teaching and learning. There is a need to pursue future investigation lines such as the ones proposed in the proposed research agenda. Therefore, gamification can be an object of further analysis and study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.D.P. and M.M.; methodology, R.D.P., B.P. and M.M.; validation, R.D.P., B.P., M.M., L.C. and M.B.; formal analysis, R.D.P.; investigation, R.D.P. and B.P.; resources, R.D.P.; data curation, R.D.P. and B.P.; writing—original draft preparation, R.D.P.; writing—review and editing, R.D.P., M.M., L.C. and M.B.; visualization, R.D.P.; supervision, M.M.; project administration, M.M.; funding acquisition, M.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is financed by the ERDF – European Regional Development Fund through the Operational Programme for Competitiveness and Internationalisation-COMPETE 2020 Programme and by National Funds through the Portuguese funding agency, FCT-Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia within project POCI-01-0145-FEDER-031309 entitled “PromoTourVR-Promoting Tourism Destinations with Multisensory Immersive Media.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| VR | Virtual Reality |
| AR | Augmented Reality |
| CAVE | Cave Automatic Virtual Environments |
| HMD | Head-Mounted Display |
| RQ | Research Question |
| IC | Inclusion Criteria |
| EC | Exclusion Criteria |
References
- Setiyadi, A. Teaching English as a Foreign Language; Graha Ilmu: Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Teevno, R.A. Challenges in teaching and learning of English at secondary level class X. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Stud. 2011, 1, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Erdem, S.; Tutkun, O. Problems in english language teaching according to secondary school students. TOJET Turk. Online J. Educ. Technol. 2016, 2016, 268–275. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, D.; Peixoto, B.; Krassmann, A.; Melo, M.; Cabral, L.; Bessa, M. Virtual reality in education: Learning a foreign language. In Proceedings of the World Conference on Information Systems and Technologies, Galicia, Spain, 16–19 April 2019; pp. 589–597. [Google Scholar]
- Marky, K.; Müller, F.; Funk, M.; Geiß, A.; Günther, S.; Schmitz, M.; Riemann, J.; Mühlhäuser, M. Teachyverse: Collaborative E-learning in virtual reality lecture halls. In Proceedings of the Mensch Und Computer 2019, Hamburg, Germany, 8–11 September 2019; pp. 831–834. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, S.A. Games and Gamification in the Classroom. In Radical Solutions and eLearning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, L.I. Immersive virtual reality for learning experiences. In Radical Solutions and eLearning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 183–198. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, P.; Moreau, G.; Guitton, P. Virtual Reality: Concepts and Technologies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J. Gamification in Learning and Education: Enjoy Learning Like Gaming: By Sangkyun Kim, Kibong Song, Barbara Lockee, and John Burton. Pp 159. Pp 138. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing AG. 2018.£ 55.16, (hbk). ISBN 978-3-319-47282-9 (hbk). Br. J. Educ. Stud. 2020, 68, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosser, J.C.; Lynch, P.J.; Cuddihy, L.; Gentile, D.A.; Klonsky, J.; Merrell, R. The impact of video games on training surgeons in the 21st century. Arch. Surg. 2007, 142, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, M.A. The Role of Language Games in Learning English as a Foreign Language at University Level. Ph.D. Thesis, Ministry of Higher Education, Halabja, Iraq, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hassani, F.; Shahrbanian, S.; Shahidi, S.H.; Sheikh, M. Playing games can improve physical performance in children with autism. Int. J. Dev. Disabil. 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.; Peixoto, B.; Gonçalves, G.; Melo, M.; Amorim, V.; Bessa, M. Developing Training Applications for Hydrogen Emergency Response Training. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Graphics and Interaction (ICGI), Faro, Portugal, 21–22 November 2019; pp. 130–136. [Google Scholar]
- Peixoto, B.; Pinto, D.; Krassmann, A.; Melo, M.; Cabral, L.; Bessa, M. Using virtual reality tools for teaching foreign languages. In Proceedings of the World Conference on Information Systems and Technologies, Galicia, Spain, 16–19 April 2019; pp. 581–588. [Google Scholar]
- Krassmann, A.L.; Melo, M.; Peixoto, B.; Pinto, D.; Bessa, M.; Bercht, M. Learning in virtual reality: Investigating the effects of immersive tendencies and sense of presence. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Copenhagen, Denmark, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 270–286. [Google Scholar]
- 50+ New PlayStation VR Games Coming This Year and into Early 2018. Available online: https://blog.playstation.com/archive/2017/10/13/60-new-playstation-vr-games-coming-this-year-and-into-early-2018/ (accessed on 13 October 2020).
- Liang, Z.; Zhou, K.; Gao, K. Development of virtual reality serious game for underground rock-related hazards safety training. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 118639–118649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Silva, T.; Marinho, E.C.R.; Cabral, G.R.E.; da Gama, K.S. Motivational impact of virtual reality on game-based learning: Comparative study of immersive and non-immersive approaches. In Proceedings of the 2017 19th Symposium on Virtual and Augmented Reality (SVR), Curitiba, Brazil, 1–4 November 2017; pp. 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Neira, C.; Sandin, D.J.; DeFanti, T.A.; Kenyon, R.V.; Hart, J.C. The CAVE: Audio visual experience automatic virtual environment. Commun. ACM 1992, 35, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, D.; Kizony, R.; Feintuch, U.; Katz, N.; Josman, N.; Rizzo, A.S.; Weiss, P.L. Comparison of Two VR Platforms for Rehabilitation: Video Capture versus HMD. Presence 2005, 14, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Chen, C.H.; Jeng, M.C. Integrating video-capture virtual reality technology into a physically interactive learning environment for English learning. Comput. Educ. 2010, 55, 1346–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, G.; Czerwinski, M.; Van Dantzich, M. Immersion in desktop virtual reality. In Proceedings of the 10th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Banff, AB, Canada, 14–17 October 1997; pp. 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, G.G.; Card, S.K.; Mackinlay, J.D. Three views of virtual reality: Nonimmersive virtual reality. Computer 1993, 26, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, R.T. A survey of augmented reality. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Env. 1997, 6, 355–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M. Virtual reality in the language classroom: Theory and practice. CALL-EJ 2019, 20, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.A.L.; Wong, K.W.; Fung, C.C. How does desktop virtual reality enhance learning outcomes? A structural equation modeling approach. Comput. Educ. 2010, 55, 1424–1442. [Google Scholar]
- Brophy, J. Conceptualizing student motivation. Educ. Psychol. 1983, 18, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, R.; Cellary, W. Evaluation of learners’ attitude toward learning in ARIES augmented reality environments. Comput. Educ. 2013, 68, 570–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.J.; Lan, Y.J. Language learning in virtual reality environments: Past, present, and future. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2015, 18, 486–497. [Google Scholar]
- Solak, E.; Erdem, G. A Content Analysis of Virtual Reality Studies in Foreign Language Education. Particip. Educ. Res. 2015, 2, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmaxi, A. Virtual reality in language learning: A systematic review and implications for research and practice. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, D.; Oliver, S.; Thomas, J. An Introduction to Systematic Reviews; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, K.S.; Kunz, R.; Kleijnen, J.; Antes, G. Five steps to conducting a systematic review. J. R. Soc. Med. 2003, 96, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; The PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, M.A.; Guerra, A.M.; Ferro, R. Analysis on the gamification and implementation of Leap Motion Controller in the IED Técnico industrial de Tocancipá. Interact. Technol. Smart Educ. 2018, 15, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreira, J.; Bessa, M.; Pereira, L.C.; Adão, T.; Peres, E.; Magalhães, L. MOW: Augmented Reality game to learn words in different languages: Case study: Learning English names of animals in elementary school. In Proceedings of the 7th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI 2012), Madrid, Spain, 20–23 June 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, K.C.; Lee, L.C. The development and evaluation of an educational game integrating augmented reality, ARCS model, and types of games for English experiment learning: An analysis of learning. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Huynh, B.; Downey, J.; Höllerer, T.; Chun, D.; O’donovan, J. Arbis pictus: A study of vocabulary learning with augmented reality. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2018, 24, 2867–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.K.; Chau, C.H.; Chau, C.H.; Ng, C.T. Using augmented reality to teach kindergarten students English vocabulary. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Symposium on Educational Technology (ISET), Hong Kong, China, 27–29 June 2017; pp. 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Limsukhawat, S.; Kaewyoun, S.; Wongwatkit, C.; Wongta, J. A development of augmented reality-supported mobile game application based on jolly phonics approach to enhancing English phonics learning performance of ESL learners. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Computers in Education, Mumbai, India, 28 November–2 December 2016; pp. 483–488. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.Y.; Chen, M.P.; Wang, L.C.; Kao, Y.T.; Zou, D.; Xie, H. Enhancing low achievers’ EFL learning with interactive digital technologies. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computers in Education, ICCE 2019, Asia-Pacific Society for Computers in Education, Kenting, Taiwan, 2–6 December 2019; pp. 617–623. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.H. The applications and effects of learning English through augmented reality: A case study of Pokémon Go. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 2019, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.; Sheldon, L.; Si, M.; Hand, A. Foreign language learning in immersive virtual environments. In Proceedings of the Engineering Reality of Virtual Reality 2012. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Burlingame, CA, USA, 8 February 2012; Volume 8289, p. 828902. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.C. The crossroads of English language learners, task-based instruction, and 3D multi-user virtual learning in Second Life. Comput. Educ. 2016, 102, 152–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo-Duarte, M.; Berns, A.; Escolano, A.Y.; Dodero, J.M. Identifying writing profiles in game-based language learning using data mining. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality, Porto, Portugal, 7–9 October 2015; pp. 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Rankin, Y.A.; McNeal, M.; Shute, M.W.; Gooch, B. User centered game design: Evaluating massive multiplayer online role playing games for second language acquisition. In Proceedings of the 2008 ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Video Games, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 9–10 August 2008; pp. 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Tazouti, Y.; Boulaknadel, S.; Fakhri, Y. ImALeG: A Serious Game for Amazigh Language Learning. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. (iJET) 2019, 14, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berns, A.; Gonzalez-Pardo, A.; Camacho, D. Game-like language learning in 3-D virtual environments. Comput. Educ. 2013, 60, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berns, A.; Palomo-Duarte, M.; Dodero, J.M.; Valero-Franco, C. Using a 3D online game to assess students’ foreign language acquisition and communicative competence. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Technology Enhanced Learning, Paphos, Cyprus, 17–21 September 2013; pp. 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- Kongmee, I.; Strachan, R.; Pickard, A.; Montgomery, C. Moving between virtual and real worlds: Second language learning through massively multiplayer online role playing games (MMORPGs). In Proceedings of the 2011 3rd Computer Science and Electronic Engineering Conference (CEEC), Colchester, UK, 13–14 July 2011; pp. 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y. Chinese character composition game with the augment paper. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2018, 21, 132–145. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y. An Augmented Paper Game with Socio-Cognitive Support. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 2019, 13, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, C.H. PILE: Physical interactive learning environment. In Proceedings of the 2007 First IEEE International Workshop on Digital Game and Intelligent Toy Enhanced Learning (DIGITEL’07), Jhongli City, Taiwan, 26–28 March 2007; pp. 218–220. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, I.C. The application of augmented reality in English phonics learning performance of ESL young Learners. In Proceedings of the 2018 1st International Cognitive Cities Conference (IC3), Okinawa, Japan, 7–9 August 2018; pp. 255–259. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, S.; Kauer, R.; Laesker, D.; Nguyen, J.; Andujar, M. A Virtual Reality Experience for Learning Languages. In Proceedings of the Extended Abstracts of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Glasgow, UK, 4–9 May 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, M.; Zhong, Z. Development of a Situational Interaction Game for Improving Preschool Children’Performance in English-Vocabulary Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Distance Education and Learning, Beijing, China, 26–28 May 2018; pp. 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, T.A.; Reynolds, B.L.; Yeh, X.P.; Huang, G.Z. Video games in the English as a foreign language classroom. In Proceedings of the 2008 Second IEEE International Conference on Digital Game and Intelligent Toy Enhanced Learning, Banff, AB, Canada, 17–19 November 2008; pp. 188–192. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, A.; Yang, L.; Andersen, E. Teaching language and culture with a virtual reality game. In Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 6–11 May 2017; pp. 541–549. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.C.; Lin, Y.L.; Wu, J.J.; Chien, K.H. Design and evaluation of a physical interactive learning environment for English learning. In Proceedings of the 2008 Second IEEE International Conference on Digital Game and Intelligent Toy Enhanced Learning, Banff, AB, Canada, 17–19 November 2008; pp. 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, T.; Petersen, A.C. “The Hunt for Harald”—Learning Language and Culture Through Gaming. In Proceedings of the 6th European Conference on Games Based Learning: ECGBL, Cork, Ireland, 4–5 October 2012; p. 184. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Y.; Hung, C.Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Lin, Y.S.; Lai, Y.H. A study on integrating augmented reality technology and game-based learning model to improve motivation and effectiveness of learning English vocabulary. In Proceedings of the 2018 1st International Cognitive Cities Conference (IC3), Okinawa, Japan, 7–9 August 2018; pp. 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, T.C. Learning English with augmented reality: Do learning styles matter? Comput. Educ. 2017, 106, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, B.; Yang, S. Nurturing Environmental Education at the Tertiary Education Level in China: Can Mobile Augmented Reality and Gamification Help? Sustainability 2019, 11, 4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kweon, S.O.; Lee, S.; Noh, H.; Lee, G.G. POSTECH immersive English study (POMY): Dialog-based language learning game. IEICE TRANSACTIONS Inf. Syst. 2014, 97, 1830–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.C. Effects of gender and different augmented reality learning systems on English vocabulary learning of elementary school students. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2019, 18, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattar, J. Games e Gamificação em Educação. In Inovação, e Formação na Sociedade Digital, Ambientes Virtuais, Tecnologias e Serious games; White Books: Santo Tirso, Portugal, 2015; pp. 207–220. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, P.S. The importance of teaching language skills to the second or foreign language learners of english: A comprehensive study. ACADEMICIA Int. Multidiscip. Res. J. 2019, 9, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Dede, C.; Huang, R.; Richards, J. Virtual, Augmented, and Mixed Realities in Education. Springer: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).