Abstract
This study aims to identify and synthesize recent literature on the effect and strategies of flipped learning in the health professions education. Participant–intervention-comparator-outcome (PICO) strategies were used to identify articles from published peer-reviewed papers from January 2017 to March 2020 in Korea Med, Korean Citation Index, National Digital Science Library, and Korean Studies Information Service System. Of the 83 screened articles, 10 published articles met all the inclusion criteria. Most of articles targeted nursing students and focused on practicum classes. The effects of flipped learning were measured based on satisfaction, self-motivated learning, information literacy, and critical thinking disposition. Further, pre-class, in-class, and post-class activities were analyzed. The findings revealed that flipped learning improved class performance, overall evaluation, self-motivated learning, self-efficacy, and problem-solving abilities. The study suggests implementing a tailored flipped learning design based on class characteristics and appropriate post-class activities for enhancing students’ learning abilities.
1. Introduction
The European Union Joint Research Center argues that traditional lecture-based education is severely limited and incapable of adequately embodying the key visions of future education [1]. The traditional classroom, focusing on knowledge delivery via rote learning, has seen a shift toward a more learner-centered classroom with the introduction of various teaching and learning methods. Flipped learning is one such methodology that is focused on interaction with students as opposed to a unidirectional monologue; it is also known as reverse learning. Flipped learning, or a student-oriented learning method, consists of pre-class, in-class, and post-class activities. Pre-class activities guide students to actively learn the lesson beforehand using multimedia materials; in-class activities involve instructor-learner interaction based on knowledge acquired via pre-class activities. Post-class activities help reinforce and expand on the acquired learning [2].
Flipped learning promotes instructor-student interaction in contrast to unidirectional teaching. With the introduction and popularization of various educational media that help increase learners’ understanding, the demand for high-quality lectures is also on the rise [3]. Many colleges use learner-centered classes to strengthen students’ competence, in which the class contents are explored in depth [4]. There is also active ongoing research on flipped learning [5,6]. Since students learn the lesson in advance using media that can be accessed anywhere and at any time, their understanding of the lesson is improved during the actual class, which leads to greater satisfaction in class [7]. However, to maximize the effectiveness of flipped learning, few conditions need to be met, such as active student participation, appropriate instructor intervention, and regulation of pre-learning. Courses must be designed specifically for each subject based on an analysis of numerous cases prior to applying flipped learning.
Learner-centered instruction is also being implemented currently in undergraduate health professions education to foster the competencies of health professionals [8]. Studies on learner-centered instruction, including flipped learning, have reported that such learning methods are effective in improving students’ self-directed learning abilities, problem-solving, interpersonal skills, clinical performance, critical thinking, and academic achievements, thereby increasing academic performance [9,10,11,12]. A recent systematic literature review on flipped learning in South Korean nursing education found improvements in students’ learning capability [5]. Hew and Lo conducted a meta-analysis on the flipped classroom approach in education for the health professions using journals in the Journal Citation Report [7]. However, no systematic literature review has been published that targeted health professions education in South Korea. It is necessary to conduct an in-depth analysis of learner-centered instruction cases in health and allied health majors to foster prospective health professionals who will be in charge of public health. Further, as flipped learning was introduced in colleges in Korea only in 2013, efforts to stabilize and enhance its efficiency of operation and develop instruments for quality control have been inadequate [13]. Therefore, this study proposes directions for research on flipped learning in health professions education and for an effective application of flipped learning in health professions education by systematically reviewing the latest pertinent studies. The specific objectives of this study are to analyze the general characteristics, the measured variables and outcomes, and the strategies used in studies on flipped learning in the health professions education.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This paper is a systematic review of studies analyzing the effects of flipped learning in undergraduate health majors in Korea to identify the latest research trend and assess the teaching strategies and their effectiveness. The literature search strategy was based on the participant-intervention-comparators-outcome (PICO) framework [14].
2.2. Literature Search
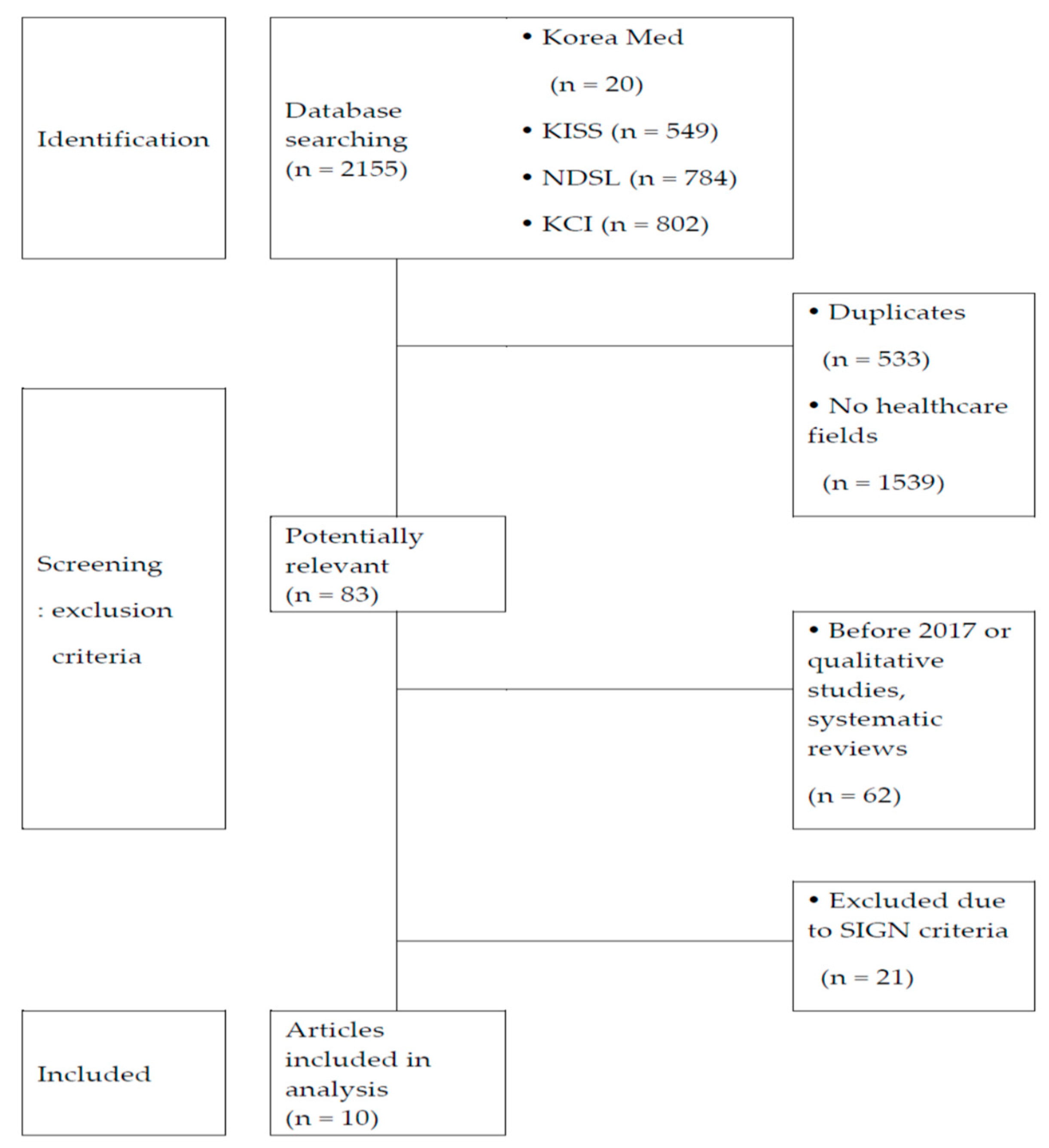
The keywords for the participants (P) of the study were undergraduate allied health majors (excluding medicine, dentistry, Korean medicine, pharmacy). The keyword for the intervention (I) was flipped learning. The comparator (C) referred to conventional lecture-based classes. The keyword of the outcomes (O) referred to the major outcomes of flipped learning. To examine the latest trend in flipped learning research, the search was limited to Korean studies published between January 2017 and March 2020. The search was performed on Korea Med, National Digital Science Library (NDSL), Korean Studies Information Service System (KISS), and the Korean Citation Index (KCI). The database used for the search was based on the report of Kim et al. [15] and included the search engine of the Core of the Core, standard ideal (COSI) model, which is the protocol for literature review databases in Korea. Four researchers performed the search independently, and studies were selected after reviewing them against the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The search strategy generated a total of 2155 studies with 20 studies from Korea Med, 549 studies from KISS, 784 studies from NDSL, and 802 studies from KCI. After excluding 1539 studies on medicine and non-health majors, 533 duplicate searches, and 62 studies that meet the exclusion criteria (but were qualitative studies, literature reviews, or published before 2017), the manuscripts of 21 studies were selected and subsequently acquired.
The quality of the selected studies was appraised independently by four researchers using the methodology checklist for cohort studies published by the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) [16]. Studies that compared the outcomes of flipped learning and conventional lecture-based classes were included, and after re-discussing studies on which the researchers had divided opinions regarding the comparison groups, a total of 10 studies were finally selected for the analysis (see Figure 1).
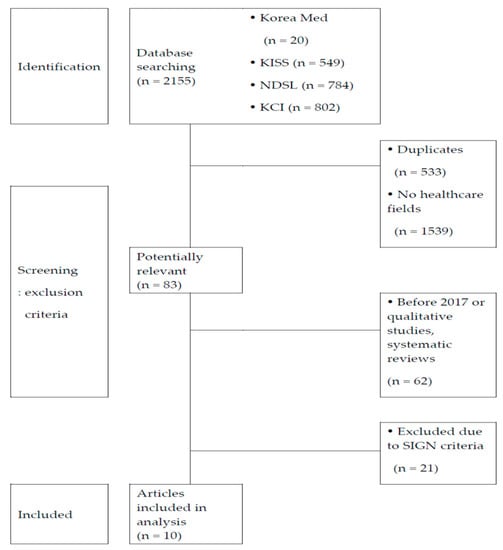
Figure 1.
Precedent studies’ selection flowchart.
2.3. Literature Analysis
All the 10 selected studies were quantitative studies. The features of each study were organized in a table by four researchers, and the assessments were reviewed among them. The following features of the studies were analyzed: author and publication year, institutional review board (IRB) review, course subject, pedagogical features (strategy, intervention period), participant features (sample size, inclusion criteria), measured variables (instruments, reliability and validity), and outcome variables (Table 1).

Table 1.
Overview of studies included in the analysis.
3. Results
3.1. General Features of the Selected Studies
The 10 selected studies were published between 2017 and 2020. The study design used to examine the effects of flipped learning was either pre-test–post-test or quasi-experimental design, and all studies were conducted on nursing students. The mean intervention period was six weeks and six days, and the mean number of participants in the flipped learning group was 91. Six studies presented evidence for determining the sample size for flipped learning (study no. 1, 3, 4, 7, 9, and 10). Eight studies were either approved by an IRB or mentioned obtaining consent from students undergoing flipped learning. Although flipped learning was generally applied to practicum courses, it was also sometimes used in theoretical courses such as fundamentals of nursing, health assessment, health education and methodology, and geriatric nursing.
3.2. Variables for Flipped Learning Outcomes and Results
The most common variable used to measure the outcomes of flipped learning was satisfaction, namely, satisfaction with learning, the course, or the teaching method (n = 5). This was followed by self-directed learning ability (n = 4), knowledge (n = 3), and critical thinking, problem-solving skills, information literacy, and academic achievement (n = 2 each). Other variables included class experience, level of communication anxiety, intent to continue learning, clinical performance, self-efficacy, learning accomplishment, learning attitude, learning motivation, class participation, undergraduate competencies, academic performance, and usefulness. The studies generally reported that flipped learning had a positive impact on the measured variables (Table 1).
3.3. Flipped Learning Teaching Strategies
To compare the teaching strategies used in studies that examined the effects of flipped learning, the activities were classified into pre-class, in-class, and post-class activities for analysis. Pre-class activities included team-based learning, video-based learning, e-learning courses, individual study, student question formation, watch-summary-question (WSQ) journal, skill practicing, and self-evaluation journal. In-class activities included team-based discussion and cooperative learning, team-based presentation, instructor feedback, hands-on training, pre-learning readiness assessment, scenario-based application, quiz on the e-learning materials, nursing diagnosis training, discussion on student-formed questions, instructor-led training (discussion, simulation, case study, conference), and 1:1 evaluation and guidance by the instructor. Post-class activities included review of key contents, peer evaluation, post-class evaluation and survey, Q&A, post-class self-study, self-evaluation journal, instructor feedback, application of case study, and team-based answer review and sharing (Table 2).

Table 2.
Major features of flipped learning strategies.
4. Discussion
This study systematically reviewed Korean studies on flipped learning in allied health majors published within the past three years and based on the results, identified the latest trends in flipped learning research. Although we attempted to include studies on flipped learning in various health majors, all 10 selected studies were conducted on nursing students. As per the SIGN checklist for cohort studies, only studies that extracted both a control group and experimental group from the source population were selected.
This led to the exclusion of a number of studies that did not include a comparator (C). These excluded studies were conducted on students majoring in radiology, emergency medicine, occupational therapy (n = 2 each), and physical therapy, dental hygiene, and dental technology (n = 1 each). This suggests that flipped learning is less frequently applied in other health majors compared to nursing, necessitating an expanded application of flipped learning in more health professions courses. A pre-post analysis with a single group is limited in comparing the effects of flipped learning with that of the traditional classroom approach. Thus, study designs should be chosen carefully to clearly assess the effects of flipped learning.
The courses in which flipped learning was applied were generally practicum courses, including comprehensive practicum II, geriatric nursing, fundamentals of nursing practicum, health assessment, surgical nursing practicum, health education, fundamentals of nursing, health education and methodology, and psychiatric nursing practicum, which was consistent with other studies that analyzed flipped learning methods in health professions education [27,28,29,30,31]. The educational effects of flipped learning approach in practicum courses included improved student attitude, fewer errors in practice [5], and improved student perception, self-directed learning, academic achievement, and satisfaction with the class [27,29,31].
In a meta-analysis of the effects of learner-centered class in nursing, Lee and Yang [9] reported that a learner-centered class is effective in enhancing clinical performance and learning of major-related knowledge; they demonstrated that learner-centered approaches, such as flipped learning, are more effective than the traditional lectures in the study of nursing. Prior to 2017, common measured variables were self-directed learning [27], academic achievement [27], self-efficacy [32,33], critical thinking and communication [32], and learning motivation [33]. On the other hand, in the past three years, a number of variables, such as knowledge and performance, self-directed learning [34,35], critical thinking [34,36,37], academic self-efficacy [36,37], satisfaction with major [36], and communication and problem-solving skills [36]. As flipped learning enables students to repeatedly learn the contents related to their lesson of the day through pre-class learning without restrictions of time and place, students are able to adequately familiarize themselves with the lesson in advance, which increases their understanding of the lesson during the actual class. Many studies on flipped learning confirmed positive changes after applying flipped learning, and they generally used variables that influence students’ tendencies or academic competence and performance, that is, variables positively correlated with the flipped learning approach [4,5,7,9]. As shown in previous studies, the results of the literature review section in this study confirmed that flipped learning improved satisfaction with class (n = 4), academic achievement (n = 3), self-directed learning, problem-solving skills, and information literacy (n = 2), and critical thinking. Future studies should discover new significant variables to examine the effects of flipped learning. To expand the utilization of the flipped learning approach, active research and effort are needed to verify its effects.
Flipped learning strategies were analyzed by dividing the class into pre-class, in-class, and post-class activities. Video lectures were primarily used in pre-class activities for practicum courses, while team-based learning or individual study were performed in pre-class activities for theoretical courses. In-class strategies included pre-class readiness assessment, instructor feedback, and hands-on training during practicum courses, while team-based discussions or presentation were performed in theoretical education. Popular post-class strategies included peer evaluation, self-evaluation journal, and instructor feedback, and post-class activities were not used in two cases. Gan et al. [13] analyzed flipped learning cases and proposed a basic operational model for theory and practicum courses, and a similar flipped learning model was used in the ten studies reviewed in this article. Lee and Chang [25] had students write a WSQ journal, which required them to watch, summarize, and question activities as a form of pre-class activity. WSQ journal writing was proposed by Kirch [38], which involves instructor-student interaction in finding the solution during in-class activities and helps students take responsibility for completing the pre-class portion. Lee and Chang [25] reported that the WSQ strategy has a positive influence on self-directed learning and academic achievement. Friedman and Friedman [39] proposed the Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation (ADDIE) model. Lee [40] applied the ADDIE model to flipped learning and proposed pre-learning, in-class learning activities, and evaluation and self-evaluation after class as the major teaching strategies. Gan et al. [13] argued that the post-class part of learning is the stage in which the learned materials are maintained and expanded. Among the studies analyzed in this review, two studies did not use post-class activities, but appropriate post-class activities, such as reviewing, summarizing, complementing, and writing self-evaluation journals, must be implemented to facilitate continuity of learning. The results of previous studies and this study highlight the need to use flipped learning designs and strategies tailored for each subject to boost their learning effects on students.
5. Conclusions
The purpose of the study is to identify and synthesize recent literature on the effects and strategies of flipped learning in education for the health professions in South Korea. We used participant–intervention-comparators-outcome (PICO) strategies to identify the published peer-reviewed articles from January 2017 to March 2020 in Korea Med, KCI, NDSL, and KISS. Ten published articles from 83 screened articles met the inclusion criteria. All articles targeted nursing students and mostly focused on practicum classes. The effects of flipped learning were measured by satisfaction, self-motivated learning, information literacy, and critical thinking disposition. We further analyzed pre-class, in-class, and post-class activities. The limitation of this study is that it was not possible to evaluate the effect of different types of flipped learning approaches under the limited number of analyzed studies. Despite these limitation, we found that the flipped learning model improved class performance, overall evaluation, self-motivated learning, self-efficacy, and problem-solving abilities. The study results suggest implementing a tailored flipped learning design based on class characteristics and emphasizing appropriate post-class activities to enhance students’ learning abilities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.L. and J.K.; methodology, H.L. and J.K.; formal analysis, J.H.P. and W.S.H.; investigation, J.H.P. and W.S.H.; data curation, J.H.P. and W.S.H.; writing—original draft preparation, J.H.P. and W.S.H.; writing—review and editing, H.L. and J.K.; visualization, J.H.P. and W.S.H.; supervision, H.L. and J.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Redecker, C.; Leis, M.; Leendertse, M.; Punie, Y.; Gijsbers, G.; Kirschners, P.; Stoyanov, S.; Hoogveld, B. The Future of Learning: Preparing for Change; Institute for Prospective Technological Studies, European Commission Joint Research Center: Luxembourg, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin, B.; Miller, K. Evidence on flipped classrooms is still coming in. Educ. Leadersh. 2013, 70, 78–80. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, J.G.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, S.J. Effect of smart learning applied on achievement goal, self-directed learning for students in health college. Korean J. Radiol. 2017, 39, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, A.C.M.; Vera, J.G.; Ruiz, G.R.; Arrebola, I.A. Flipped Classroom to improve university student centered learning and academic performance. Soc. Sci. 2019, 8, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.H.; Shin, S.J. The effect and strategies of flipped learning in nursing education: A systematic review. Health Nurs. 2018, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H. Analyzing the level of concerns about learner-centered pedagogical method of university faculty. J. Lifelong Learn. Soc. 2014, 10, 109–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hew, K.F.; Lo, C.K. Flipped classroom improves student learning in health professions education: A meta-analysis. BMC Med. Educ. 2018, 18, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, R.; Moadeb, N.; Shokrpour, N. Team-based learning: A new approach toward improving education. Acta Med. Iran. 2016, 54, 679–683. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.E.; Yang, S.H. The effects of learner-centered instruction in nursing: A meta-analysis. Asian J. Educ. 2018, 19, 1049–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J. A meta-analysis of team-based learning effects in university classes. J. Learn. Cent. Curr. Instr. 2017, 17, 721–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, M.S.; Nam, C.W. Developing a teaching and learning model using flipped learning for the course of core fundamental nursing skills in nursing education. J. Learn. Cent. Curr. Instr. 2017, 17, 375–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, C.H.; Park, J.Y. The preference of instructional methods and Kolb’s learning styles of nursing students. J. Digit. Converg. 2016, 14, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.S.; Han, S.B.; Seo, Y.J.; Lee, E.J.; Bae, S.M.; Shin, M.S.; Kim, Y.H. Case Analysis for Flipped Learning Course Operation and Development of Operational Model; The 9th Research Project Contest; Korean Association of Center for Teaching and Learning: Bucheon, Korea, 2017; pp. 3–52. [Google Scholar]
- Yensen, J. PICO search strategies. Online J. Nurs. Inform. 2013, 17. Available online: http://ojni.org/issues/?p=2860 (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.E.; Seo, H.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Son, H.J.; Jang, B.H.; Seo, H.S.; Shin, C.M. NECA’s guidance for undertaking systematic reviews and meta-analyses for intervention. Natl. Evid. Based Healthc. Collab. Agency 2011, 25, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Harbour, R.; Miller, J. A new system for grading recommendations in evidence-based guidelines. BMJ 2001, 323, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, D. Effects of convergence education by jigsaw model and flipped learning in nursing students. J. Converg. Inform. Technol. 2019, 9, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.N.; Shin, M.K.; Jeon, H.J. Analysis about the effect of flipped learning based team activity. J. Converg. Inform. Technol. 2019, 9, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, H.G.; Yang, Y.K. Effects of flipped learning-based fundamentals of nursing practice. J. Learn. Cent. Curr. Instr. 2019, 19, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, E. The effects of flipped learning based health assessment on academic achievement of nursing students. J. Korea Acad. Ind. Coop. Soc. 2018, 19, 201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.K.; Park, B.K. Effects of flipped learning using online materials in a surgical nursing practicum: A Pilot Stratified group-randomized trial. Health Inform. Res. 2018, 24, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. A case study on flipped learning of health education class-comparison with the lesson that applied the reflective journal method. J. Educ. Cult. 2017, 23, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Woo, C.H. The effects of lesson with student-generated questions: Based on flipped learning utilizing massive open online courses. J. Learn. Cent. Curr. Instr. 2017, 17, 283–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.Y.; Han, J.Y. Nursing students’ learning motivation, class participation, and class satisfaction on flipped class and instructor-centered class. J. Learn. Cent. Curr. Instr. 2017, 17, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.; Chang, S.J.; Jang, S.J. Effects of the flipped classroom approach on the psychiatric nursing practicum course. J. Korean Acad. Psychiatr. Ment. Health Nurs. 2017, 26, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.S.; Kim, N.Y. The effects of flipped learning on the self-directed learning and information literacy of nursing students. J. Learn. Cent. Curr. Instr. 2017, 17, 491–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.A.; Kim, H.S. Effect of flipped learning on self-directed learning and academic achievement in emergency medical technology students. Clin. Exp. Emerg. Med. 2016, 20, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Park, S.H.; Lee, M.Y. A study on the satisfaction of flipped learning with pre-class using video in basic medical subjects. J. Korea Entertain. Ind. Assoc. 2017, 11, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.J. The effect of flipped learning on self-directed learning and class satisfaction in a class of college physical therapy students. J. Korean Soc. Integr. Med. 2018, 6, 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.H.; Jung, H.R. The effects of flipped learning in sensory integration therapy class using online learning platform on learning participation. J. Korean Soc. Integr. Med. 2018, 12, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.S. A case study on flipped learning convergence in dental hygiene major: Focusing on learning awareness and academic achievement. J. Converg. Inform. Technol. 2019, 9, 252–263. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.S.; Eun, Y. The effect of the flipped learning on self-efficacy, critical thinking disposition, and communication competence of nursing students. J. Korea Acad. Soc. Nurs. Educ. 2016, 22, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.J. Effectiveness of flipped learning in fundamental nursing practice education. J. Korean Stat. Soc. 2016, 18, 2829–2841. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Kim, Y.H. An action research on flipped learning for fundamental nursing practice courses. J. Korean Acad. Fundam. Nurs. 2017, 24, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Kim, J.Y. Effects of flipped learning in core competencies of nursing students: Based on communication, problem-solving, and self-directed learning. J. Learn. Cent. Curr. Instr. 2018, 18, 1163–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.R.; Jeong, E. Effects of e-book-based flipped learning education on critical thinking disposition, academic self-efficacy, and major satisfaction of nursing students. J. Korea Contents Assoc. 2018, 18, 490–501. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, O.S.; Noh, Y.G. The effect of flipped learning on learning motivation, academic self-efficacy, and critical thinking disposition of nursing students. J. Digit. Converg. 2019, 17, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Kirch, C. Flipping with Kirch: The Ups and Downs from Inside My Flipped Classroom; Bretzmann Group: New Berlin, WI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, H.H.; Friedman, L.W. Crises in education: Online learning as a solution. Creat. Educ. 2011, 2, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y. Research on developing instructional design models for flipped learning. J. Digit. Converg. 2013, 11, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).